Temporary Water Holes May Benefit the Breeding of the Common Skipper Frog Euphlyctis cyanophlyctis (Anura: Dicroglossidae)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
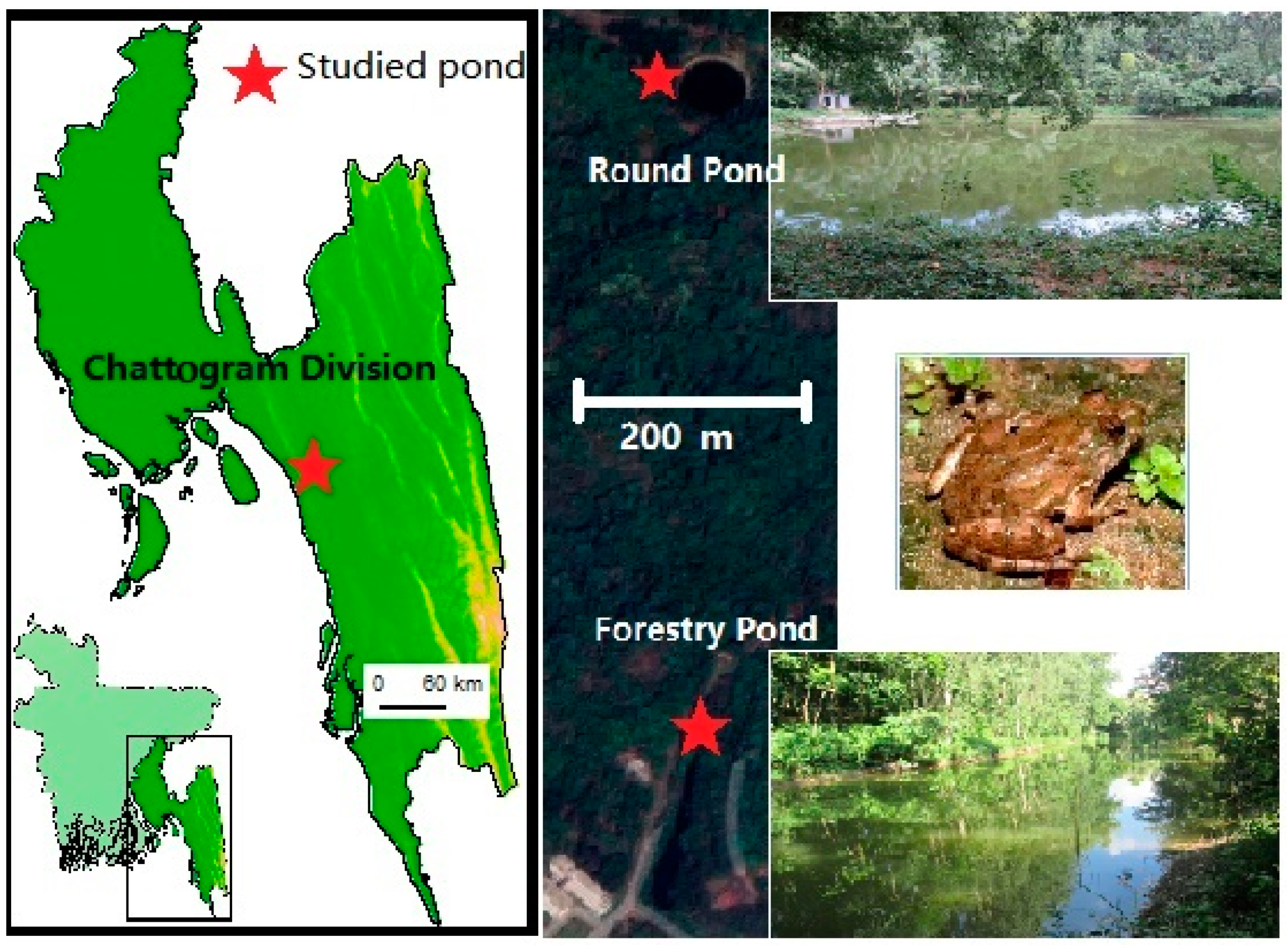
2.1. Site-1 (Round Pond)
2.2. Site-2 (Forestry Pond)
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Analysis and Modeling
3. Results
3.1. Studied Ponds
3.2. Fluctuations of Frog Population
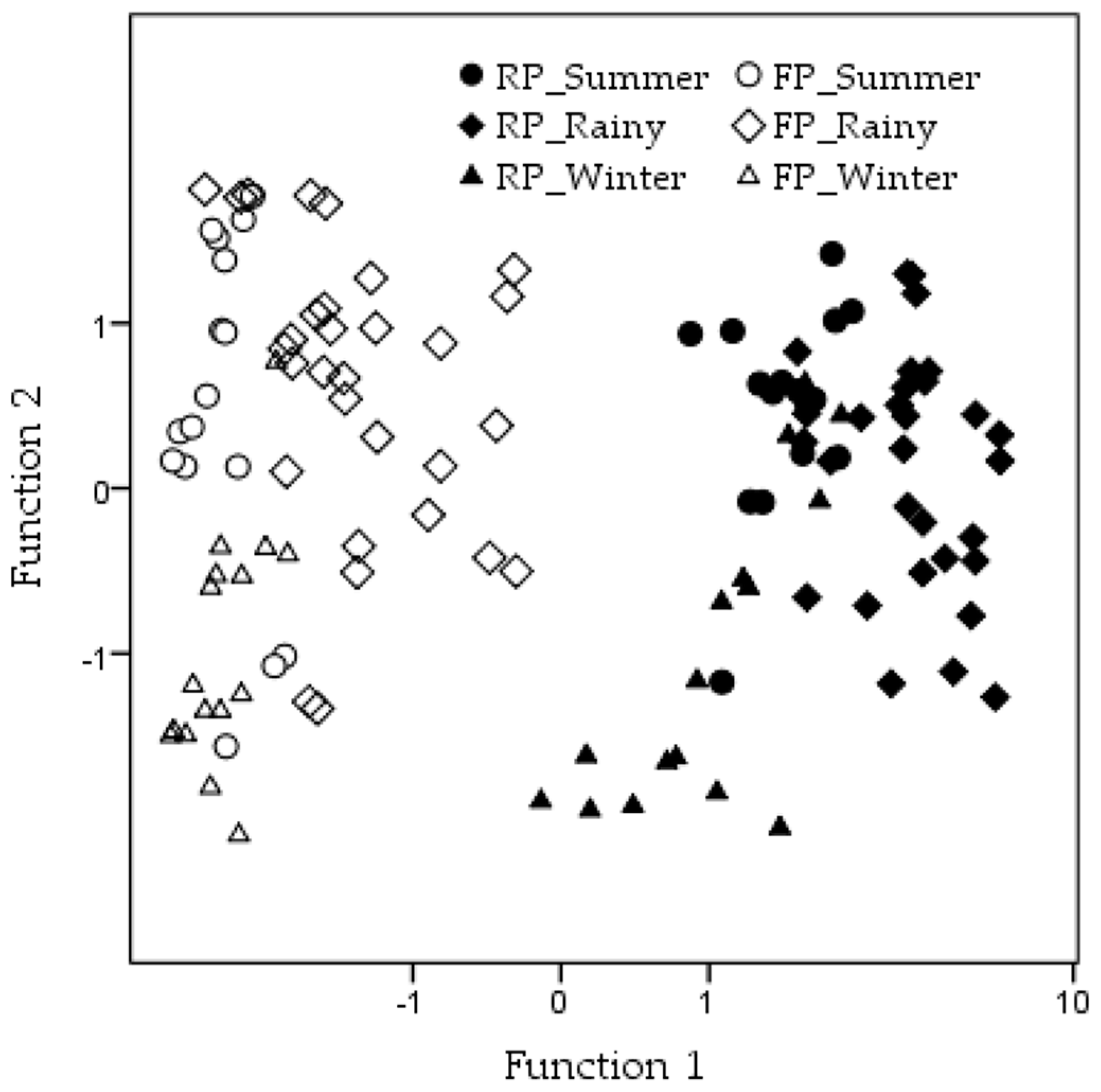
3.3. Discriminant Parameters between Habitat States
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stuart, S.N.; Chanson, J.S.; Cox, N.A.; Young, B.E.; Rodrigues, A.S.L.; Fischman, D.L.; Waller, R.W. Status and Trends of Amphibian Declines and Extinctions Worldwide. Science 2004, 306, 1783–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.J.; Scheele, B.C.; Westgate, M.J.; Yebra, M.; Newport, J.S.; Manning, A.D. Beyond the pond: Terrestrial habitat use by frogs in a changing climate. Biol. Conser. 2020, 249, 108712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, K.; Richards, S.; Pearson, R.G.; Alford, R.A.; Puschendorf, R. Seasonal, annual and decadal change in tadpole population in tropical Australian streams. Amphib. Reptil. 2019, 40, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandão, R.A.; Fenker, J.; Lopes, B.E.P.d.C.; de Sena, V.M.d.A.; Vasconcelos, B.D. Diet of terrestrial anurans in an ephemeral and simplified habitat during the dry season in the Brazilian Cerrado. Ethol. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 32, 527–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, B.; Shu, X.; Pei, E.; Yuan, X.; Sun, Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, Z. Responses of anuran communities to rapid urban growth in Shanghai, China. Urban For. Urban Green. 2016, 20, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alford, R.A. Ecology: Resource use, competition, and predation. In Tadpoles: The Biology of Anuran Larvae; McDiarmid, R.W., Altig, R., Eds.; Chicago University Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1999; pp. 240–278. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez, J.E.; Pfister, C.A. Local population dynamics in metapopulation models: Implications for conservation. Conserv. Biol. 2001, 15, 1700–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, L.A.; Smith, D.H.V.; Jones, B.L.; Prescott, D.R.C.; Moehrenschlager, A. Seasonal Differences in Extinction and Colonization Drive Occupancy Dynamics of an Imperilled Amphibian. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ron, S.R.; Duellman, W.E.; Coloma, L.A.; Bustamante, M.R. Population Decline of the Jambato Toad Atelopus ignescens (Anura: Bufonidae) in the Andes of Ecuador. J. Herpetol. 2003, 37, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orizaola, G.; Dahl, E.; Laurila, A. Compensating for delayed hatching across consecutive life-history stages in an amphibian. Oikos 2010, 119, 980–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narzary, J.; Bordoloi, S. A study on certain common pond breeding anurans and their tadpoles in a pond of western Assam, India. Int. J. Adv. Biol. Res. 2012, 2, 342–348. [Google Scholar]
- Banks, B.; Beebee, T.J.C. Factors influencing breeding site choice by the pioneering amphibian Bufo calamita. Holarct. Ecol. 1987, 10, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, A.; Rais, M.; Asadi, M.A.; Jilani, M.J.; Balouch, S.; Anwar, M.; Saleem, A. Do habitat variables correlate anuran abundance in arid terrain of Rawalpindi–Islamabad areas, Pakistan. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2015, 27, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearman, P.B. Effects of habitat size on tadpole populations. Ecology 1993, 74, 1982–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUCN Bangladesh. Red List of Bangladesh, Volume 4: Reptiles and Amphibians; IUCN: International Union for Conservation of Nature, Bangladesh Country Office: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2015; p. 336. [Google Scholar]
- Mahony, S.; Hasan, M.K.; Kabir, M.M.; Ahmed, M.; Hossain, M.K. A catalogue of amphibians and reptiles in the collection of Jahangirnagar University, Dhaka, Bangladesh. Hamadryad 2009, 34, 80–94. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, M.S.; Igawa, T.; Khan, M.M.R.; Islam, M.M.; Kuramoto, M.; Matsui, M.; Kurabayashi, A.; Sumida, M. Genetic divergence and evolutionary relationships in six species of genera Hoplobatrachus and Euphlyctis (Amphibia: Anura) from Bangladesh and other Asian countries revealed by mitochondrial gene sequences. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2008, 48, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howlader, M.S.; Nair, A.; Gopalan, S.V.; Merila, J. A new species of Euphlyctis (Anura: Dicroglossidae) from Barisal, Bangladesh. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghose, A.; Deb, J.C.; Dakwa, K.B.; Ray, J.P.; Reza, A.H.M.A. Amphibian species assemblages in a tropical forest of Bangladesh. Herpetol. J. 2017, 27, 318–325. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.S. A new subspecies of common skittering frog Euphlyctis cyanophlyctis (Schneider 1799) from Balochistan, Pakistan. Pak. J. Zool. 1997, 29, 107–112. [Google Scholar]
- Joshy, S.H.; Alam, M.S.; Kurabayashi, A.; Sumida, M.; Kuramoto, M. Two new species of the genus Euphlyctis cyanophlyctis (Anura, Ranidae) from south-western India, revealed by molecular and morphological comparisons. Alytes 2009, 26, 97–116. [Google Scholar]
- Priti, H.; Naik, C.R.; Seshadri, K.S.; Singal, R.; Vidisha, M.K.; Ravikanth, G.; Gururaja, K.V. A New Species of Euphlyctis (Amphibia, Anura, Dicroglossidae) from the West Coastal Plains of India. Asian Herp. Res. 2016, 7, 229–241. [Google Scholar]
- Shil, S.R. Analysis of Habitat Preference of Some Anurans (Family: Dicroglossidae) of the Chittagong University Campus, Chittagong; Unpublished M.S. Project 2014; Department of Zoology, University of Chittagong: Chattogram, Bangladesh, 2014; p. 52. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, M.A.W.; Rahman, M.M.; Khan, M.A.G. Influence of habitat parameters on Common Skipper Frog (Euphlyctis cyanophlyctis) in Chittagong. Bangladesh J. Zool. 2016, 44, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rahman, M.M. Habitat Ecology of Common Skipper Frog (Euphlyctis cyanophlyctis) (Schneider, 1799) of the Chittagong University Campus, Chittagong, Bangladesh. Master’s Thesis, Department of Zoology, University of Chittagong, Chattogram, Bangladesh, 2016; p. 73, Unpublished M.S. Dissertation. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, A.T.M.; Chowdhury, M.S.; Hoque, A.K.M.M.; Malek, S.A. Detailed Soil Survey Chittagong University Campus; Department of soil Survey: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 1979; p. 208. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.A.G.; Nath, S.K.; Sadique, S.B.; Biswas, S.C. Limnological conditions of three ponds and ecology of their macrobenthic invertebrates. Bangladesh J. Zool. 2007, 35, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, N. Geography of East Pakistan; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1968; p. 361. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, M.N.; Pasha, M.K. A floristic account of Chittagong University Campus. Chittagong Univ. J. Sci. 1999, 23, 81–98. [Google Scholar]
- American Public Health Association. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Waste Water, 21st ed.; APHA-AWWA-WEF: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; p. 541. [Google Scholar]
- Dubois, A.; Ohler, A. Frogs of the subgenus Pelophylax (Amphibia, Anura, genus Rana). Zool. Pol. 1995, 39, 139–204. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.S.; Mufti, S.A. Oropharyngeal morphology of detritivorous tadpole of Rana cyanophlyctis Schneider, and its ecological correlates. Pak. J. Zool. 1995, 27, 43–49. [Google Scholar]
- Das, I.; Dutta, S.K. Checklist of the amphibians of India, with English common names. Hamadryad Madras 1998, 23, 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Chakma, S. Euphlyctis cyanophlyctis. In Encyclopedia of Flora and Fauna of Bangladesh. Amphibian and Reptiles; Kabir, S.M.H., Ahmed, A.T.A., Rahman, A.K.A., Ahmed, Z.U., Begum, Z.N.T., Hassan, M.A., Khondker, M., Eds.; Asiatic society of Bangladesh: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2009; Volume 25, pp. 9–10. [Google Scholar]
- Pancharatna, M.; Saidapur, S.K. Ovarian cycle in the frog Rana cyanophlyctis: A quantitative study of follicular kinetics in relation to body mass, oviduct, and fat body cycles. J. Morphol. 1985, 186, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawar, V.G.; Pancharatna, K. Annual oviduct cycle in the Indian skipper frog, Rana cyanophlyctis (Schneider 1799): A morphological study. Trop. Zool. 1999, 12, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, S.; Rout, J.; Sahoo, G.; Sethy, J. Dietary preference of Euphlyctis cyanophlyctis tadpoles in different habitats in and around Similipal biosphere reserve, Odisha, India. Int. J. Cons. Sci. 2017, 8, 259–268. [Google Scholar]
- Tabassum, F.; Rais, M.; Anwar, M.; Mehmood, T.; Hussain, I.; Khan, S.A. Abundance and Breeding of the Common Skittering Frog (Euphlyctis cyanophlyctis) and Bull Frog (Hoplobatrachus tigerinus) at Rawal Lake, Islamabad, Pakistan. Asian Herp. Res. 2011, 2, 177–250. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, M.A.W.; Das, M.C. Habitat Selection and Population Ecology of Six Winter Active Anurans (Class: Amphibia) of the Chittagong University Campus. Bangladesh J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 67–74. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.S.; Papenfuss, T.; Anderson, S.; Rastegar-Pouyani, N.; Kuzmin, S.; Dutta, S.; Manamendra-Arachchi, K.; Sharifi, M. Euphlyctis cyanophlyctis. In The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species; Errata Version Published in 2016; Red List: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.Z.; Mahmood, N.; Ghalib, S.A.; Hussain, B.; Siddiqui, S.; Perween, S.; Abbas, D. Impact of habitat destruction on the population of amphibians with reference to current status of frogs and toads in Karachi and Thatta, Sindh. Can. J. Pure Appl. Sci. 2010, 4, 1257–1265. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, A.; Dey, S.; Roy, U.S. Seasonal diversity and abundance of herpetofauna in and around an industrial city of West Bengal, India. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Sanit. 2012, 7, 281–286. [Google Scholar]
- Solomampianina, G.; Molnár, N. Occurrence of True Frogs (Ranidae L.) in the region of Szeged as related to aquatic habitat parameters. Tiscia 2011, 38, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Glos, J.; Grafe, T.U.; Rödel, M.-O.; Linsenmair, K.E. Geographic Variation in pH Tolerance of Two Populations of the European Common Frog, Rana temporaria. Copeia 2003, 3, 650–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo-de-Andrade, C.A.; Santana, D.J.; de Carvalho-e-Silva, S.P. Predation on Scinax x-signatus (Anura: Hylidae) by the giant water bug Lethocerus annulipes (Hemiptera: Belostomatidae) in a Brazilian Restinga habitat. Herpetol. Notes. 2010, 3, 53–54. [Google Scholar]
- Dissanayake, D.S.B. Euphlyctis cyanophlyctis in Natural history notes. Herpetol. Rev. 2012, 43, 462–463. [Google Scholar]
- Mahony, S.; Reza, A.H.M.A. A herpetofaunal collection from the Chittagong Hill Tracts, Bangladesh, with two new species records for the country. Hamadryad 2008, 32, 45–56. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.A.R. Wildlife of Bangladesh: Checklist-Cum-Guide; Alam, M.J., Ed.; Chayabithi: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kabir, S.M.H.; Ahmed, A.T.A.; Rahman, A.K.A.; Ahmed, Z.U.; Begum, Z.N.T.; Hassan, M.A.; Khondker, M. Encyclopedia of Flora and Fauna of Bangladesh, Volume 25: Amphibians and Reptiles; Asiatic society of Bangladesh: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2009; Volume 25. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, M.A.W. Acoustic Analysis of the Amphibian Species Diversity in Chittagong Region. Master’s Thesis, University of Chittagong, Chattogram, Bangladesh, 2009; p. 242, Unpublished M.Phil. Dissertation. [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths, R.A. Temporary ponds as amphibian habitats. Aquatic Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2003, 7, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, E.P. Environmental watering triggers rapid frog breeding in temporary wetlands within a regulated river system. Wetlands Ecol. Manag. 2018, 26, 1073–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Z.; Xie, H.; Yuan, X.; Pei, E.; Wang, T. Effects of landscape heterogeneity and breeding habitat diversity on rice frog abundance and body condition in agricultural landscapes of Yangtze River Delta, China. Cur. Zool. 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breininger, D.R.; Mazerolle, M.J.; Bolt, M.R.; Legare, M.L.; Drese, J.H.; Hines, J.E. Habitat fragmentation effects on annual survival of the federally protected eastern indigo snake. Anim. Conser. 2012, 15, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.T.U.; Tabassum, F.; Rasheduzzaman, M.; Saba, H.; Sarkar, L.; Ferdous, J.; Uddin, S.Z.; Islam, A.Z.M.Z. Temporal dynamics of land use/land cover change and its prediction using CA-ANN model for southwestern coastal Bangladesh. Environ. Monit. Assessm. 2017, 189, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallant, A.L.; Klaver, R.W.; Casper, G.S.; Lannoo, M.J. Global rates of habitat loss and implication for amphibian conservation. Copeia 2007, 4, 967–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUCN Standards and Petitions Subcommittee. Guidelines for Using the IUCN Red List Categories and Criteria; Version 13; Prepared by the Standards and Petitions Subcommittee; Red List: Cambridge, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]

| Parameters | Round Pond | Forestry Pond | Differences between Ponds | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range | Mean ± SD | Range | Mean ± SD | t-Value | p Value | |
| Size (m2) | 2375.83 | 8093.7 | ||||
| AT (°C) | 24.00–35.00 | 30.50 ± 3.05 | 24.00–35.00 | 30.27 ± 3.00 | 0.42 | p > 0.05 |
| WT (°C) | 13.00–34.50 | 27.04 ± 5.74 | 13.00–34.50 | 24.29 ± 6.41 | 2.52 | p < 0.05 |
| pH | 4.89–7.90 | 6.39 ± 0.74 | 4.15–7.10 | 5.13 ± 0.57 | 10.67 | p < 0.001 |
| DO (mg/L) | 3.29–8.90 | 6.96 ± 1.55 | 2.50–6.97 | 5.05 ± 1.01 | 8.15 | p < 0.001 |
| Depth (m) | 1.77–3.79 | 2.54 ± 0.47 | 0.34–2.10 | 0.95 ± 0.47 | 18.92 | p < 0.001 |
| PSR | 13.00–28.00 | 19.79 ± 5.97 | 15.00–37.00 | 26.27 ± 7.73 | −5.22 | p < 0.001 |
| Ec_den (no./acre) | 0.00–39.00 | 14.79 ± 10.44 | 0.00–51.00 | 14.70 ± 13.13 | 0.05 | p > 0.05 |
| Sites | Discriminate Habitat State | Population Change (p ≤ 0.05) | Influence of Habitat Variables on Ec_den (p ≤ 0.05) | Discriminating Factor (Standardized Coefficient > 0.3) | Effect Size of the Model (p ≤ 0.001) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Cross-validation (%) | Observations (n) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Round Pond | Summer and rainy | Decreased | Yes | Depth, pH, WT | 64.64 | 68.8 | 93.3 | 84.8 | 46 |
| Rainy and winter | Increased | Yes | WT, pH, DO, AT | 84.64 | 100 | 93.8 | 97.8 | 46 | |
| Winter and summer | Decreased p > 0.05 | No | PSR, DO, WT, AT | 78.32 | 100 | 81.3 | 90.6 | 32 | |
| F 1 and UF 2 | Decreased | Yes | pH, Depth, WT, PSR | 40.96 | 74.4 | 84.2 | 77.4 | 62 | |
| NBS 3 and BS 4 | Decreased | Yes | pH, WT, Depth | 64.32 | 82.9 | 92.6 | 87.1 | 62 | |
| Forestry Pond | Summer and rainy | Decreased | Yes | Depth, pH | 63.20 | 81.3 | 80.0 | 80.4 | 46 |
| Rainy and winter | Decreased p > 0.05 | No | Depth, AT, WT | 79.21 | 96.7 | 87.5 | 93.5 | 46 | |
| Winter and summer | Increased | Yes | PSR | 83.17 | 100 | 93.8 | 96.9 | 32 | |
| F 1 and UF 2 | Decreased | Yes | Depth, WT | 55.95 | 95.0 | 72.7 | 87.1 | 62 | |
| NBS 3 and BS 4 | Decreased p > 0.05 | No | Depth, WT | 60.68 | 85.7 | 81.5 | 83.9 | 62 |
| Round Pond (Mean ± SD) | |||||||
| Habitat States | WT | pH | Depth | PSR | Ec_den | Adj. R2 | |
| Favorable habitat | 24.05 ± 4.33 | 5.92 ± 0.57 | 2.29 ± 0.22 | 17.37 ± 3.27 | 24.14 ± 9.85 | 0.542 * | |
| Unfavorable habitat | 28.37 ± 5.83 | 6.60 ± 0.71 | 2.65 ± 0.51 | 20.86 ± 6.59 | 10.66 ± 6.73 | 0.370 *** | |
| Breeding season | 30.96 ± 2.10 | 6.97 ± 0.53 | 2.86 ± 0.49 | 9.17 ± 6.94 | 0.568 *** | ||
| Non-breeding season | 24.02 ± 5.85 | 5.94 ± 0.54 | 2.29 ± 0.25 | 19.13 ± 10.69 | 0.063 (p > 0.05) | ||
| Forestry Pond (Mean ± SD) | |||||||
| Habitat States | WT | Depth | Ec_den | Adj. R2 | |||
| Favorable habitat | 27.56 ± 4.28 | 0.70 ± 0.47 | 27.14 ± 14.35 | 0.811 *** | |||
| Unfavorable habitat | 22.49 ± 6.71 | 1.08 ± 0.42 | 7.85 ± 4.84 | 0.675 *** | |||
| Breeding season | 27.46 ± 5.66 | 1.30 ± 0.41 | 13.48 ± 13.93 | 0.755 *** | |||
| Non-breeding season | 21.84 ± 5.91 | 0.67 ± 0.30 | 15.63 ± 12.60 | 0.604 *** | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chowdhury, M.A.W.; Shil, S.R.; Rahman, M.M. Temporary Water Holes May Benefit the Breeding of the Common Skipper Frog Euphlyctis cyanophlyctis (Anura: Dicroglossidae). Ecologies 2021, 2, 138-149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecologies2010007
Chowdhury MAW, Shil SR, Rahman MM. Temporary Water Holes May Benefit the Breeding of the Common Skipper Frog Euphlyctis cyanophlyctis (Anura: Dicroglossidae). Ecologies. 2021; 2(1):138-149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecologies2010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleChowdhury, Mohammad Abdul Wahed, Shimu Rani Shil, and Md. Mizanur Rahman. 2021. "Temporary Water Holes May Benefit the Breeding of the Common Skipper Frog Euphlyctis cyanophlyctis (Anura: Dicroglossidae)" Ecologies 2, no. 1: 138-149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecologies2010007
APA StyleChowdhury, M. A. W., Shil, S. R., & Rahman, M. M. (2021). Temporary Water Holes May Benefit the Breeding of the Common Skipper Frog Euphlyctis cyanophlyctis (Anura: Dicroglossidae). Ecologies, 2(1), 138-149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecologies2010007







