Characterization of Exopolysaccharides Isolated from Donkey Milk and Its Biological Safety for Skincare Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Extraction of Exolysaccharides
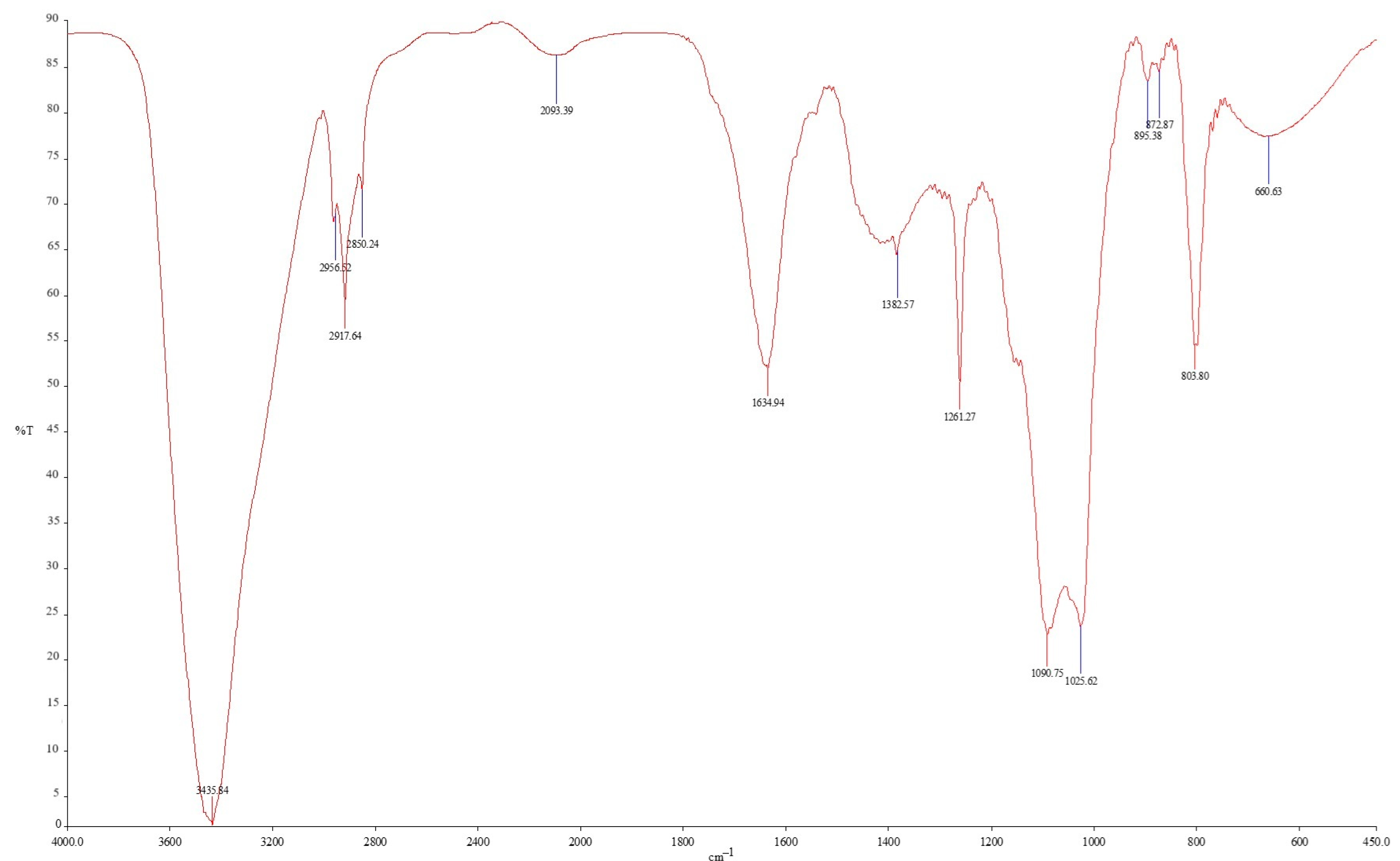
2.2. Fourier Transform Infrared
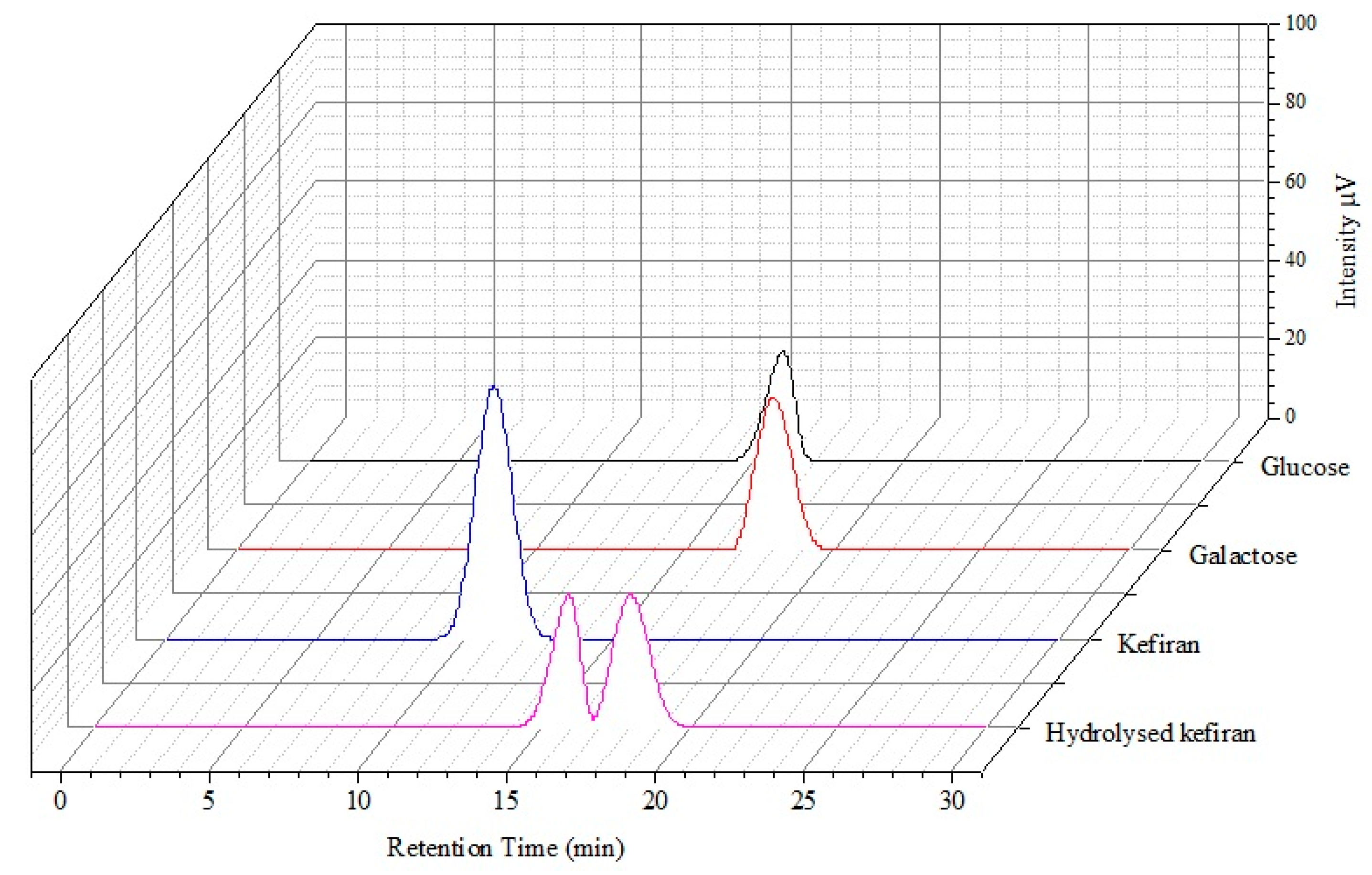
2.3. Monosaccharide Composition
2.4. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
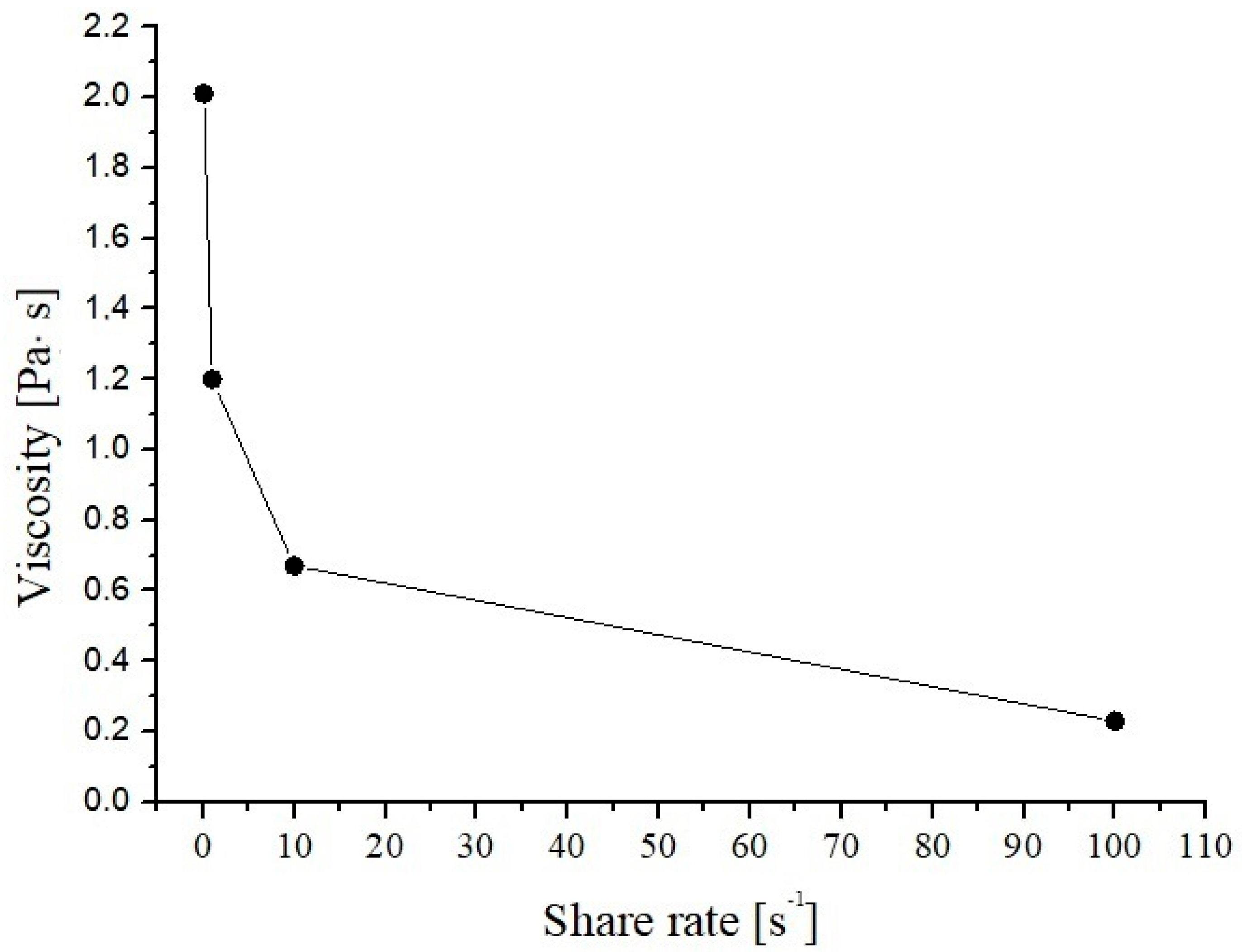
2.5. Rheological Measurement
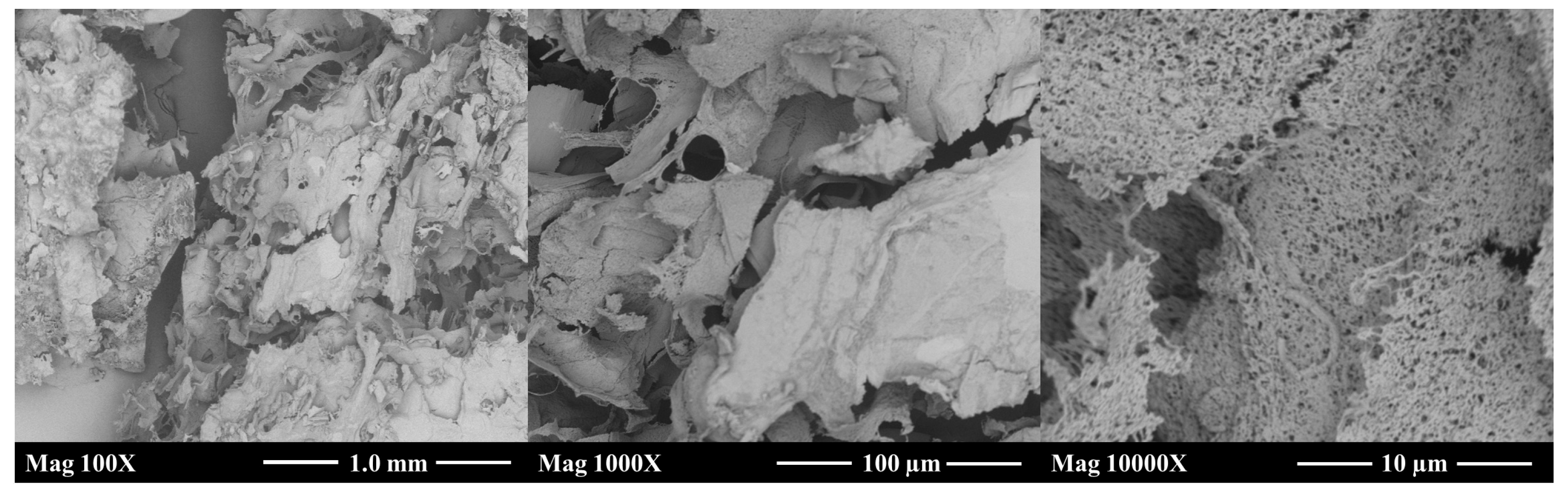
2.6. Scanning Electron Microscope Measurement
2.7. Molecular Weight Evaluetion
2.8. Haemolysis Assay
2.9. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Yield of Polysaccharides from Kefir Grains
3.2. Polymer Structural Analysis by FTIR Spectroscopy
3.3. Identification of Monosaccharide
3.4. Thermal Capacity of Donkey Milk Kefiran
3.5. Rheological Properties of Donkey Milk Kefiran
3.6. Morphological Propierties of Donkey Milk Kefiran
3.7. Molecular Weight Assessment
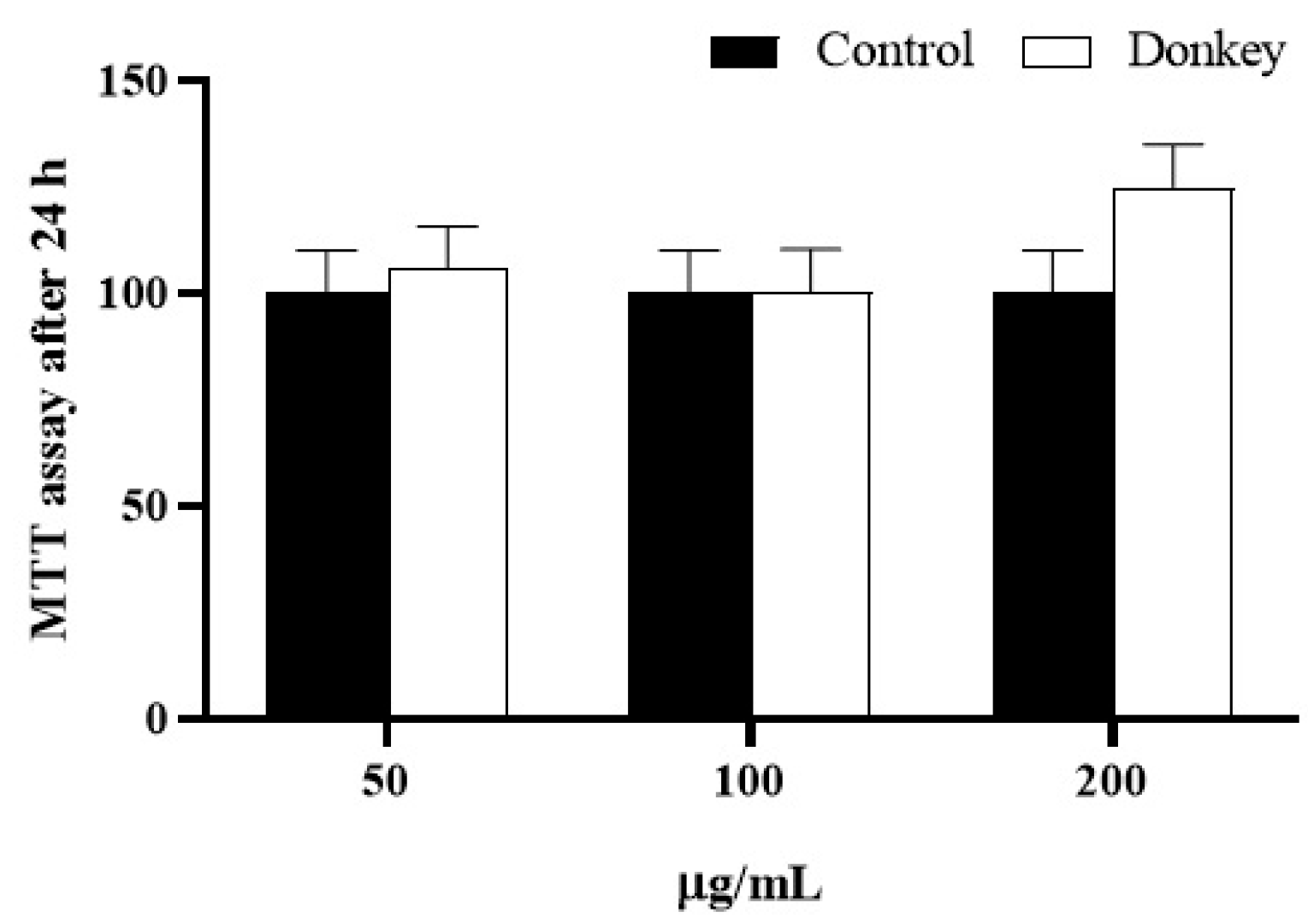
3.8. Biological Properties of Donkey Milk Kefiran
3.9. Cytotoxicity Assessment of Donkey Milk Kefiran
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fazio, A.; La Torre, C.; Caroleo, M.C.; Caputo, P.; Cannataro, R.; Plastina, P.; Cione, E. Effect of Addition of Pectins from Jujubes (Ziziphus jujube Mill.) on Vitamin C Production during Heterolactic Fermentation. Molecules 2020, 25, 2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentry, B.; Cazón, P.; O’Brien, K. A comprehensive review of the production, beneficial properties, and applications of kefiran, the kefir grain exopolysaccharide. Int. Dairy J. 2023, 144, 105691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koc, E.O.; Inal, M. Physicochemical properties of polysaccharide kefiran isolated from kefir grains biomass. Int. J. Biotechnol. Biomater. Eng. 2021, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- de Lima Barros, S.É.; dos Santos Rocha, C.; de Moura, M.S.B.; Barcelos, M.P.; de Paula da Silva, C.H.T.; da Silva Hage-Melim, L.I. Potential beneficial effects of kefir and its postbiotic, kefiran, on child food allergy. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 3770–3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, E.; Farooq, M.; Joe Dailin, D.; El Enshasy, H.; Othman, N.; Malek, R.A.; Danial, E.; Wadaan, M. In vitro and in vivo biological screening of kefiran polysaccharide produced by Lactobacillus kefiranofaciens. Biomed. Res. 2017, 28, 594–600. [Google Scholar]
- Gagliarini, N.; Diosma, G.; Garrote, G.L.; Abraham, A.G.; Piermaria, J. Whey protein-kefiran films as driver of probiotics to the gut. LWT 2019, 105, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemlou, M.; Khodaiyan, F.; Oromiehie, A. Physical, mechanical, barrier, and thermal properties of polyol-plasticized biodegradable edible film made from kefiran. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 84, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piermaría, J.; Bengoechea, C.; Abraham, A.G.; Guerrero, A. Shear and extensional properties of kefiran. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 152, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhouani, H.; Bicho, D.; Gonçalves, C.; Maia, F.; Reis, R.L.; Oliveira, J. Kefiran cryogels as potential scaffolds for drug delivery and tissue engineering applications. Mater. Today Commun. 2019, 20, 100554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Cheng, N.; Fang, D.; Wang, H.; Rahman, F.-U.; Hao, H.; Zhang, Y. Recent advances on application of polysaccharides in cosmetics. J. Dermatol. Sci. Cosmet. Technol. 2024, 1, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morone, J.; Lopes, G.; Preto, M.; Vasconcelos, V.; Martins, R. Exploitation of Filamentous and Picoplanktonic Cyanobacteria for Cosmetic Applications: Potential to Improve Skin Structure and Preserve Dermal Matrix Components. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erginer, M.; Gökalsin, B.; Tornaci, S.; Sesal, C.; Öner, E.T. Exploring the potential of Halomonas levan and its derivatives as active ingredients in cosmeceutical and skin regenerating formulations. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 240, 124418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-S.; Wang, X.-M.; Han, Z.-P.; Zhao, M.-X.; Yin, L. Purification, antioxidant and moisture-preserving activities of polysaccharides from papaya. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 2332–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Guo, Q.; Xin, Y.; Liu, Y. Comprehensive review in moisture retention mechanism of polysaccharides from algae, plants, bacteria and fungus. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 104163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Yong, J.; Lv, B.; Guo, S.; You, L.; Cheung, P.C.; Kulikouskaya, V.I. Enhanced In Vitro Anti-Photoaging Effect of Degraded Seaweed Polysaccharides by UV/H2O2 Treatment. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flom, J.; Sicherer, S. Epidemiology of Cow’s Milk Allergy. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirrincione, S.; Luganini, A.; Lamberti, C.; Manfredi, M.; Cavallarin, L.; Giuffrida, M.G.; Pessione, E. Donkey Milk Fermentation by Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris and Lactobacillus rhamnosus Affects the Antiviral and Antibacterial Milk Properties. Molecules 2021, 26, 5100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Torre, C.; Fazio, A.; Caputo, P.; Plastina, P.; Caroleo, M.C.; Cannataro, R.; Cione, E. Effects of Long-Term Storage on Radical Scavenging Properties and Phenolic Content of Kombucha from Black Tea. Molecules 2021, 26, 5474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Torre, C.; Plastina, P.; Cione, E.; Bekatorou, A.; Petsi, T.; Fazio, A. Improved Antioxidant Properties and Vitamin C and B12 Content from Enrichment of Kombucha with Jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill.) Powder. Fermentation 2024, 10, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Torre, C.; Fazio, A.; Caputo, P.; Tursi, A.; Formoso, P.; Cione, E. Influence of Three Extraction Methods on the Physicochemical Properties of Kefirans Isolated from Three Types of Animal Milk. Foods 2022, 11, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazio, A.; La Torre, C.; Dalena, F.; Plastina, P. Screening of glucan and pectin contents in broad bean (Vicia faba L.) pods during maturation. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2020, 246, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gors, S.; Kucia, M.; Langhammer, M.; Junghans, P.; Metges, C.C. Technical note: Milk composition in mice—Methodological aspects and effects of mouse strain and lactation day. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 632–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Torre, C.; Caputo, P.; Plastina, P.; Cione, E.; Fazio, A. Green Husk of Walnuts (Juglans regia L.) from Southern Italy as a Valuable Source for the Recovery of Glucans and Pectins. Fermentation 2021, 7, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Torre, C.; Caputo, P.; Cione, E.; Fazio, A. Comparing Nutritional Values and Bioactivity of Kefir from Different Types of Animal Milk. Molecules 2024, 29, 2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niknam, R.; Mousavi, M.; Kiani, H. Intrinsic viscosity, steady and oscillatory shear rheology of a new source of galactomannan isolated from Gleditsia caspica (Persian honey locust) seeds in aqueous dispersions. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2021, 247, 2579–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sæbø, I.P.; Bjørås, M.A.-O.; Franzyk, H.A.-O.; Helgesen, E.; Booth, J.A. Optimization of the Hemolysis Assay for the Assessment of Cytotoxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perri, M.; Pingitore, A.; Cione, E.; Vilardi, E.; Perrone, V.; Genchi, G. Proliferative and anti-proliferative effects of retinoic acid at doses similar to endogenous levels in Leydig MLTC-1/R2C/TM-3 cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1800, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.H.; Yen, C.C.; Chen, H.L.; Liu, Y.H.; Chen, Y.H.; Lan, Y.W.; Chen, K.R.; Chen, W.; Chen, C.M. Novel Kefir Exopolysaccharides (KEPS) Mitigate Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Systemic Inflammation in Luciferase Transgenic Mice through Inhibition of the NF-κB Pathway. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nataraj, S.; Schomacker, R.; Kraume, M.; Mishra, I.M.; Drews, A. Analyses of polysaccharide fouling mechanisms during crossflow membrane filtration. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 308, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J. Characterization of polysaccharide fractions from Allii macrostemonis bulbus and assessment of their antioxidant. LWT 2022, 165, 113687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Shang, Z.; Zhao, J. Classification and identification of Rhodobryum roseum Limpr. and its adulterants based on fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and chemometrics. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radhouani, H.; Goncalves, C.; Maia, F.R.; Oliveira, J.M.; Reis, R.L. Kefiran biopolymer: Evaluation of its physicochemical and biological properties. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2018, 33, 461–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidović, S.Z.; Miljković, M.G.; Antonović, D.G.; Rajilić-Stojanović, M.D.; Dimitrijević-Branković, S.I. Water Kefir grain as a source of potent dextran producing lactic acid bacteria. Chem. Ind. 2015, 69, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, C.R.; Salanta, L.; Rotar, A.M.; Semeniuc, C.A.; Socaciu, C.; Sindic, M. Influence of extraction conditions on characteristics of microbial polysaccharide kefiran isolated from kefir grains biomass. J. Food Nutr. Res. 2016, 55, 121–130. [Google Scholar]
- Prado, M.R.M.; Boller, C.; Zibetti, R.G.M.; de Souza, D.; Pedroso, L.L.; Soccol, C.R. Anti-inflammatory and angiogenic activity of polysaccharide extract obtained from Tibetan kefir. Microvasc. Res. 2016, 108, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Chen, R.; Tang, C.; Li, L.-Q.; Yan, J.-K.; Zhang, H. Polysaccharide extracted from cultivated Sanghuangporous vaninii spores using three-phase partitioning with enzyme/ultrasound pretreatment: Physicochemical characteristics and its biological activity in vitro. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muksing, N.; Nithitanakul, M.; Grady, B.P.; Magaraphan, R. Melt rheology and extrudate swell of organobentonite-filled polypropylene nanocomposites. Polym. Test. 2008, 27, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piermaria, J.; Pinotti, A.; García, M.; Abraham, A. Films based on kefiran, an exopolysaccharide obtained from kefir grain: Development and characterization. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, M.U.; Wood, P.J.; Weisz, J. A simple and rapid method for evaluation of Mark–Houwink–Sakurada constants of linear random coil polysaccharides using molecular weight and intrinsic viscosity determined by high performance size exclusion chromatography: Application to guar galactomannan. Carbohydr. Polym. 1999, 39, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özen, S.; Ünlü, A.; Özbek, H.; Gögüs, F. β-Glucan Extraction from Hull-Less Barley by a Novel Approach: Microwave-Assisted Pressurized CO2/H2O. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2024, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, E.; López, D.; Mijangos, C.; Duskova-Smrckova, M.; Ilavsky, M.; Dusek, K. Rheological and thermal properties of agarose aqueous solutions and hydrogels. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2008, 46, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X. Biocompatibility and characteristics of injectable chitosan-based thermosensitive hydrogel for drug delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 1643–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.; Steinle, H.; Golombek, S.; Hann, L.; Schlensak, C.; Wendel, H.; Avci-Adali, M. Blood Contacting Biomaterials: In Vitro Evaluation of the Hemocompatibility. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2018, 6, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, R.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Javeed, A.; Chen, J.; Han, B. Dynamic dual-crosslinking antibacterial hydrogel with enhanced bio-adhesion and self-healing activities for rapid hemostasis in vitro and in vivo. Mater. Des. 2023, 233, 112244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhouani, H.; Correia, S.; Gonçalves, C.; Reis, R.L.; Oliveira, J.M. Synthesis and Characterization of Biocompatible Methacrylated Kefiran Hydrogels: Towards Tissue Engineering Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazio, A.; La Torre, C.; Caroleo, M.C.; Caputo, P.; Plastina, P.; Cione, E. Isolation and Purification of Glucans from an Italian Cultivar of Ziziphus jujuba Mill. and In Vitro Effect on Skin Repair. Molecules 2020, 25, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoh, A.; Maier, K. Comparative Cytotoxicity Test with Human Keratinocytes, HaCaT Cells, and Skin Fibroblasts to Investigate Skin-Irritating Substances. In Cell and Tissue Culture Models in Dermatological Research; Bernd, A., Bereiter-Hahn, J., Hevert, F., Holzmann, H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993; pp. 341–347. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, J.; Liu, W.; Ding, Q.; Sun, S.; Zhang, S.; Wang, N.; Wang, Y.; Xi, S.; Liu, C.; et al. A Phellinus igniarius polysaccharide/chitosan-arginine hydrogel for promoting diabetic wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 249, 126014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ni, G.; Xu, J.; Tian, Y.; Liu, X.; Gao, J.; Gao, Q.; Shen, Y.; Yan, Z. Sulfated modification, basic characterization, antioxidant and anticoagulant potentials of polysaccharide from Sagittaria trifolia. Arab. J. Chem. 2023, 16, 104812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Samples Kefiran Polymer | Haemolysis Rate (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Donkey | Cow (Reference Sample) | p-Value | |
| 50 µg/mL | 1.48 ± 0.04 | 1.76 ± 0.09 | ** p < 0.01 |
| 100 µg/mL | 1.71 ± 0.14 | 1.94 ± 0.02 | * p < 0.05 |
| 200 µg/mL | 1.87 ± 0.06 | 2.04 ± 0.08 | ns |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
La Torre, C.; Plastina, P.; Abrego-Guandique, D.M.; Caputo, P.; Oliviero Rossi, C.; Saraceno, G.F.; Caroleo, M.C.; Cione, E.; Fazio, A. Characterization of Exopolysaccharides Isolated from Donkey Milk and Its Biological Safety for Skincare Applications. Polysaccharides 2024, 5, 493-503. https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides5030031
La Torre C, Plastina P, Abrego-Guandique DM, Caputo P, Oliviero Rossi C, Saraceno GF, Caroleo MC, Cione E, Fazio A. Characterization of Exopolysaccharides Isolated from Donkey Milk and Its Biological Safety for Skincare Applications. Polysaccharides. 2024; 5(3):493-503. https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides5030031
Chicago/Turabian StyleLa Torre, Chiara, Pierluigi Plastina, Diana Marisol Abrego-Guandique, Paolino Caputo, Cesare Oliviero Rossi, Giorgia Francesca Saraceno, Maria Cristina Caroleo, Erika Cione, and Alessia Fazio. 2024. "Characterization of Exopolysaccharides Isolated from Donkey Milk and Its Biological Safety for Skincare Applications" Polysaccharides 5, no. 3: 493-503. https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides5030031
APA StyleLa Torre, C., Plastina, P., Abrego-Guandique, D. M., Caputo, P., Oliviero Rossi, C., Saraceno, G. F., Caroleo, M. C., Cione, E., & Fazio, A. (2024). Characterization of Exopolysaccharides Isolated from Donkey Milk and Its Biological Safety for Skincare Applications. Polysaccharides, 5(3), 493-503. https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides5030031












