Unveiling the Immediate Impact of Prechtl’s General Movement Assessment Training on Inter-Rater Reliability and Cerebral Palsy Prediction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Setting and Participants
2.2. GMA Raters
2.3. Procedure
2.4. GMA Scoring
2.5. Statistical Analysis
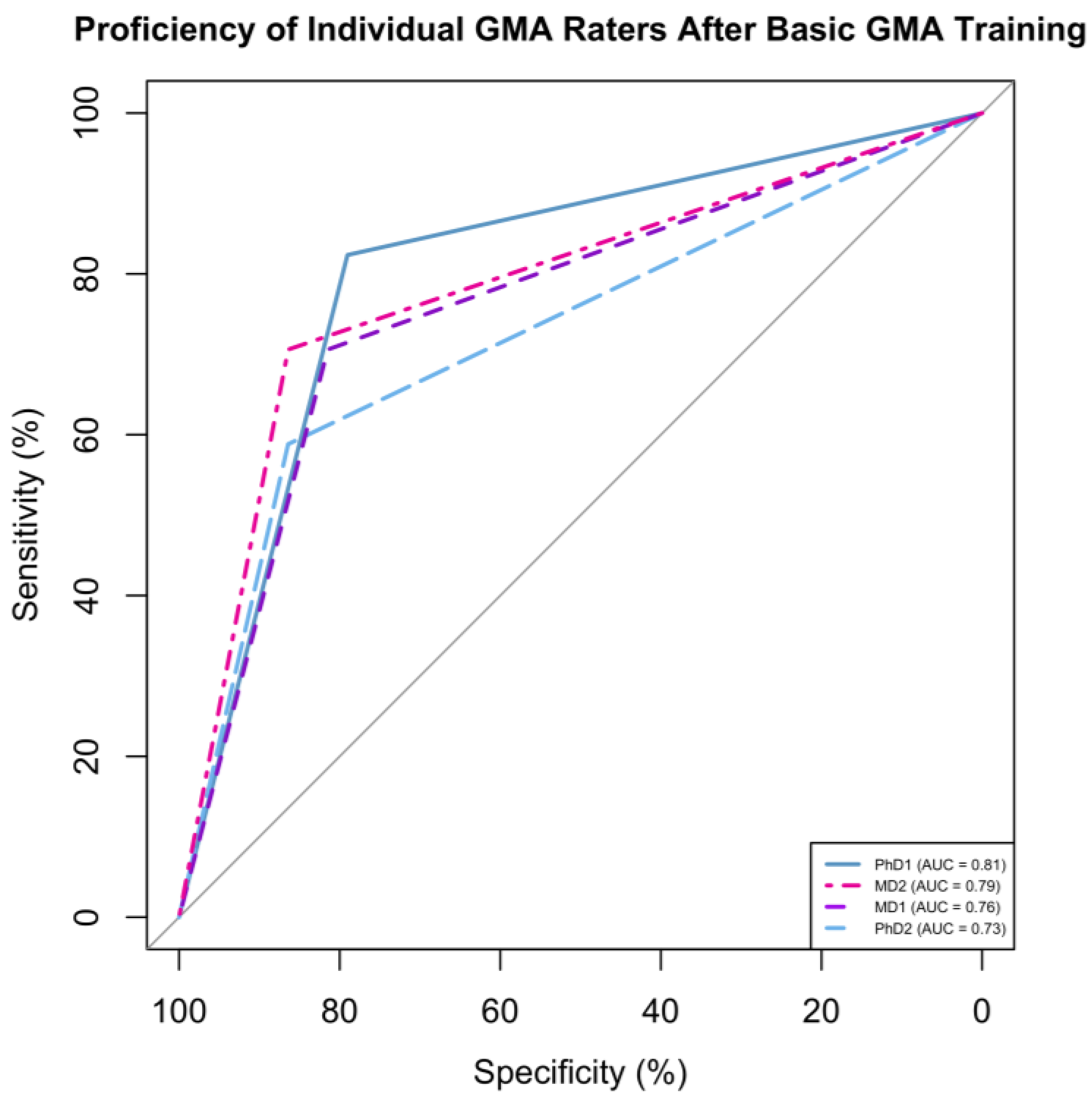
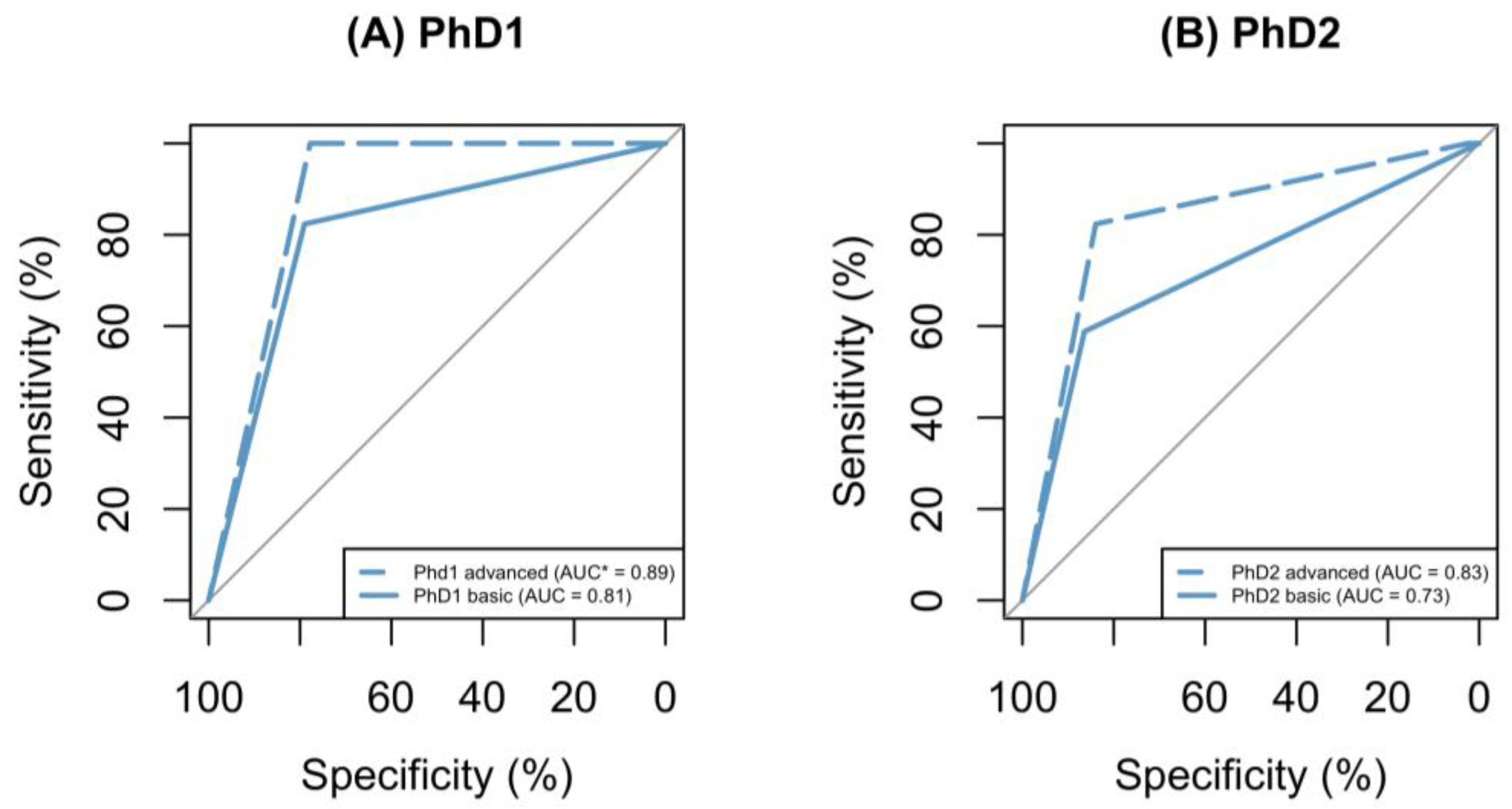
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Graham, H.K.; Rosenbaum, P.; Paneth, N.; Dan, B.; Lin, J.-P.; Damiano, D.L.; Becher, J.G.; Gaebler-Spira, D.; Colver, A.; Reddihough, D.S.; et al. Cerebral palsy. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2016, 2, 15082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- What Is Cerebral Palsy? Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/cp/facts.html#print (accessed on 26 November 2023).
- Novak, I.; Morgan, C.; Adde, L.; Blackman, J.; Boyd, R.N.; Brunstrom-Hernandez, J.; Cioni, G.; Damiano, D.; Darrah, J.; Eliasson, A.-C.; et al. Early, Accurate Diagnosis and Early Intervention in Cerebral Palsy. JAMA Pediatr. 2017, 171, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, R.; Noritz, G.; Maitre, N.L. Implementation of Early Diagnosis and Intervention Guidelines for Cerebral Palsy in a High-Risk Infant Follow-Up Clinic. Pediatr. Neurol. 2017, 76, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maitre, N.L.; Burton, V.J.; Duncan, A.F.; Iyer, S.; Ostrander, B.; Winter, S.; Ayala, L.; Burkhardt, S.; Gerner, G.; Getachew, R.; et al. Network implementation of guideline for early detection decreases age at cerebral palsy diagnosis. Pediatrics 2020, 145, e20192126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Einspieler, C.; Prechtl, H.F.R. Prechtl’s assessment of general movements: A diagnostic tool for the functional assessment of the young nervous system. Ment. Retard. Dev. Disabil. Res. Rev. 2005, 11, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Einspieler, C.; Peharz, R.; Marschik, P.B. Fidgety movements—Tiny in appearance, but huge in impact. J. Pediatr. 2016, 92, S64–S70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Einspieler, C.; Prechtl, H.F.; Ferrari, F.; Cioni, G.; Bos, A.F. The qualitative assessment of general movements in preterm, term and young infants—Review of the methodology. Early Hum. Dev. 1997, 50, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einspieler, C.; Bos, A.F.; Libertus, M.E.; Marschik, P.B. The General Movement Assessment Helps Us to Identify Preterm Infants at Risk for Cognitive Dysfunction. Front. Psychol. 2016, 7, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricci, E.; Einspieler, C.; Craig, A.K. Feasibility of Using the General Movements Assessment of Infants in the United States. Phys. Occup. Ther. Pediatr. 2017, 38, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, N.; Zhang, D.; Kulvicius, T.; Gail, A.; Barreiros, C.; Lindstaedt, S.; Kraft, M.; Bölte, S.; Poustka, L.; Nielsen-Saines, K.; et al. The future of General Movement Assessment: The role of computer vision and machine learning—A scoping review. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2021, 110, 103854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basic Course. Available online: https://general-movements-trust.info/56/invitation/gt-basic-course (accessed on 4 December 2023).
- Advance Course. Available online: https://general-movements-trust.info/57/invitation/gt-advanced-course (accessed on 4 December 2023).
- Basic Course Dates. Available online: https://general-movements-trust.info/47/dates (accessed on 4 December 2023).
- Advance Course Dates. Available online: https://general-movements-trust.info/70/dates/gt-advanced-course (accessed on 4 December 2023).
- Bernhardt, I.; Marbacher, M.; Hilfiker, R.; Radlinger, L. Inter- and intra-observer agreement of Prechtl’s method on the qualitative assessment of general movements in preterm, term and young infants. Early Hum. Dev. 2011, 87, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutlu, A.; Einspieler, C.; Marschik, P.B.; Livanelioglu, A. Intra-Individual Consistency in the Quality of Neonatal General Movements. Neonatology 2008, 93, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fjørtoft, T.; Einspieler, C.; Adde, L.; Strand, L.I. Inter-observer reliability of the “Assessment of Motor Repertoire—3 to 5 Months” based on video recordings of infants. Early Hum. Dev. 2009, 85, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cioni, G.; Prechtl, H.F.; Ferrari, F.; Paolicelli, P.B.; Einspieler, C.; Roversi, M.F. Which better predicts later outcome in fullterm infants: Quality of general movements or neurological examination? Early Hum. Dev. 1997, 50, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyton, C.; Pascal, A.; Boswell, L.; Deregnier, R.; Fjørtoft, T.; Støen, R.; Adde, L. Inter-observer reliability using the General Movement Assessment is influenced by rater experience. Early Hum. Dev. 2021, 161, 105436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, F.; Einspieler, C.; Hfr, P.; Bos, A.F.; Cioni, G. Prechtl’s Method on the Qualitative Assessment of General Movements in Preterm, Term and Young Infants; Mac Keith Press: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Valentin, T.; Uhl, K.; Einspieler, C. The effectiveness of training in Prechtl’s method on the qualitative assessment of general movements. Early Hum. Dev. 2005, 81, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwet, K.L. Computing inter-rater reliability and its variance in the presence of high agreement. Br. J. Math. Stat. Psychol. 2008, 61, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gwet, K.L. Testing the Difference of Correlated Agreement Coefficients for Statistical Significance. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 2016, 76, 609–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongpakaran, N.; Wongpakaran, T.; Wedding, D.; Gwet, K.L. A comparison of Cohen’s Kappa and Gwet’s AC1 when calculating inter-rater reliability coefficients: A study conducted with personality disorder samples. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2013, 13, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilem, L. Gwet, Testing the Difference of 2 Agreement Coefficients for Statistical Significance. 2021. Available online: https://github.com/kgwet/pairedCAC#testing-the-difference-of-2-agreement-coefficients-for-statisticalsignificance (accessed on 4 December 2023).
- Posit Team, RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R. Available online: http://www.posit.co/ (accessed on 21 July 2023).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing. 2021. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 14 January 2024).
- Aizawa, C.Y.P.; Einspieler, C.; Genovesi, F.F.; Ibidi, S.M.; Hasue, R.H. The general movement checklist: A guide to the assessment of general movements during preterm and term age. J. Pediatr. 2021, 97, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, K.A.; Örtqvist, M.; Bos, A.F.; Eliasson, A.-C.; Sundelin, H.E. Usability and inter-rater reliability of the NeuroMotion app: A tool in General Movements Assessments. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2021, 33, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Subject Demographics | Totals n = 98 (%) |
|---|---|
| Gender | |
| Female, n (%) | 33 (34) |
| Race | |
| White, n (%) | 52 (53) |
| Black or African American, n (%) | 31 (32) |
| Other, n (%) | 12 (12) |
| Unknown, n (%) | 3 (3) |
| Insurance | |
| Medicaid, n (%) | 73 (75) |
| Private, n (%) | 23 (24) |
| None, n (%) | 2 (2) |
| Medical History (known risk factors for CP) | |
| Birthweight (Kg), mean (SD) | 2.63 (1.1) |
| Premature (<37 weeks GA), n (%) | 49 (50) |
| Gestational Age, mean (SD) | 35.1 (4.9) |
| Abnormal Brain MRI, n (%) | 68 (69) |
| Abnormal Head Ultrasound, n (%) | 50 (51) |
| Seizures, n (%) | 13 (13) |
| Intracranial Bleeding | |
| Intraventricular Hemorrhage (IVH), n (%) | 27 (28) |
| Hematomas (Intraparenchymal and Subdural), n (%) | 2 (2) |
| Hemorrhages (Intracranial and Cerebellar), n (%) | 5 (5) |
| Periventricular Leukomalacia (PVL), n (%) | 12 (12) |
| Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE), n (%) | 44 (50) |
| Hypoxic Brain Injury, n (%) | 1 (1) |
| Anoxic Brain Injury, n (%) | 1 (1) |
| Positional Plagiocephaly, n (%) | 25 (26) |
| Down Syndrome, n (%) | 2 (2) |
| Hydrocephalus, n (%) | 12 (12) |
| Encephalomalacia, n (%) | 2 (2) |
| Inter-Rater Combinations | Percent Agreement | AC1 Coefficient (95% Confidence Interval) | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Post-Basic GMA * Training | |||
| {PhD1, PhD2} | 76% | 0.59 (0.43–0.76) | Moderate |
| {PhD1, MD1} | 90% | 0.83 (0.72–0.94) | Almost perfect |
| {PhD1, MD2} | 88% | 0.80 (0.68–0.91) | Substantial |
| {PhD2, MD1} | 76% | 0.61 (0.45–0.77) | Substantial |
| {PhD2, MD2} | 78% | 0.66 (0.51–0.81) | Substantial |
| {MD1, MD2} | 82% | 0.70 (0.56–0.85) | Substantial |
| Post-Advanced GMA Training | |||
| {PhD1, PhD2} | 82% | 0.76 (0.66–0.87) | Substantial |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kapil, N.; Majmudar-Sheth, B.; Escapita, A.C.; Johnson, T. Unveiling the Immediate Impact of Prechtl’s General Movement Assessment Training on Inter-Rater Reliability and Cerebral Palsy Prediction. NeuroSci 2024, 5, 244-253. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci5030019
Kapil N, Majmudar-Sheth B, Escapita AC, Johnson T. Unveiling the Immediate Impact of Prechtl’s General Movement Assessment Training on Inter-Rater Reliability and Cerebral Palsy Prediction. NeuroSci. 2024; 5(3):244-253. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci5030019
Chicago/Turabian StyleKapil, Namarta, Bittu Majmudar-Sheth, Alexa Celeste Escapita, and Tara Johnson. 2024. "Unveiling the Immediate Impact of Prechtl’s General Movement Assessment Training on Inter-Rater Reliability and Cerebral Palsy Prediction" NeuroSci 5, no. 3: 244-253. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci5030019
APA StyleKapil, N., Majmudar-Sheth, B., Escapita, A. C., & Johnson, T. (2024). Unveiling the Immediate Impact of Prechtl’s General Movement Assessment Training on Inter-Rater Reliability and Cerebral Palsy Prediction. NeuroSci, 5(3), 244-253. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci5030019







