The Effect of Mucuna pruriens on Depression-like Behavior Induced by a Mild Traumatic Brain Injury in Rats Is Associated with a Decrease in Brain Nitrite and Nitrate Levels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Drugs
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Surgical Procedure
2.5. Sucrose Preference Test
2.6. Quantification of Nitrates and Nitrites Using the Griess Method
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
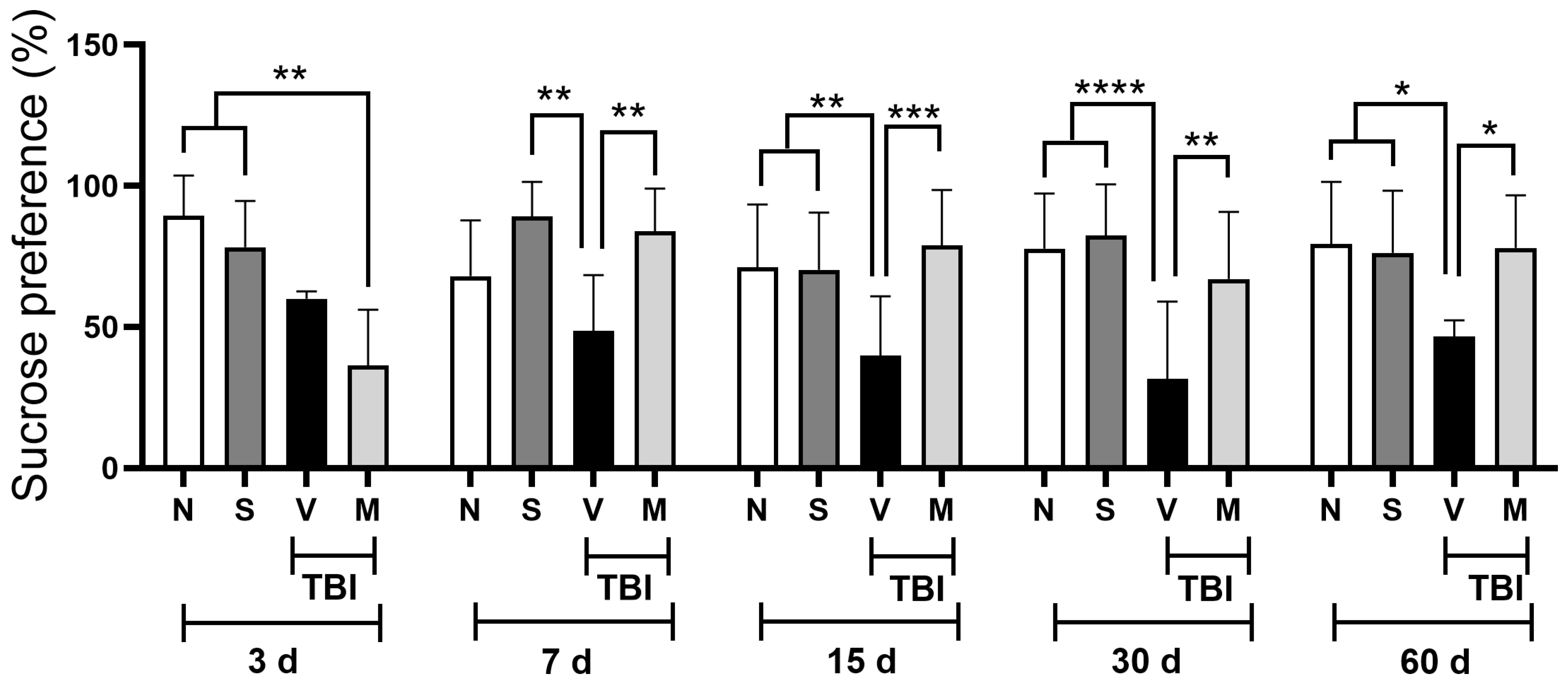
3.1. Treatment with a Lyophilized Mucuna pruriens Extract Decreases Depressive-like Behavior After Mild TBI in Rats
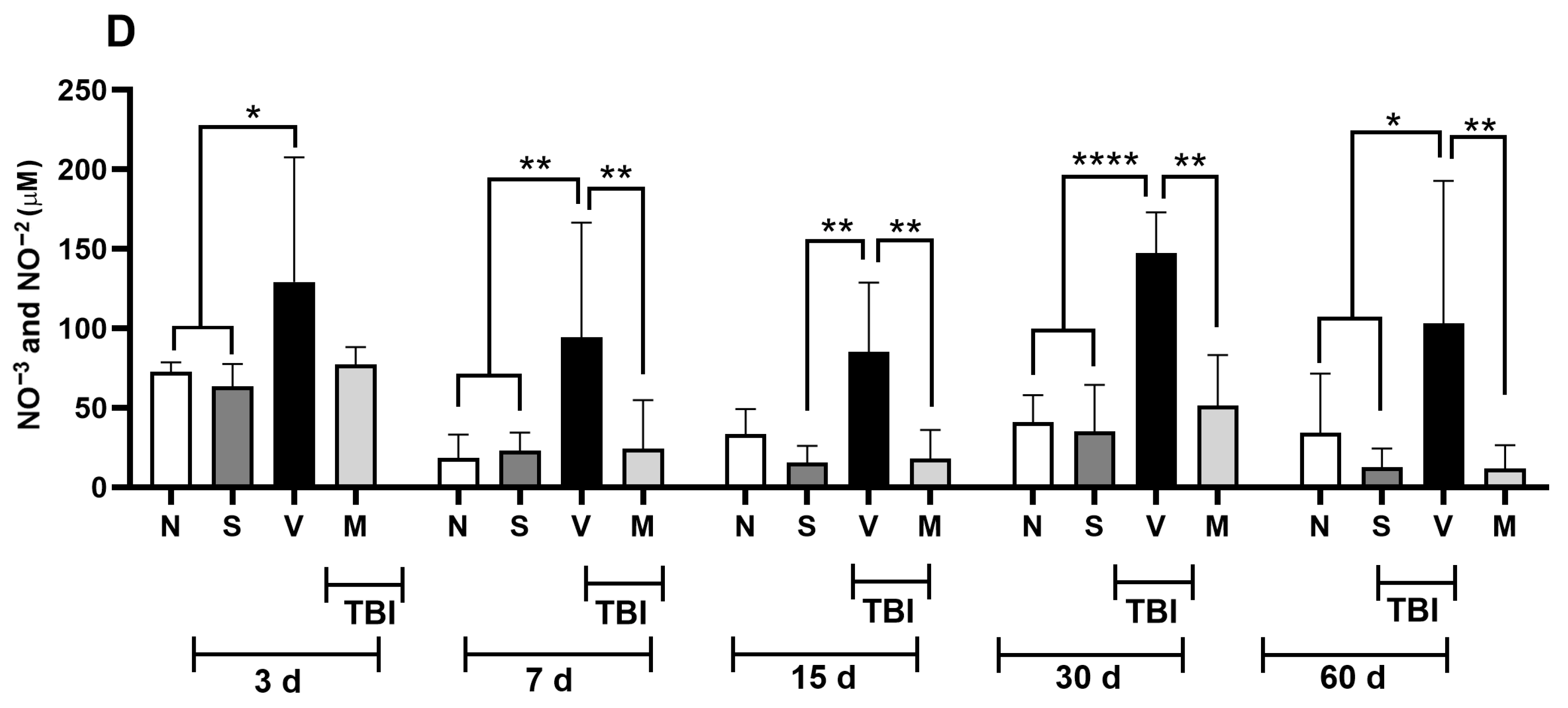
3.2. Treatment with a Lyophilized Mucuna pruriens Extract Decreases the Nitrite and Nitrate Levels in a Rat Model of Mild TBI
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BH4 | Tetrahydrobiopterin |
| cGMP | Cyclic guanosine monophosphate |
| eNOS | Endothelial NOS |
| IL-1β | Interleukin 1-beta |
| iNOS | Inducible NOS |
| L-DOPA | L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine |
| MP | Mucuna pruriens |
| mTBI | Mild traumatic brain injury |
| NMDA | N-methyl-D-aspartate |
| nNOS | Neuronal NOS |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| NOS | NO synthase |
| ONOO− | Peroxynitrite |
| RNS | Reactive nitrogen species |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| TBI | Traumatic brain injury |
| TH | Tyrosine hydroxylase |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
References
- Graham, N.S.; Sharp, D.J. Understanding neurodegeneration after traumatic brain injury: From mechanisms to clinical trials in dementia. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2019, 90, 1221–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capizzi, A.; Woo, J.; Verduzco-Gutierrez, M. Traumatic Brain Injury: An Overview of Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and Medical Management. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 104, 213–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khellaf, A.; Khan, D.Z.; Helmy, A. Recent advances in traumatic brain injury. J. Neurol. 2019, 266, 2878–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, K.; Khan, H.; Singh, T.G.; Kaur, A. Traumatic Brain Injury: Mechanistic Insight on Pathophysiology and Potential Therapeutic Targets. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2021, 71, 1725–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailes, J.E.; Borlongan, C.V. Traumatic brain injury. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2020, 26, 593–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewan, M.C.; Rattani, A.; Gupta, S.; Baticulon, R.E.; Hung, Y.C.; Punchak, M.; Agrawal, A.; Adeleye, A.O.; Shrime, M.G.; Rubiano, A.M.; et al. Estimating the global incidence of traumatic brain injury. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 130, 1080–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, S. Traumatic brain injury and mood disorders. Ment. Health Clin. 2020, 10, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlett, J.R.; Nelson, L.D.; Stein, M.B. Mental Health Consequences of Traumatic Brain Injury. Biol. Psychiatry 2022, 91, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyko, M.; Gruenbaum, B.F.; Shelef, I.; Zvenigorodsky, V.; Severynovska, O.; Binyamin, Y.; Knyazer, B.; Frenkel, A.; Frank, D.; Zlotnik, A. Traumatic brain injury-induced submissive behavior in rats: Link to depression and anxiety. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudek, K.A.; Dion-Albert, L.; Kaufmann, F.N.; Tuck, E.; Lebel, M.; Menard, C. Neurobiology of resilience in depression: Immune and vascular insights from human and animal studies. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2021, 53, 183–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverberg, N.D.; Panenka, W.J. Antidepressants for depression after concussion and traumatic brain injury are still best practice. BMC Psychiatry 2019, 19, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fann, J.R.; Hart, T.; Schomer, K.G. Treatment for Depression after Traumatic Brain Injury: A Systematic Review. J. Neurotrauma 2009, 26, 2383–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Kong, F.Z.; Hong, X.H.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, W.H.; Yang, J.C.; Zhang, H. Neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase Regulates Depression-like Behaviors in Shortening-Induced Obese Mice. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papp, M.; Moryl, E. Antidepressant activity of non-competitive and competitive NMDA receptor antagonists in a chronic mild stress model of depression. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1994, 263, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpinar, A.; Yaman, G.B.; Demirdas, A.; Onal, S. Possible role of adrenomedullin and nitric oxide in major depression. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 46, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinelli, M.A.; Do, H.T.; Miley, G.P.; Silverman, R.B. Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase: Regulation, Structure, and Inhibition. Med. Res. Rev. 2020, 40, 158–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.G.; Zhu, X.H.; Nemes, A.D.; Zhu, D.Y. Neuronal nitric oxide synthase and affective disorders. IBRO Rep. 2018, 5, 116–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlov, A.V.; Bahrami, S.; Redl, H.; Szabo, C. Alterations in nitric oxide homeostasis during traumatic brain injury. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 2627–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, S.N.; Chaturvedi, V.K.; Singh, P.; Singh, B.K.; Singh, M.P. Mucuna pruriens in Parkinson’s and in some other diseases: Recent advancement and future prospective. 3 Biotech 2020, 10, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.G.; Bae, M.J. An BJ. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Velvet Bean (Mucuna pruriens) Substances in LPS−Stimulated RAW 264.7 Macrophages. Molecules 2022, 27, 8797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, S.K.; Rai, S.N.; Singh, S.P. Mucuna pruriens reduces inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in Parkinsonian mice model. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2017, 80, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata-Bermudez, A.; Diaz-Ruiz, A.; Silva-García, L.R.; Gines-Francisco, E.M.; Noriega-Navarro, R.; Rios, C.; Romero-Sánchez, H.A.; Arroyo, D.; Landa, A.; Navarro, L. Mucuna pruriens, a Possible Treatment for Depressive Disorders. Neurol. Int. 2024, 16, 1509–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata-Bermudez, A.; Trejo-Chávez, R.; Martínez-Vargas, M.; Pérez-Arredondo, A.; Martínez-Cardenas, M.A.; Diaz-Ruiz, A.; Rios, C.; Romero-Sánchez, H.A.; Martínez-Antonio, A.; Navarro, L. Effect of Mucuna pruriens seed extract on depression-like behavior derived from mild traumatic brain injury in rats. Biomedicine 2024, 14, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NORMA Oficial Mexicana NOM-062-ZOO-1999, Especificaciones Tecnicas para la Produccion, Cuidado y uso de los Animales de Laboratorio. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/203498/NOM-062-ZOO-1999_220801.pdf (accessed on 17 September 2025).
- Hernández-Orihuela, A.L.; Castro-Cerritos, K.V.; López, M.G.; Martínez-Antonio, A. Compound Characterization of a Mucuna Seed Extract: L-Dopa, Arginine, Stizolamine, and Some Fructooligosaccharides. Compounds 2023, 3, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, L.; Jiang, P.; Chen, C.; Zhang, T. Levodopa improves learning and memory ability on global cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injured rats in the Morris water maze test. Neurosci. Lett. 2017, 636, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Vargas, M.; Soto-Nuñez, M.; Tabla-Ramon, E.; Solis, B.; Gonzalez-Rivera, R.; Perez-Arredondo, A.; Estrada-Rojo, F.; Castell, A.; Molina-Guarneros, J.; Navarro, L. Cystatin C has a dual role in post-traumatic brain injury recovery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 5807–5820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C.R.; Emson, P.C. AChE-stained horizontal sections of the rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. J. Neurosci. Methods 1980, 3, 129–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.H.; Zhao, B.L.; Li, W.T.; Zhou, X.H.; Jin, Z.; An, L.B. Changes in depressive-like behaviors induced by spinal cord injury based on the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and hippocampal neurogenesis. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2021, 20, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, K.M.; Espey, M.G.; Wink, D.A. A rapid, simple spectrophotometric method for simultaneous detection of nitrate and nitrite. Nitric Oxide Biol. Chem. 2001, 5, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbafor, K.N.; Nwachukwu, N. Phytochemical Analysis and Antioxidant Property of Leaf Extracts of Vitex doniana and Mucuna pruriens. Biochem. Res. Int. 2011, 2011, 459839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachsee, A.; Chiranthanut, N.; Kunnaja, P.; Sireeratawong, S.; Khonsung, P.; Chansakaow, S.; Panthong, A. Mucuna pruriens (L.) DC. seed extract inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in BV2 microglial cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 267, 113518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, Y.B.; Upadhyay, A.K. Effect of the alcohol extract of the seeds of Mucuna pruriens on free radicals and oxidative stress in albino rats. Phytother. Res. 2002, 16, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belovicova, K.; Bogi, E.; Csatlosova, K.; Dubovicky, M. Animal tests for anxiety-like and depression-like behavior in rats. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2017, 10, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheggi, S.; De Montis, M.G.; Gambarana, C. Making Sense of Rodent Models of Anhedonia. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018, 21, 1049–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, V.S.; Kumar, N.; D’Souza, A.S.; Nayak, S.S.; Cheruku, S.P.; Pai, K.S.R. The effects of Mucuna pruriens extract on histopathological and biochemical features in the rat model of ischemia. Neuroreport 2017, 28, 1195–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.L.; Park, H.Y.; Dasilva, N.A.; Vattem, D.A.; Ma, H.; Seeram, N.P. Levodopa-Reduced Mucuna pruriens Seed Extract Shows Neuroprotective Effects against Parkinson’s Disease in Murine Microglia and Human Neuroblastoma Cells, Caenorhabditis elegans, and Drosophila melanogaster. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, S.; Prithiviraj, E.; Lakshmi, N.V.; Ganesh, M.K.; Ganesh, L.; Prakash, S. Effect of Mucuna pruriens (Linn.) on mitochondrial dysfunction and DNA damage in epididymal sperm of streptozotocin induced diabetic rat. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 145, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, S.N.; Birla, H.; Zahra, W.; Singh, S.S.; Singh, S.P. Immunomodulation of Parkinson’s disease using Mucuna pruriens (Mp). J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2017, 85, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaváková, M.; Ďuračková, Z.; Trebatická, J. Markers of Oxidative Stress and Neuroprogression in Depression Disorder. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2015, 898393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.H.; Lee, S.W.; Yoon, D.; Lee, H.J.; Yang, J.C.; Shim, S.H.; Kim, D.H.; Ryu, S.H.; Han, C.; Kim, Y.K. Increased Plasma Nitric Oxide Metabolites in Suicide Attempters. Neuropsychobiology 2006, 53, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, E.; Yagi, G.; Nakaki, T.; Kanba, S.; Asai, M. Elevated plasma nitrate levels in depressive states. J. Affect. Disord. 2001, 63, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tisdall, M.M.; Rejdak, K.; Kitchen, N.D.; Smith, M.; Petzold, A. The prognostic value of brain extracellular fluid nitric oxide metabolites after traumatic brain injury. Neurocrit. Care 2013, 19, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhir, A.; Kulkarni, S.K. Nitric oxide and major depression. Nitric Oxide Biol. Chem. 2011, 24, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joca, S.R.; Guimarães, F.S. Inhibition of neuronal nitric oxide synthase in the rat hippocampus induces antidepressant-like effects. Psychopharmacology 2006, 185, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, A.B.; Tanev, K. Neurobiological Mechanisms of Depression Following Traumatic Brain Injury. Brain Inj. 2023, 37, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosari-Nasab, M.; Shokouhi, G.; Ghorbanihaghjo, A.; Abbasi, M.M.; Salari, A.A. Anxiolytic- and antidepressant-like effects of Silymarin compared to diazepam and fluoxetine in a mouse model of mild traumatic brain injury. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2018, 338, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaster, M.P.; Ferreira, P.K.; Santos, A.R.; Rodrigues, A.L. Effects of potassium channel inhibitors in the forced swimming test: Possible involvement of L-arginine-nitric oxide-soluble guanylate cyclase pathway. Behav. Brain Res. 2005, 165, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini-Khoei, H.; Nasiri Boroujeni, S.; Maghsoudi, F.; Rahimi-Madiseh, M.; Bijad, E.; Moradi, M.; Lorigooini, Z. Possible involvement of L-arginine-nitric oxide pathway in the antidepressant activity of Auraptene in mice. Behav. Brain Funct. 2022, 18, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherwin, E.; Gigliucci, V.; Harkin, A. Regional specific modulation of neuronal activation associated with nitric oxide synthase inhibitors in an animal model of antidepressant activity. Behav. Brain Res. 2017, 316, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.; Aguiar, D.C.; Diniz, C.R.; Guimarães, F.S.; Joca, S.R. Neuronal NOS inhibitor and conventional antidepressant drugs attenuate stress-induced fos expression in overlapping brain regions. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2012, 32, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Leal, V.M.; Bonassoli, V.T.; Soares, L.M.; Milani, H.; de Oliveira, R.M.W. Depletion of 5 hydroxy-triptamine (5-HT) affects the antidepressant-like effect of neuronal nitric oxide synthase inhibitor in mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2017, 656, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walton, J.C.; Selvakumar, B.; Weil, Z.M.; Snyder, S.H.; Nelson, R.J. Neuronal nitric oxide synthase and NADPH oxidase interact to affect cognitive, affective, and social behaviors in mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2013, 256, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, D.G.; Galani, V.J. Dopamine mediated antidepressant effect of Mucuna pruriens seeds in various experimental models of depression. Ayu 2014, 35, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felger, J.C. The role of dopamine in inflammation-associated depression: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2017, 31, 199–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manyam, B.V.; Dhanasekaran, M.; Hare, T.A. Effect of antiparkinson drug HP-200 (Mucuna pruriens) on the central monoaminergic neurotransmitters. Phytother. Res. 2004, 18, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.K.; Prakash, J.; Chouhan, S.; Westfall, S.; Verma, M.; Singh, T.D.; Singh, S.P. Comparison of the neuroprotective potential of Mucuna pruriens seed extract with estrogen in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-induced PD mice model. Neurochem. Int. 2014, 65, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago-Castañeda, C.; Huerta de la Cruz, S.; Martínez-Aguirre, C.; Orozco-Suárez, S.A.; Rocha, L. Cannabidiol Reduces Short- and Long-Term High Glutamate Release after Severe Traumatic Brain Injury and Improves Functional Recovery. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.F.; Lin, J.S.; Chang, C.F. Acute Kahweol Treatment Attenuates Traumatic Brain Injury Neuroinflammation and Functional Deficits. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orfila, J.E.; Dietz, R.M.; Schroeder, C.; Patsos, O.P.; Burch, A.; Bahamonde, K.E.; Coakley, K.A.; Carter, D.J.; Clevenger, A.C.; Hendry-Hofer, T.B.; et al. A novel peptide inhibitor of TRPM2 channels improves recovery of memory function following traumatic brain injury. Front. Synaptic Neurosci. 2025, 17, 1534379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruenbaum, S.E.; Zlotnik, A.; Gruenbaum, B.F.; Hersey, D.; Bilotta, F. Pharmacologic Neuroprotection for Functional Outcomes After Traumatic Brain Injury: A Systematic Review of the Clinical Literature. CNS Drugs 2016, 30, 791–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Mahmood, A.; Chopp, M. Investigational agents for treatment of traumatic brain injury. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2015, 24, 743–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Gary, K.W.; Neimeier, J.P.; Ward, J.; Lapane, K.L. Randomized controlled trials in adult traumatic brain injury. Brain Inj. 2012, 26, 1523–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Morris, S.M. Arginine metabolism: Nitric oxide and beyond. Biochem. J. 1998, 336, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durante, W.; Johnson, F.K.; Johnson, R.A. Arginase: A critical regulator of nitric oxide synthesis and vascular function. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2007, 34, 906–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, S.; Reid, G. Distant Site Effects of Ingested Prebiotics. Nutrients 2016, 8, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna, A.B.; Manikyam, H.K.; Sharma, V.K.; Sharma, N. Acute oral toxicity study in rats with Mucuna pruriens seed extract. Asian J. Plant Sci. Res. 2016, 6, 1–5. Available online: https://www.imedpub.com/articles-pdfs/acute-oral-toxicity-study-in-rats-with-mucuna-pruriens-seed-extract.pdf (accessed on 17 September 2025).
- Tsikas, D. Methods of quantitative analysis of the nitric oxide metabolites nitrite and nitrate in human biological fluids. Free Radic. Res. 2005, 39, 797–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piknova, B.; Park, J.W.; Cassel, K.S.; Gilliard, C.N.; Schechter, A.N. Measuring Nitrite and Nitrate, Metabolites in the Nitric Oxide Pathway, in Biological Materials using the Chemiluminescence Method. J. Vis. Exp. 2016, 118, 54879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, M.N.; Rios, N.; Trujillo, M.; Radi, R.; Denicola, A.; Alvarez, B. Detection and quantification of nitric oxide-derived oxidants in biological systems. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 14776–14802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsikas, D. Analysis of nitrite and nitrate in biological fluids by assays based on the Griess reaction: Appraisal of the Griess reaction in the L-arginine/nitric oxide area of research. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2007, 851, 51–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinbongard, P.; Dejam, A.; Lauer, T.; Rassaf, T.; Schindler, A.; Picker, O.; Scheeren, T.; Gödecke, A.; Schrader, J.; Schulz, R.; et al. Plasma nitrite reflects constitutive nitric oxide synthase activity in mammals. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2003, 35, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E.; Gladwin, M.T. The nitrate-nitrite-nitric oxide pathway in physiology and therapeutics. Nature reviews. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mata-Bermudez, A.; Trejo-Chávez, R.; Martínez-Vargas, M.; Pérez-Arredondo, A.; Diaz-Ruiz, A.; Rios, C.; Romero-Sánchez, H.A.; Martínez-Cárdenas, M.d.l.Á.; Ugalde-Muñiz, P.; Noriega-Navarro, R.; et al. The Effect of Mucuna pruriens on Depression-like Behavior Induced by a Mild Traumatic Brain Injury in Rats Is Associated with a Decrease in Brain Nitrite and Nitrate Levels. NeuroSci 2025, 6, 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6040092
Mata-Bermudez A, Trejo-Chávez R, Martínez-Vargas M, Pérez-Arredondo A, Diaz-Ruiz A, Rios C, Romero-Sánchez HA, Martínez-Cárdenas MdlÁ, Ugalde-Muñiz P, Noriega-Navarro R, et al. The Effect of Mucuna pruriens on Depression-like Behavior Induced by a Mild Traumatic Brain Injury in Rats Is Associated with a Decrease in Brain Nitrite and Nitrate Levels. NeuroSci. 2025; 6(4):92. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6040092
Chicago/Turabian StyleMata-Bermudez, Alfonso, Ricardo Trejo-Chávez, Marina Martínez-Vargas, Adán Pérez-Arredondo, Araceli Diaz-Ruiz, Camilo Rios, Héctor Alonso Romero-Sánchez, María de los Ángeles Martínez-Cárdenas, Perla Ugalde-Muñiz, Roxana Noriega-Navarro, and et al. 2025. "The Effect of Mucuna pruriens on Depression-like Behavior Induced by a Mild Traumatic Brain Injury in Rats Is Associated with a Decrease in Brain Nitrite and Nitrate Levels" NeuroSci 6, no. 4: 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6040092
APA StyleMata-Bermudez, A., Trejo-Chávez, R., Martínez-Vargas, M., Pérez-Arredondo, A., Diaz-Ruiz, A., Rios, C., Romero-Sánchez, H. A., Martínez-Cárdenas, M. d. l. Á., Ugalde-Muñiz, P., Noriega-Navarro, R., & Navarro, L. (2025). The Effect of Mucuna pruriens on Depression-like Behavior Induced by a Mild Traumatic Brain Injury in Rats Is Associated with a Decrease in Brain Nitrite and Nitrate Levels. NeuroSci, 6(4), 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6040092





