Unraveling Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Etiology: Current Challenges and Future Directions in Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Understanding ADHD
3.1. Genetic Factors and Environmental Factors
3.1.1. Genetic Factors
3.1.2. Genetic Linkage Studies
3.1.3. Candidate Gene Association Studies
3.1.4. Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS)
3.1.5. Polygenic Risk and Cross-Disorder Associations
3.1.6. The Search for Rare Genetic Variants in ADHD
3.1.7. Environmental Factors and Gene-Environment Interactions
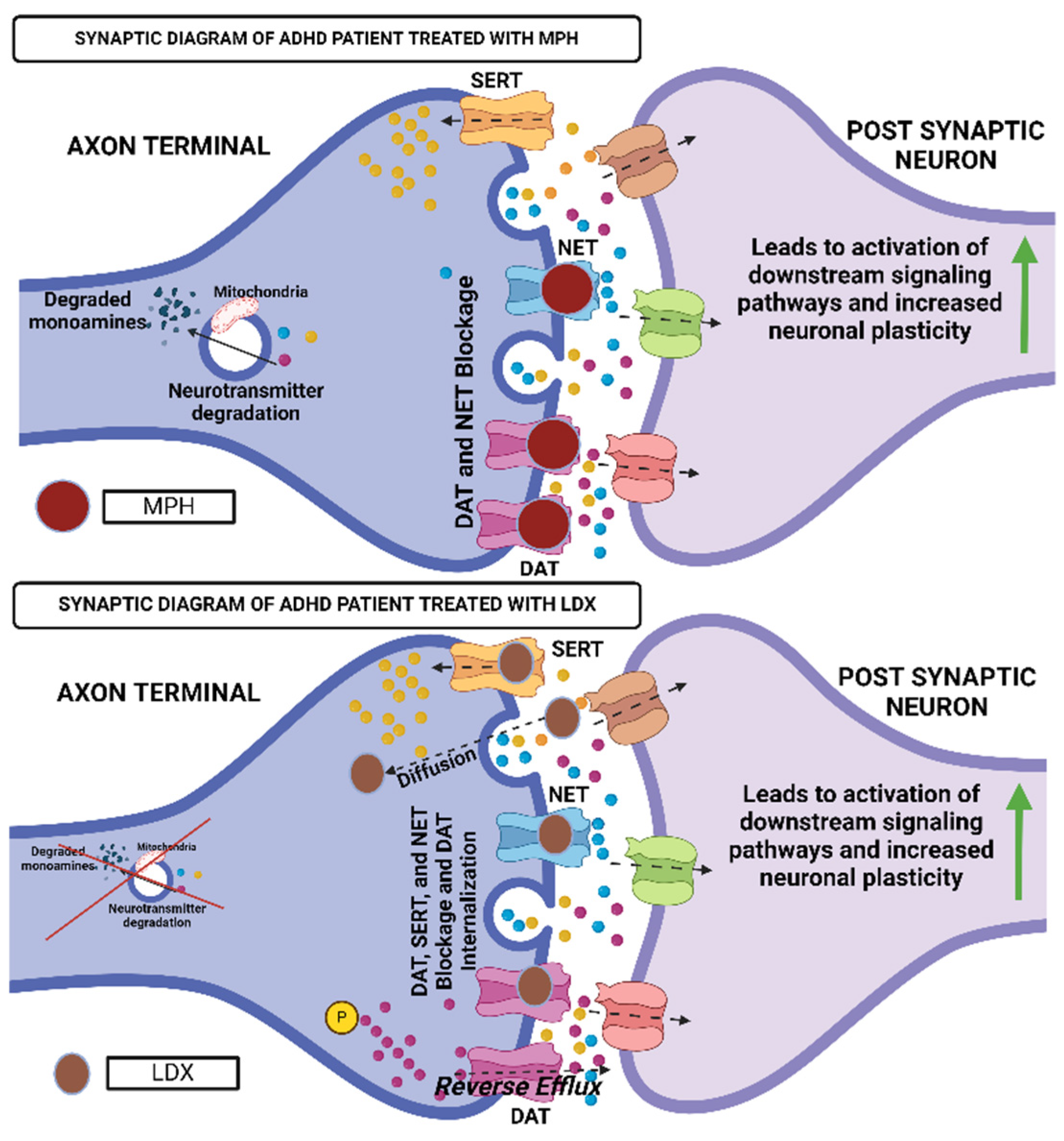
4. Current Treatment Landscape
5. Current Challenges in Addressing ADHD Etiology and Treatment Gaps
5.1. Long-Term Management of ADHD
5.2. Gaps in Current Research
5.3. Inherent Subjectivity of the Diagnostic Criteria
5.4. Sociocultural Factors
5.5. Comorbidity
5.6. Gender-Specific Diagnostic Criteria and Treatment Strategies
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thapar, A.; Cooper, M. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Lancet 2016, 387, 1240–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furman, L. What is attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)? J. Child. Neurol. 2005, 20, 994–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Strathearn, L.; Liu, B.; Yang, B.; Bao, W. Twenty-Year Trends in Diagnosed Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Among US Children and Adolescents, 1997–2016. JAMA Netw. Open 2018, 1, e181471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frick, P.J.; Lahey, B.B. The nature and characteristics of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Sch. Psychol. Rev. 1991, 20, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yan, X.; Li, Q.; Li, Q.; Xu, G.; Lu, J.; Yang, W. Prevalence and Trends in Diagnosed ADHD Among US Children and Adolescents, 2017–2022. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2336872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapkale, B.; Sawal, A. Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Causes and Diagnosis in Adults: A Review. Cureus 2023, 15, e49144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.; Barkley, R.A. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder adults: Comorbidities and adaptive impairments. Compr. Psychiatry 1996, 37, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiligenstein, E.; Guenther, G.; Levy, A.; Savino, F.; Fulwiler, J. Psychological and academic functioning in college students with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. J. Am. Coll. Health 1999, 47, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, B.; Nalbant, G.; Wright, H.; Sayal, K.; Daley, D.; Groom, M.J.; Cassidy, S.; Hall, C.L. The impacts associated with having ADHD: An umbrella review. Front. Psychiatry 2024, 15, 1343314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biederman, J.; Faraone, S.V. The effects of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder on employment and household income. Medscape Gen. Med. 2006, 8, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Eakin, L.; Minde, K.; Hechtman, L.; Ochs, E.; Krane, E.; Bouffard, R.; Greenfield, B.; Looper, K. The marital and family functioning of adults with ADHD and their spouses. J. Atten. Disord. 2004, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulauf, C.A.; Sprich, S.E.; Safren, S.A.; Wilens, T.E. The complicated relationship between attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder and substance use disorders. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2014, 16, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzman, M.A.; Bilkey, T.S.; Chokka, P.R.; Fallu, A.; Klassen, L.J. Adult ADHD and comorbid disorders: Clinical implications of a dimensional approach. BMC Psychiatry 2017, 17, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asherson, P.; Akehurst, R.; Kooij, J.J.; Huss, M.; Beusterien, K.; Sasane, R.; Gholizadeh, S.; Hodgkins, P. Under diagnosis of adult ADHD: Cultural influences and societal burden. J. Atten. Disord. 2012, 16, 20S–38S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, E.; Zhan, C.; Homer, C.J. Health care use and costs for children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: National estimates from the medical expenditure panel survey. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2002, 156, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doshi, J.A.; Hodgkins, P.; Kahle, J.; Sikirica, V.; Cangelosi, M.J.; Setyawan, J.; Erder, M.H.; Neumann, P.J. Economic impact of childhood and adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in the United States. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2012, 51, 990–1002.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupte-Singh, K.; Singh, R.R.; Lawson, K.A. Economic Burden of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder among Pediatric Patients in the United States. Value Health 2017, 20, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, S.E.; Jenkins-Jones, S.; Poole, C.D.; Morgan, C.L.; Coghill, D.; Currie, C.J. The prevalence and incidence, resource use and financial costs of treating people with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in the United Kingdom (1998 to 2010). Child Adolesc. Psychiatry Ment. Health 2013, 7, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matza, L.S.; Paramore, C.; Prasad, M. A review of the economic burden of ADHD. Cost Eff. Resour. Alloc. 2005, 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Hunter Guevara, L.R.; Dykhoff, H.J.; Sangaralingham, L.R.; Phelan, S.; Zaccariello, M.J.; Warner, D.O. Racial Disparities in Diagnosis of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder in a US National Birth Cohort. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e210321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, P.L.; Staff, J.; Hillemeier, M.M.; Farkas, G.; Maczuga, S. Racial and ethnic disparities in ADHD diagnosis from kindergarten to eighth grade. Pediatrics 2013, 132, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, P.O.; Madhoo, M. A review of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in women and girls: Uncovering this hidden diagnosis. Prim. Care Companion CNS Disord. 2014, 16, PCC.13r01596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nussbaum, N.L. ADHD and female specific concerns: A review of the literature and clinical implications. J. Atten. Disord. 2012, 16, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mowlem, F.D.; Rosenqvist, M.A.; Martin, J.; Lichtenstein, P.; Asherson, P.; Larsson, H. Sex differences in predicting ADHD clinical diagnosis and pharmacological treatment. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2019, 28, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, P.N.; Reuben, C.A. Racial and ethnic differences in ADHD and LD in young school-age children: Parental reports in the National Health Interview Survey. Public Health Rep. 2005, 120, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, P.L.; Hillemeier, M.M.; Farkas, G.; Maczuga, S. Racial/ethnic disparities in ADHD diagnosis by kindergarten entry. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2014, 55, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getahun, D.; Jacobsen, S.J.; Fassett, M.J.; Chen, W.; Demissie, K.; Rhoads, G.G. Recent trends in childhood attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. JAMA Pediatr. 2013, 167, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielson, M.L.; Bitsko, R.H.; Ghandour, R.M.; Holbrook, J.R.; Kogan, M.D.; Blumberg, S.J. Prevalence of Parent-Reported ADHD Diagnosis and Associated Treatment Among U.S. Children and Adolescents, 2016. J. Clin. Child Adolesc. Psychol. 2018, 47, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuffe, S.P.; Moore, C.G.; McKeown, R.E. Prevalence and correlates of ADHD symptoms in the national health interview survey. J. Atten. Disord. 2005, 9, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, W.; Jiang, S.F.; Paksarian, D.; Nikolaidis, A.; Castellanos, F.X.; Merikangas, K.R.; Milham, M.P. Trends in the Prevalence and Incidence of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Among Adults and Children of Different Racial and Ethnic Groups. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e1914344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Advokat, C.; Scheithauer, M. Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) stimulant medications as cognitive enhancers. Front. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarova, V.A.; Sokolov, A.V.; Chubarev, V.N.; Tarasov, V.V.; Schioth, H.B. Treatment of ADHD: Drugs, psychological therapies, devices, complementary and alternative methods as well as the trends in clinical trials. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1066988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiri, A.; Torabi Parizi, G.; Kousha, M.; Saadat, F.; Modabbernia, M.J.; Najafi, K.; Atrkar Roushan, Z. Changes in plasma Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels induced by methylphenidate in children with Attention deficit–hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 47, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wehmeier, P.M.; Schacht, A.; Barkley, R.A. Social and emotional impairment in children and adolescents with ADHD and the impact on quality of life. J. Adolesc. Health 2010, 46, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danckaerts, M.; Sonuga-Barke, E.J.; Banaschewski, T.; Buitelaar, J.; Dopfner, M.; Hollis, C.; Santosh, P.; Rothenberger, A.; Sergeant, J.; Steinhausen, H.C.; et al. The quality of life of children with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder: A systematic review. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2010, 19, 83–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, R.; Goldenberg, M.; Perry, R.; IsHak, W.W. The quality of life of adults with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: A systematic review. Innov. Clin. Neurosci. 2012, 9, 10–21. [Google Scholar]
- Rivas-Vazquez, R.A.; Diaz, S.G.; Visser, M.M.; Rivas-Vazquez, A.A. Adult ADHD: Underdiagnosis of a Treatable Condition. J. Health Serv. Psychol. 2023, 49, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortese, S.; Coghill, D. Twenty years of research on attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): Looking back, looking forward. Evid. Based Ment. Health 2018, 21, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demontis, D.; Walters, G.B.; Athanasiadis, G.; Walters, R.; Therrien, K.; Nielsen, T.T.; Farajzadeh, L.; Voloudakis, G.; Bendl, J.; Zeng, B.; et al. Author Correction: Genome-wide analyses of ADHD identify 27 risk loci, refine the genetic architecture and implicate several cognitive domains. Nat. Genet. 2023, 55, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraone, S.V.; Larsson, H. Genetics of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 562–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraone, S.V.; Perlis, R.H.; Doyle, A.E.; Smoller, J.W.; Goralnick, J.J.; Holmgren, M.A.; Sklar, P. Molecular genetics of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2005, 57, 1313–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, J.M.; Sunohara, G.A.; Kennedy, J.L.; Regino, R.; Fineberg, E.; Wigal, T.; Lerner, M.; Williams, L.; LaHoste, G.J.; Wigal, S. Association of the dopamine receptor D4 (DRD4) gene with a refined phenotype of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): A family-based approach. Mol. Psychiatry 1998, 3, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, J.M.; Flodman, P.; Kennedy, J.; Spence, M.A.; Moyzis, R.; Schuck, S.; Murias, M.; Moriarity, J.; Barr, C.; Smith, M.; et al. Dopamine genes and ADHD. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2000, 24, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, M.J.; Martin, J.; Butwicka, A.; Lichtenstein, P.; D’Onofrio, B.; Lundstrom, S.; Larsson, H.; Rosenqvist, M.A. A twin study of genetic and environmental contributions to attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder over time. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2023, 64, 1608–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Brookes, K.; Chen, C.K.; Huang, Y.S.; Wu, Y.Y.; Asherson, P. Association study between the monoamine oxidase A gene and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in Taiwanese samples. BMC Psychiatry 2007, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Kang, C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, R.; Wang, B.; Guan, L.; Yang, L.; Faraone, S.V. Monoamine oxidase A gene polymorphism predicts adolescent outcome of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2007, 144B, 430–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, A.; Maitra, S.; Verma, D.; Chakraborti, B.; Goswami, R.; Ghosh, P.; Sinha, S.; Mohanakumar, K.P.; Usha, R.; Mukhopadhyay, K. Potential contribution of monoamine oxidase a gene variants in ADHD and behavioral co-morbidities: Scenario in eastern Indian probands. Neurochem. Res. 2014, 39, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, A.; Maitra, S.; Chakraborti, B.; Verma, D.; Sinha, S.; Mohanakumar, K.P.; Rajamma, U.; Mukhopadhyay, K. Monoamine oxidase B gene variants associated with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in the Indo-Caucasoid population from West Bengal. BMC Genet. 2016, 17, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, I.W.; Lim, M.H.; Kwon, H.J.; Jin, H.J. Association of Monoamine Oxidase A (MAOA) Gene uVNTR and rs6323 Polymorphisms with Attention Deficit and Hyperactivity Disorder in Korean Children. Medicina 2018, 54, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwabe, I.; Jovic, M.; Rimfeld, K.; Allegrini, A.G.; van den Berg, S.M. Genotype-Environment Interaction in ADHD: Genetic Predisposition Determines the Extent to Which Environmental Influences Explain Variability in the Symptom Dimensions Hyperactivity and Inattention. Behav. Genet. 2024, 54, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcos-Burgos, M.; Muenke, M. Toward a better understanding of ADHD: LPHN3 gene variants and the susceptibility to develop ADHD. ADHD Atten. Deficit Hyperact. Disord. 2010, 2, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, P.; Singh, A.; Nthenge-Ngumbau, D.N.; Rajamma, U.; Sinha, S.; Mukhopadhyay, K.; Mohanakumar, K.P. Attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder suffers from mitochondrial dysfunction. BBA Clin. 2016, 6, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogutlu, H.; Kasak, M.; Tutku Tabur, S. Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Eurasian J. Med. 2022, 54, S187–S195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, I.W.; Kwon, B.N.; Kim, H.J.; Han, S.H.; Lee, N.R.; Lim, M.H.; Kwon, H.J.; Jin, H.J. Assessment of associations between mitochondrial DNA haplogroups and attention deficit and hyperactivity disorder in Korean children. Mitochondrion 2019, 47, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, I.W.; Hong, J.H.; Kwon, B.N.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, N.R.; Lim, M.H.; Kwon, H.J.; Jin, H.J. Association of mitochondrial DNA 10398 A/G polymorphism with attention deficit and hyperactivity disorder in Korean children. Gene 2017, 630, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Liu, Y.; Mentch, F.; Glessner, J.; Qu, H.; Nguyen, K.; Sleiman, P.M.A.; Hakonarson, H. Mitochondrial DNA haplogroups and risk of attention deficit and hyperactivity disorder in European Americans. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wermter, A.K.; Laucht, M.; Schimmelmann, B.G.; Banaschewski, T.; Sonuga-Barke, E.J.; Rietschel, M.; Becker, K. From nature versus nurture, via nature and nurture, to gene × environment interaction in mental disorders. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2010, 19, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, B.J.; Boyce, W.T. Differential susceptibility to the environment: Toward an understanding of sensitivity to developmental experiences and context. Dev. Psychopathol. 2011, 23, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraone, S.V.; Mick, E. Molecular genetics of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2010, 33, 159–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Dempfle, A.; Arcos-Burgos, M.; Bakker, S.C.; Banaschewski, T.; Biederman, J.; Buitelaar, J.; Castellanos, F.X.; Doyle, A.; Ebstein, R.P.; et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide linkage scans of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2008, 147B, 1392–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, B.; Faraone, S.V.; Asherson, P.; Buitelaar, J.; Bau, C.H.; Ramos-Quiroga, J.A.; Mick, E.; Grevet, E.H.; Johansson, S.; Haavik, J.; et al. The genetics of attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder in adults, a review. Mol. Psychiatry 2012, 17, 960–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonvicini, C.; Faraone, S.V.; Scassellati, C. Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis of genetic, pharmacogenetic and biochemical studies. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zayats, T.; Athanasiu, L.; Sonderby, I.; Djurovic, S.; Westlye, L.T.; Tamnes, C.K.; Fladby, T.; Aase, H.; Zeiner, P.; Reichborn-Kjennerud, T.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in Norway. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demontis, D.; Walters, R.K.; Martin, J.; Mattheisen, M.; Als, T.D.; Agerbo, E.; Baldursson, G.; Belliveau, R.; Bybjerg-Grauholm, J.; Baekvad-Hansen, M.; et al. Discovery of the first genome-wide significant risk loci for attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross-Disorder Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium; Lee, S.H.; Ripke, S.; Neale, B.M.; Faraone, S.V.; Purcell, S.M.; Perlis, R.H.; Mowry, B.J.; Thapar, A.; Goddard, M.E.; et al. Genetic relationship between five psychiatric disorders estimated from genome-wide SNPs. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 984–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bralten, J.; van Hulzen, K.J.; Martens, M.B.; Galesloot, T.E.; Arias Vasquez, A.; Kiemeney, L.A.; Buitelaar, J.K.; Muntjewerff, J.W.; Franke, B.; Poelmans, G. Autism spectrum disorders and autistic traits share genetics and biology. Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 23, 1205–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortese, S.; Moreira-Maia, C.R.; St Fleur, D.; Morcillo-Penalver, C.; Rohde, L.A.; Faraone, S.V. Association Between ADHD and Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Psychiatry 2016, 173, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo-Castro, A.; D’Agati, E.; Curatolo, P. ADHD and genetic syndromes. Brain Dev. 2011, 33, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Neale, B.M.; Liu, L.; Lee, S.H.; Wray, N.R.; Ji, N.; Li, H.; Qian, Q.; Wang, D.; Li, J.; et al. Polygenic transmission and complex neuro developmental network for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: Genome-wide association study of both common and rare variants. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2013, 162B, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elia, J.; Glessner, J.T.; Wang, K.; Takahashi, N.; Shtir, C.J.; Hadley, D.; Sleiman, P.M.; Zhang, H.; Kim, C.E.; Robison, R.; et al. Genome-wide copy number variation study associates metabotropic glutamate receptor gene networks with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Nat. Genet. 2011, 44, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, N.M.; Franke, B.; Mick, E.; Anney, R.J.; Freitag, C.M.; Gill, M.; Thapar, A.; O’Donovan, M.C.; Owen, M.J.; Holmans, P.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of copy number variants in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: The role of rare variants and duplications at 15q13.3. Am. J. Psychiatry 2012, 169, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akutagava-Martins, G.C.; Salatino-Oliveira, A.; Genro, J.P.; Contini, V.; Polanczyk, G.; Zeni, C.; Chazan, R.; Kieling, C.; Anselmi, L.; Menezes, A.M.; et al. Glutamatergic copy number variants and their role in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2014, 165, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mick, E.; Neale, B.; Middleton, F.A.; McGough, J.J.; Faraone, S.V. Genome-wide association study of response to methylphenidate in 187 children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2008, 147, 1412–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrey, N.J.; MacMaster, F.P.; Gaudet, L.; Schmidt, M.H. Striatal creatine and glutamate/glutamine in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J. Child Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 2007, 17, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demontis, D.; Lescai, F.; Borglum, A.; Glerup, S.; Ostergaard, S.D.; Mors, O.; Li, Q.; Liang, J.; Jiang, H.; Li, Y.; et al. Whole-Exome Sequencing Reveals Increased Burden of Rare Functional and Disruptive Variants in Candidate Risk Genes in Individuals With Persistent Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2016, 55, 521–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawi, Z.; Cummins, T.D.; Tong, J.; Arcos-Burgos, M.; Zhao, Q.; Matthews, N.; Newman, D.P.; Johnson, B.; Vance, A.; Heussler, H.S.; et al. Rare DNA variants in the brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene increase risk for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: A next-generation sequencing study. Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 22, 580–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapar, A.; Cooper, M.; Jefferies, R.; Stergiakouli, E. What causes attention deficit hyperactivity disorder? Arch. Dis. Child. 2012, 97, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, D.; Colvin, L.; Hagemann, E.; Bower, C. Environmental risk factors by gender associated with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Pediatrics 2014, 133, e14–e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, J.; Lanphear, B.P.; Bellinger, D.; Axelrad, D.A.; McPartland, J.; Sutton, P.; Davidson, L.; Daniels, N.; Sen, S.; Woodruff, T.J. Developmental PBDE Exposure and IQ/ADHD in Childhood: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, 086001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eubig, P.A.; Aguiar, A.; Schantz, S.L. Lead and PCBs as risk factors for attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1654–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, T.D.; Middleton, F.; Faraone, S.V. Environmental risk factors for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Acta Paediatr. 2007, 96, 1269–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.N.; Cho, S.C.; Kim, Y.; Shin, M.S.; Yoo, H.J.; Kim, J.W.; Yang, Y.H.; Kim, H.W.; Bhang, S.Y.; Hong, Y.C. Phthalates exposure and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in school-age children. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 66, 958–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Cano, S.; Zapata-Ospina, J.P.; Arcos-Burgos, M.; Palacio-Ortiz, J.D. The role of psychosocial adversity in the aetiology and course of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Rev. Colomb. Psiquiatr. 2021, 52, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claussen, A.H.; Holbrook, J.R.; Hutchins, H.J.; Robinson, L.R.; Bloomfield, J.; Meng, L.; Bitsko, R.H.; O’Masta, B.; Cerles, A.; Maher, B.; et al. All in the Family? A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Parenting and Family Environment as Risk Factors for Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in Children. Prev. Sci. 2024, 25, 249–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, N.M.; Brown, S.N.; Briggs, R.D.; German, M.; Belamarich, P.F.; Oyeku, S.O. Associations Between Adverse Childhood Experiences and ADHD Diagnosis and Severity. Acad. Pediatr. 2017, 17, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsen, F.M.; Tulve, N.S. A systematic review and meta-analysis examining the interrelationships between chemical and non-chemical stressors and inherent characteristics in children with ADHD. Environ. Res. 2020, 180, 108884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortese, S.; Adamo, N.; Del Giovane, C.; Mohr-Jensen, C.; Hayes, A.J.; Carucci, S.; Atkinson, L.Z.; Tessari, L.; Banaschewski, T.; Coghill, D.; et al. Comparative efficacy and tolerability of medications for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in children, adolescents, and adults: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Lancet Psychiatry 2018, 5, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catala-Lopez, F.; Hutton, B.; Nunez-Beltran, A.; Page, M.J.; Ridao, M.; Macias Saint-Gerons, D.; Catala, M.A.; Tabares-Seisdedos, R.; Moher, D. The pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents: A systematic review with network meta-analyses of randomised trials. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkow, N.D.; Fowler, J.S.; Wang, G.; Ding, Y.; Gatley, S.J. Mechanism of action of methylphenidate: Insights from PET imaging studies. J. Atten. Disord. 2002, 6, S31–S43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooij, J.J.S.; Bijlenga, D.; Salerno, L.; Jaeschke, R.; Bitter, I.; Balazs, J.; Thome, J.; Dom, G.; Kasper, S.; Nunes Filipe, C.; et al. Updated European Consensus Statement on diagnosis and treatment of adult ADHD. Eur. Psychiatry 2019, 56, 14–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semrud-Clikeman, M.; Filipek, P.A.; Biederman, J.; Steingard, R.; Kennedy, D.; Renshaw, P.; Bekken, K. Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: Magnetic resonance imaging morphometric analysis of the corpus callosum. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 1994, 33, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitzianti, M.B.; Spiridigliozzi, S.; Bartolucci, E.; Esposito, S.; Pasini, A. New Insights on the Effects of Methylphenidate in Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 531092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, D.F.; Steingard, R.J. New formulations of stimulants for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: Therapeutic potential. CNS Drugs 2004, 18, 1011–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, R. Comparison of the pharmacokinetics and clinical efficacy of new extended-release formulations of methylphenidate. Expert. Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2013, 9, 1001–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintero, J.; Gutierrez-Casares, J.R.; Alamo, C. Molecular Characterisation of the Mechanism of Action of Stimulant Drugs Lisdexamfetamine and Methylphenidate on ADHD Neurobiology: A Review. Neurol. Ther. 2022, 11, 1489–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajala, A.Z.; Populin, L.C.; Jenison, R.L. Methylphenidate affects task-switching and neural signaling in non-human primates. Psychopharmacology 2020, 237, 1533–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowitz, J.S.; DeVane, C.L.; Ramamoorthy, S.; Zhu, H.J. The psychostimulant d-threo-(R,R)-methylphenidate binds as an agonist to the 5HT(1A) receptor. Pharmazie 2009, 64, 123–125. [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz, J.S.; DeVane, C.L.; Pestreich, L.K.; Patrick, K.S.; Muniz, R. A comprehensive in vitro screening of d-, l-, and dl-threo-methylphenidate: An exploratory study. J. Child Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 2006, 16, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.L.; Feng, Z.J.; Liu, Y.; Ji, X.H.; Peng, J.Y.; Zhang, X.H.; Zhen, X.C.; Li, B.M. Methylphenidate enhances NMDA-receptor response in medial prefrontal cortex via sigma-1 receptor: A novel mechanism for methylphenidate action. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascoli, V.; Valjent, E.; Corbille, A.G.; Corvol, J.C.; Tassin, J.P.; Girault, J.A.; Herve, D. cAMP and extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling in response to d-amphetamine and methylphenidate in the prefrontal cortex in vivo: Role of β1-adrenoceptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2005, 68, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzell, B.B.; Muller, M.M.; Cobuzzi, J.L.; Hurwitz, Z.E.; DeCicco-Skinner, K.; Riley, A.L. Effect of age on methylphenidate-induced conditioned taste avoidance and related BDNF/TrkB signaling in the insular cortex of the rat. Psychopharmacology 2014, 231, 1493–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frampton, J.E. Lisdexamfetamine Dimesylate: A Review in Paediatric ADHD. Drugs 2018, 78, 1025–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutson, P.H.; Pennick, M.; Secker, R. Preclinical pharmacokinetics, pharmacology and toxicology of lisdexamfetamine: A novel d-amphetamine pro-drug. Neuropharmacology 2014, 87, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekstrand, E.; Murphy, H.M.; Wideman, C.H. The effects of the prodrug Vyvanse on spatial working memory and adiposity in rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2019, 186, 172765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dew, R.E.; Kollins, S.H. Lisdexamfetamine dimesylate: A new option in stimulant treatment for ADHD. Expert. Opin. Pharmacother. 2010, 11, 2907–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valvassori, S.S.; Resende, W.R.; Varela, R.B.; Arent, C.O.; Gava, F.F.; Peterle, B.R.; Dal-Pont, G.C.; Carvalho, A.F.; Andersen, M.L.; Quevedo, J. The Effects of Histone Deacetylase Inhibition on the Levels of Cerebral Cytokines in an Animal Model of Mania Induced by Dextroamphetamine. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 1430–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solanto, M.V. Neuropsychopharmacological mechanisms of stimulant drug action in attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: A review and integration. Behav. Brain Res. 1998, 94, 127–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, T.; Biederman, J. Non-stimulant treatment for Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. J. Atten. Disord. 2002, 6, S109–S119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelson, D.; Faries, D.; Wernicke, J.; Kelsey, D.; Kendrick, K.; Sallee, F.R.; Spencer, T.; the Atomoxetine ADHD Study Group. Atomoxetine in the treatment of children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: A randomized, placebo-controlled, dose-response study. Pediatrics 2001, 108, E83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnock-Jones, K.P.; Keating, G.M. Atomoxetine: A review of its use in attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents. Pediatr. Drugs 2009, 11, 203–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratochvil, C.J.; Bohac, D.; Harrington, M.; Baker, N.; May, D.; Burke, W.J. An open-label trial of tomoxetine in pediatric attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. J. Child Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 2001, 11, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bello, N.T. Clinical utility of guanfacine extended release in the treatment of ADHD in children and adolescents. Patient Prefer. Adherence 2015, 9, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pliszka, S.R. Non-stimulant treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. CNS Spectr. 2003, 8, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, L.E.; Hodgkins, P.; Caci, H.; Kahle, J.; Young, S. Effect of treatment modality on long-term outcomes in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shastry, B.S. Molecular genetics of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): An update. Neurochem. Int. 2004, 44, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, S.I.; McQuillin, A.; Gurling, H.M. Genetics of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Neuropharmacology 2009, 57, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirkovic, B.; Chagraoui, A.; Gerardin, P.; Cohen, D. Epigenetics and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: New Perspectives? Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortese, S. The neurobiology and genetics of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): What every clinician should know. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2012, 16, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripp, G.; Wickens, J.R. Neurobiology of ADHD. Neuropharmacology 2009, 57, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, K.; Russ, S.A.; Kahn, R.S.; Halfon, N. Patterns of comorbidity, functioning, and service use for US children with ADHD, 2007. Pediatrics 2011, 127, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, D.W. The consequences of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in adults. J. Psychiatr. Pract. 2007, 13, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curatolo, P.; D’Agati, E.; Moavero, R. The neurobiological basis of ADHD. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2010, 36, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- First, M.B. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 5th edition, and clinical utility. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 2013, 201, 727–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battle, D.E. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM). Codas 2013, 25, 191–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reale, L.; Bartoli, B.; Cartabia, M.; Zanetti, M.; Costantino, M.A.; Canevini, M.P.; Termine, C.; Bonati, M.; Lombardy, A.G. Comorbidity prevalence and treatment outcome in children and adolescents with ADHD. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2017, 26, 1443–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newcorn, J.H.; Halperin, J.M.; Jensen, P.S.; Abikoff, H.B.; Arnold, L.E.; Cantwell, D.P.; Conners, C.K.; Elliott, G.R.; Epstein, J.N.; Greenhill, L.L.; et al. Symptom profiles in children with ADHD: Effects of comorbidity and gender. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2001, 40, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, P.S.; Martin, D.; Cantwell, D.P. Comorbidity in ADHD: Implications for research, practice, and DSM-V. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 1997, 36, 1065–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Features | Stimulant Medications | Non-Stimulant Medications |
|---|---|---|
| Common Medications | Methylphenidate (Ritalin, Concerta), Amphetamine (Adderall, Vyvanse) | Atomoxetine (Strattera), Guanfacine (Intuniv), Clonidine (Kapvay) |
| Mechanism of Action | Increases dopamine and norepinephrine activity in the brain by blocking their reuptake at synapses | Regulates norepinephrine levels or affects adrenergic receptors, without directly boosting dopamine levels |
| Onset of Action | Fast-acting (within 30–60 min) | Slower onset (can take 2–6 weeks for full effect) |
| Window of Effectiveness | Shorter half-life, often requiring multiple doses per day or extended-release forms | Longer half-life, typically taken once a day |
| Effectiveness | Highly effective in ~70–80% of patients | Effective in ~50–70% of patients, often considered secondary when stimulants fail |
| Side Effects | Insomnia, appetite suppression, increased heart rate, anxiety, tics | Fatigue, drowsiness, dry mouth, irritability, gastrointestinal issues |
| Risk of Addiction | Higher risk, controlled substances with potential for misuse and dependence | Low to no risk of addiction or dependence |
| Use in Pregnancy and Breastfeeding | Generally not recommended due to potential risks to the fetus and infant | Caution required; atomoxetine may be safer than stimulants |
| Drug Interactions | Can interact with antidepressants, antacids, and medications for high blood pressure or hyperthyroidism | Fewer drug interactions, but can exacerbate conditions like fatigue or low blood pressure |
| Best Suited For | Patients who need rapid symptom control and have no contraindications for stimulant use | Patients who cannot tolerate stimulant side effects, or have coexisting conditions like tics or anxiety |
| Who Should Avoid | People with a history of substance abuse, heart conditions, or certain psychiatric disorders | Those with severe hypertension, or conditions aggravated by fatigue or low blood pressure |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Poddar, A.; Gaddam, S.; Sonnaila, S.; Bavaraju, V.S.M.; Agrawal, S. Unraveling Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Etiology: Current Challenges and Future Directions in Treatment. NeuroSci 2025, 6, 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6020041
Poddar A, Gaddam S, Sonnaila S, Bavaraju VSM, Agrawal S. Unraveling Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Etiology: Current Challenges and Future Directions in Treatment. NeuroSci. 2025; 6(2):41. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6020041
Chicago/Turabian StylePoddar, Abhishek, Sreelatha Gaddam, Shivakumar Sonnaila, Venkata Suryanarayana Murthy Bavaraju, and Shilpi Agrawal. 2025. "Unraveling Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Etiology: Current Challenges and Future Directions in Treatment" NeuroSci 6, no. 2: 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6020041
APA StylePoddar, A., Gaddam, S., Sonnaila, S., Bavaraju, V. S. M., & Agrawal, S. (2025). Unraveling Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Etiology: Current Challenges and Future Directions in Treatment. NeuroSci, 6(2), 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6020041






