Linking Psychological Stress to Epigenetic Regulation via the Gut–Liver–Brain Axis in Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Search Strategy and Integration of Findings
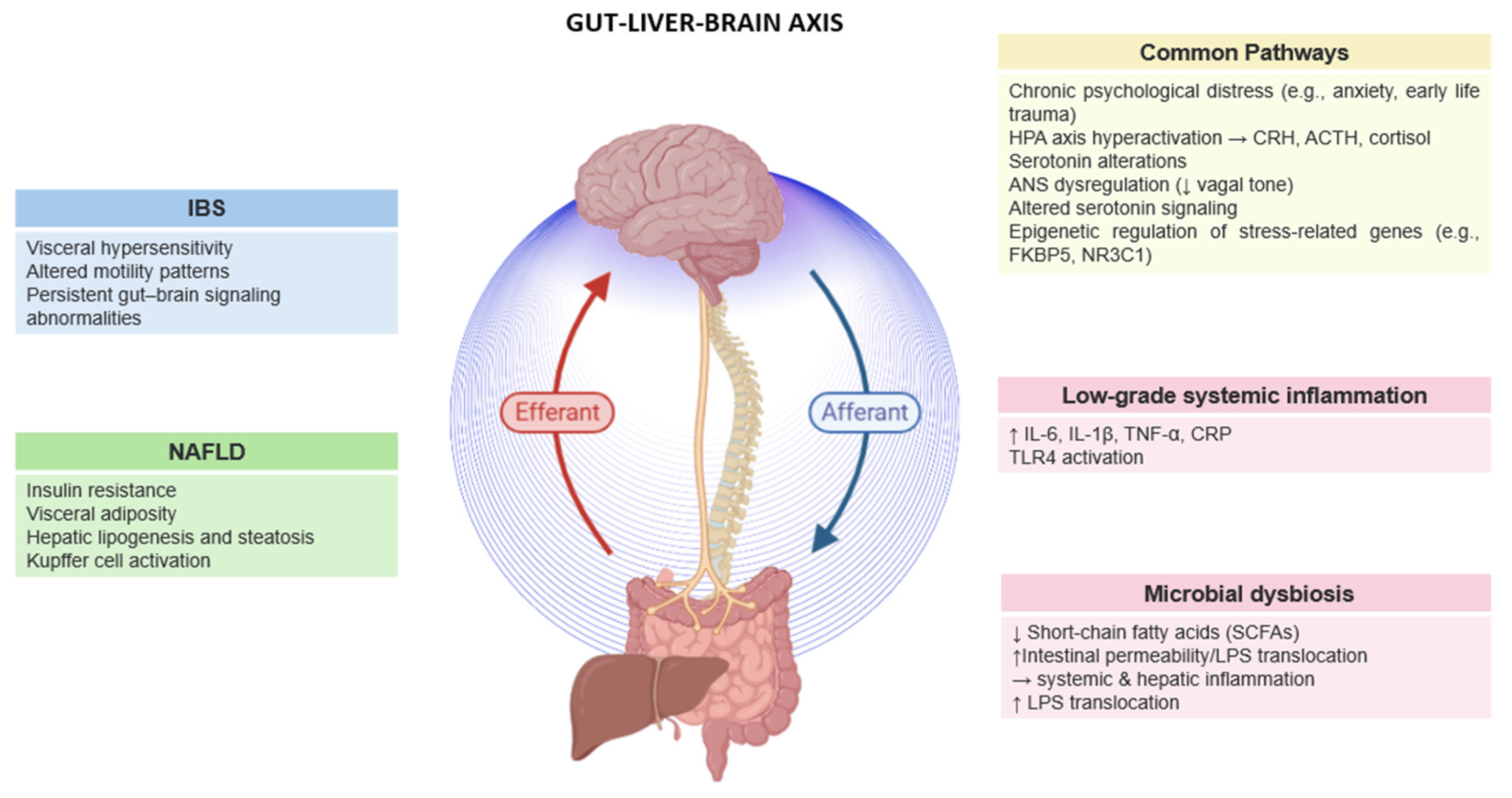
3. Co-Prevalence of IBS and MAFLD
4. Psychological Distress and the Gut–Liver–Brain Axis in IBS and MAFLD
5. Critical Mechanisms Linking Psychological Distress to IBS and MAFLD
5.1. Microbial Alterations in IBS and MAFLD
| Microbial Features Associated with IBS and MAFLD | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microbial Feature | IBS | MAFLD | Shared? | Mechanistic Role | Refs |
| ↓ Faecalibacterium prausnitzii | Significantly reduced Anti-inflammatory SCFA producer. Linked to visceral pain. | Reduced in MAFLD Correlates with systemic inflammation. | Yes | Key anti-inflammatory taxa Its loss contributes to gut and hepatic inflammation. | [38,39,40] |
| ↓ Bifidobacterium spp. | Depleted in IBS Affects SCFA production, immune modulation, barrier function. | Decreased in MAFLD, especially in advanced fibrosis. | Yes | Loss impacts mucosal immunity and SCFA levels Common sign of dysbiosis. | [41,42,43] |
| ↓ Lactobacillus spp. | Reduced in IBS Affects motility and epithelial barrier integrity. | Less consistent findings Some studies show reduction | Partial | May influence mucosal homeostasis and motility Role in MAFLD still debated. | [21,36,44] |
| ↑ Ruminococcus gnavus | Elevated Involved in mucin degradation and pro-inflammatory metabolite production. | Not consistently elevated or implicated. | No | Increases gut permeability and inflammation in IBS Unclear role in MAFLD. | [11,45] |
| ↑ Streptococcus spp. | Enriched Linked to gas production, bloating, and fermentation shifts. | Detected in some MAFLD cohorts but not considered a key feature. | No | Contributes to dysbiosis in IBS Unclear hepatic relevance. | [37,38,46] |
| ↑ Proteobacteria/ E. coli | Mild increase Associated with mucosal inflammation | Strongly increased Linked to endotoxemia and liver injury. | Yes | Gram-negative bloom promotes LPS translocation and systemic inflammation. | [38,41,47] |
| ↑ Clostridium spp. | Not significantly enriched. | Elevated in MAFLD Disrupts bile acid metabolism and promotes inflammation. | No | Impacts liver metabolism Specific to hepatic pathophysiology. | [34,35,37] |
| ↓ SCFAs | Lower levels due to depletion of key producers | Same trend Leads to impaired gut–liver anti-inflammatory signaling. | Yes | Reduced SCFA availability weakens barrier integrity and immune regulation in both conditions. | [41,48] |
| ↑ LPS translocation | Due to Gram-negative overgrowth Activates immune responses | Drives hepatic inflammation via TLR4 signaling and Kupffer cell activation. | Yes | A critical mediator linking dysbiosis to systemic and hepatic inflammation. | [36,49] |
5.2. Stress-Induced HPA Axis Dysregulation
5.3. Neurotransmitter and Neuromodulator Imbalances
5.4. Low-Grade Inflammation
5.5. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Dysregulation
5.6. Personality Traits
5.7. Bidirectional Feedback Loops
6. Neuroimaging and Central Processing
7. Epigenetic Mechanisms of Stress-Induced GLBA Dysfunction
7.1. DNA Methylation and Disease-Relevant Targets
7.2. Histone Modifications and Microbial Mediators
7.3. MicroRNAs in Stress and Barrier Regulation
7.4. Therapeutic and Transgenerational Relevance of Epigenetic Changes
8. Biomarkers of Gut–Liver–Brain Axis Dysfunction
9. Therapeutic Perspectives
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, F.; Luo, W.; Shi, Y.; Fan, Z.; Ji, G. Should we standardize the 1700-year-old fecal microbiota transplantation? Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 107, 1755–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, J.D. The first Nobel Prize for integrated systems physiology: Ivan Petrovich Pavlov, 1904. Physiology 2004, 9, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, F.; Neshat, M.; Pourjafar, H.; Jafari, S.M.; Samakkhah, S.A.; Mirzakhani, E. The role of probiotics and prebiotics in modulating of the gut-brain axis. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1173660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundman, M.H.; Chen, N.K.; Subbian, V.; Chou, Y.H. The bidirectional gut-brain-microbiota axis as a potential nexus between traumatic brain injury, inflammation, and disease. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 66, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Han, Y.; Jing, D.; Liu, R.; Jin, K.; Yi, W. Microbiota-gut–brain axis and the central nervous system. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 53829–53838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Yuan, C.; Yang, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, S. Non-alcoholic fatty liver is associated with increased risk of IBS: A prospective cohort study. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralli, T.; Saifi, Z.; Tyagi, N.; Vidyadhari, A.; Aeri, V.; Kohli, K. Deciphering the role of gut metabolites in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 49, 815–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyland, N.P.; Cryan, J.F. Microbe-host interactions: Influence of the gut microbiota on the enteric nervous system. Dev. Biol. 2016, 417, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocetta, A.; Liloia, D.; Costa, T.; Duca, S.; Cauda, F.; Manuello, J. From gut to brain: Unveiling probiotic effects through a neuroimaging perspective—A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1446854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koumbi, L.; Giannelou, M.A.; Castelli, L. The gut–brain axis in irritable bowel syndrome: Neuroendocrine and epigenetic pathways. Acad. Biol. 2025, 3, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, J.J.J.; Loo, W.M.; Siah, K.T.H. Associations between irritable bowel syndrome and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review. World J. Hepatol. 2023, 15, 925–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharjee, B.; Roy, A.; Ghosh, J. Study of interrelationship between irritable bowel syndrome and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Acta Sci. Gastrointest. Disord. 2023, 6, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Man, S.; Sun, B.; Ma, L.; Guo, L.; Huang, L.; Gao, W. Gut–liver–brain axis in diseases: Implications for therapeutic interventions. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milovanovic, T.; Pantic, I.; Dragasevic, S.; Lugonja, S.; Dumic, I.; Rajilic-Stojanovic, M. The Interrelationship Among Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Colonic Diverticulosis and Metabolic Syndrome. J. Gastrointestin. Liver Dis. 2021, 30, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, K.R.; Sherwin, L.B.; Walitt, B.; Melkus, G.D.; Henderson, W.A. Neuroimaging the brain-gut axis in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. World J. Gastrointest. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 7, 320–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinstein, G.; O’Donnell, A.; Frenzel, S.; Xiao, T.; Yaqub, A.; Yilmaz, P.; de Knegt, R.J.; Maestre, G.E.; Melo van Lent, D.; Long, M.; et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, liver fibrosis, and structural brain imaging: The Cross-Cohort Collaboration. Eur. J. Neurol. 2024, 31, e16048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, R.; Liu, R.; Zha, H.; Cheng, Y.; Ling, Z.; Li, L. Gut microbiota induced epigenetic modifications in the non-alcoholic fatty liver disease pathogenesis. Eng. Life Sci. 2023, 24, 2300016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Yang, T.; Yao, P. Association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and irritable bowel syndrome in populations undergoing health examination in Urumqi. World Chin. J. Dig. 2013, 21, 1160–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanain, A.F.A.; Abdel-Rahman, M.E.; Ali, A.M.; Abdel-Aal, S.M. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease among patients with irritable bowel syndrome: Prevalence and contribution to disease severity. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Endosc. 2018, 3, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purssell, H.; Whorwell, P.J.; Athwal, V.S.; Vasant, D.H. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in irritable bowel syndrome: More than a coincidence? World J. Hepatol. 2021, 13, 1816–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, K.N.; Kim, K.M.; Joo, N.S. Irritable Bowel Syndrome May Be Associated with Elevated Alanine Aminotransferase and Metabolic Syndrome. Yonsei Med. J. 2016, 57, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadik, R.; Björnsson, E.; Simrén, M. The relationship between symptoms, body mass index, gastrointestinal transit and stool frequency in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 22, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Niu, K.; Momma, H.; Kobayashi, Y.; Chujo, M.; Otomo, A.; Fukudo, S.; Nagatomi, R. Irritable bowel syndrome is positively related to metabolic syndrome: A population-based cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aasbrenn, M.; Høgestøl, I.; Eribe, I.; Kristinsson, J.; Lydersen, S.; Mala, T.; Farup, P.G. Prevalence and predictors of irritable bowel syndrome in patients with morbid obesity: A cross-sectional study. BMC Obes. 2017, 4, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulcan, E.; Taser, F.; Toker, A.; Korkmaz, U.; Alcelik, A. Increased frequency of prediabetes in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2009, 338, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.; Tacke, F.; Arrese, M.; Sharma, B.C.; Mostafa, I.; Bugianesi, E.; Wong, V.W.-S.; Yilmaz, Y.; George, J.; Fan, J.; et al. Global perspectives on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2019, 69, 2672–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellström, P.M.; Benno, P. The Rome, IV: Irritable bowel syndrome—A functional disorder. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2019, 40–41, 101634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodoory, V.C.; Mikocka-Walus, A.; Yiannakou, Y.; Houghton, L.A.; Black, C.J.; Ford, A.C. Impact of Psychological Comorbidity on the Prognosis of Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 116, 1485–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamani, M.; Alizadeh-Tabari, S.; Zamani, V. Systematic review with meta-analysis: The prevalence of anxiety and depression in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 50, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellentani, S. The epidemiology of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 2017, 37 (Suppl. S1), 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Zhao, D.; Ryu, S.; Guallar, E.; Cho, J.; Shin, H.; Chang, Y.; Sung, E. Perceived stress and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in apparently healthy men and women. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strandwitz, P. Neurotransmitter modulation by the gut microbiota. Brain Res. 2018, 1693 Pt B, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukudo, S.; Nomura, T.; Hongo, M. Stress and visceral pain: Focusing on irritable bowel syndrome. Pain 2013, 154 (Suppl. S1), S63–S70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Ren, C.; Mei, X.F.; Jiang, Y.F.; Zhou, Y.F. Gut microbiota and irritable bowel syndrome: Status and prospects. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1429133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolodziejczyk, A.A.; Zheng, D.; Shibolet, O.; Elinav, E. The role of the microbiome in NAFLD and NASH. EMBO Mol. Med. 2019, 11, e9302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dlugosz, A.; Winckler, B.; Lundin, E.; Zakikhany, K.; Sandström, G.; Ye, W.; Engstrand, L.; Lindberg, G. No difference in small bowel microbiota between patients with irritable bowel syndrome and healthy controls. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boursier, J.; Mueller, O.; Barret, M.; Machado, M.; Fizanne, L.; AraujoPerez, F.; Guy, C.D.; Seed, P.C.; Rawls, J.F.; David, L.A.; et al. The severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with gut dysbiosis and shift in the metabolic function of the gut microbiota. Hepatology 2016, 63, 764–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, X.; Xiong, L.; Li, L.; Li, M.; Chen, M. Alterations of gut microbiota in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 32, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.-H.; Lee, Y.; Song, E.-J.; Lee, D.; Jang, S.-Y.; Byeon, H.R.; Hong, M.-G.; Lee, S.-N.; Kim, H.-J.; Seo, J.-G.; et al. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii prevents hepatic damage in a mouse model of NASH induced by a highfructose highfat diet. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1123547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miquel, S.; Martín, R.; Lashermes, A.; Gillet, M.; Meleine, M.; Gelot, A.; Eschalier, A.; Ardid, D.; Bermúdez-Humarán, L.G.; Sokol, H.; et al. Anti-nociceptive effect of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii in non-inflammatory IBS-like models. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, C.; Rivera, L.; Furness, J.B.; Angus, P.W. The role of the gut microbiota in NAFLD. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 412–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Mahony, L.; McCarthy, J.; Kelly, P.; Hurley, G.; Luo, F.; Chen, K.; O’sUllivan, G.C.; Kiely, B.; Collins, J.K.; Shanahan, F.; et al. Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium in irritable bowel syndrome: Symptom responses and relationship to cytokine profiles. Gastroenterology 2005, 128, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.J.; Yu, J.S.; Min, B.H.; Gupta, H.; Won, S.-M.; Park, H.J.; Han, S.H.; Kim, B.-Y.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, B.K.; et al. Bifidobacterium-derived short-chain fatty acids and indole compounds attenuate nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by modulating gut-liver axis. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1129904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Lee, A.; Huang, S.; Gao, J.; Spence, J.R.; Owyang, C. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG prevents epithelial barrier dysfunction induced by interferon-gamma and fecal supernatants from irritable bowel syndrome patients in human intestinal enteroids and colonoids. Gut Microbes 2019, 10, 59–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, L.; Huang, C.; Ning, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhuang, M.; Yang, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, H.; et al. Ruminococcus gnavus plays a pathogenic role in diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome by increasing serotonin biosynthesis. Cell Host Microbe 2023, 31, 33–44.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Lin, A.; Kong, M.; Yao, X.; Yin, M.; Xia, H.; Ma, J.; Liu, H. Intestinal microbiome and NAFLD: Molecular insights and therapeutic perspectives. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 55, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, A.M. Gastrointestinal dysbiosis and Escherichia coli pathobionts in inflammatory bowel diseases. APMIS 2022, 130 (Suppl. S144), 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gargari, G.; Mantegazza, G.; Taverniti, V.; Gardana, C.; Valenza, A.; Rossignoli, F.; Barbaro, M.R.; Marasco, G.; Cremon, C.; Barbara, G.; et al. Fecal short-chain fatty acids in non-constipated irritable bowel syndrome: A potential clinically relevant stratification factor based on catabotyping analysis. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2274128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prospero, L.; Riezzo, G.; Linsalata, M.; Orlando, A.; D’Attoma, B.; Russo, F. Psychological and gastrointestinal symptoms of patients with irritable bowel syndrome undergoing a low-FODMAP diet: The role of the intestinal barrier. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moloney, R.D.; Johnson, A.C.; O’Mahony, S.M.; Dinan, T.G.; Greenwood-Van Meerveld, B.; Cryan, J.F. Stress and the microbiota–gut–brain axis in visceral pain: Relevance to irritable bowel syndrome. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2016, 22, 102–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahurkar-Joshi, S.; Chang, L. Epigenetic mechanisms in irritable bowel syndrome. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Shi, M.; Zhao, C.; Liang, G.; Li, C.; Ge, X.; Pei, C.; Kong, Y.; Li, D.; Yang, W.; et al. Role of intestinal flora in the development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e01006-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Liu, S.; Li, S.; Yang, J.; Hu, G.; Xu, C.; Song, W. Psychological stress in inflammatory bowel disease: Psychoneuroimmunological insights into bidirectional gut–brain communications. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1016578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Fan, J.; Qiao, L. Potential epigenetic mechanism in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 5161–5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Yang, L.; Larson, S.; Basra, S.; Merwat, S.; Tan, A.; Croce, C.; Verne, G.N. Decreased miR-199 augments visceral pain in patients with IBS through translational upregulation of TRPV1. Gut 2015, 65, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, M.; Zhao, W.; Cai, Y.; He, Q.; Zeng, J. Role of gut-brain axis dysregulation in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2025, 17, 3276–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.E.; Ko, S.Y.; Jo, S.; Choi, M.; Lee, S.H.; Jo, H.-R.; Seo, J.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, Y.-S.; Jung, S.J.; et al. TRPV1 regulates stress responses through HDAC2. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangopadhyay, A.; Ibrahim, R.; Theberge, K.; May, M.; Houseknecht, K.L. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and mental illness: Mechanisms linking mood, metabolism and medicines. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 1042442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; VazquezMontesino, L.M.; Li, A.A.; Cholankeril, G.; Ahmed, A. Inadequate physical activity and sedentary behavior are independent predictors of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2020, 72, 1556–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nisticò, V.; Rossi, R.E.; D’Arrigo, A.M.; Priori, A.; Gambini, O.; Demartini, B. Functional Neuroimaging in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Systematic Review Highlights Common Brain Alterations with Functional Movement Disorders. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2022, 28, 185–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, K.R.; Griffioen, M.A.; Klinedinst, N.J.; Galik, E.; Duarte, A.C.; Colloca, L.; Resnick, B.; Dorsey, S.G.; Renn, C.L. Quantitative sensory testing across chronic pain conditions and use in special populations. Front. Pain Res. 2022, 2, 779068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, G.; O’Donnell, A.; DavisPlourde, K.; ZelberSagi, S.; Ghosh, S.; DeCarli, C.S.; Thibault, E.G.; Sperling, R.A.; Johnson, K.A.; Beiser, A.S.; et al. NonAlcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Liver Fibrosis, and Regional Amyloidβ and Tau Pathology in MiddleAged Adults: The Framingham Study. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2022, 86, 1371–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.L.; Gu, J.P.; Wang, L.Y.; Zhu, Q.R.; You, N.N.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Shi, J.P. Aberrant Spontaneous Brain Activity and its Association with Cognitive Function in Non-Obese Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Resting-State fMRI Study. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2023, 22, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lai, J.; Zhang, P.; Ding, J.; Jiang, J.; Liu, C.; Huang, H.; Zhen, H.; Xi, C.; Sun, Y.; et al. Multi-omics analyses of serum metabolome, gut microbiome and brain function reveal dysregulated microbiota-gut-brain axis in bipolar depression. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 4123–4135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Hao, Z.; Li, M.; Xi, H.; Hu, S.; Wen, J.; Gao, Y.; Antwi, C.O.; Jia, X.; Yu, Y.; et al. Functional changes of default mode network and structural alterations of gray matter in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: A meta-analysis of whole-brain studies. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1236069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Icenhour, A.; Witt, S.T.; Elsenbruch, S.; Lowén, M.; Engström, M.; Tillisch, K.; Mayer, E.A.; Walter, S. Brain functional connectivity is associated with visceral sensitivity in women with irritable bowel syndrome. Neuroimage Clin. 2017, 15, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooke, M.B.; Catchlove, S.; Tooley, K.L. Examining the influence of the human gut microbiota on cognition and stress: A systematic review of the literature. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Yang, Z.; Kusumanchi, P.; Han, S.; Liangpunsakul, S. Critical role of microRNA-21 in the pathogenesis of liver diseases. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirola, C.J.; Scian, R.; Sookoian, S. Epigenetic modifications in the biology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: The role of DNA hydroxymethylation and TET proteins. Medicine 2015, 94, e1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Frick, J.M.; O’Neil, M.F.; Eller, O.C.; Morris, E.M.; Thyfault, J.P.; Christianson, J.A.; Lane, R.H. Early-life stress perturbs the epigenetics of Cd36 concurrent with adult onset of NAFLD in mice. Pediatr. Res. 2023, 94, 1942–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winston, J.H.; Li, Q.; Sarna, S.K. Chronic prenatal stress epigenetically modifies spinal cord BDNF expression to induce sex-specific visceral hypersensitivity in offspring. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2014, 26, 715–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carco, C.; Young, W.; Gearry, R.B.; Talley, N.J.; McNabb, W.C.; Roy, N.C. Increasing Evidence That Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders Have a Microbial Pathogenesis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Hori, H.; Ota, M.; Hattori, K.; Teraishi, T.; Sasayama, D.; Yamamoto, N.; Higuchi, T.; Kunugi, H. Effect of the common functional FKBP5 variant (rs1360780) on the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and peripheral blood gene expression. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2014, 42, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Pang, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, Q.; Yang, L.; Ji, M.; Xie, D.; Zhu, S.; Chen, Y.; et al. Glucocorticoid receptor-mediated Nr1d1 chromatin circadian misalignment in stress-induced irritable bowel syndrome. iScience 2023, 26, 107137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, J.d.A.; Freitas, F.V.; Borçoi, A.R.; Mendes, S.O.; Conti, C.L.; Arpini, J.K.; Vieira, T.d.S.; de Souza, R.A.; dos Santos, D.P.; Barbosa, W.M.; et al. Alcohol consumption, depression, overweight and cortisol levels as determining factors for NR3C1 gene methylation. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Rondan, F.R.; Ruggiero, C.H.; McKinley, K.L.; Koh, J.; Roberts, J.F.; Triplett, E.W.; Cousins, R.J. Enterocyte-Specific Deletion of Metal Transporter Zip14 (Slc39a14) Alters Intestinal Homeostasis through Epigenetic Mechanisms. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2023, 324, G187–G198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundakovic, M.; Gudsnuk, K.; Herbstman, J.B.; Tang, D.; Perera, F.P.; Champagne, F.A. DNA methylation of BDNF as a biomarker of earlylife adversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 6807–6813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Glaser, S.S.; Francis, H.; Yang, F.; Han, Y.; Stokes, A.; Staloch, D.; McCarra, J.; Liu, J.; Venter, J.; et al. Epigenetic Regulation of miR-34a Expression in Alcoholic Liver Injury. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 181, 804–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadan, A.-H.S.; El-Aziz, M.K.A.; Ellakwa, D.E.-S. The microbiota-gut-brain-axis theory: Role of gut microbiota modulators (GMMs) in gastrointestinal, neurological, and mental health disorders. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2025. Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyall, M.J.; Thomson, J.P.; Cartier, J.; Ottaviano, R.; Kendall, T.J.; Meehan, R.R.; Drake, A.J. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is associated with dynamic changes in DNA hydroxymethylation. Epigenetics 2020, 15, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiley, J.W.; Higgins, G.A. Epigenomics and the Brain–gut Axis: Impact of Adverse Childhood Experiences and Therapeutic Challenges. J. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2024, 2, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, S.; Lester, K.J.; Hudson, J.L.; Rapee, R.M.; Creswell, C.; Cooper, P.J.; Thirlwall, K.J.; Coleman, J.R.I.; Breen, G.; Wong, C.C.Y.; et al. Serotonin transporter methylation and response to cognitive behaviour therapy in children with anxiety disorders. Transl. Psychiatry 2014, 4, e444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quevedo, Y.; Booij, L.; Herrera, L.; Hernández, C.; Jiménez, J.P. Potential epigenetic mechanisms in psychotherapy: A pilot study on DNA methylation and mentalization change in borderline personality disorder. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 955005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penadés, R.; Almodóvar-Payá, C.; García-Rizo, C.; Ruíz, V.; Catalán, R.; Valero, S.; Wykes, T.; Fatjó-Vilas, M.; Arias, B. Changes in BDNF methylation patterns after cognitive remediation therapy in schizophrenia: A randomized and controlled trial. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2024, 173, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, N.A.; Lockwood, L.; Su, S.; Hao, G.; Rutten, B.P.F. The Effects of Trauma, with or without PTSD, on the Transgenerational DNA Methylation Alterations in Human Offsprings. Brain Sci. 2018, 8, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, R.; Lv, R.; Shi, X.; Yang, G.; Jin, J. CRISPR/dCas9 Tools: Epigenetic Mechanism and Application in Gene Transcriptional Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Wei, J.A.; Yang, F.; Wang, M.; Wang, S.; Cheng, T.; Liu, X.; Jia, Y.; So, K.F.; Zhang, L. Physical Exercise Prevented Stress-Induced Anxiety via Improving Brain RNA Methylation. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, e2105731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Epigenetic Regulation of Key Genes and miRNAs in the Gut–Liver–Brain Axis (GLBA) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Gene/miRNA | Regulation and Function in GLBA | Functional Impact on GLBA | References |
| FKBP5 | ↓ DNA methylation | Increases glucocorticoid receptor sensitivity Amplifies HPA axis reactivity and stress response | [70,71,73] |
| NR3C1 (Glucocorticoid Receptor) | ↑ DNA methylation | Reduces receptor expression; prolongs cortisol elevation and impairs stress regulation | [74,75] |
| CLDN1 (Claudin-1) | ↑ DNA methylation | Weakens tight junctions Increases gut permeability and systemic endotoxemia | [51,76] |
| TRPV1 | ↑ DNA methylation | Enhances visceral pain sensitivity and pro-inflammatory signaling | [51,57] |
| BDNF | ↑ DNA methylation | Impairs neuroplasticity and emotional regulation; contributes to neuroimmune dysregulation | [70,77] |
| CRF/NR3C1 | Histone acetylation and methylation | Modulates HPA axis tone and stress responsiveness | [13,54] |
| Tight Junction Proteins (Claudin-1, -2, Occludin, ZO-1) | Histone acetylation supports expression | Enhances gut and liver epithelial barrier integrity | [17,72] |
| miR-122 | Dysregulated expression | Alters hepatic lipid metabolism and gut–liver immune signaling | [69] |
| miR-29a | Dysregulated expression | Impairs gut barrier function; modulates fibrotic pathways in liver and intestine | [51] |
| miR-34a | Upregulated | Promotes inflammation, apoptosis, and insulin resistance across the GLBA | [78] |
| miR-155 | Upregulated | Enhances production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in liver and gut mucosa | [70,79] |
| miR-21 | Upregulated | Promotes fibrosis, inflammation, and impaired tissue repair | [68] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Crocetta, A.; Giannelou, M.-A.; Benfante, A.; Castelli, L.; Koumbi, L. Linking Psychological Stress to Epigenetic Regulation via the Gut–Liver–Brain Axis in Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease. Livers 2025, 5, 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers5030043
Crocetta A, Giannelou M-A, Benfante A, Castelli L, Koumbi L. Linking Psychological Stress to Epigenetic Regulation via the Gut–Liver–Brain Axis in Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease. Livers. 2025; 5(3):43. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers5030043
Chicago/Turabian StyleCrocetta, Annachiara, Maria-Anna Giannelou, Agata Benfante, Lorys Castelli, and Lemonica Koumbi. 2025. "Linking Psychological Stress to Epigenetic Regulation via the Gut–Liver–Brain Axis in Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease" Livers 5, no. 3: 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers5030043
APA StyleCrocetta, A., Giannelou, M.-A., Benfante, A., Castelli, L., & Koumbi, L. (2025). Linking Psychological Stress to Epigenetic Regulation via the Gut–Liver–Brain Axis in Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease. Livers, 5(3), 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers5030043







