Advanced Tolerance Optimization for Freeform Geometries Using Particle Swarm Optimization: A Case Study on Aeronautical Turbine Blades †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Modeling Framework for Tolerance Optimization in Freeform Geometries
2.1. Methodology
2.2. Modeling Tolerances for Freeform Geometries
- Manufacturing cost related to tighter tolerances.
- Inspection cost based on the complexity of the measurement process.
- Deviation in critical zones.
- : Weight factors representing the importance of each term.
2.3. Constraints
- Geometric Deviation
- Surface Continuity
- Manufacturing Constraints
3. Optimization Process for Tolerances in Freeform Geometries
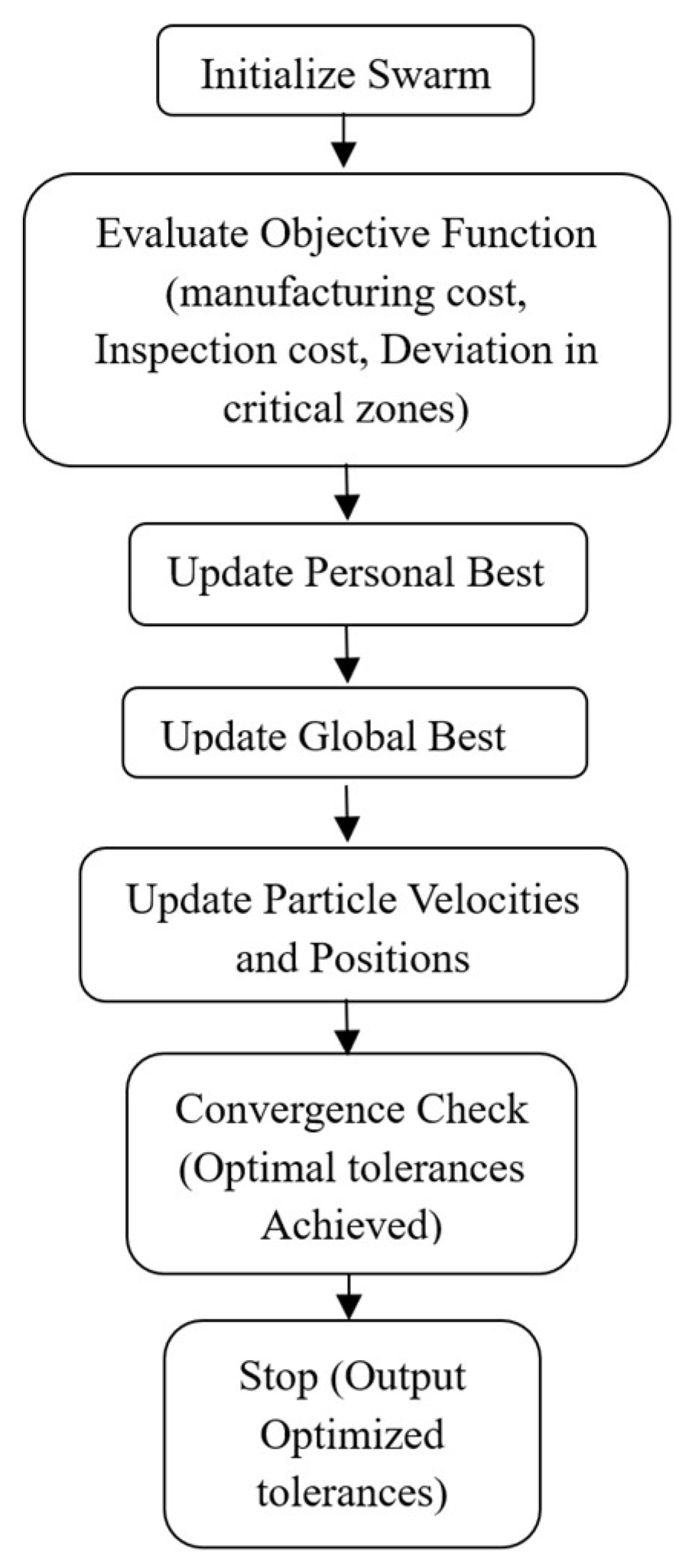
3.1. Optimization Algorithm
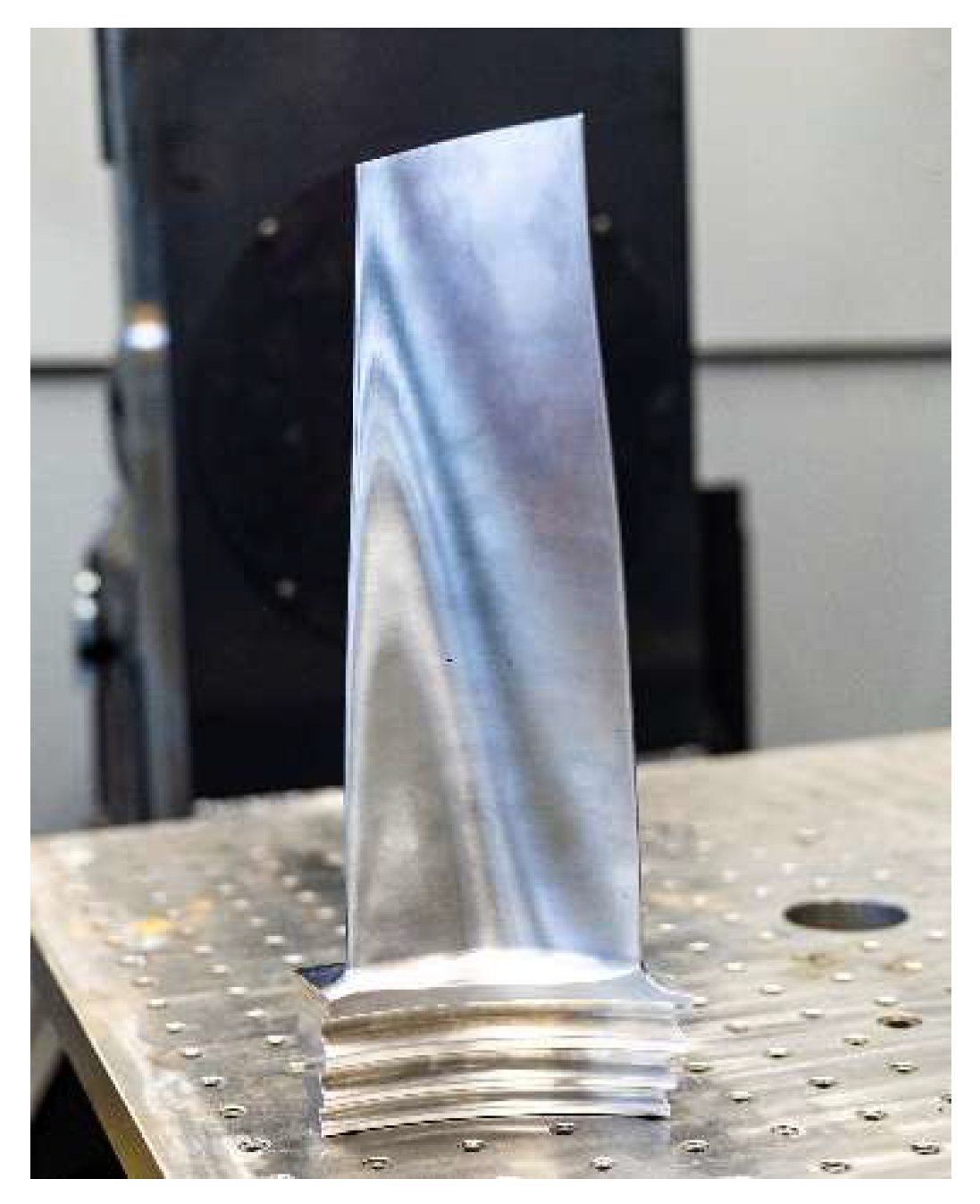
3.2. Case Study
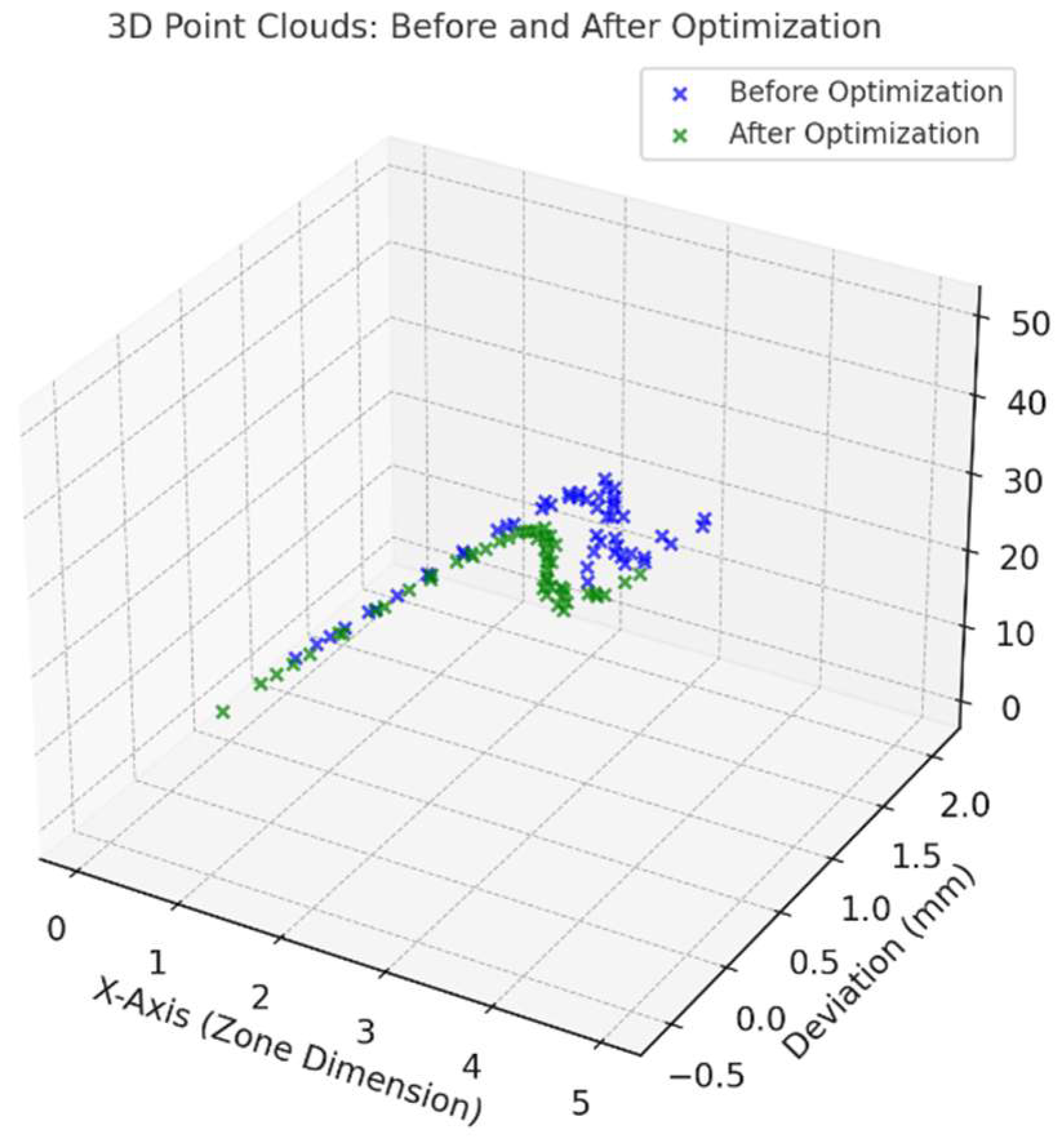
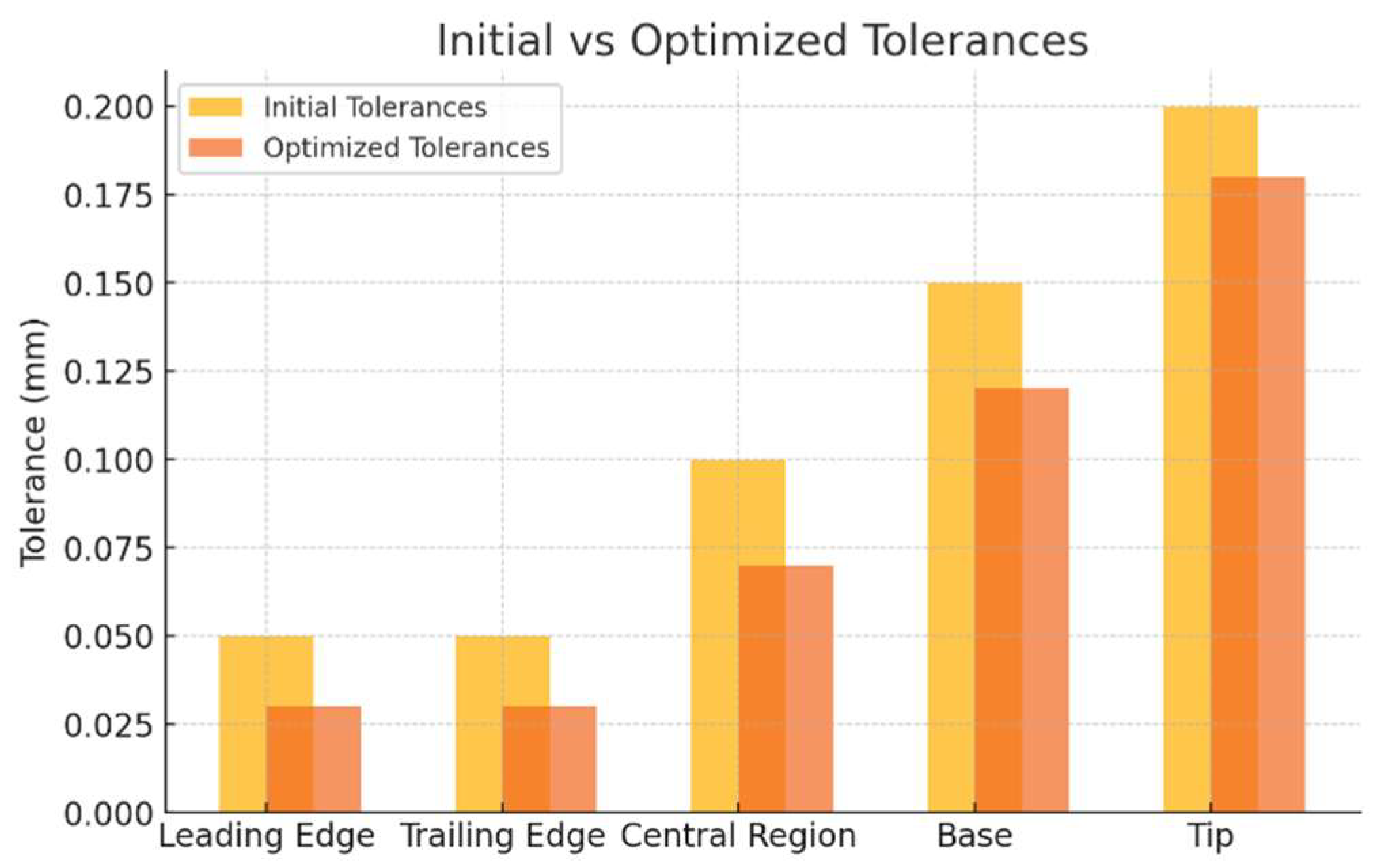
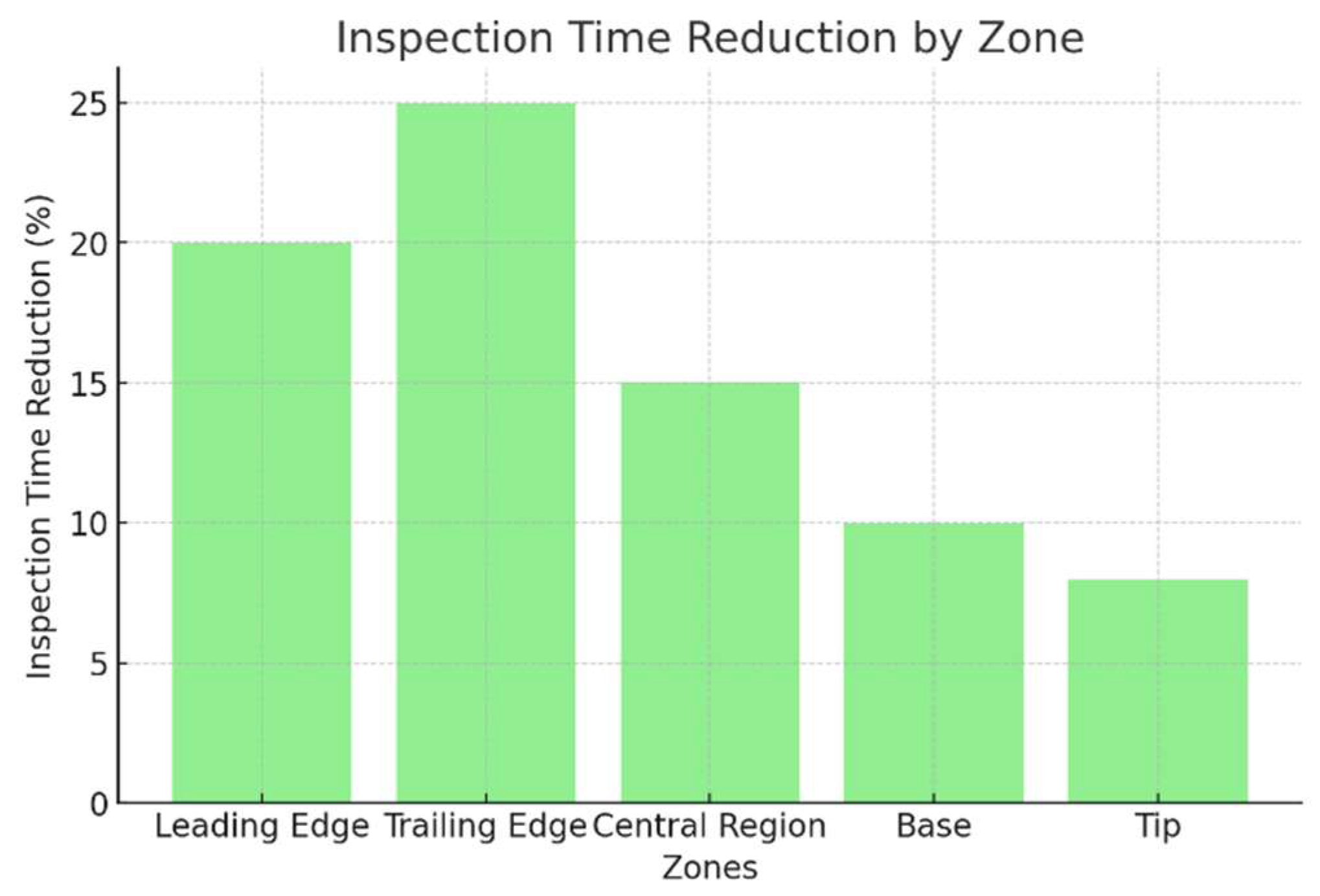
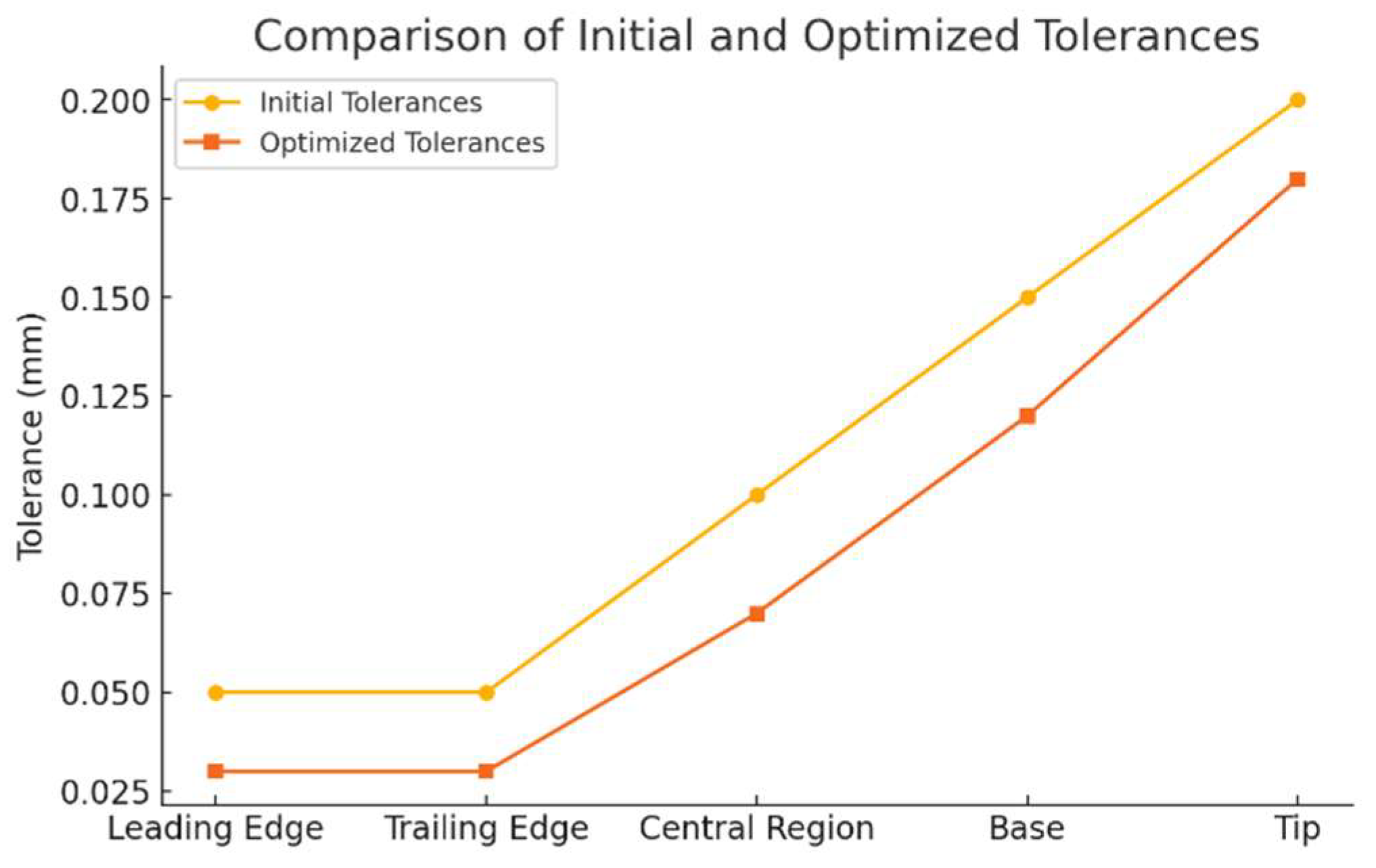
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hosseini, S.E.; Jafaripanah, S.; Saboohi, Z. Numerical Simulation and Aerodynamic Optimization of Two-Stage Axial High-Pressure Turbine Blades. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.02102. [Google Scholar]
- Geneid, A.A.; Atia, M.R.A.; Badawy, A. Multi-objective optimization of vertical-axis wind turbine’s blade structure using genetic algorithm. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2022, 69, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pholdee, N.; Bureerat, S.; Nuantong, W. Kriging Surrogate-Based Genetic Algorithm Optimization for Blade Design of a Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2020, 126, 261–273. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadi, P.; Rashidi, M.M.; Nazari, M.A. Aerodynamic Optimal Design of Wind Turbine Blades using Genetic Algorithm. Int. J. Energy Environ. Eng. 2014, 5, 373–380. [Google Scholar]
- Pholdee, N.; Bureerat, S. Multi-objective topology optimization of structures using harmony search algorithm. Eng. Optim. 2013, 45, 1489–1509. [Google Scholar]
- Rashidi, M.M.; Ahmadi, P.; Nazari, M.A. Optimization of blade profile for a horizontal axis wind turbine using genetic algorithm. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 70, 147–155. [Google Scholar]
- Jafaripanah, S.; Hosseini, S.E.; Saboohi, Z. Aerodynamic optimization of a two-stage axial high-pressure turbine using genetic algorithm. Energy 2022, 238, 46–57. [Google Scholar]
- Geneid, A.A.; Atia, M.R.A.; Badawy, A. Structural optimization of vertical-axis wind turbine blades using genetic algorithm. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2021, 68, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Pholdee, N.; Bureerat, S. Hybrid evolutionary algorithms for structural optimization: A review. Comput. Struct. 2014, 139, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadi, P.; Rashidi, M.M.; Nazari, M.A. Multi-objective optimization of a horizontal axis wind turbine blade profile using genetic algorithm. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 70, 12–20. [Google Scholar]
- Montaldo, S.; Onnis, I.I. INVARIANT CMC SURFACES IN H2×R. Glasg. Math. J. 2004, 46, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstraete, T.; Muller, L.; Mueller, J.D. CAD-Based Adjoint Optimization of the Stresses in a Radial Turbine. In Proceedings of the ASME Turbo Expo 2017, Charlotte, NC, USA, 26–30 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zielinski, M.; Ziller, G. Noncontact vibration measurements on compressor rotor blades. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2000, 11, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghdadi, S.; Aboutabit, N. View-independent vehicle category classification system. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2021, 12, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, D.; Jüngst, M.; Möller, D.; Schiffer, H.-P.; Giersch, T. Influence of pre-swirl, rotor speed and blade count on aeroelastic coupling mechanisms during stall inception of a transonic compressor. In Proceedings of the Turbo Expo: Power for Land, Sea, and Air, Online, 21–25 September 2020. GT2020-14105 9p. [Google Scholar]
- Bartolo, P. Stereolithographic Processes. In Stereolitography: Materials, Processes and Applications; Bartolo, P., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2011; pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Azlah, M.A.F.; Chua, L.S.; Rahmad, F.R.; Abdullah, F.I.; Wan Alwi, S.R. Review on techniques for plant leaf classification and recognition. Computers 2019, 8, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, C.; Ivey, P. Turbomachinery blade vibration amplitude measurement through tip timing with capacitance tip clearance probes. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2005, 118, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandstetter, C.; Ottavy, X.; Paoletti, B.; Stapelfeldt, S. Interpretation of stall precursor signatures. J. Turbomach. 2021, 143, 121011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietropaoli, M.; Ahlfeld, R.; Montomoli, F.; Ciani, A.; d’Ercole, M. Design for Additive Manufacturing: Internal Channel Optimization. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 2017, 139, 102101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stapelfeldt, S.; Brandstetter, C. Suppression of Nonsynchronous Vibration Through Intentional Aerodynamic and Structural Mistuning. J. Turbomach. 2022, 144, 021008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kielb, R.; Barter, J.; Thomas, J.; Hall, K. Blade excitation by aerodynamic instabilities: A compressor blade study. In Proceedings of the Turbo Expo: Power for Land, Sea, and Air, Atlanta, GA, USA, 16–19 June 2003; GT2003-38634. pp. 399–406. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Francis, J.M.; Wang, L.M. How tonality and loudness of noise relate to annoyance and task performance. Noise Control. Eng. J. 2017, 65, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddi, Y.; Moumen, A.; Kharchaf, A. Study of A Mobile Robot’s Obstacle Avoidance Behavior in A Radioactive Environment with A High Level of Autonomy. Int. J. Tech. Phys. Probl. Eng. (IJTPE) 2022, 14, 34–41. [Google Scholar]
- Moumen, A.; Lakhdar, A.; Mansouri, K. Elastoplastic Behavior of Polybutylene Terephthalate Polyester Bio loaded by Two Sustainable and Ecological Fibers of Animal Origin with Two Numerical Methods. Int. J. Tech. Phys. Probl. Eng. (IJTPE) 2021, 13, 29–37. [Google Scholar]


| Zone | Criticality | Number of Measurement Points | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leading Edge | High | 150 | Ensure aerodynamic precision |
| Trailing Edge | High | 150 | Ensure aerodynamic precision |
| Central Region | Medium | 80 | Capture surface deviations |
| Base | Medium | 60 | Verify dimensional conformity |
| Tip | Low | 50 | Verify overall geometry |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohamed, O.; Abdelouahad, B.; Abdelouahab, S.; Abdelilah, J. Advanced Tolerance Optimization for Freeform Geometries Using Particle Swarm Optimization: A Case Study on Aeronautical Turbine Blades. Eng. Proc. 2025, 112, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025112020
Mohamed O, Abdelouahad B, Abdelouahab S, Abdelilah J. Advanced Tolerance Optimization for Freeform Geometries Using Particle Swarm Optimization: A Case Study on Aeronautical Turbine Blades. Engineering Proceedings. 2025; 112(1):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025112020
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohamed, Oubrek, Bellat Abdelouahad, Salih Abdelouahab, and Jalid Abdelilah. 2025. "Advanced Tolerance Optimization for Freeform Geometries Using Particle Swarm Optimization: A Case Study on Aeronautical Turbine Blades" Engineering Proceedings 112, no. 1: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025112020
APA StyleMohamed, O., Abdelouahad, B., Abdelouahab, S., & Abdelilah, J. (2025). Advanced Tolerance Optimization for Freeform Geometries Using Particle Swarm Optimization: A Case Study on Aeronautical Turbine Blades. Engineering Proceedings, 112(1), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025112020






