In 1995, Noyori and co-workers made a breakthrough with their design of practical ruthenium-based catalysts, which combined the homochiral TsDPEN ligand with a Ru(II) arene [1,2]. Using (R,R)-1 at a loading of 0.5 mol% in either KOH-iPrOH or the azeotropic mixture of formic acid–triethylamine (FA:TEA, 5:2 molar ratio), the reduction of acetophenone was achieved in up to 98% ee (Figure 1).
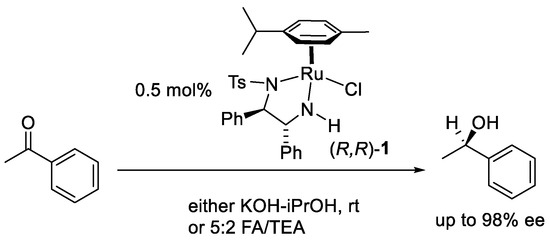
Figure 1.
Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation (ATH) with Noyori–Ikariya catalysts.
The mechanism for the asymmetric transfer hydrogenation (ATH) with Noyori–Ikariya catalysts is now well-established (Figure 2) [3,4,5,6,7,8,9]. The precatalyst can be activated by elimination of HCl to form a 16-electron neutral Ru(II) complex. Then, the 16-electron complex abstracts two hydrogen atoms from the hydrogen donor, such as isopropanol, a formic acid/triethylamine (FA/TEA) mixture or sodium formate, to form a hydride that contains an 18-electron Ru(II) centre. Finally, the two hydrogen atoms are transferred to the C=O group and reduce ketone substrates into chiral alcohol products. Meanwhile, the 16-electron neutral Ru(II) complex is regenerated and can restart the catalytic cycle. The six-membered transition state can be stabilized by the combination of electrostatic interactions and steric effects. Edge/face (or CH/π) electrostatic interaction makes the electron-rich aryl group of a substrate favour the position adjacent to the η6-arene ring of the catalyst (Figure 3), whereas the large group and electron group favour the position distal to η6-arene ring (Figure 4).
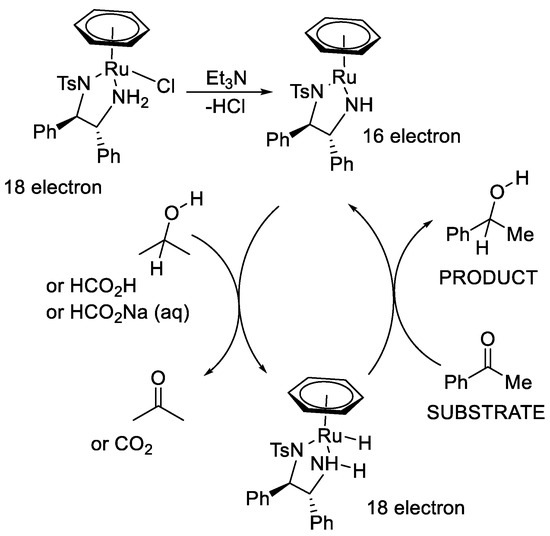
Figure 2.
Mechanism of hydrogen transfer with Noyori–Ikariya catalysts.
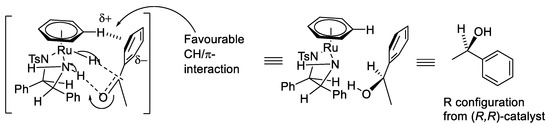
Figure 3.
Interaction of substrate with η6-arene ring.
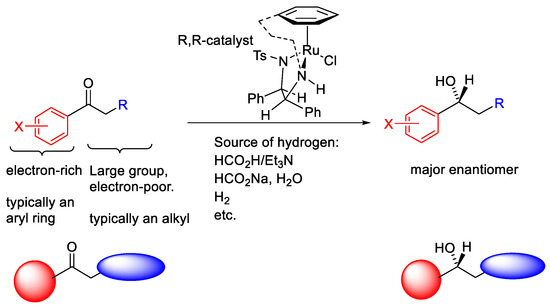
Figure 4.
Summary of stereocontrol features in ATH using Noyori–Ikariya catalysts.
Noyori [(arene)Ru(TsDPEN)Cl] catalysts with different arene rings are shown below (Figure 5) [2]. The reactivity of Noyori-type catalysts in ATH reactions is changed when the arene ligand is different, activity following the order benzene > p-cymene mesitylene > hexamethylbenzene.
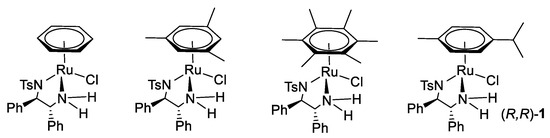
Figure 5.
Variation of the η6-arene ring in Noyori–Ikariya catalysts.
A new class of “tethered” ruthenium (II) catalyst was introduced by Wills et al. (Figure 6) [10,11,12]. In some cases, these exhibit improved activity over the non-tethered versions, which allows a reduction of catalyst loading and reaction times.
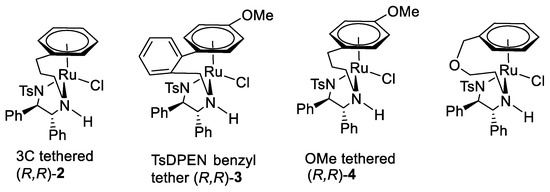
Figure 6.
Tethered catalysts introduced by Wills et al.
ATH of some benzophenone derivatives [9,13,14] and heterocyclic ketones [15,16,17] has been reported. The electronic differences between two phenyl rings caused by the electron-donating p-OMe group and electron-withdrawing p-CN group make the p-OMe substituted phenyl ring adopt the position proximal to the η6-arene. Out-of-plane aromatic rings with one or two ortho-substituent groups favour positioning distal to η6-arene and result in the formation of alcohol products with very high ees (Figure 7).
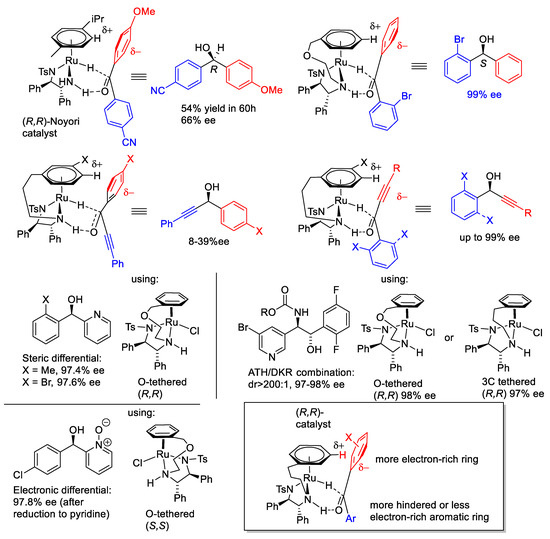
Figure 7.
Examples of ATH of benzophenone derivatives and heterocyclic ketones using Noyori–Ikariya catalysts (The red part favours positioning adjacent to η6-arene of catalyst, while the blue part favours positioning distal to η6-arene of catalyst).
We have studied ATH of ortho-hydroxyphenyl acetophenone derivatives with four different tethered catalysts (Figure 8) [18]. (R,R)-3C-tethered catalyst 2 was found to be the most active of the series tested initially with ortho-hydroxybenzophenone.
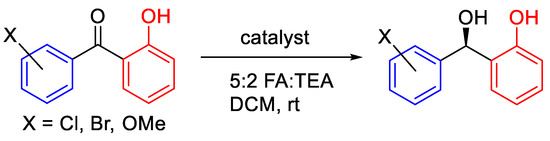
Figure 8.
ATH of ortho-hydroxy benzophenones using tethered ATH complexes.
The configuration of alcohol product 5 was confirmed after methylation by comparison of the HPLC of reduction product 6, the configuration of which is known in the literature (Figure 9).
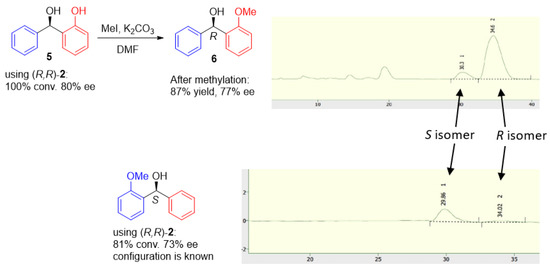
Figure 9.
Determination of product configuration in ATH of ortho-hydroxy benzophenones.
We also completed the ATH of a range of ortho-hydroxyphenyl acetophenone derivatives using four catalysts and found that most of them can provide products in good yield and high ee (Figure 10). The electron-rich ortho-hydroxyphenyl group can generate an electrostatic interaction with an η6-arene ring in the complex, whereas the hindered opposing aromatic ring can be in a position that is far from the η6-arene ring (Figure 11). Therefore, the combination of the ortho-OH directing group and steric effect provide products with high ees. The application could also be extended to a series of amide-containing benzophenones (Figure 12).
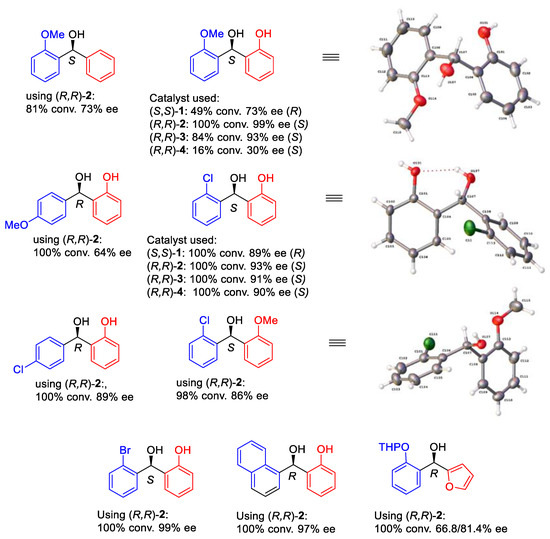
Figure 10.
Further examples of ATH of ortho-hydroxy benzophenones.
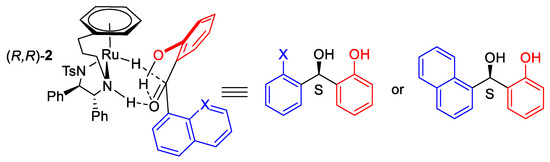
Figure 11.
Involvement of H-bond in reduction mechanism.
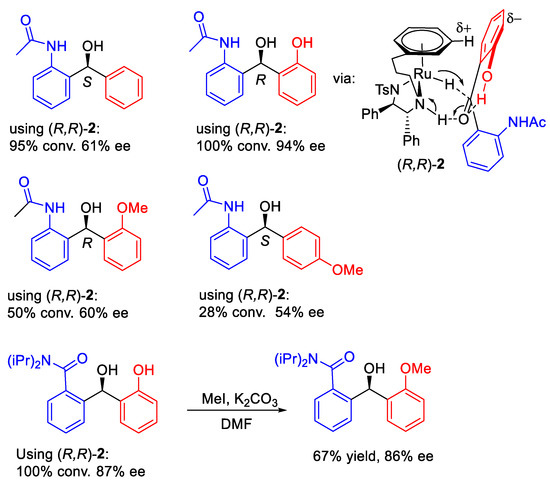
Figure 12.
ATH of benzophenones containing amides.
In addition to ketones, imines containing ortho-OH groups were also studied. However, the hydrolysis of imines is more likely to occur when using FA: TEA (5:2) as the hydrogen source. Thus, the unique condition of ATH of imines with catalyst (R,R)-2 is using ammonium formate in DCM at 70 °C in sealed tubes under a nitrogen atmosphere and with only 0.5 mol% catalyst applied [19]. Following the earlier precedents (Figure 13), ATH of imines also delivered products of good ees (Figure 14).
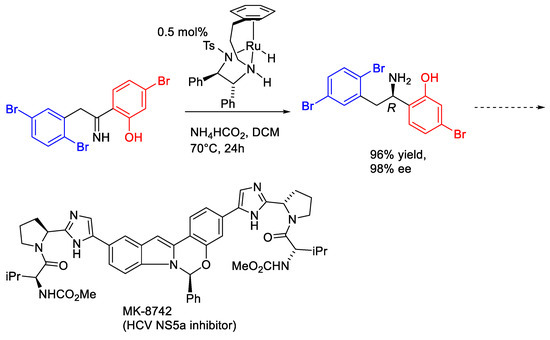
Figure 13.
A reported imine ATH using a tethered catalyst.
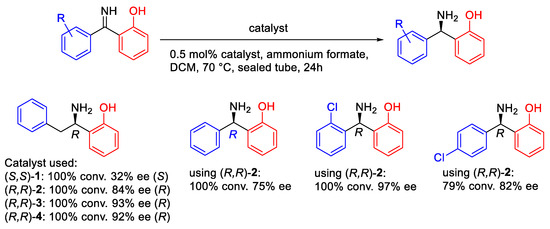
Figure 14.
ATH of imines using a tethered catalyst.
The reductions have several potential applications. The ortho-hydroxy directing effect can be applied to synthesize highly enantioselective compounds, which cannot be made in high ee by direct ATH. In addition, there is also potential to synthesize pharmaceutically valuable targets such as a sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor inhibitor precursor with high enantioselectivity by using a Suzuki coupling reaction (Figure 15).
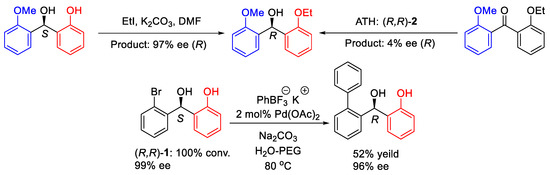
Figure 15.
Functionalizations of the ATH products.
ATH of aryl heteroaryl ketones using Noyori–Ikariya catalysts has also been studied (Figure 16) [20]. Four catalysts have been tested for reducing most of the substrates.
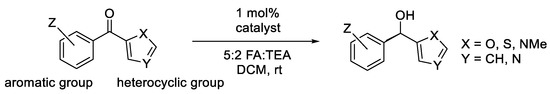
Figure 16.
ATH of hetereocyclic/aromatic ketones—reported examples.
Ketones where Ar = Ph, o-(MeO)C6H4 (oOMe), o-(Me)C6H4 (oMe), o-(Br)C6H4 (oBr), o-(Br)C6H4 (oCl) and α-naphthyl (Np) versus Het = 2-furyl (Fu), 2-thienyl (Thio), 2-N-methylimidazole (Im) and 2-N-methylpyrrole (PyMe) were studied. The results indicated that the electron-rich heterocyclic rings are more competitive and adjacent to the η6-arene ring in transition state (Figure 17).
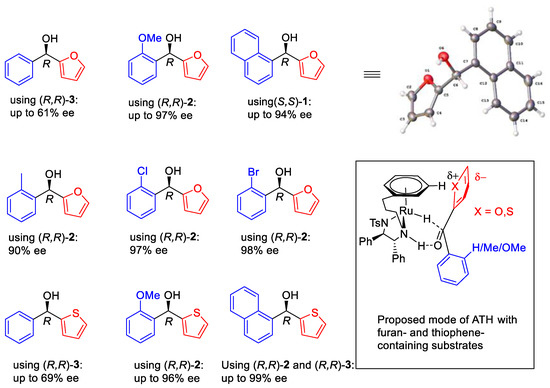
Figure 17.
ATH of aromatic/heterocyclic ketones in this product.
For the N-methylimidazole-containing ketones, the pattern becomes a little bit complex (Figure 18). The X-ray crystallographic structure of 7 showed it is in R configuration after ATH with catalyst (R,R)-2 and the naphthyl ring is out of plane. However, The X-ray crystallographic structure of 8 illustrated the product is in S configuration, which is also confirmed by methylation and comparison with the HPLC of alcohol 9. Therefore, we proposed transition states for these two substrates (Figure 18). The N-methyl imidazole is likely to be protonated under the mildly acidic reaction conditions, so the ortho-methoxyphenyl group could be adjacent to the η6-arene ring as it is more electron-rich. However, the bulky naphthyl ring has more steric effect and favours positioning distal to η6-arene ring. In addition to compounds 7 and 8, we also studied other substrates with N-methylimidazole group and some of them can provide reasonable results although some were resistant to ATH (Figure 19).
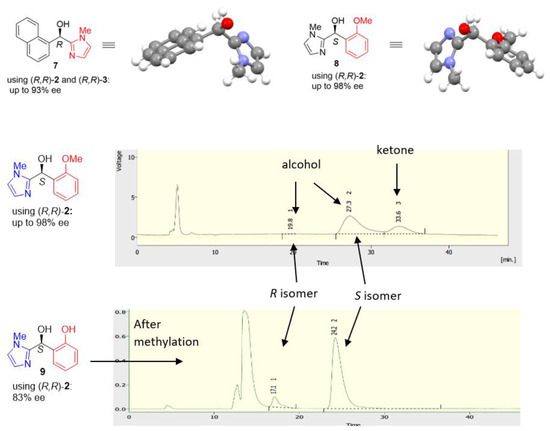
Figure 18.
Determination of configuration of ATH products containing imidazole groups.

Figure 19.
Products of ATH of an extended range of aromatic/heterocyclic ketones, and proposed modes of hydrogen transfer to substrates.
In conclusion,
- (R,R)-3C-tethered catalyst 2 was found to be the most active catalyst for ATH of a series of ortho-hydroxy benzophenone and aromatic/heterocyclic ketones.
- The enantioselectivity can be influenced by a combination of steric and electronic factors.
- The directing effect of the o-OH group in hindered ketones and imines can provide products with high enantioselectivity.
- The reduction enantioselectivity of a range of ketones flanked by a combination of an aromatic and a heterocyclic ring (furan, thiophene, N-methylimidazole) was high (up to 99% ee) in cases where the aromatic ring contained an ortho-substituent.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.Z., J.A.M.-A., L.C.A.B. and M.W.; investigation, Y.Z., J.A.M.-A., M.K., G.J.C.; data curation, Y.Z., J.A.M.-A., M.W. and G.J.C.; writing—original draft preparation, review and editing, Y.Z., L.C.A.B. and M.W.; supervision, L.C.A.B. and M.W.; funding acquisition, L.C.A.B. and M.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hashiguchi, S.; Fujii, A.; Takehara, J.; Ikariya, T.; Noyori, R.J. Asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of aromatic ketones catalyzed by chiral ruthenium (II) complexes. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 7562–7563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, A.; Hashiguchi, S.; Uematsu, N.; Ikariya, T.; Noroyi, R. Ruthenium (II)-catalyzed asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of ketones using a formic acid–triethylamine mixture. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 2521–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dub, P.A.; Ikariya, T.J. Quantum chemical calculations with the inclusion of nonspecific and specific solvation: Asymmetric transfer hydrogenation with bifunctional ruthenium catalysts. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 2604–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dub, P.A.; Gordon, J.C. The mechanism of enantioselective ketone reduction with Noyori and Noyori–Ikariya bifunctional catalysts. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 6756–6781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedden, H.G.; Zanotti-Gerosa, A.; Wills, M. The Development of Phosphine-Free “Tethered” Ruthenium (II) Catalysts for the Asymmetric Reduction of Ketones and Imines. Chem. Rec. 2016, 16, 2619–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonoso, D.A.; Brandt, P.; Nordin, S.J.M.; Andersson, P.G.J. Ru (arene)(amino alcohol)-catalyzed transfer hydrogenation of ketones: Mechanism and origin of enantioselectivity. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 9580–9588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamakawa, M.; Noyori, R. CH/π Attraction: The Origin of Enantioselectivity in Transfer Hydrogenation of Aromatic Carbonyl Compounds Catalyzed by Chiral η6-Arene-Ruthenium (ii) Complexes. Angew. Chem Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 2818–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dub, P.A.; Henson, N.J.; Martin, R.L.; Gordon, J.C. Unravelling the Mechanism of the Asymmetric Hydrogenation of Acetophenone by [RuX2 (diphosphine)(1,2-diamine)] Catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 3505–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashiguchi, S.; Noyori, R. Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation Catalyzed by Chiral Ruthenium Complexes. Acc. Chem. Res. 1997, 30, 97–102. [Google Scholar]
- Soni, R.; Jolley, K.E.; Clarkson, G.J.; Wills, M. Direct formation of tethered Ru (II) catalysts using arene exchange. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 5110–5113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soni, R.; Jolley, K.E.; Gosiewska, S.; Clarkson, G.J.; Fang, Z.; Hall, T.H.; Treloar, B.N.; Knighton, R.C.; Wills, M. Synthesis of enantiomerically pure and racemic benzyl-tethered Ru (II)/TsDPEN complexes by direct arene substitution: Further complexes and applications. Organometallics 2018, 37, 48–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touge, T.; Hakamata, T.; Nara, H.; Kobayashi, T.; Sayo, N.; Saito, T.; Kayaki, Y.; Ikariya, T.J. Oxo-tethered ruthenium (II) complex as a bifunctional catalyst for asymmetric transfer hydrogenation and H2 hydrogenation. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 14960–14963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touge, T.; Nara, H.; Fujiwhara, M.; Kayaki, Y.; Ikariya, T. Efficient Access to Chiral Benzhydrols via Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation of Unsymmetrical Benzophenones with Bifunctional Oxo-Tethered Ruthenium Catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 10084–10087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyas, V.K.; Knighton, R.C.; Bhanage, B.M.; Wills, M. Combining Electronic and Steric Effects To Generate Hindered Propargylic Alcohols in High Enantiomeric Excess. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 975–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Zhou, H.; Lu, G.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, X. Bifunctional oxo-tethered ruthenium complex catalyzed asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of aryl N-heteroaryl ketones. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 2094–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhou, H.; Wang, B.; Lv, J.; Cao, L.; Fu, Y. Iridium-catalyzed highly enantioselective transfer hydrogenation of aryl N-heteroaryl ketones with N-oxide as a removable ortho-substituent. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 971–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Bobes, G.; Hanson, R.; Strotman, N.; Guo, Z.; Goswami, A. Enantioselective Synthesis of a Positive Allosteric Modulator of the Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 (mGluR5) Receptor via Dynamic Kinetic Resolution of α-Amino Ketones. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2016, 358, 2077–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Clarkson, G.J.; Wills, M. Asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of o-hydroxyphenyl ketones: Utilizing directing effects that optimize the asymmetric synthesis of challenging alcohols. Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 3717–3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangion, I.K.; Chen, C.Y.; Li, H.; Maligres, P.; Chen, Y.; Christensen, M.; Cohen, R.; Jeon, I.; Klapars, A.; Krska, S.; et al. Enantioselective synthesis of an HCV NS5a antagonist. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 2310–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Martinez-Acosta, J.A.; Khimji, M.; Barbosa, L.C.A.; Clarkson, G.J.; Wills, M. Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation of Aryl Heteroaryl Ketones using Noyori-Ikariya Catalysts. ChemCatChem 2021, 13, 4384–4391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).