Disentangling False Memories: Gray Matter Correlates of Memory Sensitivity and Decision Bias
Abstract
1. Introduction
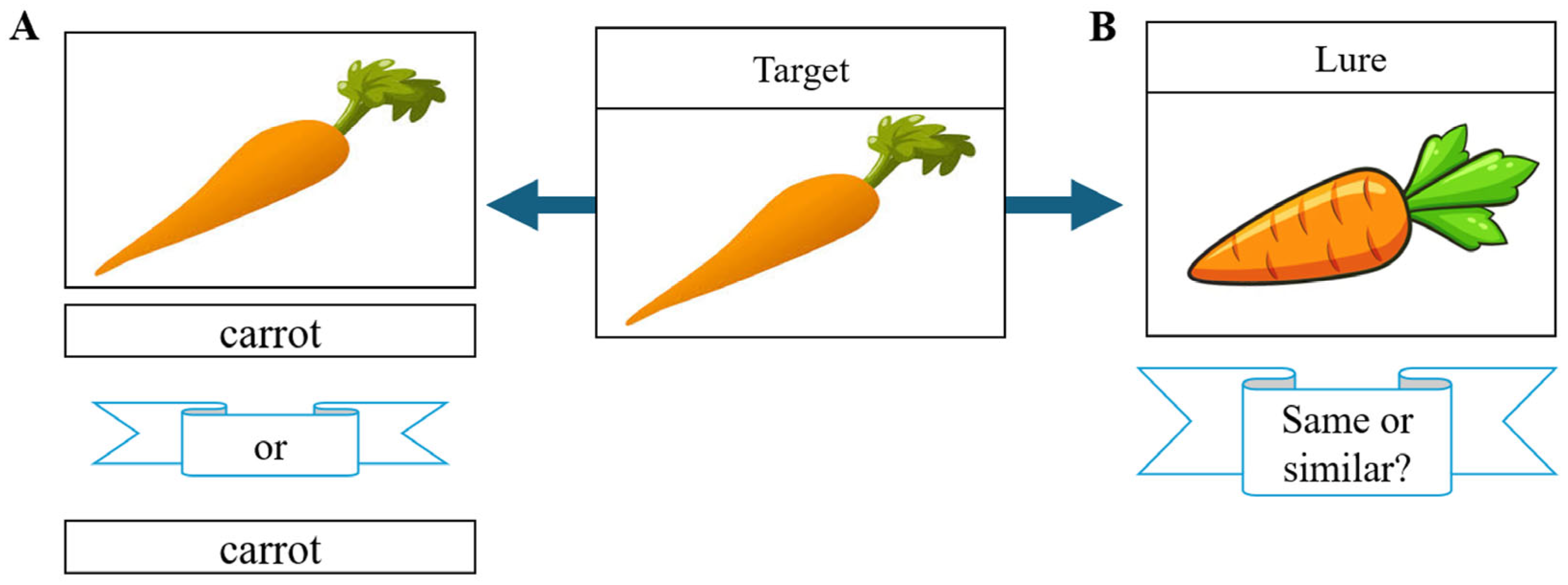
1.1. Signal Detection Theory
1.2. Functional Correlates of False Memory
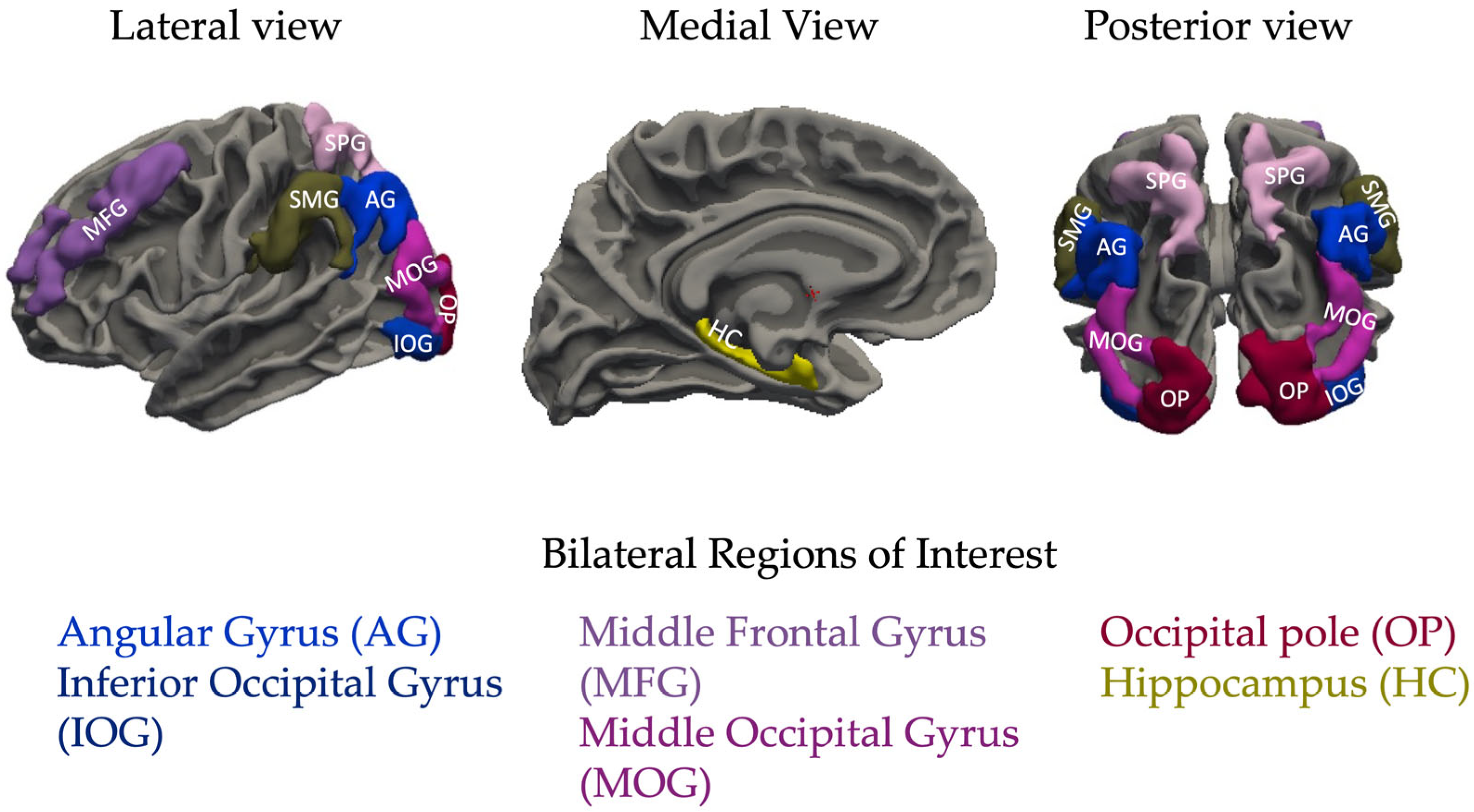
1.2.1. Frontal Lobe Regions
Middle Frontal Gyrus (MFG)
1.2.2. Occipital Lobe Regions
- Inferior Occipital Gyrus (IOG)
- 2.
- Middle Occipital Gyrus (MOG)
1.2.3. Parietal Lobe Regions
- Angular Gyrus (AG)
- 2.
- Supramarginal Gyrus (SMG)
- 3.
- Superior Parietal Lobe (SPL)
1.2.4. Temporal Lobe Regions
Hippocampus (HC)
1.3. The Current Study
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Behavioral Data
2.3. MRI Preprocessing
2.4. Data Analyses
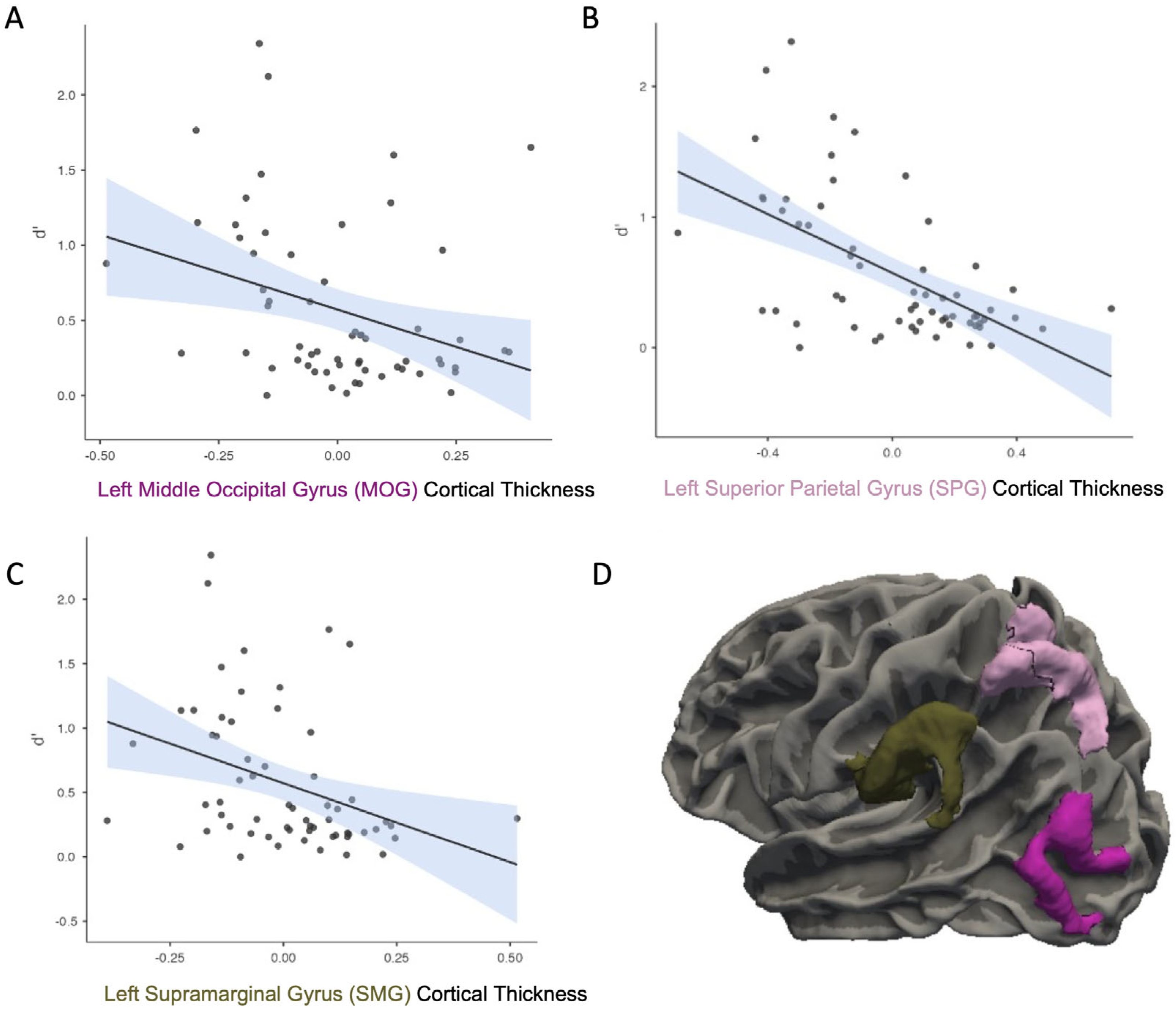
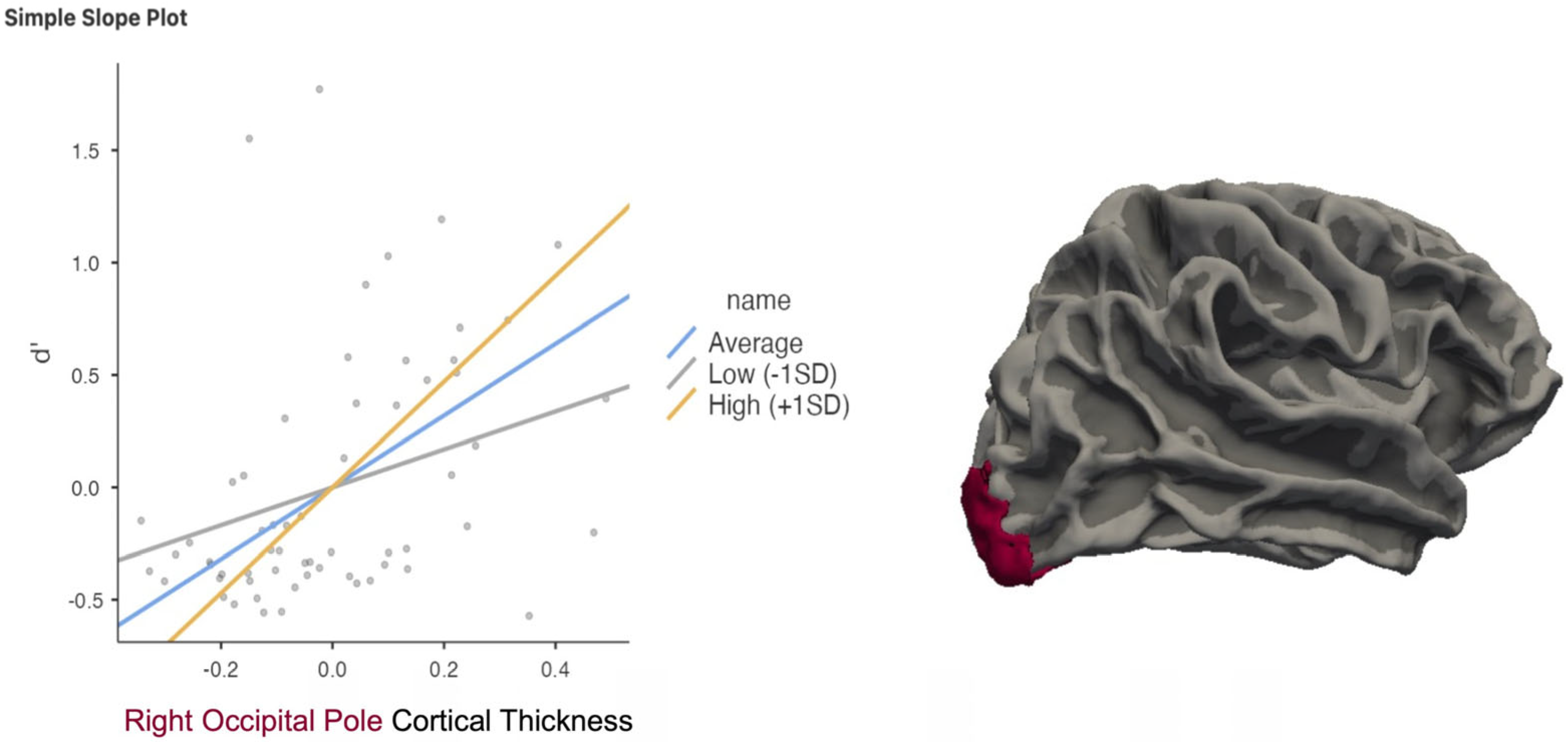
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AG | Angular Gyrus |
| ALE | Activation Likelihood Estimation |
| C | Conservative Response Bias |
| CR | Correct Rejection |
| CT | Cortical Thickness |
| d′ | Response Sensitivity |
| DRM | Deese–Roediger–McDermott |
| eTIV | Estimated Total Intracranial Volume |
| FA | False Alarm |
| FDR | False Discovery Rate |
| fMRI | Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| GMV | Gray Matter Volume |
| IOG | Inferior Occipital Gyrus |
| MFG | Middle Frontal Gyrus |
| MOG | Middle Occipital Gyrus |
| mPFC | medial Prefrontal Cortex |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| OP | Occipital Pole |
| PFC | Prefrontal Cortex |
| ROI | Region(s) of Interest |
| SDT | Signal Detection Theory |
| SMG | Supramarginal Gyrus |
| sMRI | Structural Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| SPG | Superior Parietal Gyrus (also Superior Parietal Lobe) |
References
- Schacter, D.L.; Guerin, S.A.; Jacques, P.L.S. Memory Distortion: An Adaptive Perspective. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2011, 15, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brainerd, C.J.; Reyna, V.F. Fuzzy-Trace Theory and Memory Development. Dev. Rev. 2004, 24, 396–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schacter, D.L.; Addis, D.R. The Cognitive Neuroscience of Constructive Memory: Remembering the Past and Imagining the Future. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2007, 362, 773–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roediger, H.L.; McDermott, K.B. Creating False Memories: Remembering Words Not Presented in Lists. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 1995, 21, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, S.F.C. Remembering: A Study in Experimental and Social Psychology; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- van Kesteren, M.T.R.; Ruiter, D.J.; Fernández, G.; Henson, R.N. How Schema and Novelty Augment Memory Formation. Trends Neurosci. 2012, 35, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftus, E.F. Planting Misinformation in the Human Mind: A 30-Year Investigation of the Malleability of Memory. Learn. Mem. 2005, 12, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercadante, A.; Tadi, P. Neuroanatomy, Gray Matter; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Zatorre, R.J.; Fields, R.D.; Johansen-Berg, H. Plasticity in Gray and White: Neuroimaging Changes in Brain Structure during Learning. Nat. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.A.; Brown, D.A.; Diamond, M.E.; Cattaneo, A.; Fernández De-Miguel, F. From Neuron to Brain; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez, J.; Zhen, Z.; Weiner, K.S. Human Visual Cortex Is Organized along Two Genetically Opposed Hierarchical Gradients with Unique Developmental and Evolutionary Origins. PLoS Biol. 2019, 17, e3000362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tymofiyeva, O.; Hess, C.P.; Xu, D.; Barkovich, A.J. Structural MRI Connectome in Development: Challenges of the Changing Brain. Br. J. Radiol. 2014, 87, 20140086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eklund, A.; Nichols, T.E.; Knutsson, H. Cluster Failure: Why fMRI Inferences for Spatial Extent Have Inflated False-Positive Rates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 7900–7905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellen, D.; Winiger, S.; Dunn, J.C.; Singmann, H. Testing the Foundations of Signal Detection Theory in Recognition Memory. Psychol. Rev. 2021, 128, 1022–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, M.; Charles, L.; Maniscalco, B. Optimal Metacognitive Decision Strategies in Signal Detection Theory. J. Vis. 2023, 23, 5465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickens, T.D. Elementary Signal Detection Theory; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Marchewka, A.; Jednoróg, K.; Nowicka, A.; Brechmann, A.; Grabowska, A. Grey-Matter Differences Related to True and False Recognition of Emotionally Charged Stimuli—A Voxel Based Morphometry Study. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2009, 92, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.; Chen, C.; Loftus, E.F.; He, Q.; Lei, X.; Dong, Q.; Lin, C. Hippocampal Size Is Related to Short-Term True and False Memory, and Right Fusiform Size Is Related to Long-Term True and False Memory. Brain Struct. Funct. 2016, 221, 4045–4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurkela, K.A.; Dennis, N.A. Event-Related fMRI Studies of False Memory: An Activation Likelihood Estimation Meta-Analysis. Neuropsychologia 2016, 81, 149–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muncy, N.M.; Kirwan, C.B. Correcting False Memories: The Effect of Mnemonic Generalization on Original Memory Traces. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephan-Otto, C.; Siddi, S.; Senior, C.; Muño.-Samons, D.; Ochoa, S.; Sánche.-Laforga, A.M.; Brébion, G. Visual Imagery and False Memory for Pictures: A Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study in Healthy Participants. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobbins, I.G.; Foley, H.; Schacter, D.L.; Wagner, A.D. Executive Control during Episodic Retrieval: Multiple Prefrontal Processes Subserve Source Memory. Neuron 2002, 35, 989–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Euston, D.R.; Gruber, A.J.; McNaughton, B.L. The Role of Medial Prefrontal Cortex in Memory and Decision Making. Neuron 2012, 76, 1057–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutchess, A.H.; Schacter, D.L. The Neural Correlates of Gist-Based True and False Recognition. NeuroImage 2012, 59, 3418–3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, S.; Tan, S.; Liu, L.; Yan, C.; Zou, L. Neural Correlates of Olfactory Working Memory in the Human Brain. NeuroImage 2025, 306, 121005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Chen, C.; Shao, X.; Liu, W.; Ye, Z.; Zhuang, L.; Zheng, L.; Loftus, E.F.; Xue, G. Multiple Interactive Memory Representations Underlie the Induction of False Memory. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 3466–3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huff, T.; Mahabadi, N.; Tadi, P. Neuroanatomy, Visual Cortex. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Cabeza, R.; Ciaramelli, E.; Olson, I.R.; Moscovitch, M. The Parietal Cortex and Episodic Memory: An Attentional Account. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 9, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martial, C.; Larroque, S.K.; Cavaliere, C.; Wannez, S.; Annen, J.; Kupers, R.; Laureys, S.; Di Perri, C. Resting-State Functional Connectivity and Cortical Thickness Characterization of a Patient with Charles Bonnet Syndrome. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sowell, E.R.; Tessner, K.D.; Thompson, P.M.; Narr, K.L.; Cannont, T.D.; Toga, A.W. Brain Growth and Atrophy: Relationships between Gray Matter Thinning and Cortical Surface Morphology during Normal Development and Aging. NeuroImage Orlando Fla. 2001, 13, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomyshev, A.S.; Lebedeva, I.S.; Akhadov, T.A.; Omelchenko, M.A.; Rumyantsev, A.O.; Kaleda, V.G. Alterations in White Matter Microstructure and Cortical Thickness in Individuals at Ultra-High Risk of Psychosis: A Multimodal Tractography and Surface-Based Morphometry Study. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2019, 289, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viher, P.V.; Stegmayer, K.; Kubicki, M.; Karmacharya, S.; Lyall, A.E.; Federspiel, A.; Vanbellingen, T.; Bohlhalter, S.; Wiest, R.; Strik, W.; et al. The Cortical Signature of Impaired Gesturing: Findings from Schizophrenia. NeuroImage Clin. 2018, 17, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, A.M.; Kochunov, P.; Blangero, J.; Almasy, L.; Zilles, K.; Fox, P.T.; Duggirala, R.; Glahn, D.C. Cortical Thickness or Grey Matter Volume? The Importance of Selecting the Phenotype for Imaging Genetics Studies. NeuroImage 2010, 53, 1135–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y.-S.; Yu, J. Left Superior Parietal Lobe Mediates the Link between Spontaneous Mind-Wandering Tendency and Task-Switching Performance. Biol. Psychol. 2024, 185, 108726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischl, B.; Dale, A.M. Measuring the Thickness of the Human Cerebral Cortex from Magnetic Resonance Images. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 11050–11055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straube, B. An Overview of the Neuro-Cognitive Processes Involved in the Encoding, Consolidation, and Retrieval of True and False Memories. Behav. Brain Funct. 2012, 8, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennis, N.A.; Bowman, C.R.; Vandekar, S.N. True and Phantom Recollection: An fMRI Investigation of Similar and Distinct Neural Correlates and Connectivity. NeuroImage 2012, 59, 2982–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollinger, J.; Rubens, M.T.; Zanto, T.P.; Gazzaley, A. Expectation-Driven Changes in Cortical Functional Connectivity Influence Working Memory and Long-Term Memory Performance. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 14399–14410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slotnick, S.D.; Schacter, D.L. A Sensory Signature That Distinguishes True from False Memories. Nat. Neurosci. 2004, 7, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellana, B.; Ladyka-Wojcik, N.; Lahan, S.; Moscovitch, M.; Grady, C.L. Recollection and Prior Knowledge Recruit the Left Angular Gyrus during Recognition. Brain Struct. Funct. 2023, 228, 197–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xia, M.; Dai, Z.; Liang, X.; Song, H.; He, Y.; Li, K. Differentially Disrupted Functional Connectivity of the Subregions of the Inferior Parietal Lobule in Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Struct. Funct. 2015, 220, 745–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, G.F.; Hoffman, P.; Visser, M.; Binney, R.J.; Lambon Ralph, M.A. Establishing Task- and Modality-Dependent Dissociations between the Semantic and Default Mode Networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 7857–7862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Kirino, E. Increased Functional Connectivity of the Angular Gyrus During Imagined Music Performance. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberhuber, M.; Hope, T.M.H.; Seghier, M.L.; Parker Jones, O.; Prejawa, S.; Green, D.W.; Price, C.J. Four Functionally Distinct Regions in the Left Supramarginal Gyrus Support Word Processing. Cereb. Cortex 2016, 26, 4212–4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spets, D.S.; Karanian, J.M.; Slotnick, S.D. False Memories Activate Distinct Brain Regions in Females and Males. Neuroimage Rep. 2021, 1, 100043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okado, Y.; Stark, C. Neural Processing Associated with True and False Memory Retrieval. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2003, 3, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Burgess, N.; Maguire, E.A.; O’Keefe, J. The Human Hippocampus and Spatial and Episodic Memory. Neuron 2002, 35, 625–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichenbaum, H. Hippocampus: Cognitive Processes and Neural Representations That Underlie Declarative Memory. Neuron 2004, 44, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markiewicz, C.J.; Gorgolewski, K.J.; Feingold, F.; Blair, R.; Halchenko, Y.O.; Miller, E.; Hardcastle, N.; Wexler, J.; Esteban, O.; Goncavles, M.; et al. The OpenNeuro Resource for Sharing of Neuroscience Data. eLife 2021, 10, e71774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badre, D.; Wagner, A.D. Left Ventrolateral Prefrontal Cortex and the Cognitive Control of Memory. Neuropsychologia 2007, 45, 2883–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennis, N.A.; Cabeza, R. Neuroimaging of Healthy Cognitive Aging. In The Handbook of Aging and Cognition; Psychology Press: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Stanislaw, H.; Todorov, N. Calculation of Signal Detection Theory Measures. Behav. Res. Methods Instrum. Comput. 1999, 31, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischl, B. FreeSurfer. NeuroImage 2012, 62, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas, H.D.; Liu, A.K.; Hersch, S.; Glessner, M.; Ferrante, R.J.; Salat, D.H.; van der Kouwe, A.; Jenkins, B.G.; Dale, A.M.; Fischl, B. Regional and Progressive Thinning of the Cortical Ribbon in Huntington’s Disease. Neurology 2002, 58, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OSG. Open Science Data Federation. 2015. OSG. Available online: https://doi.org/10.21231/0KVZ-VE57 (accessed on 31 July 2023).
- OSPool. 2006. Available online: https://doi.org/10.21231/906P-4D78 (accessed on 31 July 2023).
- Pordes, R.; Altunay, M.; Avery, P.; Bejan, A.; Blackburn, K.; Blatecky, A.; Gardner, R.; Kramer, B.; Livny, M.; McGee, J.; et al. New Science on the Open Science Grid. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2008, 125, 012070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destrieux, C.; Fischl, B.; Dale, A.; Halgren, E. Automatic Parcellation of Human Cortical Gyri and Sulci Using Standard Anatomical Nomenclature. NeuroImage 2010, 53, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Jamovi Project. Jamovi. 2024. Available online: https://www.jamovi.org (accessed on 2 January 2023).
- Şahin, M.; Aybek, E. Jamovi: An Easy to Use Statistical Software for the Social Scientists. Int. J. Assess. Tools Educ. 2020, 6, 670–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soch, J.; Richter, A.; Kizilirmak, J.M.; Schütze, H.; Feldhoff, H.; Fischer, L.; Knopf, L.; Raschick, M.; Schult, A.; Düzel, E.; et al. Structural and Functional MRI Data Differentially Predict Chronological Age and Behavioral Memory Performance. eNeuro 2022, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Brain Region of Interest | d′ r-Value | d′ p-Value | C r-Value | C p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Left AG | n.s. a | −0.29 | p = 0.025 a,* | |
| Left HC | n.s. a | |||
| Left MFG | 0.49 | p < 0.001 a,*,† | n.s. | |
| Left MOG | −0.32 | p = 0.013 a,*,† | n.s. | |
| Left OP | n.s. a | n.s. | ||
| Left SMG | −0.35 | p = 0.007 a,*,† | n.s. | |
| Left SPG | −0.57 | p < 0.001 a,*,† | n.s. | |
| Right AG | −0.28 | p = 0.032 a,* | n.s. | |
| Right HC | n.s. a | n.s. | ||
| Right MFG | n.s. a | n.s. | ||
| Right MOG | n.s. a | n.s. | ||
| Right OP | 0.4 | p = 0.002 a,*,† | −0.39 | p = 0.0024 a,*,† n.s. |
| Right OP X C Moderation | p = 0.015 b,*,† | |||
| Right SMG | n.s. a | n.s. a | ||
| Right SPG | n.s. a | n.s. a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pavela, R.A.; Haldeman, C.; Legault-Wittmeyer, J. Disentangling False Memories: Gray Matter Correlates of Memory Sensitivity and Decision Bias. NeuroSci 2025, 6, 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6030068
Pavela RA, Haldeman C, Legault-Wittmeyer J. Disentangling False Memories: Gray Matter Correlates of Memory Sensitivity and Decision Bias. NeuroSci. 2025; 6(3):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6030068
Chicago/Turabian StylePavela, Ryder Anthony, Chloe Haldeman, and Jennifer Legault-Wittmeyer. 2025. "Disentangling False Memories: Gray Matter Correlates of Memory Sensitivity and Decision Bias" NeuroSci 6, no. 3: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6030068
APA StylePavela, R. A., Haldeman, C., & Legault-Wittmeyer, J. (2025). Disentangling False Memories: Gray Matter Correlates of Memory Sensitivity and Decision Bias. NeuroSci, 6(3), 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6030068





