Blockade of the Proximal Pancreatic C Fiber Enhances Insulin Sensitivity in Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Treatment
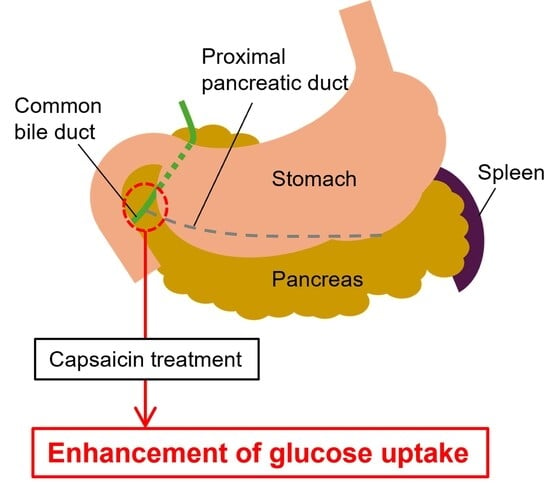
2.2. Determination of the Site of C Fiber Blockade
2.3. Measurement of Insulin Sensitivity Under C Fiber Blockade
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
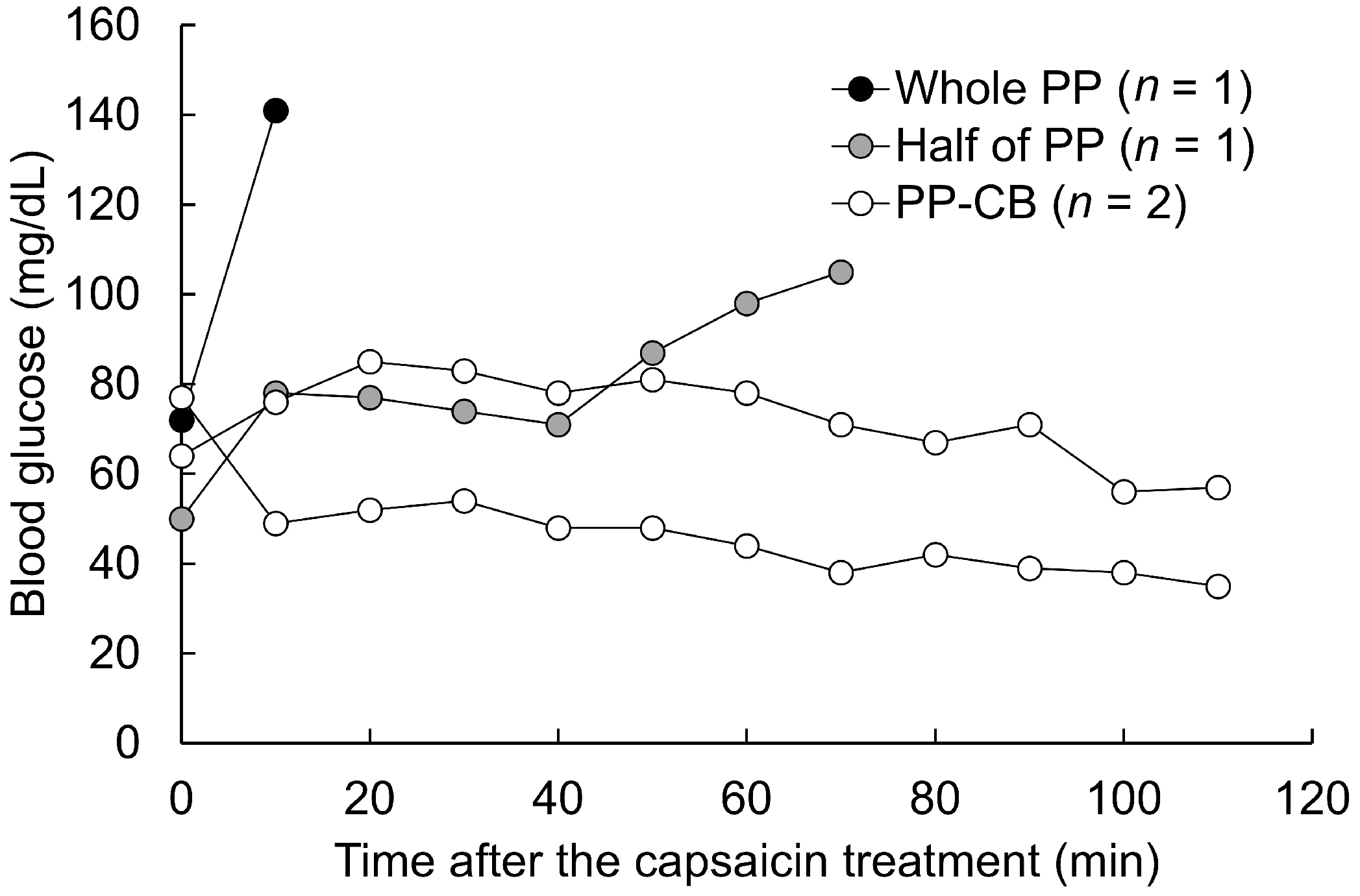
3.1. Pilot Study
3.2. Measurement of Insulin Sensitivity Under C Fiber Blockade in the Proximal Pancreatic Duct and Common Bile Duct
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CB | Common bile duct |
| GIR | Glucose infusion rate |
| PP | Proximal pancreas |
References
- Uysal, K.T.; Wiesbrock, S.M.; Marino, M.W.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Protection from obesity-induced insulin resistance in mice lacking TNF-α function. Nature 1997, 389, 610–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maegawa, H.; Shigeta, Y.; Egawa, K.; Kobayashi, M. Impaired autophosphorylation of insulin receptors from abdominal skeletal muscles in nonobese subjects with NIDDM. Diabetes 1991, 40, 815–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yki-Järvinen, H.; Daniels, M.C.; Virkamäki, A.; Mäkimattila, S.; DeFronzo, R.A.; McClain, D. Increased glutamine: Fructose-6-phosphatase amidotransferase activity in skeletal muscle of patients with NIDDM. Diabetes 1996, 45, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaburagi, Y.; Satoh, S.; Tamemoto, H.; Yamamoto-Honda, R.; Tobe, K.; Veki, K.; Yamauchi, T.; Kono-Sugita, E.; Sekihara, H.; Aizawa, S.; et al. Role of insulin receptor substrate-1 and pp60 in the regulation of insulin-induced glucose transport and GLUT4 translocation in primary adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 25839–25844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morton, G.J.; Muta, K.; Kaiyala, K.J.; Rojas, J.M.; Scarlett, J.M.; Matsen, M.E.; Nelson, J.T.; Acharya, N.K.; Piccinini, F.; Stefanovski, D.; et al. Evidence that the sympathetic nervous system elicits rapid, coordinated, and reciprocal adjustments of insulin secretion and insulin sensitivity during cold exposure. Diabetes 2017, 66, 823–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benrick, A.; Kokosar, M.; Hu, M.; Larsson, M.; Maliqueo, M.; Marcondes, R.R.; Soligo, M.; Protto, V.; Jerlhag, E.; Sazonova, A.; et al. Autonomic nervous system activation mediates the increase in whole-body glucose uptake in response to electroacupuncture. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 3288–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, K.; Butera, M.A.; Zhou, C.; Maurizi, G.; Chen, B.; Ling, L.; Shawkat, A.; Patlolla, L.; Thakker, K.; Calle, V.; et al. Overnutrition causes insulin resistance and metabolic disorder through increased sympathetic nervous system activity. Cell Metab. 2025, 37, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthoud, H.R. The vagus nerve, food intake and obesity. Regul. Pept. 2008, 149, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoornenborg, C.W.; van Dijk, T.H.; Bruggink, J.E.; van Beek, A.P.; van Dijk, G. Acute sub-diaphragmatic anterior vagus nerve stimulation increases peripheral glucose uptake in anaesthetized rats. IBRO Nurosci. Rep. 2023, 15, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, J.; Imai, J.; Izumi, T.; Takahashi, H.; Kawana, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Kodama, S.; Kaneko, K.; Gao, J.; Uno, K.; et al. Neuronal signals regulate obesity induced β-cell proliferation by FoxM1 dependent mechanism. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawana, Y.; Imai, J.; Morizawa, Y.M.; Ikoma, Y.; Kohata, M.; Komamura, H.; Sato, T.; Izumi, T.; Yamamoto, J.; Endo, A.; et al. Optogenetic stimulation of vagal nerves for enhanced glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and β cell proliferation. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2024, 8, 808–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, D.; Oda, K.; Kusunoki, M.; Nishina, A.; Takahashi, K.; Feng, Z.; Tsutsumi, K.; Nakamura, T. PPARγ activation alters fatty acid composition in adipose triglyceride, in addition to proliferation of small adipocytes, in insulin resistant high-fat fed rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 773, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, J.; Katagiri, H.; Yamada, T.; Ishigaki, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Kudo, H.; Uno, K.; Hasegawa, Y.; Gao, J.; Kaneko, K.; et al. Regulation of pancreatic β cell mass by neuronal signals from the liver. Science 2008, 322, 1250–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013, 48, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusunoki, M.; Tsutsumi, K.; Sato, D.; Nakamura, A.; Habu, S.; Mori, Y.; Morishita, M.; Yonemoto, T.; Miyata, T.; Nakaya, Y.; et al. Pioglitazone-induced body weight gain is prevented by combined administration with the lipoprotein lipase activator NO-1886. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 668, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakaplan, N.D.; Song, Y.; Laurenti, M.C.; Vella, A.; Jensen, M.D. Suppression of endogenous insulin secretion by euglycemic hyperinsulinemia. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 109, e596–e601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, Y.; Sun, R.; Yagimuma, H.; Taki, K.; Mizoguchi, A.; Kobayashi, T.; Sugiyama, M.; Onoue, T.; Tsunekawa, T.; Takagi, H.; et al. Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B deficiency improves glucose homeostasis in type 1 diabetes treated with leptin. Diabetes 2022, 71, 1902–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, D.; Shiwaku, Y.; Nakamura, R.; Koizumi, S.; Feng, Z.; Kusunoki, M.; Nakamura, T. Characteristics of sympathetic nerve activity in the rat sciatic nerve in response to microstimulation in a sympathetic fascicle in the contralateral side. Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2013, 2013, 6329–6332. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- DeFronzo, R.A.; Tripathy, D. Skeletal muscle insulin resistance is the primary defect in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2009, 32 (Suppl. S2), S157–S163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payne, S.C.; Ward, G.; MacIsaac, R.J.; Hyakumura, T.; Fallon, J.B.; Villalobos, J. Differential effects of vagus nerve stimulation strategies on glycemia and pancreatic secretions. Physiol. Rep. 2020, 8, e14479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Group | n | Glucose Infusion Rate (mg/kg/min) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Treatment | Post-Treatment | ||
| CON | 3 | 8.7 ± 1.1 | 9.6 ± 1.7 |
| CAP | 7 | 12.5 ± 1.3 | 14.6 ± 1.3 †,* |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kusunoki, M.; Sato, D.; Hisano, F.; Tsutsumi, K.; Miyata, T. Blockade of the Proximal Pancreatic C Fiber Enhances Insulin Sensitivity in Rats. Obesities 2025, 5, 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5040075
Kusunoki M, Sato D, Hisano F, Tsutsumi K, Miyata T. Blockade of the Proximal Pancreatic C Fiber Enhances Insulin Sensitivity in Rats. Obesities. 2025; 5(4):75. https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5040075
Chicago/Turabian StyleKusunoki, Masataka, Daisuke Sato, Fumiya Hisano, Kazuhiko Tsutsumi, and Tetsuro Miyata. 2025. "Blockade of the Proximal Pancreatic C Fiber Enhances Insulin Sensitivity in Rats" Obesities 5, no. 4: 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5040075
APA StyleKusunoki, M., Sato, D., Hisano, F., Tsutsumi, K., & Miyata, T. (2025). Blockade of the Proximal Pancreatic C Fiber Enhances Insulin Sensitivity in Rats. Obesities, 5(4), 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5040075