Abstract
The ecotoxicological condition of soils around mining areas is most often unsatisfactory, which affects entire ecosystems and human health. This research sought to analyze the morphological, agrochemical properties, and content of heavy metals (Cd, Cu, Zn) and metalloids (As) of soils located in a floodplain. The study was conducted within the city of Sibay (Republic of Bashkortostan, Russia). The soil samples were collected from the floodplains of the rivers Karagayly and Khudolaz. According to morphological studies, the soil cover was represented by the Lithic Leptosols, Stagnic Phaeozems, and Fluvisols. The results showed that the soils were characterized by high values of organic matter, potassium, and low levels of phosphorus. Soils that were located away from the city in the Karagayly River were not contaminated. However, the floodplain areas pertaining to the urban district and located near the quarries were characterized by severe anthropogenic soil pollution, disrupted integrity of the soil cover, decreased vegetation, and accumulating labile forms of heavy metals and metalloids. The highest degree of pollution was observed in the floodplain soil of the river Khudolaz where all elements exceeded the maximum permissible concentration (MPC) level. Soils in the floodplain of the Karagayly river were marked by an increased degree of contamination of Zn: exceeding MPC by 1.6 times. With the trend toward an arid climate, the ecotoxicological condition of floodplain soils is an important challenge.
1. Introduction
Environmental pollution by heavy metals from anthropogenic and natural sources has occurred in many cities around the world. Urban soils are especially vulnerable to contamination because they are an important sink for toxicants. The main cause of heavy metal pollution is industrial activity, especially from mining and metallurgical industries [1,2,3]. The Trans-Urals area of the Republic of Bashkortostan (Russia) is characterized by a well-developed mining production complex. In Sibay, the main source of harmful emissions is the enterprise for the extraction and enrichment of copper ores, the Sibay branch of the Uchalinsky mining and processing plant, which includes quarries, underground mines, stockpiles, tailing dumps, and a processing plant [4,5]. At the same time, the territory of the Trans-Ural plain, where this production is located, corresponds to areas with highly developed agriculture and the share of agricultural land is 60–75% [6]. Consequently, the region is faced with a number of environmental problems, including those that are associated with the contamination of agricultural land with heavy metals. Currently, vast research activities have been carried out to study the contamination degree of soils and water bodies in the area of mining operations in Sibay [5,7,8,9]. The main trends in the distribution and accumulation of heavy metals have been identified. For example, Opekunova et al. [10] showed that the soils of the Sibay ore province were marked by anomalously high natural concentrations of heavy metals—Cu, Zn, and Fe. In another study, Khasanova et al. [11] emphasized a high variability in the spatial distribution of heavy metal accumulation sites in soils in the vicinity of the Sibay quarry stockpiles. At the same time, it should be remembered that the content and distribution of heavy metals can be caused by the characteristics of parent rocks and soil types [12,13]. In an example in Nanjing (China), it was shown that the genesis of Pb and Zn were due to the parent rock, Cu was derived mainly from dumped metallurgical waste, and Cd and As came from agricultural pollution [14]. Similarly, Lv et al. [15] identified factors affecting the spatial distribution of Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Zn in Wulian (Eastern China), including both natural and anthropogenic factors.
Despite the existence of numerous studies, most of them were aimed at analyzing water bodies and urban soils. The soils of river floodplains are becoming relevant objects of research in terms of sanitary and hygienic standards, since the ongoing climate change can lead to a reduction in the area of agricultural land, including that which is suitable for grazing. Considering the arid climate of the region and the tendency to increase the duration of dry periods [16], the floodplain areas of rivers are the main forage areas for livestock. Moreover, toxic metals can migrate through the soil profile [17]. Therefore, the ecological condition of soils in these areas may affect the quality of livestock products and public health.
The aim of this research was to assess the floodplain soils of the rivers Karagayly and Khudolaz located in the area of high anthropogenic load near Sibay (Republic of Bashkortostan, Russia). The objective set included studying the morphological and agrochemical characteristics, as well as assessing the content of labile forms of heavy metals (Cd, Cu, Zn) and As in the floodplain soils of the rivers Karagayly and Khudolaz.
2. Materials and Methods
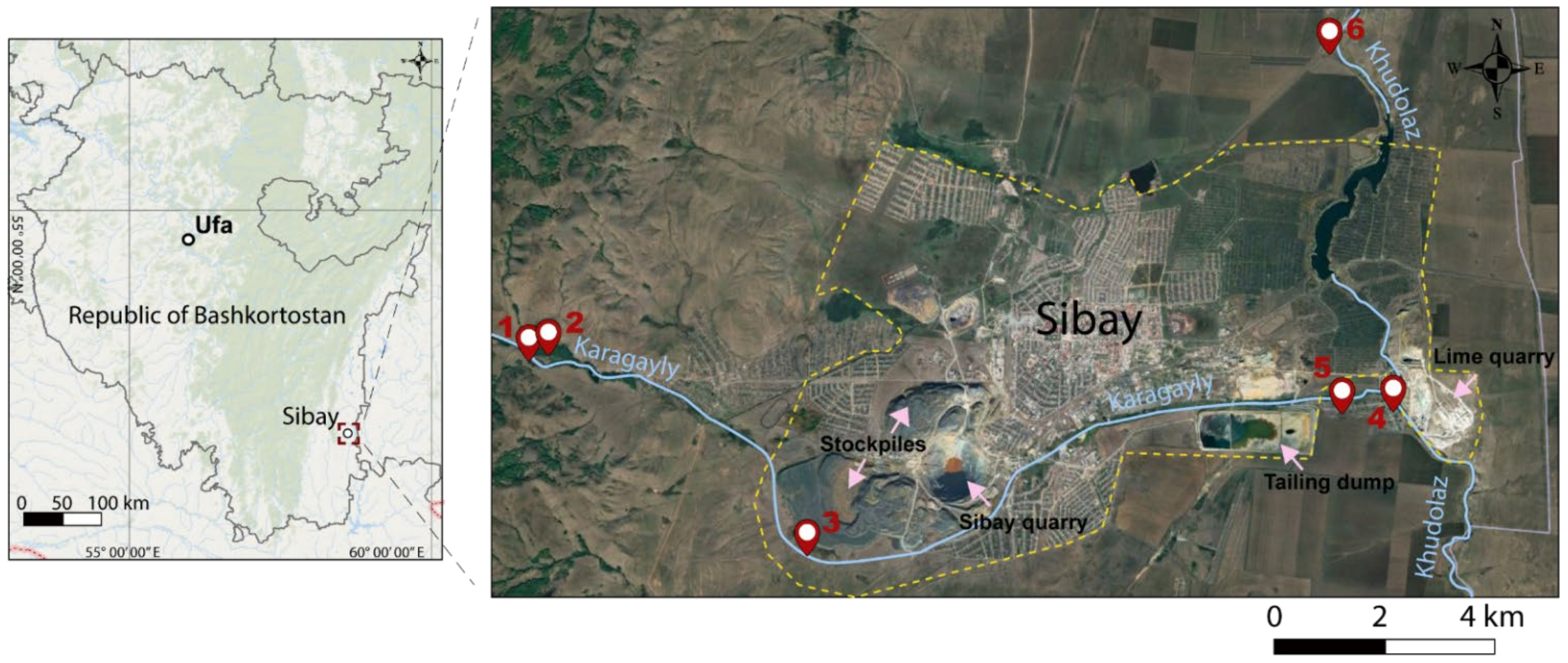
The conducted research covered floodplains and valleys of the rivers Karagayly and Khudolaz within the urban area of Sibay (Republic of Bashkortostan, Russia) (Figure 1). According to the physico-geographical zoning, the study area is a part of the Urtazym-Uzunkul district. The district is located in the sub-province of the eastern ridges and dissected foothills of the Trans-Ural peneplain. This peneplain covering the hill-chained and ridged Kizil-Urtazym plain features the denudation-accumulative type of genetic relief in the watershed of the rivers Khudolaz, Ural, Urtazymka, and Karagayly.
Figure 1.
Maps showing the location of the Republic of Bashkortostan (Russia), Sibay city, Karagayly and Khudolaz rivers, and sample points location.
The soil cover of region is represented mainly by chernozem soils (Haplic, Loamic) and Phaeozems with carbonate and alkaline inclusions on a calcareous, colluvial, and eluvial-colluvial deposits [18,19,20,21]. These soils are characterized by a predominantly low to medium content of organic carbon and pH values of 6–8 in the upper layer. Aliphatic structural fragments predominate in humic acids of chernozems. The granulometric composition of the upper horizons is clayey or heavy loam. There are many salt-affected soils here (solonchak, solonetz, and saline chernozems). Saline soils are low-humus and can reach pH values of 9–10. The salinity type is predominantly sulfate. The river valleys are represented by accumulative terraces that are composed of polymictic sand-pebble-gravel deposits, containing birch forests mixed with pines. Thin primitive stony organogenic-rubby, underdeveloped soils predominate on the slopes of banks, on the bends of slopes, and on the tops of high ridges. The lowland coasts of the river valleys are covered by soddy and meadow-chernozem-alluvial soils, having formed amidst high humidity and under meadow-steppe vegetation. The combined influence of the thick sod layer, reaching 10 cm, and moisture accumulation resulting from the surface runoff and/or the action of groundwater led to the formation of a semi-hydromorphic analogue of chernozem with a thick humus horizon up to 50 cm and high SOM content (8–10%).
The studied area is characterized by a continental climate. Winters are usually cold and snowy and summers are hot and dry, with most of the precipitation falling during the warm season (Table 1).

Table 1.
Climatic characteristics of the studied area [6].
The vegetation cover is constituted by arable lands and steppe meadows. The grass stands of forbs-feather grass-fescue steppes is sparse and poor in herbs. The protruding elements of the relief are described by extremely sparse forbs. A fescue-wormwood steppe being quite well-developed. The bottoms of the river valleys and riverbanks contain meadows of mixed herbs and gramineous plants, sedge-grass swamplands, and intermittent bands of alder forests.
There are 5 soil pits were opened up in homogeneous areas of the floodplains and valleys of the rivers, which are experiencing varying degrees of anthropogenic impact (Figure 1). There were three sites that were located within the city near the Sibay quarry and stockpiles (3–2020), and between the tailing dump and lime quarry (4– and 5–2020). The remaining three sites were located outside the city in areas with a conditional natural background (profiles 1–, 2–, and 6–2020).
Soil samples for analysis were taken in triplicate according to genetic horizons. The research activities studying the area and sampling were carried out in the middle of summer during the dry period in 2020. The locations of soil profiles are provided in Figure 1.
Soil chemical analyses were carried out in accordance with the agrochemical methods of soil research that are generally accepted in soil science [22]. In particular, the SOM content was determined by the Tyurin titrimetric (wet combustion) method in Nikitin’s modification with spectrophotometric termination according to Orlov and Grindel (Walkley–Black’s analogue); the available phosphorus (P2O5) and exchangeable potassium (K2O) according to Chirikov; and the soil reaction by potentiometry (at 1 mol/L KCl suspension (1:2.5 soil/solution)). The content of available forms of ammonium (N-NH4) and nitrate nitrogen (N-NO3) were determined using a KCl potassium chloride solution. The gradation of SOM on categories was carry out according to the scale [23], where content >10% is characterized as “very high”, 6–10%–“high”, 4–6%–“average”, 2–4%–“low”, and <4%–“very low”. The phosphorus and potassium gradations were evaluated according to the guidelines [24].
The labile forms of heavy metals (Cd, Cu, Zn) and As were measured using atomic absorption spectrophotometry according to measurement procedures RD 52.18.289–90 and RD 52.18.721–2009. Measurements were taken in two repetitions. The limits of the detection (LOD) values were 0.1 mg/kg for Cd, Zn, Cu, and 0.05 mg/kg for As. The recovery percentages of elements ranged from 90 to 102%. Measurements were taken in two repetitions. The Russian National Reference Soils Standards GSO 2508-83 was used for quality control. To assess the content of labile forms of Cu and Zn, the values of the maximum permissible concentrations (MPC) under the hygienic standard 1.2.3685–21 of 28 January 2021 were applied.
3. Results and Discussion
The morphological description of the studied soils is provided below (Table 2). According to the description, the soil cover in the valleys of the rivers Karagayly and Khudolaz was represented by dark humus lithozem (Lithic Leptosols) (profile 3–2020), dark humus gley (Stagnic Phaeozems) (profiles 1– and 6–2020), and alluvial–humus soils (Fluvisols) (profile 4–2020); while within the mountainous parts, dark-humus lithozem soils (Lithic Leptosols) were observed (profiles 2– and 5–2020). The dark-humus-gley soil was characterized by a thick humus-accumulative horizon (up to 100 cm), a granular structure, and a light loamy structure. The alluvial-humus soil and dark-humus lithozem were characterized by a low thickness of the humus-accumulative horizon (up to 20 cm), a powdery-cloddy structure, and a light loamy granulometric composition.

Table 2.
Morphological description of the studied soils.
The main agrochemical properties of the soils for each available genetic horizon are shown in Table 3. The pH values varied from slightly acidic (pH = 5.5) for profiles 2- and 5–2020 to alkaline (pH = 8) for profile 6–2020, which is typical for the soils of valleys and floodplains of the rivers in the studied area [18]. Earlier, Opekunova et al. [10] revealed that pH values ranged from 5.8 to 8.1 in the city of Sibay. However, we suggest that the weakly acidic reaction in profile 2–2020 may be due to the impact of acidic water from an upstream tailing dump. The processes of oxidation of ore minerals with subsequent hydrolysis led to an increase in the concentration of H+ ions and a sharp decrease in the pH values of waters, and consequently soils [25]. The soils were characterized by high SOM values (6–10%). The highest SOM content was found in plot 1-2020, where the upper horizon reached very high values (15.4%) and remained high to a depth of 20–40 cm (9%). The SOM content in the top layer of the profile 6–2020 had the lowest value among the top layers of other profiles (6%).

Table 3.
Chemical properties of the soils. Values ± SE (n = 3).
The values of mineral soil nitrogen in the top layers had great variability but they were within the limits for the respective soils, according to previous studies [26]. The high content of N-NH4 was found in sample plot 3–2020 (65.7 mg/kg), while the largest content of N-NO3 was found in the 0–11 cm layer of 4–2020 profile (30.2 mg/kg). The amount of nitrogen tends to decrease with the depth for both forms (according to profiles 1– and 6–2020).
The concentration of P2O5 was quite high in the soils of profiles 2–2020 and 5–2020 (100 and 141 mg/kg of soil, respectively) and very low (<25 mg/kg of soil) for all other areas, except for 1–2020, where the content of P2O5 changed from low in the upper horizon AU (27 mg/kg soil) to medium in the deeper layer AB (98 mg/kg soil). The availability of K2O was low in the profiles 1– and 2–2020 (43 and 40 mg/kg of soil, respectively), increased at profile 5–2020 (191 mg/kg of soil), and very high in profiles 6–, 3–, and 4–2020 (700, 1300, and 1300 mg/kg of soil, respectively). On the whole, the soils had a rather low content of microelements, coupled with a high availability of SOM. The high content of SOM that was observed in profile 1–2020 was probably due to the alluvial type of soil formation and the constant accumulation of silt residues in the floodplain. Profile 6–2020, also located in the floodplain, had a dark humus-gley soil type and was characterized by the presence of sandwash, carbonate mycelium, and pebbles on the surface. Such conditions most likely explain the lower SOM content in the upper layer compared to the lower layer, as well as the alkaline reaction combined with the high potassium oxide content.
The floodplain urban soils of sites 3– and 4–2020 had very high potassium content with a relatively high mineral nitrogen content. Such conditions were probably caused by leaching of elements from the waste dumps of mining and processing plants, animal grazing, and disturbance of the humus layer, which led to the exposure of the lower horizons with high salt content.
The profiles in the valleys of the river Karagayly (2–2020 and 5–2020) showed similar values of agrochemical indicators, although the urban samples (2-2020) had a higher level of accumulation of SOM and an increased content of K2O. In the meantime, both soil samples from the Karagayly valleys had an increased content of P2O5, which distinguished them from the samples that were taken in the floodplains of the rivers Karagayly and Khudolaz. However, according to Pankova et al. [27], such values corresponded to the characteristics of an area experiencing minor sulfate salinization.
A visual assessment of the studied areas within the city area of Sibay (profiles 3–, 4–, and 5–2020) showed that the soil cover in the floodplains of the rivers Karagayly and Khudolaz (profiles 3–2020 and 4–2020) experienced a powerful anthropogenic load that was caused by the storage of overburden rocks from the mining and processing plant and littering from household waste. Plot 3–2020 was also characterized by excessive grazing, which led to disturbance of the vegetation cover and contributed to water and wind erosion. No mechanical anthropogenic impact towards the soil cover in the area of profile 5–2020 (the valley of the river Karagayly) was observed.
The content of labile forms of heavy metals and metalloids is shown in Table 4. The highest degree of contamination with potentially toxic elements was noted in the soils of the Khudolaz floodplain. It was found that the content of all elements exceeded the permissible values in the profile 4–2020 (highway in the floodplain of the river Khudolaz), while the content of Zn exceeded these values several times. In the soil profile 6–2020, elevated values were found for the content of Zn and Cu. At the same time, the high Zn concentration was observed in the profile 3–2020, located near quarry dumps.

Table 4.
The content of labile forms of heavy metals and arsenic in the soils. Values ± SE (n = 3).
The pristine soils (1–, 2–, and 6–2020) that were located at a relative distance from the city were uncontaminated, indicating that the content of elements in these soils is due to internal factors (parent rocks). Meanwhile, the elevated values in the urban soils, especially near the mining enterprises (4 and 5–2020), were due to the anthropogenic impact of industrial activities. This insignificant exceeding of MPC values was expected for the study area and is consistent with the results of previous studies. A recent study reported that Zn values in soils around the quarries of Sibay City ranged from 38 to 142 mg/kg, while the Cd content ranged from 1.2 to 2.7 [11]. Opekunova et al. [10] identified that the average content of Cu and Zn in soils was two to three times higher than the background values of the region’s soils, while the Zn content was close to the permissible concentrations. At the same time, the authors emphasized that the content of mobile forms of elements that were affected by the proximity of the occurrence of heavy metal-rich bedrocks, the degree of development of the soil profile, and weather conditions. Similarly, in other parts of world, Lu et al. [28] reported, that soil contamination of As and Pb was due mainly to the soil parent materials in Shunyi (Beijing, China), while Cd, Cu, and Zn were mainly related to agricultural practices, and Hg was caused by the atmospheric deposits from Beijing. In another study, the authors concluded that mining activity was observed to affect the spatial variation of Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn at the local scale [15].
Contamination of floodplain soils requires special attention because pollutants can migrate with streams and leach down the soil profile [29]. This is especially important for urban floodplain soils that are located near mining sources. Since we assume that some areas were exposed to acidic water from an upstream tailing dump, the contamination of soil and water resources is of particular concern. Moreover, soil acidification can lead to increased mobility and migration processes of cations and heavy metals [30]. Therefore, it is necessary to apply measures to remediate contaminated floodplain soils due to the threat to human health, living organisms, and ecosystems [31,32,33].
4. Conclusions
Toxicants from soils and water bodies through food chains can enter the human organism, creating a great danger to health. The conducted research showed that the floodplain soils of the Karagayly and Khudolaz rivers were represented by Lithic Leptosols, Stagnic Phaeozems, and Fluvisols. The studied soils had a high level of SOM content in the top and sub layers. The soils that were located in the valleys of the rivers were characterized by a high content of mineral nitrogen. A high content of phosphorus was found in the soils of the Karagayly River valley, while a high content of potassium was found in the soils of the Khudolaz River. The elevated and very high content of potassium was noted at all sites.
Among the studied soils, the one profile in the floodplain of the Khudolaz River had elevated values for all the heavy metals and metalloids. We found that soils in the floodplains of rivers that were located within the urban area suffered severe anthropogenic pollution due to the close proximity of the operating mining and processing plant and the storage of its overburden. Also, an additional load is caused by overgrazing and pollution by household waste. Such negative conditions lead to destruction of vegetation, disturbance of soil cover, changes in agrochemical properties, and the accumulation of heavy metals.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.S. and E.D.; methodology, A.G. and L.B.; software, M.G. and A.S.; validation, A.G., S.Z. and A.S.; formal analysis, A.M. and S.Z.; investigation, R.S. and A.G.; resources, R.S.; data curation, I.T.; writing—original draft preparation, M.G.; writing—review and editing, A.S. and E.D.; visualization, A.M. and A.S.; supervision, R.S.; project administration, R.S.; funding acquisition, L.B. and I.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation «PRIORITY 2030» (National Project «Science and University»).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This work was carried out within the framework of the Russian Federation Government task No. 075-00326-19-00, research project No. AAAA-A18-118022190102-3.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wang, J.; Su, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, B.; Chen, G.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, S.; Yuan, W. Source apportionment of heavy metal and their health risks in soil-dustfall-plant system nearby a typical non-ferrous metal mining area of Tongling, Eastern China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 113089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, M.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Lei, K.; Li, Y.; Li, F.; Zheng, D.; Fang, X.; Cao, Y. Heavy metal contamination risk assessment and correlation analysis of heavy metal contents in soil and crops. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 278, 116911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Zhou, M.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Duan, C.; Wang, X.; Zhao, S.; Bai, X.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; et al. A global meta-analysis of heavy metal(loid)s pollution in soils near copper mines: Evaluation of pollution level and probabilistic health risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 835, 155441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuramshina, N.G.; Kuramshin, E.M.; Nikolaeva, S.V.; Imashev, Y.B. The biogeochemical characteristics of the content of heavy metals in soil, plants and animals in different natural areas of Bashkortostan. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 144, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opekunova, M.; Opekunov, A.; Somov, V.; Kukushkin, S.; Papyan, E. Transformation of metals migration and biogeochemical cycling under the influence of copper mining production (the Southern Urals). Catena 2020, 189, 104512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdrakhmanov, R.F. Atlas of the Republic of Bashkortostan; Kitap Publ.: Ufa, Russia, 2005. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Semenova, I.N.; Rafikova, Y.S.; Khasanova, R.F.; Suyundukov, Y.T. Analysis of metal content in soils near abandoned mines of Bashkir Trans-Urals and in the hair of children living in this territory. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2018, 50, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opekunov, A.Y.; Opekunova, M.G.; Kukushkin, S.Y.; Yanson, S.Y.; Arestova, I.Y.; Sheinerman, N.A.; Spasskii, V.V.; Papyan, E.E.; Elsukova, E.Y. Mineralogical–Geochemical Characteristics of the Snow Cover in Areas with Mining and Ore-Processing Facilities. Geochem. Int. 2021, 59, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suyundukov, Y.T.; Suyundukova, M.B.; Khasanova, R.F.; Semenova, I.N.; Rafikova, Y.S.; Ilbulova, G.R.; Bezuglova, O.S.; Khabirov, I.K. Physical Properties of the Soils of Sibay City of the Republic of Bashkortostan. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2022, 55, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opekunova, M.G.; Somov, V.V.; Papian, E.E. Soil contamination in the impact zone of mining enterprises in the Bashkir Transural region. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2017, 50, 732–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khasanova, R.F.; Semenova, I.N.; Suyundukov, I.T.; Rafikova, I.S.; Biktimerova, G.I.; Ilbulova, G.R.; Kuzhina, G.S.; Ilyina, I.V. Environmental assessment of heavy metal pollution of soils in industrial zones of the city of Sibay. Vestn. Orenb. Gos. Univ. 2017, 12, 74–77. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Golia, E.E.; Tsiropoulos, G.N.; Füleky, G.; Floras, S.; Vleioras, S. Pollution Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Soils of Different Taxonomy Orders in Central Greece. Env. Monit Assess 2019, 191, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos-Francés, F.; Martínez-Graña, A.; Zarza, C.Á.; Sánchez, A.G.; Rojo, P.A. Spatial Distribution of Heavy Metals and the Environmental Quality of Soil in the Northern Plateau of Spain by Geostatistical Methods. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Chen, X.; Jing, F.; Liu, W.; Wen, X. An Assessment of Spatial Distribution and Source Identification of Five Toxic Heavy Metals in Nanjing, China. Environ. Eng. Res. 2021, 26, 200135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Dai, B. Multivariate Geostatistical Analyses of Heavy Metals in Soils: Spatial Multi-Scale Variations in Wulian, Eastern China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 107, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gareev, A.M.; Galimova, R.G. Regional qualities of weather conditions global changes (by the example of the Cis-Ural forest-steppe). J. Int. Sci. Publ. Ecol. Saf. 2012, 6, 390–397. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, H.; Cui, Z. Evaluation and Analysis of Soil Migration and Distribution Characteristics of Heavy Metals in Iron Tailings. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaziev, F.K. Soils of Bashkortostan Vol. 1: Ecological-Genetic and Agricultural Production Characteristics; Gilem Publ.: Ufa, Russia, 1995; 385p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Gabbasova, I.M.; Garipov, T.T.; Komissarov, M.A.; Suleimanov, R.R.; Suyundukov, Y.T.; Khasanova, R.F.; Sidorova, L.V.; Komissarov, A.V.; Suleimanov, A.R.; Nazyrova, F.I. The Impact of Fires on the Properties of Steppe Soils in the Trans-Ural Region. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2019, 52, 1598–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleymanov, A.; Gabbasova, I.; Abakumov, E.; Kostecki, J. Soil salinity assessment from satellite data in the Trans-Ural steppe zone (Southern Ural, Russia). Soil Sci. Annu. 2021, 72, 132233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleymanov, A.; Polyakov, V.; Komissarov, M.; Suleymanov, R.; Gabbasova, I.; Garipov, T.; Saifullin, I.; Abakumov, E. Biophysicochemical properties of the eroded southern chernozem (Trans-Ural Steppe, Russia) with emphasis on the 13C NMR spectroscopy of humic acids. Soil Water Res. 2022, 17, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arinushkina, E.V. A Handbook of Chemical Analysis of Soils; Moscow State University: Moscow, Russia, 1970; 487p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Grishina, L.A.; Orlov, D.S. System of indicators of humus state of soils. In Soil Science Issues; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1978; pp. 42–47. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Mineev, V.G. (Ed.) Practical Manual on Agrochemistry; Moscow State University: Moscow, Russia, 2001; 689p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Abakumov, E.V.; Suyundokov, Y.T.; Pigareva, T.A.; Semenova, I.N.; Khasanova, R.F.; Biktimerova, G.Y.; Rafikova, Y.S.; Il-bulova, G.R. Biological and sanitary evaluation of Sibaisky quarry dumps of the Bashkortostan Republic. Hyg. Sanit. 2016, 95, 929–934. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khabirov, I.K. Ecology and Biochemistry of Nitrogen in the Soils of the Urals [Ekologiya i Biohimiya Azota v Pochvah Priural’ya]; Ufa Polygraph Plant: Ufa, Russia, 1993; 224p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Pankova, E.I. Saline Soils of Russia; Akademkniga Publ.: Moscow, Russia, 2006; 857p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Lu, A.; Wang, J.; Qin, X.; Wang, K.; Han, P.; Zhang, S. Multivariate and Geostatistical Analyses of the Spatial Distribution and Origin of Heavy Metals in the Agricultural Soils in Shunyi, Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 425, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanianska, R.; Varga, J.; Benková, N.; Kizeková, M.; Jančová, Ľ. Floodplain Soils Contamination Assessment Using the Sequential Extraction Method of Heavy Metals from Past Mining Activities. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kicińska, A.; Pomykała, R.; Izquierdo-Diaz, M. Changes in Soil PH and Mobility of Heavy Metals in Contaminated Soils. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2022, 73, e13203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelaki, A.; Dionysidis, A.; Sihag, P.; Golia, E.E. Assessment of Contamination Management Caused by Copper and Zinc Cations Leaching and Their Impact on the Hydraulic Properties of a Sandy and a Loamy Clay Soil. Land 2022, 11, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Fang, G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Su, B.; Li, D.; Xiang, B. Potentially Toxic Element Pollution Levels and Risk Assessment of Soils and Sediments in the Upstream River, Miyun Reservoir, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, A.J.; Verbruggen, F.; Rico, V.S.C.; Bergmans, J.; Spooren, J.; Yurramendi, L.; Laing, G.D.; Boon, N.; Hennebel, T. Selective Leaching of Copper and Zinc from Primary Ores and Secondary Mineral Residues Using Biogenic Ammonia. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).