Benzyl Carbamates of 4-Aminosalicylanilides as Possible BACE1 Modulators †
Abstract
1. Introduction
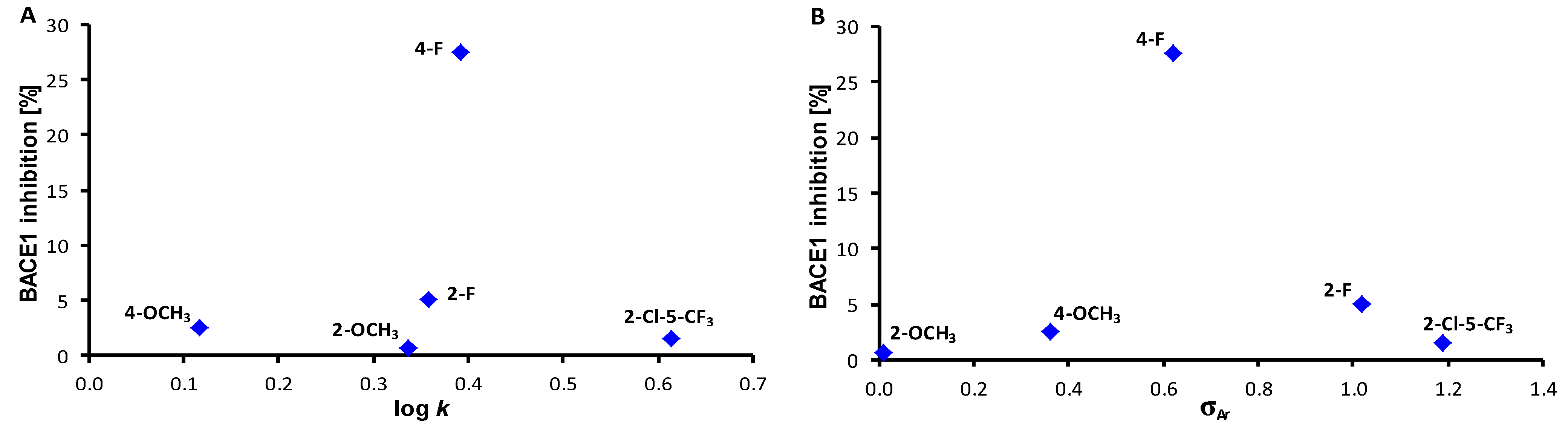
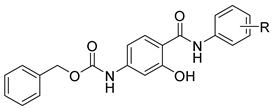
2. Results and Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Chemistry
3.2. Determination of Lipophilicity by HPLC
3.3. Determination of BACE1 Inhibitory Activity
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nieweg, K.; Andreyeva, A.; van Stegen, B.; Tanriover, G.; Gottmann, K. Alzheimer’s disease-related amyloid-β induces synaptotoxicity in human iPS cell-derived neurons. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenoglio, C.; Scarpini, E.; Serpente, M.; Galimberti, D. Role of genetics and epigenetics in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease and Frontotemporal dementia. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 62, 913–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, I.G.A.; Gamez, N.; Escobedo, G.; Calderon, O.; Moreno-Gonzalez, I. Modifiable risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Aging. Neurosci. 2019, 11, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wimo, A.; Ali, G.C.; Guerchet, M.M.; Prince, M.J.; Prina, M.; Wu, Y.T. World Alzheimer Report 2015. The Global Impact of Dementia: An Analysis of Prevalence, Incidence, Cost and Trends. Alzheimer’s Disease International: London, UK. Available online: https://www.alzint.org/resource/world-alzheimer-report-2015/ (accessed on 3 October 2022).
- 2022 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2022, 18, 700–789. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jampilek, J.; Kralova, K.; Novak, P.; Novak, M. Nanobiotechnology in neurodegenerative diseases. In Nanobiotechnology in Neurodegenerative Diseases; Rai, M., Yadav, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 65–138. [Google Scholar]
- Bajic, V.; Milovanovic, E.S.; Spremo-Potparevic, B.; Zivkovic, L.; Milicevic, Z.; Stanimirovic, J.; Bogdanovic, N.; Isenovic, E.R. Treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: Classical therapeutic approach. Curr. Pharm. Anal. 2016, 12, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, D.E.; Perez, R.G.; Kobayashi, H. Cholinesterase inhibitor therapy in Alzheimer’s disease: The limits and tolerability of irreversible CNS-selective acetylcholinesterase inhibition in primates. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2017, 55, 1285–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Li, Q.; Gu, K.; Zhu, J.; Jiang, X.; Chen, Y.; Sun, H. Therapeutic agents in Alzheimer’s disease through a multi-target directed ligands strategy: Recent progress based on tacrine core. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 3000–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magar, P.; Parravicini, O.; Stepankova, S.; Svrckova, K.; Garro, A.D.; Jendrzejewska, I.; Pauk, K.; Hosek, J.; Jampilek, J.; Enriz, R.D.; et al. Novel sulfonamide-based carbamates as selective inhibitors of BChE. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memantine as a Treatment for Dementia. Cochrane, 2022. Available online: https://www.cochrane.org/CD003154/DEMENTIA_memantine-treatment-dementia (accessed on 3 October 2022).
- Pradeepkiran, J.A.; Reddy, A.P.; Yin, X.; Manczak, M.; Reddy, P.H. Protective effects of BACE1 inhibitory ligand molecules against amyloid beta-induced synaptic and mitochondrial toxicities in Alzheimer’s disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2020, 29, 49–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hampel, H.; Hardy, J.; Blennow, K.; Chen, C.; Perry, G.; Kim, S.H.; Villemagne, V.L.; Aisen, P.; Vendruscolo, M.; Iwatsubo, T.; et al. The amyloid-β pathway in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 5481–5503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, H.; Tamaoka, A.; Ishii, K.; Shoji, S.; Kametaka, S.; Kametani, F.; Saito, Y.; Murayama, S. Beta-site APP cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE1) is increased in remaining neurons in Alzheimer’s disease brains. Neurosci. Res. 2006, 54, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.; Evin, G. Β-site APP-cleaving enzyme 1 trafficking and Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis. J. Neurochem. 2012, 120, 869–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rombouts, F.; Kusakabe, K.I.; Hsiao, C.C.; Gijsen, H.J.M. Small-molecule BACE1 inhibitors: A patent literature review (2011 to 2020). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2021, 31, 25–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egan, M.F.; Kost, J.; Voss, T.; Mukai, Y.; Aisen, P.S.; Cummings, J.L.; Tariot, P.N.; Vellas, B.; van Dyck, C.H.; Boada, M.; et al. Randomized trial of verubecestat for prodromal Alzheimer’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1408–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AstraZeneca. Update on Phase III Clinical Trials of Lanabecestat for Alzheimer’s Disease. Available online: https://www.astrazeneca.com/media-centre/press-releases/2018/update-on-phase-iii-clinical-trials-of-lanabecestat-for-alzheimers-disease-12062018.html# (accessed on 3 October 2022).
- Koriyama, Y.; Hori, A.; Ito, H.; Yonezawa, S.; Baba, Y.; Tanimoto, N.; Ueno, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Yamamoto, T.; Asada, N.; et al. Discovery of atabecestat (JNJ-54861911): A thiazine-based β-amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 1 inhibitor advanced to the phase 2b/3 early clinical trial. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 1873–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eli Lilly. Lilly Voluntarily Terminates Phase II Study for LY2886721, a Beta Secretase Inhibitor, Being Investigated as a Treatment for Alzheimer’s Disease. Available online: https://investor.lilly.com/news-releases/news-release-details/lilly-voluntarily-terminates-phase-ii-study-ly2886721-beta (accessed on 3 October 2022).
- Eisai And Biogen to Discontinue Phase III Clinical Studies Of BACE Inhibitor Elenbecestat In Early Alzheimer’s Disease. Available online: https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/eisai-and-biogen-to-discontinue-phase-iii-clinical-studies-of-bace-inhibitor-elenbecestat-in-early-alzheimers-disease-300917734.html (accessed on 3 October 2022).
- Mullard, A. Alzheimer prevention failure rattles field, anew. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDade, E.; Voytyuk, I.; Aisen, P.; Bateman, R.J.; Carrillo, M.C.; De Strooper, B.; Haass, C.; Reiman, E.M.; Sperling, R.; Tariot, P.N.; et al. The case for low-level BACE1 inhibition for the prevention of Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 17, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barao, S.; Moechars, D.; Lichtenthaler, S.F.; De Strooper, B. BACE1 physiological functions may limit its use as therapeutic target for Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Neurosci. 2016, 39, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kos, J.; Kozik, V.; Pindjakova, D.; Jankech, T.; Smolinski, A.; Stepankova, S.; Hosek, J.; Oravec, M.; Jampilek, J.; Bak, A. Synthesis and hybrid SAR property modeling of novel cholinesterase inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- β-Secretase (BACE1) Activity Detection Kit (Fluorescent). Technical Bulletin. Sigma-Aldrich. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/documents/249/088/cs0010bul.pdf (accessed on 3 October 2022).
- Das, B.; Yan, R. A close look at BACE1 inhibitors for Alzheimer’s disease treatment. CNS Drugs 2019, 33, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Comp. | R | log k | σAr 1 | Reduction of BACE1 Activity [%] |
| 1 | H | 0.1160 | 0.60 | 0 |
| 2 | 2-OCH3 | 0.3368 | 0.01 | 0.7 |
| 3 | 3-OCH3 | 0.128 | 0.66 | 0 |
| 4 | 4-OCH3 | 0.1176 | 0.36 | 2.6 |
| 5 | 2-OCF3 | 0.6227 | 0.09 | 0 |
| 6 | 3-CH3 | 0.2725 | 0.48 | 0 |
| 7 | 2-F | 0.3577 | 1.02 | 5.1 |
| 8 | 3-F | 0.2303 | 0.82 | 0 |
| 9 | 4-F | 0.3924 | 0.62 | 27.5 |
| 10 | 2-Cl | 0.5188 | 1.02 | 0 |
| 11 | 3-Cl | 0.6411 | 0.85 | 0 |
| 12 | 4-Cl | 0.6399 | 0.75 | 0 |
| 13 | 3-CF3 | 0.4477 | 0.89 | 0 |
| 14 | 4-CF3 | 0.7408 | 0.95 | 0 |
| 15 | 2,3-F | 0.4705 | 1.24 | 0 |
| 16 | 2,4-F | 0.1912 | 1.04 | 0 |
| 17 | 2,5-F | 0.4012 | 1.24 | 0 |
| 18 | 3,5-F | 0.4072 | 1.12 | 0 |
| 19 | 2,3-Cl | 0.5497 | 1.22 | 0 |
| 20 | 2,5-Cl | 0.6138 | 1.22 | 0 |
| 21 | 2,6-Cl | 0.8125 | 1.33 | 0 |
| 22 | 3,4-Cl | 0.6664 | 1.19 | 0 |
| 23 | 3,5-Cl | 0.9084 | 1.11 | 0 |
| 24 | 2,4-Br | 0.7366 | 1.11 | 0 |
| 25 | 3,5-CF3 | 0.9667 | 1.05 | 0 |
| 26 | 2,4,6-F | -0.0131 | 1.46 | 0 |
| 27 | 3,4,5-F | 0.5169 | 1.64 | 0 |
| 28 | 2,4,5-Cl | 0.9360 | 1.56 | 0 |
| 29 | 2,4,6-Cl | 0.3679 | 1.48 | 0 |
| 30 | 2,4,6-Br | 0.4427 | 1.47 | 0 |
| 31 | 2-OCH3-5-NO2 | 0.0914 | 1.32 | 0 |
| 32 | 2-CH3-5-F | 0.2694 | 0.81 | 0 |
| 33 | 2-F-3-CF3 | 0.4423 | 1.24 | 0 |
| 34 | 3-F-4-CF3 | 0.5541 | 1.11 | 0 |
| 35 | 2-Cl-5-CF3 | 0.6137 | 1.19 | 1.5 |
| 36 | 3-Br-5-CF3 | 0.8632 | 1.08 | 0 |
| 37 | 2-CF3-4-Br | 0.6270 | 1.05 | 0 |
| 38 | 2-CF3-4-NO2 | 0.4907 | 1.45 | 0 |
| CbzPAS | – | – | – | 3.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Majerova, P.; Pindjakova, D.; Jankech, T.; Gerhardtova, I.; Kos, J.; Kovac, A.; Jampilek, J. Benzyl Carbamates of 4-Aminosalicylanilides as Possible BACE1 Modulators. Chem. Proc. 2022, 12, 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-26-13680
Majerova P, Pindjakova D, Jankech T, Gerhardtova I, Kos J, Kovac A, Jampilek J. Benzyl Carbamates of 4-Aminosalicylanilides as Possible BACE1 Modulators. Chemistry Proceedings. 2022; 12(1):40. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-26-13680
Chicago/Turabian StyleMajerova, Petra, Dominika Pindjakova, Timotej Jankech, Ivana Gerhardtova, Jiri Kos, Andrej Kovac, and Josef Jampilek. 2022. "Benzyl Carbamates of 4-Aminosalicylanilides as Possible BACE1 Modulators" Chemistry Proceedings 12, no. 1: 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-26-13680
APA StyleMajerova, P., Pindjakova, D., Jankech, T., Gerhardtova, I., Kos, J., Kovac, A., & Jampilek, J. (2022). Benzyl Carbamates of 4-Aminosalicylanilides as Possible BACE1 Modulators. Chemistry Proceedings, 12(1), 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-26-13680








