Abstract
Hepatic fibrosis is a reversible wound healing process following liver injury. Although this process is necessary for maintaining liver integrity, severe excessive extracellular matrix accumulation (ECM) could lead to permanent scar formation and destroy the liver structure. The activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) is a key event in hepatic fibrosis. Previous studies show that most antifibrotic therapies focus on the apoptosis of HSCs and the prevention of HSC activation. Noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) play a substantial role in HSC activation and are likely to be biomarkers or therapeutic targets for the treatment of hepatic fibrosis. This review summarizes and discusses the previously reported ncRNAs, including the microRNAs, long noncoding RNAs, and circular RNAs, highlighting their regulatory roles and interactions in the signaling pathways that regulate HSC activation in hepatic fibrosis.
1. Introduction
Hepatic fibrosis is a continuous wound healing process seen as an outcome in various liver diseases such as viral hepatitis, alcoholic and non-alcoholic liver disease, drug abuse, and others [1]. The process of wound healing is necessary for the healthy maintenance of liver tissue integrity. However, severe fibrosis characterized by abnormal connective tissue hyperplasia and extracellular matrix (ECM) deposition could lead to scar formation and a change of the liver structure and function, eventually causing organ failure [2]. Clinical and experimental studies have shown that hepatic fibrosis is dynamic and could be reversed [3,4]. Although the mechanisms of reversibility are partly understood, the interplays between the intra- and extra-cellular environments in the hepatic stellate cell (HSC) could yield important insights [5].
Typically, HSCs are quiescent non-proliferative liver cells with intracellular lipid droplets containing vitamin A [6]. Upon pathological insults such as toxins, metabolic or viral diseases leading to liver injury, a trans-differentiation of HSCs to myofibroblasts occurs [5]. Following the injury, the apoptotic hepatocytes and Kupffer cells (resident macrophages) cause the release of the profibrotic cytokines (tumor necrosis factor-α (TNFA or also known as TNF-α), platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), and transforming growth factor-β (TGFB)), leading to HSC activation and collagen type I (COL1A1) deposition. The upregulation of cytoskeletal proteins such as α-smooth muscle actin (ACTA2 or also known as α-SMA) and desmin (DES) changes the cell phenotypes into proliferative and contractile shapes [5]. Activated HSCs then lead to the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines including interleukins (IL-6 and IL-8), and C-C motif chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2), thus recruiting the inflammatory cells to the injury site [7]. Moreover, activated HSCs also produce tissue inhibitors of matrix metallopeptidases (TIMP) and increase the ECM synthesis and deposition [5], causing fibrosis.
Previous studies of experimental models of liver fibrosis reversal showed that antifibrotic therapies focus on the apoptosis of the HSCs [3,4]. The activation of the death-related receptor such as Fas cell surface death receptor (FAS) could lead to HSC cell death. However, this effect is also observed in hepatocytes, as the FAS receptor is ubiquitously expressed on both cells [8]. Fortunately, the expression of TNF-related apoptosis-induced ligand, the TNF superfamily member 10b receptor (TNFRSF10B, also known as TRAIL-R2), is upregulated in activated human HSC cell line (LX-2) only during fibrogenesis [9]. Thus, the TNFRSF10B agonists could induce apoptosis specifically to activated HSCs to reverse the fibrosis. Another antifibrotic mechanism includes using the antifibrotic cytokines such as interferon γ (IFNG) [10] or inhibiting the TNFA and TGFB1 signals to prevent the proliferation of HSCs or inducing HSCs apoptosis [11]. Thus, identifying and recognizing the HSCs’ activation and apoptosis regulators will offer a window of reversing hepatic fibrosis.
Whole-genome sequencing and transcriptomics studies revealed that noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) play significant roles in regulating liver diseases, including hepatic fibrosis [12,13,14,15]. Generally, ncRNAs are grouped into two classes based on their sizes: small ncRNAs (size less than 200 base pairs (bp)) and large ncRNAs (size more than 200 bp). Some ncRNAs could target or regulate multiple genes simultaneously and interact to form the regulatory networks, regardless of their classes [12,14]. In this review, we summarized and discussed the roles of the main three classes of ncRNAs, the microRNA (miRNA), long noncoding RNA (lncRNA), and circular RNA (circRNA), as well as their interactions in regulating the HSC activation during hepatic fibrosis development.
2. MicroRNAs and HSCs
MicroRNA is a single-stranded short ncRNA (~25 nucleotides) that regulates gene expression. The biogenesis of miRNA has been described earlier in extensive detail, in both canonical and non-canonical pathways [16]. The RNA polymerase transcribes miRNA as individual genes or clusters of miRNA genes from the same promoter for the canonical pathway. This transcription process results in a primary transcript (pri-miRNA), which is then processed by a microprocessor complex consisting of RNAse III-type endonuclease Drosha and its associated protein, DiGeorge Syndrome Chromosomal Region 8 (DGCR8)/Pasha. This microprocessor processing leads to the formation of individual stem-loop miRNA precursors (pre-miRNA). The pre-miRNA is then exported by Exportin 5 (XPO5) into the cytoplasm and processed by the RNAse III-type endonuclease, Dicer that cleaves the loop structure producing the miRNA duplex [16]. One strand of the miRNA is incorporated into the Argonaute protein to form the miRNA-Induced Silencing Complex (miRISC). The sequence complementarity between the miRNA and target messenger RNA (mRNA) 3’ untranslated region (UTR) determines which miRNA strand is selected [17]. A perfect complementary binding will result in mRNA degradation. In contrast, an incomplete binding will result in mRNA translational repression. The non-canonical miRNAs are located in the intron region of the genes and are known as the mirtrons [18]. The splicing mechanism directly produces the stem-loop pre-miRNAs during the mRNA processing, thus bypassing the microprocessor complex of Drosha/DGCR8 processing. Then, the miRNA biogenesis continues, similar to the canonical pathway [18]. Thousands of miRNAs are currently known, and their complementary sequence bindings between the miRNA and target mRNA are listed in the database [19]. Since miRNA sequence is conserved across the species, it is possible to predict the target mRNA or gene based on the complementary sequence-binding [20,21]. Among the ncRNAs, miRNA is the most studied ncRNA concerning the HSC activation in hepatic fibrosis [12,14] (Table 1).

Table 1.
Summary of microRNA involved in human hepatic stellate cells (HSC) activation in fibrosis.
2.1. Profibrotic miRNAs
Most of the miRNAs that promote HSC activation are in the transforming growth factor-beta (TGFB) pathway (Table 1 and Figure 1). TGFB is a master fibrogenic cytokine responsible for activating and transdifferentiating quiescent HSC to a myofibroblast phenotype [82]. TGF-β binding to its receptor (TGFBR1) leads to the activation of SMAD2 and SMAD3 via direct C-terminal phosphorylation [82]. Phosphorylated SMAD2 and SMAD3 form a complex with SMAD4 and then move into the nucleus to associate with transcription factors for target-gene transcription [82]. SMAD6 and SMAD7 negatively regulate the TGFB signaling pathway, establishing the negative feedback loop [83,84]. SMAD7 binds to the TGFB receptor (TGFBR), blocking the receptor from phosphorylating the R-SMAD proteins for the downstream effects [83,85]. SMAD7 also recruits the ubiquitin ligases to the TGFBR, leading to the degradation via the proteasomal pathway [86]. Three miRNAs, miR-17-5p, miR-212-3p, and miR-503, directly regulate the SMAD family member 7 (Smad7) expression in the mouse and rat models of hepatic fibrosis [29,35,41]. Thus, upregulation of these miRNAs (miR-17-5p, miR-212-3p, and miR-503) in HSCs will reduce the expression of Smad7, preventing the negative feedback loop on TGFB-induced HSC activation. Notably, miR-145 negatively regulates Kruppel like factor 4 (KLF4) expression [28], and KLF4 is one of the transcription factors that induce the expression of SMAD7 [87]. Upregulation of miR-145 expression in human HSC cell line (LX-2) is consistent with the activation of TGFB-mediated HSC activation and ECM protein synthesis and deposition [28] via the suppression of KLF4 expression. Another negative regulator of the TGFB pathway is the Caveolin 2 (CAV2) [88]. Upregulation of miR-199a-3p expression in both human and rat HSC cell lines reduces the expression of CAV2 and leads to TGFB-mediated HSC activation [33]. Other miRNAs regulate molecules that activate the TGFB signaling. One of these is miR-125a-5p, which directly regulates hypoxia-inducible factor 1 subunit alpha (Hif1a) expression in carbon tetrachloride-induced fibrotic mice [22]. A previous study of experimental liver injuries showed that regions of hypoxia develop in the liver, and this hypoxic condition stimulates HSC activation and collagen production following the diethylnitrosamine (DEN) treatment in rats [89] by activating the Tgfb/Smad pathway [90]. Therefore, this miRNA network suppressing the TGFB/SMAD negative regulators will favor the HSC activation.
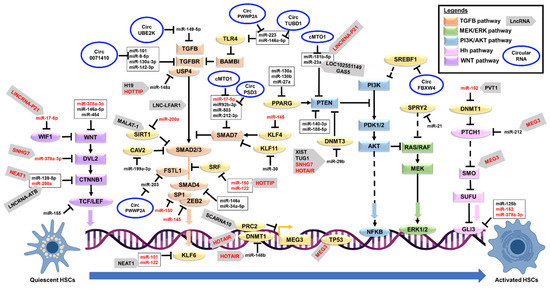
Figure 1.
A schematic diagram showing the molecular regulation of hepatic stellate cells activation. ➔ Represents the positive regulation, ┴ represents the negative regulation, dashed line represents indirect regulation, and red color text represents multiple target regulation. Abbreviations: AKT: AKT serine/threonine kinase; Circ: Circular; ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; Hh: Hedgehog; HSC: Hepatic stellate cells; MEK: dual-specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase; LncRNA: Long noncoding RNA; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase; TGFB: Transforming Growth Factor Beta; WNT: Wingless/Integrated.
Emerging evidence also indicates that other signaling pathways could induce HSC activation. An example is the Phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase (PI3K) and serine-threonine protein kinase AKT (PI3K/AKT) signaling pathway, which regulates the cell growth and proliferation of HSCs [91,92]. Although the exact mechanism is partly understood, PI3K induces AKT activation to increase cell proliferation via the upregulation of cyclin D1 (CCND1) expression, a regulatory subunit of cyclin-dependent kinases for the cell cycle G1/S transition [92]. The PI3K phosphorylates the phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) to phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-triphosphate (PIP3). This PIP3 then binds to AKT, leading to its recruitment to the membrane and the binding to phosphoinositide-dependent kinases (PDK). PDK kinases phosphorylate the AKT for its activation [93]. Phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) negatively regulate PI3K/AKT signaling by reversing the PIP3 into PIP2 [93], thus acting as a negative regulator for this pathway. Previous studies of miRNAs reported that four miRNAs, miR-140-3p [26], miR-181b [30], miR-188-5p [32], and miR-23a [39] directly suppress the Pten expression to promote the PI3K/AKT signaling. Subsequently, the HSC activation and hepatic fibrosis in carbon tetrachloride (CCI(4)) mouse models. Importantly, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARG) can transcriptionally upregulate PTEN expression [93], contributing to the complex co-regulatory network. Three miRNAs (miR-130a [24], miR-130b [24], and miR-27a [40]) reduce the Pparg expression to promote HSC activation as observed in the mouse and rat models of fibrosis, therefore, adding another layer of negative regulation to the PTEN enzyme.
Another reported pathway is the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling pathway [94]. The release of PDGF cytokine and phosphorylation of the PDGF receptor activates the Rat Sarcoma Virus (RAS) and its downstream signaling pathways (RAF proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase (RAF1), dual-specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase (MEK), PI3K/AKT, and ERK signaling) [95]. These signaling pathways promote the phosphorylation and activation of cytoplasmic proteins and transcription factors (activator protein 1 (AP-1) and nuclear factor kappa B (NFKB)), thus, causing the synthesis and accumulation of ECM proteins [95]. Among the miRNAs, miR-21 negatively regulates Sprouty RTK signaling antagonist 2 (SPRY2) and Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha (HNF4A) expressions [34]. Upregulation of miR-21 expression stimulates HSC activation in the mouse HSC cell line via reducing the Spry2 expression to increase ERK1 signaling, as Spry2 is a known inhibitor for ERK signaling pathways [96]. At the same time, miR-21 reduces the expression of Hnf4a to trigger the HSC synthesis of collagen proteins in both human and murine HSC cell lines [97,98]. Since PDGF is the most potent factor to stimulate HSC activation [95], the inhibition of miR-21 action may provide a new alternative to treat hepatic fibrosis.
2.2. Anti-Fibrotic miRNAs
Similar to profibrotic miRNAs, the majority of the antifibrotic miRNAs are suppressing the TGFB signaling pathways. These miRNAs’ expressions are reduced in HSC activation, thus releasing the suppressions of their target genes and allowing the TGFB signaling activation. Examples include miR-146a [55] and miR-34a-5p [71] that negatively regulate the expression of Smad4 as observed in the CCI(4)-induced fibrotic mice, and Smad4 is an essential signal transducer in the TGFB pathway. Other miRNAs are the miR-101 that negatively regulates the Tgfb receptor and Kruppel like factor 6 (Klf6, a TGFB downstream effector) [45], miR-9-5p and miR-130a-3p that also negatively regulates both Tgfb receptors [51,80], miR-142-3p that negatively regulates Tgfbr1 [53], miR-200a that negatively regulates Tgfb2 [64] and Sirtuin 1 (Sirt1, an inhibitor of TGFB signaling) [65], miR-378 that also negatively regulates TGFB2 [74], miR-30 that negatively regulates Kruppel like factor 11 (Klf11, an inhibitor of SMAD7) [67], miR-708 that negatively regulates Zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 2 (Zeb2, the EMT transcription factor that interacts with SMAD proteins) [42], miR-30a that negatively regulates Beclin 1 (BECN1, a SMAD2 downstream effector) [68], miR-122 that negatively regulates Serum response factor (SRF, a suppressor of SMAD2-mediated TGFB action) [48], miR-150 that negatively regulates SP1 transcription factor 1 (SP1, SMAD protein complex) [58], and miR-34a-5p that negatively regulates Snail family transcriptional repressor 1 (Snai1, the EMT downstream effector of TGFB signaling) [71] in both human and murine HSC cell lines. In addition, some of these miRNAs reduce the TGFB-mediated fibrosis proteins such as miR-122 that negatively regulates Fibronectin 1 (FN1) [48], miR-29b that negatively regulates Collagen type I alpha 1 chain (Col1a1) [66], miR-150 that negatively regulates Collagen type IV alpha 4 chain (COL4A4) [58], and miR-335 that negatively regulates Tenascin C (Tnc) [69], as observed in both human and murine HSC cell lines. Identifying more miRNA regulatory networks that inhibit the TGFB-mediated HSC activation and ECM accumulation is essential, as these miRNAs could be used for future developments of therapeutics drugs to treat hepatic fibrosis.
Besides the TGFB pathway, miRNAs also regulate the Wnt/Beta-catenin signaling to inhibit HSC activation. One example is miR-200a which reduces the expression of Beta-catenin (Ctnnb1) in the CCI(4)-induced rat fibrosis model and mouse HSC cell line [64]. The Ctnnb1 is a component of Wingless/Integrated (WNT) signaling [99]. Although WNT signaling does not directly contribute to the HSC phenotype change, this pathway activation leads to the inducements of various players in the TGFB pathway [100]. Loss of miR-200a expression increases the expression of Ctnnb1, and beta-catenin will then form complexes with Transcription factor (Tcf) and Lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1 (Lef1) to regulate the transcription of downstream target genes [100]. Notably, miR-155 negatively regulates the expression of TCF4 as observed in the human HSC cell line [60], thus adding another layer of this co-regulatory miRNA network. Two miRNAs, miR-378a-3p [76] and miR-454 [77], negatively regulate the WNT family member 10A (Wnt10a) expression in the murine models of fibrosis, and thus cause the inhibition of WNT signaling, as the Wnt10a is a member of the WNT/beta-catenin pathway. Another miRNA, miR-146a-5p, also negatively regulates the expression of WNT family members (Wnt1 and Wnt5a), and the loss of this miRNA expression promotes HSC proliferation and activation [56].
Another suppressed pathway is the Hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway. Three miRNAs (miR-125b [49], miR-152 [59], and miR-378a-3p [75]) directly reduce the expression of GLI family zinc finger 3 (Gli3), the final effector of Hh signaling, as observed in the murine models of hepatic fibrosis. Hh signaling is essential to control embryonic development during early life. This function is inactive during the postnatal life, where the Hh signaling is minimally involved in stem cell maintenance, cell/tissue repair, and proliferation [101]. Although the exact mechanism of GLI3 in HSC activation is partly understood, a previous study of primary rat HSCs showed that Gli3 might be involved in the control of the cell cycle and regeneration during HSC activation [102]. Besides GLI3, other miRNAs also regulate cell cycle regulators such as miR-195 that negatively regulates Cyclin E1 (CCNE1) in human HSC cell lines [63], and miR-338-3p that negatively regulates Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (Cdk4) in both rat primary and cell line HSCs [70]. These miRNAs negatively regulate the profibrotic molecules and effectors to maintain a healthy liver environment and prevent HSC activation upon restoring their expressions. Therefore, further research is needed to elucidate whether these miRNAs could be used as future treatments for hepatic fibrosis.
3. Long Noncoding RNAs and HSCs
Like miRNAs, the long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) regulates important biological pathways. LncRNAs are large RNA transcripts (size is more than 200 bp) without protein-coding capacity [103]. The biogenesis and classification of the lncRNAs have been described previously [103,104]. The lncRNA is produced similarly to the mRNA, often having the 5′-capped, splicing, and sometimes the poly-A tail [105]. The classifications of the lncRNAs are complex as these lncRNAs are diverse and lack primary sequence conservation [104]. Generally, lncRNAs are grouped based on their genomic origins: (1) sense exonic lncRNA (produced from the sense strand of a gene), (2) antisense exonic lncRNA (produced from the exons of a gene on the opposite strand), (3) sense intronic lncRNA (produced from the sense strand of a gene overlapping partially or entirely with intron), (4) antisense intronic lncRNA, (5) intergenic lncRNA (lincRNA, transcribed from the region between two genes), and (6) bidirectional lncRNA (produced from the opposite strand, in the opposite direction and within 1 kb of the promoter of a gene) [104]. Importantly, lncRNAs exhibit more specific expression profiles than mRNAs [106,107], in which they are cell-, tissue-, developmental stage- or disease state-specific, despite being lowly expressed [108].
The interactions between the lncRNAs and their target molecules elucidate the biological mechanisms of their regulation. The lncRNAs could act as cis- or trans-regulating actions on their target gene [103,104]. For example, lncRNAs cis-regulate their target gene at the point of transcription or nearby location, whereas lncRNAs trans-regulate their target gene at different loci or other locations in the cell [103,104]. LncRNAs regulate gene expression by epigenetic regulation, chromatin remodeling, transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation via the interactions with DNA, other RNA, and proteins [103]. Mechanistically, lncRNAs can act as (1) scaffolds, providing a site for molecular interactions, (2) decoys, preventing proteins from accessing other proteins, and (3) sponges, binding to the target RNAs such as miRNAs via the complementary base-pairing and thus preventing other binding events [103,104,109]. Moreover, cellular localization can influence the lncRNA regulatory role in which the nuclear lncRNAs regulate the gene expression via chromatin remodeling and epigenetic regulation, whereas the cytoplasmic lncRNAs regulate the gene expression via post-transcriptional and post-translational regulation [103,109]. Previous studies have reported various lncRNAs in liver health and fibrosis [13,110,111,112] (Table 2 and Figure 1).
Like miRNAs, most of the previously reported lncRNAs in HSC are in the TGFB signaling pathway. An example is the lncRNA Liver fibrosis-associated lncRNA 1 (Lnc-Lfar1) that was higher upon HSC activation in CCl(4)-induced hepatic fibrosis [113]. Lnc-Lfar1 binds to the Smad2/3 complex and acts as a scaffold to facilitate the interaction between Smad2/3 and TGFB receptor (Tgfbr) [113], thus activating TGFB signaling. Intriguingly, another lncRNA, H19 imprinted maternally expressed transcript (H19), acts as a miR-148a sponge to release the suppression on Ubiquitin specific peptidase 4 (Usp4) expression in CCl(4)-induced hepatic fibrosis [114]. USP4 is required to stabilize the TGFBR for TGFB signaling [115]. Like H19, another lncRNA, HOXA distal transcript antisense RNA (HOTTIP), also acts as a miR-148a sponge, and this binding increases the TGFBR expression in both human and mouse HSC cell lines [116]. LncRNA HOTTIP directly binds to miR-148a expression and prevents its suppression on TGFBR [116], thus adding another layer of the co-regulatory networks between these lncRNAs on TGFBR regulation. In contrast, in a study of mouse HSCs, the lncRNA HOTTIP acts as a miR-150 sponge and increases the expression of Srf [117], and Srf is a suppressor of Smad2-mediated Tgfb action [48], showing the dual regulatory roles of HOTTIP in HSC activation. Another suppressor of SMAD protein is SIRT1 that stimulates the deacetylation of SMAD3 and prevents its binding to the promoter region of fibrogenic genes, as observed in human HSC cell lines [118]. LncRNA MALAT-1 is higher in HSC activation and liver fibrosis, and this lncRNA negatively regulates SIRT1 expression [118].

Table 2.
Summary of long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) involved in human hepatic stellate cells (HSC) activation in fibrosis.
Table 2.
Summary of long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) involved in human hepatic stellate cells (HSC) activation in fibrosis.
| LncRNA | Expression | Target Molecule | Disease Model | Function | Role in Fibrosis | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPR137B-PS | Up | miR-200a-3p/CXCL14 | Mouse CCI(4)-treated | HSC activation and collagen production | Profibrotic | [119] |
| H19 | Up | miR-148a/Usp4 | Mouse CCI(4)-treated, Human LX-2, L02 and HEK293T/17 cell lines | HSC activation via TGFB1 pathway | Profibrotic | [114] |
| HOTAIR | Up | miR-29b/Dnmt3b/Pten | Patient samples, Mouse CCI(4)-treated | HSC activation and collagen production | Profibrotic | [120] |
| Up | miR-148b/DNMT1 | Patient samples, Mouse CCI(4)-treated, Human LX-2, AML-12 and RAW264.7 cell lines | HSC activation and collagen production | Profibrotic | [121] | |
| Up | PRC2 | Patient samples, Mouse CCI(4)-treated, Human LX-2, AML-12 and RAW264.7 cell lines | HSC activation and collagen production | Profibrotic | [121] | |
| HOTTIP | Up | miR-148a/TGFBR | Patient samples, Mouse CCI(4)-treated | HSC activation | Profibrotic | [116] |
| Up | miR-150/Srf | Mouse CCI(4)-treated | Activates HSC proliferation | Profibrotic | [117] | |
| LINC-SCRG1 | Up | ZFP36 | Patient samples, Human LX-2 cell line | Activates HSC proliferation and ECM protein accumulation | Profibrotic | [122] |
| Lnc-Lfar1 | Up | Smad2/3 | Mouse CCI(4)-treated, AML-12 and HEK293T cell lines | HSC activation via TGFB1 and Notch pathways | Profibrotic | [113] |
| LNCRNA-ATB | Up | miR-200a/CTNNB1 | Patient samples, Human LX-2 cell line | HSC activation via Wnt/β-catenin pathway | Profibrotic | [123] |
| MALAT1 | Up | miR-101b/RAC1 | Mouse CCI(4)-treated | HSC activation and collagen production | Profibrotic | [124] |
| Up | SIRT1 | Mouse CCI(4)-treated, Human LX-2 cell line | HSC activation and collagen production | Profibrotic | [118] | |
| MEG8 | Up | NOTCH2/3 | Human LX-2 and AML-12 cell line | Suppresses HSC activation and collagen production | Anti-fibrotic | [125] |
| NEAT1 | Up | miR-122/Klf6 | Mouse CCI(4)-treated | HSC activation and collagen production | Profibrotic | [126] |
| Up | miR-148a-3p/miR-22-3p/Cyth3 | Mouse CCI(4)-treated | HSC activation and collagen production | Profibrotic | [127] | |
| Up | miR-139-5p/CTNNB1 | Mouse CCI(4)-treated, Human LX-2 cell line | Activates HSC proliferation | Profibrotic | [128] | |
| Pvt1 | Up | miR-152/Dnmt1/Ptch1 | Mouse CCI(4)-treated | HSC activation and collagen production | Profibrotic | [129,130] |
| Scarna10 | Up | Prc2 | Patient samples, AML-12 cell line; Mouse CCI(4)-treated | HSC activation | Profibrotic | [131] |
| Snhg7 | Up | miR-29b/Dnmt3a | Mouse CCI(4)-treated | Activates HSC proliferation | Profibrotic | [132] |
| Up | miR-378a-3p/Dvl2 | Patient samples; Mouse CCI(4)-treated, Human LX-2 cell line | Activates HSC proliferation | Profibrotic | [133] | |
| Tug1 | Up | miR-29b | Patient samples, Mouse CCI(4)-treated, Human LX-2 and HEK293T cell lines | HSC activation and profibrogenic factors | Profibrotic | [134] |
| XIST | Up | miR-29b/HMGB1 | Mouse model, Human LX-2 cell line | HSC activation and profibrogenic factors | Profibrotic | [135] |
| Gas5 | Down | miR-222/CDKN1B | Patient samples, Mouse CCI(4)-treated | Suppresses HSC activation and collagen production | Anti-fibrotic | [136] |
| Down | miR-23a/Pten | Rat CCI(4)-treated | Suppresses HSC activation | Anti-fibrotic | [39] | |
| HIF1A-AS1 | Down | TET3 | Human LX-2 cell line | Suppresses HSC proliferation | Anti-fibrotic | [137] |
| LINCRNA-P21 | Down | miR-181b/PTEN | Patient samples, Human LX-2 cell line | Suppresses HSC activation and collagen production | Anti-fibrotic | [138] |
| Down | miR-17-5p | Mouse HSC cells | HSC proliferation upon Salvianolic acid B treatment | Profibrotic | [139] | |
| Loc102551149 | Down | miR-23a/Pten | Rat NDMA-treated, Rat HSC-T6 cell line | Suppresses HSC activation | Anti-fibrotic | [140] |
| MEG3 | Down | TP53 | Mouse CCI(4)-treated, Human LX-2 cell line | Suppresses HSC proliferation and ECM proteins | Anti-fibrotic | [141] |
| Down | miR-212/Ptch1/ Smo | Patient samples, Mouse CCI(4)-treated | Suppresses HSC proliferation and ECM proteins | Anti-fibrotic | [142] |
Abbreviation: CCI(4): Carbon tetrachloride; CTNNB1: Catenin beta 1; CXCL14: C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 14; CYTH3: Cytohesin 3; DNMT: DNA methyltransferase; DVL2: Dishevelled segment polarity protein 2; ECM: Extracellular matrix; GAS5: Growth arrest-specific transcript 5; GPR137B-PS: G protein-coupled receptor 137 B pseudogene; H19: H19 imprinted maternally expressed transcript; HIF1A-AS1: HIF1A antisense RNA 1; HMGB1: High-mobility group box-1; HOTAIR: HOX transcript antisense RNA; HOTTIP: HOXA distal transcript antisense RNA; HSC: Hepatic stellate cell; KLF6: Kruppel like factor 6; LNC-LFAR1: Liver fibrosis-associated lncRNA 1; LNCRNA-ATB: Long Noncoding RNA Activated By TGFB; MALAT1: Metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1; MEG3: Maternally expressed 3; MEG8: Maternally expressed 8; NDMA: N-nitrosodimethylamine; NEAT1: Nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1; NOTCH: Notch receptor; PTCH1: Patched 1; PTEN: Phosphatase and tensin homolog; PRC2: Polycomb repressive complex 2; PVT1: Pvt1 oncogene; RAC1: Rac family small GTPase 1; SCARNA10: small Cajal body-specific RNA 10; SMAD: SMAD family member; SMO: Smoothened, frizzled class receptor; SNHG7: Small nucleolar RNA host gene 7; SRF: Serum response factor; TET3: Tet methylcytosine dioxygenase 3; TGFBR: Transforming growth factor beta receptor; TP53: tumor protein p53; TUG1: Taurine up-regulated 1; USP4: Ubiquitin specific peptidase 4; XIST: X inactive specific transcript; ZFP36: ZFP36 ring finger protein.
Another lncRNA involved in the TGFB pathway is the Nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 (Neat1) that acts as a miR-122 sponge in the mouse model of fibrosis and releases the suppression on Klf6 expression (a TGFB downstream effector) [126]. As discussed above, miR-122 is an antifibrotic miRNA, that suppresses the P4HA1 [46,47], SRF, and FN1 [48] expressions; thus, miR-122 inhibition by the lncRNA NEAT1 promotes HSC activation and hepatic fibrosis. LncRNA Scarna10 is also a positive regulator for the TGFB signaling pathway. This lncRNA acts as a decoy to the Polycomb repressive complex 2 (Prc2, a repressor protein) and inhibits its binding to the promoter regions of genes involved in the TGFB pathway [131]. Silencing of Scarna10 lncRNA in primary HSC cells caused the reduction of the Tgfb, Tgfbr, Smad2/3, and Klf6 expressions [131]. Like SCARNA10, lncRNA HOX transcript antisense RNA (HOTAIR) acts as a scaffold to recruit the PRC2 repressor protein to another lncRNA, maternally expressed gene 3 (MEG3) promoter region [121], thus suppressing the MEG3 action as demonstrated in the human HSC cell line. In this study [121], a further investigation revealed that HOTAIR lncRNA acts as a miR-148b sponge to increase the DNMT1 expression suppressing the MEG3 lncRNA via hypermethylation at the promoter region. Consistent with these findings, a previous study of human fibrotic tissues and HSC cell lines showed that MEG3 lncRNA is an antifibrotic lncRNA that increases the tumor protein p53 (TP53) expression to promote apoptosis [141]. Therefore, the TGFB pathway induced the suppression of lncRNA MEG3 to facilitate HSC proliferation and activation.
Some of the lncRNAs regulate the PI3K/AKT pathway in HSCs. One such lncRNA is HOTAIR which was higher in HSC activation and acted as a miR-29b sponge through competitive binding [120]. In the primary mouse HSCs, the suppression of miR-29b action causes hypermethylation on the promoter region of the Pten gene (a negative regulator of PI3K/AKT) [120], thus reducing the Pten expression. This hypermethylation occurs due to the upregulation of DNA methyltransferase 3B (Dnmt3b) expression, as miR-29b directly binds to Dnmt3b and lncRNA HOTAIR prevents the binding [120]. Like HOTAIR, lncRNA Small Nucleolar RNA Host Gene 7 (SNHG7) suppressed the miR-29b action by competitive binding and resulted in a higher Dnmt3a expression in the primary mouse HSCs [132]. An increase of Dnmt3a causes the upregulation of HSC activation factors Acta2, Col1a1 and autophagy factors Becn1 [132]. LncRNA X Inactive Specific Transcript (XIST) also negatively regulates miR-29b [135]. In this study of human HSC cell line [135], the suppression of miR-29b action caused an increase of High-Mobility Group Box-1 (HMGB1) expression and subsequently activated the transcription of the fibrogenic genes. Another miR-29b sponge lncRNA is the Taurine up-regulated 1 (Tug1) [134]. Although no specific direct target of miR-29b was identified in the CCI(4)-treated mouse model, the HSC fibrogenic factors’ expressions were upregulated [111]. In contrast to the above lncRNAs, Growth arrest-specific transcript 5 (Gas5) lncRNA was reduced in HSC activation, as demonstrated in the CCI(4)-treated mouse models [39]. GAS5 lncRNA acts as a miR-23a sponge to increase Pten expression [39]. Since Pten is a negative regulator of the PI3K/AKT pathway, HSC activation was suppressed [39]. Like Gas5, Loc102551149 lncRNA also sponges miR-23a as observed in the primary rat HSCs, and subsequently increases the expression of Pten [140], thus adding another layer of the co-regulatory network between lncRNAs on miR-23a. Long Intergenic Non-Coding RNA-p21 (LINCRNA-P21) negatively suppresses HSC activation in the human HSC cell line by acting as a miR-181b sponge and consequently increasing the expression of PTEN [138]. These studies show that the complex molecular regulation of PTEN expression consists of lncRNAs targeting the miR-29b (a positive regulator of PI3K/AKT pathway) and lncRNAs targeting miR-23a or miR-181b (negative regulators of PI3K/AKT pathway). Therefore, this lncRNA-miRNA axis could offer new targets for the treatment of hepatic fibrosis.
In HSCs, some lncRNAs regulate the WNT/Beta-catenin signaling pathway. For example, Long Noncoding RNA Activated By TGFB (LNCRNA-ATB) was higher during HSC activation in the human fibrotic tissue and HSC cell line, and this lncRNA acts as a miR-200a sponge, thus increasing the expression of beta-catenin (CTNNB1) [123]. Since beta-catenin is an essential regulator of WNT signaling [99], the upregulation of CTNNB1 will promote hepatic fibrosis. Similarly, in human HSC cell lines, another lncRNA, NEAT1, sponges miR-139-5p to increase CTNNB1 expression [128]. A study of CCI(4)-induced mouse fibrosis models and the isolated primary mouse HSCs showed that lncRNA Snhg7 acts as a miR-378a-3p sponge, and this suppression of miR-378a-3p led to the upregulation of Dishevelled segment polarity protein 2 (Dvl2) expression and consequently increased the expression of Ctnnb1 [133]. Another lncRNA regulating the WNT signaling is the LincRNA-p21 which suppresses miR-17-5p action, and this lncRNA expression is reduced in HSC activation as observed in the primary HSC cells [139]. Although this study [139] did not specify the direct downstream target of miR-17-5p, a previous study of primary mouse HSC and cell lines reported that the WNT inhibitory factor 1 (Wif1) is a direct target of miR-17-5p, and higher expression of miR-17-5p led to a lower expression of Ctnnb1 [143]. Moreover, another study also showed that miR-17-5p suppresses Smad7 expression, and thus a restoration of miR-17-5p action could also contribute to the TGFB pathway suppression [29].
In addition, some lncRNAs are involved in the Hh signaling pathway during HSC activation. For example, the Plasmacytoma variant translocation 1 (Pvt1) lncRNA acts as a miR-152 sponge to increase the expression of Dnmt1 in the isolated primary HSC cells [129,130]. This Dnmt1 enzyme then promotes the hypermethylation of the promoter region of the Patched 1 (Ptch1) gene. Since Ptch1 is a negative modulator of Hh signaling [144], the loss of Ptch1 expression promotes Hh signaling and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in HSC activation. In contrast to Pvt1, Meg3 lncRNA inhibits the EMT process, as this lncRNA binds to Smoothened (Smo) protein and partly suppresses the EMT process [142]. Notably, the Meg3 also acts as a miR-212 sponge and increases the expression of Ptch1, thus further completely suppressing Hh signaling and the EMT process, as demonstrated in the mouse HSCs [142]. Another reported lncRNA is the MEG8 lncRNA that suppresses the EMT process by reducing the expression of NOTCH signaling receptors (NOTCH2 and NOTCH3) in both human and mouse HSC cell lines [125]. However, the expression of MEG8 was higher in activated HSCs, despite its antifibrotic role [125], suggesting that this lncRNA may be upregulated as part of the compensatory mechanisms following HSC activation. Further work is needed to confirm this lncRNA MEG8 role in hepatic fibrosis. Most of these reported lncRNAs interact with the miRNAs as their sponges and releases the target genes or mRNAs. Since lncRNAs’ expressions are very specific in cell type, developmental, and disease status [106,107], these lncRNAs could be used as biomarkers for HSC activation. In some cases, the restoration of lncRNA expression improves and prevents hepatic fibrosis [112].
4. Circular RNAs and HSCs
Circular RNA (circRNA) is a covalently closed continuous loop RNA derived from the back-splicing event during transcription, in which the 3′ end of the splice donor site is joined to a 5′ end of the upstream exon forming a closed-loop structure [145]. This splicing event generates different classes of circRNAs such as (1) exonic circRNAs (contains exons only), (2) exon-intron circRNAs (EIciRNAs), and (3) intronic circRNAs (ciRNAs) [145,146,147]. The biogenesis of circRNA has been discussed in detail previously [145,148]. Generally, circRNAs have similar regulatory action like lncRNAs, with both cis- and trans-regulation of the target molecules, and tissue-, developmental stage-, and subcellular location-specific expression [145,149]. Mechanistically, circRNAs regulate gene expression by (1) acting as a miRNA sponge, (2) as a protein sponge or decoy, (3) as parental gene regulators, and (4) regulating the expression of a parental gene; and (5) translating into peptides for circRNAs with a start codon [145,146,148]. Previous studies have discussed the role of circRNAs in liver diseases [150,151,152]; however, knowledge of this RNA type is still lacking. The circRNAs involved in HSC activation are summarized in Table 3 and Figure 1.

Table 3.
Summary of circular RNA (circRNA) involved in hepatic stellate cells (HSC) activation in fibrosis.
Most of the circRNAs in HSC activation are in the TGFB pathways. One example is the circUBE2K circRNA, derived from the Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 K (UBE2K) gene via the back splicing event. The UBE2K is involved in the suppression of gene transcription via the histone H3K9 trimethylation [165]. The circUBE2K expression was higher in both activated human and mouse HSCs, and this circRNA acts as a miR-149-5p sponge, consequently increasing the expression of TGB2 to promote the expression of ACTA2 and COL1A1 in HSC cells [158]. Silencing this circRNA resulted in the suppression of HSC activation and restoration of miR-149-5p expression [158], confirming the interaction between the two RNAs. Another circRNA is the circ_0071410 that was higher in HSC activation, and this circRNA acts as a miR-9-5p sponge as observed in the human HSC cell line [154]. Although no specific direct target was reported for miR-9-5p, a previous study of HSCs showed that miR-9-5p negatively regulates both TGFB receptors expressions [80], thus a higher circ_0071410 expression will promote the TGFB signaling via the suppression of miR-9-5p. The expression of circPWWP2A was also higher in the activated human HSC cell line, and this circRNA negatively regulates the expression of miR-203, subsequently increasing the expression of Follistatin like 1 (FSTL1) [155]. A previous knockdown of the FSTL1 study showed that FSTL1 associates with SMAD3 protein and its expression is important for the TGFB/SMAD3 signaling [166]. In this same study [155], circPWWP2A also negatively regulated the expression of miR-223 and subsequently increased the expression of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4). This upregulation of TLR4 expression enhances the TGFB signaling by reducing the TGFB pseudoreceptor, BMP and Activin Membrane-Bound Inhibitor (BAMBI), to sensitize HSCs to TGFB signals [155,167]. Interestingly, another circRNA, circTUBD1, negatively regulates miR-146a-5p action and activates the human HSC cell line proliferation via the TLR4 pathway [157]. Although no direct target was reported in this study [157], the loss of miR-146a-5p expression promoted HSC proliferation and activation via the WNT signaling pathway [56]. Another pro-fibrotic circRNA is the circRSF1 that negatively suppresses the action of miR-146a-5p in human the HSC cell line [156]. The reduced expression of miR-146a-5p causes the increase of Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 (RAC1) expression [156], which previously reported to regulate hepatic fibrosis via the Hh signaling [73]. The identification of more pro-fibrotic circRNAs in the TGFB signaling pathway would offer newer therapeutic targets to prevent HSC activation.
In contrast, some of the circRNAs are antifibrotic by suppressing the TGFB pathway. One such circRNA is the circ_0007874, also known as the cMTO1, reported in the human patients and HSC cell line. This cMTO1 acts as a miR-17-5p sponge and subsequently increases the expression of this miRNA target, the SMAD7 [161]. Since SMAD7 is the negative regulator of the TGFB pathway [83,84], the high expression of cMTO1 is needed to suppress the TGFB signaling. Recently, another circRNA was also reported to regulate SMAD7 expression via the suppression of miRNA expression. CircPSD3 expression was reduced in the activated mouse HSCs, and this circRNA can act as a miR-92b-3p sponge [164]. The loss of circPSD3 expression causes the miR-92b-3p to suppress the expression of Smad7 [161] and consequently activates HSC activation via the TGFB signaling pathway. Another antifibrotic circRNA in the TGFB pathway is the circ_0070963 that acts as a miR-223-3p sponge in the human HSC cell line [162]. The suppression of miR-223-3p causes the increase of LEM Domain Containing 3 (LEMD3) expression [162]. LEMD3 is an antagonist to the TGFB-mediated signaling [168]. Thus, the increase of circ_0070963 expression will suppress the HSC activation.
Another affected pathway for circRNA regulation is the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. One circRNA, circ_0067835, promotes the HSC activation via the suppression of miR-155 expression in the human HSC cell line [153]. This suppression of miR-155 causes the increase of the Forkhead box O3 (FOXO3) transcription factor, which is associated with HSC proliferation via the PI3K/AKT pathway [153,169]. Another circRNA that regulates the PI3K/AKT pathway is the cMTO1, and this circRNA negatively regulates the miR-181b-5p [160]. In this study of CCI(4)-induced mouse models and primary HSC cells [160], the suppression of miR-181b-5p leads to the increase of Pten expression. Since Pten is a negative regulator of the PI3K/AKT pathway [93], circRNA cMTO1 is antifibrotic to suppress the miR-181b-5p action. Similarly, the circFBXW4 negatively regulates miR-18b-3p action, consequently increasing the expression of F-box and WD repeat domain containing 7 (Fbxw7) in the CCI(4)-induced mice [163]. The FBXW7 reduces Sterol regulatory element-binding transcription factor 1 (SREBF1) expression and subsequently suppresses the PI3K/AKT signaling [170,171]. FBXW7 also prevented the ZFP36-mediated autophagy inactivation in isolated murine HSC by acting as a decoy to ZFP36, thus sensitizing the HSCs to a ferroptosis (a program of cell death) [172]. The last reported circRNA is the circ_0004018 that was reduced in the activated primary mouse HSCs [159]. In this study [159], circ_0004018 acts as a miR-660-3p sponge and causes the increase of Telomerase associated protein 1 (Tep1) expression. Although the function of Tep1 in HSC activation is unknown, the increase of both circ_0004018 and Tep1 suppress HSC proliferation [159]. These previous findings show that circRNAs regulate HSC activation via interactions with miRNAs. Even though the current research area is still new, some of these circRNAs are pro-fibrotic, and some are antifibrotic; thus, they could be used as therapeutic targets.
5. Noncoding RNA Interactions in HSCs
Noncoding RNAs’ (ncRNAs) roles in HSC activation and their co-regulatory networks could offer the future development of newer therapeutic targets for hepatic fibrosis treatment. Most of the ncRNAs are involved in the TGFB signaling pathway, with some of these ncRNAs forming the co-regulatory network on the essential regulators. One of these is the regulation of the SMAD7 expression, the negative regulator of the TGFB pathway. The SMAD7 expression is regulated with multiple miRNAs and circRNAs (Figure 1), indicating strict and multi-layer regulation. These findings could offer information on the selection of which RNA molecules inhibit HSC activation and, therefore, treat hepatic fibrosis. For example, miR-17-5p is a profibrotic miRNA that negatively regulates Smad7 expression [29] to promote TGFB signaling. However, higher expression of cMTO1 circular RNA will suppress miR-17-5p action due to endogenous competitive binding or sponging [161]. Thus, increasing cMTO1 expression is an excellent strategy to prevent HSC activation by restoring the Smad7 expression. In addition, LNCRNA-P21 also negatively regulates miR-17-5p action [139]; thus, it can compete with cMTO1 to regulate miR-17-5p action. This competitive binding between the lncRNA and circRNA sponging the miRNA could be used as a new therapeutic target to treat hepatic fibrosis by modulating their interactions and expressions.
In other pathways, another target of cMTO1 and LINCRNA_P21 is the miR-181b, and this miRNA negatively regulates Pten expression [30], a negative modulator of the PI3K/AKT pathway. Like SMAD7, PTEN is also negatively regulated with multiple miRNAs (Figure 1), indicating its important function to suppress HSC activation. Interestingly, Pten is also negatively regulated by miR-23a [39], and for this miRNA, two lncRNAs, Gas5 [39] and Loc102551149 [140] sponge the miR-23a and thus restore Pten expression. A more complicated multi-layer regulation of Pten expression is with the miR-29b action. On the promoter region of the Pten gene, hypermethylation could be induced by the upregulation of the Dnmt3s due to the suppression of miR-29b action [120,132]. Thus, to ensure the Pten gene is hypermethylated and suppressed, four lncRNAs (HOTAIR, Snhg7, Tug1, and XIST) co-regulate the expression of miR-29b [120,132,134,135], and they could be a new target for the development of future drugs for hepatic fibrosis. The manipulation of miR-29b expression to improve or prevent hepatic fibrosis is beneficial, as this miRNA is antifibrotic and could suppress the ECM production and HSC activation. Indeed, a previous study of the mouse fibrosis model showed that inducing miR-29b expression by estrogen treatment in vivo relieved hepatic fibrosis [173]. Therefore, the new strategy or treatment approach is to suppress these four lncRNAs (HOTAIR, Snhg7, Tug1, and XIST) to increase miR-29b action.
In Hh signaling, the core RNA negative regulator is the Meg3 lncRNA. This lncRNA directly binds to the Smo protein to release its suppression on the Sufu, thus allowing the inhibition of Gli-mediated Hh signaling [142]. To further suppress the Smo, MEG3 lncRNA also sponges the miR-122 to increase the expression of Ptch1 [142], which, in turn, also suppresses the Smo action. Thus, restoring Meg3 lncRNA expression will benefit the patients, suppressing the EMT process in HSC activation. In WNT/ Beta-catenin signaling, the core RNA negative regulator is the miR-378a-3p, as this miRNA regulates the critical effectors in the WNT signaling, such as the Wnt10a [76] and Dvl2 [133] proteins. However, this miR-378a-3p action is prevented by the binding of Snhg7 lncRNA [133]. Therefore, suppression of Snhg7 lncRNA expression will prevent HSC activation by suppressing WNT/Beta-catenin signaling.
Although the ncRNAs could potentially be used for therapeutic targets to improve or prevent HSC activation, some challenges and issues exist [174]. One issue is to understand that ncRNAs work in groups and co-regulate each other. From the discussion above, some of these ncRNAs target the same single target and critical molecules. Thus, the identification of these key molecules could efficiently improve the target specificity for the therapeutics development. This prospect is promising, as the ncRNA-based therapy has been successfully implemented in the preclinical studies. One example is a miRNA-based therapy for hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection (Miravirsen) [175]. This Miravirsen is a β-D-oxy-locked nucleic acid (LNA)-modified phosphorothioate antisense oligonucleotide, suppressing miR-122 action and demonstrating significant antiviral activity without evidence of viral resistance [175]. Furthermore, this Miravirsen is currently in phase II clinical investigation [176], thus supporting the potential for more future drugs utilizing the ncRNAs.
Another issue concerns the methodology used to manipulate the therapeutic target expression, particularly the in vivo settings. The specific delivery of these ncRNAs to the liver without affecting other organs is critical. The usage of nanoparticle technology as carriers could address the off-target issue. A mouse study of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) showed that the LNP-DP1, a cationic lipid nanoparticle, could be used as a carrier of miR-122 mimics in vitro and in vivo delivery to reduce the target genes miR-122 [177]. The hepatocytes took in the nanoparticles without any toxicity observed and resulted in an almost 50% reduction of HCC xenografts within 30 days [177]. Similarly, in a mouse model of NAFLD induced by the methionine-choline-deficient diet (MCD), miR-146b expression was significantly reduced. Lactosylated PDMAEMA (a water-soluble cationic polymer) nanoparticles effectively delivered the miR-146b mimic to the hepatocytes in vivo and alleviated the hepatic steatosis [178]. Another possible carrier is the extracellular vesicles (EVs), the naturally occurring small lipid membrane vesicles released by various cells. EVs carry bioactive components, including the ncRNAs in their cargos, and mediate the changes in the recipient cells [179,180]. Studies of EVs released from the normal hepatocyte and taken in by the activated HSCs show that EVs could suppress fibrosis [181,182], suggesting their potential to carry information to improve or prevent fibrosis. From these findings, the advancement of specific delivery tools or technologies will make the usage of ncRNAs-based therapy to suppress liver fibrosis possible.
6. Conclusions
Identifying the essential regulators in HSC activation will provide an excellent window and strategy to treat hepatic fibrosis. Since the fibrosis process is reversible, the restoration of the hepatic function is plausible. In this review, previous findings show that HSC activation is regulated by multi-layer co-regulatory networks between the ncRNAs (circRNA-lncRNA-miRNA), and they could be used to treat liver fibrosis. Using these ncRNAs as the alternative newer treatment drug is possible. The success of some ncRNA-based therapies in the preclinical and clinical trials opens up the potential of using these ncRNAs for future treatment. Therefore, more studies are needed to address the potential of these regulatory ncRNAs as therapeutic targets for the treatment of hepatic fibrosis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.A.S. and N.A.A.M.; writing—original draft preparation, S.A.S., V.D. and K.N.A.G.; writing—review and editing, S.A.S. and N.A.A.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This manuscript was funded by the UKM University Research Grant, grant number: GUP-2021-067.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
A part of the figure is created using BioRender.com via a licensed account.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Weiskirchen, R.; Weiskirchen, S.; Tacke, F. Organ and tissue fibrosis: Molecular signals, cellular mechanisms and translational implications. Mol. Aspects Med. 2019, 65, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parola, M.; Pinzani, M. Liver fibrosis: Pathophysiology, pathogenetic targets and clinical issues. Mol. Aspects Med. 2019, 65, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, B.; He, Q.; Weng, Q. Intercellular crosstalk of hepatic stellate cells in liver fibrosis: New insights into therapy. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 155, 104720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisseleva, T.; Brenner, D.A. Hepatic stellate cells and the reversal of fibrosis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 21, S84–S87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zeng, J.; Xing, L.; Li, C. Extra- and intra-cellular mechanisms of hepatic stellate cell activation. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senoo, H.; Mezaki, Y.; Fujiwara, M. The stellate cell system (vitamin a-storing cell system). Anat. Sci. Int. 2017, 92, 387–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, T.; Narumiya, S. Roles of hepatic stellate cells in liver inflammation: A new perspective. Inflamm. Regen. 2016, 36, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Faubion, W.A.; Gores, G.J. Death receptors in liver biology and pathobiology. Hepatology 1999, 29, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taimr, P.; Higuchi, H.; Kocova, E.; Rippe, R.A.; Friedman, S.; Gores, G.J. Activated stellate cells express the trail receptor-2/death receptor-5 and undergo trail-mediated apoptosis. Hepatology 2003, 37, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saile, B.; Eisenbach, C.; Dudas, J.; El-Armouche, H.; Ramadori, G. Interferon-gamma acts proapoptotic on hepatic stellate cells (hsc) and abrogates the antiapoptotic effect of interferon-alpha by an hsp70-dependant pathway. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 83, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela-Rey, M.; Montiel-Duarte, C.; Osés-Prieto, J.A.; López-Zabalza, M.J.; Jaffrèzou, J.P.; Rojkind, M.; Iraburu, M.J. P38 mapk mediates the regulation of alpha1 (i) procollagen mrna levels by tnf-alpha and tgf-beta in a cell line of rat hepatic stellate cells (1). FEBS Lett. 2002, 528, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sulaiman, S.A.; Muhsin, N.I.A.; Jamal, R. Regulatory non-coding rnas network in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Yang, D.; Fan, X.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Gu, X.; Yang, M. The roles and mechanisms of lncrnas in liver fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farooq, R.; Dongmin, L. Non-coding rna associated competitive endogenous rna regulatory network: Novel therapeutic approach in liver fibrosis. Curr. Gene Ther. 2019, 19, 305–317. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Z.; Dou, G.; Wang, L. Micrornas in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 1851–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomasello, L.; Distefano, R.; Nigita, G.; Croce, C.M. The microrna family gets wider: The isomirs classification and role. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 668648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medley, J.C.; Panzade, G.; Zinovyeva, A.Y. Microrna strand selection: Unwinding the rules. Wiley Interdiscip Rev. RNA 2021, 12, e1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, U.; Kumar, A.; Kulshreshtha, R.; Vivekanandan, P. Biogenesis, characterization, and functions of mirtrons. Wiley Interdiscip Rev. RNA 2021, e1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozomara, A.; Birgaoanu, M.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: From microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 47, D155–D162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chipman, L.B.; Pasquinelli, A.E. Mirna targeting: Growing beyond the seed. Trends Genet. 2019, 35, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ab Mutalib, N.-S.; Sulaiman, S.A.; Jamal, R. Chapter 6—computational tools for microrna target prediction. In Computational Epigenetics and Diseases; Wei, L.K., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 79–105. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Li, J.; Li, C.; Qi, H.; Dong, P.; Zheng, J.; Yu, F. Microrna-125a-5p contributes to hepatic stellate cell activation through targeting fih1. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 38, 1544–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Tan, W.; Cheng, S.; Wang, H.; Ye, S.; Yu, C.; He, Y.; Zeng, J.; Cen, J.; Hu, J.; et al. Upregulation of microrna-126 in hepatic stellate cells may affect pathogenesis of liver fibrosis through the nf-κb pathway. DNA Cell Biol. 2015, 34, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Wang, J.; Lu, H.; Zhang, G.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shang, H.; Ji, H.; Chen, X.; et al. Microrna-130a and -130b enhance activation of hepatic stellate cells by suppressing pparγ expression: A rat fibrosis model study. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 465, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, W.; Wei, S.; Shi, C.; Qiu, J.; Ni, M.; Rao, J.; et al. Mirna-130b-5p promotes hepatic stellate cell activation and the development of liver fibrosis by suppressing sirt4 expression. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 7381–7394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.M.; Li, T.H.; Yun, H.; Ai, H.W.; Zhang, K.H. Mir-140-3p knockdown suppresses cell proliferation and fibrogenesis in hepatic stellate cells via pten-mediated akt/mtor signaling. Yonsei Med. J. 2019, 60, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.; Wang, X.; Si, C.; Duan, Y.; Chen, B.; Liang, H.; Yang, D. Downregulation of mir-141 deactivates hepatic stellate cells by targeting the pten/akt/mtor pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 46, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, R.; Wen, M.; Zhao, M.; Dan, X.; Yang, Z.; Wu, W.; Wang, M.H.; Liu, X.; Yang, L. Mircorna-145 promotes activation of hepatic stellate cells via targeting krüppel-like factor 4. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Guo, Y.; Chen, B.; Dong, P.; Zheng, J. Microrna-17-5p activates hepatic stellate cells through targeting of smad7. Lab. Investig. 2015, 95, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, J.; Wu, C.; Xu, Z.; Xia, P.; Dong, P.; Chen, B.; Yu, F. Hepatic stellate cell is activated by microrna-181b via pten/akt pathway. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 398, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, W.; Guo, K.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fan, J. Mir-181b promotes hepatic stellate cells proliferation by targeting p27 and is elevated in the serum of cirrhosis patients. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 421, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, F.; Chen, Q.; Lu, K.; Osoro, E.K.; Wu, L.; Feng, L.; Zhao, R.; Yang, L.; Zhou, Y.; He, Y.; et al. Inhibition of mir-188-5p alleviates hepatic fibrosis by significantly reducing the activation and proliferation of hscs through pten/pi3k/akt pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 4073–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ma, L.; Wei, R.; Ye, T.; Zhou, J.K.; Wen, M.; Men, R.; Aqeilan, R.I.; Peng, Y.; Yang, L. Twist1-induced mir-199a-3p promotes liver fibrosis by suppressing caveolin-2 and activating tgf-β pathway. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Tang, N.; Wu, K.; Dai, W.; Ye, C.; Shi, J.; Zhang, J.; Ning, B.; Zeng, X.; Lin, Y. Mir-21 simultaneously regulates erk1 signaling in hsc activation and hepatocyte emt in hepatic fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Zheng, W.; Yu, J.; Wang, B.; Chen, L.; Zhuo, Q.; Chen, L.; et al. Microrna-212 activates hepatic stellate cells and promotes liver fibrosis via targeting smad7. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 496, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Yang, X.; Wei, R.; Ye, T.; Zhou, J.K.; Wen, M.; Men, R.; Li, P.; Dong, B.; Liu, L.; et al. Microrna-214 promotes hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis by suppressing sufu expression. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, T.; Enomoto, M.; Fujii, H.; Sekiya, Y.; Yoshizato, K.; Ikeda, K.; Kawada, N. Microrna-221/222 upregulation indicates the activation of stellate cells and the progression of liver fibrosis. Gut 2012, 61, 1600–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.; Xu, H.; Hong, Y. Mir221 regulates tgf-β1-induced hsc activation through inhibiting autophagy by directly targeting lamp2. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 24, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Si, L.; Ma, R.; Bao, L.; Bo, A. Lncrna gas5 restrains ccl(4)-induced hepatic fibrosis by targeting mir-23a through the pten/pi3k/akt signaling pathway. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2019, 316, G539–G550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yan, X.L.; Guo, X.X.; Shi, M.J.; Lu, Y.Y.; Zhou, Q.M.; Chen, Q.L.; Hu, Y.Y.; Xu, L.M.; Huang, S.; et al. Mir-27a as a predictor for the activation of hepatic stellate cells and hepatitis b virus-induced liver cirrhosis. Oncotarget 2017, 9, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, X.; Dou, C.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Tang, H.B. Microrna-503 targets mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 7 enhancing hepatic stellate cell activation and hepatic fibrosis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2021, 66, 1928–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Pan, L.; Li, L.; Hu, S.; Zhou, H.; Yang, C.; Yang, J.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Meng, X.; et al. Microrna-708 modulates hepatic stellate cells activation and enhances extracellular matrix accumulation via direct targeting tmem88. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 7127–7140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Tao, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Q.; Li, L.; Hu, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shu, J.; Zhang, X.; et al. Microrna-708 represses hepatic stellate cells activation and proliferation by targeting zeb1 through wnt/β-catenin pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 871, 172927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Xue, D.; Shen, D.; Ma, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Wu, L.; Pan, K.; Yang, Y.; et al. Microrna-942 mediates hepatic stellate cell activation by regulating bambi expression in human liver fibrosis. Arch. Toxicol. 2018, 92, 2935–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, S.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Chen, J.; Dong, L.; Zang, Y.; et al. Microrna-101 suppresses liver fibrosis by targeting the tgfβ signalling pathway. J. Pathol. 2014, 234, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ghazwani, M.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, J.; Li, J.; Fan, J.; Gandhi, C.R.; Li, S. Mir-122 regulates collagen production via targeting hepatic stellate cells and suppressing p4ha1 expression. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sabater, L.; Locatelli, L.; Oakley, F.; Hardy, T.; French, J.; Robinson, S.M.; Sen, G.; Mann, D.A.; Mann, J. Rna sequencing reveals changes in the micrornaome of transdifferentiating hepatic stellate cells that are conserved between human and rat. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Wang, Y.L.; Xie, C.; Sang, Y.; Li, T.J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, L.; Zhuang, S.M. Identification of a novel tgf-β-mir-122-fibronectin 1/serum response factor signaling cascade and its implication in hepatic fibrogenesis. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 12224–12233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, Z.; Li, L.; Ran, J.; Chu, G.; Gao, H.; Guo, L.; Chen, J. Mir-125b acts as anti-fibrotic therapeutic target through regulating gli3 in vivo and in vitro. Ann. Hepatol. 2019, 18, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.J.; Pan, Q.; Xiong, H.; Qiao, Y.Q.; Bian, Z.L.; Zhong, W.; Sheng, L.; Li, H.; Shen, L.; Hua, J.; et al. Dynamic expression of mir-126 * and its effects on proliferation and contraction of hepatic stellate cells. FEBS Lett. 2013, 587, 3792–3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Du, J.; Niu, X.; Fu, N.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Sun, D.; Nan, Y. Mir-130a-3p attenuates activation and induces apoptosis of hepatic stellate cells in nonalcoholic fibrosing steatohepatitis by directly targeting tgfbr1 and tgfbr2. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, C.; Shu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, R.; Yang, X. The mir-139-5p/peripheral myelin protein 22 axis modulates tgf-β-induced hepatic stellate cell activation and ccl(4)-induced hepatic fibrosis in mice. Life Sci. 2021, 276, 119294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Dan, X.; Men, R.; Ma, L.; Wen, M.; Peng, Y.; Yang, L. Mir-142-3p blocks tgf-β-induced activation of hepatic stellate cells through targeting tgfβri. Life Sci. 2017, 187, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.D.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, X.J.; Liang, Z.C.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, A.; Bi, C.H.; Zhang, L. Microrna-145 inhibits hepatic stellate cell activation and proliferation by targeting zeb2 through wnt/β-catenin pathway. Mol. Immunol. 2016, 75, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Huang, C.; Sun, X.; Long, X.R.; Lv, X.W.; Li, J. Microrna-146a modulates tgf-beta1-induced hepatic stellate cell proliferation by targeting smad4. Cell. Signal. 2012, 24, 1923–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Niu, X.; Wang, Y.; Kong, L.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Nan, Y. Mir-146a-5p suppresses activation and proliferation of hepatic stellate cells in nonalcoholic fibrosing steatohepatitis through directly targeting wnt1 and wnt5a. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.Y.; Chen, Y.H.; Wu, Z.F.; Zhuang, Y.; Chen, G.W.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.G.; Cheng, J.C.; Lin, Q.; Zeng, Z.C. Microrna-146a-5p attenuates fibrosis-related molecules in irradiated and tgf-beta1-treated human hepatic stellate cells by regulating ptpra-src signaling. Radiat. Res. 2019, 192, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Lin, Z.; Dong, P.; Lu, Z.; Gao, S.; Chen, X.; Wu, C.; Yu, F. Activation of hepatic stellate cells is suppressed by microrna-150. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 32, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, X.; Cao, J.; Li, J.; Chu, G. Downregulation of mir-152 contributes to the progression of liver fibrosis via targeting gli3 in vivo and in vitro. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 18, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dai, W.; Zhao, J.; Tang, N.; Zeng, X.; Wu, K.; Ye, C.; Shi, J.; Lu, C.; Ning, B.; Zhang, J.; et al. Microrna-155 attenuates activation of hepatic stellate cell by simultaneously preventing emt process and erk1 signalling pathway. Liver Int. 2015, 35, 1234–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, B.; Nie, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, X.; Li, F.; Wang, M.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H. Mir-193a/b-3p relieves hepatic fibrosis and restrains proliferation and activation of hepatic stellate cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 3824–3832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.C.; Chen, R.; Luo, X.; Li, Z.H.; Luo, S.Z.; Xu, M.Y. Microrna-194 inactivates hepatic stellate cells and alleviates liver fibrosis by inhibiting akt2. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 4468–4480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiya, Y.; Ogawa, T.; Iizuka, M.; Yoshizato, K.; Ikeda, K.; Kawada, N. Down-regulation of cyclin e1 expression by microrna-195 accounts for interferon-β-induced inhibition of hepatic stellate cell proliferation. J. Cell. Physiol. 2011, 226, 2535–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; He, Y.; Ma, T.T.; Huang, C.; Zhang, L.; Li, J. Participation of mir-200a in tgf-β1-mediated hepatic stellate cell activation. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2014, 388, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.J.; Tao, H.; Liu, L.P.; Hu, W.; Deng, Z.Y.; Li, J. Mir-200a controls hepatic stellate cell activation and fibrosis via sirt1/notch1 signal pathway. Inflamm. Res. 2017, 66, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekiya, Y.; Ogawa, T.; Yoshizato, K.; Ikeda, K.; Kawada, N. Suppression of hepatic stellate cell activation by microrna-29b. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 412, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, X.; Zheng, X.; Li, H.; Cao, Z.; Chang, H.; Luan, S.; Zhu, J.; Chen, J.; Zang, Y.; Zhang, J. Microrna-30 protects against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis by attenuating transforming growth factor beta signaling in hepatic stellate cells. Toxicol. Sci. 2015, 146, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Yu, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Cao, S.; Yin, J.; Li, G. Microrna-30a ameliorates hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting beclin1-mediated autophagy. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 3679–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wu, C.Q.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Yao, D.K.; Zhu, L. Loss of expression of mir-335 is implicated in hepatic stellate cell migration and activation. Exp. Cell Res. 2011, 317, 1714–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, B.; Hu, J.; Zhang, T.; Luo, X.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhu, L.; Wu, C.; Liu, W.; Chen, C.; et al. Mirna-338-3p/cdk4 signaling pathway suppressed hepatic stellate cell activation and proliferation. BMC Gastroenterol. 2017, 17, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feili, X.; Wu, S.; Ye, W.; Tu, J.; Lou, L. Microrna-34a-5p inhibits liver fibrosis by regulating tgf-β1/smad3 pathway in hepatic stellate cells. Cell Biol. Int. 2018, 42, 1370–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Wang, W.; Yu, F.; Dong, P.; Chen, B.; Zhou, M.T. Microrna-30a suppresses the activation of hepatic stellate cells by inhibiting epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 46, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Li, J.; Zhao, L.; Deng, Y. Mir-375 affects the hedgehog signaling pathway by downregulating rac1 to inhibit hepatic stellate cell viability and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Yang, J.; Huang, K.; Pan, X.; Chen, B.; Dong, P.; Zheng, J. The epigenetically-regulated microrna-378a targets tgf-β2 in tgf-β1-treated hepatic stellate cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 40, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyun, J.; Wang, S.; Kim, J.; Rao, K.M.; Park, S.Y.; Chung, I.; Ha, C.S.; Kim, S.W.; Yun, Y.H.; Jung, Y. Microrna-378 limits activation of hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis by suppressing gli3 expression. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, F.; Fan, X.; Chen, B.; Dong, P.; Zheng, J. Activation of hepatic stellate cells is inhibited by microrna-378a-3p via wnt10a. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 39, 2409–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.H.; Fu, X.L.; Xue, C.Q. Repression of liver cirrhosis achieved by inhibitory effect of mir-454 on hepatic stellate cells activation and proliferation via wnt10a. J. Biochem. 2019, 165, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, H.; Qiu, J.; Li, C.; Shi, C.; Zhou, S.; Liu, R.; Lu, L. Mir-455-3p alleviates hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis by suppressing hsf1 expression. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 16, 758–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, L.; Yu, L.; Fu, L. Microrna-9 limits hepatic fibrosis by suppressing the activation and proliferation of hepatic stellate cells by directly targeting mrp1/abcc1. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 1698–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, F.; Chen, B.; Fan, X.; Li, G.; Dong, P.; Zheng, J. Epigenetically-regulated microrna-9-5p suppresses the activation of hepatic stellate cells via tgfbr1 and tgfbr2. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 2242–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Wei, S.; Zhou, H.; Li, L.; Zhou, S.; Shi, C.; Shi, Y.; Qiu, J.; Lu, L. Microrna-98 inhibits hepatic stellate cell activation and attenuates liver fibrosis by regulating hlf expression. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabregat, I.; Caballero-Díaz, D. Transforming growth factor-β-induced cell plasticity in liver fibrosis and hepatocarcinogenesis. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, X.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y. Regulation of tgf-beta signaling by smad7. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2009, 41, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, X.; Liao, H.; Cheng, M.; Shi, X.; Lin, X.; Feng, X.-H.; Chen, Y.-G. Smad7 protein interacts with receptor-regulated smads (r-smads) to inhibit transforming growth factor-β (tgf-β)/smad signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayashi, H.; Abdollah, S.; Qiu, Y.; Cai, J.; Xu, Y.Y.; Grinnell, B.W.; Richardson, M.A.; Topper, J.N.; Gimbrone, M.A.; Wrana, J.L.; et al. The mad-related protein smad7 associates with the tgfbeta receptor and functions as an antagonist of tgfbeta signaling. Cell 1997, 89, 1165–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Xie, F.; Zhang, Z.; van Dam, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, F. The regulation of tgf-β/smad signaling by protein deubiquitination. Protein Cell 2014, 5, 503–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, H.; Peng, Z.; Tang, H.; Xie, D.; Jia, Z.; Zhong, L.; Zhao, S.; Ma, Z.; Gao, Y.; Zeng, L.; et al. Loss of klf4 and consequential downregulation of smad7 exacerbate oncogenic tgf-β signaling in and promote progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2017, 36, 2957–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xie, L.; Vo-Ransdell, C.; Abel, B.; Willoughby, C.; Jang, S.; Sowa, G. Caveolin-2 is a negative regulator of anti-proliferative function and signaling of transforming growth factor-β in endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2011, 301, C1161–C1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Corpechot, C.; Barbu, V.; Wendum, D.; Kinnman, N.; Rey, C.; Poupon, R.; Housset, C.; Rosmorduc, O. Hypoxia-induced vegf and collagen i expressions are associated with angiogenesis and fibrogenesis in experimental cirrhosis. Hepatology 2002, 35, 1010–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingyuan, X.; Qianqian, P.; Shengquan, X.; Chenyi, Y.; Rui, L.; Yichen, S.; Jinghong, X. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α activates transforming growth factor-β1/smad s.signaling and increases collagen deposition in dermal fibroblasts. Oncotarget 2017, 9, 3188–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, C.X.; Buddha, H.; Castelino-Prabhu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Britton, R.S.; Bacon, B.R.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A. Activation of insulin-pi3k/akt-p70s6k pathway in hepatic stellate cells contributes to fibrosis in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2017, 62, 968–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reif, S.; Lang, A.; Lindquist, J.N.; Yata, Y.; Gabele, E.; Scanga, A.; Brenner, D.A.; Rippe, R.A. The role of focal adhesion kinase-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-akt signaling in hepatic stellate cell proliferation and type i collagen expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 8083–8090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsuda, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Kitagishi, Y. Roles for pi3k/akt/pten pathway in cell signaling of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. ISRN Endocrinol. 2013, 2013, 472432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foglia, B.; Cannito, S.; Bocca, C.; Parola, M.; Novo, E. Erk pathway in activated, myofibroblast-like, hepatic stellate cells: A critical signaling crossroad sustaining liver fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ying, H.Z.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, W.Y.; Zhang, H.H.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, S.Z.; Fang, J.; Yu, C.H. Pdgf signaling pathway in hepatic fibrosis pathogenesis and therapeutics (review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 7879–7889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chandramouli, S.; Yu, C.Y.; Yusoff, P.; Lao, D.H.; Leong, H.F.; Mizuno, K.; Guy, G.R. Tesk1 interacts with spry2 to abrogate its inhibition of erk phosphorylation downstream of receptor tyrosine kinase signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 1679–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, K.; Guo, M.-G.; Lou, X.-L.; Li, X.-Y.; Xu, Y.; Ji, W.-D.; Huang, X.-D.; Yang, J.-H.; Duan, J.-C. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α induces a tendency of differentiation and activation of rat hepatic stellate cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 5856–5866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Poenisch, M.; Khanal, R.; Hu, Q.; Dai, Z.; Li, R.; Song, G.; Yuan, Q.; Yao, Q.; Shen, X.; et al. Therapeutic hnf4a mrna attenuates liver fibrosis in a preclinical model. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 1420–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monga, S.P. Β-catenin signaling and roles in liver homeostasis, injury, and tumorigenesis. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 1294–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Lamouille, S.; Derynck, R. Tgf-β-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Cell Res. 2009, 19, 156–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelullo, M.; Zema, S.; Nardozza, F.; Checquolo, S.; Screpanti, I.; Bellavia, D. Wnt, notch, and tgf-β pathways impinge on hedgehog signaling complexity: An open window on cancer. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, T.; Leng, X.-S.; Zhu, J.-Y.; Wang, G. Suppression of hedgehog signaling regulates hepatic stellate cell activation and collagen secretion. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 14574–14579. [Google Scholar]
- Tsagakis, I.; Douka, K.; Birds, I.; Aspden, J.L. Long non-coding rnas in development and disease: Conservation to mechanisms. J. Pathol. 2020, 250, 480–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dhanoa, J.K.; Sethi, R.S.; Verma, R.; Arora, J.S.; Mukhopadhyay, C.S. Long non-coding rna: Its evolutionary relics and biological implications in mammals: A review. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2018, 60, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Derrien, T.; Johnson, R.; Bussotti, G.; Tanzer, A.; Djebali, S.; Tilgner, H.; Guernec, G.; Martin, D.; Merkel, A.; Knowles, D.G.; et al. The gencode v7 catalog of human long noncoding rnas: Analysis of their gene structure, evolution, and expression. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 1775–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Xie, S.; Liu, Y.; Xie, Z. Global and cell-type specific properties of lincrnas with ribosome occupancy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 2786–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.H.; Pan, X.; Liu, M.; Wang, S.; Huang, T.; Cai, Y.D. Tissue expression difference between mrnas and lncrnas. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Sun, Z. Novel lincrna discovery and tissue-specific gene expression across 30 normal human tissues. Genes 2021, 12, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.B.T.; Uchida, S. Functional characterization of long noncoding rnas. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2020, 35, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wu, J.; Liangpunsakul, S.; Wang, L. Long non-coding rna in liver metabolism and disease: Current status. Liver Res. 2017, 1, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Wan, L.-Y.; Liang, J.-J.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Ai, W.-B.; Wu, J.-F. The roles of lncrna in hepatic fibrosis. Cell Biosci. 2018, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, S.; Zheng, X.; Gu, S.; Xu, Q.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Fu, B.; Tang, L. Regulatory long non-coding rnas of hepatic stellate cells in liver fibrosis (review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 21, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Han, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, L.; Hu, Z.; Yao, Q.; Cui, H.; Shu, G.; Si, M.; Li, C.; et al. The liver-enriched lnc-lfar1 promotes liver fibrosis by activating tgfβ and notch pathways. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, J.; Luo, Z.; Pan, Y.; Zheng, W.; Li, W.; Zhang, Z.; Xiong, P.; Xu, D.; Du, M.; Wang, B.; et al. H19/mir-148a/usp4 axis facilitates liver fibrosis by enhancing tgf-β signaling in both hepatic stellate cells and hepatocytes. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 9698–9710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhou, F.; Drabsch, Y.; Gao, R.; Snaar-Jagalska, B.E.; Mickanin, C.; Huang, H.; Sheppard, K.A.; Porter, J.A.; Lu, C.X.; et al. Usp4 is regulated by akt phosphorylation and directly deubiquitylates tgf-β type i receptor. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 14, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Zeng, Q.; Hu, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Yan, J.; Li, H.; Yu, Z. Long noncoding rna hottip promotes mouse hepatic stellate cell activation via downregulating mir-148a. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 51, 2814–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Mao, Y.; Dong, P.; Huang, Z.; Yu, F. Long noncoding rna hottip mediates srf expression through sponging mir-150 in hepatic stellate cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 1572–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, C.; Meng, X.; Xu, F.; Li, J. Silent information regulator 1 (sirt1) ameliorates liver fibrosis via promoting activated stellate cell apoptosis and reversion. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2015, 289, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, Q.; Liu, Q.; Kuang, J.; Fang, Y.; Hu, X. A lncrna gpr137b-ps/mir-200a-3p/cxcl14 axis modulates hepatic stellate cell (hsc) activation. Toxicol. Lett. 2021, 336, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Chen, B.; Dong, P.; Zheng, J. Hotair epigenetically modulates pten expression via microrna-29b: A novel mechanism in regulation of liver fibrosis. Mol. Ther. 2017, 25, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bian, E.B.; Wang, Y.Y.; Yang, Y.; Wu, B.M.; Xu, T.; Meng, X.M.; Huang, C.; Zhang, L.; Lv, X.W.; Xiong, Z.G.; et al. Hotair facilitates hepatic stellate cells activation and fibrogenesis in the liver. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 674–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-C.; Luo, S.-Z.; Liu, T.; Lu, L.-G.; Xu, M.-Y. Linc-scrg1 accelerates liver fibrosis by decreasing rna-binding protein tristetraprolin. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 2105–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, N.; Zhao, S.X.; Kong, L.B.; Du, J.H.; Ren, W.G.; Han, F.; Zhang, Q.S.; Li, W.C.; Cui, P.; Wang, R.Q.; et al. Lncrna-atb/microrna-200a/β-catenin regulatory axis involved in the progression of hcv-related hepatic fibrosis. Gene 2017, 618, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Lu, Z.; Cai, J.; Huang, K.; Chen, B.; Li, G.; Dong, P.; Zheng, J. Malat1 functions as a competing endogenous rna to mediate rac1 expression by sequestering mir-101b in liver fibrosis. Cell Cycle 2015, 14, 3885–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, T.; Lin, H.; Chen, X.; Li, G.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, L.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, K.; Hong, W.; Han, T.; et al. Lncrna meg8 suppresses activation of hepatic stellate cells and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocytes via the notch pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 521, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Jiang, Z.; Chen, B.; Dong, P.; Zheng, J. Neat1 accelerates the progression of liver fibrosis via regulation of microrna-122 and kruppel-like factor 6. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 95, 1191–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Huang, F.; Zhang, R.; Luo, H. Lncrna neat1 expedites the progression of liver fibrosis in mice through targeting mir-148a-3p and mir-22-3p to upregulate cyth3. Cell Cycle 2021, 20, 490–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wei, S.; Li, L.; Bu, Q.; Zhou, H.; Su, W.; Liu, Z.; Wang, M.; Lu, L. Mir-139-5p sponged by lncrna neat1 regulates liver fibrosis via targeting β-catenin/sox9/tgf-β1 pathway. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Yu, F.; Dong, P.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zheng, L. Long non-coding rna pvt1 activates hepatic stellate cells through competitively binding microrna-152. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 62886–62897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, F.; Lu, Z.; Chen, B.; Wu, X.; Dong, P.; Zheng, J. Salvianolic acid b-induced microrna-152 inhibits liver fibrosis by attenuating dnmt1-mediated patched1 methylation. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2015, 19, 2617–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Han, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Shao, S.; Yao, Q.; Zheng, L.; Wang, J.; Han, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Scarna10, a nuclear-retained long non-coding rna, promotes liver fibrosis and serves as a potential biomarker. Theranostics 2019, 9, 3622–3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Wu, Y.; Liu, S.; Lai, Y.; Tang, S. Lncrna-snhg7/mir-29b/dnmt3a axis affects activation, autophagy and proliferation of hepatic stellate cells in liver fibrosis. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2021, 45, 101469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Dong, P.; Mao, Y.; Zhao, B.; Huang, Z.; Zheng, J. Loss of lncrna-snhg7 promotes the suppression of hepatic stellate cell activation via mir-378a-3p and dvl2. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 17, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, X.; Hong, Y.; Zhang, K. Tug1 is involved in liver fibrosis and activation of hscs by regulating mir-29b. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 503, 1394–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.Y.; Wang, F.F.; Xiao, Z.H.; Liu, S.F.; Lai, Y.L.; Tang, S.L. Long noncoding rna xist enhances ethanol-induced hepatic stellate cells autophagy and activation via mir.r.r.r-29b/hmgb1 axis. IUBMB Life 2019, 71, 1962–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Zheng, J.; Mao, Y.; Dong, P.; Lu, Z.; Li, G.; Guo, C.; Liu, Z.; Fan, X. Long non-coding rna growth arrest-specific transcript 5 (gas5) inhibits liver fibrogenesis through a mechanism of competing endogenous rna. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 28286–28298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.-Q.; Xu, M.-Y.; Qu, Y.; Hu, J.-J.; Li, Z.-H.; Zhang, Q.-D.; Lu, L.-G. Tet3 mediates the activation of human hepatic stellate cells via modulating the expression of long non-coding rna hif1a-as1. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 7744–7751. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Lu, Z.; Chen, B.; Dong, P.; Zheng, J. Identification of a novel lincrna-p21-mir-181b-pten signaling cascade in liver fibrosis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 9856538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, F.; Guo, Y.; Chen, B.; Shi, L.; Dong, P.; Zhou, M.; Zheng, J. Lincrna-p21 inhibits the wnt/β-catenin pathway in activated hepatic stellate cells via sponging microrna-17-5p. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 41, 1970–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Li, S.; Si, L.; Ma, R.; Bao, L.; Bo, A. Identification lncrna loc102551149/mir-23a-5p pathway in hepatic fibrosis. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 50, e13243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wu, Y.; Huang, C.; Meng, X.M.; Ma, T.; Wu, B.M.; Xu, F.; Zhang, L.; Lv, X.W.; Li, J. Inhibitory effects of long noncoding rna meg3 on hepatic stellate cells activation and liver fibrogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1842, 2204–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, F.; Geng, W.; Dong, P.; Huang, Z.; Zheng, J. Lncrna-meg3 inhibits activation of hepatic stellate cells through smo protein and mir-212. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Lu, Z.; Huang, K.; Wang, X.; Xu, Z.; Chen, B.; Dong, P.; Zheng, J. Microrna-17-5p-activated wnt/β-catenin pathway contributes to the progression of liver fibrosis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Machado, M.V.; Diehl, A.M. Hedgehog signalling in liver pathophysiology. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 550–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patop, I.L.; Wüst, S.; Kadener, S. Past, present, and future of circrnas. Embo J. 2019, 38, e100836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santer, L.; Bär, C.; Thum, T. Circular rnas: A novel class of functional rna molecules with a therapeutic perspective. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27, 1350–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abu, N.; Jamal, R. Circular rnas as promising biomarkers: A mini-review. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragan, C.; Goodall, G.J.; Shirokikh, N.E.; Preiss, T. Insights into the biogenesis and potential functions of exonic circular rna. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, S.A.; Abdul Murad, N.A.; Mohamad Hanif, E.A.; Abu, N.; Jamal, R. Prospective advances in circular rna investigation. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1087, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Yuan, X.; Cai, Q.; Tang, C.; Gao, J. Circular rna as an epigenetic regulator in chronic liver diseases. Cells 2021, 10, 1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.Y.; Wang, S.W.; Hu, M.Y.; Jiang, Z.L.; Shen, L.L.; Zhou, Y.P.; Guo, J.M.; Hu, Y.R. Circular rnas in liver diseases: Mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Life Sci. 2021, 264, 118707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.; Xia, L.; Sun, M.; Yang, C.; Wang, F. Circular rna in liver: Health and diseases. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1087, 245–257. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Ren, T.; Zhu, Z.; Cheng, M.; Mou, Q.; Mu, M.; Liu, Y.; Yao, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, B.; et al. Thymosin-β4 mediates hepatic stellate cell activation by interfering with circrna-0067835/mir-155/foxo3 signaling pathway. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 51, 1389–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yuan, B.; Wu, Z.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, Z. Microarray profiling of circular rnas and the potential regulatory role of hsa_circ_0071410 in the activated human hepatic stellate cell induced by irradiation. Gene 2017, 629, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Feng, R.; Li, X.; Li, D.; Zhai, W. Tgf-β- and lipopolysaccharide-induced upregulation of circular rna pwwp2a promotes hepatic fibrosis via sponging mir-203 and mir-223. Aging 2019, 11, 9569–9580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yuan, B.; Chen, G.; Zhang, L.; Zhuang, Y.; Niu, H.; Zeng, Z. Circular rna rsf1 promotes inflammatory and fibrotic phenotypes of irradiated hepatic stellate cell by modulating mir-146a-5p. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 8270–8282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.H.; Yuan, B.Y.; Wu, Z.F.; Cheng, J.C.; Lin, Q.; Zeng, Z.C. Circular rna tubd1 acts as the mir-146a-5p sponge to affect the viability and pro-inflammatory cytokine production of lx-2 cells through the tlr4 pathway. Radiat. Res. 2020, 193, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.N.; Xu, J.J.; Wang, A.; Li, J.J.; Wu, S.; Wu, Y.Y.; Li, X.F.; Huang, C.; et al. Circular rna circube2k promotes hepatic fibrosis via sponging mir-149-5p/tgf-β2 axis. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Song, F.; Lei, X.; Li, J.; Li, F.; Tan, H. Hsa_circ_0004018 suppresses the progression of liver fibrosis through regulating the hsa-mir-660-3p/tep1 axis. Aging 2020, 12, 11517–11529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Li, C.; Dong, P.; Huang, J.; Yu, J.; Zheng, J. Circular rna cmto1 promotes pten expression through sponging mir-181b-5p in liver fibrosis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Dong, R.; Guo, Y.; He, J.; Shao, C.; Yi, P.; Yu, F.; Gu, D.; Zheng, J. Circmto1 inhibits liver fibrosis via regulation of mir-17-5p and smad7. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 5486–5496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, D.; Chen, G.F.; Wang, J.C.; Ji, S.H.; Wu, X.W.; Lu, X.J.; Chen, J.L.; Li, J.T. Hsa_circ_0070963 inhibits liver fibrosis via regulation of mir-223-3p and lemd3. Aging 2020, 12, 1643–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, H.D.; Bu, F.T.; Li, X.F.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, S.; Wang, J.N.; Chen, S.Y.; Sun, Y.Y.; Pan, X.Y.; et al. Circular rna circfbxw4 suppresses hepatic fibrosis via targeting the mir-18b-3p/fbxw7 axis. Theranostics 2020, 10, 4851–4870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, F.T.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, A.; Zhang, Y.F.; You, H.M.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.R.; Huang, C.; Li, J. Circular rna circpsd3 alleviates hepatic fibrogenesis by regulating the mir-92b-3p/smad7 axis. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2021, 23, 847–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatima, A.; Irmak, D.; Noormohammadi, A.; Rinschen, M.M.; Das, A.; Leidecker, O.; Schindler, C.; Sánchez-Gaya, V.; Wagle, P.; Pokrzywa, W.; et al. The ubiquitin-conju.ugating enzyme ube2k determines neurogenic potential through histone h3 in human embryonic stem cells. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, H.; Liu, X.; Guo, H. Knockdown of fstl1 attenuates hepatic stellate cell activation through the tgf-β1/smad3 signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 7119–7123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seki, E.; De Minicis, S.; Österreicher, C.H.; Kluwe, J.; Osawa, Y.; Brenner, D.A.; Schwabe, R.F. Tlr4 enhances tgf-β signaling and hepatic fibrosis. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 1324–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, D.M.; Moretti, L.; Zhang, J.J.; Cooper, S.W.; Chambers, D.M.; Santangelo, P.J.; Barker, T.H. Lem domain-containing protein 3 antagonizes tgfβ-smad2/3 signaling in a stiffness-dependent manner in both the nucleus and cytosol. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 15867–15886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, B.; Wang, G.; Zhang, J.; Cao, W.; Chen, X. Resveratrol decreases foxo protein expression through pi3k-akt-dependent pathway inhibition in H2O2-treated synoviocytes. Histol. Histopathol. 2017, 32, 1305–1315. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Yang, J.; Li, F.; Zhu, L.; Hao, J.; Gao, F. Fbxw7 mediates high glucose-induced srebp-1 expression in renal tubular cells of diabetic nephropathy under pi3k/akt pathway regulation. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundqvist, A.; Bengoechea-Alonso, M.T.; Ye, X.; Lukiyanchuk, V.; Jin, J.; Harper, J.W.; Ericsson, J. Control of lipid metabolism by phosphorylation-dependent degradation of the srebp family of transcription factors by scf(fbw7). Cell Metab. 2005, 1, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Guo, M.; Li, Y.; Shen, M.; Kong, D.; Shao, J.; Ding, H.; Tan, S.; Chen, A.; Zhang, F.; et al. Rna-binding protein zfp36/ttp protects against ferroptosis by regulating autophagy signaling pathway in hepatic stellate cells. Autophagy 2020, 16, 1482–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, L.; Zhu, D.; Li, X.; Gu, H.; Zhang, C.Y.; Zen, K. Protective role of estrogen-induced mirna-29 expression in carbon tetrachloride-induced mouse liver injury. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 14851–14862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; He, Y.; Mackowiak, B.; Gao, B. Micrornas as regulators, biomarkers and therapeutic targets in liver diseases. Gut 2021, 70, 784–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, H.L.; Reesink, H.W.; Lawitz, E.J.; Zeuzem, S.; Rodriguez-Torres, M.; Patel, K.; van der Meer, A.J.; Patick, A.K.; Chen, A.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Treatment of hcv infection by targeting microrna. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1685–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ottosen, S.; Parsley, T.B.; Yang, L.; Zeh, K.; van Doorn, L.J.; van der Veer, E.; Raney, A.K.; Hodges, M.R.; Patick, A.K. In vitro antiviral activity and preclinical and clinical resistance profile of miravirsen, a novel anti-hepatitis c virus therapeutic targeting the human factor mir-122. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hsu, S.H.; Yu, B.; Wang, X.; Lu, Y.; Schmidt, C.R.; Lee, R.J.; Lee, L.J.; Jacob, S.T.; Ghoshal, K. Cationic lipid nanoparticles for therapeutic delivery of sirna and mirna to murine liver tumor. Nanomedicine 2013, 9, 1169–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, S.; Guo, W.; Deng, F.; Chen, K.; Jiang, Y.; Dong, M.; Peng, L.; Chen, X. Targeted delivery of microrna 146b mimic to hepatocytes by lactosylated pdmaema nanoparticles for the treatment of nafld. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, L.A.; Sorich, M.J.; Rowland, A. Role of extracellular vesicles in the pathophysiology, diagnosis and tracking of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorairaj, V.; Sulaiman, S.A.; Abu, N.; Abdul Murad, N.A. Extracellular vesicles in the development of the non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: An update. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, R.; Kemper, S.; Brigstock, D.R. Extracellular vesicles from hepatocytes are therapeutic for toxin-mediated fibrosis and gene expression in the liver. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, R.; Kemper, S.; Brigstock, D.R. Structural and functional characterization of fibronectin in extracellular vesicles from hepatocytes. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 640667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).