A Computational Investigation of Potential 5-HT 2C Receptor Inhibitors for Treating Schizophrenia by ADMET Profile Analysis, Molecular Docking, DFT, Network Pharmacology, and Molecular Dynamic Simulation †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Preparation of Protein and Ligands
2.2. ADMET Analysis
2.3. Molecular Docking and Network Pharmacology Study
2.4. Optimization
2.5. Molecular Dynamic Simulation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Molecular Docking
3.2. ADMET Analysis
3.3. Network Pharmacology
3.4. Optimization
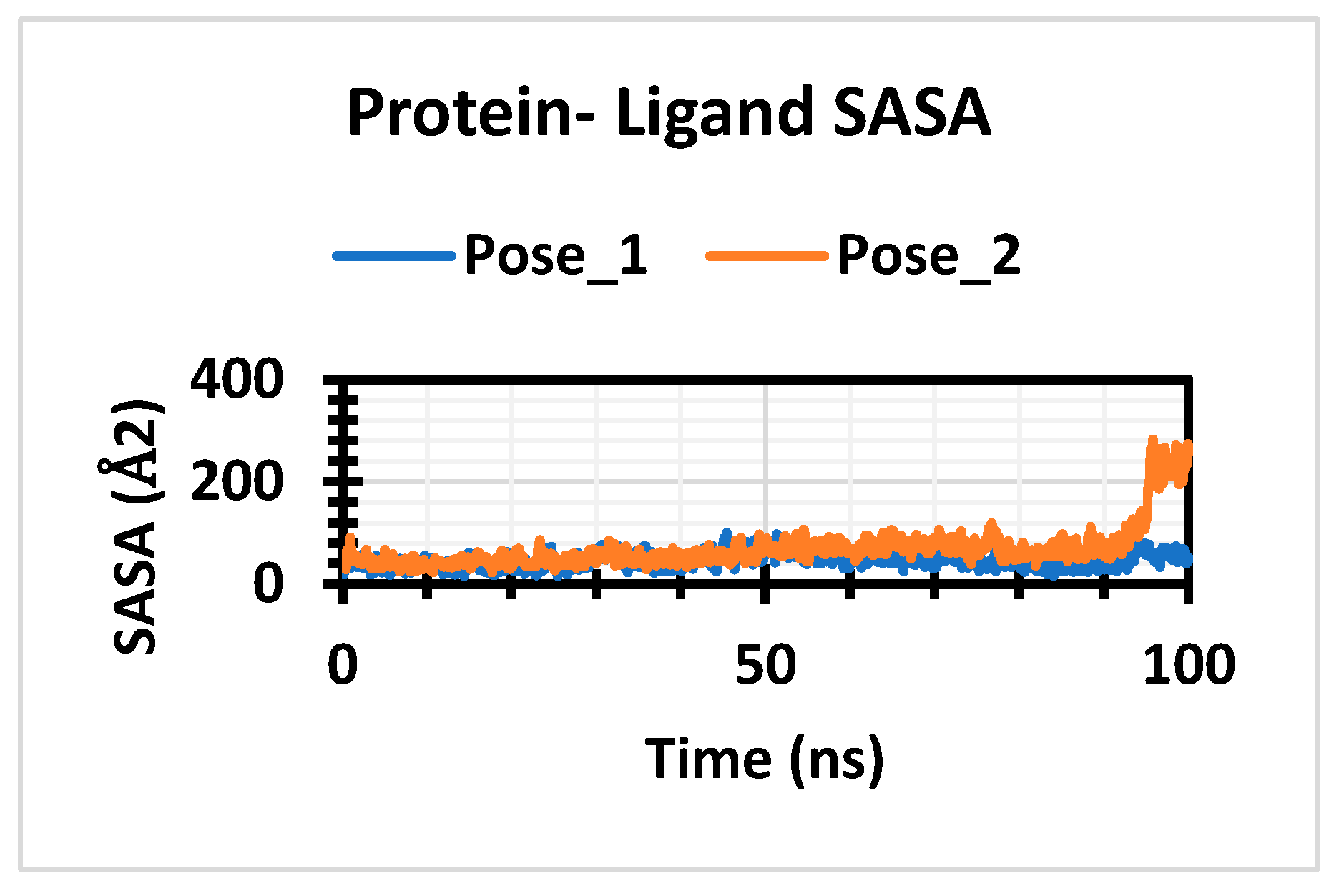
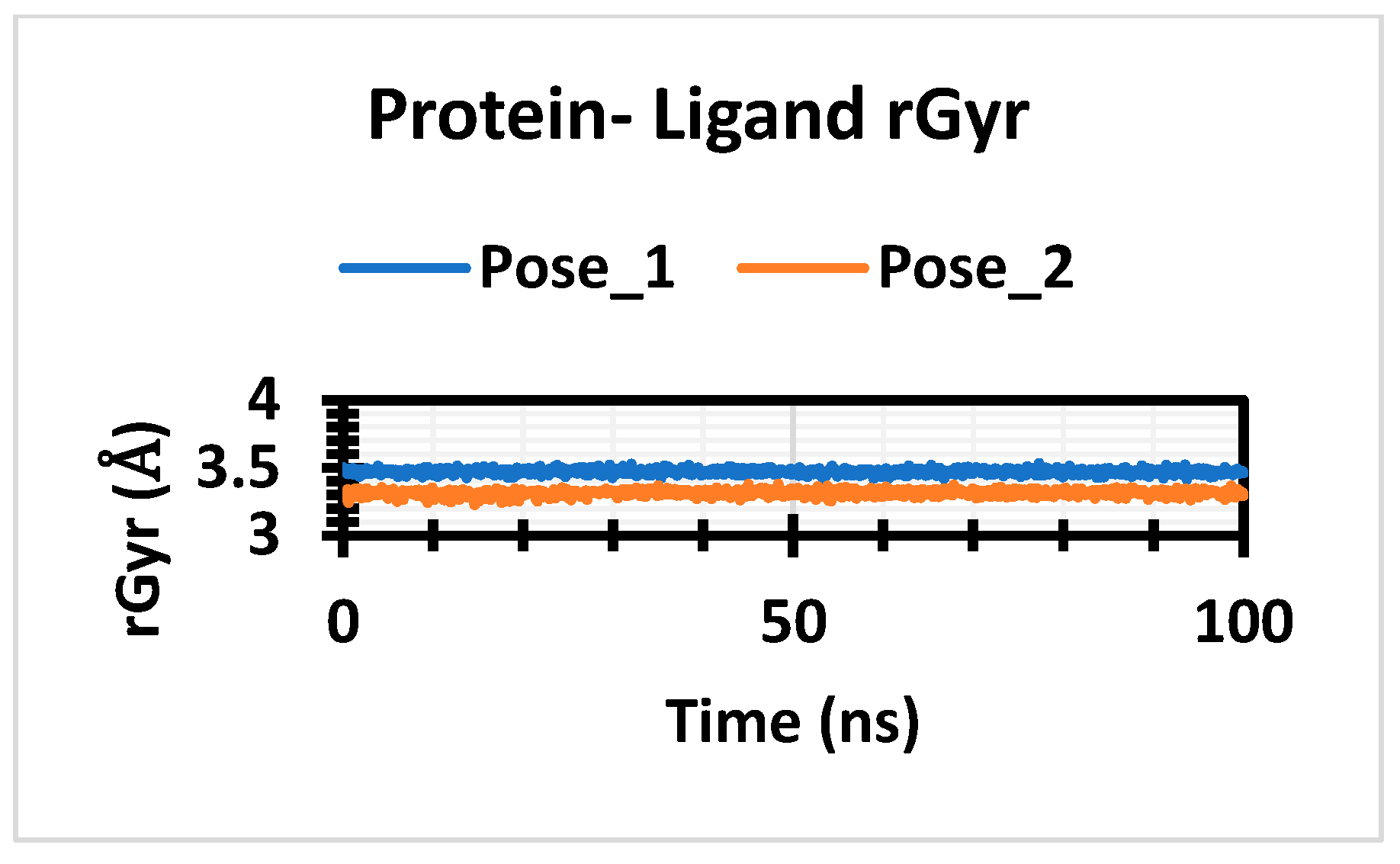
3.5. Molecular Dynamic Simulation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhalala, O.G.; Nath, A.P.; Consortium, U.B.E.; Inouye, M.; Sibley, C.R. Identification of expression quantitative trait loci associated with schizophrenia and affective disorders in normal brain tissue. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blokhin, I.O.; Khorkova, O.; Saveanu, R.V.; Wahlestedt, C. Molecular mechanisms of psychiatric diseases. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 146, 105136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munawar, N.; Ahsan, K.; Ahmad, A. Natural molecules in the treatment of schizophrenia. In Natural Molecules in Neuroprotection and Neurotoxicity; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 259–280. [Google Scholar]
- Stępnicki, P.; Kondej, M.; Kaczor, A.A. Current concepts and treatments of schizophrenia. Molecules 2018, 23, 2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacabelos, R.; Martínez-Bouza, R. Genomics and pharmacogenomics of schizophrenia. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2011, 17, 541–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

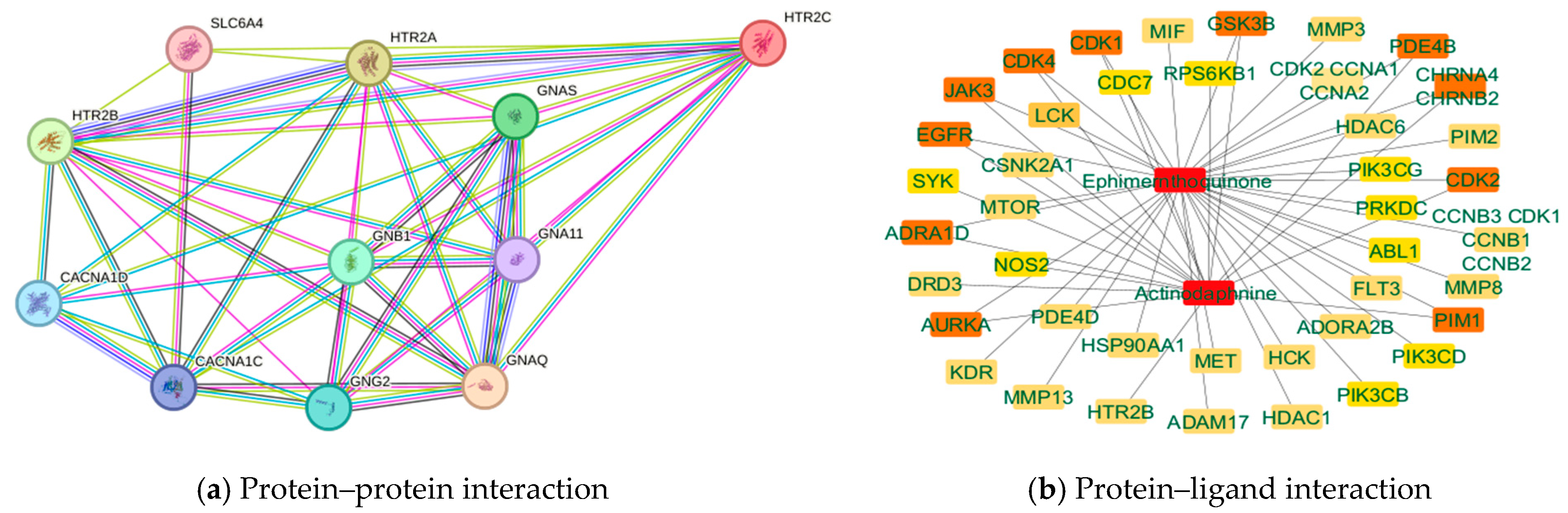
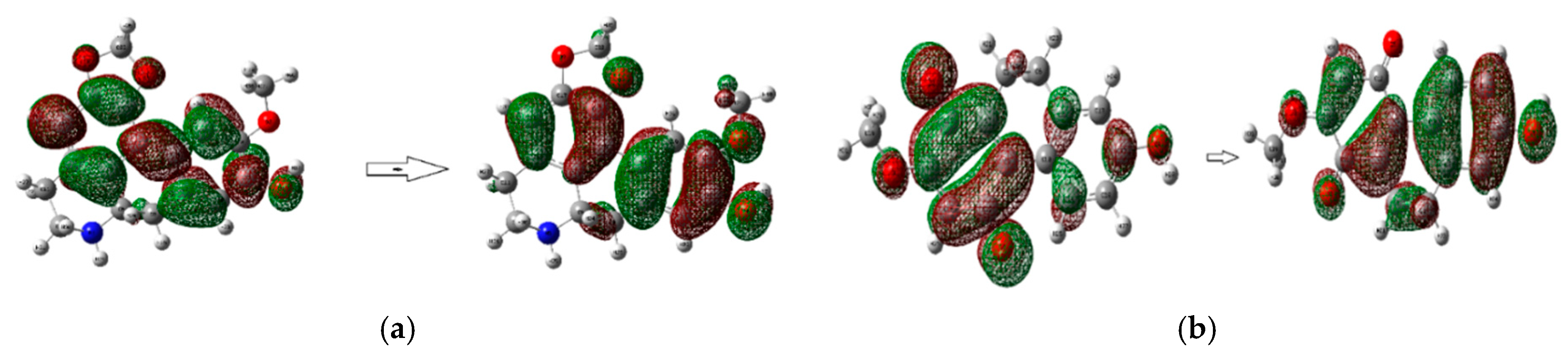
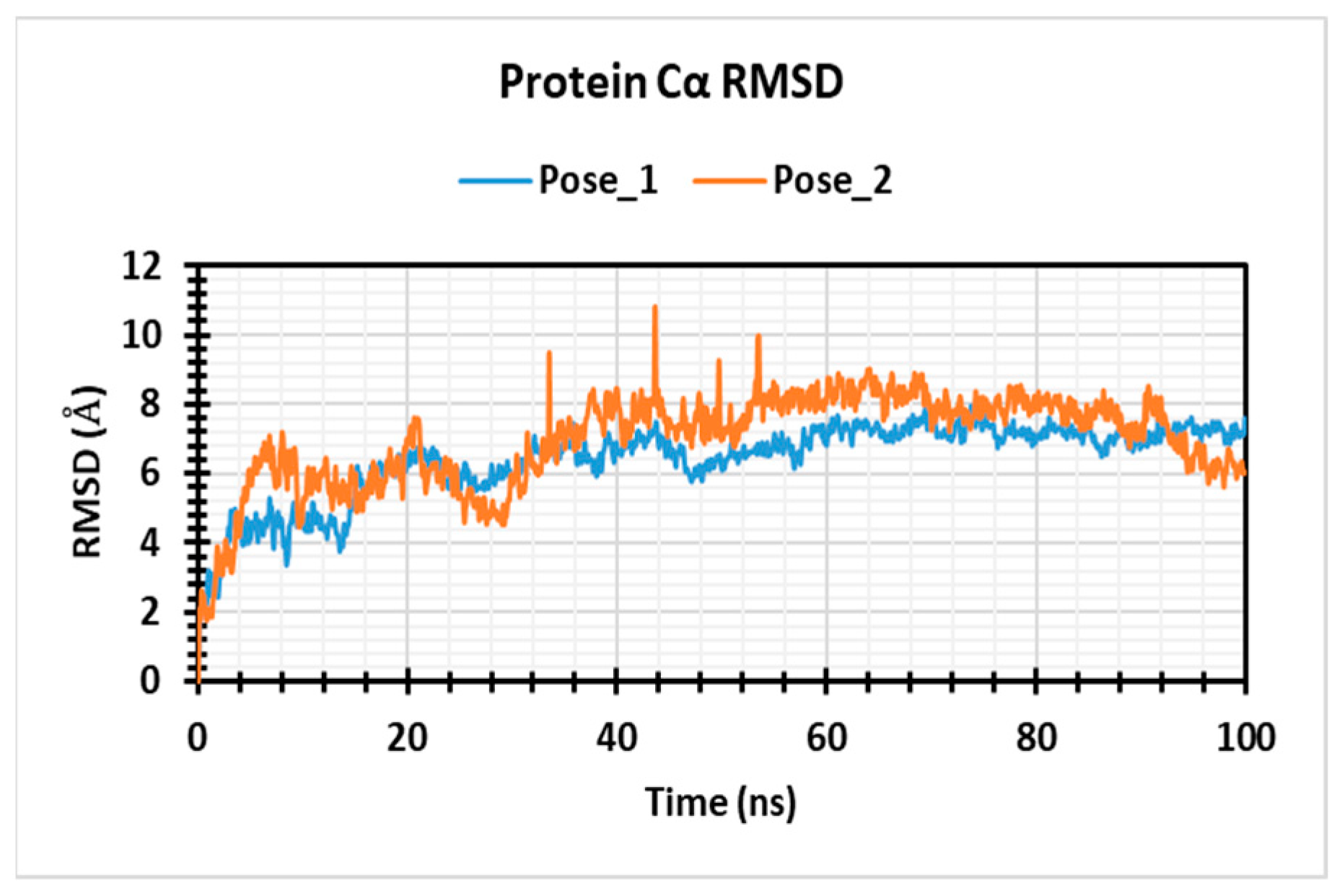
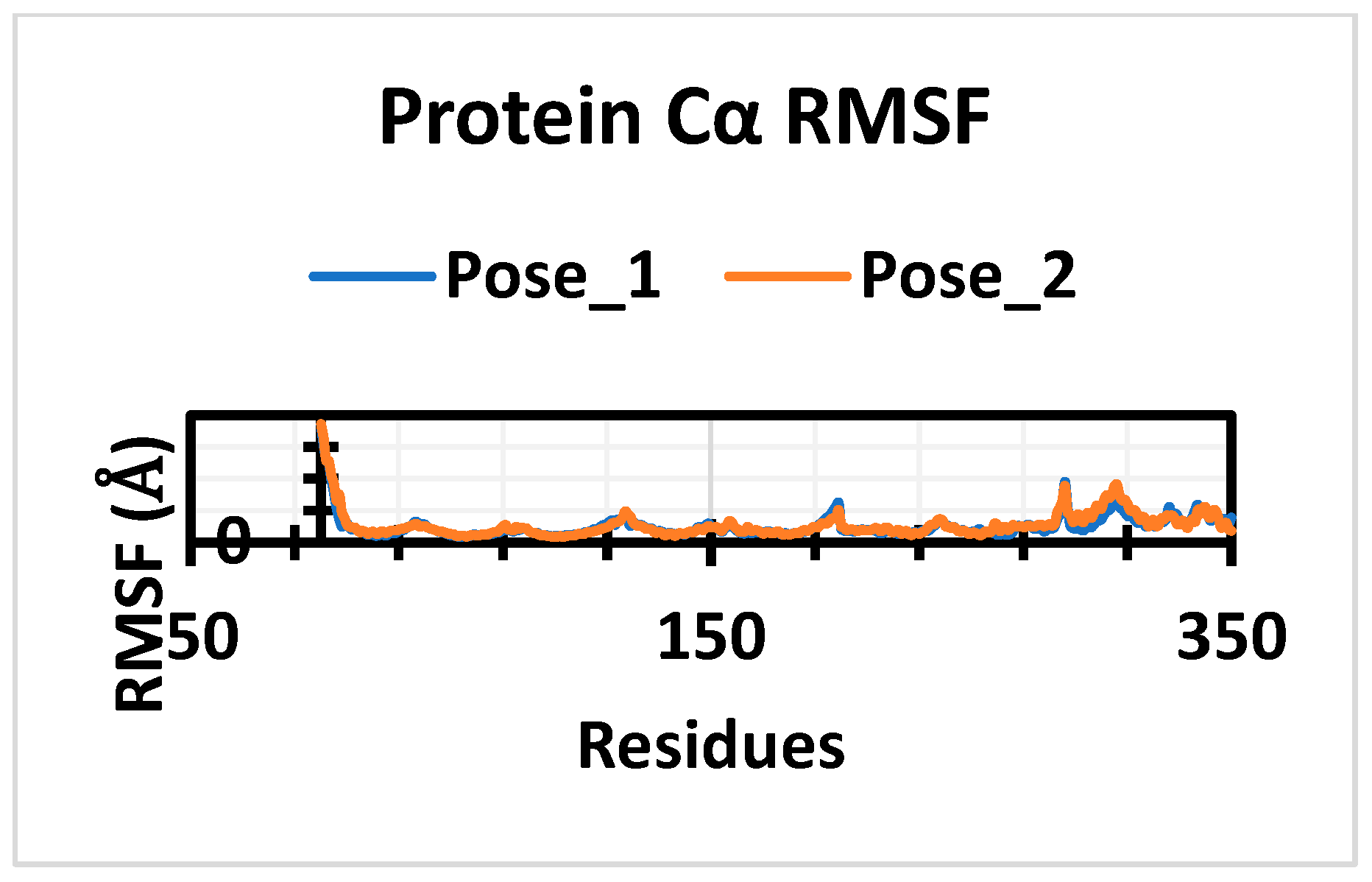
| Compounds | Ligands (Pubchem ID and Binding Energy) | Binding Affinity | RMSD/ub | RMSD/lb |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ephemeranthoquinone | Pubchem CID: 10038025, E = 289.17 | −9.4 | 0 | 0 |
| Actinodaphnine | Pubchem CID: 160502, E = 516.18 | −9.3 | 0 | 0 |
| Ligands | Residues | Distances (Å) | Bonding Category | Bonding Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ephemeranthoquinone | PHE214 | 3.56622 | Hydrogen Bond | Carbon Hydrogen Bond |
| N:UNK1—A:PHE223 | 5.36526 | Hydrophobic | Pi-Pi T-shaped | |
| N:UNK1—A:TRP324 | 4.8013 | Hydrophobic | Pi-Pi T-shaped | |
| N:UNK1—A:PHE328 | 4.96592 | Hydrophobic | Pi-Pi T-shaped | |
| A:TRP324—N:UNK1 | 5.32573 | Hydrophobic | Pi-Pi T-shaped | |
| N:UNK1—A:VAL135 | 4.38739 | Hydrophobic | Pi-Alkyl | |
| Actinodaphnine | N:UNK1:H—A:ALA222:O | 2.3234 | Hydrogen Bond | Conventional Hydrogen Bond |
| N:UNK1:C—A:ASP134:OD1 | 3.77496 | Hydrogen Bond | Carbon Hydrogen Bond | |
| N:UNK1:C—A:SER138:O | 3.14898 | Hydrogen Bond | Carbon Hydrogen Bond | |
| N:UNK1:C—A:TRP324 | 3.76078 | Hydrophobic | Pi-Sigma | |
| N:UNK1:C—A:TRP324 | 3.93109 | Hydrophobic | Pi-Sigma | |
| A:TRP324—N:UNK1 | 5.48968 | Hydrophobic | Pi-Pi T-shaped | |
| A:PHE328—N:UNK1 | 4.72948 | Hydrophobic | Pi-Pi T-shaped |
| Compounds Name | Molecular Weight (g/mol) | Lipophilicity (XLOGP3) | Water Solubility (Log S (ESOL)) | GI Absorption | BBB Permeant | Lipinski |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ephemeranthoquinone | 256.25 | 1.8 | −2.73 | High | Yes | Yes; 0 violation |
| Actinodaphnine | 311.33 | 2.45 | −3.63 | High | Yes | Yes; 0 violation |
| Compounds | Hepatotoxicity | Carcinogenicity | Mutagenicity | Cytotoxicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ephemeranthoquinone | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive |
| Actinodaphnine | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive |
| Molecule | HOMO | LUMO | Gap | Hardness | Softness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actinodaphnine | −0.18821 | −0.02135 | 0.16686 | 0.08343 | 11.98 |
| Ephemeranthoquinone | −0.21416 | −0.11263 | 0.10153 | 0.050765 | 19.69 |
| Name | Stoichiometry | Electron Energy | Enthalpy | Gibbs Free Energy | Dipole Moment (Debye) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actinodaphnine | C18H17NO4 | −1051.46 | −1051.46 | −1051.52 | 2.220016 |
| Ephemeranthoquinone | C15H12O4 | −879.45 | −879.45 | −879.51 | 1.437410 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uddin, M.R.; Rahman, M.; Rafin, M.J.N.; Ripa, J.D. A Computational Investigation of Potential 5-HT 2C Receptor Inhibitors for Treating Schizophrenia by ADMET Profile Analysis, Molecular Docking, DFT, Network Pharmacology, and Molecular Dynamic Simulation. Chem. Proc. 2024, 16, 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-28-20242
Uddin MR, Rahman M, Rafin MJN, Ripa JD. A Computational Investigation of Potential 5-HT 2C Receptor Inhibitors for Treating Schizophrenia by ADMET Profile Analysis, Molecular Docking, DFT, Network Pharmacology, and Molecular Dynamic Simulation. Chemistry Proceedings. 2024; 16(1):69. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-28-20242
Chicago/Turabian StyleUddin, Mohammed Raihan, Mahira Rahman, Mosammad Jannatun Nayem Rafin, and Joya Datta Ripa. 2024. "A Computational Investigation of Potential 5-HT 2C Receptor Inhibitors for Treating Schizophrenia by ADMET Profile Analysis, Molecular Docking, DFT, Network Pharmacology, and Molecular Dynamic Simulation" Chemistry Proceedings 16, no. 1: 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-28-20242
APA StyleUddin, M. R., Rahman, M., Rafin, M. J. N., & Ripa, J. D. (2024). A Computational Investigation of Potential 5-HT 2C Receptor Inhibitors for Treating Schizophrenia by ADMET Profile Analysis, Molecular Docking, DFT, Network Pharmacology, and Molecular Dynamic Simulation. Chemistry Proceedings, 16(1), 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-28-20242






