Abstract
The enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE) acts in mammalians and insects. Its inhibitors are considered to treat human disease and to develop insecticides. Docking calculations were performed by using AutoDock Vina and Protein–Ligand ANTSystem (PLANTS) on the Torpedo californica AChE complexes of natural pyrrolizidine alkaloids previously evaluated in vitro as AChE inhibitors. Due to the known hepatoxicity of these alkaloids, the computational analysis was also directed to their activity on Drosophila melanogaster AChE (6XYU). The parameters here predicted for human and eco-toxicities may serve as a further indication in future investigations of these natural structures as scaffolds for the potential development of insecticides.
1. Introduction
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) is an enzyme acting efficiently as a hydrolase in the nerve signal system. This enzyme acts in mammalians and insects, presenting structural differences in amino acid sequences and conformation of the active sites.
In patients affected by Alzheimer’s disease (AD), low levels of acetylcholine, which acts as a neurotransmitter, are present. Although there are no decisive therapies so far, the drugs currently used are based on AChE inhibition by increasing the activity of the nervous system and accordingly preventing acetylcholine breakdown. AD has been recognized to occur with a multitarget approach where AChE inhibition is regarded as one of the main targets in the treatment of this disease [1].
Organophosphorus and methylcarbamate compounds are AChE inhibitors acting on the central nervous systems of insects and have been used for a long time as insecticides. Their application is of interest due to the need to counter insects as disease vectors, e.g., malaria [2]. However, anti-AChE insecticides mainly target the same serine residue common in insects and mammals, causing toxicity problems for humans. Despite their current decline, chiefly due to their intense use in agriculture, they are still a topic of interest in understanding their mechanism and metabolism [3]. Irreversible inhibitors are the most toxic for humans, such as organophosphorus insecticides. Reversible inhibitors can be competitive or non-competitive and have the highest interest in applications, such as carbamate insecticides, which are toxic to humans, and agents for human therapy against AD [4]. All these aspects are being studied with the aim of developing more effective AD therapies and pest control agents.
In the ethnobotanical approach, the use of local plants has been applied to protect against insects, as well as extracts from plants and flowers to treat parasites. This procedure is advantageous due to metabolites showing environmental safety and selectivity toward target organisms [5]. Inside the wide structural diversity of plant compounds displaying insecticidal activities [5], our attention has been recently focused on pyrrolizidine alkaloids (PAs). They are secondary metabolites identified in over 6000 plant species and show more than 500 structural modifications. In particular, the heliotridine-type PAs are produced by plants belonging to Boraginaceae, Asteraceae, and Fabaceae families and are structurally characterized by a necine-based 1,2-unsaturated pyrrolizidine unit functionalized by both an ester group derived from angelic acid and a branched hydroxylated chain. Some were isolated from Solenthatus lanatus and Echium confusum Coincy extracts and experimentally evaluated as AChE inhibitors [6,7].
We report a computational analysis including the molecular docking of these heliotridine alkaloids in complexes with AChEs to compare with the data from previous bioassays and to evaluate their insecticidal activity, supported by human and environmental toxicity prediction.
2. Materials and Methods
The AutoDock Tools (ADT) package version 1.5.6rc3 [8] was applied to generate the docking input files used for the calculations. The structures of Torpedo californica AChE (6G1V) [9] and of Drosophila melanogaster (6XYU) [10] were available from the Protein Data Bank (PDB; http://www.pdb.org/ (accessed on 10 July 2024)). Two different computational approaches were used: AutoDock Vina 1.2.3 (in the future text reported as Vina), [11] which employs a genetic algorithm, and Protein–Ligand ANTSystem (PLANTS), which uses a class of stochastic optimization algorithms called ant colony optimization (ACO) [12]. For PLANTS calculations, the structures of the enzyme and the ligands were saved in mol2 extension, a sphere with radius = 14 Å was centered at the same position used for Vina, and the chemPLP scoring function was employed [13], saving 10 cluster structures with RMSD = 2.00 Å. The visual inspection of the ligand–enzyme interactions was displayed using the Biovia Discovery Studio visualizer (Discovery Studio Visualizer v21.1.0.20298) [14]. More details on calculations are reported in the Supplementary Materials.
Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion/Toxicity (ADME)/T) Analysis was performed using admetSAR software [15,16] available online [17].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Molecular Docking of Natural Alkaloids 1–8 as AChE Inhibitors and Correlation with Known Experimental Data
In 2016, Benamar et al. [6] reported the isolation from Solenthatus lanatus DC of the new 7-O-angeloylechinatine N-oxide (1) and the known 3′-O-acetylheliosupine N-oxide (2), heliosupine N-oxide (3) and heliosupine (4) (Figure 1). Later, the same authors isolated 7-O-angeloyllycopsamine N-oxide (5), echimidine N-oxide (6), echimidine (7), and 7-O-angeloylretronecine (8) (Figure 1) for the first time from Echium confusum Coincy [7]. The lower AChE inhibition displayed by the ethanolic extract of Solenthatus lanatus than the one of Echium confusum (467 µg/mL and 268 µg/mL, respectively) was in line with the better IC50 values obtained for some metabolites isolated from Echinium confusum plant [6,7]. However, the inhibition was in sub-millimolar range values (0.537–0.602 mM for 1–4 and 0.276–0.769 mM for 5–8) and, therefore, only moderate in comparison with active agents showing sub-micromolar IC50 values as an inhibitor of the same tested type of enzyme.
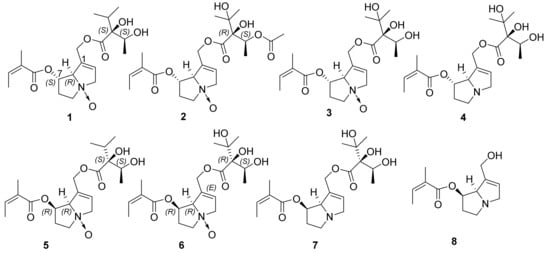
Figure 1.
Molecular structures of pyrrolizidine alkaloids tested as acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitors by Benamar et al. [6,7], reported as in the original papers.
Our interest has been focused on data accessible by molecular docking to be correlated with bioassay results obtained with AChE from electric eel (eeAChE, EC 3.1.1.7) [6,7]. No PDB files for complexes involving this particular type of enzyme are available. Therefore, AChE from Torpedo californica was adopted as a model system. This choice is supported by our previous comparison using the TM-align algorithm between the two AChEs, which shows a very good overlap of their secondary structures. Furthermore, they display identical amino acid residues in the active sites, except for the Phe330 unit in Torpedo californica AChE replaced by Tyr330 in eeAChE [18]. The Vina docking for the complexes of Torpedo californica AChE, with each of the tested PA alkaloids 1–8 and the original ligand have given results in terms of energy values (Table 1), and both the number and type of interactions involved in each complex (Figure S1). The protein–ligand docking software PLANTS provided the score values listed in Table 1, for which a more negative value corresponds to a more robust interaction.

Table 1.
Data from docking calculations by using Vina and PLANTS software of alkaloids 1–8 with Torpedo californica AChE (PDB-ID: 6G1V) and Drosophila melanogaster AChE (PDB-ID: 6XYU).
The following indications emerge from a correlation between the experimental biological evaluation and data from this computational analysis. 7-O-angeloylretronecine (8) gives the highest energy value and the lowest number of interactions in the series, in line with its simplest structure, and shows a good agreement with the AChE inhibition assay where it was the least active. In the Protein–Ligand ANTSystem (PLANTS) calculation, its score is the second highest, enough to reflect the bioassay result (IC50 0.769 mM).
For molecules 3 and 7 having the same energy values (Table 1), what makes the difference are the interactions, mainly the number of hydrogen bonds, which are higher for 3, despite the presence of an unfavorable interaction (Figure S1). Therefore, by Vina calculations, the AChE complex is more stable for 3 than 6, in line with the PLANT score, but not matching with the biological results where 3 resulted in less active than 6 (IC50 0.602 mM and 0.347 mM, respectively) [6,7]. Any other possible considerations regarding the presence of oxygen on the N atom by comparing the pairs 2/4 and 6/7, the stereochemistry in C-7 positions of 1/5, and the additional OH on the chain evaluated in the couples 1/3 and 5/7, the replacement of an OH group by an acetate in 2/3 find no decisive correlation. This can be ascribed to the small variability of energy for compounds 1–8 (from −7.463 to −9.120 kcal/mol, Table 1) ranging within the 2 kcal/mol deviation associated with the energy data accessible by Vina docking. On the other hand, the moderate and similar IC50 values (falling in the range of 0.602–0.537 mM for 1–4 [6], from 0.397 mM to 0.347 mM for 7 and 6, respectively, and 0.276 mM for the most active 5 [7]) do not allow further specific correlations.
3.2. Molecular Docking of Natural Alkaloids 1–8 as Insect AChE Inhibitors
The potential of PAs for the development of drugs to treat human diseases is prevented by their hepatotoxicity, which mainly involves glutathione metabolism [19]. This toxicity has long been known, and several countries and organizations have established regulations to restrict the use of plants and plant products containing PAs [20]. Besides the pyrrolizidine ring, the entity of toxicity is affected by the presence of ester groups, hydroxyl functionalities, and branched chains [19]. For many species of insects, plant PAs act against their predators. In particular, the heliotridine-type alkaloid echimidine (7, Figure 1) has shown potent antifeedant activity without toxic effects on Leptinotarsa decemlineata, which is one of the most destructive insect pests of potatoes [21].
In this context and based on the role of AChE as a target of environmentally safe insecticides [22], we focused on the molecular docking for the alkaloids 1–8 as ligands of Drosophila melanogaster AChE (6XYU). The corresponding energy values from Vina and score values from PLANTS are reported in Table 1.
PLANTS scores indicate that compound 8 is the worst inhibitor, as suggested by the most straightforward molecular structures in the series, making fewer interactions possible, similar to the docking result for Torpedo californica AChE. Vina data are evaluated according to both energy values (Table 1) and interactions of each ligand 1–8 in the enzyme active site (Figure S2). Hydrogen bonds are the most stabilizing interactions, and it is evident that their lower number is obtained with the structure of alkaloid 8 where the ester group with the hydroxylated chain is missing. Compound 1 turns out to be one of the most interesting from Vina’s calculation. A specific hydrogen bond between Tyr370 and the oxygen in the N-oxidized group is present for 3 and 6, but this is not achieved in all N-oxidized compounds. Unfavorable interactions are also possible, as in the case of compound 2, when one of the two destabilizing interactions involves the acetate group. In short, no further considerations can be confidently inferred regarding structural correlations.
3.3. Structural Comparison of Torpedo californica AChE and Drosophila melanogaster AChE
For all compounds 1–8, the data from both Vina and PLANTS calculations on Drosofila melanogaster AChE show similar energy and score values to those obtained in the corresponding complexes with Torpedo californica AChE (Table 1). These findings encouraged us to consider a comparison between the two enzyme types. AChEs of different species show a very high similarity in both function and structure, or they are different depending on how similar the species are, based on their evolution. Additionally, it was reported the possibility to distinguish between mammals and insects in terms of the specificity of the enzyme inhibition [23]. We have carried out the comparison between Torpedo californica (6G1V) and Drosophila melanogaster (6XYU) AChEs (Figure S3), quantifying the average distance between the atoms of the superimposed structures by the root-mean-square deviation (RMSD), whose value is given by a pairwise matrix. The obtained similarity was good, as indicated by an RMSD value of 1.817 Å.
3.4. ADME/Toxicity Prediction of the Compounds 1–8
The ADME parameters of compounds 1–8 were predicted by using the tool admetSAR [15,16,17]. The results (Table S1) indicate the absence of human oral bioavailability, no permeation of the brain–blood barrier (BBB) except for 7-O-angeloylretronecine (8) and human intestinal absorption, evaluated as positive for values higher than 30%, only for 4, 7, and 8. Considering the human toxicity, neither corrosion and irritation for eyes and skin, nor carcinogenic potency are reported according to the model considered by the software. For the Ames test, able to identify carcinogens using mutagenicity in bacteria, most compounds are considered active. With a model built to study 10207 molecules with effects against rats, the lowest acute oral toxicity was foreseen for compounds 2 and 8, next to the values estimated for 3 and 6. Regarding the environmental toxicity, all molecules are suggested to have no biodegradation effect, no activity toward honey bees, as evaluated by a model based on toxic pesticides or pesticide-like molecules or non-toxic compounds (with LD50 ≥ 11 μg/bee), and no effects on avian species, selected as a model because of sensitivity to pesticides and industrial chemicals. The alkaloids 4, 7, and 8, with structures in which the N-O functionality is missing, are referred to as not toxic for fishes. Lastly, the C-7 epimeric molecules 4 and 7 show the lowest toxicity towards the protozoa Tetrahymena pyriformis present in all aquatic environments and often used as a toxic endpoint as a response against xenobiotic substances.
4. Conclusions
We performed a computational analysis to study the inhibition of AChE by the plant-derived heliotridine-type pyrrolizidine alkaloids 1–8. Molecular docking calculations provided energy and interaction details used for a correlation with known experimental AChE inhibition data. It was established that the presence of the hydroxylated chain is crucial for the activity. For this class of molecules, hepatoxicity prevents the potential use for human treatment. Therefore, we evaluated their molecular docking with an insect AChE and conducted a virtual screening to predict their human and environmental toxicities. Based on the recognized role of AChE as a target of environmentally safe insecticides of natural origin, this computational study supports structures 1–8 as interesting scaffolds for the design and optimization of new potential pesticides.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ecsoc-28-20223/s1, Figures S1 and S2: representations by AutoDock Vina for the interactions of 1–8 with T. californica and Drosofila melanogaster AChE, respectively; Figure S3: alignment of T. californica and Drosophila melanogaster AChE structures; Table S1: data by ADME/toxicity prediction for compounds 1–8.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.M. and T.C.; methodology, I.M. and A.D.; formal analysis, A.D.; investigation, I.M. and A.D.; data curation, A.D. and I.M.; writing—original draft preparation, I.M. and A.D.; writing—review and editing, I.M., A.D. and T.C.; supervision, I.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
We thank Nicole Innocenti for her careful reading of this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Peitzika, S.C.; Pontiki, E. A Review on Recent Approaches on Molecular Docking Studies of Novel Compounds Targeting Acetylcholinesterase in Alzheimer Disease. Molecules 2023, 28, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casida, J.E.; Durkin, K.A. Anticholinesterase insecticide retrospective. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2013, 203, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Y.-P.; Brimijoin, S.; Ragsdale, D.W.; Zhu, K.Y.; Suranyi, R. Novel and Viable Acetylcholinesterase Target Site for Developing Effective and Environmentally Safe Insecticides. Curr. Drug Targets 2012, 13, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazuki, I.N.; Shukor, M.Y. Acetylcholinesterase as an In Vitro Assay for Insecticides: A Mini Review. JEMAT 2018, 6, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavela, R. History, Presence and Perspective of Using Plant Extracts as Commercial Botanical Insecticides and Farm Products for Protection against Insects—A Review. Plant Protect. Sci. 2016, 52, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benamar, H.; Tomassini, L.; Venditti, A.; Marouf, A.; Bennaceur, M.; Nicoletti, M. Pyrrolizidine alkaloids from Solenanthus lanatus DC. with acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity. Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 30, 2567–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benamar, H.; Tomassini, L.; Venditti, A.; Marouf, A.; Bennaceur, M.; Serafini, M.; Nicoletti, M. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity of pyrrolizidine alkaloids from Echium confusum Coincy. Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 31, 1277–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanner, M.F. Python: A programming language for software integration and development. J. Mol. Graph. Mod. 1999, 17, 57.e61. [Google Scholar]
- Galdeano, C.; Coquelle, N.; Cieslikiewicz-Bouet, M.; Bartolini, M.; Perez, B.; Clos, M.V.; Silman, I.; Jean, L.; Colletier, J.P.; Renard, P.Y.; et al. Increasing Polarity in Tacrine and Huprine Derivatives: Potent Anticholinesterase Agents for the Treatment of Myasthenia gravis. Molecules 2018, 23, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nachon, F.; Rosenberry, T.L.; Silman, I.; Sussman, J.L. A Second Look at the Crystal Structures of Drosophila melanogaster Acetylcholinesterase in Complex with Tacrine Derivatives Provides Insights Concerning Catalytic Intermediates and the Design of Specific Insecticides. Molecules 2020, 25, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading, J. Comp. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korb, O.; Stützle, T.; Exner, T.E. PLANTS: Application of Ant Colony Optimization to Structure-Based Drug Design. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006; Volume 4150, pp. 247–258. [Google Scholar]
- Korb, O.; Stützle, T.; Exner, T.E. Empirical Scoring Functions for Advanced Protein-Ligand Docking with PLANTS. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2009, 49, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BIOVIA; Dassault Systèmes. Discovery Studio Visualizer, v21.1.0.20298; Dassault Systèmes: San Diego, CA, USA, 2021; Available online: https://discover.3ds.com/discovery-studio-visualizer-download (accessed on 20 December 2023).
- Yang, H.; Lou, C.; Sun, L.; Li, J.; Cai, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, W.; Liu, G.; Tang, Y. admetSAR 2.0: Web-service for prediction and optimization of chemical ADMET properties. Bioinformatics 2018, 35, bty707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, F.; Li, W.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, J.; Wu, Z.; Liu, G.; Lee, P.W.; Tang, Y. admetSAR: A compre-hensive source and free tool for evaluating chemical ADMET properties. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2012, 52, 3099–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AdmetSAR. Available online: http://lmmd.ecust.edu.cn/admetsar2/ (accessed on 8 January 2024).
- Botić, T.; Defant, A.; Zanini, P.; Žužek, M.C.; Frangež, R.; Janussen, D.; Kersken, D.; Knez, Ž.; Sepčić, K.; Mancini, I. Discorhabdin alkaloids from Antarctic Latrunculia spp. sponges as a new class of cholinesterase inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 136, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Kang, H.; Feng, J.; Yang, Y.; Tang, K.; Zhu, R.; Yang, L.; Wang, Z.; Cao, Z. Identification of Toxic Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids and Their Common Hepatotoxicity Mechanism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Ruan, W.; Vrieling, K. Current Knowledge and Perspectives of Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids in Pharmacological Applications: A Mini-Review. Molecules 2021, 26, 1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Coloma, A.; Reina, M.; Gutierrez, C.; Fraga, B.M. Natural insecticides: Structure diversity, effects and structure-activity relationships. a case study. Atta-ur-Rahman (Ed.) Stud. Nat. Prod. Chem. 2002, 26, 849–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.P. Insect Acetylcholinesterase as a Target for Effective and Environmentally Safe Insecticides. In Advances in Insect Physiology; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 46, pp. 435–494. ISSN 0065-2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesner, J.; Kříž, Z.; Kuča, K.; Jun, D.; Koča, J. Acetylcholinesterases—The structural similarities and differences. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2007, 22, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).