Abstract
(1) Background: To analyze the prevalence and factors associated with diabetes mellitus in adults and the elderly in Rio Branco, Acre, Western Brazilian Amazon. (2) Methods: The R software version 4.0.5 was used for estimating the prevalence of diabetes mellitus, odds ratios, and 95% confidence intervals. Multiple analysis was conducted through hierarchical variable selection. (3) Results: 1.095 individuals aged 18 years and older participated in this study, with 6.4% of the respondents showing prevalence of diabetes mellitus. The prevalence of diabetes mellitus was positively associated with a prior medical diagnosis of obesity (OR: 3.2; 95% CI: 1.67–6.12), dyslipidemia (OR: 4.17; 95% CI: 2.08–8.36), and increasing age (OR: 1.07; 95% CI: 1.05–1.09). Conversely, an inverse association was observed with higher education (12 or more years of study; OR: 0.20; 95% CI: 0.07–0.61). (4) Conclusions: The prevalence of diabetes mellitus in the municipality of Rio Branco, Acre, Brazil, has significantly increased with advancing age. Education, obesity, and dyslipidemia were also identified as factors associated with diabetes mellitus in this population. Awareness campaigns regarding dietary patterns and lifestyle choices may serve as preventive and control measures.
1. Introduction
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is characterized as a multifaceted metabolic disorder marked by persistent hyperglycemia [1]. According to the International Diabetes Federation, the global prevalence in adults and the elderly was approximately 10.5% in 2021, affecting around 537 million people, suggesting that more than 1 in 10 adults had the disease. A prospective increase is estimated by 2045, driven by demographic transition and changes in habits and lifestyles [2]. Additionally, studies have highlighted that a significant portion of individuals with diabetes mellitus are not diagnosed in a timely manner and, consequently, do not receive treatment, facing a significantly higher risk of complications [3,4].
In 2021, Brazil ranked sixth in the world in terms of the highest frequency of adults with DM, with approximately 16 million adults affected [5]. According to data from the Surveillance System for Risk and Protective Factors for Chronic Diseases by Telephone Survey (Vigitel) in 2023, the prevalence of diabetes reached 10.2% of the Brazilian population, making this comorbidity a significant public health issue leading to substantial public expenditures [6].
The high prevalence of diabetes and its impact on global health underscore the need to understand its associated factors and thereby address the various aspects of this condition. The literature has highlighted genetic, sociodemographic, and economic factors, but there are also behavioral factors related to urbanization, lifestyle, and dietary habits that are modifiable and contribute to the increasing incidence and prevalence in many countries [7,8,9].
Despite the upward trend worldwide, some regions lack information on the prevalence and severity of this condition in the population. Moreover, while the factors associated with diabetes mellitus are well known in the literature, there are clear sociocultural and economic differences between municipalities within a country, and these geographic differences can influence intrinsic factors associated with chronic diseases. Therefore, for government actions to be more effective, it is essential to consider these diverse realities and conduct more research at the municipal level, enabling the investigation of system failures and the intensification of preventive policies aimed at controlling these associated factors [10,11].
Considering the scenario of diabetes mellitus in Brazil and worldwide, as well as the differences among Brazilian municipalities, it is crucial to reflect on the care provided to diabetic patients residing in more remote areas from major urban centers such as the Brazilian Amazon. The state of Acre is in a region with one of the highest percentages of environmental preservation areas in the country, where more than half of its territory is composed of protected areas. That is, 14.92% of its lands are destined for indigenous lands, which amounts to an area of approximately 2.5 million hectares [12], while conservation units cover an area of 47.3% of the state’s territory, equivalent to 7.7 million hectares [13]. However, despite the biodiversity and variety of natural resources, Acre is a state with a low socioeconomic index, considering that a significant portion of the local economy comes from extractivism and family agriculture and products derived manually or artisanally. Therefore, it is possible that the factors associated with diabetes mellitus in the region differ from those reported in the literature [14].
In the municipality of Rio Branco, Acre, population health has been a challenge for policymakers, and the lack of population-based epidemiological studies has hindered the support for possible health interventions. Therefore, this study aimed to analyze the prevalence and factors associated with diabetes mellitus in adults and the elderly in Rio Branco, Acre, in the Western Brazilian Amazon.
2. Materials and Methods
This is a cross-sectional study based on population data obtained from the National Health Survey (PNS), which was conducted in 2019 by the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics (IBGE) in collaboration with the Ministry of Health. The study encompassed individuals aged 18 years and older, including young adults and the elderly, who participated in the data collection of the PNS and resided in Rio Branco, Acre, situated in the Western Brazilian Amazon. Rio Branco serves as the capital of the state of Acre, located in the Northern Region of Brazil, boasting a population of 413,418 residents, representing 46.2% of the state’s total population [15].
The PNS is a household survey that follows a three-stage cluster sampling approach: I) primary sampling units (census tracts)—PSU, II) secondary units (households/PSU), and III) tertiary units (residents aged 15 or older to answer the individual questionnaire). The gathered data encompass inquiries related to the household, its occupants, and the designated adult. Initially, contact was established with a member of the chosen household. Following the introduction of the study and its objectives, the household questionnaire was completed by the respondent, and the individual questionnaire was administered to the designated resident [16].
For this study, individuals aged 18 years and older were chosen as respondents, with pregnant women and those suspected of being pregnant being excluded. Since it is a complex sample, estimates were adjusted using weights based on eligible adult residents, which correspond to the capital and the state being analyzed, to ensure a representative sample of the population of Rio Branco, Acre, in 2019.
The dependent variable in this study was the prevalence of individuals who reported having received a previous medical diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. Independent variables were categorized as follows: sociodemographic characteristics (age group, gender, and skin color), socioeconomic factors (income per capita, education level, possession of health insurance, and employment status), lifestyle habits (regular consumption of fruits, vegetables, and leafy greens, intake of ultra-processed foods, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption), and health indicators (self-rated health status, regular physical activity in the last 3 months, overweight, obesity, hypertension, and dyslipidemias) [16].
The ages of each resident were recorded in years and treated as continuous numerical variables for analysis. Gender was collected using binary options: male or female, as the database utilized did not include gender distinctions. Skin color was recorded with the following options: white, black, yellow, brown, and indigenous. Due to challenges associated with self-perception and phenotypic self-identification of skin color, particularly in multiracial countries like Brazil [17,18], only the white category was retained for analysis, while the remaining categories were reclassified as non-white.
Economic factors such as per capita income were calculated by dividing the entire household income by the population and presented as multiples of the minimum wage (MW), classified as follows: up to ½ MW, ½–1 MW, 1–2 MW, and >2 MW. The minimum wage in Brazil in 2019 was BRL 998.00, equivalent to USD 205.67 using the 2023 exchange rate. The education variable was based on the highest level of education attained at the time of the interview and the duration of studies, later classified into the following categories: 0 to 8 years, 9 to 11 years, and 12 years or more. The possession of health insurance and employment status variables were reported by the interviewee using binary alternatives: yes or no [16].
Regular consumption of fruits, vegetables, and leafy greens was defined as the consumption of both food groups on five or more days per week, categorized as yes or no. The binary variable for ultra-processed food consumption was determined by the consumption of at least five ultra-processed food items on the day preceding the survey, including sweetened, artificially flavored drinks, snacks, industrialized biscuits, desserts, processed meats, bread, and ready-made pasta and sauces. The binary variable for smoking was defined by current usage, regardless of the type, quantity, frequency, or duration of the smoking habit. Abusive alcohol consumption was considered if reported within the 30 days preceding the survey. The PNS defined abusive alcohol consumption as the consumption of five or more alcoholic beverages on a single occasion, applicable to both men and women [17].
The variable for poor self-rated health, categorized as yes or no, was assigned to individuals who self-assessed their health negatively as poor or very poor. Regular physical activity was evaluated based on the frequency (in the last three months prior to the survey) and duration (more than 20 min per day) across various domains: leisure time, occupational activity, commuting, and household tasks. Dichotomous variables for overweight and obesity were determined using weight and height measurements obtained during the individual interview. Diagnosis was established using the body mass index (BMI), calculated as weight in kilograms divided by the square of height in meters. Overweight was defined as BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2, and obesity as BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2. Dichotomous variables for arterial hypertension and dyslipidemias were considered when participants reported a previous medical diagnosis for these conditions, except for women diagnosed during pregnancy [16].
Statistical analysis of this complex sample was conducted using R software, version 4.0.5. To identify independent variables potentially associated with diabetes mellitus in the studied population, unconditional logistic regression was initially employed, providing estimates of odds ratios (OR) and their respective 95% confidence intervals (CI95%). Variables demonstrating statistical significance at a level of up to 20% (p ≤ 0.20) were chosen for inclusion in the multiple model. For the multiple analysis, independent variables were hierarchically entered based on the distal, intermediate, and proximal order [16], as outlined in the hierarchical model presented in Figure 1. The final model comprised variables that enhanced fit and remained statistically significant (p < 0.05).
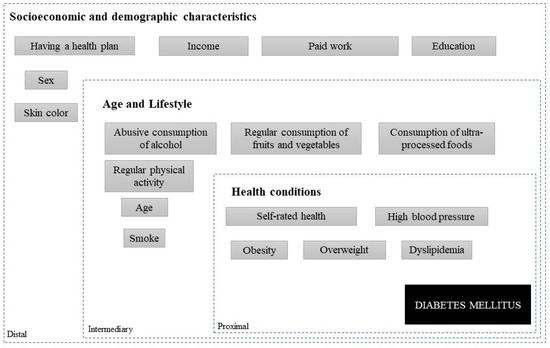
Figure 1.
Hierarchical conceptual model for investigating factors associated with diabetes mellitus in adults and the elderly in Rio Branco, Acre.
As this study utilized publicly available data provided by the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics (Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística—IBGE) without restrictions and devoid of nominal identifications, it falls under the category exempt from ethical review as per the guidelines outlined in the National Health Council Resolution, CNS 466/12, which governs research involving human subjects in Brazil [16].
3. Results
Out of the total 1225 individuals surveyed in Rio Branco through the household survey of the National Health Survey (PNS) in 2019, 130 respondents were excluded, comprising 8 pregnant women and 122 who did not adequately respond to questions related to diabetes diagnosis. Thus, the population of this study consisted of 1095 participants aged 18 years or older, representing an expanded sample (N) of 205,201 inhabitants.
Participants ranged in age from 18 to 91 years (mean age 44 years), with 12.1% in the age group of 18 to 24 years, 32.3% in the age group of 25 to 39 years, 35.9% in the age group of 40 to 59 years, and 19.7% aged 60 years or older.
Regarding socioeconomic and demographic characteristics, 57.4% were female, 78.4% declared themselves non-white, 25.1% received up to half a minimum wage, 34.7% had 12 years or more of education, 80.6% did not have health insurance, and 65.2% were engaged in some form of remunerated work (Table 1).

Table 1.
Prevalence of diabetes mellitus based on sociodemographic and economic characteristics of adults and seniors in Rio Branco, Acre, 2019.
Regarding lifestyle and health characteristics, 12.4% regularly consumed fruits, vegetables, and greens, 11.2% reported the consumption of 5 or more ultra-processed foods on the previous day, 8.9% had a smoking habit, 12.6% engaged in abusive alcohol consumption, 6.0% self-evaluated their health condition as poor, and 56.6% did not engage in regular physical activities. Concerning the diagnosis of non-communicable chronic conditions, 60.7% were overweight, 21.4% were obese, 23.4% had high blood pressure, and 22.1% had dyslipidemia (Table 2).

Table 2.
Prevalence of diabetes mellitus based on lifestyle and health of adults and seniors in Rio Branco, Acre, 2019.
The prevalence of diabetes mellitus was 6.4% (95% CI: 5.1–8.0%).
3.1. Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus in Adults and Seniors Based on Sociodemographic, Economic, Lifestyle, and Health Characteristics
The distribution of the prevalence of individuals with diabetes mellitus according to sociodemographic and economic variables is presented in Table 1. Diabetes prevalence was significantly higher in older age groups. In individuals aged 18 to 39 years, it was 0.3% (95% CI: 0.1–1.3%), in the age group of 40 to 59 years, it was 7.3% (95% CI: 5.1–10.3%), and in elderly individuals (60 years or older), it was 18.5% (95% CI: 12.9–25.8%). The prevalences were also significantly higher among individuals with lower educational levels and among respondents who did not have paid work.
The prevalence of Individuals with diabetes mellitus according to lifestyle and health variables is presented in Table 2. The prevalence of diabetes mellitus was significantly higher in respondents with obesity (10.9%; OR: 2.24; 95% CI: 1.31–3.84), high blood pressure (17.0%; OR: 6.11; 95% CI: 3.35–11.17), and dyslipidemias (22.1%; OR: 6.25; 95% CI: 3.60–10.84). As well as in individuals who reported poor self-assessment of health status (15.9%; OR: 3.05; 95% CI: 1.44–6.49), does not engage in regular physical activity (8.7%; OR: 2.68; 95% CI: 1.51–4.75), and overweight (8.2%; OR: 2.39; 95% CI: 1.25–4.59).
3.2. Factors Associated with Diabetes Mellitus
Table 3 presents the multiple logistic regression models, referring to the adjusted odds ratios (OR) of diabetes mellitus according to sociodemographic, economic, lifestyle, and health variables of adults in Rio Branco, Acre. According to the final model, higher education showed a negative association with diabetes mellitus (12 or more years of study; OR: 0.20; 95% CI: 0.07–0.61). Positive associations with diabetes were observed for the previous medical diagnosis of obesity (OR: 3.2; 95% CI: 1.67–6.12) and dyslipidemia (OR: 4.17; 95% CI: 2.08–8.36), as well as age. For each additional year of age, the chance of diabetes mellitus in the studied population increased by 7% (OR: 1.07; 95% CI: 1.05–1.09).

Table 3.
Factors associated with diabetes mellitus in adults and seniors in Rio Branco, 2019.
4. Discussion
In this study, it was observed that the prevalence of diabetes in Rio Branco was 6.4% and was associated with education, age, and a previous diagnosis of other chronic conditions such as obesity and dyslipidemia.
In Brazil, research has shown varying prevalences of diabetes mellitus in the adult and elderly population, based on sociodemographic and health characteristics. According to the National Health Survey in 2019, the prevalence of diabetes was 7.7% (7.4–8.0%), indicating a relative increase of 24% compared to the prevalence recorded in 2013. In terms of the number of cases, approximately 12.3 million were reported in 2019, representing a 36.4% increase compared to the 9.0 million recorded in 2013. Key factors associated with higher prevalence included advanced age (RP = 27.2, 95% CI: 1.2–42.9 for ≥ 65 years vs. 18–24 years), hypertension (RP = 2.6, 95% CI: 2.4–2.8 vs. normotension), and obesity (RP = 2.3; 95% CI: 2.1–2.5 vs. BMI < 25 kg/m2). Individuals with complete higher education showed a 40% lower prevalence (RP = 0.6; 95% CI: 0.54–0.70 compared to those with incomplete elementary education) [19].
Following a global trend, Brazil faces a continuous prevalence of diabetes mellitus in all its regions with similar risk factors, posing a significant challenge to the country’s population and health systems [19]. In adults from Ribeirão Preto, São Paulo, the prevalence of diabetes mellitus was significantly associated with education, income, and employment status [20]. In Viçosa, Minas Gerais, the prevalence of this condition in the elderly according to health variables was significant when there was a history of arterial hypertension and dyslipidemias [10].
Other countries have highlighted the association of diabetes mellitus prevalence with social, demographic, and health characteristics. In Dessie Town, Northeast Ethiopia, the prevalence of diabetes mellitus in individuals over 18 years of age was present in those with hypertension and dyslipidemia [21]. The population of Guinea-Bissau showed a significant prevalence of diabetes mellitus when reported over the age of 65 in both sexes, and no individuals under 25 years old with diabetes mellitus were identified [22].
In this study, higher education of 12 years or more was negatively associated with diabetes mellitus in adults. This result is consistent with national and international studies that have shown a positive association between the prevalence of diabetes mellitus and lower educational levels [23,24,25]. Educational attainment can influence knowledge for disease prevention through dietary habits and lifestyle, as well as seeking healthcare assistance [26]. Additionally, education is an indicator of socioeconomic conditions; therefore, financial crises and socioeconomic inequalities faced by many Brazilian families reflect adverse experiences arising from poverty and difficulty accessing specialized healthcare in the Unified Health System, leading to delayed diagnoses of some preventable chronic health conditions [27,28].
Some results from a systematic review showed a clear relationship between socioeconomic status and the risk of developing and experiencing complications of diabetes mellitus, where low educational or socioeconomic levels were associated with increased risk [29]. Inequalities observed in educational, work, and housing conditions place families in situations of food and nutritional insecurity. Changing dietary habits are strategies to deal with high costs and maintain daily nutrition; however, despite being more economically accessible, ultra-processed foods such as canned and processed meats, as well as cassava flours, have high glycemic indexes and elevated levels of fats, sodium, and sweeteners, leading to metabolic alterations that trigger NCDs such as diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and dyslipidemia. Therefore, these socioeconomic inequalities impact both behaviorally and biologically on the prevention and control of diabetes mellitus [30].
The study found that the higher the age, the greater the chance of having diabetes mellitus. This fact may also be associated with the aging process, which brings about various important physiological and metabolic changes. Insulin secretion in the elderly decreases by 0.7% per year, doubling in people with glucose intolerance, possibly due to a decrease in the mass of pancreatic beta cells [31,32,33]. Additionally, various external factors drive this comorbidity. Functional mobility difficulties and the characteristic of old age interfere with regular physical activities and worsen sarcopenia, with a significant reduction in muscle mass and an increase in adipose tissue, contributing to insulin resistance [33,34,35]. It is also worth noting that elderly individuals usually resist changing their dietary habits and preferences, which often have high glycemic indices [36,37]. This set of modifications leads to persistent hyperglycemia that can progress to diabetes mellitus [34].
Corroborating with these findings, a study conducted with 60 adults and the elderly observed whether age is a predictor of sensitivity to the peripheral effects of insulin. They found that there was a decline in insulin sensitivity associated with age, body mass index, and blood pressure. Therefore, this decline should not be isolated from aging itself. Furthermore, the metabolic effects of insulin with aging appear to reflect lifestyles that lead to increased adiposity and decreased physical activity [35]. Some studies have discussed the importance of a healthy diet and physical activity in reducing the incidence of diabetes mellitus, emphasizing that the control of modifiable risk factors such as diet, weight loss, smoking restriction, and physical activity can reduce the risk of developing diabetes by 88% in individuals with a family history [38,39].
The diagnosis of obesity, arterial hypertension, and dyslipidemia showed a positive association with diabetes mellitus in the simple model; however, only obesity and dyslipidemia variables remained in the final model. These chronic conditions present intrinsic relationships in their pathophysiologies, as they cause metabolic changes such as the accumulation of lipids in adipocytes, increasing visceral obesity and the risk of developing arterial hypertension, as well as the activation of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as leukocytes, lymphocytes, monocytes, and neutrophils, which likely contribute to the induction of insulin resistance and diabetes mellitus [40,41,42].
Some studies have shown that the link between obesity, dyslipidemia, and diabetes mellitus is generally due to two main factors: insulin resistance and lack of insulin. Excess weight causes an increase in blood levels of free fatty acids, derived from diet and the release of excess fat deposits. The increase in plasma levels of free fatty acids induces mitochondrial β-oxidation, blocking various processes such as gene transcription in glucose metabolism. This results in the predominance of lipid use over glucose, decreased glucose uptake by muscles, and reduced glycogen synthesis in skeletal muscles. This state of chronic hyperglycemia (glucotoxicity) further impairs insulin sensitivity, leading to a cascade of events through hyperglycemia, compensatory hyperinsulinemia, insulin resistance, glucose intolerance, and apoptosis of pancreatic beta cells [43,44,45].
This finding aligns with the Social Dimensions of Inequality Survey (PDSD), which showed a positive association with the presence of obesity, diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension, and dyslipidemias in Brazilian diabetics [24]. A study conducted in Canada assessed the association between the consumption of ultra-processed foods, obesity, and diabetes mellitus in a representative population sample. Adults who had the habit of consuming ultra-processed foods were 31% more likely to be obese (OR = 1.31, 95% CI: 1.06–1.60) and 37% more likely to develop diabetes (OR = 1.37, 95% CI: 1.01–1.85) [46,47].
In this study, it was observed that, even in remote regions such as the Amazon, the factors associated with the prevalence of diabetes mellitus are similar to those found in other urban areas. This represents a significant finding, as it had not previously been documented in the Amazon. These results suggest that the social, demographic, and health determinants of diabetes mellitus may be consistent across the country. This understanding is crucial for the development of appropriate prevention and treatment strategies, especially in geographically remote regions where healthcare resources may be more limited, as is often the case in Rio Branco, Acre municipality [38,39,46,47,48].
It is pertinent to consider that this study has some limitations. The cross-sectional analysis methodology prevents applying causal or temporal factors; thus, it is not possible to determine over time the order in which associated factors may have affected participants before data collection was performed. Despite this limitation, the discussed results highlight the importance of individually analyzing the prevalence and factors associated with diabetes mellitus, as they may present considerable municipal and regional differences.
5. Conclusions
This study revealed that the prevalence of diabetes mellitus in the municipality of Rio Branco, Acre, Brazil, increased with advancing age. Education, obesity, and dyslipidemia were also associated with diabetes mellitus. These findings stimulate debate and reflection on the persistence of this chronic disease in many Brazilian municipalities and its association with social, demographic, and health determinants, which have also been consistent in geographically remote regions from major economic centers. Additionally, the discussions raise awareness about some effective ways to combat, control, and prevent diabetes mellitus.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.A.R. and Y.d.M.M.L.; methodology, Y.d.M.M.L., F.A.M. and A.A.R.; formal analysis, Y.d.M.M.L. and A.A.R.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.d.M.M.L., F.A.M. and A.A.R.; writing—review and editing, Y.d.M.M.L., F.A.M. and A.A.R.; project administration A.A.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval for this study were waive since it used data of public use and access, made available by the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics—IBGE in an unrestricted manner and without nominal identifications, under the terms of the National Health Council Resolution, CNS 466/12, which provides for research involving human beings in Brazil.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained by National Health Survey (Pesquisa Nacional de Saúde—PNS), from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data presented in this study are publicly and unrestrictedly available from the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics (IBGE) on the website https://www.ibge.gov.br/estatisticas/downloads-estatisticas.html?caminho=PNS/2019/Microdados/Dados (accessed on 6 February 2022).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cho, N.H.; Kirigia, J.; Claude, J.; Katherine, M.O.; Guariguata, L.; Rathmann, W.; Roglic, G.; Forouhi, N.; Dajani, R.; Esteghamati, A.; et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 8th ed.; International Diabetes Federation: Bruxelas, Belgium, 2017; pp. 1–150. [Google Scholar]
- Dysted, M.P.; Esztergályos, B.; Gautam, S.; Helman, B.; Pinkepank, M.; Randi, A.; Salim, A.; Wallis, K.; Jiménez, B.Y.; Ysebaert, M. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 10th ed.; International Diabetes Federation: Bruxelas, Belgium, 2021; pp. 1–141. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Ley, S.H.; Hu, F.B. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, N.H.; Shaw, J.E.; Karuranga, S.; Huang, Y.; Rocha Fernandes, J.D.; Ohlrogge, A.W.; Malanda, B. Atlas de diabetes da IDF: Estimativas globais de prevalência de diabetes para 2017 e projeções para 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 138, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sociedade Brasileira de Diabetes. Diretrizes da Sociedade Brasileira de Diabetes 2019–2020. Available online: https://diretriz.diabetes.org.br/ (accessed on 5 January 2024).
- Brasil. Ministério da Saúde. Vigitel Brasil 2023: Vigilância de Fatores de Risco e Proteção para Doenças Crônicas por Inquérito Telefônico. Available online: https://www.gov.br/saude/pt-br/centrais-de-conteudo/publicacoes/svsa/vigitel/vigitel-brasil-2023-vigilancia-de-fatores-de-risco-e-protecao-para-doencas-cronicas-por-inquerito-telefonico/view (accessed on 3 January 2024).
- Marinho, N.B.P.; Vasconcelos, H.C.A.; Alencar, A.M.P.G.; Almeida, P.C.; Damasceno, M.M.C. Risk for type 2 diabetes mellitus and associated factors. Acta Paul. De Enferm. 2013, 26, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naranjo, A.A.; Rodríguez, Á.Y.; Llera, R.E.; Aroche, R. Diabetes risk in a Cuban primary care setting in persons with no known glucose abnormalities. MEDICC Rev. 2013, 15, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arruda, G.O.; Schmidt, D.B.; Marcon, S.S. Hospitalizations for diabetes mellitus and the Family Health Strategy, Paraná, Brazil, 2000–2012. Ciências E Saúde Coletiva, 2018; 23, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayla, V.C.; Aline, F.S.; Clarissa, N.M.; Sylvia, F.C.C.; Andréia, R.Q. Prevalence and associated factors of diabetes in the elderly population in Viçosa, Minas Gerais, Brazil. Rev. Bras. De Epidemiol. 2015, 18, 953–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzy, J.; Campos, M.R.; Emmerick, I.; Silva, R.S.D.; Schramm, J.M.A. Prevalence of diabetes mellitus and its complications and characterization of healthcare gaps based on triangulation of studies. Cad. De Saúde Pública 2021, 37, e00076120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Povos Indígenas no Brasil. Localização e Extensão das Tis. Available online: https://pib.socioambiental.org/pt/Localiza%C3%A7%C3%A3o_e_extens%C3%A3o_das_TIs (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- Secretaria de Estado de Meio Ambiente. Divisão De Áreas Naturais Protegidas E Biodiversidade. Available online: http://sema.acre.gov.br/divisao-de-areasnaturais-protegidas-e-biodiversidade/ (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- De Azevedo, E.M. A efetividade das reservas extrativistas no estado do acre. Científic-Multidiscip. J. 2022, 9, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística. Cidades e Estados: Rio Branco. 2020. Available online: https://cidades.ibge.gov.br/brasil/ac/rio-branco/panorama (accessed on 30 January 2023).
- Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística. Pesquisa Nacional de saúde 2019–Percepção do Estado de Saúde, Estilos de Vida, Doenças Crônicas e Saúde Bucal: Brasil e Grandes Regiões. Available online: https://biblioteca.ibge.gov.br/index.php/biblioteca-catalogo?view=detalhes&id=2101764 (accessed on 29 January 2023).
- Reis, R.C.P.; Duncan, B.B.; Malta, D.C.; Iser, B.P.M.; Schmidt, M.I. Evolução do diabetes no Brasil: Dados de prevalência da Pesquisa Nacional de Saúde de 2013 e 2019. Cad. De Saúde Pública 2022, 38, e00149321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, Y.M.M.; Martins, F.A.; Ramalho, A.A. Prevalence of ultra-processed food, alcohol and tobacco consumption and chronic non-communicable diseases in Rio Branco, capital city of the state of Acre, Brazil, 2019: Comparative analysis of two epidemiological surveys. Epidemiol. E Serviços De Saúde Rev. Do Sist. Único De Saúde Do Bras. 2022, 31, e2021607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victora, C.G.; Huttly, S.R.; Fuchs, S.C.; Olinto, M.T. The role of conceptual frameworks in epidemiological analysis: A hierarchical approach. Int. J. Epidemiol. 1997, 26, 224–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deborah, C.M.; Bruce, B.D.; Maria, I.S.; Ísis, E.M.; Alanna, G.S.; Regina, T.I.B. Prevalence of diabetes mellitus as determined by glycated hemoglobin in the Brazilian adult population, National Health Survey. Rev. Bras. De Epidemiol. 2019, 22, e190006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzana, A.M.; Isabel, C.M.F.; Suely, G.A.G.; Lenise, M. Diabetes mellitus prevalence and associated factors in adults in Ribeirão Preto, São Paulo, Brazil, 2006: OBEDIARP Project. Cad. De Saúde Pública 2010, 26, 929–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyba, E.; Abebaw, W.; Daniel, A. Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus, Prediabetes and Its Associated Factors in Dessie Town, Northeast Ethiopia: A Community-Based Study. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 2799–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andre, C.C.; Nena, N.; Gina, S. The Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus and Obesity in the Adult Population of Guinea-Bissau: A Pilot Study. Rev. Port. De Endocrinol. Diabetes E Metab. 2018, 13, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betine, P.M.I.; Deborah, C.M.; Bruce, B.D.; Lenildo, M.; Alvaro, V. Prevalence, correlates, and description of self-reported diabetes in brazilian capitals–results from a telephone survey. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luisa, F.S.; Monica, C.R. The prevalence of diabetes mellitus and its associated factors in the Brazilian adult population: Evidence from a population-based survey. Rev. Bras. De Epidemiol. 2017, 20, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nancy, P.M.; Karl, P.; Witness, C.; Alfred, M.; Zamakayise, K.; Ebrahim, H. Self-reported prevalence of chronic non-communicable diseases and associated factors among older adults in South Africa. Glob. Health Action 2013, 6, 20936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ana Luísa, B.P.; Guilherme, L.W.; Luis, S.N.; Rosane, A.S. Avaliação da literacia para a saúde de pacientes portadores de diabetes acompanhados em um ambulatório público. Cad. De Saúde Pública 2021, 37, e00084819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.Y. On the relationship between economic conditions around the time of birth and late life cognitive abilities: Evidence from Taiwan. Econ. Hum. Biol. 2016, 22, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macinko, J.; Mullachery, P.H. Education-related health inequities in noncommunicable diseases: An analysis of the Brazilian National Health Survey, 2013 and 2019. Cad. De Saúde Pública 2022, 38, e00137721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatulashvili, S.; Fagherazzi, G.; Dow, C.; Cohen, R.; Fosse, S.; Bihan, H. Socioeconomic inequalities and complications of type 2 diabetes: A systematic review. Diabetes Metab. 2020, 46, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill-Briggs, F.; Adler, N.E.; Berkowitz, S.A.; Chin, M.H.; Gary-Webb, T.L.; Navas-Acien, A.; Thornton, P.L.; Haire-Joshu, D. Social Determinants of Health and Diabetes: A Scientific Review. Diabetes Care 2020, 44, 258–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, J.; Chen, P.-J.; Xiao, W.-H. Mechanism of increased risk of insulin resistance in aging skeletal muscle. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2020, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFronzo, R.A.; Barzilai, N.; Simonson, D.C. Mechanism of metformin action in obese and lean noninsulin-dependent diabetic subjects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1991, 73, 1294–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, A.E.; Janson, J.; Bonner-Weir, S.; Ritzel, R.; Rizza, R.A.; Butler, P.C. Beta-cell deficit and increased beta-cell apoptosis in humans with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2003, 52, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.M.; Halter, J.B. Aging and insulin secretion. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 284, E7–E12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark, A.; Supiano, R.V.; Hogikyan, L.A.; Morrow, F.J.; Ortiz-Alonso, W.H.; Andrzej, T.G.; Jeffrey, B.H. Aging and Insulin Sensitivity: Role of Blood Pressure and Sympathetic Nervous System Activity. J. Gerontol. 1993, 48, M237–M243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, H.; Fukunishi, S.; Asai, A.; Yokohama, K.; Ohama, H.; Nishiguchi, S.; Higuchi, K. Sarcopenia, frailty and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 24, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fostinelli, S.; De Amicis, R.; Leone, A.; Giustizieri, V.; Binetti, G.; Bertoli, S.; Cappa, S.F. Eating behavior in aging and dementia: The need for a comprehensive assessment. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 604488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.B.; Manson, J.E.; Stampfer, M.J.; Colditz, G.; Liu, S.; Solomon, C.G.; Willett, W.C. Diet, lifestyle, and the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in women. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 790–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, T.D.A.B.; Goldbaum, M.; Segri, N.J.; Barros, M.B.D.A.; Cesar, C.L.G.; Carandina, L.; Alves, M.C.G.P. Diabetes mellitus: Factors associated with prevalence in the elderly, control measures and practices, and health services utilization in São Paulo, Brazil. Cad. De Saúde Pública 2011, 27, 1233–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolitski, M.F.; Macedo, D.S.; Benincá, S.C.; Schmitt, V.; Mazur, C.E. Associação entre o nível glicêmico, risco cardiovascular e qualidade de vida em idosos diabéticos. Saúde E Desenvolv. Hum. 2019, 7, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwona, K.; Marta, C.; Agnieszka, B.Z. Obesity, bioactive lipids, and adipose tissue inflammation in insulin resistance. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilton, R.C.M.; Neif, M. Hipertensão, diabetes e dislipidemia–mecanismos envolvidos. Rev. Bras. De Hipertens. 2014, 21, 92–97. [Google Scholar]
- Lois, K.; Kumar, S. Obesity and diabetes. Endocrinol. Nutr. 2009, 56, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravussin, E.; Smith, S.R. Increased fat intake, impaired fat oxidation, and failure of fat cell proliferation result in ectopic fat storage, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2002, 967, 363–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, G.F.; Carpentier, A.; Adeli, K.; Giacca, A. Disordered fat storage and mobilization in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Endocr. Rev. 2002, 23, 201–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wei, Q.; Li, H.; Yang, H.; Wu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Chen, Q.; He, B.; Chen, F. Association of remnant cholesterol with hypertension, type 2 diabetes, and their coexistence: The mediating role of inflammation-related indicators. Lipids Health Dis. 2023, 22, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milena, N.; Jane, P.Y.; Jean, C.M. Consumption of ultra-processed foods is associated with obesity, diabetes and hypertension in Canadian adults. Can. J. Public Health 2021, 112, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).