Correlations of Tinel and Phalen Signs with Nerve Conduction Study Test Results in a Randomly Chosen Population of Patients with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants, Study Design, and Clinical Evaluation
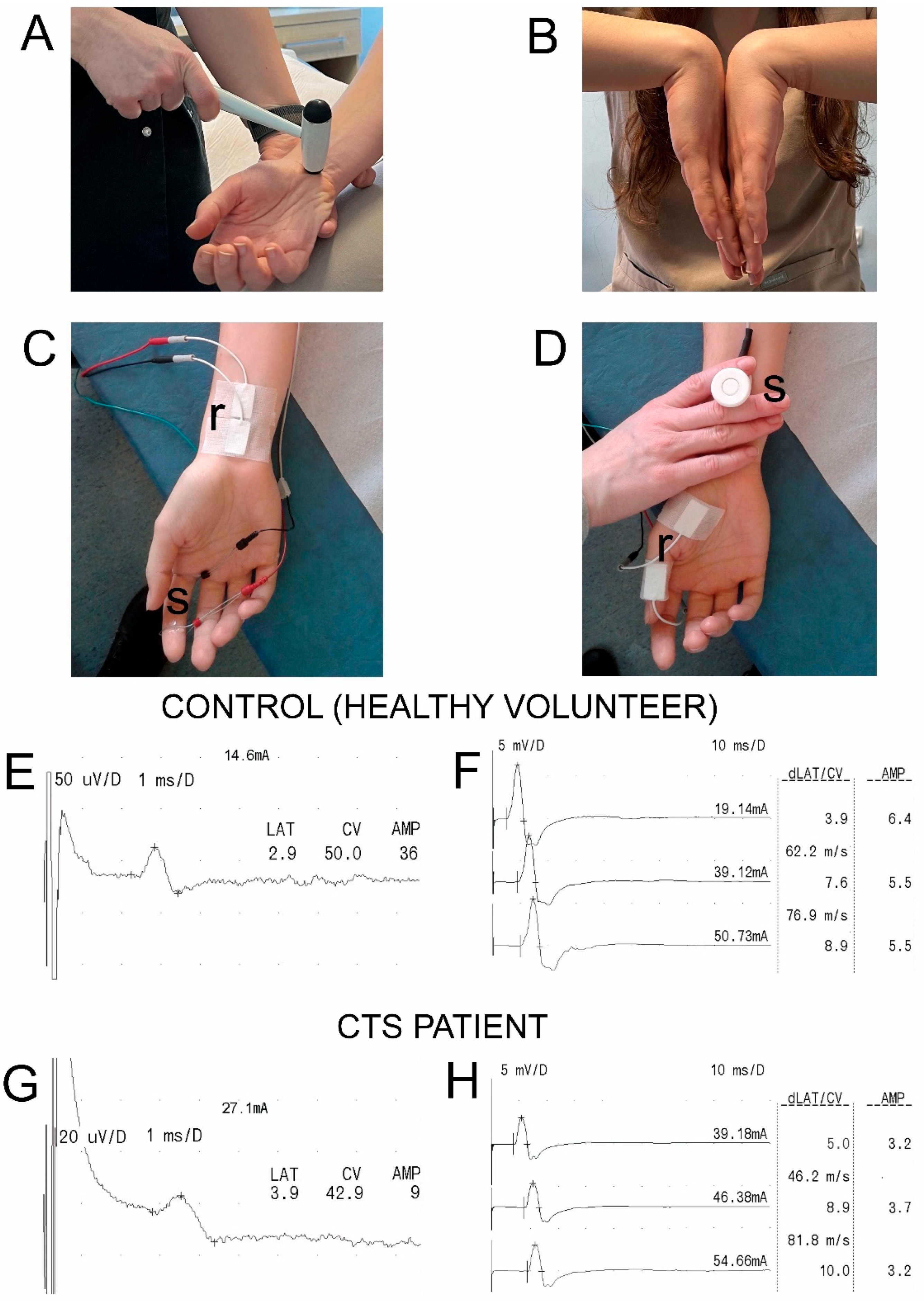
2.2. Nerve Conduction Studies (NCSs)
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Padua, L.; Coraci, D.; Erra, C.; Pazzaglia, C.; Paolasso, I.; Loreti, C.; Caliandro, P.; Hobson-Webb, L.D. Carpal tunnel syndrome: Clinical features, diagnosis, and management. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 1273–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genova, A.; Dix, O.; Saefan, A.; Thakur, M.; Hassan, A. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Review of Literature. Cureus 2020, 12, e7333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, C.; Chesterton, L.S.; Davenport, G. Diagnosing and managing carpal tunnel syndrome in primary care. Br. J. Gen. Pract. 2014, 64, 262–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiri, R.; Pourmemari, M.H.; Falah-Hassani, K.; Viikari-Juntura, E. The effect of excess body mass on the risk of carpal tunnel syndrome: A meta–analysis of 58 studies. Obes. Rev. 2015, 16, 1094–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harinesan, N.; Silsby, M.; Simon, N.G. Carpal tunnel syndrome. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2024, 201, 61–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, K.T. Carpal tunnel syndrome: The role of occupational factors. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2011, 25, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntani, G.; Palmer, K.T.; Linaker, C.; Harris, E.C.; Van der Star, R.; Cooper, C.; Coggon, D. Symptoms, signs and nerve conduction velocities in patients with suspected carpal tunnel syndrome. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2013, 14, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newington, L.; Harris, E.C.; Walker-Bone, K. Carpal tunnel syndrome and work. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2015, 29, 440–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegmann, K.T.; Merryweather, A.; Thiese, M.S.; Kendall, R.; Garg, A.; Kapellusch, J.; Foster, J.; Drury, D.; Wood, E.M.; Melhorn, J.M. Median Nerve Symptoms, Signs, and Electrodiagnostic Abnormalities Among Working Adults. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2018, 26, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajczewski, A.; Daroszewski, P.; Fabijański, A.; Bogusławski, K.; Kaźmierczak, M.; Huber, J. Incidence of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Other Coexisting Brachial Plexus Neuropathies in Bullseye Shooters—A Pilot Retrospective Clinical and Neurophysiological Assessment. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milandri, A.; Farioli, A.; Gagliardi, C.; Longhi, S.; Salvi, F.; Curti, S.; Foffi, S.; Caponetti, A.G.; Lorenzini, M.; Ferlini, A.; et al. Carpal tunnel syndrome in cardiac amyloidosis: Implications for early diagnosis and prognostic role across the spectrum of aetiologies. Eur. J. Hear. Fail. 2020, 22, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquardt, T.L.; Gabra, J.N.; Evans, P.J.; Seitz, W.H.; Li, Z.-M. Thickness and stiffness adaptations of the transverse carpal ligament associated with carpal tunnel syndrome. J. Musculoskelet. Res. 2016, 19, 1650019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padua, L.; Cuccagna, C.; Giovannini, S.; Coraci, D.; Pelosi, L.; Loreti, C.; Bernabei, R.; Hobson-Webb, L.D. Carpal tunnel syndrome: Updated evidence and new questions. Lancet Neurol. 2022, 22, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanazy, M.H. Clinical and electrophysiological evaluation of carpal tunnel syndrome: Approach and pitfalls. Neurosciences 2017, 22, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yunoki, M.; Kanda, T.; Suzuki, K.; Uneda, A.; Hirashita, K.; Yoshino, K. Importance of Recognizing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome for Neurosurgeons: A Review. Neurol. Med.-Chir. 2017, 57, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginanneschi, F.; Mondelli, M.; Cioncoloni, D.; Rossi, A. Impact of carpal tunnel syndrome on ulnar nerve at wrist: System-atic review. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2018, 40, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, D.H.; Kim, C.H. The Quantitative Relationship Between Physical Examinations and the Nerve Conduction of the Carpal Tunnel Syndrome in Patients With and Without a Diabetic Polyneuropathy. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2014, 38, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Padua, L.; LoMonaco, M.; Aulisa, L.; Tamburrelli, F.; Valente, E.M.; Padua, R.; Gregori, B.; Tonali, P. Surgical prognosis in carpal tunnel syndrome: Usefulness of a preoperative neurophysiological assessment. Acta Neurol. Scand. 1996, 94, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atroshi, I.; Gummesson, C.; Johnsson, R.; Ornstein, E.; Ranstam, J.; Rosén, I. Prevalence of carpal tunnel syndrome in a gen-eral population. JAMA 1999, 282, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondelli, M.; Passero, S.; Giannini, F. Provocative tests in different stages of carpal tunnel syndrome. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2001, 103, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padua, L.; Padua, R.; Lo Monaco, M.; Aprile, I.; Tonali, P. Multiperspective assessment of carpal tunnel syndrome: A multicenter study. Italian CTS Study Group. Neurology. 1999, 53, 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wipperman, J.; Goerl, K. Carpal tunnel syndrome: Diagnosis and management. Am. Fam. Physician 2016, 94, 993–999. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Phalen, G.S. The carpal-tunnel syndrome. Seventeen years’ experience in diagnosis and treatment of six hundred fifty-four hands. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1966, 48, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinel, J. The Sign of “Tingling” in Lesions of the Peripheral Nerves. Arch. Neurol. 1971, 24, 574–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seror, P. Tinel’s sign in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. J. Hand Surg. 1987, 12, 364–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDermid, J.C.; Wessel, J. Clinical diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome: A systematic review. J. Hand Ther. 2004, 17, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabbagh, A.; MacDermid, J.C.; Yong, J.; Packham, T.L.; Grewal, R.; Boutsikari, E.C. Diagnostic Test Accuracy of Provocative Maneuvers for the Diagnosis of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Phys. Ther. 2023, 103, pzad029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, R.A.; Andary, M. Carpal tunnel syndrome: Pathophysiology and clinical neurophysiology. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2002, 113, 1373–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dekel, S.; Papaioannou, T.; Rushworth, G.; Coates, R. Idiopathic carpal tunnel syndrome caused by carpal stenosis. BMJ 1980, 280, 1297–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faeghi, F.; Ardakani, A.A.; Acharya, U.R.; Mirza-Aghazadeh-Attari, M.; Abolghasemi, J.; Ejtehadifar, S.; Mohammadi, A. Accurate automated diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome using radiomics features with ultrasound images: A comparison with radiologists’ assessment. Eur. J. Radiol. 2021, 136, 109518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakalis, D.; Kontogiannis, P.; Ntais, E.; Simos, Y.V.; Tsamis, K.I.; Manis, G. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Automated Diagnosis: A Motor vs. Sensory Nerve Conduction-Based Approach. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanazy, M.H.; Albulaihe, H.; Alhumayyd, Z.; Albarrak, A.M.; Abuzinadah, A.R. A timed Phalen’s test predicts abnormal electrophysiology in carpal tunnel syndrome. Brain Behav. 2021, 11, e02056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lew, H.L.; Date, E.S.; Pan, S.S.; Wu, P.; Ware, P.F.; Kingery, W.S. Sensitivity, specificity, and variability of nerve conduction velocity measurements in carpal tunnel syndrome. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2005, 86, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandin, K.J.; Asch, S.M.; Jablecki, C.K.; Kilmer, D.D.; Nuckols, T.K. Clinical quality measures for electrodiagnosis in suspected carpal tunnel syndrome. Muscle Nerve 2010, 41, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozsoy-Unubol, T.; Bahar-Ozdemir, Y.; Yagci, I. Diagnosis and grading of carpal tunnel syndrome with quantitative ultra-sound: Is it possible? J. Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 75, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obuchowicz, R.; Kruszyńska, J.; Strzelecki, S. Classifying median nerves in carpal tunnel syndrome: Ultrasound image anal-ysis. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 41, 335–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciuffreda, G.; Bueno-Gracia, E.; Argüello-Espinosa, M.I.; Shacklock, M.; Navarrete-Navarro, S.; Vicente-Garza, I.; Rodríguez-Mena, D.; Estébanez-De-Miguel, E. Accuracy of the Standard and Distal-to-Proximal Sequence of the Upper Limb Neurodynamic Test 1 for the Diagnosis of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: The Role of Side-to-Side Comparisons. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 7122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twardowska, M.; Czarnecki, P.; Jokiel, M.; Bręborowicz, E.; Huber, J.; Romanowski, L. Delayed Surgical Treatment in Patients with Chronic Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Is Still Effective in the Improvement of Hand Function. Medicina 2023, 59, 1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulisa, L.; Tamburrelli, F.; Padua, R.; Romanini, E.; Monaco, M.L.; Padua, L. Carpal tunnel syndrome: Indication for surgical treatment based on electrophysiologic study. J. Hand Surg. 1998, 23, 687–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, J.D. Do nerve conduction studies predict the outcome of carpal tunnel decompression? Muscle Nerve 2001, 24, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, B. The Value Added by Electrodiagnostic Testing in the Diagnosis of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2008, 90, 2587–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, A.; Cavanaugh, P.; Beredjiklian, P.K.; Matzon, J.L.; Seigerman, D.; Jones, C.M. Correlation of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 6 Score and Physical Exam Maneuvers With Electrodiagnostic Test Severity in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Blinded Prospective Cohort Study. J. Hand Surg. 2023, 48, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, J.D. A neurophysiological grading scale for carpal tunnel syndrome. Muscle Nerve 2000, 23, 1280–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padua, L.; Monaco, M.L.; Padua, R.; Gregori, B.; Tonali, P. Neurophysiological classification of carpal tunnel syndrome: Assessment of 600 symptomatic hands. Ital. J. Neurol. Sci. 1997, 18, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, J.C. AAEM minimonograph #26: The electrodiagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. American Association of Elec-trodiagnostic Medicine. Muscle Nerve 1997, 20, 1477–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padua, L.; LoMonaco, M.; Gregori, B.; Valente, E.M.; Padua, R.; Tonali, P. Neurophysiological classification and sensitivity in 500 carpal tunnel syndrome hands. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2009, 96, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, T.; Koyama, T.; Kuroiwa, T.; Nimura, A.; Okawa, A.; Wakabayashi, Y.; Fujita, K. Evaluation of the Existing Electro-physiological Severity Classifications in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez-Sánchez, F.; Gómez-Menéndez, A.I.; López-Veloso, M.; Calvo-Simal, S.; Lloria-Gil, M.C.; González-Santos, J.; Muñoz-Alcaraz, M.N.; Jiménez-Vilchez, A.J.; González-Bernal, J.J.; García-López, B. A Proposal for Neurography Referral in Patients with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Based on Clinical Symptoms and Demographic Variables of 797 Patients. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haloua, M.H.; Sierevelt, I.; Theuvenet, W.J. Semmes-Weinstein mono-filaments: Influence of temperature, humidity and age. J Hand Surg. 2011, 36, 1191–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarek, A.M.; Huber, J.; Leszczyńska, K.; Wietrzak, P.; Kaczmarek, K. Relationships between the Clinical Test Results and Neurophysiological Findings in Patients with Thoracic Outlet Syndrome. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turchin, D.C.; Beaton, D.E.; Richards, R.R. Validity of Observer-Based Aggregate Scoring Systems as Descriptors of Elbow Pain, Function, and Disability*. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 1998, 80, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonoo, M.; Menkes, D.L.; Bland, J.D.; Burke, D. Nerve conduction studies and EMG in carpal tunnel syndrome: Do they add value? Clin. Neurophysiol. Pract. 2018, 3, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Córdova-Martínez, A.; Caballero-García, A.; Pérez-Valdecantos, D.; Roche, E.; Noriega-González, D.C. Peripheral Neuropa-thies Derived from COVID-19: New Perspectives for Treatment. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lifchez, S.D.; Means, K.R.; Dunn, R.E.; Williams, E.H. Intra- and Inter-Examiner Variability in Performing Tinel’s Test. J. Hand Surg. 2010, 35, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stålberg, E.; van Dijk, H.; Falck, B.; Kimura, J.; Neuwirth, C.; Pitt, M.; Podnar, S.; Rubin, D.I.; Rutkove, S.; Sanders, D.B.; et al. Standards for quantification of EMG and neurography. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2019, 130, 1688–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jablecki, C.K.; Andary, M.T.; Floeter, M.K.; Miller, R.G.; Quartly, C.A.; Vennix, M.J.; Wilson, J.R. Practice parameter: Electrodiagnostic studies in carpal tunnel syndrome [RETIRED]. Neurology 2002, 58, 1589–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunderland, S.; Smith, J.W. NERVES AND NERVE INJURIES. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1969, 44, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullerton, P.M. The effect of ischaemia on nerve conduction in the carpal tunnel syndrome. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1963, 26, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundborg, G. The intrinsic vascularization of human peripheral nerves: Structural and functional aspects. J. Hand Surg. 1979, 4, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, R.A.; Andary, M. Electrodiagnostic evaluation of carpal tunnel syndrome. Muscle Nerve 2011, 44, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seror, P. Phalen’s test in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. J. Hand Surg. Br. 1988, 13, 383–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, I.; Ring, H. Median nerve conduction tests and Phalen’s sign in carpal tunnel syndrome. Electromyogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1995, 35, 107–112. [Google Scholar]
- Saggar, S.K.; Thaman, R.G.; Mohan, G.; Kumar, D. Mapping Neurophysiological Patterns in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Correlations With Tinel’s and Phalen’s Signs. Cureus 2024, 16, e58168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, N.N.; Adelmanesh, F.; Naghdi, S.; Mousavi, S. The relationship between symptoms, clinical tests and nerve conduction study findings in carpal tunnel syndrome. Electromyogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2009, 49, 53–57. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.S.; Oh, C.S.; Chung, I.H.; Sunwoo, I.N. An anatomic study of the Martin-Gruber anastomosis: Electrodiagnostic im-plications. Muscle Nerve 2004, 31, 95–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Secorún, M.; Montaña-Cortés, R.; Hidalgo-García, C.; Rodríguez-Sanz, J.; Corral-De-Toro, J.; Monti-Ballano, S.; Hamam-Alcober, S.; Tricás-Moreno, J.M.; Lucha-López, M.O. Effectiveness of Conservative Treatment According to Severity and Systemic Disease in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijaz, M.J.; Karimi, H.; Ahmad, A.; Gillani, S.A.; Anwar, N.; Chaudhary, M.A.; Hidalgo-García, C. Comparative Efficacy of Routine Physical Therapy with and without Neuromobilization in the Treatment of Patients with Mild to Moderate Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 2155765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paquette, P.; Higgins, J.; Gagnon, D.H. Peripheral and Central Adaptations After a Median Nerve Neuromobilization Program Completed by Individuals With Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: An Exploratory Mechanistic Study Using Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Imaging and Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2020, 43, 566–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaheer, S.A.; Ahmed, Z. Neurodynamic Techniques in the Treatment of Mild-to-Moderate Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- del Barrio, S.J.; Gracia, E.B.; García, C.H.; de Miguel, E.E.; Moreno, J.T.; Marco, S.R.; Laita, L.C. Conservative treatment in patients with mild to moderate carpal tunnel syndrome: A systematic review. Neurologia 2018, 33, 590–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.-T.; Lee, H.-J.; Kim, T.-G.; Jeon, I.-H. Current Approaches for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. Clin. Orthop. Surg. 2014, 6, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdugo, R.J.; Salinas, R.A.; Castillo, J.L.; Cea, J.G. Surgical versus non-surgical treatment for carpal tunnel syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2008, 2016, CD001552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Study Group Variable | Healthy Volunteers (Control) N = 75 ♀ = 53, ♂ = 22 | CTS Patients N = 75 ♀ = 52, ♂ = 23 | Control vs. Patients | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Min–Max | Mean ± SD | Min–Max | p-Value | |
| Age (years) | 57.6 ± 12.9 | 18–60 | 56.4 ± 9.6 | 18–59 | 0.07 |
| Height (cm) | 166.4 ± 8.2 | 156–181 | 165.7 ± 7.1 | 155–182 | 0.08 |
| Weight (kg) | 56.3 ± 8.4 | 48.5–87.0 | 57.3 ± 8.1 | 46.3–85.1 | 0.09 |
| BMI | 20.3 | 20.9 | 0.08 | ||
| Test Conditions | Parameter | Controls | CTS Patients | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Injured Upper Extremities CMAP n = 112 SNAP n = 112 | Symptomatic Side CMAP n = 108 SNAP n = 66 | |||
| CMAP (M-wave) Stimulation at wrist, APB recording | Amplitude (µV) | 5000–12050 7325.4 ± 944.2 | 400–13500 5440.2 ± 530.2 | 0.04 |
| Latency (ms) | 2.8–4.1 3.6 ± 0.2 | 2.7–10.7 5.5 ± 1.5 | 0.03 | |
| SNAP (SCV) Stimulation of 2nd finger, recording at wrist | Amplitude (µV) | 10.4–28.6 18.8 ± 1.3 | 8.9–15.9 5.9 ± 1.3 | 0.009 |
| Latency (ms) | 2.7–3.8 3.1 ± 0.2 | 2.5–5.4 4.1 ± 0.7 | 0.04 |
| All Results n = 112 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test | Patients with Recorded SNAP (n = 66) | Patients Without Recorded SNAP | |||
| n = 7 | n = 26 | n = 27 | n = 6 | n = 46 | |
| SNAP latency (ms) | |||||
| ≤3 | ≤4 | ≤5 | ≤6 | NA | |
| Phalen positive | 0 | 10 | 15 | 3 | 27 |
| Phalen negative | 7 | 16 | 12 | 3 | 19 |
| Tinel positive | 0 | 7 | 7 | 2 | 23 |
| Tinel negative | 7 | 19 | 20 | 4 | 23 |
| Test | Tinel Positive | Tinel Negative | All Tests |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phalen positive | 27 | 28 | 55 |
| Phalen negative | 12 | 45 | 57 |
| All tests | 39 | 73 | 112 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaczmarek, K.; Pepliński, J.; Kaczmarek, A.; Andrzejuk, D.; Andruszkiewicz, K.; Wysocka, A.; Witkowska, M.; Huber, J. Correlations of Tinel and Phalen Signs with Nerve Conduction Study Test Results in a Randomly Chosen Population of Patients with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. NeuroSci 2025, 6, 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6040094
Kaczmarek K, Pepliński J, Kaczmarek A, Andrzejuk D, Andruszkiewicz K, Wysocka A, Witkowska M, Huber J. Correlations of Tinel and Phalen Signs with Nerve Conduction Study Test Results in a Randomly Chosen Population of Patients with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. NeuroSci. 2025; 6(4):94. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6040094
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaczmarek, Katarzyna, Jędrzej Pepliński, Anna Kaczmarek, Dariusz Andrzejuk, Kacper Andruszkiewicz, Alicja Wysocka, Matylda Witkowska, and Juliusz Huber. 2025. "Correlations of Tinel and Phalen Signs with Nerve Conduction Study Test Results in a Randomly Chosen Population of Patients with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome" NeuroSci 6, no. 4: 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6040094
APA StyleKaczmarek, K., Pepliński, J., Kaczmarek, A., Andrzejuk, D., Andruszkiewicz, K., Wysocka, A., Witkowska, M., & Huber, J. (2025). Correlations of Tinel and Phalen Signs with Nerve Conduction Study Test Results in a Randomly Chosen Population of Patients with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. NeuroSci, 6(4), 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6040094







