Effect of Enriched Environment on Cerebellum and Social Behavior of Valproic Zebrafish
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. EE Improves Socialization in VPA-Treated Zebrafish
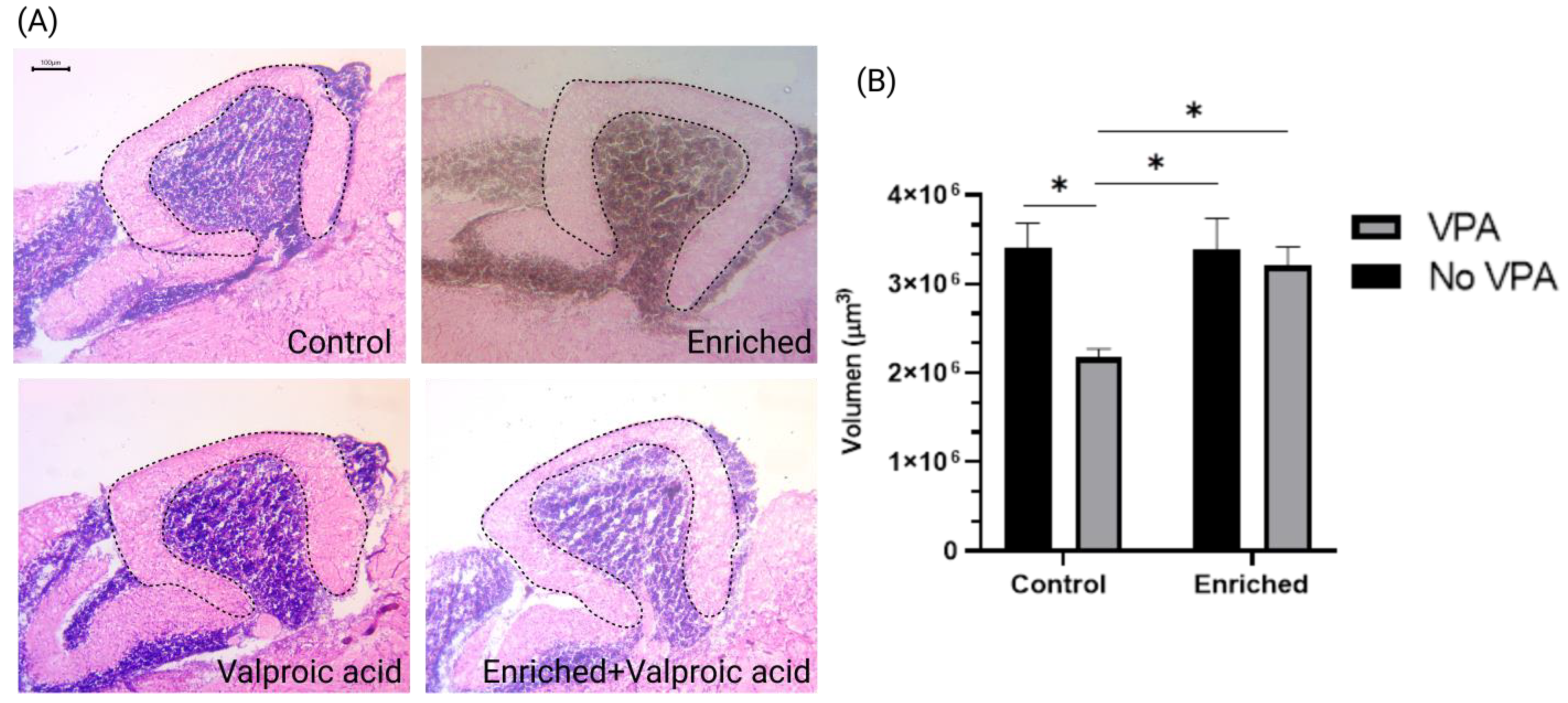
2.2. The Volume of the Molecular Layer in VPA-Treated Fish Exposed to EE Is like the Control Fish
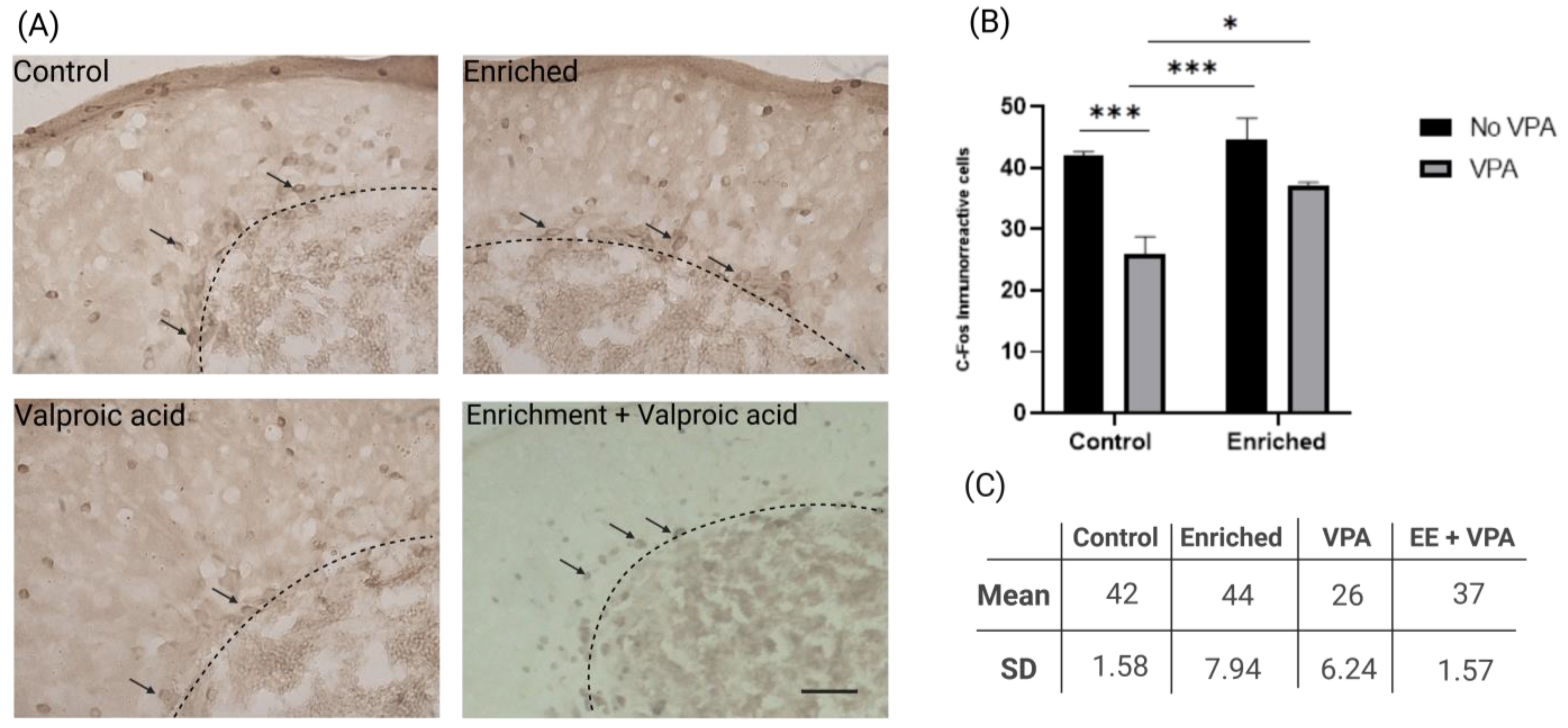
2.3. EE Increases the Number of c-Fos Positive Cells in VPA-Treated Fish Exposed to EE
2.4. Neuronal Counting of the NP
3. Discussion
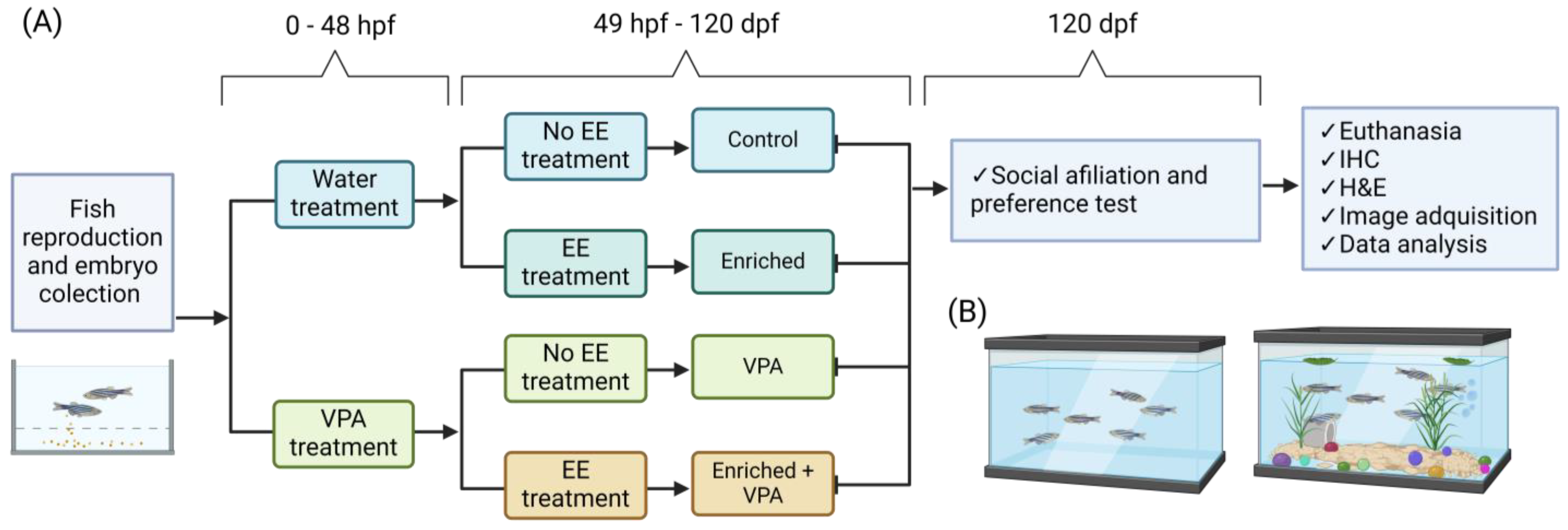
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Subjects
4.2. Embryo Collection
4.3. Pharmacological Treatment
4.4. Environmental Treatments
4.5. Behavioral Assessment
4.5.1. Social Preference Test
4.5.2. Social Affiliation Test
4.6. Brain Extraction
4.7. Histology
4.8. Image Analysis and Volumetric Estimation
4.9. Immunohistochemistry
4.10. Cell Counting
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pickett, J.; London, E. The Neuropathology of Autism: A Review. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2005, 64, 925–935. Available online: http://jnen.oxfordjournals.org/ (accessed on 1 February 2005). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, N.E.; Lord, C.; Volkmar, F.R. The Diagnosis of Autism: From Kanner to DSM-III to DSM-5 and Beyond. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2021, 51, 4253–4270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Psychiatric Association. DSM-5: Manual Diagnóstico y Estadístico de Los Trastornos Mentales DSM-5®; Editorial Médica Panamericana; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Eissa, N.; Al-Houqani, M.; Sadeq, A.; Ojha, S.K.; Sasse, A.; Sadek, B. Current Enlightenment about Etiology and Pharmacological Treatment of Autism Spectrum Disorder. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 325601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauer, A.K.; Stanton, J.E.; Hans, S.; Grabrucker, A.M. Autism Spectrum Disorders: Etiology and Pathology. Autism Spectr. Disord. 2021, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, K.A.; Sills, G. A Scientific Review: Mechanisms of Valproate-Mediated Teratogenesis. Biosci. Horiz. Int. J. Stud. Res. 2013, 6, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaliha, D.; Albrecht, M.; Vaccarezza, M.; Takechi, R.; Lam, V.; Al-Salami, H.; Mamo, J. A Systematic Review of the Valproic-Acid-Induced Rodent Model of Autism. Dev. Neurosci. 2020, 42, 12–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bambini-Junior, V.; Baronio, D.; MacKenzie, J.; Zanatta, G.; dos Santos Riesgo, R.; Gottfried, C. Prenatal Exposure to Valproate in Animals and Autism. Compr. Guide Autism 2014, 1, 1779–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranger, P.; Ellenbroek, B.A. Perinatal Influences of Valproate on Brain and Behaviour: An Animal Model for Autism. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2016, 29, 363–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolini, C.; Fahnestock, M. The Valproic Acid-Induced Rodent Model of Autism. Exp. Neurol. 2018, 299, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mapelli, L.; Soda, T.; D’Angelo, E.; Prestori, F. The Cerebellar Involvement in Autism Spectrum Disorders: From the Social Brain to Mouse Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dozawa, M.; Kono, H.; Sato, Y.; Ito, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Ohshima, T. Valproic Acid, a Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor, Regulates Cell Proliferation in the Adult Zebrafish Optic Tectum. Dev. Dyn. 2014, 243, 1401–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rea, V.; Van Raay, T.J. Using Zebrafish to Model Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Comparison of ASD Risk Genes Between Zebrafish and Their Mammalian Counterparts. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 13, 575575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Lei, L.; Tian, L.; Hou, F.; Roper, C.; Ge, X.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Dong, Q.; Tanguay, R.L.; et al. Development and Behavior Alterations in Zebrafish Embryonically Exposed to Valproic Acid (VPA): Animal Model of Autism. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2018, 66, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, F.F.; Gaspary, K.V.; Leite, C.E.; De Paula Cognato, G.; Bonan, C.D. Embryological Exposure to Valproic Acid Induces Social Interaction Deficits in Zebrafish (Danio rerio): A Developmental Behavior Analysis. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2015, 52, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Puchulen, M.; Miquel, M.; Saft, P.; Brug, B.; Toledo, R.; Hernandez, M.E.; Manzo, J. The Cerebellum in Autism. Eneurobiologia 2012, 3, 310312. [Google Scholar]
- Haldipur, P.; Millen, K.J.; Aldinger, K.A. Human Cerebellar Development and Transcriptomics: Implications for Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2022, 45, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, E.B.E.; Stoodley, C.J. Autism Spectrum Disorder and the Cerebellum. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2013, 113, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, M.; Sierra-Arregui, T.; Peñagarikano, O. The Cerebellum and Autism: More than Motor Control. In Behavioral Neuroscience; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Roostaei, T.; Nazeri, A.; Sahraian, M.A.; Minagar, A. The Human Cerebellum: A Review of Physiologic Neuroanatomy. Neurol. Clin. 2014, 32, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mark, M.; Pakusch, J.; Ernst, T.M.; Timmann, D. Cerebellum and Emotion Memory. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2022, 1378, 53–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Aparicio, S.Y.; Laureani-Fierro, A.J.; Morgado-Valle, C.; Beltrán-Parrazal, L.; Rojas-Durán, F.; García, L.I.; Toledo-Cárdenas, R.; Hernández, M.E.; Manzo, J.; Pérez, C.A. Latest Research on the Anatomy and Physiology of the Cerebellum. Neurol. Perspect. 2022, 2, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agata, F.; Orsi, L. Cerebellum and Emotion Recognition. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2022, 1378, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Overwalle, F.; Manto, M.; Cattaneo, Z.; Clausi, S.; Ferrari, C.; Gabrieli, J.D.E.; Guell, X.; Heleven, E.; Lupo, M.; Ma, Q.; et al. Consensus Paper: Cerebellum and Social Cognition. Cerebellum 2020, 19, 833–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sydnor, L.M.; Aldinger, K.A. Structure, Function, and Genetics of the Cerebellum in Autism. J. Psychiatr. Brain Sci. 2022, 7, e220008. [Google Scholar]
- Harmon, T.C.; McLean, D.L.; Raman, I.M. Integration of Swimming-Related Synaptic Excitation and Inhibition by Olig2 + Eurydendroid Neurons in Larval Zebrafish Cerebellum. J. Neurosci. 2020, 40, 3063–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pose-Méndez, S.; Schramm, P.; Valishetti, K.; Köster, R.W. Development, Circuitry, and Function of the Zebrafish Cerebellum. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2023, 80, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaslin, J.; Brand, M. Cerebellar Development and Neurogenesis in Zebrafish. In Handbook of the Cerebellum and Cerebellar Disorders; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2013; pp. 1441–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heap, L.; Goh, C.C.; Kassahn, K.S.; Scott, E.K. Cerebellar Output in Zebrafish: An Analysis of Spatial Patterns and Topography in Eurydendroid Cell Projections. Front. Neural Circuits 2013, 7, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, J.; Bodznick, D. Functional Origins of the Vertebrate Cerebellum from a Sensory Processing Antecedent. Curr. Zool. 2010, 56, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, C.C.; Donnelly, J.H.; Steinberg-Epstein, R.; Leon, M. Environmental Enrichment as a Therapy for Autism: A Clinical Trial Replication and Extension. Behav. Neurosci. 2015, 129, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aronoff, E.; Hillyer, R.; Leon, M. Environmental Enrichment Therapy for Autism: Outcomes with Increased Access. Neural Plast. 2016, 2016, 2734915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, C.H.; Reed, B.T.; Hawkins, P. Enrichment for Laboratory Zebrafish—A Review of the Evidence and the Challenges. Animals 2021, 11, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figuracion, K.C.F.; Lewis, F.M. Environmental Enrichment: A Concept Analysis. Nurs. Forum 2021, 56, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempermann, G. Environmental Enrichment, New Neurons and the Neurobiology of Individuality. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 20, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ball, N.J.; Mercado, E.; Orduña, I. Enriched Environments as a Potential Treatment for Developmental Disorders: A Critical Assessment. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velázquez-Landa, X.; Carrillo, P.; Coria-Avila, G.A.; Herrera-Covarrubias, D.; García, L.I.; Toledo-Cárdenas, M.R.; Hernández-Aguilar, M.E.; Manzo, J. Zebrafish Sexual Behavior in Plain and Enriched Environments: Parameters in the Valproate Model of Autism. Fishes 2023, 8, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baronio, D.; Puttonen, H.A.J.; Sundvik, M.; Semenova, S.; Lehtonen, E.; Panula, P. Embryonic Exposure to Valproic Acid Affects the Histaminergic System and the Social Behaviour of Adult Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 797–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhinn, M.; Lun, K.; Ahrendt, R.; Geffarth, M.; Brand, M. Zebrafish Gbx1 Refines the Midbrain-Hindbrain Boundary Border and Mediates the Wnt8 Posteriorization Signal. Neural Dev. 2009, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stednitz, S.J.; Washbourne, P. Rapid Progressive Social Development of Zebrafish. Zebrafish 2020, 17, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreosti, E.; Hoffman, E.J.; Rihel, J. Modeling Autism Spectrum Disorders in Zebrafish. Behav. Neural Genet. Zebrafish 2020, 451–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Polavieja, G.G.; Orger, M.B. Social Behavior: A Neural Circuit for Social Behavior in Zebrafish. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, R828–R830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Sanroman, D.; Sanchis-Segura, C.; Toledo, R.; Hernandez, M.E.; Manzo, J.; Miquel, M. The Effects of Enriched Environment on BDNF Expression in the Mouse Cerebellum Depending on the Length of Exposure. Behav. Brain Res. 2013, 243, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volgin, A.D.; Yakovlev, O.V.; Demin, K.A.; De Abreu, M.S.; Rosemberg, D.B.; Meshalkina, D.A.; Alekseeva, P.A.; Friend, A.J.; Amstislavskaya, T.G.; Kalueff, A.V. Understanding the Role of Environmental Enrichment in Zebrafish Neurobehavioral Models. Zebrafish 2018, 15, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemmer, A.; Mirkes, K.; Anneser, L.; Eilers, T.; Kibat, C.; Mathuru, A.; Ryu, S.; Schuman, E. Oxytocin Receptors Influence the Development and Maintenance of Social Behavior in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati-Holasoo, H.; Maghsoudi, A.S.; Akbarzade, M.; Gholami, M.; Shadboorestan, A.; Vakhshiteh, F.; Armandeh, M.; Hassani, S. Oxytocin Protective Effects on Zebrafish Larvae Models of Autism-like Spectrum Disorder. Iran. J. Basic. Med. Sci. 2023, 26, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetit, R.; Hillary, R.F.; Price, D.J.; Lawrie, S.M. The Neuropathology of Autism: A Systematic Review of Post-Mortem Studies of Autism and Related Disorders. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 129, 35–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courchesne, E.; Karns, C.M.; Davis, H.R.; Ziccardi, R.; Carper, R.A.; Tigue, Z.D.; Chisum, H.J.; Moses, P.; Pierce, K.; Lord, C.; et al. Unusual Brain Growth Patterns in Early Life in Patients with Autistic Disorder: An MRI Study. Neurology 2001, 57, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Mello, A.M.; Crocetti, D.; Mostofsky, S.H.; Stoodley, C.J. Cerebellar Gray Matter and Lobular Volumes Correlate with Core Autism Symptoms. Neuroimage Clin. 2015, 7, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, L.; Dai, X.; Yin, Y. Valproic Acid Exposure Sequentially Activates Wnt and MTOR Pathways in Rats. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2016, 75, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, J.; Xia, Q.; Guo, N.; Li, Q. Social Preference Deficits in Juvenile Zebrafish Induced by Early Chronic Exposure to Sodium Valproate. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 198395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, T.P.; Zhou, F.; Sai, L.Y.; Chen, H.; Lin, S.L.; Schachner, M. Duloxetine Ameliorates Valproic Acid-Induced Hyperactivity, Anxiety-like Behavior, and Social Interaction Deficits in Zebrafish. Autism Res. 2022, 15, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.H.; Wu, N.; Yuan, X.B. Toward a Better Understanding of Neuronal Migration Deficits in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Lee, B.; Lee, C.J. Valproic Acid Decreases Cell Proliferation and Migration in the Cerebellum of Zebrafish Larvae. Anim. Cells Syst. 2014, 18, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.C.; Calder, B.J.; Lilya, S.M.; Davies, B.M.; Martin, A.; Peterson, M.; Hansen, J.M.; Suli, A. Valproic Acid Affects Neuronal Specification and Differentiation during Early Optic Tectum Development of Zebrafish. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji, J.; Lotfi, H.; Moharrerie, A.; Jafari, S.Y.; Soltanpour, N.; Tamannaiee, R.; Marjani, K.; Roudaki, S.; Naseri, F.; Moeeini, R.; et al. Regional Differences in BDNF Expression and Behavior as a Function of Sex and Enrichment Type: Oxytocin Matters. Cereb. Cortex 2022, 32, 2985–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Rodríguez, J.A.; Toledo-Cárdenas, M.R.; Herrera-Covarrubias, D.; Coria-Ávila, G.A.; García-Hernández, L.I.; Hernández-Aguilar, M.E.; Manzo-Denes, J. Efectos del ambiente enriquecido en la expresión de los receptores GABA en el vermis cerebeloso en un modelo de autismo en ratas inducido con valproato. Eneurobiología 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, C.M.; Betancur, C.; Boeckers, T.M.; Bockmann, J.; Chaste, P.; Fauchereau, F.; Nygren, G.; Rastam, M.; Gillberg, I.C.; Anckarsäter, H.; et al. Mutations in the Gene Encoding the Synaptic Scaffolding Protein SHANK3 Are Associated with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 25–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Peng, X.; Hu, C.; Li, C.; Li, Q.; Xu, X. Developmental Profiling of ASD-Related Shank3 Transcripts and Their Differential Regulation by Valproic Acid in Zebrafish. Dev. Genes Evol. 2016, 226, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ángel Alberto Puig-Lagunes, M.; Eliseo Velazco-Cercas, M.; Issac Zamora-Bello Issac, Q.; Beltrán-Parrazal, L.; Consuelo Morgado-Valle, D.; Manzo, J.; María Leonor López-Meraz, D. Congenital Malformations in Rats Prenatally Exposed to Valproic Acid and Their Relationship with Purkinje Cells Counts. Rev. Mex. Neurocienc. 2016, 16, 28–40. [Google Scholar]
- Clemenson, G.D.; Deng, W.; Gage, F.H. Environmental Enrichment and Neurogenesis: From Mice to Humans. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2015, 4, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bartolo, P.; Florenzano, F.; Burello, L.; Gelfo, F.; Petrosini, L. Activity-Dependent Structural Plasticity of Purkinje Cell Spines in Cerebellar Vermis and Hemisphere. Brain Struct. Funct. 2015, 220, 2895–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelfo, F.; Petrosini, L. Environmental Enrichment Enhances Cerebellar Compensation and Develops Cerebellar Reserve. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sale, A.; Berardi, N.; Maffei, L. Environment and Brain Plasticity: Towards an Endogenous Pharmacotherapy. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 189–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zappala, C.; Barrios, C.D.; Depino, A.M. Social Deficits in Mice Prenatally Exposed to Valproic Acid Are Intergenerationally Inherited and Rescued by Social Enrichment. Neurotoxicology 2023, 97, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NOM-063-ZOO-1999; Especificaciones Técnicas Para la Producción, Cuidado y Uso de los Animales de Laboratorio. Diario Oficial de la Federación: Ciudad de México, México, 1999.
- Nasiadka, A.; Clark, M.D. Zebrafish breeding in the laboratory environment. ILAR J. 2012, 53, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen Sarma, O.; Frymus, N.; Axling, F.; Thörnqvist, P.O.; Roman, E.; Winberg, S. Optimizing Zebrafish Rearing−Effects of Fish Density and Environmental Enrichment. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1204021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalueff, A.V. The Rights and Wrongs of Zebrafish: Behavioral Phenotyping of Zebrafish. Rights Wrongs Zebrafish Behav. Phenotyping Zebrafish 2017, 1–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, A.M.; Nguyen, M.; Wong, K.; Poudel, M.K.; Kalueff, A.V. Developing Zebrafish Models of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 50, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, M.; Raymond, J.; Hester, J.; Kyzar, E.; Gaikwad, S.; Bruce, I.; Fryar, C.; Chanin, S.; Enriquez, J.; Bagawandoss, S.; et al. Assessing Social Behavior Phenotypes in Adult Zebrafish: Shoaling, Social Preference, and Mirror Biting Tests. In Zebrafish Protocols for Neurobehavioral Research; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogi, A.; Licitra, R.; Naef, V.; Marchese, M.; Fronte, B.; Gazzano, A.; Santorelli, F.M. Social Preference Tests in Zebrafish: A Systematic Review. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 7, 590057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, C.K.; Bright, L.A.; Marx, J.O.; Andersen, R.P.; Mullins, M.C.; Carty, A.J. Effectiveness of Rapid Cooling as a Method of Euthanasia for Young Zebrafish (Danio Rerio). J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2018, 57, 58. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Köhler, A.; Valentim, A.M. Analgesia, Anesthesia, and Euthanasia in Zebrafish. In Laboratory Fish in Biomedical Research: Biology, Husbandry and Research Applications for Zebrafish, Medaka, Killifish, Cavefish, Stickleback, Goldfish and Danionella Translucida; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebrafish Brain Atlas. Available online: https://azba.wayne.edu/ (accessed on 24 October 2023).
- Ruhl, T.; Zeymer, M.; von der Emde, G. Cannabinoid Modulation of Zebrafish Fear Learning and Its Functional Analysis Investigated by C-Fos Expression. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2017, 153, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, D.; Tran, S.; Shams, S.; Gerlai, R. A Simple Method for Immunohistochemical Staining of Zebrafish Brain Sections for C-Fos Protein Expression. Zebrafish 2015, 12, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Flores-Prieto, B.; Caycho-Salazar, F.; Manzo, J.; Hernández-Aguilar, M.E.; Coria-Avila, A.G.; Herrera-Covarrubias, D.; Rojas-Dúran, F.; Aranda-Abreu, G.E.; Pérez-Estudillo, C.A.; Toledo-Cárdenas, M.R. Effect of Enriched Environment on Cerebellum and Social Behavior of Valproic Zebrafish. NeuroSci 2024, 5, 128-140. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci5020009
Flores-Prieto B, Caycho-Salazar F, Manzo J, Hernández-Aguilar ME, Coria-Avila AG, Herrera-Covarrubias D, Rojas-Dúran F, Aranda-Abreu GE, Pérez-Estudillo CA, Toledo-Cárdenas MR. Effect of Enriched Environment on Cerebellum and Social Behavior of Valproic Zebrafish. NeuroSci. 2024; 5(2):128-140. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci5020009
Chicago/Turabian StyleFlores-Prieto, Bernardo, Flower Caycho-Salazar, Jorge Manzo, María Elena Hernández-Aguilar, Alfonso Genaro Coria-Avila, Deissy Herrera-Covarrubias, Fausto Rojas-Dúran, Gonzalo Emiliano Aranda-Abreu, Cesar Antonio Pérez-Estudillo, and María Rebeca Toledo-Cárdenas. 2024. "Effect of Enriched Environment on Cerebellum and Social Behavior of Valproic Zebrafish" NeuroSci 5, no. 2: 128-140. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci5020009
APA StyleFlores-Prieto, B., Caycho-Salazar, F., Manzo, J., Hernández-Aguilar, M. E., Coria-Avila, A. G., Herrera-Covarrubias, D., Rojas-Dúran, F., Aranda-Abreu, G. E., Pérez-Estudillo, C. A., & Toledo-Cárdenas, M. R. (2024). Effect of Enriched Environment on Cerebellum and Social Behavior of Valproic Zebrafish. NeuroSci, 5(2), 128-140. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci5020009









