Does the Efficacy of Semaglutide Treatment Differ between Low-Risk and High-Risk Subgroups of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity Based on SCORE2, SCORE2-Diabetes, and ASCVD Calculations?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
Statistical Analysis
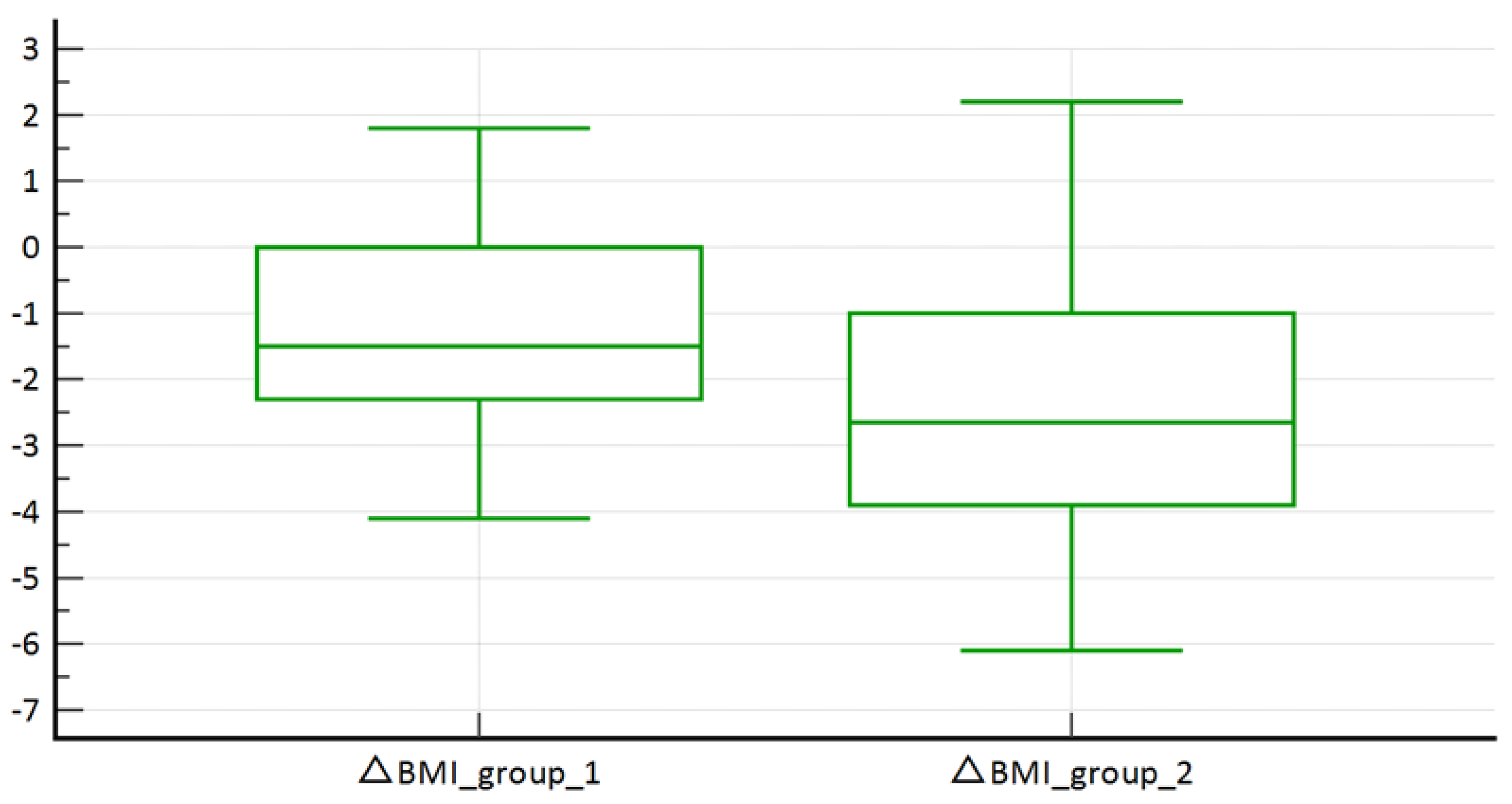
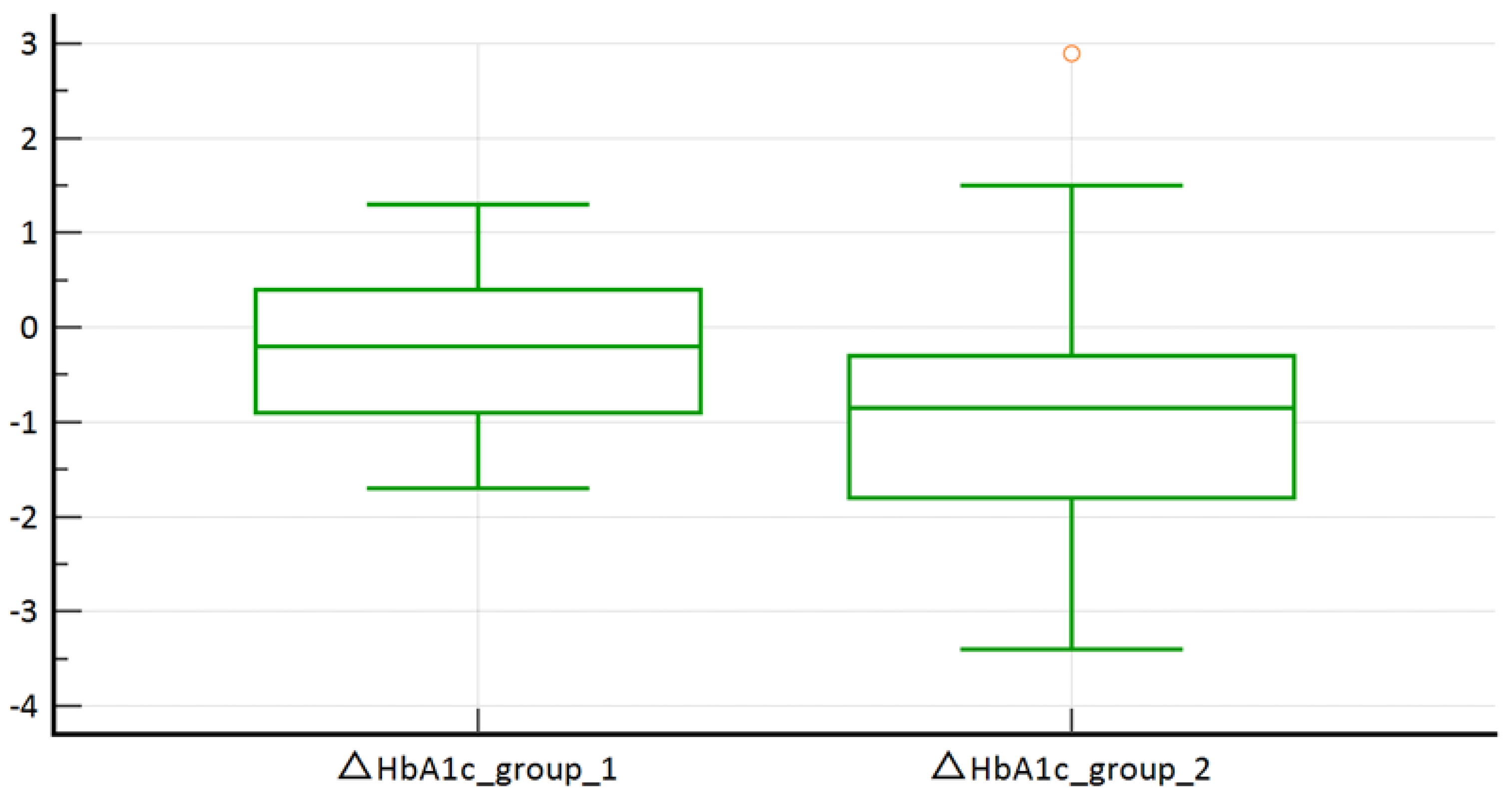
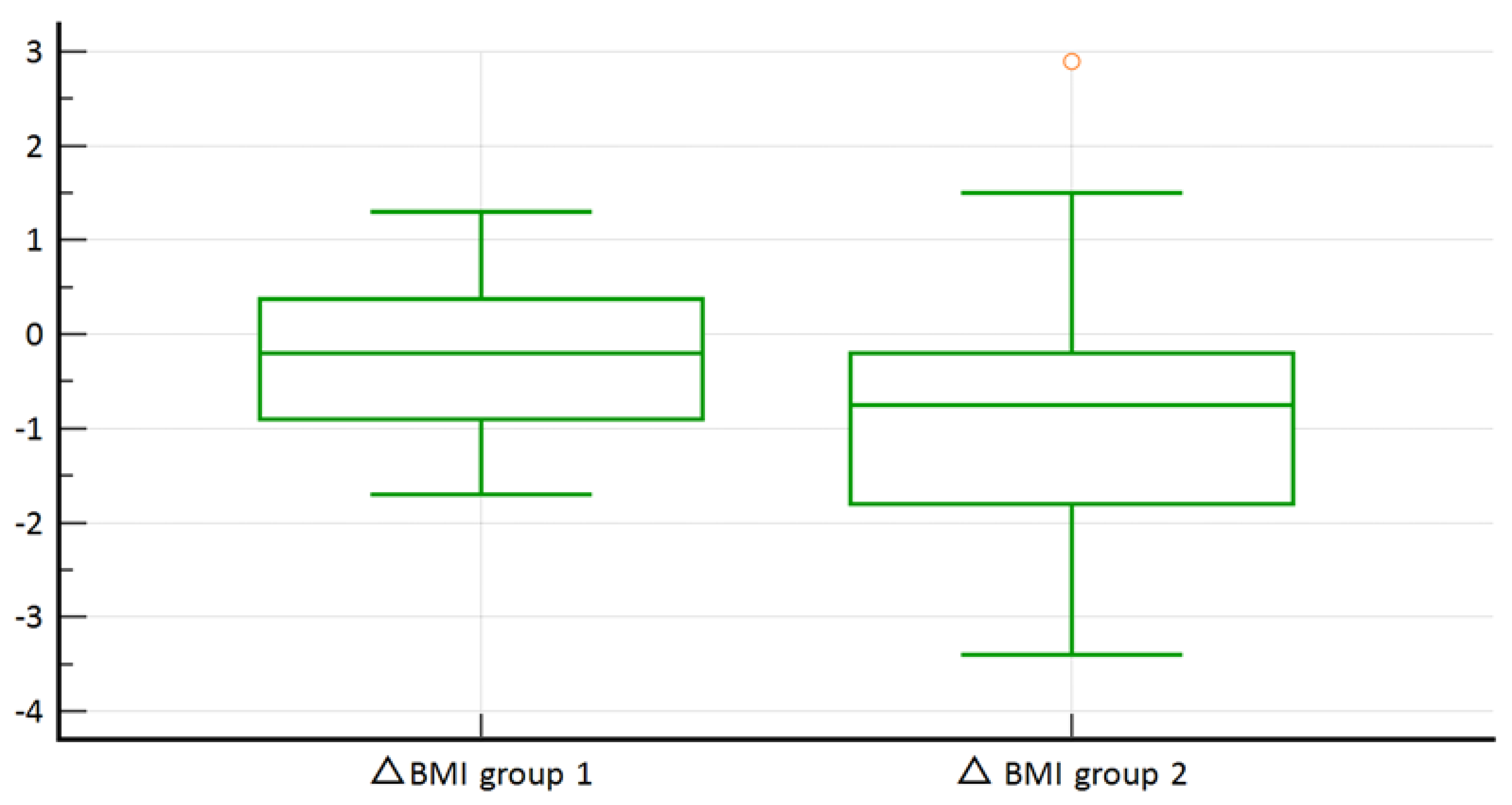
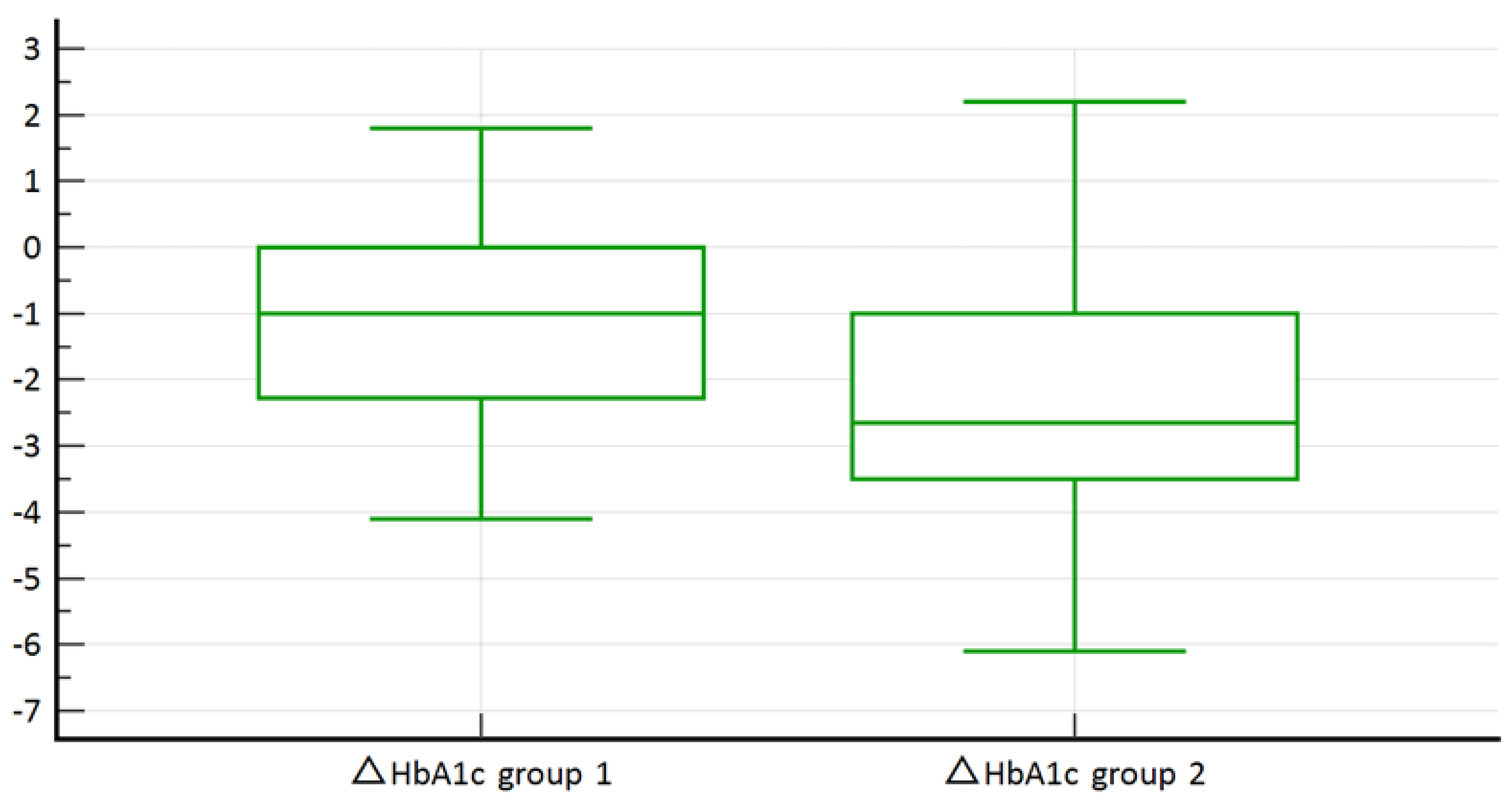
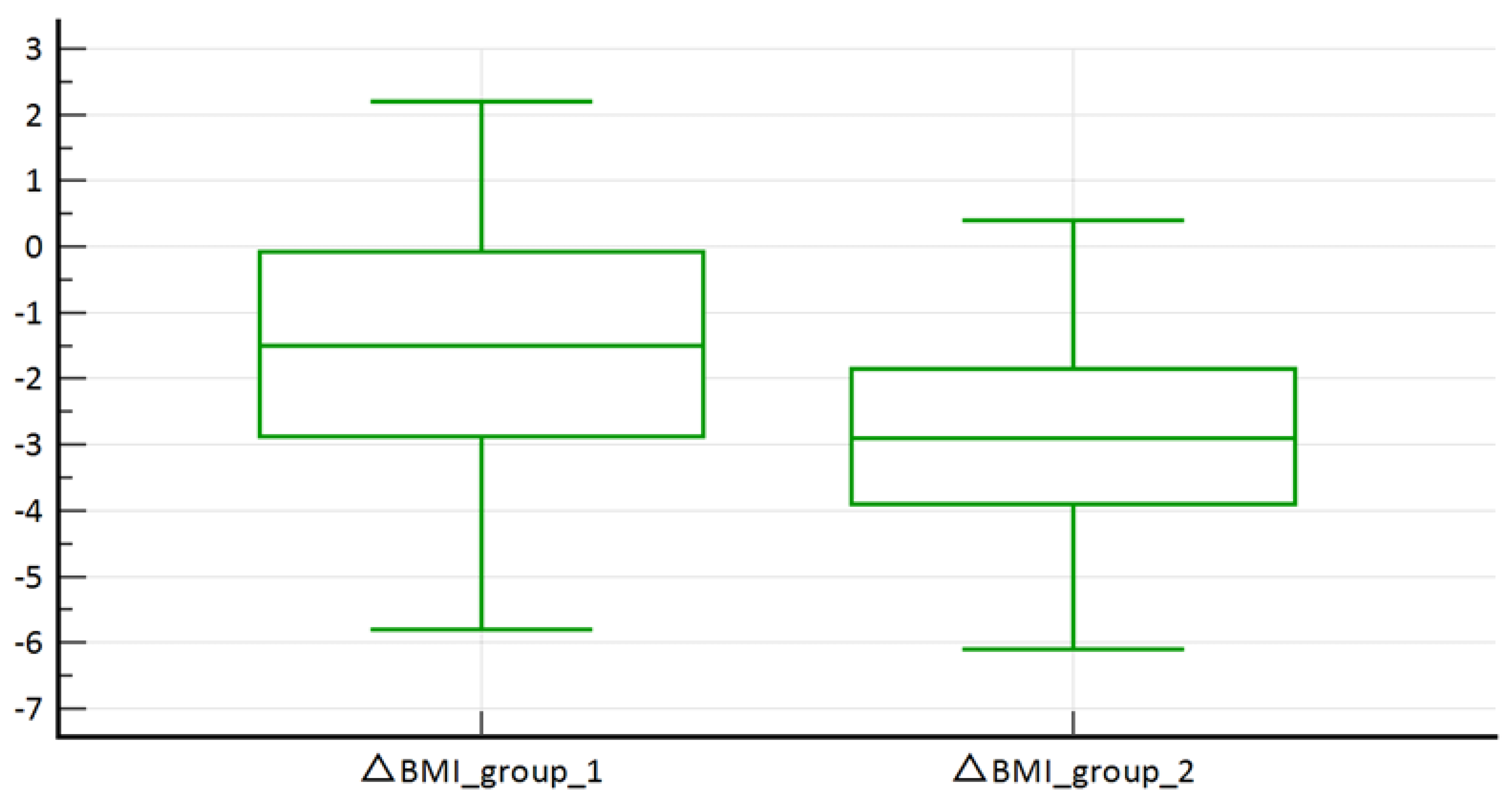
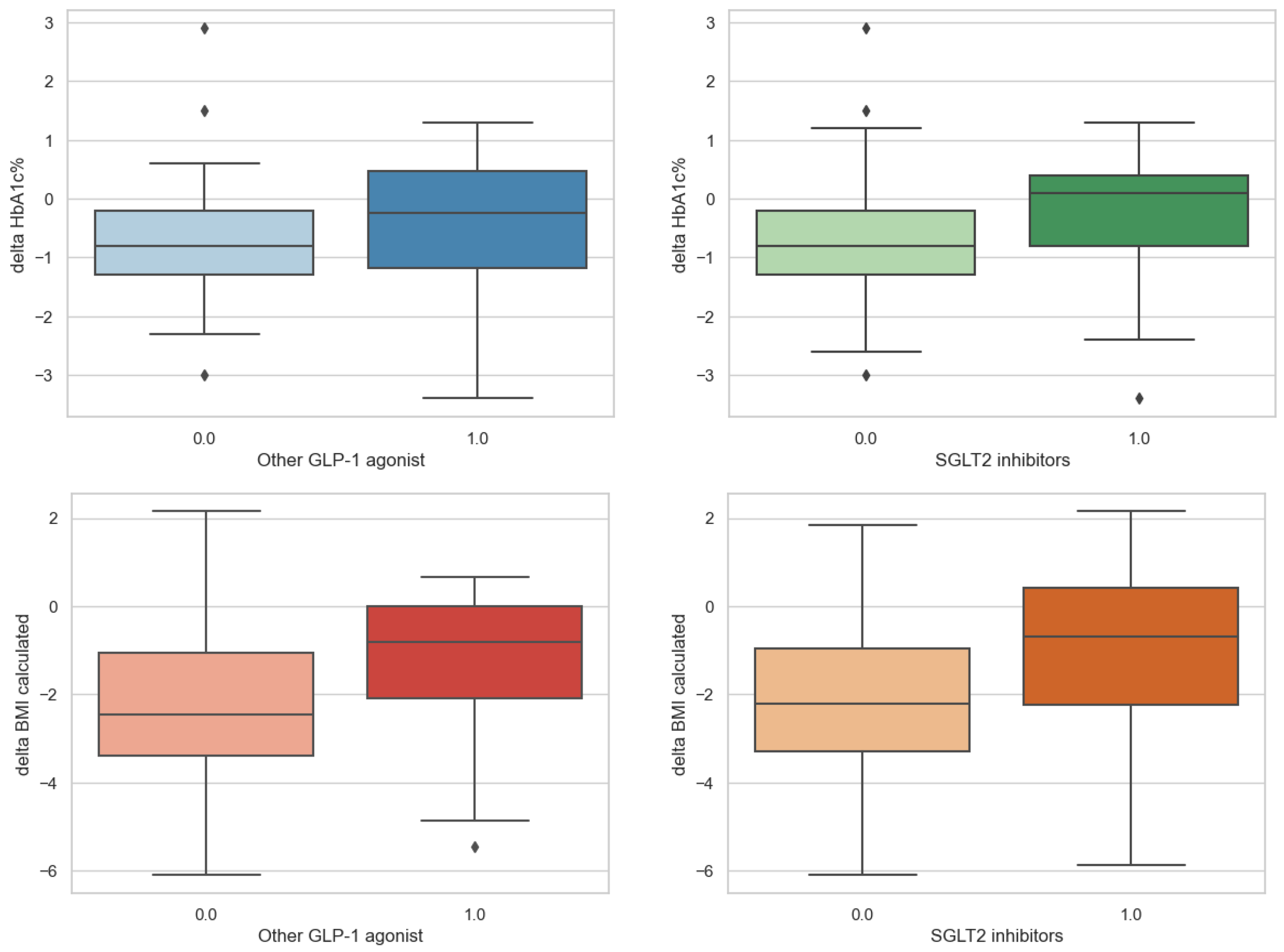
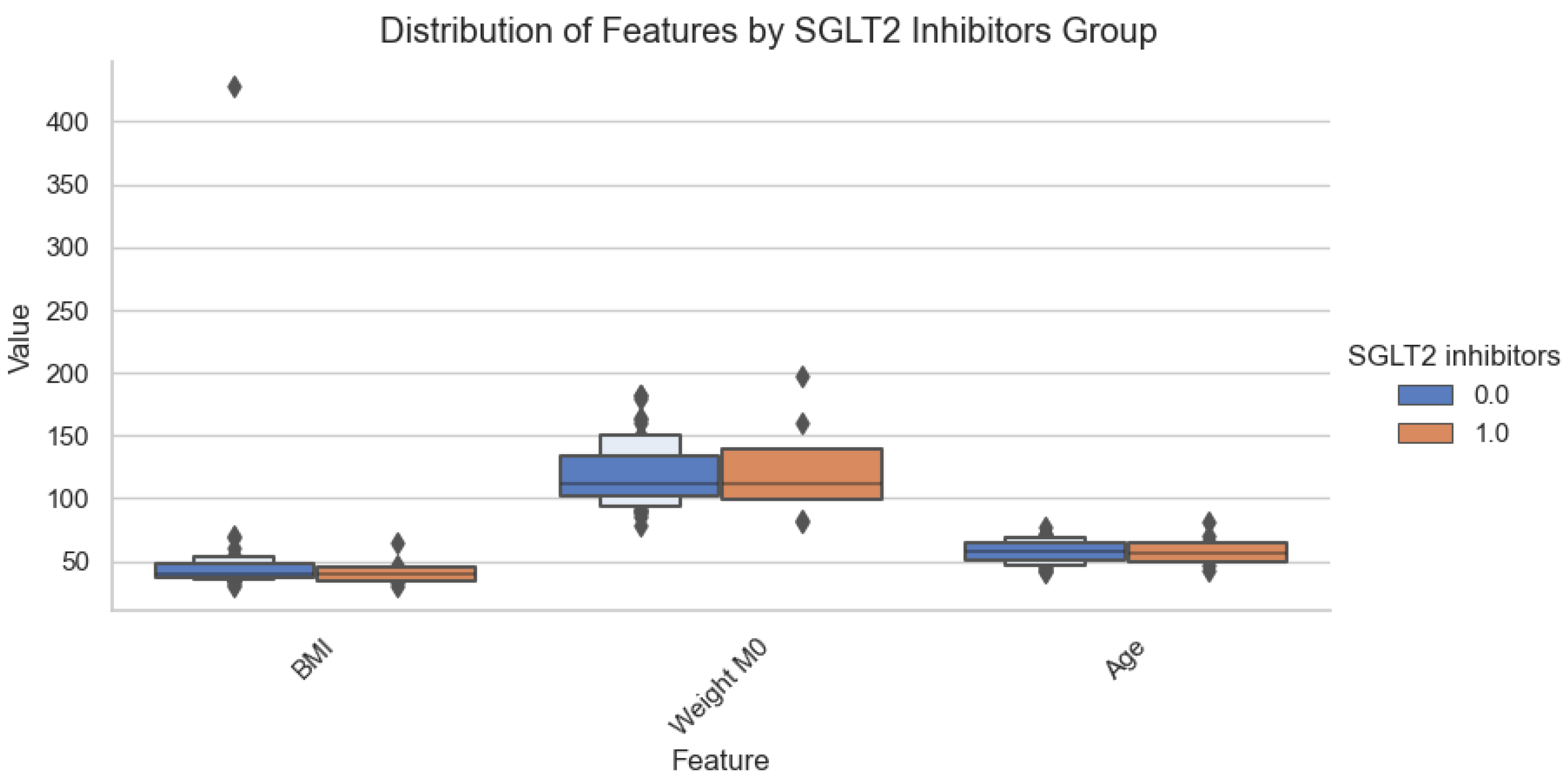
3. Results
Results of the Statistical Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization Diabetes. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/diabetes (accessed on 11 October 2023).
- Yusuf, S.; Hawken, S.; Ounpuu, S.; Dans, T.; Avezum, A.; Lanas, F.; McQueen, M.; Budaj, A.; Pais, P.; Varigos, J.; et al. Effect of Potentially Modifiable Risk Factors Associated with Myocardial Infarction in 52 Countries (the INTERHEART Study): Case-Control Study. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2004, 364, 937–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASCVD Risk Estimator Plus. Available online: https://www.acc.org/Tools-and-Practice-Support/Mobile-Resources/Features/http%3a%2f%2fwww.acc.org%2fTools-and-Practice-Support%2fMobile-Resources%2fFeatures%2f2013-Prevention-Guidelines-ASCVD-Risk-Estimator (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- SCORE2 Working Group and ESC Cardiovascular Risk Collaboration. SCORE2 Risk Prediction Algorithms: New Models to Estimate 10-Year Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in Europe. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 2439–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goff, D.C.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Bennett, G.; Coady, S.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Gibbons, R.; Greenland, P.; Lackland, D.T.; Levy, D.; O’Donnell, C.J.; et al. 2013 ACC/AHA Guideline on the Assessment of Cardiovascular Risk: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2014, 129, S49–S73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conroy, R.M.; Pyörälä, K.; Fitzgerald, A.P.; Sans, S.; Menotti, A.; De Backer, G.; De Bacquer, D.; Ducimetière, P.; Jousilahti, P.; Keil, U.; et al. SCORE project group. Estimation of ten-year risk of fatal cardiovascular disease in Europe: The SCORE project. Eur. Heart J. 2003, 24, 987–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SCORE2-OP Working Group and ESC Cardiovascular Risk Collaboration. SCORE2-OP Risk Prediction Algorithms: Estimating Incident Cardiovascular Event Risk in Older Persons in Four Geographical Risk Regions. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 2455–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, C.S.; Golden, S.H.; Anderson, C.; Bray, G.A.; Burke, L.E.; de Boer, I.H.; Deedwania, P.; Eckel, R.H.; Ershow, A.G.; Fradkin, J.; et al. Update on Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Light of Recent Evidence: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association and the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 1777–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association. Economic Costs of Diabetes in the U.S. in 2017. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElSayed, N.A.; Aleppo, G.; Aroda, V.R.; Bannuru, R.R.; Brown, F.M.; Bruemmer, D.; Collins, B.S.; Hilliard, M.E.; Isaacs, D.; Johnson, E.L.; et al. Obesity and Weight Management for the Prevention and Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2023. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, S128–S139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombi, A.M.; Wood, G.C. Obesity in the Workplace: Impact on Cardiovascular Disease, Cost, and Utilization of Care. Am. Health Drug Benefits 2011, 4, 271–278. [Google Scholar]
- SCORE2-Diabetes Working Group and the ESC Cardiovascular Risk Collaboration; Pennells, L.; Kaptoge, S.; Østergaard, H.B.; Read, S.H.; Carinci, F.; Franch-Nadal, J.; Petitjean, C.; Taylor, O.; Hageman, S.H.J.; et al. SCORE2-Diabetes: 10-Year Cardiovascular Risk Estimation in Type 2 Diabetes in Europe. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 2544–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marso, S.P.; Bain, S.C.; Consoli, A.; Eliaschewitz, F.G.; Jódar, E.; Leiter, L.A.; Lingvay, I.; Rosenstock, J.; Seufert, J.; Warren, M.L.; et al. Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1834–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, M.K.; Karuppasamy, M.; Sahoo, B.M. Semaglutide, a Glucagon like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist with Cardiovascular Benefits for Management of Type 2 Diabetes. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2022, 23, 521–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadden, T.A.; Bailey, T.S.; Billings, L.K.; Davies, M.; Frias, J.P.; Koroleva, A.; Lingvay, I.; O’Neil, P.M.; Rubino, D.M.; Skovgaard, D.; et al. Effect of Subcutaneous Semaglutide vs Placebo as an Adjunct to Intensive Behavioral Therapy on Body Weight in Adults with Overweight or Obesity: The STEP 3 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2021, 325, 1403–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA Approves Higher Semaglutide Dose for Obesity. Available online: https://diabetes.medicinematters.com/semaglutide/obesity/step-trials-fda-approves-semaglutide-dose-obesity/19231776 (accessed on 27 November 2023).
- EMA Wegovy. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/wegovy (accessed on 27 November 2023).
- Bažadona, D.; Matovinović, M.; Krbot Skorić, M.; Grbavac, H.; Belančić, A.; Malojčić, B. The Interconnection between Carotid Intima–Media Thickness and Obesity: Anthropometric, Clinical and Biochemical Correlations. Medicina 2023, 59, 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marx, N.; Federici, M.; Schütt, K.; Müller-Wieland, D.; Ajjan, R.A.; Antunes, M.J.; Christodorescu, R.M.; Crawford, C.; Di Angelantonio, E.; Eliasson, B.; et al. 2023 ESC Guidelines for the Management of Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Diabetes: Developed by the Task Force on the Management of Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Diabetes of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 4043–4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittwer, J.A.; Golden, S.H.; Joseph, J.J. Diabetes and CVD Risk: Special Considerations in African Americans Related to Care. Curr. Cardiovasc. Risk Rep. 2020, 14, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, M.; Bain, S.C.; Jeppesen, O.K.; Lingvay, I.; Sørrig, R.; Treppendahl, M.B.; Vilsbøll, T. Semaglutide (SUSTAIN and PIONEER) Reduces Cardiovascular Events in Type 2 Diabetes across Varying Cardiovascular Risk. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020, 22, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahrén, B.; Masmiquel, L.; Kumar, H.; Sargin, M.; Karsbøl, J.D.; Jacobsen, S.H.; Chow, F. Efficacy and Safety of Once-Weekly Semaglutide versus Once-Daily Sitagliptin as an Add-on to Metformin, Thiazolidinediones, or Both, in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes (SUSTAIN 2): A 56-Week, Double-Blind, Phase 3a, Randomised Trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017, 5, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmann, A.J.; Capehorn, M.; Charpentier, G.; Dotta, F.; Henkel, E.; Lingvay, I.; Holst, A.G.; Annett, M.P.; Aroda, V.R. Efficacy and Safety of Once-Weekly Semaglutide Versus Exenatide ER in Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes (SUSTAIN 3): A 56-Week, Open-Label, Randomized Clinical Trial. Diabetes Care 2017, 41, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroda, V.R.; Bain, S.C.; Cariou, B.; Piletič, M.; Rose, L.; Axelsen, M.; Rowe, E.; DeVries, J.H. Efficacy and Safety of Once-Weekly Semaglutide versus Once-Daily Insulin Glargine as Add-on to Metformin (with or without Sulfonylureas) in Insulin-Naive Patients with Type 2 Diabetes (SUSTAIN 4): A Randomised, Open-Label, Parallel-Group, Multicentre, Multinational, Phase 3a Trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017, 5, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorli, C.; Harashima, S.-I.; Tsoukas, G.M.; Unger, J.; Karsbøl, J.D.; Hansen, T.; Bain, S.C. Efficacy and Safety of Once-Weekly Semaglutide Monotherapy versus Placebo in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes (SUSTAIN 1): A Double-Blind, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled, Parallel-Group, Multinational, Multicentre Phase 3a Trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017, 5, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodbard, H.W.; Lingvay, I.; Reed, J.; de la Rosa, R.; Rose, L.; Sugimoto, D.; Araki, E.; Chu, P.-L.; Wijayasinghe, N.; Norwood, P. Semaglutide Added to Basal Insulin in Type 2 Diabetes (SUSTAIN 5): A Randomized, Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 2291–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dziopa, K.; Asselbergs, F.W.; Gratton, J.; Chaturvedi, N.; Schmidt, A.F. Cardiovascular Risk Prediction in Type 2 Diabetes: A Comparison of 22 Risk Scores in Primary Care Settings. Diabetologia 2022, 65, 644–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damaskos, C.; Garmpis, N.; Kollia, P.; Mitsiopoulos, G.; Barlampa, D.; Drosos, A.; Patsouras, A.; Gravvanis, N.; Antoniou, V.; Litos, A.; et al. Assessing Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Diabetes: An Update. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2021, 16, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Qin, L.; Sheng, C.-S.; Niu, Y.; Gu, H.; Lu, S.; Yang, Z.; Tian, J.; Su, Q. ASCVD Risk Stratification Modifies the Effect of HbA1c on Cardiovascular Events among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus with Basic to Moderate Risk. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2020, 8, e000810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuksan-Ćusa, B.; Jakšić, N.; Matovinović, M.; Baretić, M.; Vuksan-Ćusa, Z.; Mustač, F.; Tudor, K.I.; Šagud, M.; Marčinko, D. Depression and Hopelessness as Possible Predictors of Weight Change among Obese Day-Hospital Patients: A 6-Months Follow-Up Study. Psychiatr. Danub. 2020, 32, 217–218. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.L.; Ong, K.W.; Johal, J.; Han, C.Y.; Yap, Q.V.; Chan, Y.H.; Chooi, Y.C.; Zhang, Z.P.; Chandra, C.C.; Thiagarajah, A.G.; et al. Effect of a Smartphone App on Weight Change and Metabolic Outcomes in Asian Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2112417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustač, F.; Tomašić, L.; Peček, M.; Galijašević, T.; Grkinić, A.; Medić, F.; Matovinović, M.; Marčinko, D. Mobile Applications and Improving the Quality of Life in People with Obesity. In Proceedings of the 2022 7th International Conference on Smart and Sustainable Technologies (SpliTech), Split/Bol, Croatia, 5–8 July 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Castelnuovo, G.; Pietrabissa, G.; Manzoni, G.M.; Cattivelli, R.; Rossi, A.; Novelli, M.; Varallo, G.; Molinari, E. Cognitive behavioral therapy to aid weight loss in obese patients: Current perspectives. Psychol. Res. Behav. Manag. 2017, 10, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhaury, K.; Chaware, S. Relation between Diabetes and Psychiatric Disorders. Cureus 2022, 14, e30733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krejčí, H.; Vyjídák, J.; Kohutiar, M. Low-Carbohydrate Diet in Diabetes Mellitus Treatment. Vnitr. Lek. 2018, 64, 742–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magkos, F.; Mittendorfer, B. Editorial: Type 2 Diabetes Therapeutics: Weight Loss and Other Strategies. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2022, 25, 256–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandouk, Z.; Lansang, M.C. Diabetes with Obesity—Is There an Ideal Diet? Cleve. Clin. J. Med. 2017, 84, S4–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, B.-Y.; He, L.-X.; Xue, L. Intermittent Fasting: Potential Bridge of Obesity and Diabetes to Health? Nutrients 2022, 14, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Gender distribution (%, N of female patients) | 60.9%, 39 | |
| Age (Median, Min-Max, yr.) | 57.5 (41–81) | |
| Height (X ± SD, cm) | 168.1 ± 10.1 | |
| Weight (X ± SD, kg) | 120.4 ± 27.3 | |
| BMI (X ± SD, kg/m2) | 42.5 ± 8.5 | |
| BMI category distribution (%, N) | BMI < 25 kg/m2 | 0%, 0 |
| Overweight | 0%, 0 | |
| Obesity class I | 14.1%, 9 | |
| Obesity class II | 31.3%, 20 | |
| Obesity class III | 54.7%, 35 | |
| Comorbidities (%, N) | Arterial hypertension | 79.7%, 51 |
| Dyslipidemia | 84.4%, 54 | |
| Hypothyroidism 1 | 17.2%, 11 | |
| HbA1c (X ± SD, %) | 7.2 ± 1.3 | |
| Fasting glucose (X ± SD, mmol/L) | 8.6 ± 2.2 | |
| Semaglutide dose achieved (%, N) | 0.5 mg | 60.9%, 39 |
| 1 mg | 39.1%, 25 | |
| SCORE2 distribution (%, N) | Low | 0%, 0 |
| Moderate | 34.4%, 22 | |
| High | 43.7%, 28 | |
| Very high | 21.9%, 14 | |
| SCORE2-Diabetes distribution (%, N) 2 | Low | 10.5%, 6 |
| Moderate | 22.8%, 13 | |
| High | 42.1%, 24 | |
| Very high | 24.6%, 14 | |
| ASCVD distribution (%, N) | Low | 15.6%, 10 |
| Borderline | 14.1%, 9 | |
| Intermediate | 37.5%, 24 | |
| High | 32.8%, 21 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matovinović, M.; Belančić, A.; Jug, J.; Mustač, F.; Sirovica, M.; Santini, M.; Bošnjaković, A.; Lovrić, M.; Lovrić Benčić, M. Does the Efficacy of Semaglutide Treatment Differ between Low-Risk and High-Risk Subgroups of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity Based on SCORE2, SCORE2-Diabetes, and ASCVD Calculations? Diabetology 2024, 5, 26-39. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology5010003
Matovinović M, Belančić A, Jug J, Mustač F, Sirovica M, Santini M, Bošnjaković A, Lovrić M, Lovrić Benčić M. Does the Efficacy of Semaglutide Treatment Differ between Low-Risk and High-Risk Subgroups of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity Based on SCORE2, SCORE2-Diabetes, and ASCVD Calculations? Diabetology. 2024; 5(1):26-39. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology5010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatovinović, Martina, Andrej Belančić, Juraj Jug, Filip Mustač, Maja Sirovica, Mihovil Santini, Anja Bošnjaković, Mario Lovrić, and Martina Lovrić Benčić. 2024. "Does the Efficacy of Semaglutide Treatment Differ between Low-Risk and High-Risk Subgroups of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity Based on SCORE2, SCORE2-Diabetes, and ASCVD Calculations?" Diabetology 5, no. 1: 26-39. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology5010003
APA StyleMatovinović, M., Belančić, A., Jug, J., Mustač, F., Sirovica, M., Santini, M., Bošnjaković, A., Lovrić, M., & Lovrić Benčić, M. (2024). Does the Efficacy of Semaglutide Treatment Differ between Low-Risk and High-Risk Subgroups of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity Based on SCORE2, SCORE2-Diabetes, and ASCVD Calculations? Diabetology, 5(1), 26-39. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology5010003








