Abstract
Background: Liver cancer, either primary or metastatic, is a leading cause of cancer-related deaths and in many cases is presented in stages requiring major hepatectomy. Adequate future liver remnant (FLR) volume is essential before any major hepatectomy. Portal vein embolization (PVE) has long been the standard technique for preoperative liver hypertrophy, but liver venous deprivation (LVD) has emerged as a novel method, potentially offering faster and superior results. The aim of this study is to compare FLR hypertrophy outcomes between LVD and PVE in patients undergoing major hepatectomy for liver malignancy. Methods: A systematic literature search was conducted across PubMed, Cochrane library, and clinicaltrials.gov for studies assessing FLR volume changes after LVD or PVE in patients with primary or secondary liver tumors undergoing liver resection. Data extraction was performed independently by two reviewers. The study protocol was registered in PROSPERO and was prepared according to the PRISMA guidelines. Results: Twelve retrospective cohort studies were included in this systematic review. Liver venous deprivation consistently demonstrated superior FLR hypertrophy, with a faster and higher percentage increase compared to PVE. Time to resection was also shorter in the LVD groups in most studies. Safety outcomes were comparable, with no consistent difference in post-procedural complications or mortality. Conclusions: Liver venous deprivation may potentially be a safe and effective alternative to PVE, offering more robust and rapid FLR hypertrophy with similar morbidity and mortality rates. While current evidence supports its superiority in selected patients, future validation with larger prospective clinical trials is essential before it can be adopted as standard management of patients with insufficient FLR volume.
1. Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) accounts for approximately 75% of primary liver cancers and remains a leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide. Despite advances in surveillance and treatment, many patients present at a stage requiring major hepatectomy to achieve oncologic clearance. Extended liver resections, defined as removal of five or more hepatic segments, are increasingly performed for HCC, cholangiocarcinoma (CCA), and colorectal liver metastases (CRLM), offering potential for long-term survival in selected patients [1,2,3].
Although improvements in surgical technique and patient selection have contributed to reduced perioperative morbidity and mortality, postoperative liver dysfunction remains a principal cause of delayed recovery, prolonged hospitalization, and post-hepatectomy liver failure (PHLF) [1,4]. One of the most critical determinants of postoperative outcomes is the volume and functional reserve of the future liver remnant (FLR). During preoperative evaluation, patients are often excluded from curative resection due to concerns of inadequate FLR volume [1,3,4].
To mitigate this risk, strategies to induce hypertrophy of the FLR have been integrated into preoperative planning. Portal vein embolization (PVE), firstly introduced by Makuuchi et al. in 1990, remains the standard approach for inducing compensatory hypertrophy of the non-embolized liver segments [5]. By occluding the portal venous inflow to the planned resection segments, PVE redirects portal flow to the contralateral lobe, triggering hypertrophy through the atrophy-hypertrophy complex. PVE is typically indicated when the anticipated FLR volume is ≤40% of the total liver volume [1]. This technique has expanded resectability in patients who would otherwise be deemed ineligible for curative surgery due to insufficient FLR volume, particularly in the context of underlying fibrosis or cirrhosis [2,4,6].
Despite its widespread adoption, PVE is not without limitations. Up to 20% of patients may fail to achieve sufficient hypertrophy, while 4–11% may experience tumor progression during the 4–6 week hypertrophy waiting interval, ultimately rendering resection unfeasible [2,3,4,6]. These shortcomings have prompted the development of alternative or adjunctive approaches to augment liver regeneration and improve surgical outcomes. Among them, associating liver partition and portal vein ligation for staged hepatectomy (ALPPS) and, more recently, liver venous deprivation (LVD), have gained attention [7,8].
Liver venous deprivation combines PVE with simultaneous or sequential embolization of the ipsilateral hepatic vein, enhancing FLR hypertrophy by promoting greater parenchymal ischemia and limiting venous collaterals [4]. Preliminary studies have reported superior hypertrophy rates and comparable safety profiles compared to PVE alone [9,10,11]. Histologic analyses suggest greater hepatocellular apoptosis and regenerative activity following LVD, and emerging data indicate higher rates of completed resections with lower postoperative morbidity.
While both PVE and LVD aim to optimize preoperative liver volume, the comparative efficacy and safety of these techniques remain areas of active investigation. A systematic evaluation of the existing literature is essential to clarify their relative benefits and inform surgical decision-making.
This systematic review aims to compare FLR hypertrophy outcomes between LVD and PVE in patients undergoing major hepatectomy for liver malignancy.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
A thorough literature search was conducted on PubMed, clinicaltrials.gov and the Cochrane library for publications including patients with liver malignancy undergoing PVE or LVD due to low FLR. Four hundred and seventy-six (476) studies were identified in PubMed after applying the following search string: (hepatocellular carcinoma OR liver cancer OR HCC) AND (portal vein embolization OR PVE) AND (hepatic vein embolization OR HVE OR liver venous deprivation) AND (future liver remnant OR liver remnant volume OR FLR OR liver volume). After applying the article type filters “clinical study”, “clinical trial”, “Phase I”, “Phase II”, “Phase III”, “Phase IV”, “clinical trial protocol”, “comparative study”, “pragmatic clinical trial”, “randomized controlled trial”, “twin study”, “validation study” and “observational study”, 70 remaining studies underwent title and abstract screening. After excluding 47 duplicate and irrelevant studies, 23 were eligible for full text assessment.
In the Cochrane library the search string “(hepatocellular carcinoma OR liver cancer OR HCC) AND (portal vein embolization OR PVE) AND (hepatic vein embolization OR HVE OR liver venous deprivation) AND (future liver remnant OR liver remnant volume OR FLR OR liver volume)” yielded 47 results. After excluding duplicates and irrelevant studies, 17 remaining studies were eligible for full text assessment. Finally, in clinicaltrials.gov, 5 completed clinical trials were identified after searching for “liver cancer” or “liver malignancy” as Condition and “poral vein embolization” or “liver venous deprivation” as Intervention. The results of none of the studies were reported neither could be retrieved after reaching for the corresponding researcher, therefore all 5 studies were excluded from our systematic review.
In clinicaltrials.gov a search for “liver cancer” “liver tumor” as condition/disease and “liver venous deprivation” or “LVD” as intervention/treatment was conducted. Four studies were identified, two of which were completed and underwent further assessment. No published results could be retrieved; therefore, the studies were not included in our review.
The literature search was completed by two independent reviewers (MP and ADG). Any conflict during the study selection process was resolved by consulting a third reviewer (PC) or a senior reviewer. This systematic review was prepared according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement [12]. The PRISMA algorithm is shown in Figure 1. The study protocol was registered at the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO) under the ID CRD420251065115.
Figure 1.
PRISMA flowchart.
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
In this systematic review the following inclusion criteria were applied: adult patients with liver malignancy, low FLR, patients undergoing PVE or LVD to increase the FLR, clinical trials, prospective studies, retrospective studies, full text available in the English language.
We excluded records of adolescent patients, in non-English language, records of patients undergoing other interventions than PVE or LVD to increase the preoperative FLR as well as preliminary reports, incomplete clinical trials, conference abstracts, editorials and letters to the editor.
2.3. Data Extraction
The following data were extracted to a predetermined datasheet: author, year and country of the study, study period, number of patients, sex, age, patient groups, diagnosis, cancer staging, number of tumors and size of the tumors, type of intervention (PVE or LVD), FLR at presentation and preoperatively, FLR alteration, time from embolization to operation, type of neoadjuvant treatment (if any), type of hepatectomy and resection margins, reasons for surgery drop-out, complications, length of stay, mortality and follow-up. Any data not reported in the original publications or not obtained after contacting the corresponding authors were excluded from the analysis.
Future liver remnant volume before and after intervention was the primary endpoint, while secondary endpoints included resection margins, postoperative morbidity and mortality.
2.4. Data Synthesis
Descriptive statistical analysis of patients’ demographics was performed using Microsoft Excel version 16.97.2. Results were reported as mean ± standard deviation (SD), where applicable. A meta-analysis was not feasible due to substantial heterogeneity in reporting of the primary outcomes. Any missing data that could not be obtained after contacting the corresponding authors were excluded from the pooled analysis.
2.5. PVE and LVD Procedures
In the included studies, PVE was performed either through ipsilateral or contralateral portal vein catheterization. Reported embolic agents varied and included polyvinyl alcohol, butyl-cyanoacrylate, iodized oils, microcoils, gelfoams and vascular plugs.
Liver venous deprivation consisted of PVE combined with sequential or simultaneous HVE. Hepatic vein embolization was achieved through either a transhepatic or transjugular approach. Embolic materials included vascular plugs, polyvinyl alcohol and microspheres. Vascular access in both cases was obtained under ultrasound guidance.
2.6. Risk of Bias and Quality Assessment
The Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool In non-Randomized Studies—of Interventions, Version 2 (ROBINS-I VS) (2024) was used to assess the risk of bias of the included studies [13]. This tool consists of 7 domains of bias: confounding, classification of interventions, participant selection, deviation from intended interventions, missing data, measurement of outcome, and selection of the reported result. It is the preferred method of assessing risk of bias in the results of non-randomized studies that examine the effects of one or more interventions.
The Newcastle–Ottawa scale (NOS) was used to assess the quality of the included cohort studies [14]. This tool assesses the quality of non-randomized trials based on three domains: selection of study groups, comparability of the groups and ascertainment of the outcomes. A point is awarded for each quality item with a maximum of 9 points.
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Included Studies
Twelve cohort studies comprising 992 patients with primary or secondary liver malignancies requiring major hepatectomy were included in this systematic review [1,2,3,6,7,8,15,16,17,18,19,20]. The studies were conducted across Europe, the United States, and Asia and were published between 2002 and 2025 (Table 1).

Table 1.
Characteristics of the included studies.
In total, 542 males and 194 females were studied in 11 cohorts, with a pooled mean age of 63.9 years. One study did not report patient demographics and therefore was excluded from this cumulative analysis. Of the 992 patients, 841 patients were diagnosed with primary liver tumors, including HCC, CCA, gallbladder cancer or neuroendocrine tumor (NET), while 151 had CRLM.
In each study, patients were stratified into those who underwent PVE or LVD preoperatively to increase the FLR, and those with an adequate FLR who did not receive any preoperative intervention. Overall, 318 patients underwent PVE, 191 LVD, and 483 underwent upfront hepatectomy. Patient demographics, diagnoses and tumor characteristics are detailed in Table 2 and Table 3.

Table 2.
Patient groups and demographics.

Table 3.
Subgroup diagnosis and tumor staging.
3.2. Effect of PVE and LVD on FLR Volume
In five studies, 233 patients who underwent PVE were compared to 269 patients who did not require any preoperative intervention due to sufficient FLR volume [1,2,15,17,18]. Among these, 228 patients received neoadjuvant chemotherapy, including transarterial chemoembolization (TACE). In the study of Okabe et al., TACE was selectively administered in patients with inadequate FLR four weeks after PVE. Reported baseline FLR volumes ranged from 18% to 60.5%, increasing post-PVE to 25–55%. Four of the five studies demonstrated a post-PVE FLR increase that met or exceeded the FLR of the comparison group. It is of note that Beppu et al. reported a statistically significant decrease in FLR following PVE. Among the included studies, hypertrophy was statistically significant in two, while the remaining studies did not report statistical analysis.
Three studies compared directly 69 patients who underwent LVD and 85 patients who received PVE [6,7,8]. In all three, LVD resulted in a statistically significantly greater increase in FLR volume compared to PVE.
In four studies, liver hypertrophy following LVD was evaluated in a total of 122 patients [3,16,19,20]. Fifty-two patients received TACE prior to embolization. Three studies reported a statistically significant FLR increase following LVD, which rendered patients eligible for hepatectomy. In the study of Hwang et al., the FLR increased by more than 4% per week in 34 patients with bile duct tumors and in 4 patients with other intrahepatic malignancies, a rate deemed sufficient for resection. However, statistical significance was either not assessed or not reported. The baseline and post-intervention FLR percentages are summarized in Table 4 and are illustrated in Figure 2.

Table 4.
Changes in FLR following preoperative PVE or LVD.
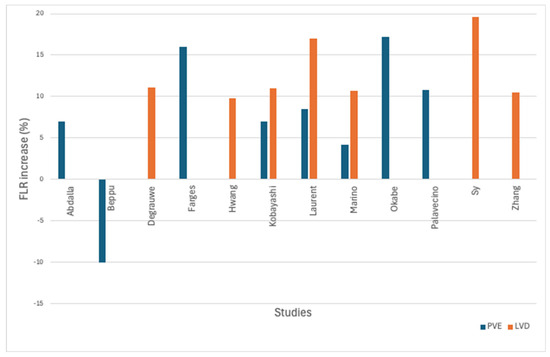
Figure 2.
Bar chart of FLR change after PVE (blue) and LVD (orange).
3.3. Hepatectomy Outcomes
Following PVE, 312 patients underwent right, extended right or extended left hepatectomy. Thirteen patients underwent additional resections involving the common bile duct, caudate lobe, portal vein, or inferior vena cava. Surgery was abandoned in five patients due to disease progression and in one due to insufficient liver hypertrophy. Complete resection was reported in 30 patients, while incomplete resection in 4. Data regarding resection margins were not available in 4 studies.
Following LVD, 167 patients underwent right, extended right or extended left hepatectomy. Six patients declined surgery despite adequate hypertrophy, 15 could not proceed due to disease progression and 2 were excluded because of cardiopulmonary complications. One patient was lost to follow-up before surgery. Complete resection was feasible in 100 out of 105 patients of whom data were available. Resection margin data were not reported in 4 studies (Table 5).

Table 5.
Type of hepatectomy and tumor resection margin.
Major postoperative complications (Clavien-Dindo > III) were reported in 34 patients in the PVE group and in 20 in the LVD group (Table 6).

Table 6.
Postoperative outcomes.
3.4. Risk of Bias and Quality Assessment
Risk of bias was assessed using the Cochrane ROBINS-I tool. One study was rated as having moderate risk of bias, while another was considered to have moderate-to-high risk, due to missing FLR data in two small subgroups.
Study quality was evaluated using the NOS, with one star awarded for each criterion met. Ten studies received more than seven stars and were considered high quality. Four studies scored six stars, primarily due to the absence of a comparison group.
Scoring details for each study are provided in Supplementary Tables S1 and S2.
4. Discussion
In this systematic review we attempted to summarize the available literature up to date regarding PVE and LVD as a method of increasing the FLR in patients undergoing major hepatectomy due to both primary and metastatic liver disease. This pooled quantitative analysis of 992 patients is, to our knowledge, the largest existing comparative review of PVE and LVD effects on FLR volume increase in patients with malignant liver disease. Our results showed that LVD consistently demonstrated greater hypertrophic efficacy than PVE with shorter hypertrophy intervals and more favorable trends in resection rates. While complication profiles were similar, the enhanced function and more robust FLR response with LVD suggest a clinically meaningful advantage. Unfortunately, the reporting of FLR volume data was not uniform across all studies, precluding a meta-analysis. Specifically, some studies presented results as mean ± standard deviation, while others reported medians with ranges. Furthermore, the post-intervention change in FLR was inconsistently expressed, with certain studies reporting absolute volume differences and others presenting percentage increases. Therefore, the results of this review, even though promising, should be interpreted with caution.
Preoperative strategies to induce hypertrophy of the FLR are critical in extending the safety and eligibility for major hepatectomy in patients with insufficient baseline liver volume. Portal vein embolization has long been the standard approach in this setting, with widespread adoption across centers performing complex hepatic resections. While PVE offers a favorable safety profile, it has several limitations including but not limited to delayed hypertrophy, interindividual variability, or tumor progression during the waiting interval [21,22]. Of note, tumor progression was the most common reason for failure of progression to hepatectomy after PVE or LVD according to recent observational studies by Alvarez et al. and Cardoso et al. [23,24].
One of the key mechanisms of liver regeneration after PVE is the redirection of portal flow from the embolized part to the remaining liver, which may cause a compensatory increase in arterial inflow to the embolized segments via the hepatic arterial buffer response (HABR). First described by Lautt et al. in 1985, the physiology of HABR is not yet fully understood. The most prevalent opinion is that the accumulation of adenosine due to decreased portal washout in the embolized segment may cause arterial vasodilation, and therefore increased blood supply via the hepatic artery [25,26]. This mechanism, although protective in normal physiology, has been implicated in promoting tumor growth due to increased nutrient and oxygen delivery to the tumor-bearing liver segments [27,28]. To mitigate these effects, PVE combined with TACE was thoroughly studied. This approach utilized the effects of both portal vein and arterial embolization to overcome the HABR and gradually led to the broadening of liver resection indications [29,30,31].
Even though the combination of PVE with TACE was promising in reducing tumor progression while enhancing FLR hypertrophy, the complications related to the latter nourished the research for a more potent and physiologically effective method [32]. This led to the development of LVD, a technique that combines PVE and HVE proposed and implemented by Guiu et al. in 2016 followed by Le Roy et al. in 2017 in two small retrospective cohorts of seven patients showing safe and reproducible FLR growth before major hepatectomy [33,34]. The rationale for LVD lies in its dual vascular inflow and outflow occlusion, which leads to sinusoidal congestion and attenuates the hepatic arterial buffer response, thereby reducing compensatory arterial perfusion to the embolized lobe. This creates a more intense atrophic stimulus to the embolized liver segments and a stronger hypertrophic drive to the contralateral lobe [19,34].
From a mechanistic standpoint, LVD offers several theoretical advantages. Hepatic vein embolization contributes to reducing residual portal venous inflow via intrahepatic collaterals, which may otherwise blunt the effect of isolated PVE [35]. Additionally, hepatic venous outflow obstruction limits interlobar portal redistribution and potentiates the hemodynamic and cellular stress needed to stimulate regenerative signaling in the FLR [36,37]. Clinical data increasingly support the superiority of LVD in terms of both volumetric and functional hypertrophy. In a prospective study, Kobayashi et al. demonstrated that LVD induced faster and more substantial FLR growth compared to PVE alone, although the authors acknowledged a limited sample size and called for larger trials [6]. Guiu et al., in a retrospective analysis, corroborated these findings, reporting that LVD not only improved FLR volume but also translated into a greater increase in function, a critical factor for clinical outcomes following resection [35].
Even though volumetric liver augmentation is essential in major hepatic resections, since lower FLR correlates with a higher risk of PHLF, the assessment of functional hypertrophy holds a distinctive role as well. An increase in liver volume does not equate to functional liver mass, especially in case of damaged liver parenchyma which may be present after hepatic regeneration interventions [38,39,40]. Many liver function assessment modalities have been utilized, including indocyanine green clearance test, liver scintigraphy combined with nuclear medicine tracers, and magnetic resonance imaging with gadolinium ethoxybenzyl diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid (Gd-EOB-DTPA) [41]. A study by Marino et al. showed that while volumetric results were comparable between LVD and PVE, functional assessments using hepatobiliary scintigraphy revealed significantly higher function in the FLR after LVD [7]. This underscores the relevance of the physiological mechanisms triggered by LVD in promoting liver regeneration and highlights its potential to enhance surgical outcomes in marginal candidates. Unfortunately, most studies do not assess the functional liver capacity, which could significantly affect the outcomes since reduced functional liver capacity is the main cause of PHLF. Future research should aim to report both volumetric and functional hypertrophy endpoints of the remaining liver lobe for a more accurate interpretation of the ensuing results.
Other hepatic hypertrophy procedures that have been utilized include portal vein ligation (PVL) and ALPPS. Both are two-stage operations and are inherently more invasive than portal and hepatic vein embolization [42,43]. Today, PVL has been practically replaced by PVE since advancements in interventional radiology and its minimal invasive nature outweigh the risks of a two-step surgical operation [44]. This is not true for ALPPS however, since it can induce significant and rapid liver hypertrophy reaching an FLR increase of 50–80% in 7–10 days and over 90% resectability rate [45,46,47]. In fact, there are reports that support ALPPS superiority over PVE and TACE for HCC patients with insufficient FRL [48,49]. While ALPPS induces the most rapid hypertrophy, it is associated with higher morbidity and mortality rates. In contrast, LVD appears to achieve near-comparable hypertrophy with a more favorable safety profile [50,51,52]. Yi et al.’s meta-analysis concluded that although ALPPS led in volumetric gain, LVD provided a better balance of hypertrophy and complication risk [7]. Bozkurt et al. echoed these findings, positioning LVD as superior to PVE in both FLR volume and the rate of successful resection without compromising safety [51].
This study has several limitations that need to be acknowledged. First, although current data favor LVD, much of the available evidence remains retrospective or observational, which are susceptible to recall and selection bias. Patients were selected based on clinical criteria rather than random assignment, leading to a moderate risk of bias, therefore the presented outcomes should be interpreted with caution before generalized. The increase in FLR after liver volume augmentation interventions should be further validated by prospective large clinical trials in the future. Second, technical variability in embolization protocols, including differences in embolic agents, vein access route, timing of PVE, sequential or simultaneous HVE and time to surgery may have contributed to variability in liver hypertrophy and could confound direct comparisons. Third, data reporting and comparison groups were highly heterogeneous, limiting the reliability of a quantitative meta-analysis. Studies differed in intervention groups and in reporting of FLR volume, with some providing mean ± SD and others median with range of FLR ratio, sFLR or estimated FLR. These inconsistencies underscore the need for standardized outcome reporting in future studies. Finally, most studies used volumetric rather than functional endpoints, despite emerging evidence that functional assessments may better predict PHLF risk.
Ongoing prospective trials will be pivotal in resolving these uncertainties. The DRAGON 2 and the DRAGON-PLC trials are two-armed randomized controlled trials that directly compare PVE to LVD in patients with CRLM and primary liver cancer, respectively [53,54]. The HYPER-LIV01 trial, a randomized phase II multicenter study, is expected to provide high-level evidence by directly comparing PVE and LVD in terms of FLR hypertrophy, safety, and surgical conversion rates [55]. Its results may refine the standard of care for preoperative liver augmentation and validate the routine use of LVD in centers performing high-volume hepatobiliary surgery.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, LVD emerges as a physiologically rational and clinically promising technique for FLR augmentation in patients with liver cancer requiring major hepatectomy. By combining inflow and outflow modulation, it elicits a more robust and potentially more functional hypertrophic response compared to PVE alone, without the added risks associated with ALPPS. While current evidence supports its superiority in selected patients with acceptable postoperative outcomes, further prospective validation with larger clinical trials and more standardized outcome reporting is essential before it can be universally adopted in the management of liver tumors in patients with inadequate FLR volume.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/livers5040048/s1, Table S1: Cochrane risk of bias tool (ROBINS-I); Table S2: Newcastle–Ottawa scale for quality assessment. References [1,2,3,6,7,8,15,16,17,18,19,20] are cited in the supplementary materials.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.P., V.P. and A.G.; Methodology, M.P.; Validation, A.D.G. and P.C.; Formal Analysis, D.G.; Investigation, M.P. and A.D.G.; Resources, A.D.G.; Data Curation, M.P.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, M.P., A.D.G., P.C. and V.P.; Writing—Review & Editing, V.N.P., A.G. and D.G.; Supervision, D.G.; Project Administration, V.N.P. and A.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study is a literature review; therefore, ethical committee approval was not required.
Informed Consent Statement
This study is a literature review; therefore, patient informed consent was not required.
Data Availability Statement
Data supporting the reported results are available from the corresponding authors upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| HCC | hepatocellular carcinoma |
| CCA | cholangiocarcinoma |
| CRLM | colorectal liver metastases |
| PHLF | post-hepatectomy liver failure |
| FLR | future liver remnant |
| PVE | portal vein embolization |
| ALPPS | associated liver partition and portal vein ligation for staged hepatectomy |
| LVD | liver venous deprivation |
| PRISMA | preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses |
| PROSPERO | international prospective register of systematic reviews |
| ROBINS-I | Cochrane risk of bias tool in non-randomized studies of interventions |
| NOS | Newcastle–Ottawa scale |
| NET | neuroendocrine tumor |
| TACE | transarterial chemoembolization |
| HABR | hepatic arterial buffer response |
| HVE | hepatic vein embolization |
| PVL | portal vein ligation |
References
- Abdalla, E.K. Extended Hepatectomy in Patients with Hepatobiliary Malignancies with and Without Preoperative Portal Vein Embolization. Arch. Surg. 2002, 137, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beppu, T.; Okabe, H.; Okuda, K.; Eguchi, S.; Kitahara, K.; Taniai, N.; Ueno, S.; Shirabe, K.; Ohta, M.; Kondo, K.; et al. Portal Vein Embolization Followed by Right-Side Hemihepatectomy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients: A Japanese Multi-Institutional Study. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2016, 222, 1138–1148.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degrauwe, N.; Duran, R.; Melloul, E.; Halkic, N.; Demartines, N.; Denys, A. Induction of Robust Future Liver Remnant Hypertrophy Before Hepatectomy with a Modified Liver Venous Deprivation Technique Using a Trans-venous Access for Hepatic Vein Embolization. Front. Radiol. 2021, 1, 736056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.M.; Cornman-Homonoff, J.; Lucatelli, P.; Madoff, D.C. Image-guided percutaneous strategies to improve the resectability of HCC: Portal vein embolization, liver venous deprivation, or radiation lobectomy? Clin. Imaging 2024, 111, 110185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makuuchi, M.; Thai, B.L.; Takayasu, K.; Takayama, T.; Kosuge, T.; Gunvén, P.; Yamazaki, S.; Hasegawa, H.; Ozaki, H. Preoperative portal embolization to increase safety of major hepatectomy for hilar bile duct carcinoma: A preliminary report. Surgery 1990, 107, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, K.; Yamaguchi, T.; Denys, A.; Perron, L.; Halkic, N.; Demartines, N.; Melloul, E. Liver venous deprivation compared to portal vein embolization to induce hypertrophy of the future liver remnant before major hepatectomy: A single center experience. Surgery 2020, 167, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, R.; Ratti, F.; Della Corte, A.; Santangelo, D.; Clocchiatti, L.; Canevari, C.; Magnani, P.; Pedica, F.; Casadei-Gardini, A.; De Cobelli, F.; et al. Comparing Liver Venous Deprivation and Portal Vein Embolization for Perihilar Cholangiocarcinoma: Is It Time to Shift the Focus to Hepatic Functional Reserve Rather than Hypertrophy? Cancers 2023, 15, 4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, C.; Fernandez, B.; Marichez, A.; Adam, J.-P.; Papadopoulos, P.; Lapuyade, B.; Chiche, L. Radiological Simultaneous Portohepatic Vein Embolization (RASPE) Before Major Hepatectomy: A Better Way to Optimize Liver Hypertrophy Compared to Portal Vein Embolization. Ann. Surg. 2020, 272, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hocquelet, A.; Sotiriadis, C.; Duran, R.; Guiu, B.; Yamaguchi, T.; Halkic, N.; Melloul, E.; Demartines, N.; Denys, A. Preoperative Portal Vein Embolization Alone with Biliary Drainage Compared to a Combination of Simultaneous Portal Vein, Right Hepatic Vein Embolization and Biliary Drainage in Klatskin Tumor. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2018, 41, 1885–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, F.; Lim, C.; Lahat, E.; Shwaartz, C.; Eshkenazy, R.; Salloum, C.; Azoulay, D. Combined hepatic and portal vein embolization as preparation for major hepatectomy: A systematic review. HPB 2019, 21, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heil, J.; Schadde, E. Simultaneous portal and hepatic vein embolization before major liver resection. Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 2021, 406, 1295–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risk of Bias Tools-ROBINS-I V2 Tool. Available online: https://www.riskofbias.info/welcome/robins-i-v2 (accessed on 10 July 2025).
- Wells, G.A.; Shea, B.; O’Connell, D.; Peterson, J.; Welch, V.; Losos, M.; Tugwell, P. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomised Studies in Meta-Analyses. 2000. Available online: http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp (accessed on 17 September 2025).
- Farges, O.; Belghiti, J.; Kianmanesh, R.; Marc Regimbeau, J.; Santoro, R.; Vilgrain, V.; Denys, A.; Sauvanet, A. Portal Vein Embolization Before Right Hepatectomy: Prospective Clinical Trial. Ann. Surg. 2003, 237, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.; Ha, T.; Ko, G.; Kwon, D.; Song, G.; Jung, D.; Kim, M.; Lee, S.; Lee, S. Preoperative Sequential Portal and Hepatic Vein Embolization in Patients with Hepatobiliary Malignancy. World J. Surg. 2015, 39, 2990–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okabe, H.; Beppu, T.; Ishiko, T.; Masuda, T.; Hayashi, H.; Otao, R.; Hasita, H.; Okabe, K.; Sugiyama, S.; Baba, H. Preoperative portal vein embolization (PVE) for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma can improve resectability and may improve disease-free survival. J. Surg. Oncol. 2011, 104, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palavecino, M.; Chun, Y.S.; Madoff, D.C.; Zorzi, D.; Kishi, Y.; Kaseb, A.O.; Curley, S.A.; Abdalla, E.K.; Vauthey, J.-N. Major hepatic resection for hepatocellular carcinoma with or without portal vein embolization: Perioperative outcome and survival. Surgery 2009, 145, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sy, T.-V.; Dung, L.T.; Giang, B.-V.; Nghia, N.Q.; Viet Khai, N.; Manh Thau, C.; Gia Anh, P.; Hong Son, T.; Minh Duc, N. Safety and Efficacy of Liver Venous Deprivation Following Transarterial Chemoembolization Before Major Hepatectomy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2023, 19, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Song, R.; Hou, C.; Yao, H.; Xu, J.; Zhou, H.; Li, S.; Cai, W.; Fei, Y.; Meng, F.; et al. Simultaneous Liver Venous Deprivation Following Hepatic Arterial Chemoembolization Before Major Hepatectomy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A New Methods to Achieve Hypertrophy Liver Remnant. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2025, 12, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abulkhir, A.; Limongelli, P.; Healey, A.J.; Damrah, O.; Tait, P.; Jackson, J.; Habib, N.; Jiao, L.R. Preoperative portal vein embolization for major liver resection: A meta-analysis. Ann. Surg. 2008, 247, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Lienden, K.P.; van den Esschert, J.W.; de Graaf, W.; Bipat, S.; Lameris, J.S.; van Gulik, T.M.; van Delden, O.M. Portal vein embolization before liver resection: A systematic review. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2013, 36, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, F.A.; Castaing, D.; Figueroa, R.; Allard, M.A.; Golse, N.; Pittau, G.; Ciacio, O.; Sa Cunha, A.; Cherqui, D.; Azoulay, D.; et al. Natural history of portal vein embolization before liver resection: A 23-year analysis of intention-to-treat results. Surgery 2018, 163, 1257–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, S.A.; Clarke, G.; Nayak, A.; Joshi, K.; Sudereyan, R.; Karkhanis, S.; Chatzizacharias, N.; Roberts, K.J.; Condati, N.; Papamichail, M.; et al. Factors influencing failure of progression to completion hepatectomy following liver venous deprivation procedures (PVE or DVE): A longitudinal observational study. HPB 2025, 27, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lautt, W.W.; Legare, D.J.; d’Almeida, M.S. Adenosine as putative regulator of hepatic arterial flow (the buffer response). Am. J. Physiol. 1985, 248 Pt 2, H331–H338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lautt, W.W. Mechanism and role of intrinsic regulation of hepatic arterial blood flow: Hepatic arterial buffer response. Am. J. Physiol. 1985, 249 Pt 1, G549–G556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamecha, V.; Levene, A.; Grillo, F.; Woodward, N.; Dhillon, A.; Davidson, B.R. Effect of portal vein embolisation on the growth rate of colorectal liver metastases. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 100, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoekstra, L.T.; van Lienden, K.P.; Doets, A.; Busch, O.R.C.; Gouma, D.J.; van Gulik, T.M. Tumor progression after preoperative portal vein embolization. Ann. Surg. 2012, 256, 812–817; discussion 817–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata, S.; Belghiti, J.; Farges, O.; Varma, D.; Sibert, A.; Vilgrain, V. Sequential arterial and portal vein embolizations before right hepatectomy in patients with cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Br. J. Surg. 2006, 93, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, H.; Kim, J.H.; Ko, G.-Y.; Kim, K.W.; Gwon, D.I.; Lee, S.-G.; Hwang, S. Sequential transcatheter arterial chemoembolization and portal vein embolization versus portal vein embolization only before major hepatectomy for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2011, 18, 1251–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reig, M.; Forner, A.; Rimola, J.; Ferrer-Fàbrega, J.; Burrel, M.; Garcia-Criado, Á.; Kelley, R.K.; Galle, P.R.; Mazzaferro, V.; Salem, R.; et al. BCLC strategy for prognosis prediction and treatment recommendation: The 2022 update. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandieh, G.; Yazdaninia, I.; Afyouni, S.; Shaghaghi, M.; Borhani, A.; Mohseni, A.; Shaghaghi, S.; Liddell, R.; Kamel, I.R. Spectrum of Imaging Findings and Complications After Hepatic Transarterial Chemoembolization for Liver Tumors. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2024, 48, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiu, B.; Chevallier, P.; Denys, A.; Delhom, E.; Pierredon-Foulongne, M.-A.; Rouanet, P.; Fabre, J.-M.; Quenet, F.; Herrero, A.; Panaro, F.; et al. Simultaneous trans-hepatic portal and hepatic vein embolization before major hepatectomy: The liver venous deprivation technique. Eur. Radiol. 2016, 26, 4259–4267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Roy, B.; Dupré, A.; Gallon, A.; Chabrot, P.; Gagnière, J.; Buc, E. Liver hypertrophy: Underlying mechanisms and promoting procedures before major hepatectomy. J. Visc. Surg. 2018, 155, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guiu, B.; Quenet, F.; Panaro, F.; Piron, L.; Cassinotto, C.; Herrerro, A.; Souche, F.-R.; Hermida, M.; Pierredon-Foulongne, M.-A.; Belgour, A.; et al. Liver venous deprivation versus portal vein embolization before major hepatectomy: Future liver remnant volumetric and functional changes. Hepatobiliary Surg. Nutr. 2020, 9, 564–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schadde, E.; Guiu, B.; Deal, R.; Kalil, J.; Arslan, B.; Tasse, J.; Olthof, P.B.; Heil, J.; Schnitzbauer, A.A.; Jakate, S.; et al. Simultaneous hepatic and portal vein ligation induces rapid liver hypertrophy: A study in pigs. Surgery 2019, 165, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, G.-Y.; Hwang, S.; Sung, K.-B.; Gwon, D.-I.; Lee, S.-G. Interventional oncology: New options for interstitial treatments and intravascular approaches. J. Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat. Sci. 2010, 17, 410–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishi, Y.; Abdalla, E.K.; Chun, Y.S.; Zorzi, D.; Madoff, D.C.; Wallace, M.J.; Curley, S.A.; Vauthey, J.-N. Three hundred and one consecutive extended right hepatectomies: Evaluation of outcome based on systematic liver volumetry. Ann. Surg. 2009, 250, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truant, S.; Boleslawski, E.; Sergent, G.; Leteurtre, E.; Duhamel, A.; Hebbar, M.; Pruvot, F.-R. Liver function following extended hepatectomy can be accurately predicted using remnant liver volume to body weight ratio. World J. Surg. 2015, 39, 1193–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golse, N.; Bucur, P.O.; Adam, R.; Castaing, D.; Sa Cunha, A.; Vibert, E. New paradigms in post-hepatectomy liver failure. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2013, 17, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubaddi, M.; Marichez, A.; Adam, J.-P.; Lapuyade, B.; Debordeaux, F.; Tlili, G.; Chiche, L.; Laurent, C. Comprehensive Review of Future Liver Remnant (FLR) Assessment and Hypertrophy Techniques Before Major Hepatectomy: How to Assess and Manage the FLR. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2024, 31, 9205–9220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, R.; Laurent, A.; Azoulay, D.; Castaing, D.; Bismuth, H. Two-stage hepatectomy: A planned strategy to treat irresectable liver tumors. Ann. Surg. 2000, 232, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnitzbauer, A.A.; Lang, S.A.; Goessmann, H.; Nadalin, S.; Baumgart, J.; Farkas, S.A.; Fichtner-Feigl, S.; Lorf, T.; Goralcyk, A.; Hörbelt, R.; et al. Right portal vein ligation combined with in situ splitting induces rapid left lateral liver lobe hypertrophy enabling 2-staged extended right hepatic resection in small-for-size settings. Ann. Surg. 2012, 255, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aussilhou, B.; Lesurtel, M.; Sauvanet, A.; Farges, O.; Dokmak, S.; Goasguen, N.; Sibert, A.; Vilgrain, V.; Belghiti, J. Right portal vein ligation is as efficient as portal vein embolization to induce hypertrophy of the left liver remnant. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2008, 12, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olthof, P.B.; Tomassini, F.; Huespe, P.E.; Truant, S.; Pruvot, F.-R.; Troisi, R.I.; Castro, C.; Schadde, E.; Axelsson, R.; Sparrelid, E.; et al. Hepatobiliary scintigraphy to evaluate liver function in associating liver partition and portal vein ligation for staged hepatectomy: Liver volume overestimates liver function. Surgery 2017, 162, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, H.; de Santibañes, E.; Schlitt, H.J.; Malagó, M.; van Gulik, T.; Machado, M.A.; Jovine, E.; Heinrich, S.; Ettorre, G.M.; Chan, A.; et al. 10th Anniversary of ALPPS-Lessons Learned and quo Vadis. Ann. Surg. 2019, 269, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chebaro, A.; Buc, E.; Durin, T.; Chiche, L.; Brustia, R.; Didier, A.; Pruvot, F.-R.; Kitano, Y.; Muscari, F.; Lecolle, K.; et al. Liver Venous Deprivation or Associating Liver Partition and Portal Vein Ligation for Staged Hepatectomy?: A Retrospective Multicentric Study. Ann. Surg. 2021, 274, 874–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, H.; Kong, Q.; Teng, F.; Chen, Z. Preoperative Hepatic Augmentation Versus Transarterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Insufficient Remnant Liver Volume: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancer Med. 2025, 14, e71050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.-P.; Huang, G.; Jia, N.-Y.; Pan, Z.-Y.; Liu, H.; Yang, Y.; He, C.-J.; Lau, W.Y.; Yang, Y.-F.; Zhou, W.-P. Associating liver partition and portal vein ligation for staged hepatectomy versus sequential transarterial chemoembolization and portal vein embolization in staged hepatectomy for HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomized comparative study. Hepatobiliary Surg. Nutr. 2022, 11, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassese, G.; Troisi, R.I.; Khayat, S.; Quenet, F.; Tomassini, F.; Panaro, F.; Guiu, B. Liver venous deprivation versus associating liver partition and portal vein ligation for staged hepatectomy for colo-rectal liver metastases: A comparison of early and late kinetic growth rates, and perioperative and oncological outcomes. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 43, 101812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, E.; Sijberden, J.P.; Kasai, M.; Abu Hilal, M. Efficacy and perioperative safety of different future liver remnant modulation techniques: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. HPB 2024, 26, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, P.; Vien, P.; Kessler, J.; Lafaro, K.; Wei, A.; Melstrom, L.G. Augmenting the Future Liver Remnant Prior to Major Hepatectomy: A Review of Options on the Menu. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2025, 32, 5694–5709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, S.; Smits, J.; Van Der Velden, A.L.; Korenblik, R.; Dewulf, M.; Van Der Leij, C.; Van Dam, R.M. An international multicenter randomized controlled trial to compare combined portal and hepatic vein embolization with portal vein embolization alone in patients with primary liver cancers—The DRAGON PLC trial. HPB 2024, 26, S202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maastricht University. The DRAGON PLC Trial—An International Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial to Compare Combined Portal and Hepatic Vein Embolization (PVE/HVE) with PVE Alone in Primary Liver Cancers. 2025. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06914648 (accessed on 10 July 2025).
- Deshayes, E.; Piron, L.; Bouvier, A.; Lapuyade, B.; Lermite, E.; Vervueren, L.; Laurent, C.; Pinaquy, J.-B.; Chevallier, P.; Dohan, A.; et al. Study protocol of the HYPER-LIV01 trial: A multicenter phase II, prospective and randomized study comparing simultaneous portal and hepatic vein embolization to portal vein embolization for hypertrophy of the future liver remnant before major hepatectomy for colo-rectal liver metastases. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).