Customized Screen-Printed Electrodes Based on Ag-Nanoseeds for Enhanced Electroanalytical Response towards Cd(II), Pb(II) and As(V) in Aqueous Samples †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Apparatus
2.2. Preparation of Working Electrodes
2.3. Electrochemical Measurements
3. Results
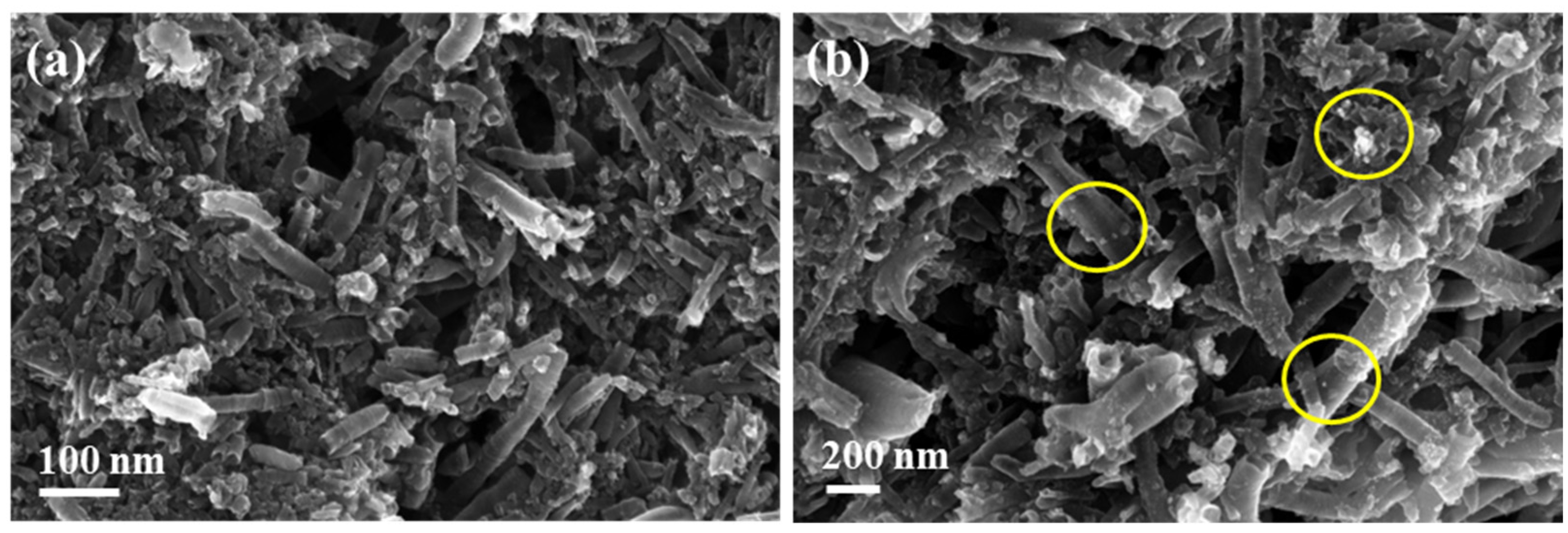
3.1. Microscopic Characterization
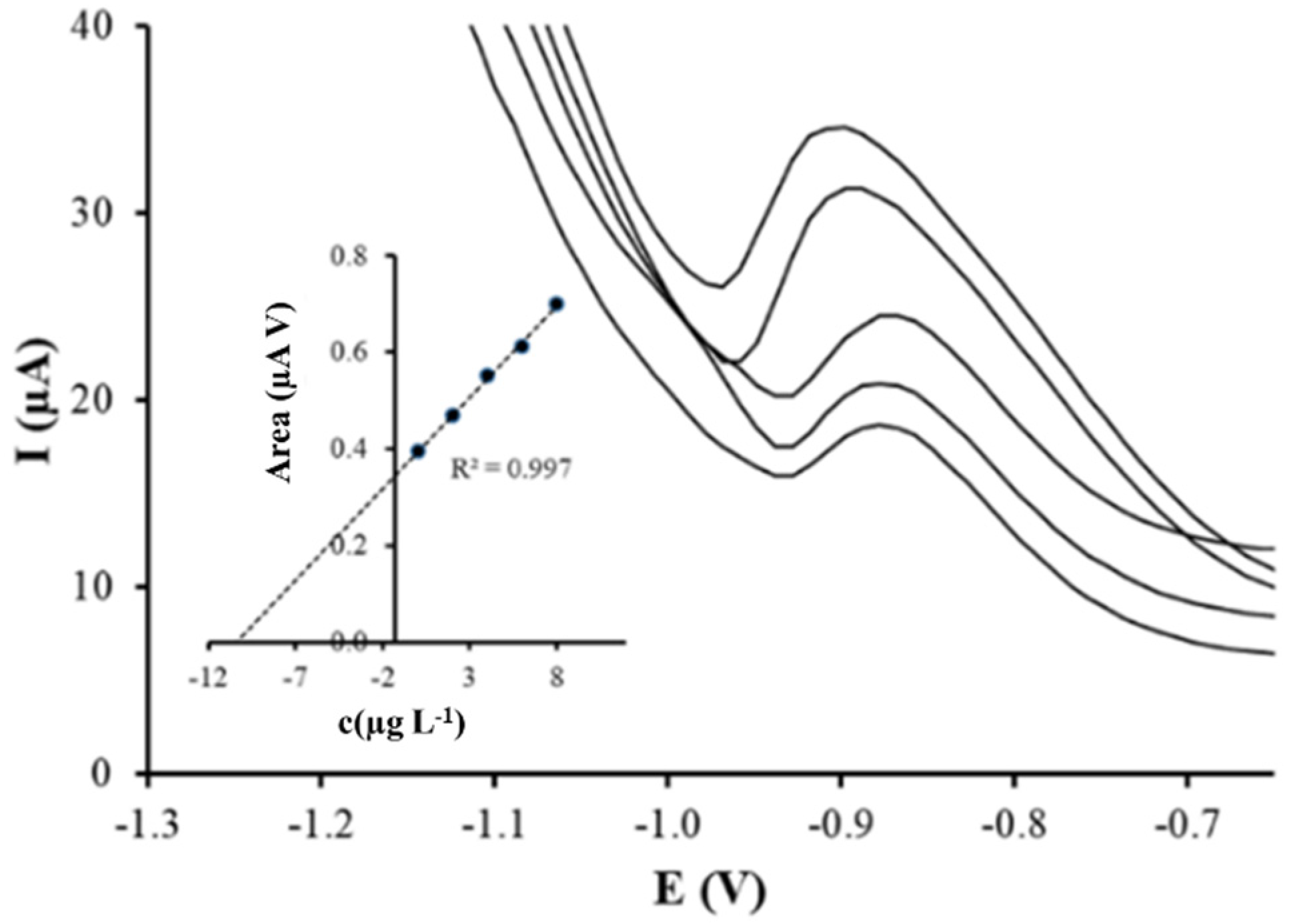
3.2. Electrochemical Characterization
3.3. Application to the Analysis of Spiked Tap Water
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barton, J.; García, M.B.G.; Santos, D.H.; Fanjul-Bolado, P.; Ribotti, A.; McCaul, M.; Diamond, D.; Magni, P. Screen-printed electrodes for environmental monitoring of heavy metal ions: A review. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 503–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; WHO, Ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; ISBN 978-92-4-154995-0. [Google Scholar]
- Daşbaşi, T.; Saçmaci, Ş.; Çankaya, N.; Soykan, C. A new synthesis, characterization and application chelating resin for determination of some trace metals in honey samples by FAAS. Food Chem. 2016, 203, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azimi, S.; Es’haghi, Z. A Magnetized Nanoparticle Based Solid-Phase Extraction Procedure Followed by Inductively Coupled Plasma Atomic Emission Spectrometry to Determine Arsenic, Lead and Cadmium in Water, Milk, Indian Rice and Red Tea. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2017, 98, 830–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, G.; Zhou, J.; Tao, G. Determination of trace amounts of lead, arsenic, nickel and cobalt in high-purity iron oxide pigment by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry after iron matrix removal with extractant-contained resin. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 584, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirkhanloo, H.; Mousavi, H.Z.; Rouhollahi, A. Speciation and determination of trace amount of inorganic arsenic in water, environmental and biological samples. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2011, 58, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, D.; Zhao, J.; Liu, J.; Yang, W.; Qu, K. On-site determination of Pb2+and Cd2+in seawater by double stripping voltammetry with bismuth-modified working electrodes. Microchem. J. 2016, 126, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.G.; Huang, X.J. Voltammetric determination of inorganic arsenic. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 60, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Rivero, K.; Florido, A.; Bastos-Arrieta, J. Recent Trends in the Improvement of the Electrochemical Response of Screen-Printed Electrodes by Their Modification with Shaped Metal Nanoparticles. Sensors 2021, 21, 2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Song, W.; Shi, L.; Li, Y.; Long, Y. High Sensitive On-Site Cadmium Sensor Based on AuNPs Amalgam Modified Screen-Printed. IEEE Sen. J. 2010, 10, 1583–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, J.; Jia, X.; Wang, E. Gold nanoparticles decorated carbon fiber mat as a novel sensing platform for sensitive detection of Hg(II). Electrochem. Commun. 2014, 42, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Rivero, K.; Pérez-Ràfols, C.; Bastos-Arrieta, J.; Florido, A.; Martí, V.; Serrano, N. Direct As(V) determination using screen-printed electrodes modified with silver nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Luo, X.K.; Li, Y.H.; Zhao, Q.N.; Li, M.M.; Zhao, Y.T.; Sun, T.S.; Ma, C. Simultaneous determination of trace Cd(II), Pb(II) and Cu(II) by differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry using a reduced graphene oxide-chitosan/poly-L-lysine nanocomposite modified glassy carbon electrode. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 490, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, T.; Dhanalakshmi, N.; Thennarasu, S.; Thinakaran, N. A novel voltammetric sensor for the simultaneous detection of Cd2+and Pb2+using graphene oxide/κ-carrageenan/L-cysteine nanocomposite. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 182, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Rivero, K.; Torralba-Cadena, L.; Espriu-Gascon, A.; Casas, I.; Bastos-Arrieta, J.; Florido, A. Strategies for Surface Modification with Ag-Shaped Nanoparticles: Electrocatalytic Enhancement of Screen-Printed Electrodes for the Detection of Heavy Metals. Sensors 2019, 19, 4249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murray, R.W. Nanoelectrochemistry: Metal Nanoparticles, Nanoelectrodes, and Nanopores. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 2688–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanllorente-Méndez, S.; Domínguez-Renedo, O.; Arcos-Martínez, M.J. Determination of arsenic(III) using platinum nanoparticle-modified screen-printed carbon-based electrodes. Electroanalysis 2009, 21, 635–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairy, M.; Kampouris, D.K.; Kadara, R.O.; Banks, C.E. Gold Nanoparticle Modified Screen Printed Electrodes for the Trace Sensing of Arsenic(III) in the Presence of Copper(II). Electroanalysis 2010, 22, 2496–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Sun, Q.; Li, H.; Sun, F.; Hu, N.; Wang, P. Screen-printed gold electrode with gold nanoparticles modification for simultaneous electrochemical determination of lead and copper. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 209, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tukur, S.; Azah Yusof, N.; Hajian, R. Gold Nanoparticles Modified Screen Printed Electrode for Determination of Pb (II) Ion Using Linear Sweep Anodic Stripping Voltammetry. IEEE Sens. J. 2014, 15, 2780–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico, M.Á.G.; Olivares-Marín, M.; Gil, E.P. Modification of carbon screen-printed electrodes by adsorption of chemically synthesized Bi nanoparticles for the voltammetric stripping detection of Zn(II), Cd(II) and Pb(II). Talanta 2009, 80, 631–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, G.; Yin, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, G. Screen-Printed Electrode Modified by Bismuth /Fe3O4 Nanoparticle/Ionic Liquid Composite Using Internal Standard Normalization for Accurate Determination of Cd(II) in Soil. Sensors 2017, 18, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pérez-Ràfols, C.; Bastos-Arrieta, J.; Serrano, N.; Díaz-Cruz, J.M.; Ariño, C.; de Pablo, J.; Esteban, M. Ag nanoparticles drop-casting modification of screen-printed electrodes for the simultaneous voltammetric determination of Cu(II) and Pb(II). Sensors 2017, 17, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aherne, D.; Ledwith, D.M.; Gara, M.; Kelly, J.M. Optical properties and growth aspects of silver nanoprisms produced by a highly reproducible and rapid synthesis at room temperature. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 2005–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aherne, D.; Cara, M.; Kelly, J.M.; Gun’Ko, Y.K. From Ag nanoprisms to triangular AuAg nanoboxes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 1329–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.N.; Miller, J. Métodos de Calibración en Análisis Instrumental: Regresión y Correlación, 4th ed.; Capella, I., Ed.; Prentice Hall: Madrid, Spain, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz, J.; Bastos-Arrieta, J.; Muñoz, M.; Muraviev, D.; Céspedes, F.; Baeza, M. CdS quantum dots as a scattering nanomaterial of carbon nanotubes in polymeric nanocomposite sensors for microelectrode array behavior. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 1610–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Promphet, N.; Rattanarat, P.; Rangkupan, R.; Chailapakul, O.; Rodthongkum, N. An electrochemical sensor based on graphene/polyaniline/polystyrene nanoporous fibers modified electrode for simultaneous determination of lead and cadmium. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 207, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaoka, Y.; Ivandini, T.A.; Yamada, D.; Fujita, S.; Yamanuki, M.; Einaga, Y. Selective detection of As(V) with high sensitivity by as-deposited boron-doped diamond electrodes. Chem. Lett. 2010, 39, 1055–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Analyte | LOD (µg L−1) | Linear Range (µg L−1) a | R2 | Sensitivity (nA µg−1 L) b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb(II) | 3.3 | 11.00–99.6 | 0.999 | 103 (1) |
| Cd(II) | 3.7 | 12.2–73.4 | 0.992 | 22 (1) |
| As(V) | 2.6 | 8.9–40.0 | 0.991 | 260 (10) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Torres-Rivero, K.; Pérez-Ràfols, C.; Bastos-Arrieta, J.; Serrano, N.; Martí, V.; Florido, A. Customized Screen-Printed Electrodes Based on Ag-Nanoseeds for Enhanced Electroanalytical Response towards Cd(II), Pb(II) and As(V) in Aqueous Samples. Chem. Proc. 2021, 5, 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/CSAC2021-10469
Torres-Rivero K, Pérez-Ràfols C, Bastos-Arrieta J, Serrano N, Martí V, Florido A. Customized Screen-Printed Electrodes Based on Ag-Nanoseeds for Enhanced Electroanalytical Response towards Cd(II), Pb(II) and As(V) in Aqueous Samples. Chemistry Proceedings. 2021; 5(1):87. https://doi.org/10.3390/CSAC2021-10469
Chicago/Turabian StyleTorres-Rivero, Karina, Clara Pérez-Ràfols, Julio Bastos-Arrieta, Núria Serrano, Vicenç Martí, and Antonio Florido. 2021. "Customized Screen-Printed Electrodes Based on Ag-Nanoseeds for Enhanced Electroanalytical Response towards Cd(II), Pb(II) and As(V) in Aqueous Samples" Chemistry Proceedings 5, no. 1: 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/CSAC2021-10469
APA StyleTorres-Rivero, K., Pérez-Ràfols, C., Bastos-Arrieta, J., Serrano, N., Martí, V., & Florido, A. (2021). Customized Screen-Printed Electrodes Based on Ag-Nanoseeds for Enhanced Electroanalytical Response towards Cd(II), Pb(II) and As(V) in Aqueous Samples. Chemistry Proceedings, 5(1), 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/CSAC2021-10469










