Identifying Angiogenic Factors in Pediatric Choroid Plexus Papillomas
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patient Selection
2.2. Multiplex Immunoassay for CSF Samples
2.3. Patient-Derived Tumor Cell Cultures and In Vitro Experiments
2.4. Proteome Blot Array
2.5. Referencing Protein–Protein Biomolecular Networks In Silico
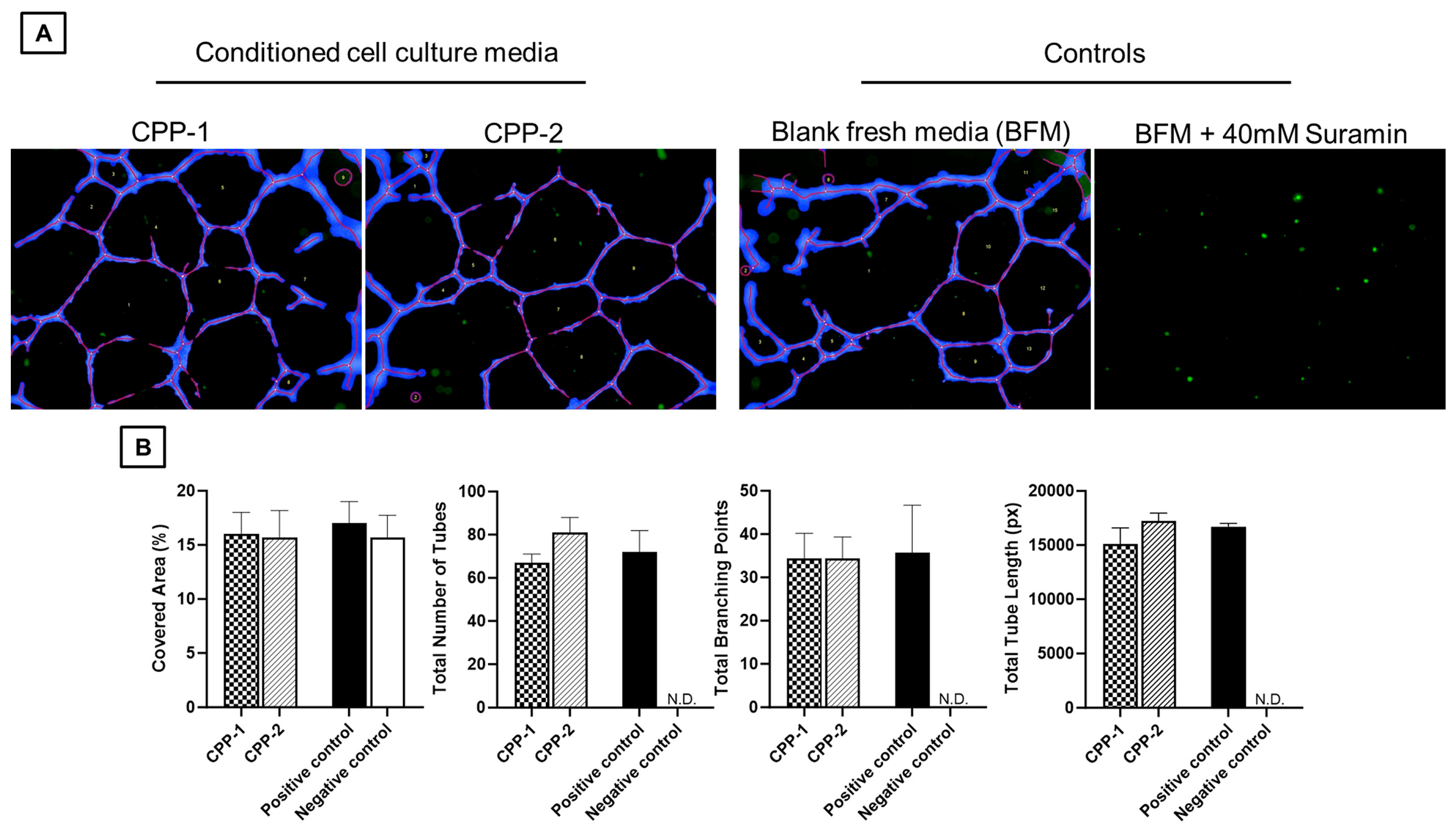
2.6. Assessment of In Vitro Angiogenesis: HUVEC Functional Assay
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
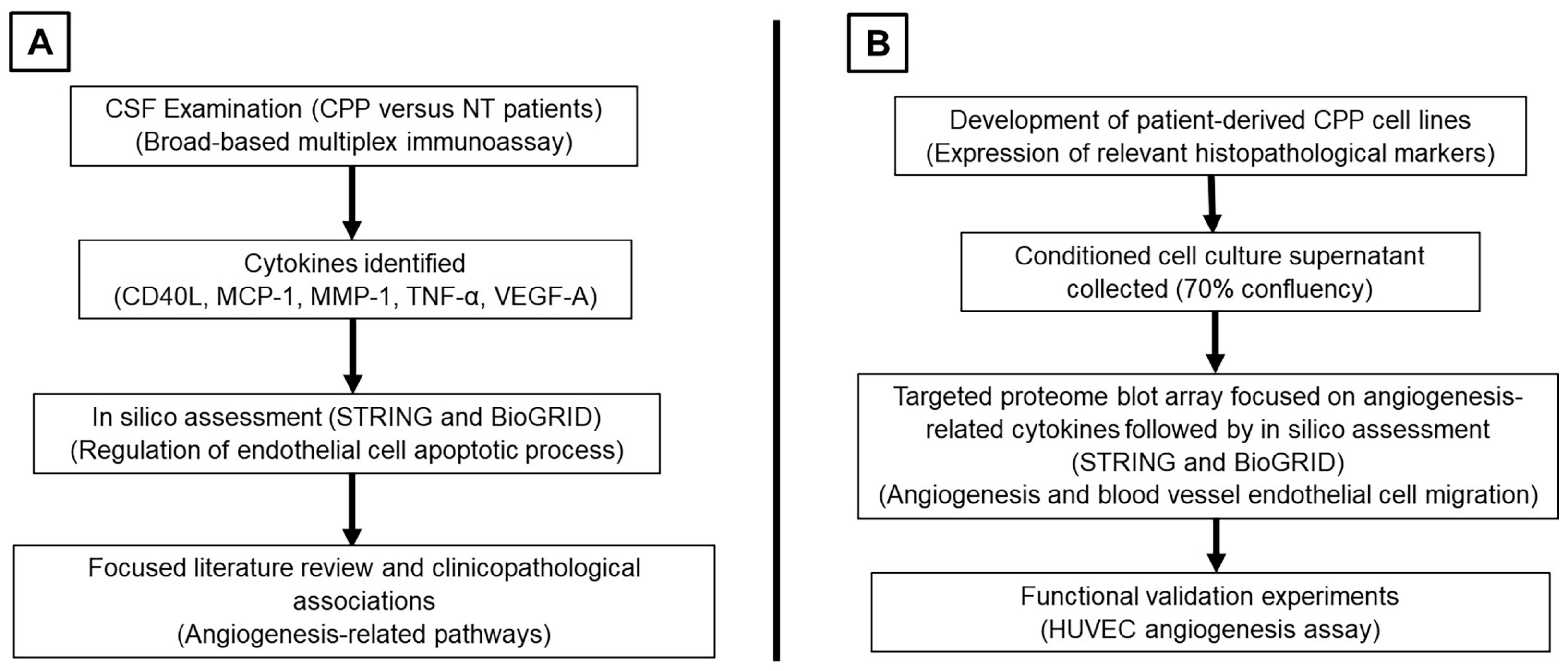
3.1. Summary of Study Workflow and Findings
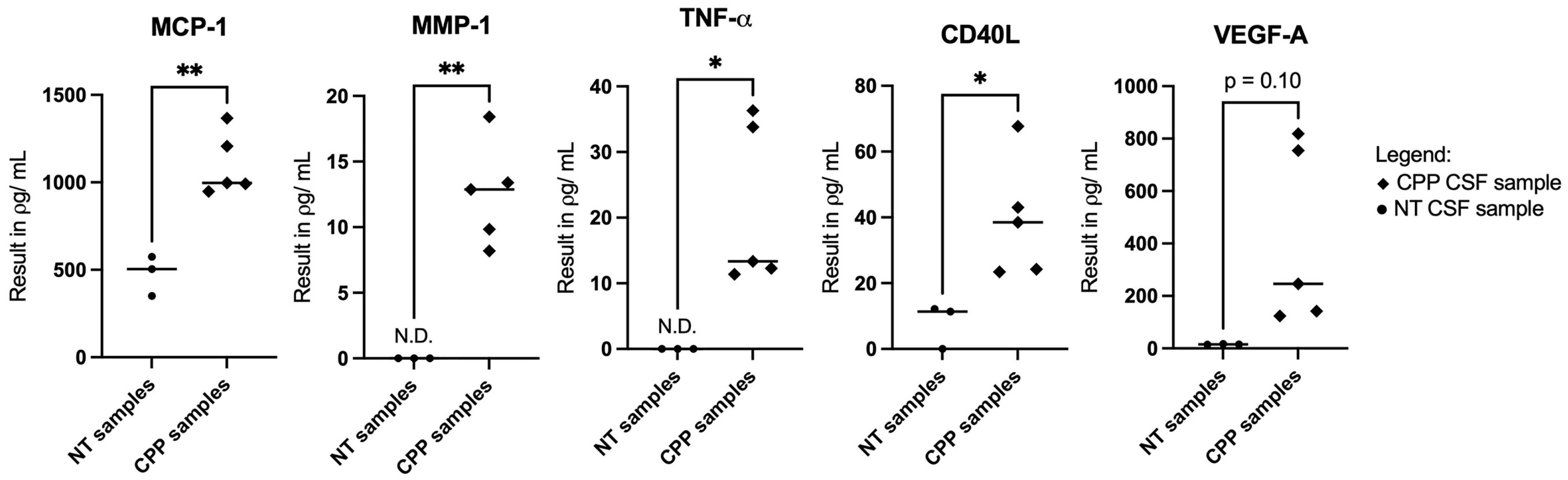
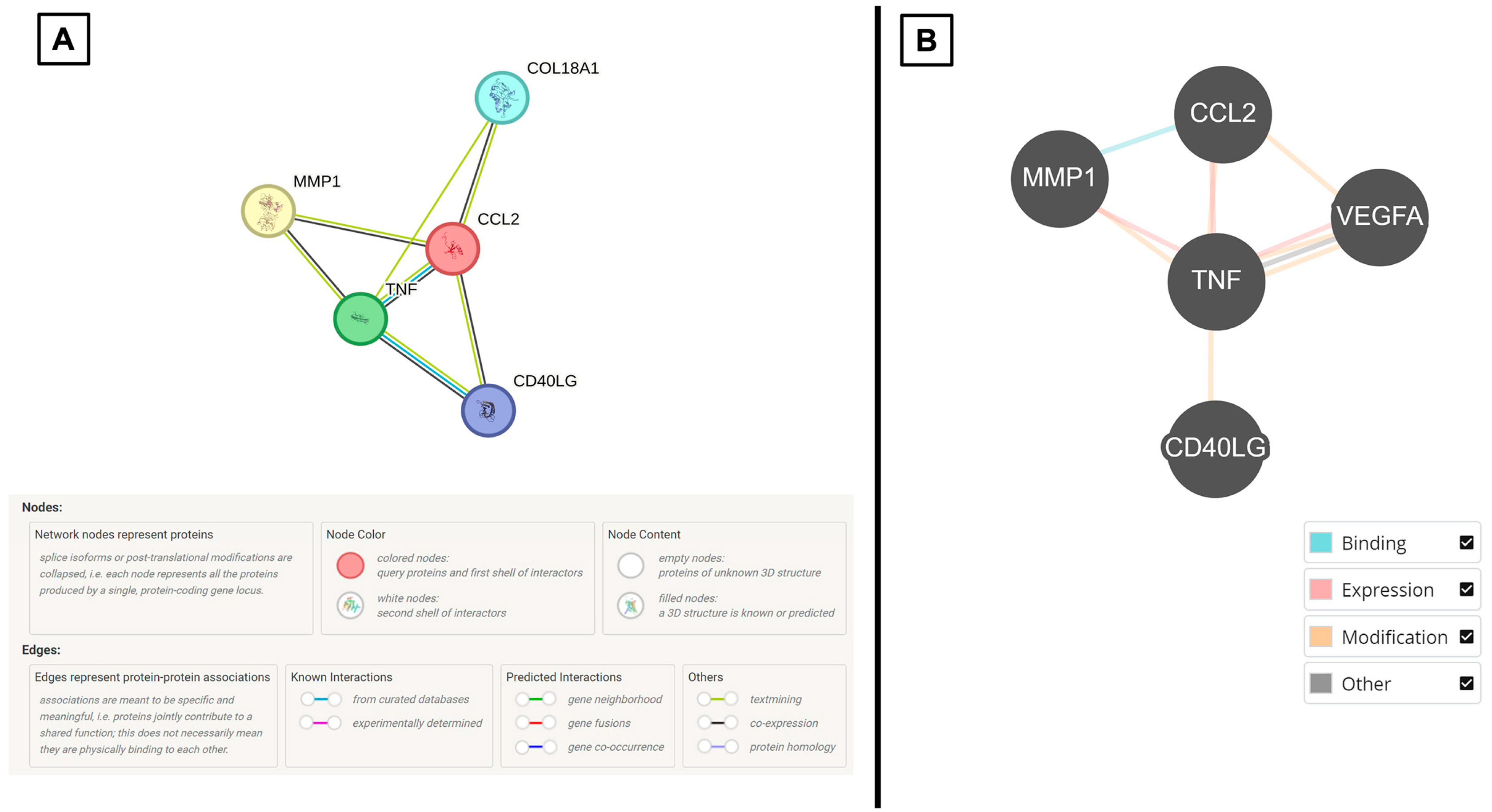
3.2. Selective CSF Cytokines Are Differentially Expressed Between CPP Versus Non-Tumor Samples and They Demonstrate Biomolecular Associations In Silico
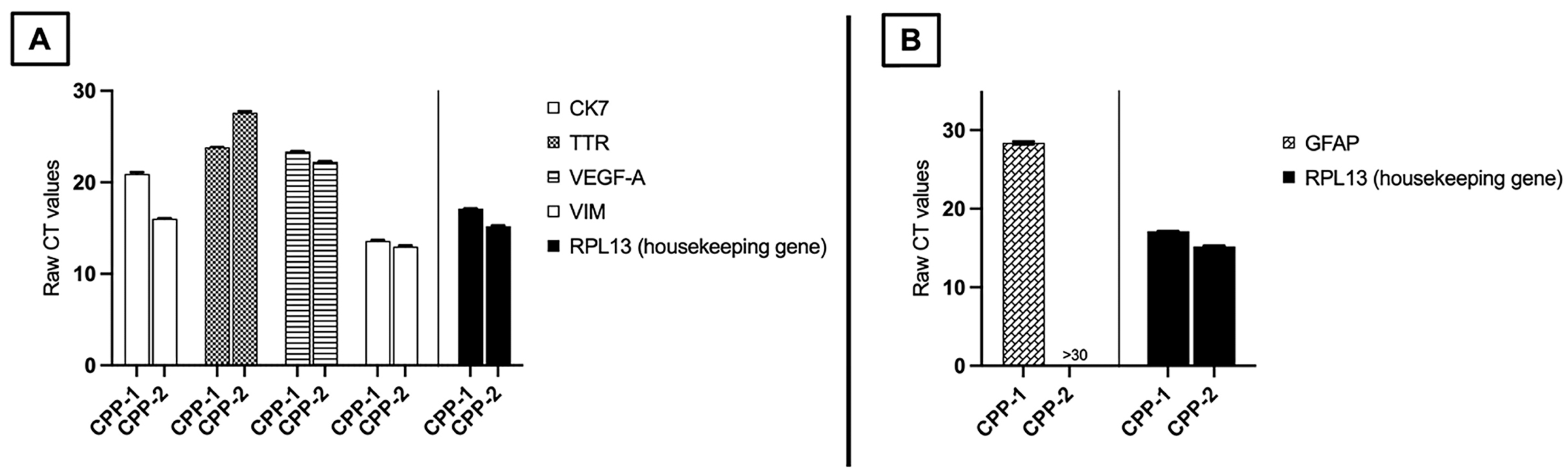
3.3. Patient-Derived CPP Cell Lines Secrete Cytokines That Are Associated with Vascular-Related Pathways
3.4. Secreted Cytokines from CPP Cell Lines Demonstrate In Vitro Angiogenesis by HUVEC Functional Assay
4. Discussion
4.1. Overview of Choroid Plexus Papillomas in Children
4.2. The Relevance of Angiogenic CSF Cytokines in CPP Tumors
4.3. Study Critique and Future Work
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR) for mRNA Expression
| Gene of Interest | Forward Primer Sequence | Reverse Primer Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| Cytokeratin 7 (CK7) | GAAAGGCTGCTGATGACACC | TCAGTTGTGAGCCCATGCAG |
| Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) | CTGGAGGTTGAGAGGGACAA | CAGCCTCAGGTTGGTTTCAT |
| Transthyretin (TTR) | GAAAGGCTGCTGATGACACC | TCAGTTGTGAGCCCATGCAG |
| Vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) | TTGCCTTGCTGCTCTACCTCCA | GATGGCAGTAGCTGCGCTGATA |
| Vimentin (VIM) | TGCAGGAGGCAGAAGAATGG | ATTTCACGCATCTGGCGTTC |
| Ribosomal protein L13 (RPL13) * | CATAGGAAGCTGGGAGCAAG | GCCCTCCAATCAGTCTTCTG |
Appendix B
| S/N | Age (Months) | Tumor Location | Diagnosis | WHO CNS Grade | Treatment |
| CPP-1* | 10 | Right atrium | CPP | 1 | GTR |
| CPP-2* | 84 | Fourth ventricle | Atypical CPP | 2 | STR |
| CPP-3 | 24 | Left atrium | CPP | 1 | GTR |
| CPP-4 | 15 | Right frontal horn | CPP | 1 | GTR |
| CPP-5 | 2 | Right atrium | Atypical CPP | 2 | GTR |
| NT-001 | 2.5 | Congenital hydrocephalus | N.A. | N.A. | CSF diversion |
| NT-002 | 3 | Congenital hydrocephalus | N.A. | N.A. | CSF diversion |
| NT-003 | 72 | Post-traumatic hydrocephalus | N.A. | N.A. | CSF diversion |
References
- Louis, D.N.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Ellison, D.W.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; von Deimling, A. WHO Classification of Tumours of the Central Nervous System, Revised, 4th ed.; IARC: Lyon, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bahar, M.; Hashem, H.; Tekautz, T.; Worley, S.; Tang, A.; de Blank, P.; Wolff, J. Choroid plexus tumors in adult and pediatric populations: The Cleveland Clinic and University Hospitals experience. J. Neurooncol. 2017, 132, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board (Ed.) WHO Classification of Tumours, 5th edition: Central Nervous System Tumours, 5th ed.; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2021; p. 568. [Google Scholar]
- Safaee, M.; Clark, A.J.; Bloch, O.; Oh, M.C.; Singh, A.; Auguste, K.I.; Gupta, N.; McDermott, M.W.; Aghi, M.K.; Berger, M.S.; et al. Surgical outcomes in choroid plexus papillomas: An institutional experience. J. Neurooncol. 2013, 113, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Park, B.J.; Kim, E.J.; Lim, Y.J. Atypical choroid plexus papilloma in an adult. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2009, 46, 74–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamar, F.G.; Kairouz, V.F.; Nasser, S.M.; Faddoul, S.G.; Saikali, I.C. Atypical choroid plexus papilloma treated with single agent bevacizumab. Rare Tumors 2014, 6, 4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaee, M.; Oh, M.C.; Bloch, O.; Sun, M.Z.; Kaur, G.; Auguste, K.I.; Tihan, T.; Parsa, A.T. Choroid plexus papillomas: Advances in molecular biology and understanding of tumorigenesis. Neuro-Oncology 2013, 15, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razzaq, A.A.; Cohen, A.R. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy for hypervascular malignant brain tumors of childhood. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 1997, 27, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuivenvolt, M.; Mandl, E.; Verheul, J.; Fleischeuer, R.; Tijssen, C.C. Atypical transformation in sacral drop metastasis from posterior fossa choroid plexus papilloma. BMJ Case Rep. 2012, 2012, bcr0120125681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavallaii, A.; Keykhosravi, E.; Rezaee, H.; Kianbakht, C. Role of available adjuvant therapies following surgical resection of atypical choroid plexus papilloma—A systematic review and pooled analysis. Neuro-Oncol. Adv. 2020, 2, vdaa139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, H.; Mineta, T.; Ueda, S.; Nakahara, Y.; Shiraishi, T.; Tamiya, T.; Tabuchi, K. Detection of JC virus DNA sequences in brain tumors in pediatric patients. J. Neurosurg. 2005, 102, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, H.N.; Zhang, X.; Bu, X.Y.; Zhang, Z.W.; Huang, W.J.; Zhang, P.; Liang, J.W.; Wang, X.L. Expression of the simian virus 40 large tumor antigen (Tag) and formation of Tag-p53 and Tag-pRb complexes in human brain tumors. Cancer 1999, 86, 2124–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, S.Y.Y.; Bte Syed Sulaiman, N.; Tan, E.E.K.; Ng, L.P.; Kuick, C.H.; Chang, K.T.E.; Tang, P.H.; Wong, R.X.; Looi, W.S.; Low, D.C.Y.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid cytokines in metastatic group 3 and 4 medulloblastoma. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bte Syed Sulaiman, N.; Kuick, C.H.; Chang, K.T.E.; Wan, K.R.; Looi, W.S.; Low, D.C.Y.; Seow, W.T.; Low, S.Y.Y. Cytokines in Pediatric Pilocytic Astrocytomas: A Clinico-Pathological Study. NeuroSci 2021, 2, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, J.E.; Aschenbrenner, D.; Uhlig, H.H.; Coles, M.C.; Gaffney, E.A. A method for the inference of cytokine interaction networks. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2022, 18, e1010112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wautier, J.L.; Wautier, M.P. Pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Prostaglandins and Cytokines in Humans: A Mini Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.M.; An, J. Cytokines, inflammation, and pain. Int. Anesth. Clin. 2007, 45, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, A.; Allavena, P.; Sica, A.; Balkwill, F. Cancer-related inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sooreshjani, M.; Tripathi, S.; Dussold, C.; Najem, H.; de Groot, J.; Lukas, R.V.; Heimberger, A.B. The Use of Targeted Cytokines as Cancer Therapeutics in Glioblastoma. Cancers 2023, 15, 3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albulescu, R.; Codrici, E.; Popescu, I.D.; Mihai, S.; Necula, L.G.; Petrescu, D.; Teodoru, M.; Tanase, C.P. Cytokine patterns in brain tumour progression. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 979748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Nastou, K.C.; Lyon, D.; Kirsch, R.; Pyysalo, S.; Doncheva, N.T.; Legeay, M.; Fang, T.; Bork, P.; et al. The STRING database in 2021: Customizable protein-protein networks, and functional characterization of user-uploaded gene/measurement sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D605–D612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oughtred, R.; Rust, J.; Chang, C.; Breitkreutz, B.J.; Stark, C.; Willems, A.; Boucher, L.; Leung, G.; Kolas, N.; Zhang, F.; et al. The BioGRID database: A comprehensive biomedical resource of curated protein, genetic, and chemical interactions. Protein Sci. 2021, 30, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean-Quartier, C.; Jeanquartier, F.; Holzinger, A. Open Data for Differential Network Analysis in Glioma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Dombrowski, S.M.; Deshpande, A.; Krajcir, N.; Luciano, M.G. VEGF/VEGFR-2 changes in frontal cortex, choroid plexus, and CSF after chronic obstructive hydrocephalus. J. Neurol. Sci. 2010, 296, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharaj, A.S.; Walshe, T.E.; Saint-Geniez, M.; Venkatesha, S.; Maldonado, A.E.; Himes, N.C.; Matharu, K.S.; Karumanchi, S.A.; D’Amore, P.A. VEGF and TGF-beta are required for the maintenance of the choroid plexus and ependyma. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, N.B.S.; Merchant, K.Z.; Seow, W.T.; Ng, L.P.; Low, S.Y.Y. STEM-08. ANGIOGENESIS IN PEDIATRIC CHOROID PLEXUS PAPILLOMAS. Neuro-Oncology 2024, 26, 0. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megerian, C.A.; Pilch, B.Z.; Bhan, A.K.; McKenna, M.J. Differential expression of transthyretin in papillary tumors of the endolymphatic sac and choroid plexus. Laryngoscope 1997, 107, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Lim, Q.E.; Wan, G.; Too, H.P. Normalization with genes encoding ribosomal proteins but not GAPDH provides an accurate quantification of gene expressions in neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouno, M.; Kumanishi, T.; Washiyama, K.; Sekiguchi, K.; Saito, T.; Tanaka, R. An immunohistochemical study of cytokeratin and glial fibrillary acidic protein in chroid plexus papilloma. Acta Neuropathol. 1988, 75, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, C.P.; Micklem, K.; Watt, S.M. A comparison of methods for quantifying angiogenesis in the Matrigel assay in vitro. Tissue Eng. Part. C Methods 2011, 17, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, J.E.; Sajedi, M.; Brant, R.; Coppes, M.J.; Egeler, R.M. Choroid plexus tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2002, 87, 1086–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japp, A.S.; Gessi, M.; Messing-Jünger, M.; Denkhaus, D.; zur Mühlen, A.; Wolff, J.E.; Hartung, S.; Kordes, U.; Klein-Hitpass, L.; Pietsch, T. High-Resolution Genomic Analysis Does Not Qualify Atypical Plexus Papilloma as a Separate Entity Among Choroid Plexus Tumors. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2015, 74, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morshed, R.A.; Lau, D.; Sun, P.P.; Ostling, L.R. Spinal drop metastasis from a benign fourth ventricular choroid plexus papilloma in a pediatric patient: Case report. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2017, 20, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeibmann, A.; Wrede, B.; Peters, O.; Wolff, J.E.; Paulus, W.; Hasselblatt, M. Malignant progression in choroid plexus papillomas. J. Neurosurg. 2007, 107, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, E.; Jenkins, J.J.; Burger, P.C.; Reardon, D.A.; Langston, J.W.; Sanford, R.A.; Heideman, R.L.; Kun, L.E.; Merchant, T.E. Malignant evolution of choroid plexus papilloma. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 1999, 31, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggeri, L.; Alberio, N.; Alessandrello, R.; Cinquemani, G.; Gambadoro, C.; Lipani, R.; Maugeri, R.; Nobile, F.; Iacopino, D.; Urrico, G.; et al. Rapid malignant progression of an intraparenchymal choroid plexus papillomas. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2018, 9, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niikawa, S.; Ito, T.; Murakawa, T.; Hirayama, H.; Ando, T.; Sakai, N.; Yamada, H. Recurrence of choroid plexus papilloma with malignant transformation—Case report and lectin histochemistry study. Neurol. Med. Chir 1993, 33, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Krishnan, S.; Brown, P.D.; Scheithauer, B.W.; Ebersold, M.J.; Hammack, J.E.; Buckner, J.C. Choroid plexus papillomas: A single institutional experience. J. Neurooncol. 2004, 68, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosmann, A.; Hinker, F.; Dorfer, C.; Slavc, I.; Haberler, C.; Dieckmann, K.; Knosp, E.; Czech, T. Management of choroid plexus tumors-an institutional experience. Acta Neurochir. 2019, 161, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addo, N.K.; Kamaly-Asl, I.D.; Josan, V.A.; Kelsey, A.M.; Estlin, E.J. Preoperative vincristine for an inoperable choroid plexus papilloma: A case discussion and review of the literature. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2011, 8, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, M.L.; Goldfarb, A.; Hyder, D.J.; Gonzales-Gomez, I.; Nelson, M.; Gilles, F.H.; McComb, J.G. Choroid plexus tumors in children: Significance of stromal invasion. Neurosurgery 2001, 48, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasselblatt, M.; Mertsch, S.; Koos, B.; Riesmeier, B.; Stegemann, H.; Jeibmann, A.; Tomm, M.; Schmitz, N.; Wrede, B.; Wolff, J.E.; et al. TWIST-1 is overexpressed in neoplastic choroid plexus epithelial cells and promotes proliferation and invasion. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 2219–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolburg, H.; Paulus, W. Choroid plexus: Biology and pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 119, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janelidze, S.; Lindqvist, D.; Francardo, V.; Hall, S.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Adler, C.H.; Beach, T.G.; Serrano, G.E.; van Westen, D.; et al. Increased CSF biomarkers of angiogenesis in Parkinson disease. Neurology 2015, 85, 1834–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepkowska, A.; Wąsowska, B.; Gilun, P.D.; Lagaraine, C.; Robert, V.; Dufourny, L.; Thiéry, J.-C.; Skipor, J. Pattern of expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors in the ovine choroid plexus during long and short photoperiods. Cell Tissue Res. 2012, 350, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geindreau, M.; Bruchard, M.; Vegran, F. Role of Cytokines and Chemokines in Angiogenesis in a Tumor Context. Cancers 2022, 14, 2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanotelli, M.R.; Reinhart-King, C.A. Mechanical Forces in Tumor Angiogenesis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1092, 91–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes-Coelho, F.; Martins, F.; Pereira, S.A.; Serpa, J. Anti-Angiogenic Therapy: Current Challenges and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Bent, M.J.; Klein, M.; Smits, M.; Reijneveld, J.C.; French, P.J.; Clement, P.; de Vos, F.Y.F.; Wick, A.; Mulholland, P.J.; Taphoorn, M.J.B.; et al. Bevacizumab and temozolomide in patients with first recurrence of WHO grade II and III glioma, without 1p/19q co-deletion (TAVAREC): A randomised controlled phase 2 EORTC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 1170–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanovas, O.; Hicklin, D.J.; Bergers, G.; Hanahan, D. Drug resistance by evasion of antiangiogenic targeting of VEGF signaling in late-stage pancreatic islet tumors. Cancer Cell 2005, 8, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelsen, S.R.; Staberg, M.; Pedersen, H.; Jensen, K.E.; Majewski, W.; Broholm, H.; Nedergaard, M.K.; Meulengracht, C.; Urup, T.; Villingshøj, M.; et al. VEGF-C sustains VEGFR2 activation under bevacizumab therapy and promotes glioblastoma maintenance. Neuro Oncol. 2018, 20, 1462–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Cortés, M.; Delgado-Bellido, D.; Oliver, F.J. Vasculogenic Mimicry: Become an Endothelial Cell “But Not So Much”. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, K.H.; Aziz, S.; Al-Reshidi, M.A. Endothelial progenitor cells for cellular angiogenesis and repair: Lessons learned from experimental animal models. Regen. Med. 2017, 12, 969–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczynski, E.A.; Vermeulen, P.B.; Pezzella, F.; Kerbel, R.S.; Reynolds, A.R. Vessel co-option in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 469–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugano, R.; Ramachandran, M.; Dimberg, A. Tumor angiogenesis: Causes, consequences, challenges and opportunities. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 1745–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Shi, J.L.; Chen, M.; Zheng, Z.M.; Li, M.Q.; Shao, J. CCL2: An important cytokine in normal and pathological pregnancies: A review. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1053457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmane, S.L.; Kremlev, S.; Amini, S.; Sawaya, B.E. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1): An overview. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2009, 29, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goede, V.; Brogelli, L.; Ziche, M.; Augustin, H.G. Induction of inflammatory angiogenesis by monocyte chemoattractant protein-1. Int. J. Cancer 1999, 82, 765–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salcedo, R.; Ponce, M.L.; Young, H.A.; Wasserman, K.; Ward, J.M.; Kleinman, H.K.; Oppenheim, J.J.; Murphy, W.J. Human endothelial cells express CCR2 and respond to MCP-1: Direct role of MCP-1 in angiogenesis and tumor progression. Blood 2000, 96, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatovic, S.M.; Keep, R.F.; Mostarica-Stojkovic, M.; Andjelkovic, A.V. CCL2 Regulates Angiogenesis via Activation of Ets-1 Transcription Factor1. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 2651–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, S.Y.; Wong, M.P.; Chung, L.P.; Chan, A.S.; Yuen, S.T. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression and macrophage infiltration in gliomas. Acta Neuropathol. 1997, 93, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lien, M.-Y.; Chang, A.-C.; Tsai, H.-C.; Tsai, M.-H.; Hua, C.-H.; Cheng, S.-P.; Wang, S.-W.; Tang, C.-H. Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein 1 Promotes VEGF-A Expression in OSCC by Activating ILK and MEK1/2 Signaling and Downregulating miR-29c. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 592415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murao, K.; Ohyama, T.; Imachi, H.; Ishida, T.; Cao, W.M.; Namihira, H.; Sato, M.; Wong, N.C.W.; Takahara, J. TNF-α Stimulation of MCP-1 Expression Is Mediated by the Akt/PKB Signal Transduction Pathway in Vascular Endothelial Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 276, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Park, Y.; Zhang, H.; Gao, X.; Wilson, E.; Zimmer, W.; Abbott, L.; Zhang, C. Role of MCP-1 in tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced endothelial dysfunction in type 2 diabetic mice. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2009, 297, H1208–H1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visse, R.; Nagase, H. Matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases: Structure, function, and biochemistry. Circ. Res. 2003, 92, 827–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, R.K.; Sørensen, M.D.; Aaberg-Jessen, C.; Hermansen, S.K.; Kristensen, B.W. Expression and prognostic impact of matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) in astrocytomas. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, L.; Wu, D.; Zou, J.; Chen, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Ni, C.; Yuan, H. Prognostic impact of serum and tissue MMP-9 in non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 18458–18468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazor, R.; Alsaigh, T.; Shaked, H.; Altshuler, A.E.; Pocock, E.S.; Kistler, E.B.; Karin, M.; Schmid-Schönbein, G.W. Matrix Metalloproteinase-1-mediated Up-regulation of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-2 in Endothelial Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Q.X.A. Complex role of matrix metalloproteinases in angiogenesis. Cell Res. 1998, 8, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unemori, E.N.; Ferrara, N.; Bauer, E.A.; Amento, E.P. Vascular endothelial growth factor induces interstitial collagenase expression in human endothelial cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 1992, 153, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourboulia, D.; Stetler-Stevenson, W.G. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs): Positive and negative regulators in tumor cell adhesion. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2010, 20, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moens, S.; Goveia, J.; Stapor, P.C.; Cantelmo, A.R.; Carmeliet, P. The multifaceted activity of VEGF in angiogenesis-Implications for therapy responses. Cytokine Growth Factor. Rev. 2014, 25, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, X.; Ai, L.; Yuan, R.; Ye, J. Clinicohistopathological implications of MMP/VEGF expression in retinoblastoma: A combined meta-analysis and bioinformatics analysis. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barh, D.; Chaitankar, V.; Yiannakopoulou, E.C.; Salawu, E.O.; Chowbina, S.; Ghosh, P.; Azevedo, V. Chapter 21-In Silico Models: From Simple Networks to Complex Diseases. In Animal Biotechnology; Verma, A.S., Singh, A., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2014; pp. 385–404. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, D.B.; McLucas, B.C.; Montoya, L.A.; Brotski, C.M.; Das, S.; Miholits, M.; Sebata, T.H. Multiplexing protein and gene level measurements on a single Luminex platform. Methods 2019, 158, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraghty, A.C.; Acosta-Alvarez, L.; Rotiroti, M.C.; Dutton, S.; O’Dea, M.R.; Kim, W.; Trivedi, V.; Mancusi, R.; Shamardani, K.; Malacon, K.; et al. Immunotherapy-related cognitive impairment after CAR T cell therapy in mice. Cell 2025, 188, 3238–3258.e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
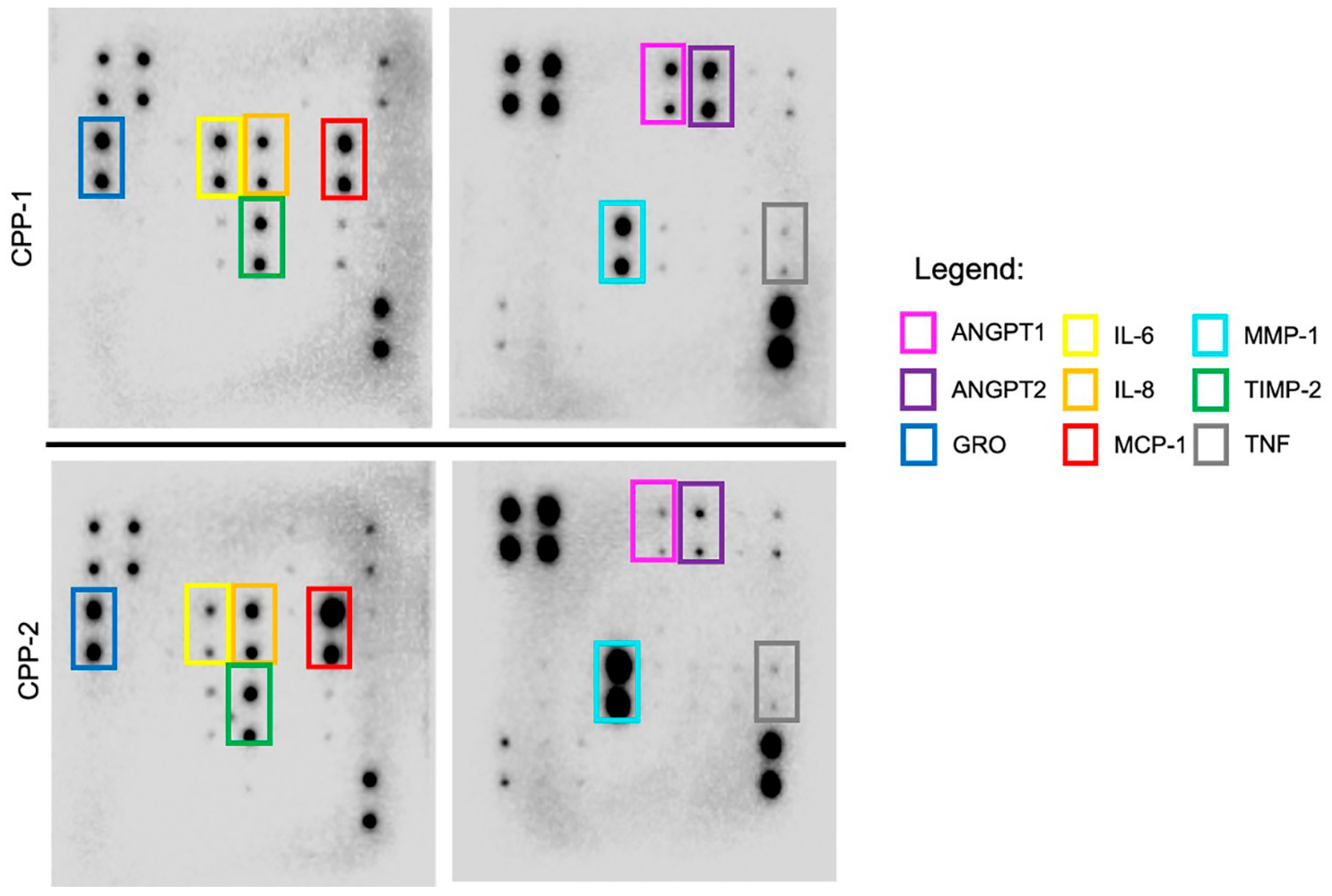

| Cytokine Abbreviation (Other Aliases) | Protein Name |
|---|---|
| MCP-1 (CCL2) | Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 |
| MMP1 (Interstitial collagenase, fibroblast collagenase) | Matrix metalloproteinase-1 |
| TNF-α (TNF, cachexin, cachectin) | Tumor necrosis factor |
| VEGF-A (VEGF) | Vascular endothelial growth factor A |
| CD40L (CD40LG, CD154) | CD40 ligand |
| Online Resource | Biological Process/Enriched Pathways |
|---|---|
| STRING | Regulation of endothelial cell apoptosis process Cellular extravasation |
| BioGRID | Endothelial cell apoptotic process regulation |
| Cytokine Abbreviation (Other Aliases) | Protein Name |
|---|---|
| MCP-1 (CCL2) | Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 |
| MMP1 (interstitial collagenase, fibroblast collagenase) | Matrix metalloproteinase-1 |
| TNF-α (TNF, cachexin, cachectin) | Tumor necrosis factor |
| TIMP-2 | Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 2 |
| CXCL1 (C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 1, GRO-α, GRO-1) | Growth-regulated oncogene alpha |
| IL-6 | Interleukin 6 |
| IL-8 (CXCL8, MDNCF) | Interleukin 8 |
| ANGPT1 (ANG1) | Angiopoietin 1 |
| ANGPT2 (ANG2) | Angiopoietin 2 |
| Online Resource | Biological Process/Enriched Pathways |
|---|---|
| STRING | Tie signaling pathway Angiogenesis Maintenance of blood–brain barrier |
| BioGRID | Blood vessel endothelial cell migration Vasculature development Endothelial cell apoptotic process regulation |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Syed Sulaiman, N.B.; Sng, S.M.Y.; Merchant, K.Z.; Ng, L.P.; Low, D.C.Y.; Seow, W.T.; Low, S.Y.Y. Identifying Angiogenic Factors in Pediatric Choroid Plexus Papillomas. NeuroSci 2025, 6, 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6030076
Syed Sulaiman NB, Sng SMY, Merchant KZ, Ng LP, Low DCY, Seow WT, Low SYY. Identifying Angiogenic Factors in Pediatric Choroid Plexus Papillomas. NeuroSci. 2025; 6(3):76. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6030076
Chicago/Turabian StyleSyed Sulaiman, Nurfarhanah Bte, Sofiah M. Y. Sng, Khurshid Z. Merchant, Lee Ping Ng, David C. Y. Low, Wan Tew Seow, and Sharon Y. Y. Low. 2025. "Identifying Angiogenic Factors in Pediatric Choroid Plexus Papillomas" NeuroSci 6, no. 3: 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6030076
APA StyleSyed Sulaiman, N. B., Sng, S. M. Y., Merchant, K. Z., Ng, L. P., Low, D. C. Y., Seow, W. T., & Low, S. Y. Y. (2025). Identifying Angiogenic Factors in Pediatric Choroid Plexus Papillomas. NeuroSci, 6(3), 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6030076





