Abstract
Cells are continually exposed to a range of electromagnetic fields (EMFs), including those from the Schumann resonance to radio waves. The effects of EMFs on cells are diverse and vary based on the specific EMF type. Recent research suggests potential therapeutic applications of EMFs for various diseases. In this study, we explored the impact of a physiologically patterned EMF, inspired by the H3 receptor associated with wakefulness, on PC-12 cells in vitro. Our hypothesis posited that the application of this EMF to differentiated PC-12 cells could enhance firing patterns at specific frequencies. Cell electrophysiology was assessed using a novel device, allowing the computation of spectral power density (SPD) scores for frequencies between 1 Hz and 128 Hz. T-tests comparing SPD at certain frequencies (e.g., 29 Hz, 30 Hz, and 79 Hz) between the H3-EMF and control groups showed a significantly higher SPD in the H3 group (p < 0.050). Moreover, at 7.8 Hz and 71 Hz, a significant correlation was observed between predicted and percentages of cells with neurites (R = 0.542). Key findings indicate the efficacy of the new electrophysiology measure for assessing PC-12 cell activity, a significant increase in cellular activity with the H3-receptor-inspired EMF at specific frequencies, and the influence of 7.8 Hz and 71 Hz frequencies on neurite growth. The overall findings support the idea that the electrical frequency profiles of developing cell systems can serve as an indicator of their progression and eventual cellular outcomes.
1. Introduction
We are continuously immersed in the electromagnetic environment. Biological systems have developed within this context, and the role of electromagnetic fields (EMF) in cell growth and maintenance is an ongoing and complex field of research. Depending on the type of applied EMF, various cellular outcomes can be expected [1,2]. Cellular processes like apoptosis, cell regulation, and cell proliferation have all been demonstrated to be affected by an applied external EMF [3,4,5]. Recent research [6,7] has also explored how specific electromagnetic environments can enhance tissue regeneration and wound healing by modulating cell growth and differentiation. It is at the intersection of the background electromagnetic environment and applied EMFs that this research fits. Here, we aim to identify if physiologically patterned EMFs can enhance the growth processes of PC-12 cells in vitro. PC-12 cells are widely used in neuroscience and cell biology research given their capacity to differentiate into neuron-like cells [8]. It has been previously reported that the application of a cAMP activator can induce differentiation in PC-12 cells, leading them to develop into neuron-like cells characterized by the presence of small extensions called ‘neurites’ [8]. Our group [9] has previously demonstrated that the application of weak physiologically patterned EMF can induce the growth of neurites in PC-12 cells in vitro. However, this only focused on the presence of neurites; no physiological data were obtained during data collection. In this experiment, we developed a novel EMF model based on the H3 receptor and exposed PC-12 cells to this physiologically patterned EMF, or a sine wave EMF, while recording electrophysiological measurements of the cells throughout the experiment. We discuss our measures, the rationale behind choosing the H3 receptor as a model for EMF, and the inclusion of the Schumann resonance as part of the electromagnetic environment below.
1.1. Electromagnetic Fields
An especially promising method is the use of electromagnetic fields (EMFs) as a novel therapeutic for the treatment of disorders. Previous work by our lab [10,11] and others using rTMS [12,13,14] has illustrated the therapeutic power of applied EMFs. This non-invasive tool elicits its effects through the generation of a brief magnetic pulse produced by a pulse generator that discharges current through the scalp [15]. Depending on the frequency of the stimulus, intensity, how long it is applied, and structure of the magnetic pulse, there are several lasting effects of rTMS application [16]. This can be explained by Michael Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, wherein he states that magnetic fields interact with electrical currents. Furthermore, the Maxwell-Faraday equation states that every electrical current has a corresponding magnetic field and vice versa. Therefore, given the electrical nature of our neurons, the short electrical pulses from this technology can allow for the initiation of neuronal firing within cortical and subcortical areas of the brain, resulting in the release of neurotransmitters [17]. Wang et al. [13] have demonstrated that rTMS appears to be quite effective in targeting the cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB1) to treat depressive disorders. Additionally, an increase in cell proliferation, hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), and Bcl-2/Bax expression were induced by rTMS through the CB1 receptor, indicating promising results for stimulation of subcortical receptors for the treatment of neurological disorders [13].
1.2. Histamine-H3-Receptor and Wakefulness
In terms of wakefulness and arousal, the tuberomammillary nucleus (TMN) of the posterior hypothalamus has been implicated in the facilitation of these functions due to the presence of histaminergic neurons within this area [18,19]. Additionally, the projections to the cholinergic basal forebrain and locus coeruleus, which are involved in regulating wakefulness and cortical arousal, are suggested to be stimulated by histamine [18]. The function of histamine in maintaining wakefulness is further established through the deficiencies in waking and attention in mice lacking histidine decarboxylase (HDC), an enzyme responsible for the biosynthesis of histamine [19]. It is strongly and consistently suggested that the regulation of sleep-wakefulness is strongly influenced by both the H1 and H3 receptors of the TMN, where stimulation of the H1-receptor induces wakefulness and blocking the receptor promotes sleep, and the opposite effects are seen for the H3-receptor [20]. To pave the way for further experimentation, the focus of this experiment will be the modulation of the H3-receptor because there are known effective pharmaceuticals that target this receptor in vivo and can cross the blood–brain barrier [21]. The H3-receptor is a presynaptic auto-receptor shown to be essential in both the regulation and synthesis of histamine via negative feedback, restricting excessive synthesis and release [22]. The current literature has substantiated the effectiveness of H3-receptor antagonists, like thioperamide, in increasing histamine release by blocking histamine from binding to the H3-receptor and thus inhibiting the negative feedback from occurring [22,23,24,25]. Because an increase in histamine has been implicated in an increase in wakefulness, it is then reasonable to suggest that blocking the H3-receptor will also result in increasing wakefulness, and evidence for this claim has been supported by several research articles [22,23,24,25,26,27]. Other experiments have observed and demonstrated that EMFs patterned after the distinct pattern seen during memory consolidation, called long-term potentiation (LTP), significantly altered the memory of rats during spatial tasks [28]. Although some evidence has shown that EMFs can be utilized to manipulate cortical circuits, there is much to be explored in this area, specifically whether EMFs can elicit effects on specific subcortical receptors, like the H3-receptor. Several studies have demonstrated the presence of the H3-receptor in rat parenchymal PC-12 cells, making them an adequate model for this study [29,30,31].
1.3. Schumann Resonances and Their Effect on Biological Systems
The Schumann resonances (SRs) are a series of global electromagnetic resonances primarily generated by lightning discharges between the ionosphere and the Earth’s surface [32]. These frequency peaks occur within the extremely low frequency (ELF) range of the Earth’s electromagnetic field spectrum, consisting of 7.8 Hz, 14.3 Hz, 20.8 Hz, and 27.3 Hz up to approximately 60 Hz [32]. As previously discussed, the effects of electromagnetic fields and their effects on biological systems have been well documented. Therefore, given the electromagnetic nature of the Schumann resonances, several research articles have investigated their various effects on humans and other biological systems. A review article by Danho et al. [33] mentions how the SR has been implicated in altering certain neural circuits and cortical regions like the hippocampus and the melatonin/serotonin balance, which can impact sleep and may influence the development of illnesses such as cancer and heart disease. Other experimental studies have further suggested the potential influence of the SR on various cardiac-related features, such as inducing cardioprotection from stress conditions by reducing calcium transients through applying magnetic fields in the SR band (7.6–8 Hz) [34] its influence on heart rate variability and circadian rhythms [35]; and a coincidence between the number of cardiovascular-related hospital admissions and the amplitudes of SR and energy, specifically within the North–South orientation [36].
While no studies to date have investigated the relationship between Ca2+ ions and the histamine H3-receptor specifically, it is quite possible that a relationship does in fact exist and may also help explain the connection between the H3-receptor and the Schumann resonance. Previous studies have outlined how the SR can alter levels of Ca2+ transients in biological systems [34,37], which could potentially impact histamine synthesis and therefore overall activation of the H3-receptor [38,39]. The connection between histamine, EMFs, and neurite outgrowth is central to this project. In this experiment, we aimed to identify if physiologically pattered EMFs (modeled after the H3 receptor) have an influence on neurite outgrowth and if any inherent electrical activity is indicative of differentiation of PC12 cells.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. PC-12 Cell Maintenance
An RPMI-1640 medium (Cytiva from FisherScientific, Toronto, ON, Canada) that was supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Cytiva from FisherScientific, Toronto, ON, Canada), 100 U/mL penicillin, 5% horse serum (Gibco from FisherScientific, Toronto, ON, Canada), and 0.1 mg/mL streptomycin (Corning from FisherScientific, Toronto, ON, Canada) was used to culture PC-12 cell stocks. These stocks were grown to approximately 95% confluence while stored in a humidified incubator at 37 °C and 5% CO2, before being split (7–14 days). Mini-adherence 35 mm culture dishes were used to culture the experimental, SINE, and control samples. Poly-L-Lysine was first used to coat the bottom of the plates, and 100 μL of cell solution was added after the coating dried. After growing in the supplemented media for approximately 24 h, the media was then exchanged with serum-free RPMI media, and 10 μM forskolin was subsequently added [9].
2.2. Electromagnetic Field (EMF) Design
The pattern of the EMF was based on the amino acid sequence of the Histamine-3-receptor, which was obtained from [40]. Each amino acid in the sequence was matched to its corresponding EIIP value, as shown in Cosic [41]. To ensure the field would be read by the computer, the values were then standardized into voltage binary values, where the max EIIP of 0.1263 Ry was multiplied by the max binary value of 255, yielding 2019.002. This value was then multiplied by every EIIP value in the amino acid sequence to standardize the EMF pattern.
2.3. Exposure Protocol
Two experimental cells were stacked on top of each other and placed in the middle of a milk crate coiled with insulated copper wire. The exposure device was then connected to a computer (Zenith) where the EMF pattern was stored. By running the EMF from the computer, it transmits the electrical pattern to the exposure device, resulting in the corresponding magnetic field being emitted at a strength of approximately 1 μT. The exposure period lasted 40 min, after which the cells were promptly once again stored in the incubators. For the SINE wave group, the procedure was the same as in the H3 group. During exposure, the two control groups were stored in a Styrofoam box in another room to avoid any possible crossover exposure.
Two application geometries were employed to apply the electromagnetic field: (1) an EMF applicator supplied with two solenoids and (2) a Helmholtz coil, which was fabricated by coiling insulated copper wire around a typical milk crate. A custom-built digital-to-analogue converter (DAC) was used to produce the field through both geometries. The field pattern was stored and applied using a Zenith ZF 148-42 (Intel 8008 16-bit CPU with 4.7 or 8 MHz operation) computer equipped with the custom-made software called Complex-2 [42]. Each point on the EMF pattern was a value between 0 and 255 mV, which the DAC then converted to values between −5 and +5 mV.
2.4. Data Collection
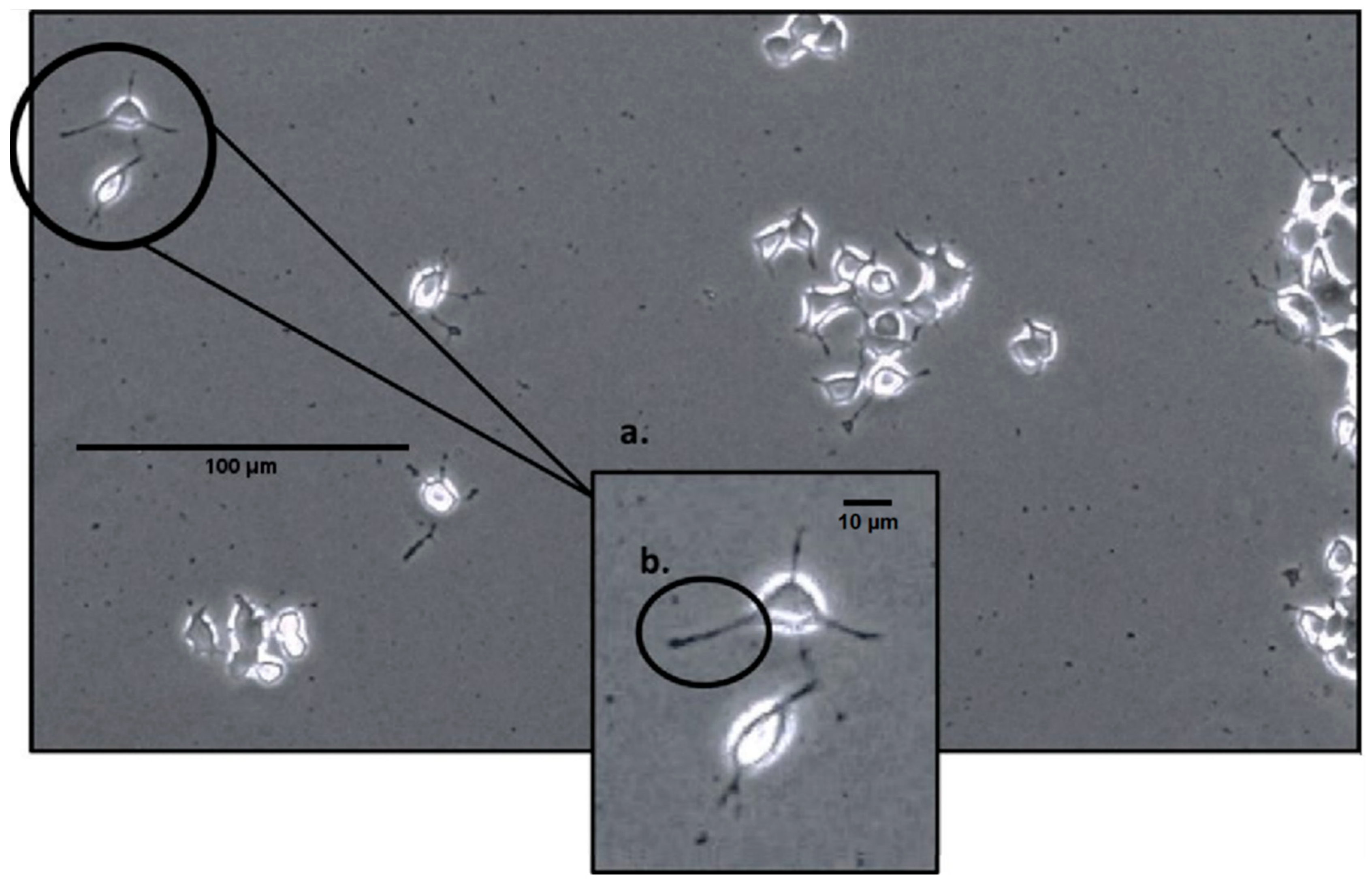
On the second day after EMF exposure, each of the plates (2 per condition; 3 conditions for 4 trials yielding a total N = 24) was analyzed using a phase-contrast microscope at 100× magnification. The microscope was connected to a computer, and six pictures (two pictures for three different areas of the cell plate) were taken for each plate using the InfinityCapture software (https://pdf.directindustry.com/pdf/lumenera/infinity-capture-microscopy-software/17338-625411.html, accessed on 24 January 2024). After all the pictures were taken, they were stored, and the number of cells was counted, as well as whether cells bore 0, 1 or 2 ≤ neurite extensions. The technical classification of a neurite was defined as any extension or protrusion from the cell body that measured at least half the length of the cell, as seen in Figure 1. Due to unavoidable circumstances, only 18 of the 24 cell plates had their neurites counted and recorded.
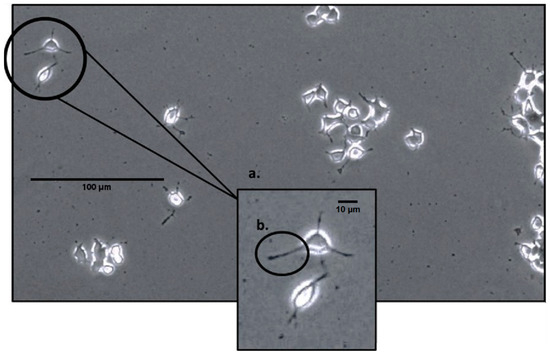
Figure 1.
An image of PC-12 cells under a phase-contrast microscope at 100× magnification; (a) demonstrates a close-up of two cells displaying neurites; (b) demonstrates a neurite, a short extension from the cell body that is at least half of its length.
In addition, electrophysiological measures of the cells were also conducted. This measure took place two days after EMF exposure. The measuring technique consisted of two sets of copper wires: one wrapped around the bottom of the control, SINE, or H3 groups, and another in a plate containing only the medium and a ground. This was necessary as a control for the activity of the media compared to the actual PC-12 cells. Each of these wires was connected to an amplifier, which was connected to a laptop via USB. The laptop then monitored the electrophysiological activity of the cells and the medium. Spectral power density (SPD) was then quantified for each group for frequencies between 1 Hz and 128 Hz.
2.5. Data Analysis
All statistical operations were conducted in IBM SPSS 18 software for PCs. The two most important data points were the total number of cells (CTotal) and the total number of cells that presented neurites (CNeur). To acquire the percentage of cells that bore neurites, the following equation was utilized:
All electrophysiology scores were standardized by converting each score (between 1 Hz and 128 Hz) to a Z-score. The data were then compared between each experimental group (i.e., control, SINE, and H3) using linear regression analysis to investigate the relationship with neurite outgrowth and a non-parametric Kruskal–Wallis test to investigate the differences in SPD across frequencies. To corroborate the Kruskal–Wallis results and demonstrate significance between groups, post hoc Mann–Whitney U tests were subsequently utilized.
3. Results
3.1. Neurite Outgrowth and Frequency Analysis
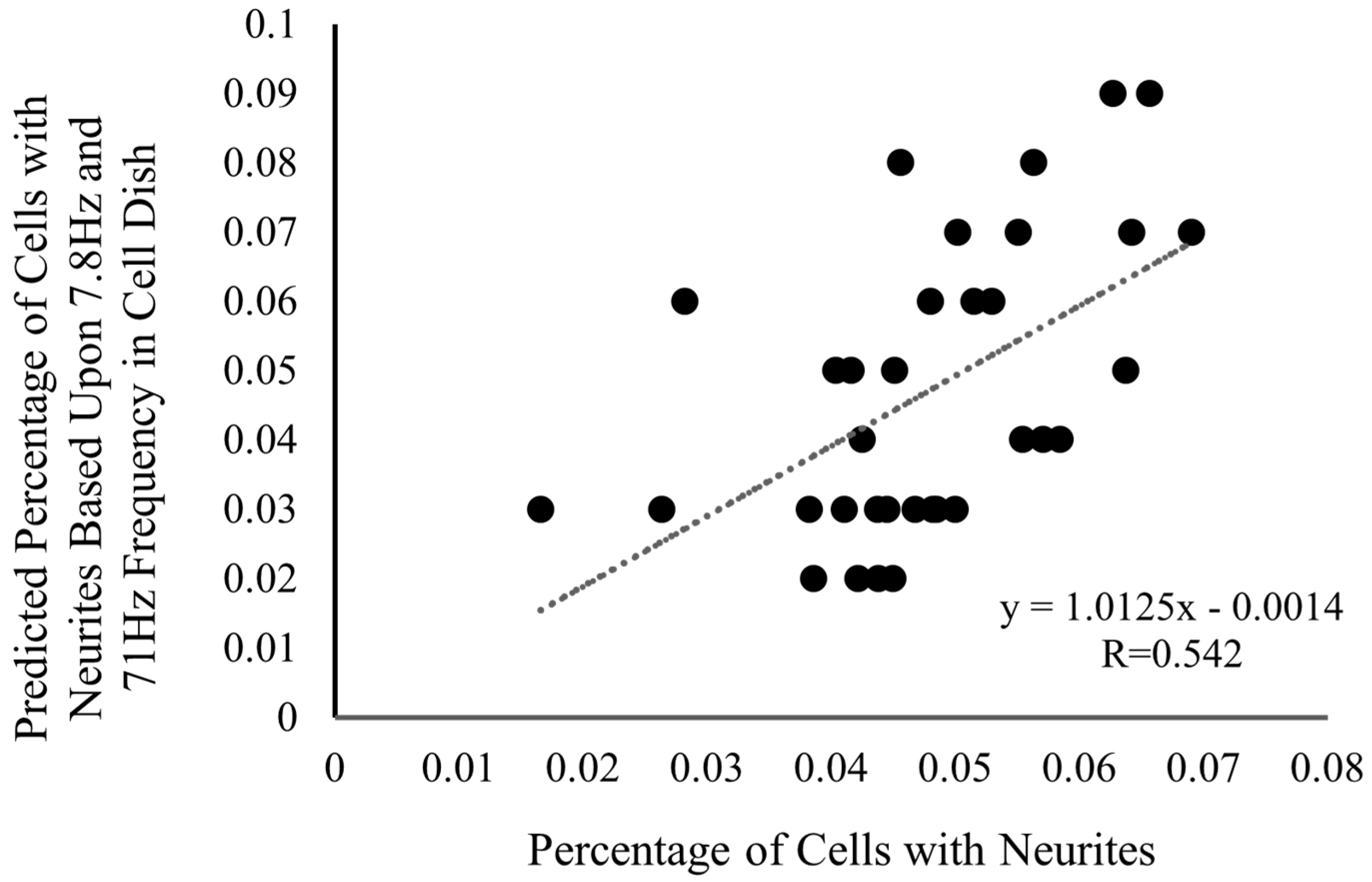
Following spectral analysis, it was revealed that among the 128 frequencies examined (n = 18), only one was correlated with neurite outgrowth: 71 Hz. The correlation was r = 0.365 71 Hz; this was confirmed with Spearman correlations and alpha error correction (p < 0.05). Following this, a stepwise multiple regression was run, and results demonstrated a strong correlation (R = 0.542) between the predicted percentage of cells with neurites and the actual percentage of cells with neurites in the dish when utilizing two frequencies in conjunction: 71 Hz and 7.8 Hz. The prediction equation was: [y = (0.01) × 71 Hz − (0.008) × 7.8 Hz + 0.048], where 71 Hz is positively related, and 7.8 Hz is negatively related. This relationship can be seen in Figure 2. These frequencies are intriguing for distinct reasons, as 7.8 Hz corresponds to the fundamental mode of the Schumann resonance, while the 71 Hz frequency remains to be fully validated. It is, however, worth mentioning that it is the 71 Hz frequency that appears to be the main factor in this relationship, and the 7.8 Hz is only observed when 71 Hz is present, indicating a potential supplemental role of the Schumann resonance in the growth of neurites.
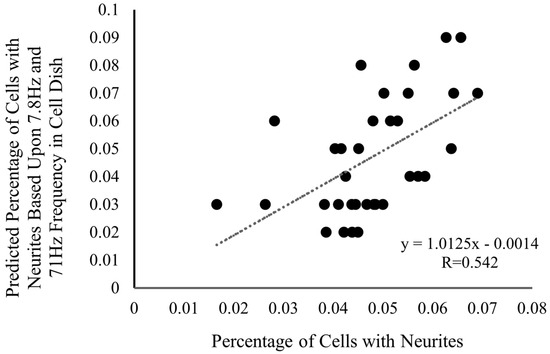
Figure 2.
The predicted percentage of cells with neurites at 7.8 Hz and 71 Hz versus the actual percentage of cells with neurites depicts a relatively strong correlation (R = 0.542; n = 18). A neurite in this paper is defined as any extension from the cell that is at least half of the cell’s body length. The prediction equation is defined as: y = (0.01) × 71 Hz − (0.008) × 7.8 Hz + 0.048.
3.2. Electrophysiology of PC-12 Cells–Control vs. SINE vs. H3
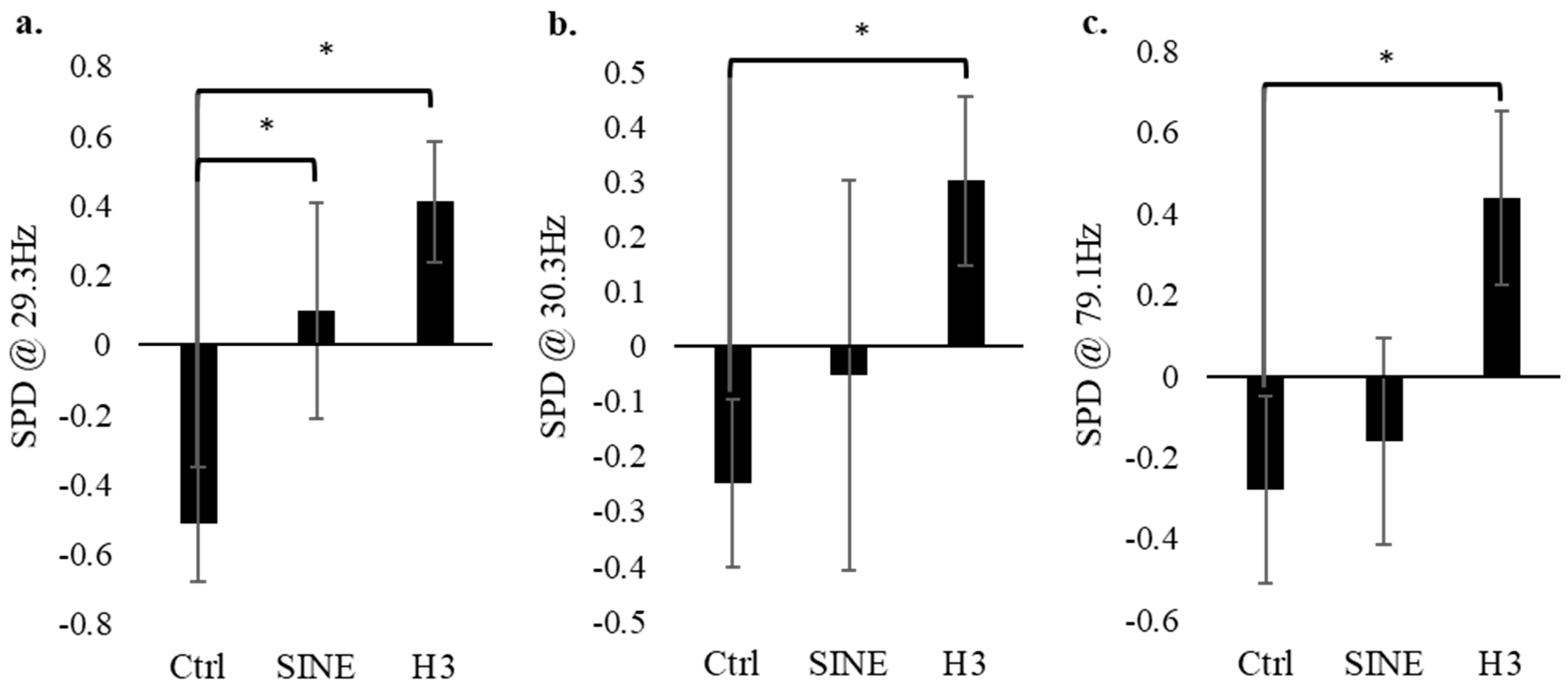
A non-parametric Mann–Whitney U test (n = 24) of the standardized electrophysiology values between 1 Hz and 128 Hz revealed significance in three main frequencies: 29.3 Hz, 30.3 Hz, and 79.1 Hz. In each case, their p-values were less than 0.016 (Figure 3). In each of these frequencies, the control (no EMF conditions) had significantly lower electrical activity compared to the H3 field condition. The electrophysiology data for the control group were quite consistent throughout all 128 frequencies measured, primarily showing a consistently low SPD. The SINE data also remained consistent, typically displaying SPD values that circulate around the baseline. Finally, the H3 group also showed significantly higher SPD values across the three aforementioned frequencies, indicating that the H3-receptor-modeled EMF evoked significantly more cellular activity at 29.3 Hz, 30.3 Hz, and 79.1 Hz.
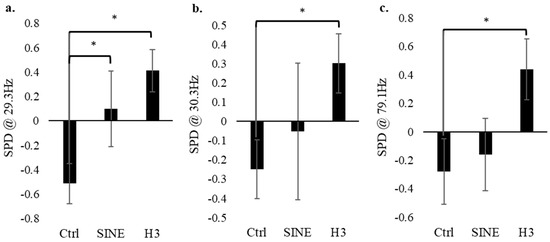
Figure 3.
The spectral power density (SPD) at 29.3 Hz, 30.3 Hz, and 79.1 Hz for the control (no EMF), SINE-EMF and H3-EMF cell groups (n = 24). Analysis indicates that at certain frequencies, i.e., 21.5 Hz (a), 30.3 Hz (b), 79.1 Hz (c), there is significantly more activity in the H3 group compared to the control. Error bars represent the standard error. * Refers to significance p < 0.050.
4. Discussion
The data presented demonstrate two major features: cell electrical activity within specific frequency bands is heightened when exposed to physiologically patterned EMFs, and the generation of neurites from these cells correlates with the recorded amounts of 71 Hz and 7.8 Hz. The significance of the 71 Hz frequency has not been fully substantiated; nevertheless, intriguing results have emerged from studies examining disorders of consciousness. Zhuang and colleagues [43] demonstrated that stimulating the spinal cord at 70 Hz in patients in a vegetative state elicited a positive EEG response. This stimulation increased parietal-occipital connectivity and beta frequencies. While this is a single case, results from a large sample study [44] demonstrate physiological relevance to the 71 Hz frequency band. This relevance is to the central nervous system (CNS), and our specific focus was on the generation of neurites—a key aspect of neuronal connectivity, which was the primary metric we measured. As previously stated, the 7.8 Hz frequency coincides with the fundamental mode frequency of the Schumann resonance. Given the nature of electromagnetic fields and how they have been shown to interact with not only cell cultures but also our brains, this might be a potent finding that suggests that neurite generation and outgrowth could be influenced by the Earth’s magnetic field. Studies have analyzed the influence of this background magnetic field on human behaviour by measuring the EEGs of several participants over the course of years and simultaneously monitoring the activity of this background magnetic field [45]. They found that during cosmic disturbances like solar storms, where we see a perturbation in the Earth’s magnetic field, there are certain associated decreases within the right prefrontal cortex, which manifest in marked behaviors like erroneous reconstruction of memory and emotional lability [45,46]. However, subsequent research would have to be conducted to confirm the validity of this result, perhaps with different cell lines, to conclusively determine how the Earth’s magnetic field and the 71 Hz frequency might influence cell development and proliferation.
The observation that weak physiologically patterned EMFs can influence cell systems is supported by previous research from our lab and others [5,42,47]. With respect to our novel H3 EMF, it has been demonstrated that higher cortical rhythms between 20 and 60 Hz can be enhanced by certain inverse agonists of the H3-receptor, which might possibly explain the increased cellular activity demonstrated by the H3-EMF at these three frequencies, suggesting that this EMF might have a similar inverse agonist effect on the receptors [21,48]. As for the significance of the 79 Hz frequency, Atzori et al. [49] have shown that high-frequency oscillations (>70 Hz) were significantly decreased following the application of an H2-agonist. While this does not specifically rationalize the significance of the 79 Hz outlined in this article, it could perhaps provide additional credence to the H3-EMF having an inverse agonist effect considering its augmentation of cellular activity.
Given that culturing human neurons can oftentimes be quite strenuous and cumbersome, we decided that PC-12 cells would prove to be a simple and effective alternative model. These cells are one of the most commonly used cell lines in neurobiological studies due to their striking similarities to a typical neuron, such as that they share comparable morphology, can differentiate (neurites), secrete similar neurotransmitters (i.e., dopamine, histamine, serotonin, etc.), and possess receptors and ion channels [29,50,51]. It is therefore sensible to argue that the results outlined in this paper may perhaps shed light on the potential influences on cellular differentiation in other biological systems.
Here, we have demonstrated a correlation between the percentage of cells displaying neurites and the levels of 7.8 Hz and 71 Hz directly measured from these cells. The incorporation of the 71 Hz frequency may suggest a connection to neural connectivity or even consciousness within the CNS. Ultimately, the study supports the notion that appropriately patterned, weak EMFs can influence the development of cell systems. Furthermore, the frequency profile of developing cell systems serves as an indicator of their progression and eventual cellular outcomes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.M.L. and B.T.D.; methodology, L.M.L. and B.T.D.; validation, K.S.S.; formal analysis, L.M.L. and B.T.D.; investigation, L.M.L. and A.D.P.-K.; resources, K.S.S. and B.T.D.; data curation, L.M.L. and K.S.S.; writing—original draft preparation, L.M.L.; writing—review and editing, L.M.L. and B.T.D.; supervision, B.T.D.; project administration, B.T.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data is available upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Adey, W.R. Biological effects of electromagnetic fields. J. Cell. Biochem. 1993, 51, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacic, P.; Somanathan, R. Electromagnetic fields: Mechanism, cell signaling, other bioprocesses, toxicity, radicals, antioxidants and beneficial effects. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. 2010, 30, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Li, X.; Bai, L.; Uchida, K.; Bai, W.; Wu, B.; Xu, W.; Zhu, H.; Huang, H. Effects of low frequency electromagnetic field on proliferation of human epidermal stem cells: An in vitro study. Bioelectromagnetics 2013, 34, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rain, B.; Plourde-Kelly, A.; Lafrenie, R.L.; Dotta, B.T. Induction of apoptosis in B16-BL6 Melanoma Cells Following Exposure to Electromagnetic Fields modelled after Intercellular Calcium Waves. FEBS Open Biol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, R.; Branigan, K.S.; Lefebvre, L.M.; Dotta, B.T. Effects of Patterned Electromagnetic Fields and Light-Emitting Diodes on Cancer Cells: Impact on Cell Density and Biophoton Emission When Applied Individually vs. Simultaneously. Appl. Biosci. 2023, 2, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesce, M.; Patruno, A.; Speranza, L.; Reale, M. Extremely low frequency electromagnetic field and wound healing: Implication of cytokines as biological mediators. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2013, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caliogna, L.; Medetti, M.; Bina, V.; Brancato, A.M.; Castelli, A.; Jannelli, E.; Ivone, A.; Gastaldi, G.; Annunziata, S.; Mosconi, M.; et al. Pulsed electromagnetic fields in bone healing: Molecular pathways and clinical applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter-Landsberg, C.; Jastorff, B. The role of cAMP in nerve growth factor-promoted neurite outgrowth in PC-12 cells. J. Cell Biol. 1986, 102, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carniello, T.N.; Lafrenie, R.M.; Dotta, B.T. The Influence of Burst-Firing EMF on Forskolin-Induced Pheochromocytoma (PC-12) Plasma Membrane Extensions. NeuroSci 2021, 2, 383–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachapelle, H.M. Neuroprotective Effects of Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase Inhibitor (URB597) and Low-Frequency EMF against Paraquat-Induced Neurotoxicity: Relevance to Neurodegenerative Disease. Ph.D. Thesis, Laurentian University of Sudbury, Sudbury, ON, Canada, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Plourde-Kelly, A. Protein-Patterned EMF as Enzymatic Moderators: Evidence for a Non-Invasive Method of Cellular Manipulation. Ph.D. Thesis, Laurentian University of Sudbury, Sudbury, ON, Canada, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Naeser, M.A.; Martin, P.I.; Treglia, E.; Ho, M.; Kaplan, E.; Bashir, S.; Hamilton, R.; Coslett, H.B.; Pascual-Leone, A. Research with rTMS in the treatment of aphasia. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 2010, 28, 511–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.N.; Wang, L.; Zhang, R.G.; Chen, Y.C.; Liu, L.; Gao, F.; Nie, H.; Hou, W.-G.; Peng, Z.-W.; Tan, Q. Anti-depressive mechanism of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in rat: The role of the endocannabinoid system. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2014, 51, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutherford, G.; Lithgow, B.; Moussavi, Z. Short and long-term effects of rTMS treatment on Alzheimer’s disease at different stages: A pilot study. J. Exp. Neurosci. 2015, 9, JEN-S24004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefaucheur, J.P.; André-Obadia, N.; Antal, A.; Ayache, S.S.; Baeken, C.; Benninger, D.H.; Cantello, R.M.; Cincotta, M.; de Carvalho, M.; De Ridder, D.; et al. Evidence-based guidelines on the therapeutic use of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS). Clin. Neurophysiol. Off. J. Int. Fed. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2014, 125, 2150–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogendam, J.M.; Ramakers, G.M.; Di Lazzaro, V. Physiology of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of the human brain. Brain Stimul. 2010, 3, 95–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priori, A.; Hallett, M.; Rothwell, J.C. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation or transcranial direct current stimulation? Brain Stimul. 2009, 2, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramesh, V.; Thakkar, M.M.; Strecker, R.E.; Basheer, R.; McCarley, R.W. Wakefulness-inducing effects of histamine in the basal forebrain of freely moving rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2004, 152, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, M.; Huang, Z.L.; Qu, W.M.; Eguchi, N.; Yao, M.H.; Urade, Y. Extracellular histamine level in the frontal cortex is positively correlated with the amount of wakefulness in rats. Neurosci. Res. 2004, 49, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakkar, M.M. Histamine in the regulation of wakefulness. Sleep Med. Rev. 2011, 15, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonaventure, P.; Letavic, M.; Dugovic, C.; Wilson, S.; Aluisio, L.; Pudiak, C.; Lord, B.; Mazur, C.; Kamme, F.; Nishino, S.; et al. Histamine H3 receptor antagonists: From target identification to drug leads. Pharmacology 2007, 73, 1084–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.L.; Mochizuki, T.; Qu, W.M.; Hong, Z.Y.; Watanabe, T.; Urade, Y.; Hayaishi, O. Altered sleep–wake characteristics and lack of arousal response to H3 receptor antagonist in histamine H1 receptor knockout mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 4687–4692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leurs, R.; Blandina, P.; Tedford, C.; Timmerman, H. Therapeutic potential of histamine H3 receptor agonists and antagonists. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1998, 19, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmentier, R.; Anaclet, C.; Guhennec, C.; Brousseau, E.; Bricout, D.; Giboulot, T.; Bozyczko-Coyne, D.; Spiegel, K.; Ohtsu, H.; Williams, M.; et al. The brain H3-receptor as a novel therapeutic target for vigilance and sleep–wake disorders. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007, 73, 1157–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.S.; Dauvilliers, Y.; Arnulf, I.; Bastuji, H.; Anaclet, C.; Parmentier, R.; Kocher, L.; Yanagisawa, M.; Lehert, P.; Ligneau, X.; et al. An inverse agonist of the histamine H3 receptor improves wakefulness in narcolepsy: Studies in orexin−/− mice and patients. Neurobiol. Dis. 2008, 30, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, A.J.; Berridge, C.; Dugovic, C.; Laposky, A.D.; Wilson, S.J.; Boggs, J.; Aluisio, L.; Lord, B.; Mazur, C.; Pudiak, C.M.; et al. Acute wake-promoting actions of JNJ-5207852, a novel, diamine-based H3 antagonist. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 143, 649–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passani, M.B.; Lin, J.S.; Hancock, A.; Crochet, S.; Blandina, P. The histamine H3 receptor as a novel therapeutic target for cognitive and sleep disorders. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2004, 25, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mach, Q.H.; Persinger, M.A. Behavioral changes with brief exposures to weak magnetic fields patterned to stimulate long-term potentiation. Brain Res. 2009, 1261, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Hu, W.-W.; Fan, Y.-Y.; Dai, H.-B.; Fu, Q.-L.; Wei, E.-Q.; Luo, J.-H.; Chen, Z. Carnosine protects against NMDA-induced neurotoxicity in differentiated rat PC-12 cells through carnosine-histidine-histamine pathway and H1/H3 receptors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007, 73, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Q.; Dai, H.; He, P.; Hu, W.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Z. The H3 receptor antagonist clobenpropit protects against Abeta42-induced neurotoxicity in differentiated rat PC-12 cells. Die Pharm. 2010, 65, 257–260. [Google Scholar]
- Hashikawa-Hobara, N.; Chan, N.Y.K.; Levi, R. Histamine 3 receptor activation reduces the expression of neuronal angiotensin II type 1 receptors in the heart. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 340, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, C. ELF electromagnetic waves from lightning: The Schumann resonances. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danho, S.; Schoellhorn, W.; Aclan, M. Innovative technical implementation of the Schumann resonances and its influence on organisms and biological cells. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 564, 012081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhalel, G.; Price, C.; Fixler, D.; Shainberg, A. Cardioprotection from stress conditions by weak magnetic fields in the Schumann Resonance band. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martel, J.; Chang, S.H.; Chevalier, G.; Ojcius, D.M.; Young, J.D. Influence of electromagnetic fields on the circadian rhythm: Implications for human health and disease. Biomed. J. 2023, 46, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fdez-Arroyabe, P.; Fornieles-Callejon, J.; Santurtun, A.; Szangolies, L.; Donner, R.V. Schumann resonance and cardiovascular hospital admission in the area of Granada, Spain: An event coincidence analysis approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherry, N.J. Human intelligence: The brain, an electromagnetic system synchronised by the Schumann resonance signal. Med. Hypotheses 2003, 60, 843–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bongers, G.; Bakker, R.A.; Leurs, R. Molecular aspects of the histamine H3 receptor. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007, 73, 1195–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhowmik, M.; Khanam, R.; Vohora, D. Histamine H3 receptor antagonists in relation to epilepsy and neurodegeneration: A systemic consideration of recent progress and perspectives. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 167, 1398–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, C.; Lovenberg, T.W. Molecular and pharmacological characterization of the mouse histamine H3 receptor. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 467, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosic, I. Macromolecular bioactivity: Is it resonant interaction between macromolecules?-theory and applications. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1994, 41, 1101–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, M.L.; Koren, S.A.; Persinger, M.A. Physiologically patterned weak magnetic fields applied over left frontal lobe increase acceptance of false statements as true. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2008, 27, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Ge, Q.; Li, Q.; Xu, L.; Geng, X.; Wang, R.; He, J. Combined behavioral and EEG evidence for the 70 Hz frequency selection of short-term spinal cord stimulation in disorders of consciousness. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanno, T.; Morita, I.; Yamaguchi, S.; Yokoyama, T.; Kamei, Y.; Anil, S.M.; Karagiozov, K.L. Dorsal column stimulation in persistent vegetative state. Neuromodul. Technol. Neural Interface 2009, 12, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulligan, B.P. Biological Effects of Actual and Simulated Geomagnetic Fields. Master’s Thesis, Library and Archives Canada = Bibliothèque et Archives Canada, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Rouleau, N.; Dotta, B.T. Electromagnetic fields as structure-function zeitgebers in biological systems: Environmental orchestrations of morphogenesis and consciousness. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plourde-Kelly, A.D.; Dotta, B.; Koren, S. p38 MAPK patterned EMF affects PC-12 neurite outgrowth after 2 days of treatment. Brain Stimul. 2021, 14, 1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.S.; Sergeeva, O.A.; Haas, H.L. Histamine H3 receptors and sleep-wake regulation. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2011, 336, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzori, M.; Lau, D.; Tansey, E.P.; Chow, A.; Ozaita, A.; Rudy, B.; McBain, C.J. H2 histamine receptor-phosphorylation of Kv3. 2 modulates interneuron fast spiking. Nat. Neurosci. 2000, 3, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, G.; Costa, L.G. Primary neurons in culture and neuronal cell lines for in vitro neurotoxicological studies. In In Vitro Neurotoxicology: Methods and Protocols; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 13–27. [Google Scholar]
- Oprea, D.; Sanz, C.G.; Barsan, M.M.; Enache, T.A. PC-12 cell line as a neuronal cell model for biosensing applications. Biosensors 2022, 12, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).