Estimation of the Negative Charge of Phi6 Virus and Its Variations with pH Using the Literature XPS Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Virus Choice and XPS Data
2.2. Surface Molecular Composition
2.3. The Calculation of RCOOH and R2PO4H Concentration
2.4. Evolution of the Concentration of RCOO− and of R2PO4− as a Function of pH
- [B]: Concentration in mol/g of RCOO− or R2PO4−.
- [TC]: Concentration in mol/g of RCOOH or R2PO4H.
- pKa: Acidity constant of RCOOH/RCOO− or R2PO4H/R2PO4−.
3. Results
3.1. Surface Molecular Composition
3.2. The Concentration of Chemical Functions RCOOH and R2PO4H
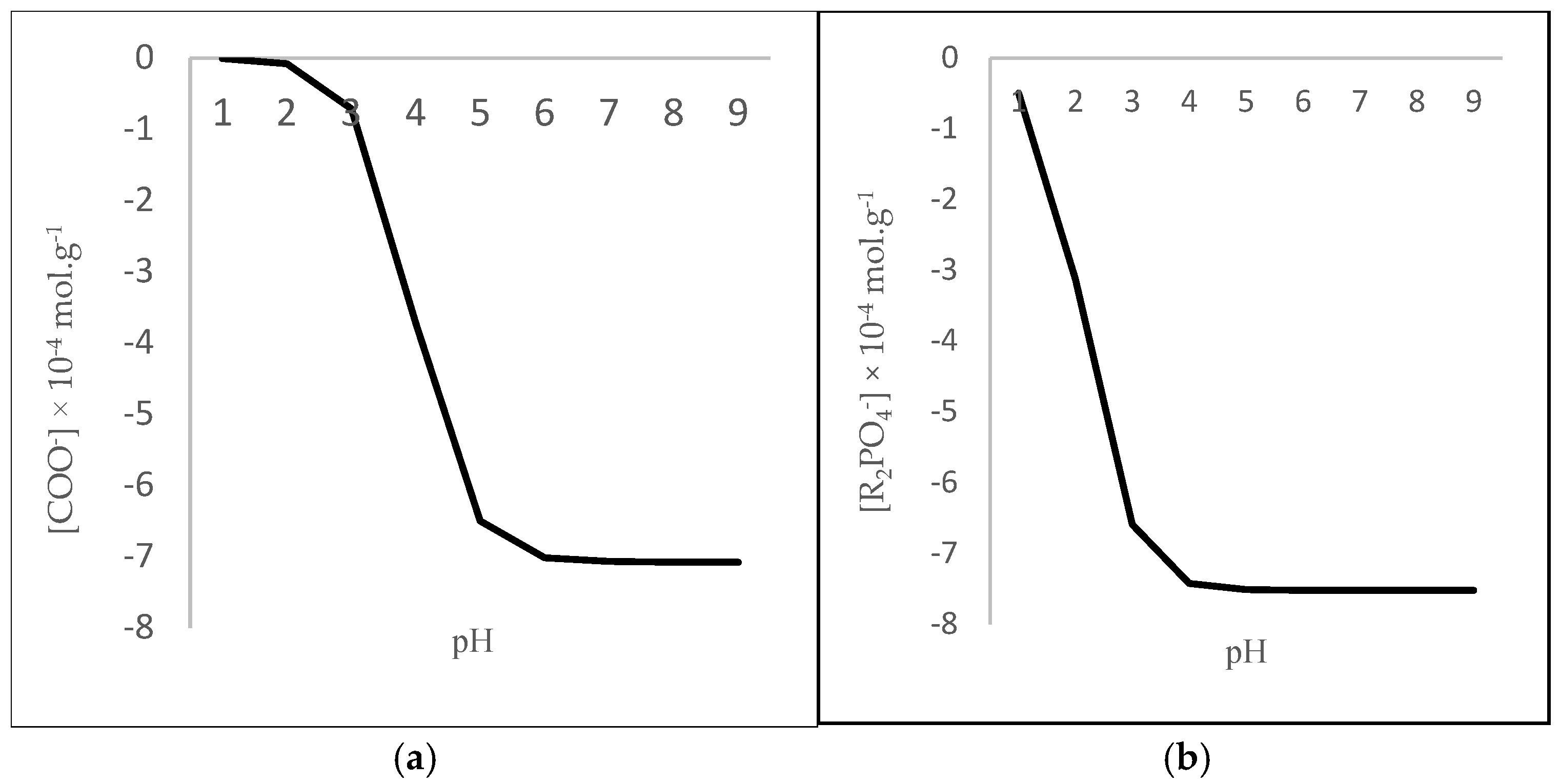
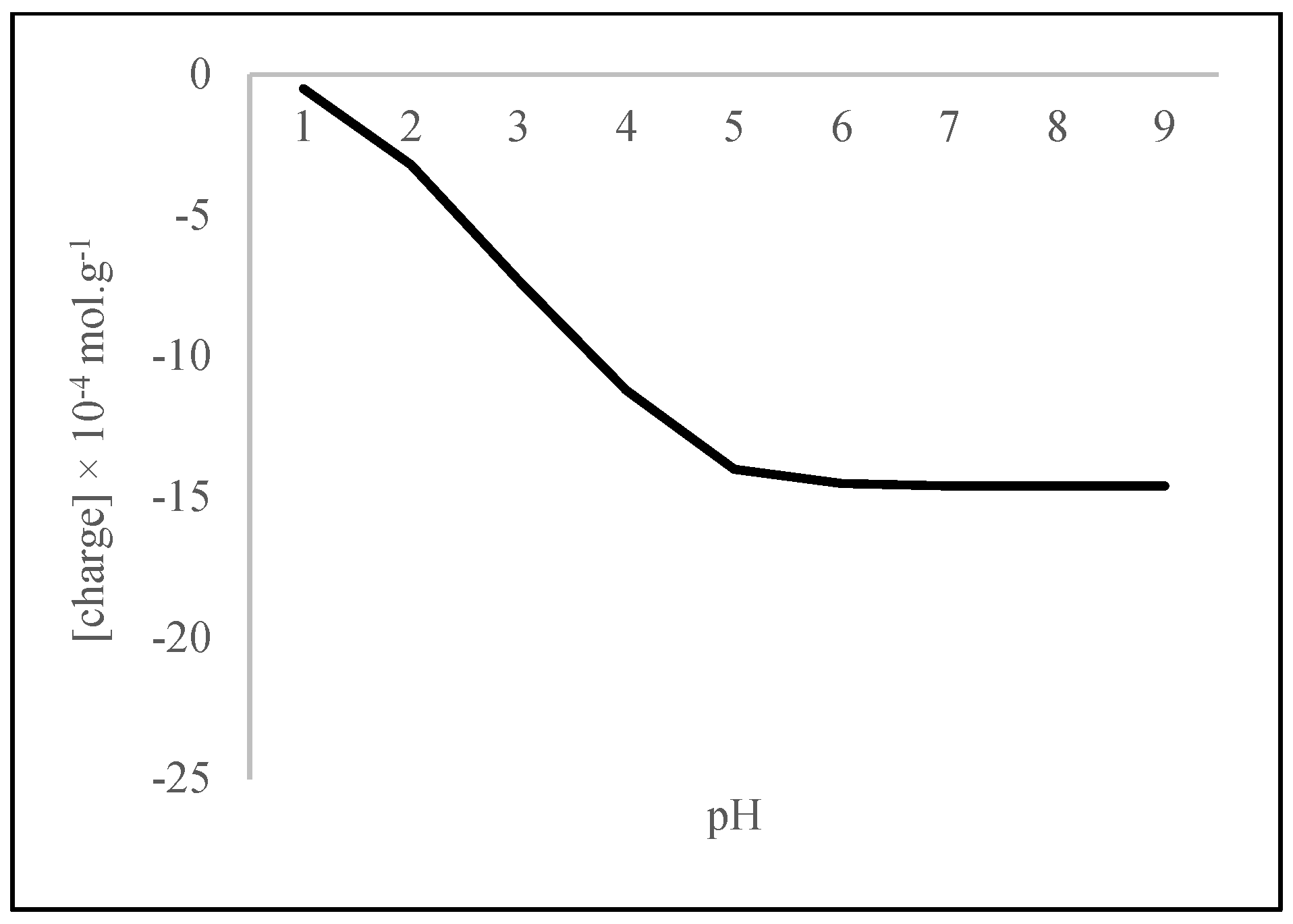
3.3. The Variation in the Concentrations of RCOO−, R2PO4−, and the Negative Charge with pH
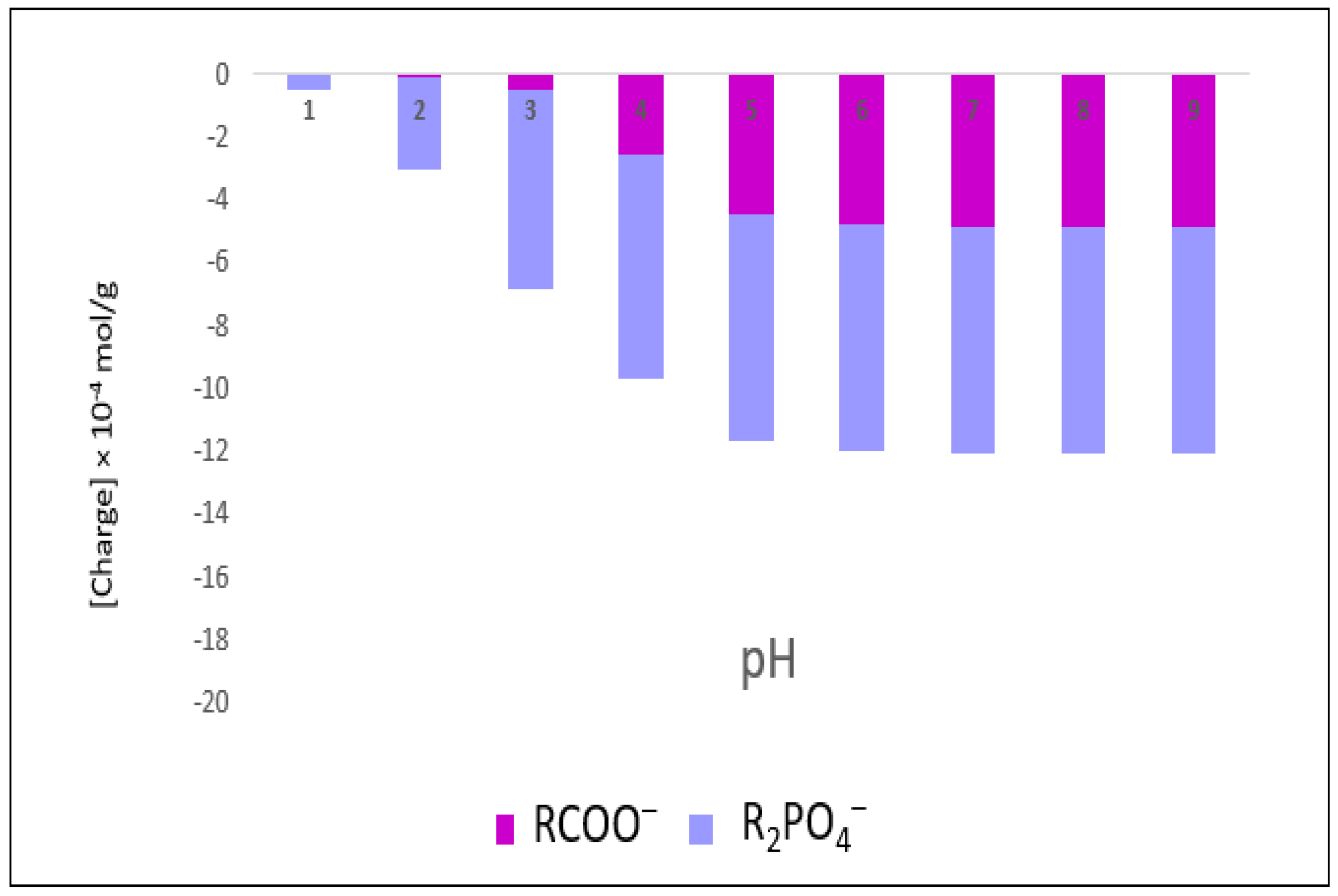
3.4. Contribution of Carboxyl and Phosphate Groups Phi6 Surface Negative Charges
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heffron, J.; Mayer, B.K. Virus isoelectric point estimation: Theories and methods. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e02319-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michen, B.; Graule, T. Isoelectric points of viruses. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 109, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heffron, J.; Mayer, B.K. Emerging investigators series: Virus mitigation by coagulation: Recent discoveries and future directions. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2016, 2, 443–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heffron, J.; McDermid, B.; Maher, E.; McNamara, P.J.; Mayer, B.K. Mechanisms of virus mitigation and suitability of bacteriophages as surrogates in drinking water treatment by iron electrocoagulation. Water Res. 2019, 163, 114877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattle, M.J.; Crouzy, B.; Brennecke, M.; Wigginton, K.R.; Perona, P.; Kohn, T. Impact of virus aggregation on inactivation by peracetic acid and implications for other disinfectants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 7710–7717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dika, C.; Duval, J.F.L.; Francius, G.; Perrin, A.; Gantzer, C. Isoelectric point is an inadequate descriptor of MS2, Phi X 174 and PRD1 phages adhesion on abiotic surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 446, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantini, J.; Azzaz, F.; Chahinian, H.; Yahi, N. Electrostatic surface potential as a key parameter in virus transmission and evolution: How to manage future virus pandemics in the post-COVID-19 era. Viruses 2023, 15, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopalan, R.; Hiemenz, P.C. Principles of Colloid and Surface Chemistry; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1997; Volume 8247, p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- Rouxhet, P.; Misselyn-Bauduin, A.; Ahimou, F.; Genet, M.; Adriaensen, Y.; Desille, T.; Bodson, P.; Deroanne, C. XPS analysis of food products: Toward chemical functions and molecular compounds. Surf. Interface Anal. 2008, 40, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amory, D.; Mozes, N.; Hermesse, M.; Leonard, A.; Rouxhet, P. Chemical analysis of the surface of microorganisms by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1988, 49, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mozes, N.; Léonard, A.; Rouxhet, P.G. On the relations between the elemental surface composition of yeasts and bacteria and their charge and hydrophobicity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Biomembr. 1988, 945, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozes, N.; Amory, D.E.; Léonard, A.J.; Rouxcet, P.G. Surface properties of microbial cells and their role in adhesion and flocculation. Colloids Surf. 1989, 42, 313–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozes, N. Microbial Cell Surface Analysis; VCH Publishers: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Rouxhet, P.; Mozes, N.; Dengis, P.; Dufrêne, Y.; Gerin, P.A.; Genet, M. Application of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy to microorganisms. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 1994, 2, 347–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dengis, P.B.; Rouxhet, P.G. Surface Properties of Top- and Bottom-Fermenting Yeast. Yeast 1997, 13, 931–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouxhet, P.G.; Genet, M.J. XPS analysis of bio-organic systems. Surf. Interface Anal. 2011, 43, 1453–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Haecht, J.L.; Defosse, C.; van den Bogaert, B.; Rouxhet, P.G. Surface properties of yeast cells: Chemical composition By XPS and isoelectric point. Colloids Surf. 1982, 4, 343–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genet, M.J.; Dupont-Gillain, C.C.; Rouxhet, P.G. XPS analysis of biosystems and biomaterials. In Medical Applications of Colloids; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; p. 177. [Google Scholar]
- Gerin, P.A.; Dufrene, Y.; Bellon-Fontaine, M.N.; Asther, M.; Rouxhet, P.G. Surface properties of the conidiospores of Phanerochaete chrysosporium and their relevance to pellet formation. J. Bacteriol. 1993, 175, 5135–5144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Laurinavičius, S.; Käkelä, R.; Bamford, D.H.; Somerharju, P. The origin of phospholipids of the enveloped bacteriophage phi6. Virology 2004, 326, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorenko, A.; Grinberg, M.; Orevi, T.; Kashtan, N. Survival of the enveloped bacteriophage Phi6 (a surrogate for SARS-CoV-2) in evaporated saliva microdroplets deposited on glass surfaces. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 22419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, R.; Dlusskaya, E.; Ashbolt, N.J. SARS-CoV-2 surrogate (Phi6) environmental persistence within free-living amoebae. J. Water Health 2022, 20, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- String, G.M.; White, M.R.; Gute, D.M.; Mühlberger, E.; Lantagne, D.S. Selection of a SARS-CoV-2 Surrogate for Use in Surface Disinfection Efficacy Studies with Chlorine and Antimicrobial Surfaces. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2021, 8, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franke, G.; Knobling, B.; Brill, F.H.; Becker, B.; Klupp, E.M.; Belmar Campos, C.; Pfefferle, S.; Lütgehetmann, M.; Knobloch, J.K. An automated room disinfection system using ozone is highly active against surrogates for SARS-CoV-2. J. Hosp. Infect. 2021, 112, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.; Marr, L.C. Aerosolization of Ebola virus surrogates in wastewater systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2669–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitworth, C.; Mu, Y.; Houston, H.; Martinez-Smith, M.; Noble-Wang, J.; Coulliette-Salmond, A.; Rose, L. Persistence of bacteriophage phi 6 on porous and nonporous surfaces and the potential for its use as an Ebola virus or coronavirus surrogate. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e01482-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adcock, N.J.; Rice, E.W.; Sivaganesan, M.; Brown, J.D.; Stallknecht, D.E.; Swayne, D.E. The use of bacteriophages of the family Cystoviridae as surrogates for H5N1 highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses in persistence and inactivation studies. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2009, 44, 1362–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shchukarev, A.; Backman, E.; Watts, S.; Salentinig, S.; Urban, C.F.; Ramstedt, M. Applying Cryo-X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy to Study the Surface Chemical Composition of Fungi and Viruses. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 666853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufrêne, Y.F.; Boonaert, C.J.; Rouxhet, P.G. Surface analysis by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy in study of bioadhesion and biofilms. Methods Enzymol. 1999, 310, 375–389. [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Mei, H.C.; Busscher, H.J. The Use of X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy for the Study of Oral Streptococcal Cell Surfaces. Adv. Dent. Res. 1997, 11, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armanious, A.; Aeppli, M.; Jacak, R.; Refardt, D.; Sigstam, T.; Kohn, T.; Sander, M. Viruses at Solid–Water Interfaces: A Systematic Assessment of Interactions Driving Adsorption. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 732–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, A.M.Q.; Adams, M.J.; Carstens, E.B.; Lefkowitz, E.J. Virus Taxonomy; Elsevier Academic Press Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ramstedt, M.; Leone, L.; Persson, P.; Shchukarev, A. Cell wall composition of Bacillus subtilis changes as a function of pH and Zn2+ exposure: Insights from cryo-XPS measurements. Langmuir 2014, 30, 4367–4374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamadi, F.; Latrache, H.; Zahir, H.; Bengourram, J.; Kouider, N.; Elghmari, A.; Habbari, K. Evaluation of the relative cell surface charge by using microbial adhesion to hydrocarbon. Microbiology 2011, 80, 488–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latrache, H.; Mozes, N.; Pelletier, C.; Bourlioux, P. Chemical and physicochemical properties of Escherichia coli: Variations among three strains and influence of culture conditions. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 1994, 2, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.; Henrich, V.; Casey, W.; Clark, D.; Eggleston, C.; Felmy, A.F.A.; Goodman, D.; Gratzel, M.; Maciel, G.; McCarthy, M.; et al. Metal Oxide Surfaces and Their Interactions with Aqueous Solutions and Microbial Organisms. Chem. Rev. 1999, 1, 77–174. [Google Scholar]
- Po, H.N.; Senozan, N.M. The Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation: Its History and Limitations. J. Chem. Educ. 2001, 78, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Bacteriophage | C [285.0]/Ctot | C [286.5]/Ctot | C [288.2]/Ctot | C [289.5]/Ctot | P | C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phi6 | 0.42 ± 0.02 | 0.39 ± 0.01 | 0.18 ± 0.01 | 0.01 ± 0.00 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 50.2 ± 4.4 |
| Constituent | C-(C,H)/C | C-(O,N)/C | C=O/C | Carbon Concentration (mmol/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein | 0.428 | 0.293 | 0.279 | 43.5 |
| Polysaccharide | 0.000 | 0.833 | 0.167 | 37 |
| Hydrocarbon | 1.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 71.4 |
| Proteins | Polysaccharides | Hydrocarbons | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phi6 | 46.3 ± 0.7 | 30.5 ± 1.7 | 22.1 ± 1.2 |
| [RCOOH] × 10−4 mol/g | [R2PO4H] × 10−4 mol/g | |
|---|---|---|
| Phi6 | 7.08 ± 1.08 | 7.52 ± 0.58 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chennoufi, I.H.; Zanane, C.; Hakim, T.; Zahir, H.; Hamadi, F.; El Ghmari, A.; El Louali, M.; Latrache, H. Estimation of the Negative Charge of Phi6 Virus and Its Variations with pH Using the Literature XPS Data. Biophysica 2025, 5, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/biophysica5010008
Chennoufi IH, Zanane C, Hakim T, Zahir H, Hamadi F, El Ghmari A, El Louali M, Latrache H. Estimation of the Negative Charge of Phi6 Virus and Its Variations with pH Using the Literature XPS Data. Biophysica. 2025; 5(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/biophysica5010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleChennoufi, Ikhlas Hani, Chorouk Zanane, Taoufik Hakim, Hafida Zahir, Fatima Hamadi, Abderrahmene El Ghmari, Mostafa El Louali, and Hassan Latrache. 2025. "Estimation of the Negative Charge of Phi6 Virus and Its Variations with pH Using the Literature XPS Data" Biophysica 5, no. 1: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/biophysica5010008
APA StyleChennoufi, I. H., Zanane, C., Hakim, T., Zahir, H., Hamadi, F., El Ghmari, A., El Louali, M., & Latrache, H. (2025). Estimation of the Negative Charge of Phi6 Virus and Its Variations with pH Using the Literature XPS Data. Biophysica, 5(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/biophysica5010008






