Dermal Cosmetic Migration after Lip Augmentation Procedure: Clinical Management and Histological Analysis in a Case Report with Review of the Literature
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
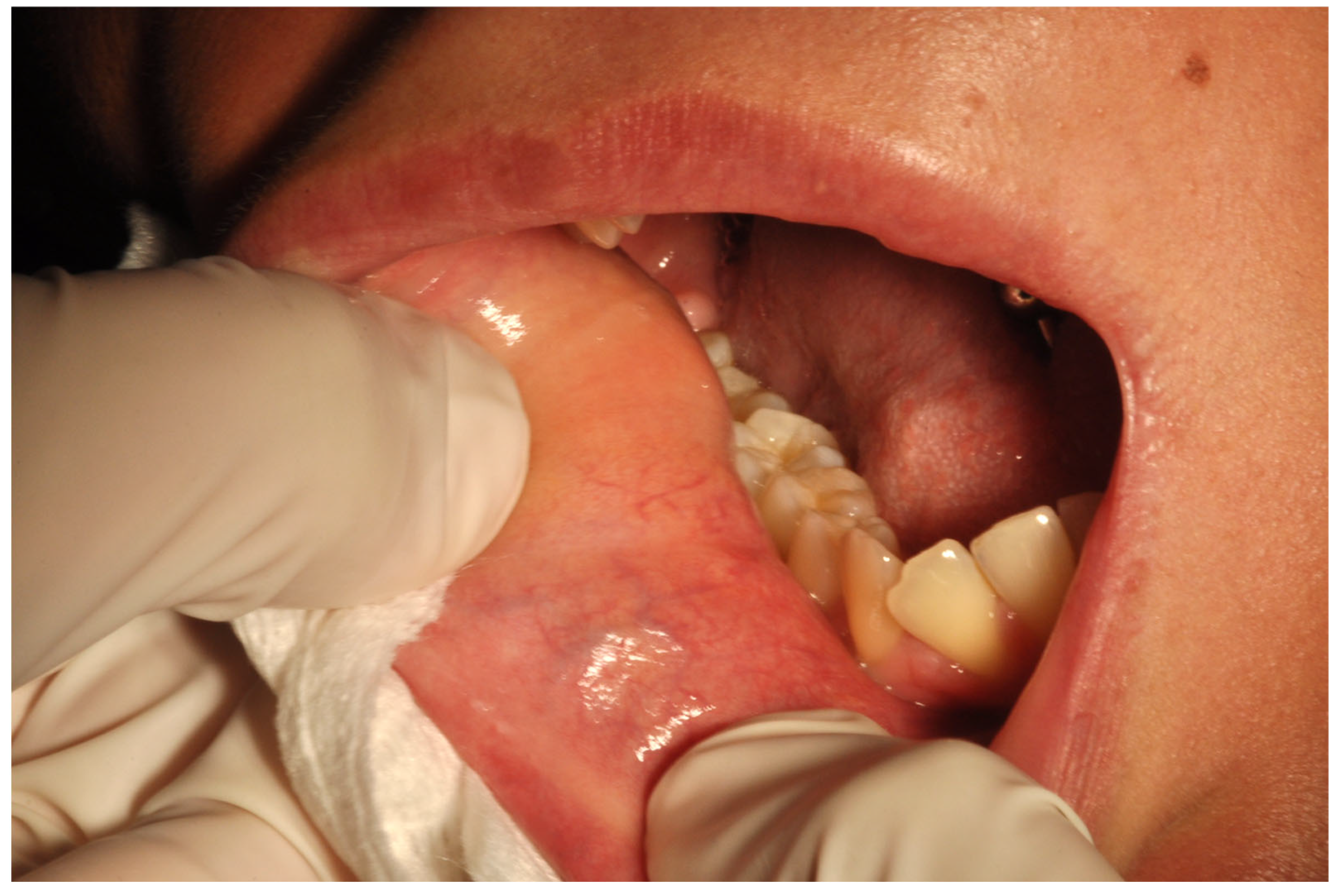
2.1. Case Report
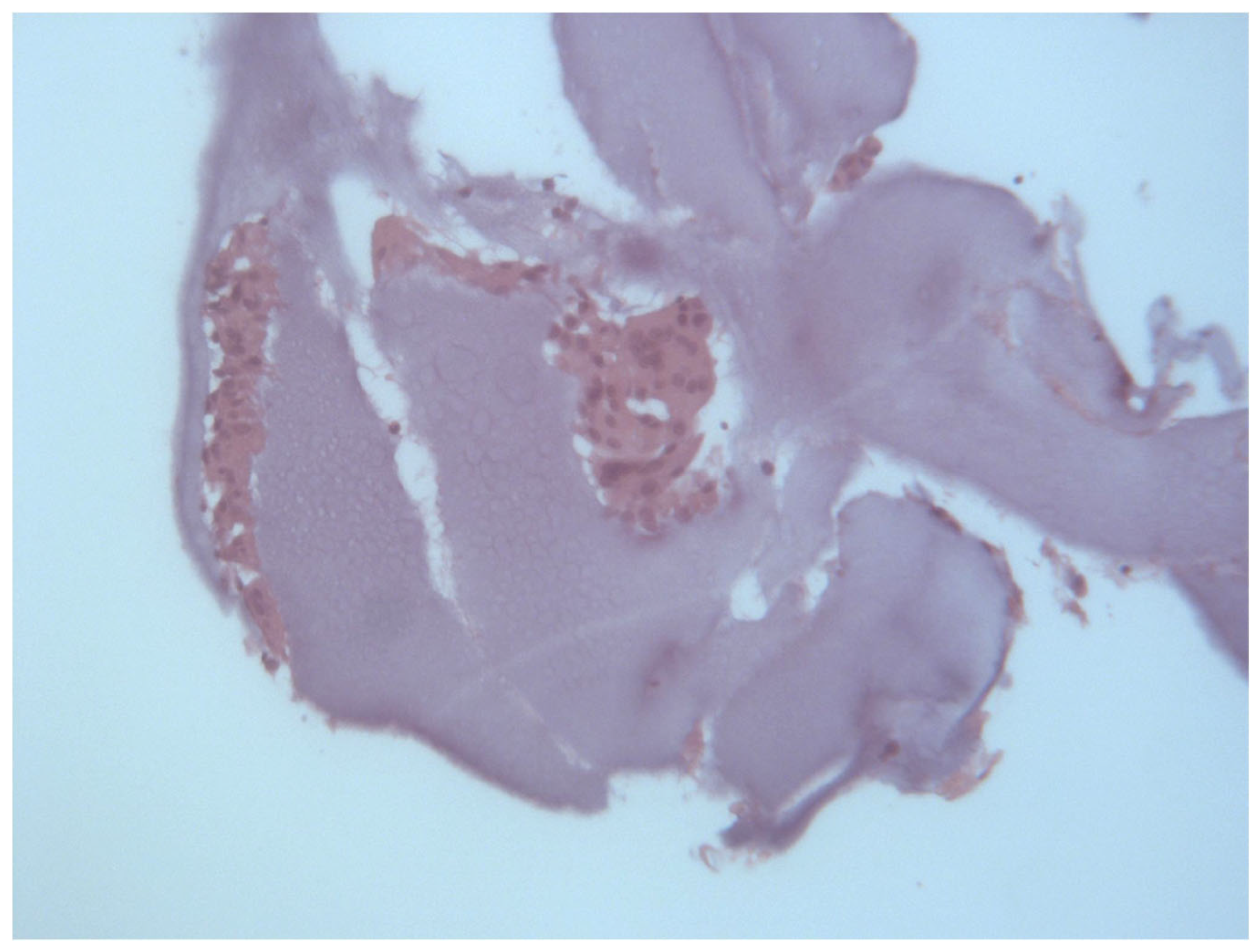
2.2. Histological Analysis
2.3. Systematic Literature Review Strategy
2.3.1. Articles Screening
2.3.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
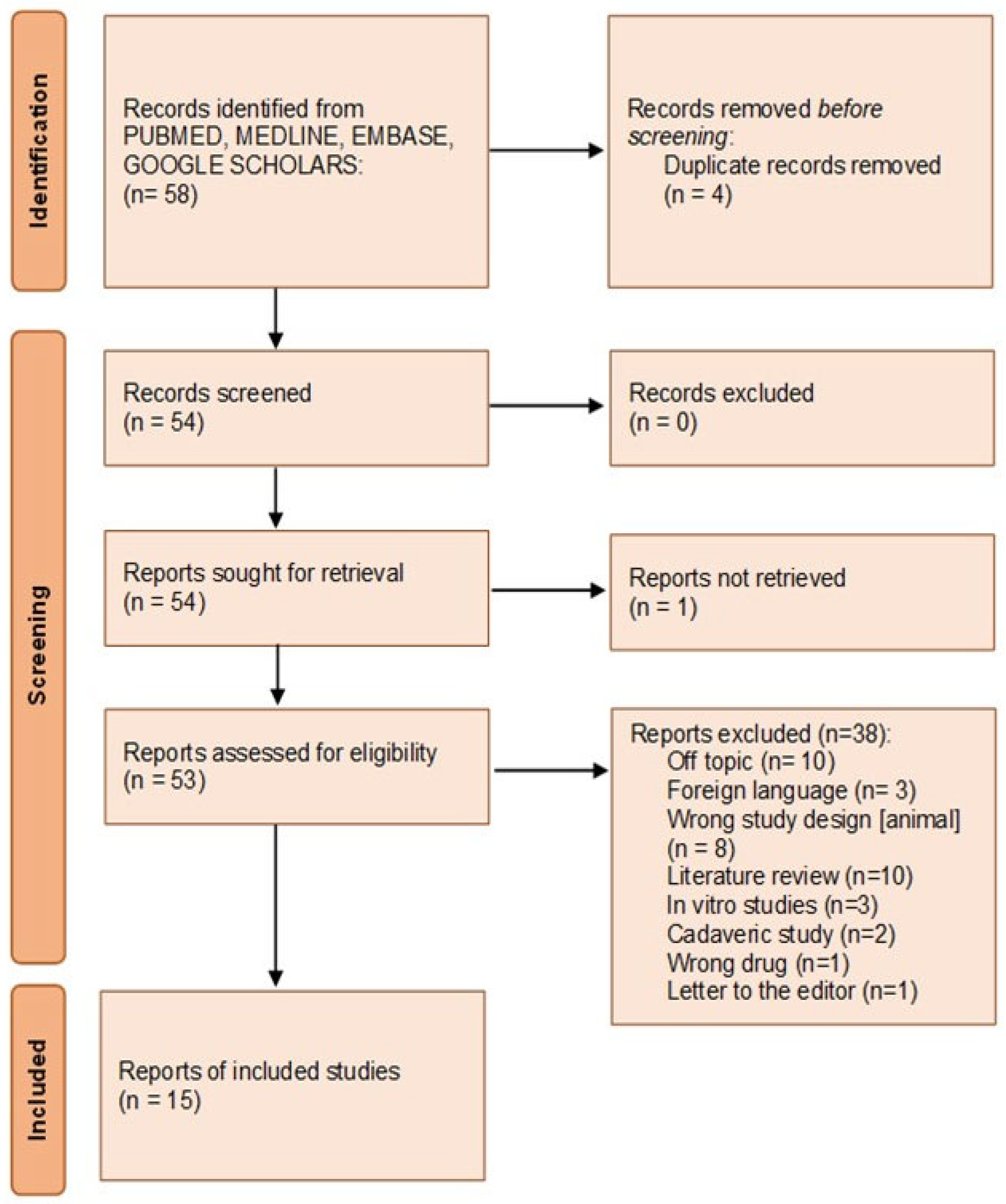
2.3.3. Eligibility Process
2.3.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Histological and Clinical Follow-Up
3.2. Literature Review Findings
3.2.1. Selection Characteristic
3.2.2. Characteristic of the Included Studies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ISAPS. International Survey on Aesthetic/Cosmetic Procedures; ISAPS: Mount Royal, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ballin, A.C.; Brandt, F.S.; Cazzaniga, A. Dermal Fillers: An Update. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2015, 16, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarano, A.; Puglia, F.; Cassese, R.; Mordente, I.; Amore, R.; Ferraro, G.; Sbarbati, A.; Russo, L.; Amuso, D. Hyaluronic Acid Fillers in Lip Augmentation Procedure: A Clinical and Histological Study. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2019, 33, 103–108. [Google Scholar]
- Scarano, A.; Rapone, B.; Amuso, D.; Inchingolo, F.; Lorusso, F. Hyaluronic Acid Fillers Enriched with Glycine and Proline in Eyebrow Augmentation Procedure. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2022, 46, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vartanian, A.J.; Frankel, A.S.; Rubin, M.G. Injected Hyaluronidase Reduces Restylane-Mediated Cutaneous Augmentation. Arch. Facial Plast. Surg. 2005, 7, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Ahn, D.K.; Jeong, H.S.; Suh, I.S. Treatment Algorithm of Complications after Filler Injection: Based on Wound Healing Process. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2014, 29, S176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, R.; Fakhro, A.; Cox, J.; Izaddoost, S. Etiology, Prevention, and Management of Infectious Complications of Dermal Fillers. Semin. Plast. Surg. 2016, 30, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, D.S.; Barber, M.S.; Kienle, G.S.; Aronson, J.K.; von Schoen-Angerer, T.; Tugwell, P.; Kiene, H.; Helfand, M.; Altman, D.G.; Sox, H.; et al. CARE Guidelines for Case Reports: Explanation and Elaboration Document. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2017, 89, 218–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed-Azzam, S.; Burkat, C.; Mukari, A.; Briscoe, D.; Joshi, N.; Scawn, R.; Alon, E.; Hartstein, M. Filler Migration to the Orbit. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2021, 41, NP559–NP566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grippaudo, F.R.; Di Girolamo, M.; Mattei, M.; Pucci, E.; Grippaudo, C. Diagnosis and Management of Dermal Filler Complications in the Perioral Region. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2014, 16, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrabi-Farahani, S.; Lerman, M.A.; Noonan, V.; Kabani, S.; Woo, S.-B. Granulomatous Foreign Body Reaction to Dermal Cosmetic Fillers with Intraoral Migration. Oral. Surg. Oral. Med. Oral. Pathol. Oral. Radiol. 2014, 117, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-K.; Kim, S.M.; Cho, S.H.; Lee, J.D.; Kim, H.S. Adverse Reactions to Injectable Soft Tissue Fillers: Memorable Cases and Their Clinico-Pathological Overview. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2015, 17, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadouch, J.A.; Tutein Nolthenius, C.J.; Kadouch, D.J.; van der Woude, H.-J.; Karim, R.B.; Hoekzema, R. Complications After Facial Injections With Permanent Fillers: Important Limitations and Considerations of MRI Evaluation. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2014, 34, 913–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Shen, H.; Liu, T.; Li, Q.; Lyu, Z.; Yu, Y. An Efficacy and Safety Study of Intra-Arterial Recanalization of Occluded Ophthalmic Arteries in Patients with Monocular Blindness Caused by Injection of Hyaluronic Acid in Facial Tissues. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2021, 45, 1573–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kästner, S.; Gonser, P.; Paprottka, F.; Kaye, K.O. Removal of Polyacrylamide Gel (Aquamid®) from the Lip as a Solution for Late-Onset Complications: Our 8-Year Experience. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2018, 42, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abtahi-Naeini, B.; Faghihi, G.; Shahmoradi, Z.; Saffaei, A. Filler Migration and Extensive Lesions after Lip Augmentation: Adverse Effects of Polydimethylsiloxane Filler. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2018, 17, 996–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehily, E.; Hayes, M.; McCreary, C. Adverse Reactions to Facial Dermal Fillers: A Case Report. J. Ir. Dent. Assoc. 2015, 61, 36–39. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.-H.; Chiang, C.-P.; Wu, B.-Y.; Gao, H.-W. Filler Migration to the Forehead Due to Multiple Filler Injections in a Patient Addicted to Cosmetic Fillers. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2017, 19, 124–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dryden, S.C.; Gabbard, R.D.; Meador, A.G.; Stoner, A.E.; Klippenstein, K.A.; Wesley, R.E. A Case of Orbital Granuloma Secondary to Dermal Filler Injection. Cureus 2021, 13, e20606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.J. Pseudocyst of the Neck after Facial Augmentation with Liquid Silicone Injection. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2014, 25, e474–e475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.; Mehta, P.; Adesanya, O.; Ahluwalia, H.S. Migrated Periocular Filler Masquerading as Arteriovenous Malformation: A Diagnostic and Therapeutic Dilemma. Ophthalmic Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2013, 29, e18–e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeltzer, A.A.; Craggs, B.; Van Thielen, J.; Hendrickx, B.; Seidenstuecker, K.; Hamdi, M. Massive Hemi-Facial Edema After Permanent Filler Removal in an HIV-Positive Patient. Precautions and Patient Information. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2015, 39, 425–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Cho, S.H.; Lee, J.D.; Kim, H.S. Delayed Onset Filler Complication: Two Case Reports and Literature Review. Dermatol. Ther. 2017, 30, e12513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Povolotskiy, R.; Oleck, N.C.; Hatzis, C.M.; Paskhover, B. Adverse Events Associated with Aesthetic Dermal Fillers: A 10-Year Retrospective Study of FDA Data. Am. J. Cosmet. Surg. 2018, 35, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Miller, P.J. Management of Lip Complications. Facial Plast. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 27, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funt, D.; Pavicic, T. Dermal Fillers in Aesthetics: An Overview of Adverse Events and Treatment Approaches. Plastic Surgical Nursing 2015, 35, 13–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarano, A.; Di Carmine, M.S.; Greco Lucchina, A.; Giacomello, M.; Petrini, M.; Amore, R.; Frisone, A.; Amuso, D. Chronic Lip Edema and Pain Secondary to Lip Augmentation Procedure: Histological, Scanning Electron Microscopy and X-Ray Microanalysis Evaluation. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 27, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercer, S.E.; Kleinerman, R.; Goldenberg, G.; Emanuel, P.O. Histopathologic Identification of Dermal Filler Agents. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2010, 9, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar]
- Scarano, A.; Sbarbati, A.; Amore, R.; Iorio, E.L.; Ferraro, G.; Marchetti, M.; Amuso, D. The Role of Hyaluronic Acid and Amino Acid against the Aging of the Human Skin: A Clinical and Histological Study. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2020, 20, 2296–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.K.; Sun, B.; Shin, S.H.; Kim, B.J. Late-Onset Filler-Induced Granuloma After Polycaprolactone-Based Filler Treated With High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound and Quantum Molecular Resonance Technology. Dermatol. Surg. 2022, 48, 693–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, S.Y.; Lee, K.C.; Jang, Y.H.; Lee, S.-J.; Kim, D.W.; Lee, W.J. A Case of the Migration of Hyaluronic Acid Filler from Nose to Forehead Occurring as Two Sequential Soft Lumps. Ann. Dermatol. 2016, 28, 645–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urdiales-Gálvez, F.; Delgado, N.E.; Figueiredo, V.; Lajo-Plaza, J.V.; Mira, M.; Moreno, A.; Ortíz-Martí, F.; del Rio-Reyes, R.; Romero-Álvarez, N.; del Cueto, S.R.; et al. Treatment of Soft Tissue Filler Complications: Expert Consensus Recommendations. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2018, 42, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, A.; Wollina, U. Polymethylmethacrylate-Induced Nodules of the Lips: Clinical Presentation and Management by Intralesional Neodymium:YAG Laser Therapy. Dermatol. Ther. 2019, 32, e12755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Population\Patients | Intervention | Comparison | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Subjects affected by facial dermal filler migration | Patients subjected to surgical removal | Patients subjected to alternative medical treatment | Efficacy and prognosis of surgical removal treatment for dermal filler migration |
| Search Strategies | |
|---|---|
| Keywords: | Advanced keyword search: (Facial Dermal fillers AND migration) |
| Databases | PubMed/Medline, EMBASE |
| Authors | Journal | Year | Study Design | Population | Gender | Subject (s) Age | Filler Type | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hamed-Azzam et al. [9] | Aesthet Surg J | 2021 | Retrospective Study | 7 subjects | 6 female 1 male | Age range 42–67 years | NA | |
| Grippaudo et al. [10] | J Cosmet Laser Ther | 2014 | Retrospective Study | 26 subjects | 26 female | Age range 28–74 years | 3 silicone (S); 1 S + AH, (Acrylic hydrogel particles (copolymer of 40% hydroxyl-ethyl-methacrylates); 7 polyacrylamide gel (PAAG); 1 AH + PAAG; 2 AH; 1 PMMA; 1 collagen; 1 hyaluronic Acid; (HA); 1 HA + S; 1 polyalkylimide gel (PAIG) | |
| Abtahi-Naeini et al. [16] | J Cosmet Dermatol | 2018 | Case report | 1 subject | 1 female | 35 years old | Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) | |
| Shahrabi-Farahani et al. [11] | Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol | 2014 | Retrospective Study | 25 subjects | 25 female | 35 to 78 years (median, 55 years) | 13 calcium hydroxylapatite (CHA);12 poly-L-lactic acid (PLA) | |
| Kehily et al. [17] | J Ir Dent Assoc | 2015 | Case report | 1 subject | 1 male | 33 years old | Na | |
| Lee et al. [12] | J Cosmet Laser Ther. | 2015 | Retrospective Study | 8 subjects | 6 female; 2 male | Mean 48.6 years (range, 30–74). | 1 (porcine atelocollagen1 2.5% cross-linked PAAG 2 Unknown 1 HA 1 HA)/NLF 1 Paraffin 1 Vaseline | |
| Kadouch et al. [13] | Aesthet Surg J. | 2014 | Retrospective Study | 32 subjects (107 clinically assessed deposits) | 16 male, 16 female | 25 to 76 years (mean, 55.4 years) | Polyalkylimide gel and polyacrylamide gel; hydrogels 2.5% polyacrylamide gel and 4% polyalkylimide gel) | |
| Kim et al. [23] | Dermatol Ther. | 2017 | Case series | 2 subjects | 2 female | 54 yo and 60 yo | Na | |
| Wang et al. [14] | Aesthetic Plast Surg | 2021 | Retrospective study | 30 subjects | 1 male, 29 female | aged 18–35 years | Na | |
| Lin et al. [18] | J Cosmet Laser Ther | 2017 | Case report | 1 subject | 1 female | 50 years old | Poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA), | |
| Dryden et al. [19] | Cureus | 2021 | Case report | 1 subject | 1 female | 57 years old | Injectable hyaluronic acids | |
| Choi et al. [20] | J Craniofac Surg. | 2004 | Case report | 1 subject | 1 female | 55 years old | Silicone injection | |
| Kästner et al. [15] | Aesthetic Plast Surg | 2018 | Retrospective study | 11 subjects | 10 female, 1 male | 31 and 53 years old | Cross-linked polyacrylamide | |
| Malik et al. [21] | Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. | 2013 | Case report | 1 subject | 1 female | 52 years old | Polyalkylimide | |
| Zeltzer et al. [22] | Aesthetic Plast Surg | 2015 | Case report | 1 subject | 1 male | 42 years old | Polyalkylimide | |
| Authors | Journal | Year | Filling Region | Complications | Time from the Treatment | Failed Intervention | Intervention | Follow-Up |
| Hamed-Azzam et al. [9] | Aesthet Surg J | 2021 | 3 nasolabial fold; (NFL); 1 temples/lateral brow rim; 1 NFL, cheeks; 1 jawline; 1 cheeks | (1) Orbital complitations (7): 3 inferior; 1 superolateral; 1 inferomedial;1 medial; 1 lacrimal sac | Post-operative complications (<1 month) | Steroid injection and hyalurodinase injections | 4 subjects: orbitotomy surgery 1 subject: lacrymal surgery 1 subject: strabismus surgery 1 subject: hyalurodinase injections | 11 months (range 2–15 months) |
| Grippaudo et al. [10] | J Cosmet Laser Ther | 2014 | Lip augmentation with injectable materials | Lip enlargement, asymmetry, edema, ulcers, lip hardening, Asymmetry, dyschromia, Lumps | 6 subj. Post operative complications (<1 month) 3 subj.at 1 year 17 subj. > 2 years | - | 9 patient surgeries, 10 medical treatments + drainage, 6 received both, 1 refused treatment. | 3 years |
| Abtahi-Naeini et al. [16] | J Cosmet Dermatol | 2018 | Lip augmentation with injectable materials | Lips extreme erythema, edema, fever and warmness; Periorbital area implant migration | 9 months | Local injection of triamcinolone | Gel implant surgical removal from the lip and periorbital area | 2 months |
| Shahrabi-Farahani et al. [11] | Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol | 2014 | Lips, nasolabial area, or mental area | Intraoral nodules (labial/buccal or vestibular mucosa) distant from the site of injections | 2–26 months | - | Surgical removal | 2–12 months |
| Kehily et al. [17] | J Ir Dent Assoc | 2015 | Lip augmentation with injectable materials; ‘marionette lines’ | Lower labial sulcus migration (4.1, 4.2, 4.3 teeth) painless swelling | 12 days | - | No treatment/monitoring | 3 months |
| Lee et al. [12] | J Cosmet Laser Ther. | 2015 | Nlfs Nasal tip and dorsum, Glabellar cheek & temple Nose | Allergic reaction (25%), filler material migration (12.5%), embolism (25%), foreign body granuloma (37.5%) | Immediately to 14 years | Surgical removal | no follow up | |
| Kadouch et al. [13] | Aesthet Surg J. | 2014 | Facial soft-tissue augmentation; (forehead, glabella, temporal region, tear troughs, cheeks/zygomatic arch, nasolabial area, perioral region, marionette lines, and chin. | Deposit/without inflammation deposit with inflammation abscess formation migration | 6 to 120 months (mean, 47.5 months). | - | Antibiotic treatment; surgical intervention (8%) | weeks |
| Kim et al. [23] | Dermatol Ther. | 2017 | Right lower eyelid; left temple | Subcutaneous nodule; multiple granulomas: filler migration with foreign body at | 7 years; | - | Surgical removal and histological analysis | 4 weeks |
| Wang et al. [14] | Aesthetic Plast Surg | 2021 | Forehead and nasal bridge | Monocular blindness | 20–120 h | - | Intra-arterial thrombolysis (hyaluronidase injection) (25) | 2 h |
| Lin et al. [18] | J Cosmet Laser Ther | 2017 | Cheeks | Temple subcutaneous nodule filler migration | 1 years | - | Surgical removal and histological analysis | 2 weeks |
| Dryden et al. [19] | Cureus | 2021 | Lower eyelid and lateral cheek junction | Occluded ophthalmic arteries | 6 months | Steroids and injected hyaluronidase (multiple periocular and perioral hard nodules) | Anterior orbitotomy through a transconjunctival incision t | 3 months |
| Choi et al. [20] | J Craniofac Surg. | 2004 | Multiple face liquid injection | Worsening edema and extensive necrosis of the face (malar;cheek, and preauricular region) palpable mass on her neck (palpable mass on her neck) | 2 years | Antibiotics were initiated, and multiple debridements of the face | Incision line on the neck | 5 days |
| Kästner et al. [15] | Aesthetic Plast Surg | 2018 | Eleven upper and six lower lips | Gel migration within the lips and into the surrounding perioral zone | 2–10 years | - | Surgical removal | 12 monhs |
| Malik et al. [21] | Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. | 2013 | Periocular filler | Mass and swelling left eyebrow, temple, and glabella. | 10 years | Sclerotherapy | Surgical removal | 2-weeks |
| Zeltzer et al. [22] | Aesthetic Plast Surg | 2015 | Facial lipodystrophy | Spontaneous abscess formation right cheek | 5 years | A high dose of oral ciprofloxacin; emergency percutaneous drainage of the multi-compartment abscess | Surgical removal | 3–4 weeks |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scarano, A.; Inchingolo, F.; Di Carmine, M.; Marchetti, M.; Lorusso, F.; Amore, R.; Amuso, D. Dermal Cosmetic Migration after Lip Augmentation Procedure: Clinical Management and Histological Analysis in a Case Report with Review of the Literature. Surgeries 2023, 4, 223-234. https://doi.org/10.3390/surgeries4020023
Scarano A, Inchingolo F, Di Carmine M, Marchetti M, Lorusso F, Amore R, Amuso D. Dermal Cosmetic Migration after Lip Augmentation Procedure: Clinical Management and Histological Analysis in a Case Report with Review of the Literature. Surgeries. 2023; 4(2):223-234. https://doi.org/10.3390/surgeries4020023
Chicago/Turabian StyleScarano, Antonio, Francesco Inchingolo, Maristella Di Carmine, Marco Marchetti, Felice Lorusso, Roberto Amore, and Domenico Amuso. 2023. "Dermal Cosmetic Migration after Lip Augmentation Procedure: Clinical Management and Histological Analysis in a Case Report with Review of the Literature" Surgeries 4, no. 2: 223-234. https://doi.org/10.3390/surgeries4020023
APA StyleScarano, A., Inchingolo, F., Di Carmine, M., Marchetti, M., Lorusso, F., Amore, R., & Amuso, D. (2023). Dermal Cosmetic Migration after Lip Augmentation Procedure: Clinical Management and Histological Analysis in a Case Report with Review of the Literature. Surgeries, 4(2), 223-234. https://doi.org/10.3390/surgeries4020023










