Can Robots Keep You Upright? An Ergonomic Analysis of Surgeon Posture in Robotic Versus Conventional Total Knee Arthroplasty
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
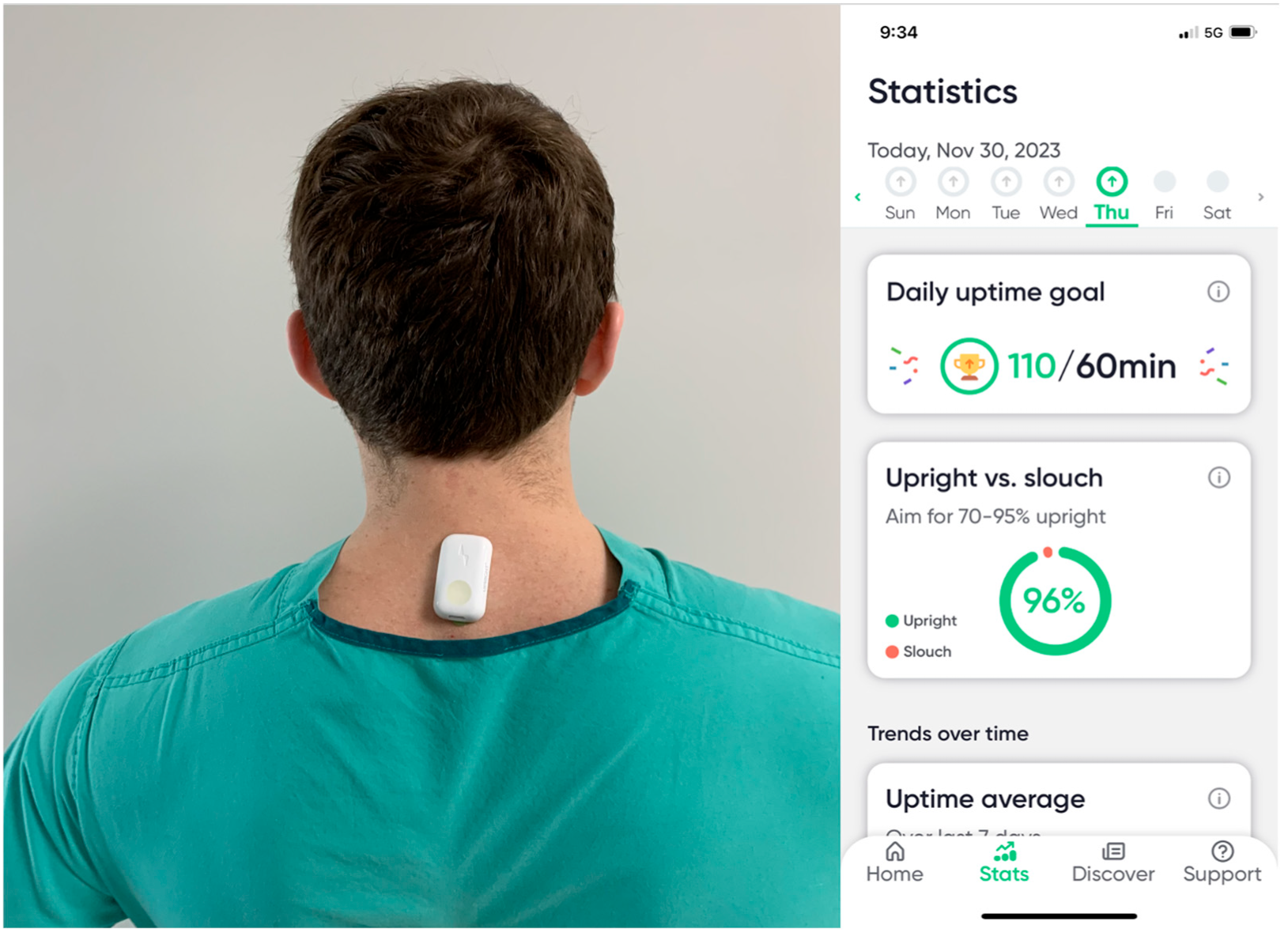
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Demographics
2.3. Controlling for Surgeon Posture
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TKA | Total knee arthroplasty |
| raTKA | Robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty |
| cTKA | Conventional total knee arthroplasty |
References
- Epstein, S.; Sparer, E.H.; Tran, B.N.; Ruan, Q.Z.; Dennerlein, J.T.; Singhal, D.; Lee, B.T. Prevalence of work-related musculoskeletal disorders among surgeons and interventionalists: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Surg. 2018, 153, e174947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seagull, F.J. Disparities between industrial and surgical ergonomics. Work 2012, 41 (Suppl. S1), 4669–4672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirbod, S.M.; Yoshida, H.; Miyamoto, K.; Miyashita, K.; Inaba, R.; Iwata, H. Subjective complaints in orthopedists and general surgeons. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 1995, 67, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rademacher, K.; Pichler, K.V.; Erbse, S.; Boeckmann, W.; Rau, G.; Jakse, G.; Staudte, H. Using human factor analysis and VR simulation techniques for the optimization of the surgical worksystem. Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 1996, 29, 532–541. [Google Scholar]
- Lester, J.D.; Hsu, S.; Ahmad, C.S. Occupational hazards facing orthopaedic surgeons. Am. J. Orthop. 2012, 41, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alqahtani, S.M.; Alzahrani, M.M.; Tanzer, M. Adult Reconstructive Surgery: A High-Risk Profession for Work-Related Injuries. J. Arthroplast. 2016, 31, 1194–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vajapey, S.P.; Li, M.; Glassman, A.H. Occupational hazards of orthopaedic surgery and adult reconstruction: A cross-sectional study. J. Orthop. 2021, 25, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, R.C.; Behrens, P.H.; Malik, A.T.; Lester, J.D.; Ahmad, C.S. Are we putting ourselves in danger? Occupational hazards and job safety for orthopaedic surgeons. J. Orthop. 2021, 24, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, W.T.; Sathiyakumar, V.; Jahangir, A.A.; Obremskey, W.T.; Sethi, M.K. Occupational injury among orthopaedic surgeons. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2013, 95, e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQuivey, K.S.; Christopher, Z.K.; Deckey, D.G.; Mi, L.; Bingham, J.; Spangehl, M.J. Surgical ergonomics and musculoskeletal pain in arthroplasty surgeons. J. Arthroplast. 2021, 36, 3781–3787.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auerbach, J.D.; Weidner, Z.D.; Milby, A.H.; Diab, M.; Lonner, B.S. Musculoskeletal disorders among spine surgeons: Results of a survey of the Scoliosis Research Society membership. Spine 2011, 36, E1715–E1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.C.; Piple, A.S.; Hill, W.J.; Chen, M.S.; Gettleman, B.S.; Richardson, M.; Heckmann, N.D.; Christ, A.B. Computer-Navigated and Robotic-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty: Increasing in Popularity Without Increasing Complications. J. Arthroplast. 2022, 37, 2358–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bautista, M.; Manrique, J.; Hozack, W.J. Robotics in Total Knee Arthroplasty. J. Knee Surg. 2019, 32, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.H.; Yoon, S.H.; Park, J.W. Does Robotic-assisted TKA Result in Better Outcome Scores or Long-Term Survivorship Than Conventional TKA? A Randomized, Controlled Trial. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2020, 478, 266–275, Erratum in Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2021, 479, 1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batailler, C.; Fernandez, A.; Swan, J.; Servien, E.; Haddad, F.S.; Catani, F.; Lustig, S. MAKO CT-based robotic arm-assisted system is a reliable procedure for total knee arthroplasty: A systematic review. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2021, 29, 3585–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haffar, A.; Krueger, C.A.; Goh, G.S.; Lonner, J.H. Total Knee Arthroplasty With Robotic Surgical Assistance Results in Less Physician Stress and Strain Than Conventional Methods. J. Arthroplast. 2022, 37, S193–S200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansraj, K.K. Assessment of stresses in the cervical spine caused by posture and position of the head. Surg. Technol. Int. 2014, 25, 277–279. [Google Scholar]
- Lindegård, A.; Gustafsson, M.; Hansson, G.Å. Effects of prismatic glasses including optometric correction on head and neck kinematics, perceived exertion and comfort during dental work in the oral cavity—A randomized controlled intervention. Appl. Ergon. 2012, 43, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholl, L.Y.; Hampp, E.L.; Alipit, V.; Sodhi, N.; Bhowmik-Stoker, M.; Dropkin, J.; Chen, A.F.; Mont, M.A. Effect of Manual versus Robotic-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty on Cervical Spine Static and Dynamic Postures. J. Knee Surg. 2022, 35, 1010–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meltzer, A.J.; Hallbeck, M.S.; Morrow, M.M.; Lowndes, B.R.; Davila, V.J.; Stone, W.M.; Money, S.R. Measuring Ergonomic Risk in Operating Surgeons by Using Wearable Technology. JAMA Surg. 2020, 155, 444–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, E.P.; Kothari, E.A.; Zumsteg, J.W.; Romero, A.B.; Schwartz-Fernandes, F.A.; Lewellyn, B.J. Hand Surgeon Posture: An Evaluation and Factors That Affect It. J. Hand Microsurg. 2024, 16, 100044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kothari, E.A.; Urakov, T.M. Spine surgery is kyphosing to spine surgeon. Acta Neurochir. 2020, 162, 967–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, R.H.; Peper, E.; Mason, L.; Joy, M. Effect of Posture Feedback Training on Health. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback 2020, 45, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krämer, B.; Neis, F.; Reisenauer, C.; Walter, C.; Brucker, S.; Wallwiener, D.; Seibt, R.; Gabriel, J.; Rieger, M.A.; Steinhilber, B. Save our surgeons (SOS)—An explorative comparison of surgeons’ muscular and cardiovascular demands, posture, perceived workload and discomfort during robotic vs. laparoscopic surgery. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2023, 307, 849–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yu, D.; Dural, C.; Morrow, M.M.; Yang, L.; Collins, J.W.; Hallbeck, S.; Kjellman, M.; Forsman, M. Intraoperative workload in robotic surgery assessed by wearable motion tracking sensors and questionnaires. Surg. Endosc. 2017, 31, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Robotic TKA n = 48 | Conventional TKA n = 55 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (SD) | 66.8 (7.7) | 66.8 (8.4) | 0.980 |
| Women % (n) | 60.4 (29) | 61.8 (34) | 0.499 |
| BMI (SD) | 31.1 (5.0) | 31.2 (4.3) | 0.863 |
| ASA Classification % (n) | |||
| 1 | 6.3 (3) | 0.0 (0) | 0.560 |
| 2 | 41.7 (20) | 37.0 (20) | |
| 3 | 52.1 (25) | 63.0 (34) |
| Variable (SD) | Surgeon 1 | Surgeon 2 | Surgeon 3 | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TKA Primary | n = 31 | n = 67 | n= 5 | |
| Upright % | 66.8 (17.8) | 29.1 (18.0) | 51.8 (18.0) | <0.001 |
| Slouch % | 33.2 (17.8) | 70.9 (18.0) | 42.8 (18.0) | <0.001 |
| Procedure Time (min) | 74.5 (14.6) | 82.4 (20.0) | 52.4 (8.6) | 0.001 |
| Clinic Values | n = 4 | n = 15 | n = 3 | |
| Upright % | 54.8 (6.2) | 66.1 (25.0) | 75.3 (37.5) | 0.301 |
| Slouch % | 45.2 (6.2) | 33.9 (25.0) | 24.7 (37.5) | 0.301 |
| Device Time (min) | 287.5 (166.7) | 455.7 (88.2) | 158.7 (30.4) | 0.009 |
| Robotic TKA n = 48 | Conventional TKA n = 55 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Posture (SD) | |||
| Upright % | 57.6 (22.1) | 27.5 (17.5) | <0.001 |
| Upright (Min) | 44.9 (17.4) | 21.0 (14.8) | <0.001 |
| Slouch % | 42.4 (22.1) | 72.5 (17.5) | <0.001 |
| Slouch (Min) | 35.4 (22.9) | 54.7 (20.7) | 0.037 |
| Procedure Time (SD) | 80.3 (17.2) | 77.0 (21.0) | 0.430 |
| Case Number % (n) | 0.711 | ||
| 1–3 | 70.8 (34) | 72.7 (40) | |
| 4+ | 29.2 (14) | 27.3 (15) | |
| Helmet % (n) | 0.198 | ||
| Original | 0.0 (0) | 9.1 (5) | |
| New/Lightweight | 100.0 (48) | 90.9 (50) |
| Predicting Slouching % | Predicting Total Slouching (min) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | 95% CI | p-Value | B | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| Age | −0.28 | −0.5, −0.1 | 0.009 | −0.25 | −0.5, −0.0 | 0.048 |
| Female Gender | 2.15 | −2.9, 7.1 | 0.402 | 2.84 | −1.5, 7.2 | 0.198 |
| BMI | 0.08 | −0.4, 0.6 | 0.759 | 0.14 | −0.29, 0.56 | 0.529 |
| ASA 2 Classification | −7.17 | −12.4, −2.0 | 0.007 | −6.49 | −11.4, −1.6 | 0.009 |
| Procedure Time | 0.10 | −0.1, 0.3 | 0.388 | 0.73 | 0.64, 0.83 | <0.001 |
| Robotic TKA | −28.9 | −40.9, −17.0 | <0.001 | −21.5 | −29.9, −13.2 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gapinski, Z.; Mason, E.; Kothari, E.; Desai, P.; Haidukewych, G.; Green, C. Can Robots Keep You Upright? An Ergonomic Analysis of Surgeon Posture in Robotic Versus Conventional Total Knee Arthroplasty. Surgeries 2025, 6, 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/surgeries6020043
Gapinski Z, Mason E, Kothari E, Desai P, Haidukewych G, Green C. Can Robots Keep You Upright? An Ergonomic Analysis of Surgeon Posture in Robotic Versus Conventional Total Knee Arthroplasty. Surgeries. 2025; 6(2):43. https://doi.org/10.3390/surgeries6020043
Chicago/Turabian StyleGapinski, Zachary, Eric Mason, Ezan Kothari, Pratik Desai, George Haidukewych, and Cody Green. 2025. "Can Robots Keep You Upright? An Ergonomic Analysis of Surgeon Posture in Robotic Versus Conventional Total Knee Arthroplasty" Surgeries 6, no. 2: 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/surgeries6020043
APA StyleGapinski, Z., Mason, E., Kothari, E., Desai, P., Haidukewych, G., & Green, C. (2025). Can Robots Keep You Upright? An Ergonomic Analysis of Surgeon Posture in Robotic Versus Conventional Total Knee Arthroplasty. Surgeries, 6(2), 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/surgeries6020043







