Abstract
This study applies consistent fuzzy preference relations (CFPR) to evaluate the influential criteria of revitalization strategies (RS) for the hospitality industry in the post-pandemic (COVID-19) era in Taiwan. A real case applies CFPR in order to analyze the relationship between governmental implementation and industrial expectations in Taiwan. The results indicate that “market revitalization”, such as the Taiwanese government’s implementation of various stimulus vouchers and coupons to encourage market consumption and revitalize the overall economy, is considered the most essential/important criteria for RS. This study strengthens the government sector by evaluating the heterogeneity of revitalization strategies best used to formulate the actions to pilot industries as a global contribution to fight the COVID-19 pandemic within a global crisis.
1. Introduction
The unpredictability of crises is one of the external factors that can tremendously impact the hospitality industry [1,2]. A number of unpredicted crises have affected contemporary society globally, none of which have had such an arduous effect on the hospitality sector as the COVID-19 pandemic [3]. The COVID-19 outbreak has incurred the hospitality sector to experience significant financial pain due to the pandemic, which coalesced with a virtual shutdown of entire global economies [2]. The “hostile challenge” of the COVID-19 pandemic has involved many issues for governments to adopt the best applications in surmounting the diverse challenges that have impacted the hospitality sectors foremost. Some current research studies have pointed out millions of jobs in related hospitality industries immediately became at risk, and overall industries’ incomes suffered losses of trillions of dollars worldwide while many restaurants and hotels became shuttered in the early phase of the COVID-19 outbreak. Consequently, efficient and effective government performance during the pandemic enhanced public confidence in economic agencies capable of revitalizing the economy. Considerable discussion in the literature has focused on relevant government measures such as infection prevention [4], distribution of personal protective equipment [5], tax relief [6], unemployment compensation [7] and industrial innovation [8]. Measures related to the digital environment and business intelligence [9,10] have also received considerable attention and development during the epidemic, while at the same time, the related application of sustainable supply-chain management has also been a focus of the literature [11,12].
However, several challenges will persistently remain after the pandemic has run its course, so the implementation of a revitalization strategy (RS) has swiftly converted into an appropriate and practical alternative. In addition, it is advisable that the government develop accurate and effective RS to facilitate the necessary transformational acceleration and developmental stabilization during the post-pandemic phase [13]. As disease threats change, it is a concern whether government policy tools can meet the needs of industry; however, with multiple policy instruments, how to evaluate the priority of policy instruments is an important issue that needs to be addressed.
Initially, this study reviewed novel academic articles and publications from industrial journals and other relevant materials focused on COVID-19 issues in the hospitality dimension that broadened comprehension of governmental, industrial, and academic perceptions [14,15]. The study illustrated an empirical case study by conducting an interview survey of 16 hospitality experts in Taiwan; moreover, the study summarized eight influential criteria from two essential data: the first key data explores secondary data from an academic perspective while the other investigates primary data collected from 11 July~15 July 2020 by conducting interviews of experts and surveys.
Secondly, this study advocates a prediction model of analytical hierarchy reliant on CFPR to facilitate the hospitality sector to become more aware of COVID-19′s unparalleled impact [16]; hence, the priority weights of influential criteria by conducting pairwise comparisons determine the rankings of outcomes amongst which the best decision-making model for governments may be adopted to make accurate revitalization strategies possible [17]. The proposed model should not only assist governments in realizing what criteria could determine successful and appropriate decision-making processes but contribute appropriate strategies and acts to pilot the hospitality industry implementing RS in the post-pandemic future as well.
Finally, we conduct discussions and conclusions directly related to formulating the priority of a decision-making model for governments to overcome the global crises in RS. The results indicate that “market revitalization” is considered the most essential/important criteria for RS under a zero-tolerance policy regarding the COVID-19 outbreak in Taiwan. The contribution of this paper lies in the use of expert interviews and the CFPR to explore the industry’s preferential order for policy measures and to provide a reference for the government in the revitalization of hospitality.
This article is organized as follows. Section 2 presents the literature review. The COVID-19 outbreak real situation in Taiwan is introduced in Section 3. Section 4 introduces the research method, while the framework and influential criteria to implement a revitalization strategy for the hospitality industry in Taiwan are provided in Section 5. Empirical illustration and discussion are provided in Section 6, while Section 7 provides brief results. Section 8 concludes the paper, and Section 9 points out the limitations and future research directions.
2. Literature Review Related to the COVID-19 Crisis
2.1. Academic Perspective
Reviews of current journal articles and research on COVID-19 identify typologies and characteristics of crises in order to develop insight into phenomena and derive effective crisis management strategies. Sigala [18] mentions researchers and practitioners should not only implement and design crisis-recovery models and response strategies but also develop elastic capacity and knowledge to address further crises. At present, this capacity and knowledge are still deficient for measuring and predicting hospitality impacts and strategies during the pandemic but can be sourced from small-scale organizational issues to staff challenges and industrial misdeeds to large-scale external factors such as natural disasters. Initiative COVID-19 research has also concentrated on diverse governments’ published material to determine stages of prescriptive models and assist government in comprehending strategic and proactive methodologies while also delineating the best actions and policies to be implemented in the future [14].
Further to this, Willis Towers Watson [19] illustrated the three phases of action for government and decision-maker alike, with the principles providing a road map of management framework in an ongoing response to the COVID-19 pandemic, with the findings from related studies being useful in informing decision-makers as to what strategies could be evaluated or implemented at the several phases of any crisis or disaster, and how to intervene, thereby alleviating, minimizing or simply blocking crises from moving forward.
Some studies investigate the COVID-19 impact on the effect of crisis response strategies, while some explore the role of government in affecting people’s perceptions of crises [18]. Fong et al. [13] comment that crisis management should strengthen the relationship between industry and government in order to improve accuracy and relevancy. Enhancing comprehension of governmental action predominantly induces progressive understanding leading to the prevention of any crisis while managing a global pandemic.
2.2. Industry and Government Perspective
Awareness of the threat of hospitality crises and the potential to inflict harm is reflected in several academic publications, including special edition journals and articles devoted to this topic, as referred to in the earlier part of the report. Manuals and handbooks for practitioners and industry associations are also available; additionally, many official authorities and government bodies have been involved in the production of such publications where at the international level, UNWTO (United Nations World Tourism Organization) and PATA (Pacific Asia Travel Association) have both developed crisis management guidelines for hospitality businesses, operators and official agencies around the world to assist in dealing with crises and disasters. In essence, the difference between both guidelines is only in the form, not the content [20].
In terms of government policy, for example, Taiwan’s Ministry of Economic Affairs has proposed eight major industrial rescue and revitalization measures, including financial aid, employment assistance, tax breaks, infrastructure facilities, utility discounts, innovation and transformation, market revitalization and COVID-19 prevention measures.
2.3. Comparison of Academic, Industry, and Government Perspectives
2.3.1. Differences
In terms of the COVID-19 outbreak in academic publications devoted to theoretical themes, many works are centered on case studies with an emphasis on extrinsic causes of crises rather than on intrinsic industrial weakness and destination perspectives. Such presented frameworks and models are very theoretical and not readily understood by hospitality industry practitioners and operators, so more appropriate models are difficult to implement as a crisis management plan; moreover, the academic literature is lacking in qualitative and quantitative research data about crisis management planning in the hospitality industry.
In contrast with academia, guidebooks and manuals developed by industry associations and governments are more practical, as most materials present step-by-step outlined procedures to follow in developing and designing effective crisis management strategies based on multidimensional resources for hospitality industries of all sizes. Most of the plans afford insight into the problems and provide crisis plan templates individually, which assist the industry in determining appropriate components best fitting the nature of the business and its needs.
2.3.2. Similarities
The study has found there is a consensus among academics, hospitality sectors, and governments that it is essential for both public and private hospitality industries to have a crisis management plan or contingency plan in place in order to provide more successful responses when a crisis occurs, thereby mitigating the severity of such crisis. Several similar issues are noted and addressed in both academic and industry or government publications, which are summarized below. This presents the aim of testing leadership, communications, and the role of government and industry plus others so concerned, including the ability of individual actors, while appraising the effectiveness of all such actions in a crisis. The actions and strategies should be followed by evaluation; each situation should be carefully assessed in order to improve the crisis management plan.
Crisis management leadership—the first step in developing a crisis management plan should be to implement group or individual leadership that can control challenges and impacts within a COVID-19 outbreak. Leaders should not only have the knowledge to evaluate problems and make accurate strategies but also the capacity to make appropriate decisions by utilizing popular computational methodology in leading the industry to overcome the pandemic. This is the key and most difficult part of crisis planning [21].
Importance of communication—a formal communication channel should be put in place to assist with the dissemination of information and the establishment of a unified response. It is important that perceptions of COVID-19 have an impact on predicting future hospitality demand and drafting appropriate recovery strategies. Government should develop transparent communication opportunities to improve the confidence of its audiences: employees, consumers, business partners, and local community politicians, and local, regional, national, and international authorities [22,23].
Role of government—the involvement of government is important in crisis planning as governments rely on prediction to provide stimulus packages and interventions for real demand from industry. COVID-19 has resulted in the enormous intervention of governments in the functions and operations of the hospitality industry [13,18,24].
3. The COVID-19 Outbreak Real Situation in Taiwan
Throughout the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) outbreak, the Taiwanese government has swiftly implemented disseminated prevention measures and systemic prophylaxis to the public in a timely fashion. Taiwan Centers for Disease Control (TCDC) successfully managed the COVID-19 outbreak from 12 April to 26 July 2020. In Taiwan, no positive domestic cases were reported for more than 100 consecutive days, with no incidences of local transmission occurring. The report of 19 July 2020 stated that the total of positive cases was capped at 458. Since the outbreak initially, 80,499 cases have had tests conducted, of which 79,555 were negative. Out of 458 total confirmed cases, 55 were domestic, 403 were imported, and 7 deaths occurred as a result of infection. According to the TCDC, prevention measures required citizens to utilize face masks, have their temperature checked, and undergo ethanol hand washes before entering public facilities, hospitals, schools, hotels, and restaurants during the pandemic threat [25]. COVID-19 prevention measures also included the implementation of social distancing that contributed significantly to the observed decline in infection rate [26]. Additional various factors have contributed to the lower frequency of pneumococcal disease and complex influenza in Taiwan. In 2020, Taiwanese people experienced a low intensity of disease transmission, lower occupancy of hospital beds and ICUs, and assumed proactive public-led responses for effective preventive measures [27].
As the COVID-19 pandemic in Taiwan began to spread, the government swiftly rolled out a three-pronged plan of prevention measure, relief for industries and stimulus steps for the economy. The initial step was disease prevention, as mentioned above. The second step involved direct industrial relief in those economic areas hardest hit by the pandemic, with this step being taken regardless of the industry. The third step of providing economic stimulus was made with the aim of equal benefit distributions, immediate result achievements, expansion of an affluent industrial foundation, and creation of sustainable public works projects [28]. According to Taiwan’s Executive Yuan, a special act was promulgated to create a total relief package of NT$1.05 trillion dollars tied directly to COVID-19 prevention, relief, and revitalization on 18 March 2020. The Taiwanese government authorized an initial relief package worth NT$200 billion that included funds for household expenses, individual and business tax break subsidies, and industrial relief; moreover, the government amended the COVID-19 relief act to append a special budget of an additional NT$150 billion and other budgets of NT$700 billion in loans [28].
After these effective preventive acts and plans were applied, the domestic epidemic slowed down, people’s lives gradually returned to normal, and after the 1 May Labor holiday and Mother’s Day effects were added, the restaurant industry’s revenue in May was NT$100.86 billion, already a sharp increase of 15.95% from the previous month of April. When considering the largest monthly increase change rate in comparison with the same month of the previous year, there was still a decrease of 7.87% since the pandemic, as seen in Figure 1. After 7 June 2020, Taiwan reset its economy and market significantly by applying revitalization actions and plans, providing several factors capable of being utilized as accurate or appropriate strategies for industries to follow.
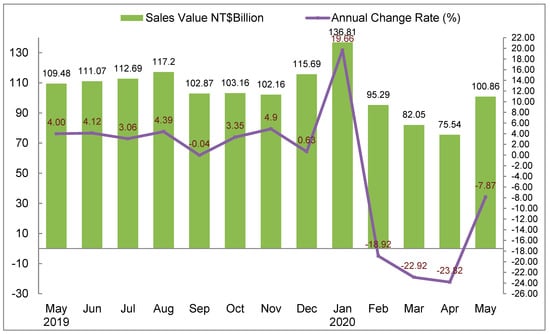
Figure 1.
Statistics related to restaurant sales index and annual change rate from May 2019 to May 2020; Source: [29].
4. Research Method
The study applies the CFPR procedure to assess the criteria most effective in implementing a Taiwanese governmental revitalization strategy in the hospitality sector. Herera-Viedma et al. [30] conducted CFPR for designing pairwise comparison-preference decision matrices and utilizing the reciprocal additive transitivity property, where the CFPR methodology not only enables industrial experts to represent the level of preference taken from within a number of alternatives but it can also check the consistency in the process of decision-making [30,31,32,33]. In brief, descriptive propositions and definitions are presented, delineating how they are applied throughout this study.
4.1. Fuzzy Preference Relations
Definition 1.
According to fuzzy preference relations P on a number of options X is represented by a positive preference relations matrix PXX advancing the function:: XXFurthermore, = ( interprets the preference intensity of ratio of option over . When = intimates indifference between and ( ~ ), = 1 denotes that is absolutely preferred to = 0 represents is absolutely preferred to and > represents that is preferred to , > .
The preference matrix P is supposed as an additive reciprocal [16]:
Proposition 1.
Considersomeoptions,X = {,…,}, is related to a reciprocal multiplicative preference relation) with ∈ [, 9]. In addition, the parallelism reciprocal additive fuzzy preference relation, P = () with, ∈ [0, 1], association of formula that A is stated as follows:
The study concentrates on the consistent decision model that relies on CFPR that is able to obtain the type of transformation function g relatable to the research issues.
4.2. Consistency of the Fuzzy Preference Relations
Proposition 2.
Where) can provide consistent multiplicative preference relations, the parallelism reciprocal additive fuzzy preference relation, P = g(), proves the additive transitive property.
Proof.
For being ) consistent which or equivalently On both sides, by assuming logarithms that illustrate,
By dividing Equation (2) and adding Equation (3), equivalently
The fuzzy preference relation P = g(), being affirms
Undoubtedly, summarizing P = g() proves the additive transitive property. □
In this study, the definition of consideration is as follows:
Definition 2.
A reciprocal additive CFPR ) is consistent if
4.3. Additive Transitive Consistency of the Fuzzy Preference Relations
In the following, this study utilized additive consistency, referring to the consistency for fuzzy preference relations on the additive transitive property.
Proposition 3.
For a reciprocal fuzzy preference relation), the equivalent declaration is stated:
Proposition 4.
A fuzzy preference relation) is consistent if and only if
Proposition 5.
For a reciprocal additive fuzzy preference relation P = (), given Equation (8) is hold, the equivalent declaration is stated:
5. Framework and Influential Criteria to Implement a Revitalization Strategy (RS) for the Hospitality Industry in Taiwan
5.1. The Framework and Evaluated Criteria in Case Study Model
A total of 16 questionnaires were conducted with nine managers, two owners, two scholars, two employees, and one councilor who have all been involved in the hospitality field for more than ten to forty years and all of whom possess a fundamental understanding of the real impact of the pandemic described. A practical decision-making model was proposed to demonstrate how to guide industries during this crisis to relevant government authorities. Evaluators identified criteria and attributions to be conducted as follows: financial aid; employment assistance; tax breaks; infrastructure facilities; utilities discount; innovation and transformation; market revitalization; and, COVID-19 prevention measures. An analytical hierarchy framework based upon eight influential criteria was illustrated, as shown in Figure 2 [16,28,33].
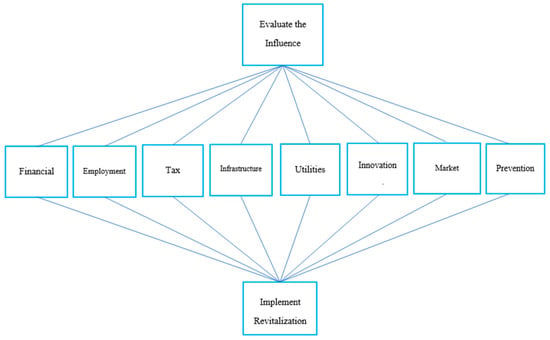
Figure 2.
The analytical hierarchy framework of this study. Source: The authors’ own drawing.
On 25 February 2020, the Taiwanese Executive Yuan announced a three-pronged plan of prevention measures, relief industry, and stimulus economy to meet the COVID-19 pandemic’s significant impact on the global political, socio-cultural, and economic systems [18]. Influential criteria not only followed the government’s policies and actions but were also derived from professional investigation and consultation along with the sixteen evaluators involved in this study’s survey.
Eight key influential criteria were yielded, as provided below [28]:
- C1—Financial aid. The government provides financial assistance to industries and employees with a total relief package of NT$1.05 trillion in stimulus loans and operational aid for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). The authority not only allows generous interest subsidies, lenient processing of returned checks and reducing interest to SME, but also provides relief loans to workers [28].
- C2—Employment assistance. Employees are furloughed and supplemental employee salaries and subsidies are available while also encouraging employees to undergo training during the pandemic. Moreover, the government not only provides usual unemployment payments for employees but also subsidizes compensation to companies for hiring the unemployed [13].
- C3—Tax breaks. Small businesses are automatically exempted from tax payments from reported sales revenue. Tax deadlines and government-provided subsidies allow taxpayers and employers to postpone payment of taxes or to pay through installments [24].
- C4—Infrastructure facilities. This includes the public markets and the basic projects subsidized by the government to help industry innovation and transformation. The government has expanded facilities for improvement and allowed project development to be advantaged in order to improve safe and sanitary conditions in public facilities. Business districts, public markets and regulated night markets have assisted with environmental disinfection, and have enhanced the usable space [15].
- C5—Utilities discount. Companies have experienced a 15% reduction in revenue for two consecutive months, as compared with last year, with the water fee discount being 5% and the monthly limit reduced by NT$5000. For electricity costs, users not only receive a 10% discount and the monthly limit is reduced by NT$100,000 but contractual capacity and basic electricity fees charged within the past two years are reduced as well [2].
- C6—Innovation and transformation. Public industry associations connect counties and municipal governments that integrate relevant government assistance resources to serve as a one-stage-service platform. Attention is given to simplify and improve the efficiency of administrative procedures for industry. Innovative subsidies related to industrial products, services, and technology to increase market occupancy and competitive have been the primary focus. In addition, diversified exhibitions have invited international purchasers to Taiwan to stimulate and increase consumption, and to assist industry revitalization, transformation and upgrading [13,34].
- C7—Market revitalization. After the pandemic has stabilized, various promotional and stimulus measures are to be taken, such as triple stimulus vouchers subsided by the government for every citizen to stimulate consumption in domestic-demand industries, especially regarding retail department stores, hotels, restaurants, night markets, traditional markets, conventions and exhibitions, shopping malls, etc. [3,34].
- C8—COVID-19 prevention measures. Taiwan Centers for Disease announced COVID prevention measures to the public in requiring face masks, social distancing, temperature checking and ethanol hand washing before entering public facilities, hotels, restaurants and public transportation venues. COVID-19 prevention measures could contribute significantly to the observed decline in infection rates [26,27].
5.2. The Hierarchy Analytical Process for Evaluating the Influence of Criteria
5.2.1. Linguistic Variables
The study compares pairs of criteria by utilizing representation as follows: “Absolutely important (AB)”, “Very strongly important (VS)”, “Strongly important (ST)”, “Moderately important (MO)”, “Equally important (EQ)”, and by applying a nine-level scale with numbers denoted by real scores (see Table 1).

Table 1.
Influential criteria in linguistic terms for priority weights.
5.2.2. Reciprocal Additive Consistent Fuzzy Preference Relations for Weighting the Influential Criteria
Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) is a traditional decision-making method [35], and it is initially applied to resolve problems by the illustration of a hierarchical model. The AHP method requires a questionnaire model for each cluster of n-criteria pairwise comparison to be made in a preference matrix that contains many questions and comparisons. Due to analytic efficiency, this study utilizes the reciprocal additive CFPR that establishes computational simplicity by only requiring n − 1 comparisons for a number of n criteria. The procedures for establishing the reciprocal additive CFPR for prioritizing the evaluation criteria are given below [36].
The study established pairwise comparison matrices for n criteria (, i = 1, 2, …, n) in a dimension of a hierarchical system. Evaluators (, k = 1, 2, …, m) presented the essential data of each pair of criteria for a number of n − 1 preference values as below:
where indicates the preference intensity regarding influential criteria i and j as compared by evaluator k, = 1 represents indifference of influential criteria i and j, evidence that criteria i is comparatively essential to criteria j, and denotes that influential criteria i is less essential than criteria j. The symbol “” represents preserved , which has been denoted via opposite comparison [37].
- Conversion of preference value into utilizing an interval scale follows, resulting in the preserved relying on the reciprocal transitivity property gives:
The absolute value of the maximum positive score or minimum negative score can be minus one in the preference decision matrix [39,40,41].
- 2.
- The evaluators’ opinions can aggregate weights of influential criteria. Moreover, let indicate transforming the fuzzy preference score of evaluator k for evaluating criteria i and j. This study obtained integral values of m evaluators by applying the symbol of the average score [42], viz.:
- 3.
- The aggregated fuzzy preference relations matrices by normalizing is utilized to refer to the normalized fuzzy preference scores of every criterion, namely
Utilizing represents the average priority weight of influential criteria, that n denotes the number of influential criteria, and the priority of each criterion can be defined, such as
6. Empirical Illustration and Discussion
6.1. Empirical Illustration
The study demonstrates the revitalization strategy used in Taiwan as an exemplification to illustrate the framework. Questionnaires reflecting linguistic variability, as seen in Table 1, were sent to 16 evaluators in order to investigate the actual situation affecting the hospitality sector during the COVID-19 outbreak. Eight influential criteria were synthesized via survey with the evaluation representatives indicated. The pairwise comparisons utilized computational analysis in obtaining priority weights to evaluate how the Taiwanese government applied accurate SR to assist the hospitality sector during the time of the global crisis.
- According to the interviews with the 16 evaluators that indicated the essential eight influential criteria, Table 2 shows pairwise comparison matrices from a number of n − 1 adjacent criteria into the parallelism scores [38].
As seen in Table 2, evaluators indicate values for a set of criteria, such as the value ( representing the preference level of the first criterion () when compared with a second criterion (). Suppose is the ratio scale with 1–9 scales of criteria, when = 1 indicates the equivalence between and , while = 9 indicates that is absolutely preferred to , whereas = is a reciprocal value representing as being absolutely preferred to . For example, in Table 2, in terms of linguistic variables, = represents that is of very strong importance compared to [35].


Table 2.
Preference relation matrix for pairwise comparison of the criteria.
Table 2.
Preference relation matrix for pairwise comparison of the criteria.
| Evaluators | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E1 | E2 | E3 | E4 | E5 | E6 | E7 | E8 | E9 | E10 | E11 | E12 | E13 | E14 | E15 | E16 | ||
| 1/7 | 1 | 1/3 | 1/3 | 1 | 1/9 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 1/5 | 1/7 | 1/4 | 1 | 5 | 7 | 1 | ||
| 1/5 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 9 | 3 | 1/7 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 7 | 1/5 | 1/5 | 7 | 4 | ||
| 9 | 7 | 1/5 | 1/3 | 5 | 7 | 1/3 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 1/3 | 1/6 | 3 | 3 | 1/3 | ||
| 1/9 | 1/8 | 1/5 | 3 | 1/5 | 1/7 | 1/7 | 1/5 | 1/3 | 3 | 7 | 4 | 1 | 1/5 | 1/3 | 3 | ||
| 8 | 1 | 1 | 1/3 | 1/3 | 1/7 | 7 | 1/9 | 1/3 | 1/7 | 1/8 | 1/7 | 8 | 1/3 | 1/7 | 1/5 | ||
| 1/2 | 1/2 | 1 | 1/5 | 1/7 | 1/5 | 1/9 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 1/6 | 2 | 1/8 | 1/7 | 1/5 | 1 | ||
| 9 | 1 | 5 | 3 | 1/5 | 7 | 7 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 7 | 4 | 6 | 7 | 1/5 | 1 | ||
- 2.
- The appraisal of evaluator 1 (E1) can serve as an instance, see Table 3. The linguistic terms may be transformed into parallelism scores.
 Table 3. Interval pairwise comparisons of the criteria.
Table 3. Interval pairwise comparisons of the criteria.
- 3.
- Transform the elements by applying Equation (2) (listed in Table 3) into an interval [0, 1], with the illustration providing the following:
The evaluation score can be calculated by applying Equations (1) and (11) with being utilized, for instance:
The CFPR matrix for the eight influential criteria as determined by evaluator 1 is shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
CFPR matrix of criteria E1.
Table 4 lists , , ,,,,, elements not found in the interval [0, 1]. Therefore, Equation (13) states a linear transformation applied to confirm the reciprocity and additive transitivity for the preference relations matrix (see Table 5).

Table 5.
Linear solution for transformation matrix of criteria.
- 4.
- The calculated procedures illustrate the fuzzy preference relation matrices of another 15 evaluators; moreover, the aggregated pairwise comparison matrix of 16 evaluators is acquired by utilizing Equation (14), as listed in Table 6.
 Table 6. Aggregated pairwise comparison matrices of 16 evaluators.
Table 6. Aggregated pairwise comparison matrices of 16 evaluators.
Equation (15) is utilized to normalize the aggregated pairwise comparison matrix. Taking as an example:
The priority weight and rank of every influential criterion by 16 evaluators are acquired by applying Equation (16), as indicated in Table 7.

Table 7.
Normalized matrix of priority weight and rank of influential criteria.
The ranks of the influential criteria weights are substituted as:
6.2. Discussions
Using the CFPR model has far more advantages than using the traditional AHP method. Initially, the CFPR method can not only reduce the set of questions, but CFPR can effectively decrease pairwise comparison frequency. For example, utilizing the traditional AHP method requires preparing and answering = = 28 questions where inconsistency is likely to occur through comparison while using CFPR requires only preparation, and the answer n − 1 for just seven questions. Secondly, computational simplicity is applied in order to provide a relative weight of each of the influential criteria by utilizing the CFPR method. Thirdly, as a consequence of the COVID-19 outbreak, governments, organizations, and industries should make appropriate strategic decisions objectively and rapidly while utilizing CFPR for decision matrices, thereby guaranteeing consistency in the decision-making procedure [17,42].
7. Results
The results are shown in Figure 3. The primary four assessment attributes are as follows: market revitalization (0.1620), innovation and transformation (0.1416), COVID-19 prevention measure (0.1332), and employment assistance (0.1229). Meanwhile, the four least important attributes are as follows: utility discounts (0.1197), tax breaks (0.1192), financial aid (0.1082), and infrastructure facilities (0.1025).
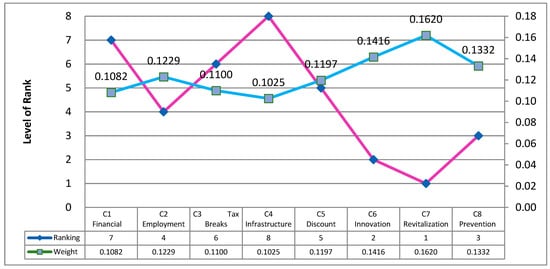
Figure 3.
Rank of priority weight and influential criteria of evaluators.
According to Figure 3. the ranking of the main criteria is > > > > > > > C4, which reveals the opinions of experts in the hospitality field. The results indicate that “market revitalization” (criterion ) is considered as the most essential/important criteria for RS. The market revitalization included some stimulus actions, such as the Taiwanese government’s implementation of various stimulus vouchers and coupons to encourage market consumption and revitalize the overall economy in the form of triple-stimulus vouchers. The second important criterion is “innovation and transformation” (criterion ) that involves the support of new technology, services, and marketing of innovative training opportunities subsidized by the government. The COVID-19 pandemic has intensified the role of innovation in the recovery, re-shaping, and re-imagining of hospitality. Innovational trends and the adoption of the latest technologies and services can benefit the economy and create a transformation in the hospitality industry [18]. Of tertiary importance is” COVID-19 prevention measure” (criterion ), which presents that effective government measures in the pandemic promote public confidence in economic agencies beneficial for the recovery of the economy [13]. Moreover, the fourth-place criterion is “employment assistance” (criterion ). Some current research on the impact of COVID-19 on the tourism and hospitality sector indicates that for unemployed staff from different restaurants or hotels, employees were asked for unpaid leave [14,21,43], necessitating the address of a range of small-scale organizational issues related to employee challenges [44]. “Utilities discount” (criterion ) and tax breaks (criterion ) involved in government subsidies were seen as less important criteria. The last criterion to be considered is “infrastructure facilities and environmental improvement” (criterion . This study determined an interesting phenomenon in that “financial aid” (criterion ) is of second-to-last importance. Sigala [18] indicated the COVID-19 outbreak had an enormous international economic impact leading to the largest decline in the history of the modern hospitality industry, and it became the epicenter of all international discussions [14,23,24,34]. Some evaluators who are in executive positions indicated that the application process to obtain financial aid procedures was too complex, leading many SMEs to give up on this course of action entirely. Financial aid for the hospitality industry will become a future research issue to be addressed from different dimensional characteristics of the hospitality industry, the strategy of implementation, and what the industry will require for eventual relief.
8. Conclusions
In Taiwan, the government has adopted a zero-tolerance policy regarding the COVID-19 outbreak. The results indicate that “market revitalization” is considered the most essential/important criteria for RS under a zero-tolerance policy regarding the COVID-19 outbreak. The contribution of this paper lies in the use of expert interviews and the CFPR technology to explore the industry’s preference order for policy measures and to provide the government with a reference for the revitalization of hospitality.
This study presents the CFPR method to evaluate the influential criteria in an RS for the hospitality industry, including expert surveys and interviews. This selected method makes it simple to construct multi-criteria decision matrices and evaluate the essentialness of every criterion for government strategies or actions to take place [37]. The efficient strategies or actions can be directly evaluated by calculating expert scores into priority weights, with the procedure of computation becoming both practical and popular. The ranking results could provide significant analysis data to governments and decision-makers of organizations for purposes of RS in future implementation [17].
Furthermore, whether the hospitality industry will accept governmental assistance still depends on the revitalization strategies yet to be implemented, the relative convenience of procedures and services, and the nature of business encouragement policies. The government should premeditate several aspects for formulated actions or policies. The popularization and development of industry demand should show powerful and unequivocal support from the government. In this study, only 16 experts’ opinions were collected to evaluate and confirm the concept model. In reality, real industrial perspectives and expectations are essential to enhance strategic effectiveness, and such preferences would be more accurate in estimating the model during the crisis [23,45]. Furthermore, the sample of evaluators should be enlarged in future works to acquire more instructive results. Promoting the success of the RS had some obvious implementations. According to Wang and Hsieh [44], several methods may be used to promote the governmental decision-making process, with the conclusion as follows [22]:
- Nurture an awareness of potential crises that may inflict economic harm;
- Establish a priority-setting process during a crisis;
- Identify influential factors from expert opinions that reflect real needs for different industries;
- Determine the accuracy, urgency, and relevance of revitalization strategy implementation policies;
- Supervise disaster control to make accurate decisions to pilot industry-recall of a product or the shutdown of a system;
- Mobilize and utilize resources or methods to deal with critical impact effectively and objectively;
- Promptly notify and then provide support for one-stage-services of critical industrial demand to deal with the coronavirus pandemic outbreak or similar events; and,
- Establish a governmental “hotline” for the public, industry, media, and private individuals to announce the transparency situation of the COVID-19 outbreak.
9. Limitations and Future Research
The study’s findings and contributions, and limitations are demonstrated for further research. Initially, the study was illustrated in a continuous pandemic with the hospitality sector being seriously impacted. In Taiwan, due to the COVID-19 epidemic, a large number of hospitals were closed under the government’s zero-tolerance policy. However, the path taken by Europe and the United States is to coexist with the virus, but it has also caused more infections and deaths. Therefore, the government’s attitude towards the epidemic may also affect the industry’s assessment of the importance of policy implementation. In future research, we can explore the importance of relevant policies in the face of differences in government policies on disease control. Secondly, the study provides an overview of Taiwan’s hospitality situation. Further research should focus on exploring the comparison of different sizes and types of industries or countries. Thirdly, regarding the prevention measures of social distancing, the study conducted a survey of 16 evaluators; subsequently, the sample could be enlarged to enhance the level of reliability and validity. Fourthly, the COVID-19 pandemic has continuously impacted several countries; nevertheless, uncertainty concerning surroundings and questions regarding RS implementation continue to prevail regarding the best RS m implementation strategy. The essentialness of RS as a mechanism is paramount for hospitality stakeholders to sustain or create competitive performance advantages in the future.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.-C.H., J.-Y.L. and T.-C.W.; methodology, H.-C.H., J.-Y.L. and T.-C.W.; software, H.-C.H. and T.-C.W.; validation, H.-C.H., J.-Y.L., C.-Y.H. and T.-C.W.; formal analysis, H.-C.H.; investigation, H.-C.H. and C.-Y.H.; resources, H.-C.H.; data curation, H.-C.H., C.-Y.H. and X.-H.N.; writing—original draft preparation, H.-C.H.; writing—review and editing, H.-C.H., J.-Y.L., C.-Y.H. and T.-C.W.; visualization, X.-H.N. and C.-Y.H.; supervision, J.-Y.L. and T.-C.W.; project administration, J.-Y.L. and T.-C.W.; funding acquisition, non. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wang, T.-C.; Hsieh, H.-C. Crisis Management in Tourism Industry. Int. J. Bus. Manag. Res. 2016, 6, 97–102. [Google Scholar]
- Tsionas, M. COVID-19 and Gradual Adjustment in The Tourism, Hospitality, and Related Industries. Tour. Econ. 2020, 27, I828–I832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, S.; Supard, S. Revitalization Strategy for Small and Medium Enterprises after Corona Virus Disease Pandemic (COVID-19) in Yogyakarta. J. Xi’an Univ. Archit. Technol. 2020, 7, 4068. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Kamarudin, K.M.; Liu, Y.; Zou, J.; Zhang, J. Developing a Behavior Change Framework for Pandemic Prevention and Control in Public Spaces in China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, P.-S.; Lee, J.-Y. Analysis of Taiwan’s Mask Collection and Plan Evasion during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Pietro, M.; Marattin, L.; Minetti, R. Fiscal Policies Amid a Pandemic: The Response of Italy to the COVID-19 Crisis. Natl. Tax J. 2020, 73, 927–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria-e-Castro, M. Fiscal policy during a pandemic. J. Econ. Dyn. Control. 2021, 125, 104088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, A.; Chaurasia, R. Emerging Technologies and Global Pandemic. In Global Pandemic and Human Security; Shaw, R., Gurtoo, A., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 367–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, M.L.; Tran, T.P.T.; Ha, H.M.; Bui, T.-D.; Lim, M.K. Sustainable Industrial and Operation Engineering Trends and Challenges Toward Industry 4.0: A Data Driven Analysis. J. Ind. Prod. Eng. 2021, 38, 581–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fettermann, D.C.; Cavalcante, C.G.S.; de Almeida, T.D.; Tortorella, G.L. How Does Industry 4.0 Contribute to Operations Management? J. Ind. Prod. Eng. 2018, 35, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, T.-D.; Tsai, F.M.; Tseng, M.L.; Tan, R.R.; Yu, K.D.S.; Lim, M.K. Sustainable Supply Chain Management Towards Disruption and Organizational Ambidexterity: A Data Driven Analysis. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 26, 373–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prataviera, L.B.; Creazza, A.; Melacini, M.; Dallari, F. Heading for Tomorrow: Resilience Strategies for Post-COVID-19 Grocery Supply Chains. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, L.; Law, R.; Ye, B. Outlook of Tourism Recovery Amid an Epidemic: Importance of Outbreak Control by the Government. Ann. Tour. Res. 2020, 86, 102951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, W.; Haque, A.; Anis, Z.; Ulfy, M. The Movement Control Order (MCO) for COVID-19 Crisis and its Impact on Tourism and Hospitality Sector in Malaysia. Int. Tour. Hosp. J. 2020, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Noble, J. Competition Law in Times of Crisis-Tackling the COVID-19 Challenge: A Producer Perspective. J. Antitrust Enforc. 2020, 8, 293–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.-C.; Chang, T.-H. Application of Consistent Fuzzy Preference Relations in Predicting the Success of Knowledge Management Implementation. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2007, 182, 1313–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Guo, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, C.; Wang, W. Analyzing the Effectiveness of Policy Instruments on New Energy Vehicle Industry using Consistent Fuzzy Preference Relations. Int. Rev. Spat. Plan. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 4, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sigala, M. Tourism and COVID-19: Impacts and Implications for Advancing and Resetting Industry and Research. J. Bus. Res. 2020, 117, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis Towers Watson. Global Crisis Human Capital Road Map: Responding to the COVID-19 Pandemic Managing Through the Crisis; Willis Tower Waston: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- United Nation World Tourism Organisation. 2020. Available online: http://www.world-tourism.org/projects/projects.htm (accessed on 10 July 2016).
- Higgins-Desbiolles, F. Socialising Tourism for Social and Ecological Justice after COVID19. Tour. Geogr. 2020, 22, 610–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Y.; Goh, E.; Wen, J. The Effects of Misleading Media Reports about COVID19 on Chinese Tourists’ Mental Health: A Perspective Article. Anatolia 2020, 31, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zenker, S.; Kock, F. The Coronavirus Pandemic—A Critical Discussion of A Tourism Research Agenda. Tour. Manag. 2020, 81, 104164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaha, A.U.; Safria, S.N.; Thevadasb, R.; Noordinc, N.K.; Rahmand, A.A.; Sekawie, Z.; Ideris, A.; Sultan, M.T.H. COVID-19 Outbreak in Malaysia: Actions Taken by the Malaysian Government. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 97, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taiwan Centers for Disease Control. Taiwan Centers for Disease Control. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov.tw/.en (accessed on 26 July 2020).
- Ministry of Foreign Affairs. How Taiwan Can Turn Coronavirus Victory. Available online: https://foreignpolicy.com/2020/06/01/taiwancoronavirus-pandemic-china-economy-technology/ (accessed on 25 June 2020).
- Galvin, J.C.; Li, Y.-C.; Malwade, S.; Syed-Abdul, S. COVID-19 Preventive Measures Showing an Unintended Decline in. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 98, 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Economic Affairs. Taiwan’s COVID-19 Relief Plan. Available online: https://english.ey.gov.tw/News3/9E5540D592A5FECD/09d1d995-fe7f45b8-89ee-6a42d279a280 (accessed on 25 June 2020).
- Department of Statistic. The Statistic of Restaurant Sales Index and Annual Change Rate from May 2019 to 2020. 2020. Available online: http://www.moea.gov.tw/mns/dos/bulletin/bulletin.aspx?kind=8&html=1&menu_id=6727 (accessed on 18 July 2020).
- Herrera-Viedma, E.; Herrera, F.; Chiclana, F.; Luque, M. Some Issues on Consistency of Fuzzy Preference Relations. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2004, 154, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, F.; Herrera-Viedma, E.; Chiclana, F. Theory and Methodology Multiperson Decision-Making Based on Multiplicative Preference Relations. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2001, 129, 372–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Viedma, E.; Francisco, C.; Herrera, F.; Alonso, S. Group Decision-Making Model With Incomplete Fuzzy Preference Relations Based on Additive Consistency. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 2007, 37, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.-C.; Hsieh, H.-C.; Hsu, S.-C. Predicting the Success of Promoting a Decisionmaker’s Judgment by InLinPreRa. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Business and Management, Shenzhen, China, 7–8 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Crick, J.; Crick, D. Coopetition and COVID-19: Collaborative Business-to-Business Marketing Strategies in A Pandemic Crisis. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2020, 88, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T. The Analytic Hierarchy Process, Planning Priority Setting and Resource Allocation; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Mata, F.; Martínez, L.; Herrera-Viedma, E. An Adaptive Consensus Support Model for Group Decision-Making Problems in a Multigranular Fuzzy Linguistic Context. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2009, 17, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z. Goal Programming Models for Obtaining the Priority Vector of Incomplete Fuzzy Preference Relation. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 2004, 36, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, T.-C.; Wang, C.-N.; Nguyen, X.H. Evaluating the Influence of Criteria to Attract Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) to Develop Supporting Industries in Vietnam by Utilizing Fuzzy Preference Relations. Sustainability 2016, 8, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiclana, F.; Herrera, F.; Herrera-Viedma, E. Integrating Multiplicative Preference Relations in A Multipurpose Decision-Making Model Based on Fuzzy Preference Relations. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2001, 122, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiclana, F.; Herrera-Viedma, E.; Herrera, F.; Alonso, S. Some Induced Ordered Weighted Averaging Operators and their Use for Solving Group Decision-Making Problems Based on Fuzzy Preference Relations. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2007, 182, 383–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Viedma, E.; Alonso, S.; Chiclana, F.; Herrera, F. A Consensus Model for Group Decision Making with Incomplete Fuzzy Preference Relations. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2007, 15, 863–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, R.-J.; Chen, Y.-H. Evaluation of The Criteria and Effectiveness of Distance E-learning with Consistent Fuzzy Preference Relations. J. Adv. Transp. 2009, 36, 10657–10662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Labour Organization. International Labour Organization. 2020. Available online: Ilo.org/global/topics/coronavirus (accessed on 15 July 2020).
- Wang, T.-C.; Hsieh, H.-C. An Analysis of Diversity Management for a Diverse Workforce in the Hospitality and Tourism Industry. Adv. Manag. Sci. 2016, 5, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Tafra-Vlahović, M. Leadership in Crisis Management. In Recent Advances in Business Management and Marketing; North Atlantic University Union: Dubrovnik, Croatia, 2013; pp. 85–90. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).