2. Materials and Methods
In silico bioactivity screening for 4,6-dihydroxy-2-methylpyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde (2) was performed using the PASS Online web resource.
The interaction of substrate
1 with Vilsmeier’s reagent in a 1:1 ratio gave 4,6-dihydroxy-2-methylpyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde (
2). The substitution of hydroxyl groups for chlorine observed in reactions with similar substrates did not occur [
3] (
Scheme 1).
The synthesis was monitored by thin-layer chromatography (TLC) in a 1:9 methanol/dichloromethane system with UV detection. The structure of product
2 was proven by NMR spectroscopy at
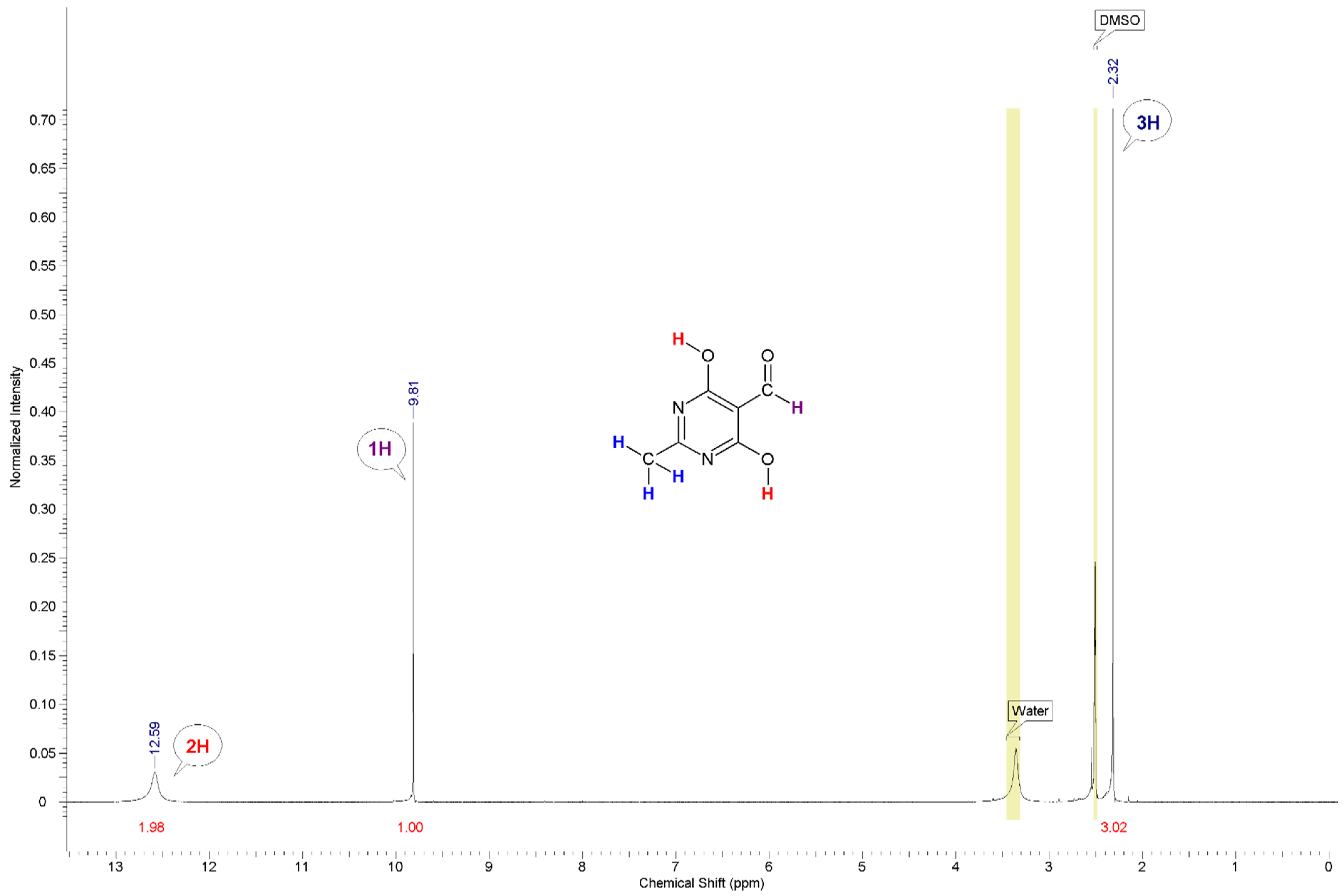
1H (
Figure 1) and
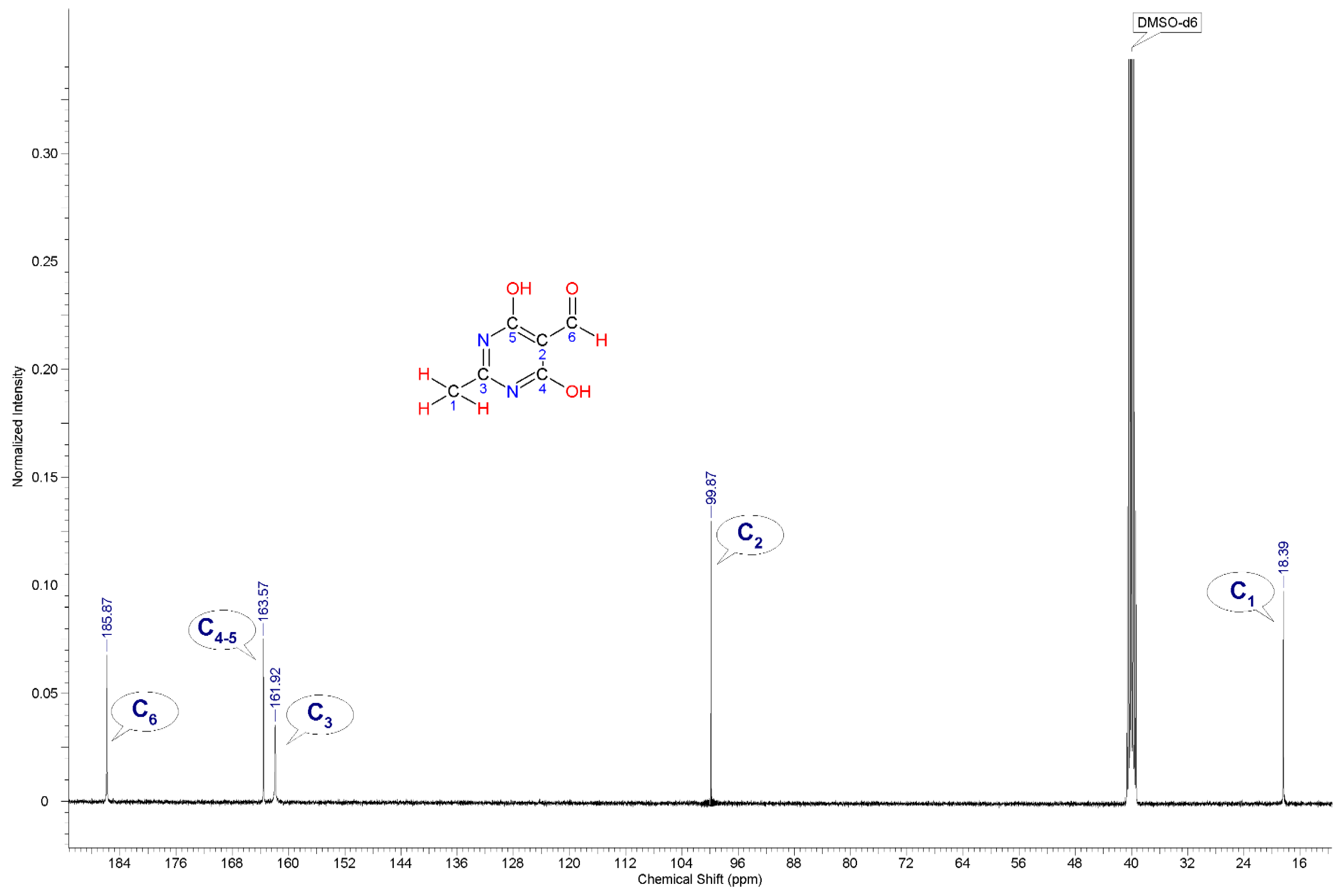
13C (
Figure 2) nuclei and by mass spectrometry.
In each individual experiment, strictly equivalent amounts of substrate 1 and Vilsmeier’s reagent were taken.
2.1. Interaction of 2-Methylpyrimidine-4,6-diol with Vilsmeier’s Reagent in Benzene
The prepared and cooled mixture of phosphorus chloroxide (0.29 mL, 3.16 mmol) and DMF (0.49 mL, 6.3 mmol) under vigorous stirring was added dropwise to a suspension of 0.4 g (3.16 mmol) of substrate 1 in benzene (20 mL). The reaction was boiled with reflux condenser for 6 h. The reaction was monitored by thin-layer chromatography in a 1:9 system of methanol and dichloromethane with UV detection for the absence of the starting compound in the reaction mixture. The reaction mixture was poured on ice and stirred overnight. The resulting precipitate was filtered off then dried at 60 °C. The practical yield of product 2 was 48%.
The NMR spectrum (1H, DMSO-d6) of the synthesised compound 2 is characterised by the presence of an aldehyde group proton singlet at 9.81 ppm with an integrated intensity of 1. There is also an OH-group proton singlet at 12.59 ppm with an integrated intensity of 1.96 and a methyl group proton singlet at 2.32 ppm with an integrated intensity of 3.02.
The NMR spectrum (13C, DMSO-d6) of the synthesised compound 2 is characterised by signals of methyl group carbon atoms (C1) in the region of 18.39 ppm, a C2 atom in the region of 99.7 ppm, C3 in the region of 161.92 ppm, C4 and C5 carbon atoms at −163.57 ppm, and a carbon atom of carbonyl group (C6) in the region of 185.87 ppm.
MS-ESI mass spectrometry: m/z [M-H]—calculated: 153.33; found: 153.20.
2.2. Interaction of 2-Methylpyrimidine-4,6-diol with Vilsmeier’s Reagent in 1,2-Dichloroethane
A previously prepared and cooled mixture of phosphorus chloroxide (0.29 mL, 3.16 mmol) and DMF (0.49 mL, 6.3 mmol) was added carefully dropwise to a suspension of 0.4 g (3.16 mmol) of substrate 1 in 1,2-dichloroethane (20 mL) under vigorous stirring. The reaction was boiled with reverse refrigerator for 6 h. The reaction was monitored by thin-layer chromatography in a 1:9 methanol/dichloromethane system with UV detection for the absence of the starting compound in the reaction mixture. The reaction mixture was poured on ice and stirred overnight. The resulting precipitate was filtered and dried at 60 °C. The practical yield of product 2 was 50%.
The NMR spectrum (1H, DMSO-d6) of the synthesised compound 2 is characterised by the presence of an aldehyde group proton singlet at 9.79 ppm with an integrated intensity of 1.01; there is also an OH-group proton singlet at 12.53 ppm with an integrated intensity of 2.04 and a methyl group proton singlet at 2.41 ppm with an integrated intensity of 2.96.
The NMR spectrum (13C, DMSO-d6) of the synthesised compound 2 is characterised by signals of methyl group carbon atoms (C1) in the region of 18.21 ppm, a C2 atom in the region of 99.56 ppm, C3 in the region of 161.13 ppm, C4 and C5 carbon atoms at −163.69 ppm, and a carbon atom of carbonyl group (C6) in the region of 185.55 ppm.
MS-ESI mass spectrometry: m/z [M-H]—calculated: 153.33; found: 153.11.
2.3. Interaction of 2-Methylpyrimidine-4,6-diol with Vilsmeier’s Reagent in DMF
The prepared and cooled mixture of phosphorus chloroxide (0.29 mL, 3.16 mmol) and DMF (0.49 mL, 6.3 mmol) was carefully added dropwise to a suspension of 0.4 g (3.16 mmol) of substrate 1 in DMF (3 mL) under vigorous stirring. The reaction was incubated at 80 °C for 5 h. The reaction was monitored by thin-layer chromatography in a 1:9 methanol/dichloromethane system with UV detection for the absence of the starting compound in the reaction mixture. The reaction mixture was poured on ice and stirred overnight. The resulting precipitate was filtered off and dried at 60 °C. The practical yield of product 2 was 61%.
The NMR spectrum (1H, DMSO-d6) of the synthesised compound 2 is characterised by the presence of an aldehyde group proton singlet in the region of 9.8 ppm with an integrated intensity of 0.96; there is also an OH-group proton singlet in the region of 12.6 ppm with an integrated intensity of 2.20 and a methyl group proton singlet in the region of 2.31 ppm with an integrated intensity of 2.94.
The NMR spectrum (13C, DMSO-d6) of the synthesised compound 2 is characterised by signals of methyl group carbon atoms (C1) in the region of 18.91 ppm, a C2 atom in the region of 99.34 ppm, C3 in the region of 161.35 ppm, C4 and C5 carbon atoms at −163.54 ppm, and a carbon atom of carbonyl group (C6) in the region of 185.76 ppm.
MS-ESI mass spectrometry: m/z [M-H]—calculated: 153.33; found: 153.47.
2.4. Interaction of 2-Methylpyrimidine-4,6-diol with Vilsmeier’s Reagent in o-Xylene
The prepared and cooled mixture of phosphorus chloroxide (0.29 mL, 3.16 mmol) and DMFA (0.49 mL, 6.3 mmol) was added dropwise to a suspension of 0.4 g (3.16 mmol) of substrate 1 in o-xylene (20 mL) under vigorous stirring. The reaction was incubated at 100 °C for 7. The reaction was monitored by thin-layer chromatography in a 1:9 methanol/dichloromethane system with UV detection for the absence of the starting compound in the reaction mixture. The reaction mixture was poured on ice and stirred overnight. The resulting precipitate was filtered off and dried at 60 °C. The practical yield of product 2 was 49%.
The NMR spectrum (1H, DMSO-d6) of the synthesised compound 2 is characterised by the presence of an aldehyde group proton singlet in the region of 9.91 ppm with an integrated intensity of 0.94; there is also an OH-group proton singlet in the region of 12.58 ppm with an integrated intensity of 1.89 and a methyl group proton singlet in the region of 2.54 ppm with an integrated intensity of 3.13.
The NMR spectrum (13C, DMSO-d6) of the synthesised compound 2 is characterised by signals of methyl group carbon atoms (C1) in the region of 18.23 ppm, a C2 atom in the region of 99.44 ppm, C3 in the region of 161.33 ppm, C4 and C5 carbon atoms −163.78 ppm, and a carbon atom of carbonyl group (C6) in the region of 185.45 ppm.
MS-ESI mass spectrometry: m/z [M-H]—calculated: 153.33; found: 153.01.
3. Results and Discussion
Based on the PASS Online screening data, product 2 has a probability (probably active) greater than 0.8 of being an agonist of I1-imidazoline receptors, which accounts for its antihypertensive activity.
I1-imidazoline receptors are responsible for the antihypertensive activity.
Regardless of the solvent used, the reaction of substrate
1 with Vilsmeier’s reagent in a 1:1 ratio resulted in the formation of product
2, which was confirmed by NMR spectroscopy data at
1H (
Figure 1) and
13C nuclei (
Figure 2), as well as by mass spectrometry (
Figure 3).
As a result of this work, the optimal solvent for the above reaction was selected. In DMF medium, product
2 was obtained with the highest practical yield of 61% at a holding time of 5 h (
Table 1).