Evaluation of the Stress-Shielding Effect of a PEEK Knee Prosthesis. A Finite Element Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
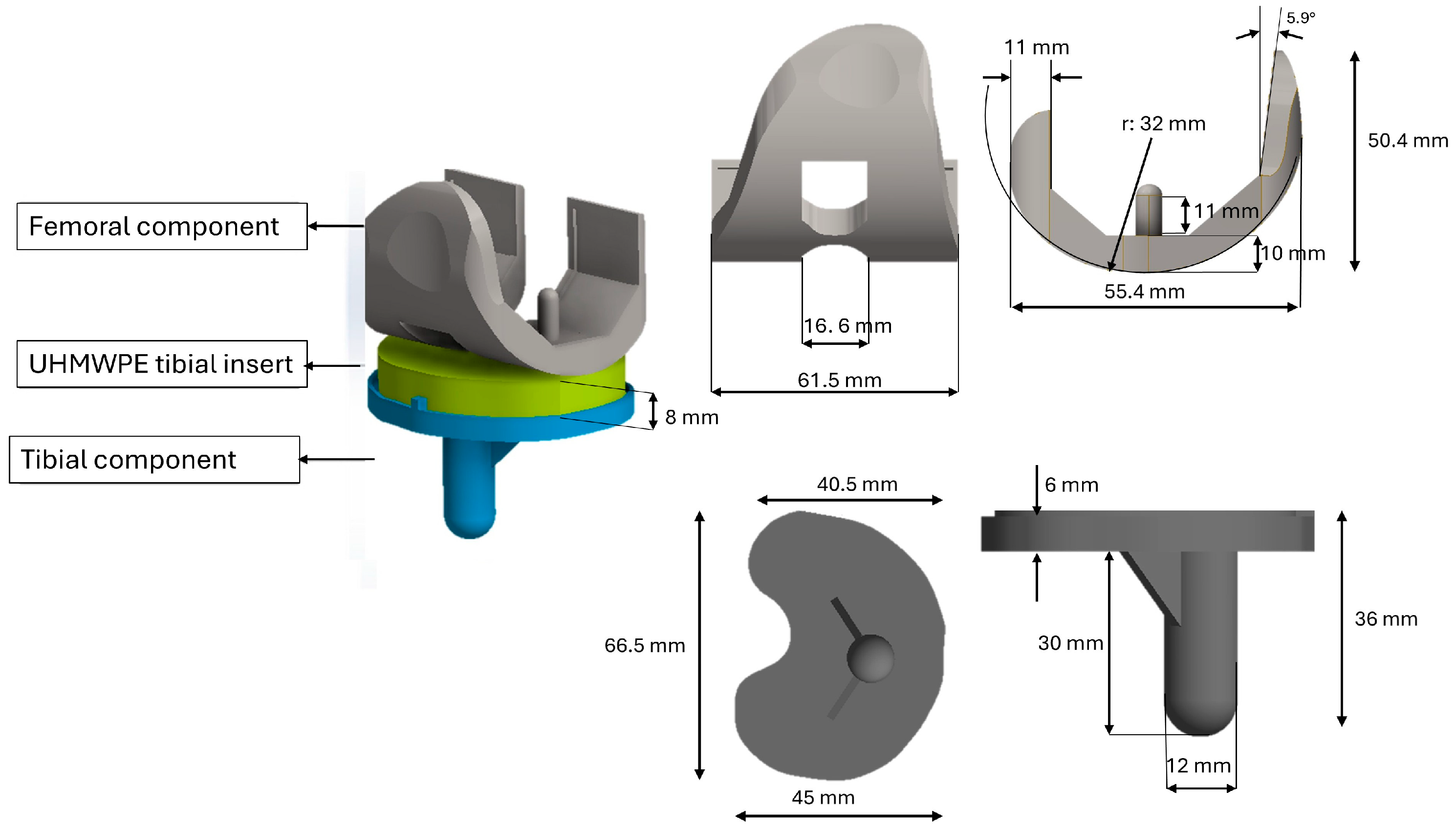
2.1. Geometries
2.2. Materials
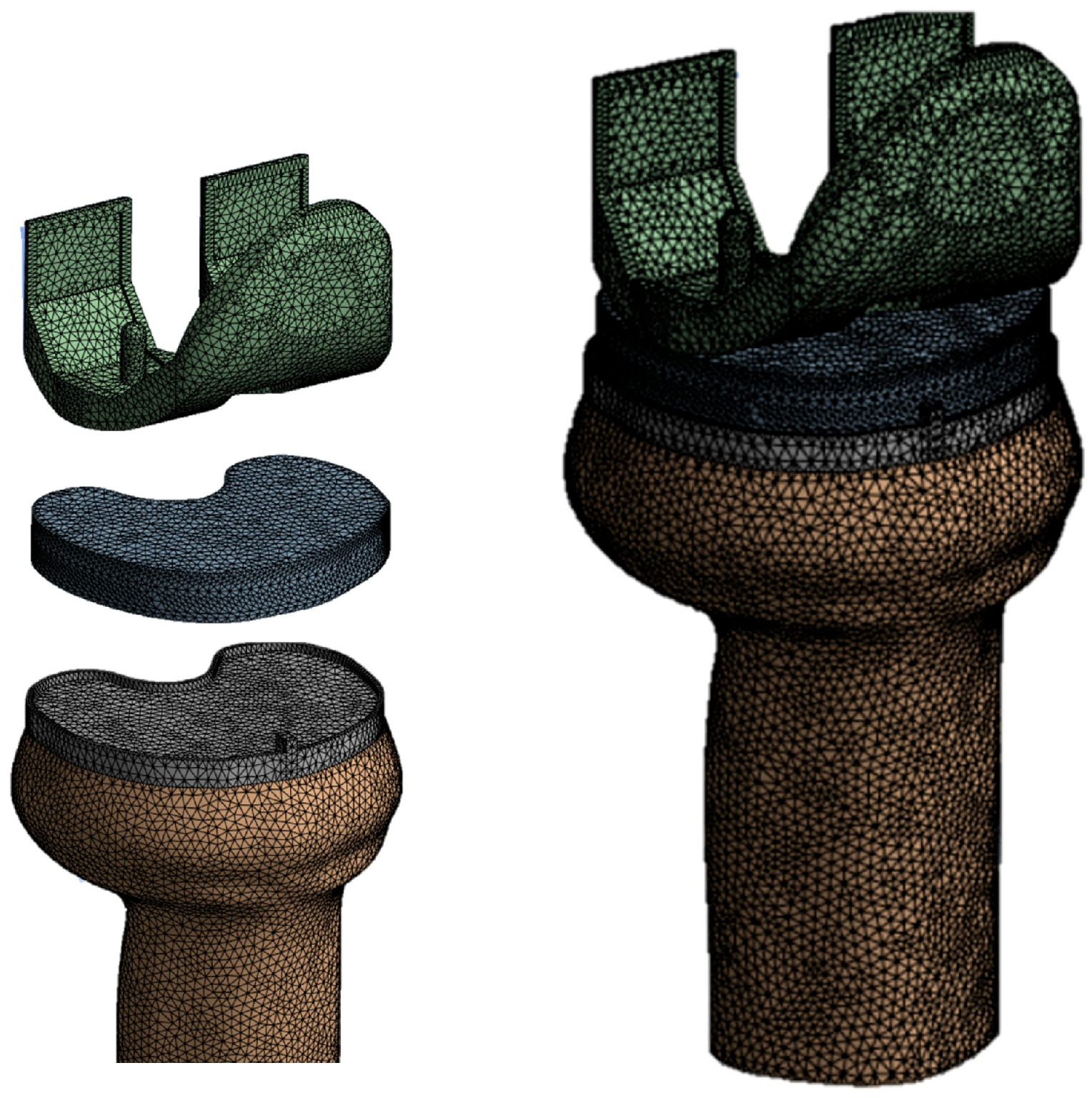
2.3. Finite Element Model
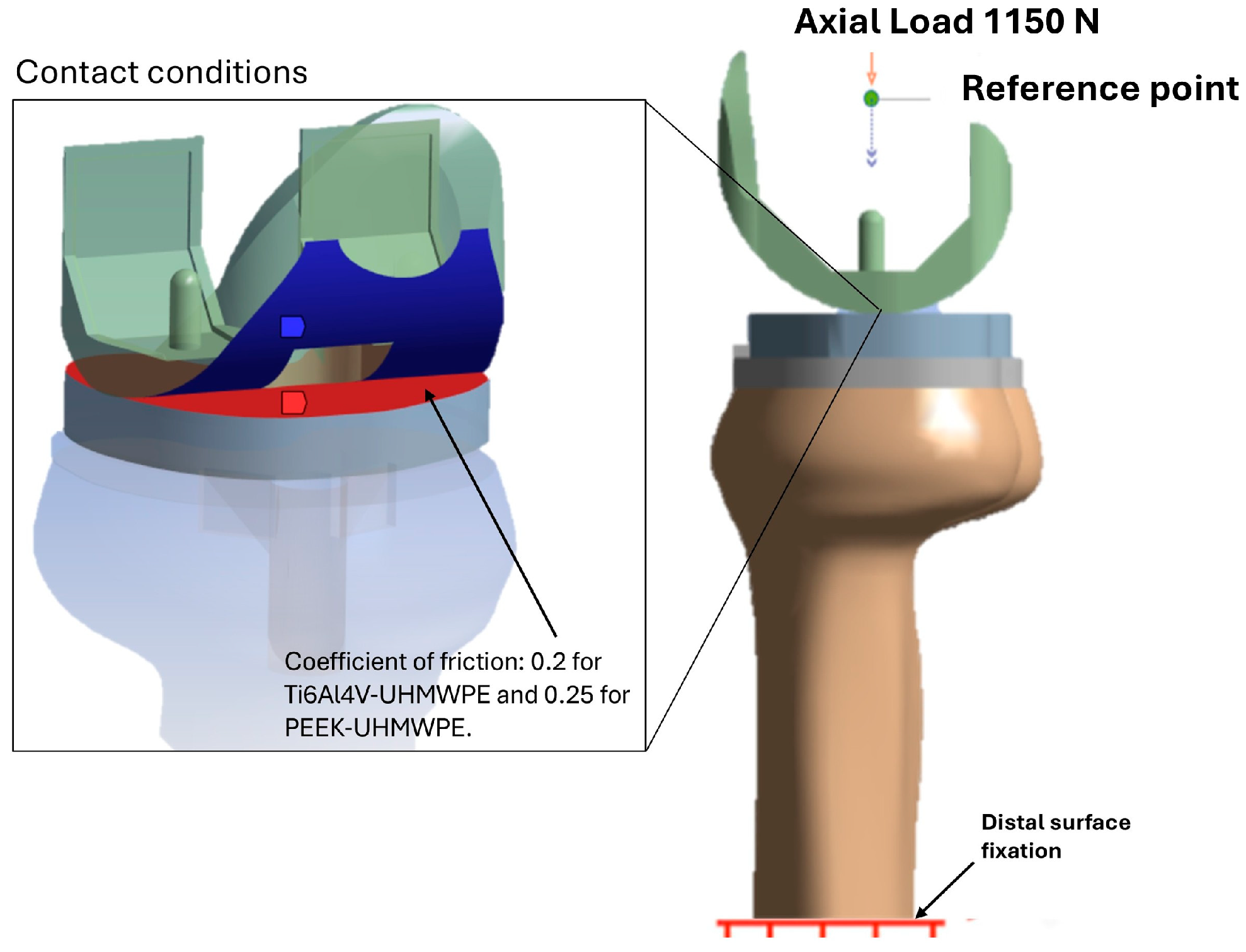
2.4. Contact, Loading, and Boundary Conditions
3. Results
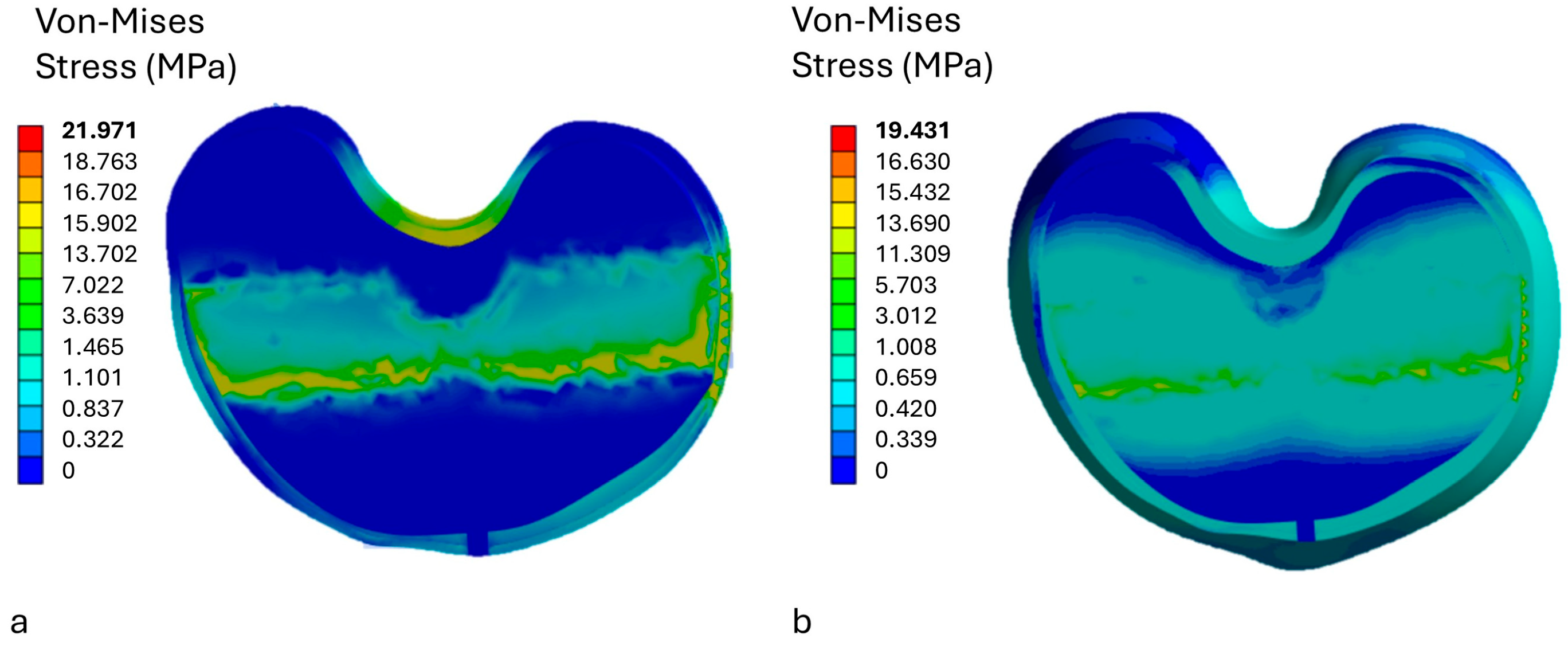
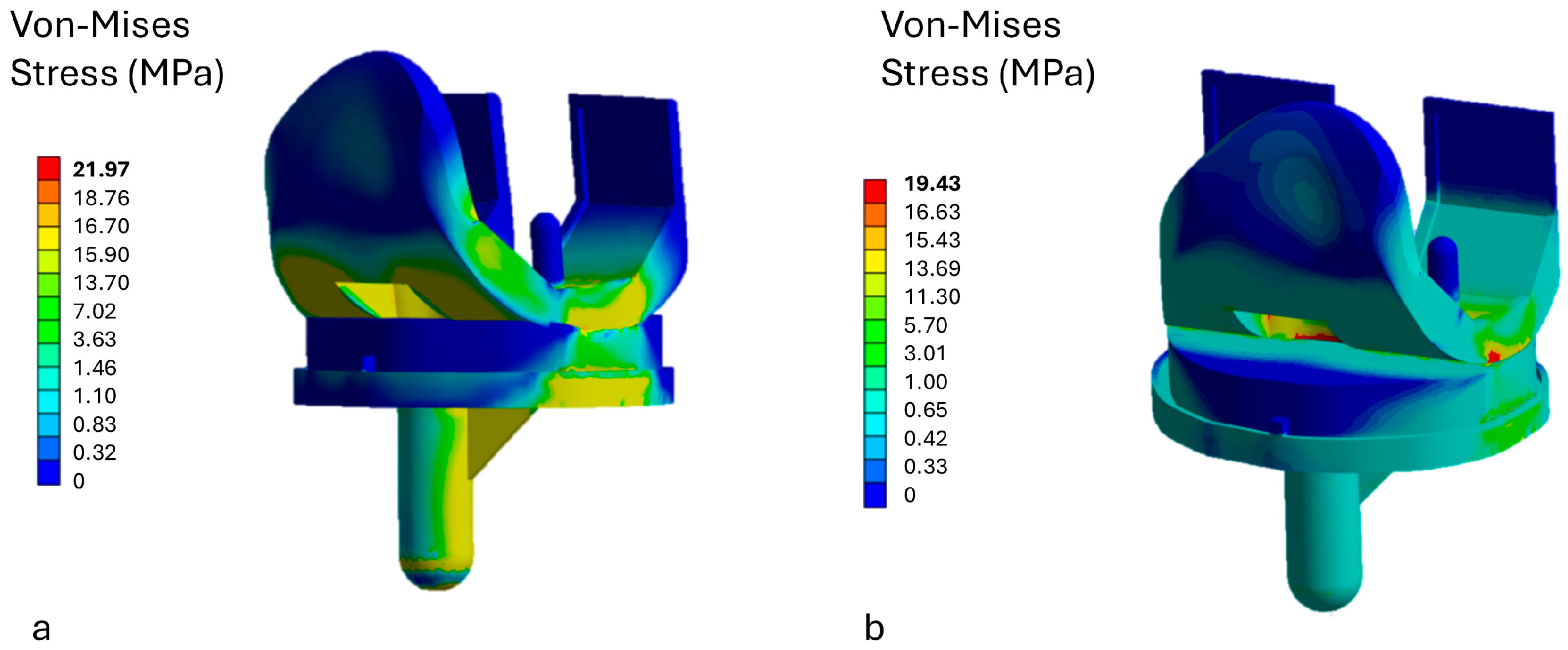
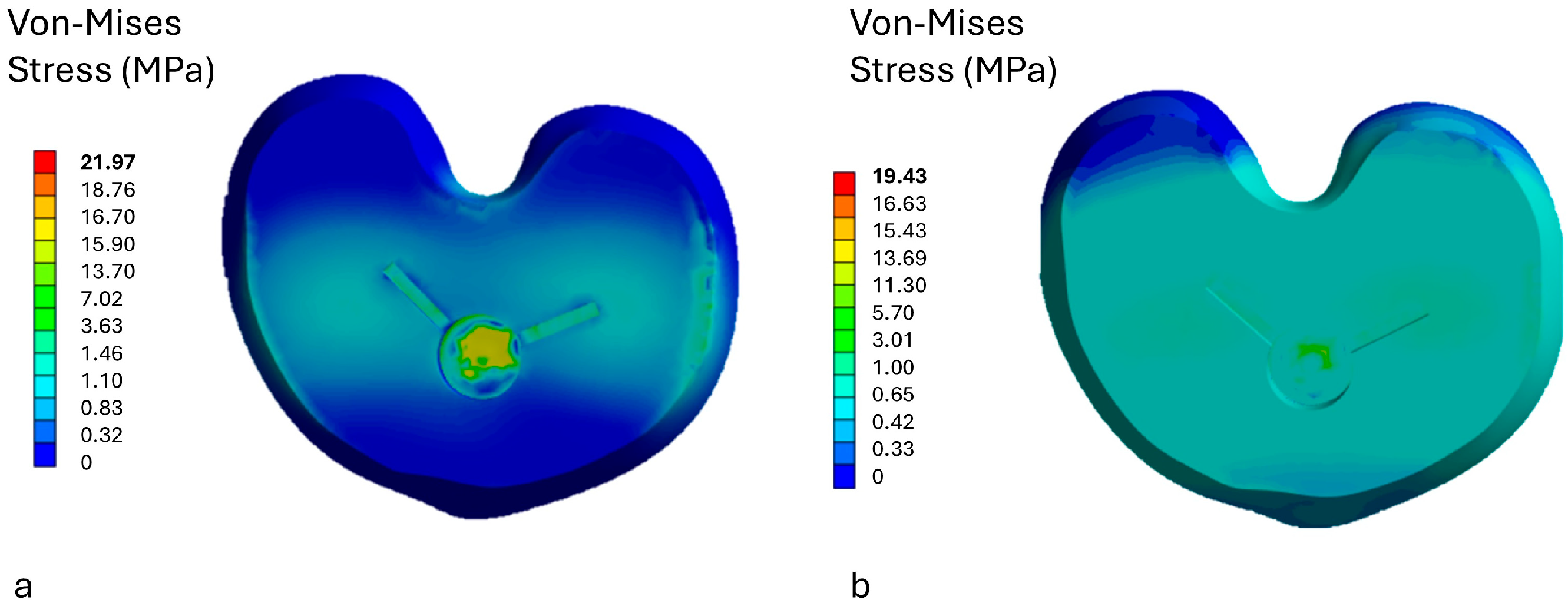
3.1. Stress Analysis on the Insert
3.2. Stress Analysis on Prosthetic Components
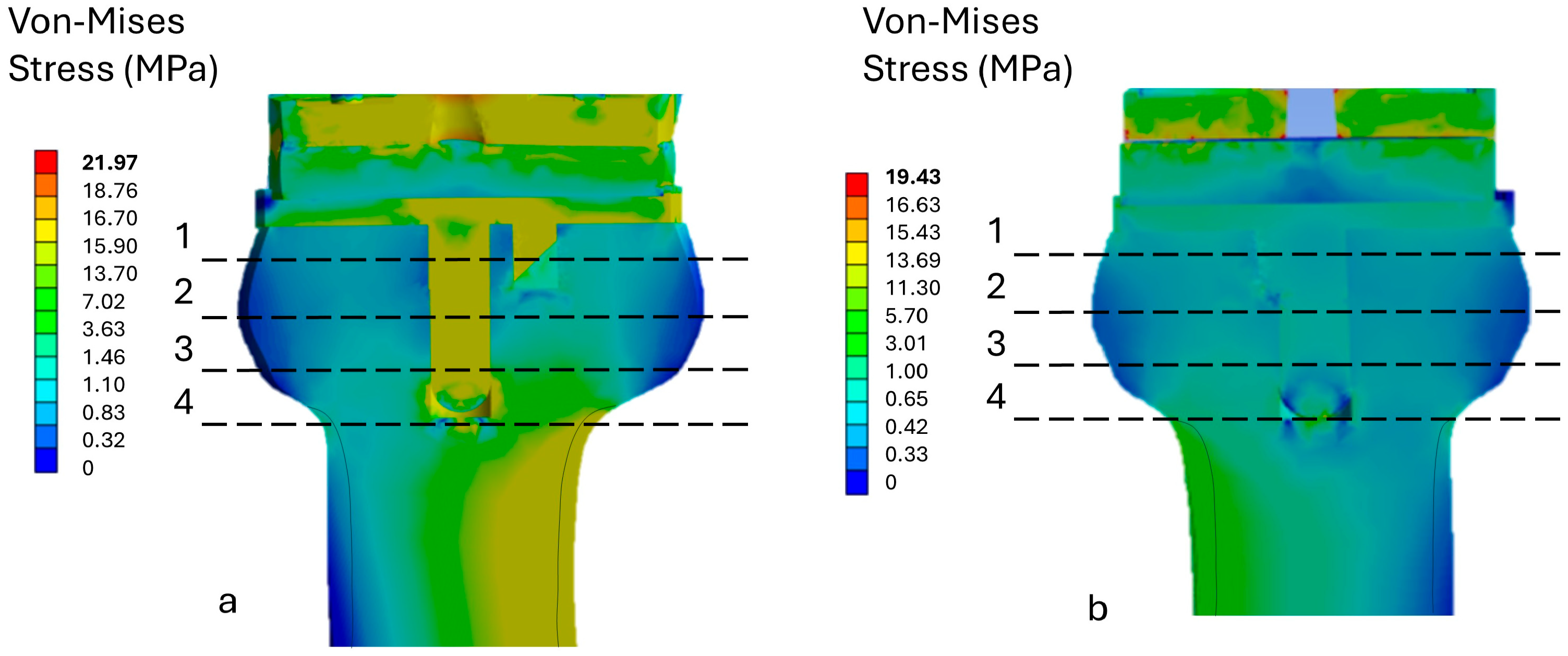
3.3. Stress Analysis on Bone
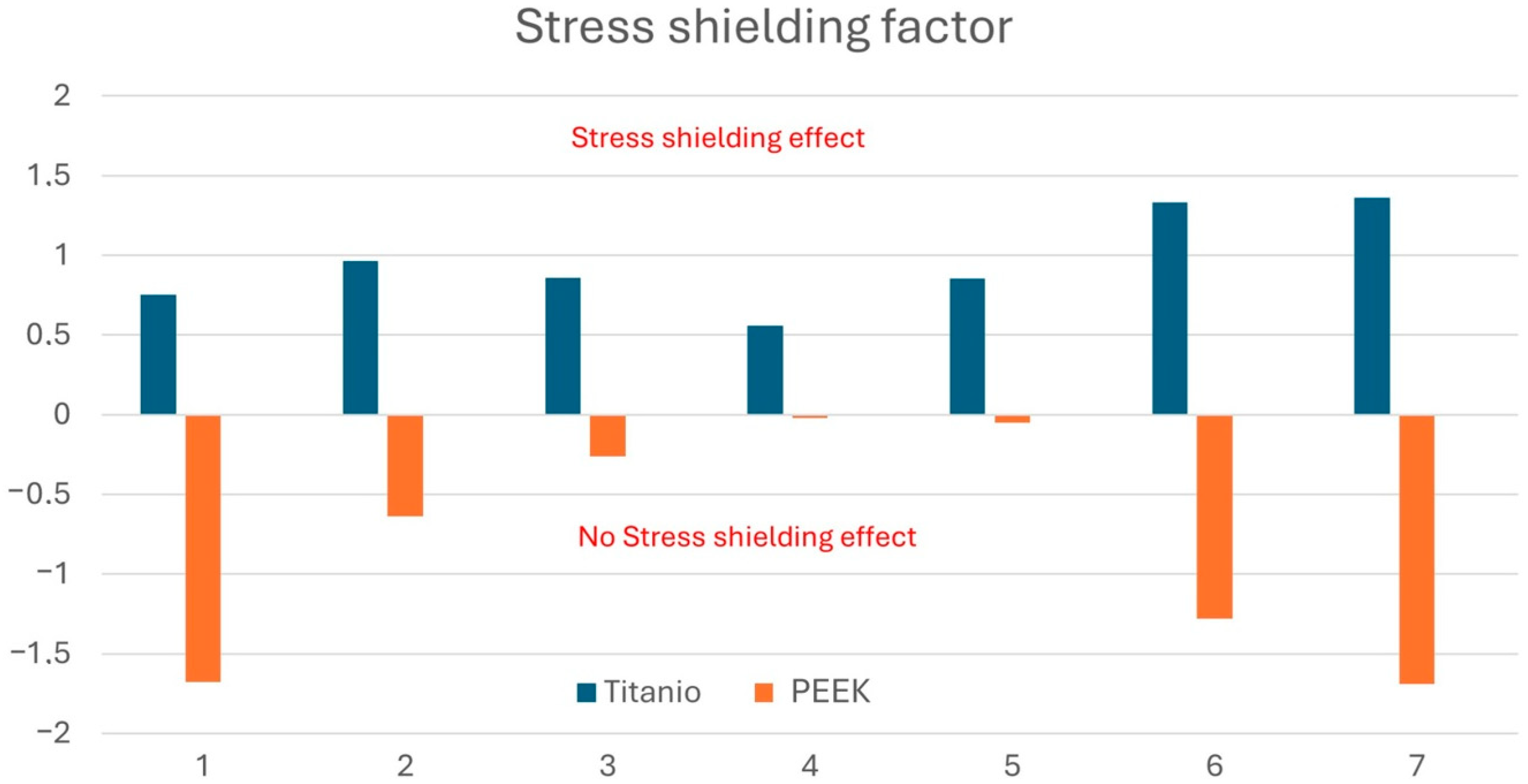
3.4. Stress Shielding Evaluation
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Konnyu, K.J.; Thoma, L.M.; Cao, W.; Aaron, R.K.; Panagiotou, O.A.; Bhuma, M.R.; Adam, G.P.; Balk, E.M.; Pinto, D. Rehabilitation for total knee arthroplasty: A systematic review. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2023, 102, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrawashdeh, W.; Eschweiler, J.; Migliorini, F.; El Mansy, Y.; Tingart, M.; Rath, B. Effectiveness of total knee arthroplasty rehabilitation programmes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Rehabil. Med. 2021, 53, 2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karasavvidis, T.; Moldenhauer, C.A.P.; Haddad, F.S.; Hirschmann, M.T.; Pagnano, M.W.; Vigdorchik, J.M. Current concepts in alignment in total knee arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2023, 38, S29–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lustig, S.; Sappey-Marinier, E.; Fary, C.; Servien, E.; Parratte, S.; Batailler, C. Personalized alignment in total knee arthroplasty: Current concepts. SICOT-J 2021, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minoda, Y. Alignment techniques in total knee arthroplasty. J. Jt. Surg. Res. 2023, 1, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rullán, P.J.; Xu, J.R.; Emara, A.K.; Molloy, R.M.; Krebs, V.E.; Mont, M.A.; Piuzzi, N.S. Major national shifts to outpatient total knee arthroplasties in the United States: A 10-year trends analysis of procedure volumes, complications, and healthcare utilizations (2010 to 2020). J. Arthroplast. 2023, 38, 1209–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carender, C.N.; Glass, N.A.; DeMik, D.E.; Elkins, J.M.; Brown, T.S.; Bedard, N.A. Projected prevalence of obesity in primary total knee arthroplasty: How big will the problem get? J. Arthroplast. 2022, 37, 1289–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huitema, G.C.; de Vries, L.M.; Verboom, T.W.; Spekenbrink–Spooren, A.; Steens, J. Patella related problems as common reason for revision of NexGen PS® total knee arthroplasty without patella resurfacing: An analysis of 5911 primary total knee arthroplasties registered in the Dutch Arthroplasty Register. Knee 2022, 34, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Xing, M.; Jiang, S.; Zou, W. Effect of intravenous dexamethasone on postoperative pain in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pain Physician 2022, 25, E169. [Google Scholar]
- Sabah, S.A.; Alvand, A.; Knight, R.; Beard, D.J.; Price, A.J. Patient-reported function and quality of life after revision total knee arthroplasty: An analysis of 10,727 patients from the NHS PROMs program. J. Arthroplast. 2021, 36, 2887–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haslhofer, D.J.; Kraml, N.; Winkler, P.W.; Gotterbarm, T.; Klasan, A. Risk for total knee arthroplasty after tibial plateau fractures: A systematic review. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2023, 31, 5145–5153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pander, P.; Fransen, B.L.; Hagemans, F.J.A.; Keijser, L.C.M. Functional outcome of total knee arthroplasty following tibial plateau fractures: A systematic review. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2023, 143, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, H.R.; Judge, A.; Murray, D.W. A comparison of the periprosthetic fracture rate of cemented and cementless total knee arthroplasties: An analysis of data from the national joint registry. J. Arthroplast. 2024, 39, 1505–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Başdelioğlu, K. Effects of body mass index on outcomes of total knee arthroplasty. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2021, 31, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.S.; Rodriguez, S.; LeBrun, D.G.; Yu, J.S.; Della Valle, A.G.; Ast, M.P.; Rodriguez, J.A. Reasons and risk factors for failed same-day discharge after primary total knee arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2023, 38, 668–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, P.L.; Campbell, D.G.; Lorimer, M.F.; Requicha, F.; W-Dahl, A.; Robertsson, O. Primary total knee arthroplasty revised for instability: A detailed registry analysis. J. Arthroplast. 2022, 37, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogalo, C.; Meena, A.; Abermann, E.; Fink, C. Complications and downsides of the robotic total knee arthroplasty: A systematic review. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2023, 31, 736–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safavi, S.; Yu, Y.; Robinson, D.L.; Gray, H.A.; Ackland, D.C.; Lee, P.V. Additively manufactured controlled porous orthopedic joint replacement designs to reduce bone stress shielding: A systematic review. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2023, 18, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garabano, G.; Rodriguez, J.; Alamino, L.P.; Pesciallo, C.A.; Del Sel, H.; Lopreite, F. Stress shielding in total knee replacements: Comparative analysis between titanium and all-polyethylene bases at 10 years follow-up. J. Orthop. 2022, 34, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Ruiter, L.; Rankin, K.; Browne, M.; Briscoe, A.; Janssen, D.; Verdonschot, N. Decreased stress shielding with a PEEK femoral total knee prosthesis measured in validated computational models. J. Biomech. 2021, 118, 110270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.W.; Kang, K.T.; Kwon, H.M.; Lee, W.S.; Yang, I.H.; Nam, J.H.; Koh, Y.G.; Park, K.K. Biomechanical effect of anatomical tibial component design on load distribution of medial proximal tibial bone in total knee arthroplasty: Finite element analysis indicating anatomical design prevents stress-shielding. Bone Jt. Res. 2022, 11, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceddia, M.; Trentadue, B. Evaluation of rotational stability and stress shielding of a stem optimized for hip replacements—A finite element study. Prosthesis 2023, 5, 678–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceddia, M.; Trentadue, B.; De Giosa, G.; Solarino, G. Topology optimization of a femoral stem in titanium and carbon to reduce stress shielding with the FEM method. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceddia, M.; Solarino, G.; Giannini, G.; De Giosa, G.; Tucci, M.; Trentadue, B. A Finite Element Analysis Study of Influence of Femoral Stem Material in Stress Shielding in a Model of Uncemented Total Hip Arthroplasty: Ti-6Al-4V versus Carbon Fibre-Reinforced PEEK Composite. J. Compos. Sci. 2024, 8, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizlan, M.; Kiat, R.Y.D.; Rashid, A.H. The Fate of Coracoid Graft after Latarjet Procedure: Arthroscopic and Open Findings of Graft Union and Glenoid Remodelling. J. Coll. Physicians Surg.-Pak. JCPSP 2022, 32, 1356–1359. [Google Scholar]
- Tverier, V.M.; Chikova, T.N. Modelling of bone tissue adaptation in Ilyushin’s spaces. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2022; Volume 2317, p. 012009. [Google Scholar]
- Forlenza, E.M.; Serino, J., III; Terhune, E.B.; Weintraub, M.T.; Nam, D.; Della Valle, C.J. Cementless total knee arthroplasty is associated with early aseptic loosening in a large national database. J. Arthroplast. 2023, 38, S215–S220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.; Chen, Y. Comprehensive evaluation of risk factors for aseptic loosening in cemented total knee arthroplasty: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Exp. Orthop. 2024, 11, e12095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levent, A.; Suero, E.M.; Gehrke, T.; Citak, M. Risk factors for aseptic loosening after total knee arthroplasty with a rotating-hinge implant: A case-control study. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2021, 103, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savio, D.; Bagno, A. When the total hip replacement fails: A review on the stress-shielding effect. Processes 2022, 10, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seechaipat, T.; Rooppakhun, S.; Phombut, C. Finite Element Analysis of Contact Stress Distribution on Insert Conformity Design of Total Knee Arthroplasty. Int. J. Online Biomed. Eng. 2022, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahjavan, Y.; Naserkhaki, S.; Farahmand, F. A Parametric Study on the Geometrical Design of Augmented Cones for Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty. In Proceedings of the 2024 31st National and 9th International Iranian Conference on Biomedical Engineering (ICBME), Tehran, Iran, 28–29 November 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 372–379. [Google Scholar]
- Bendich, I.; Lawrie, C.M.; Riegler, V.; Barrack, R.L.; Nunley, R.M. The impact of component design and fixation on stress shielding after modern total knee arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2022, 37, S221–S225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbogori, M.; Vaish, A.; Vaishya, R.; Haleem, A.; Javaid, M. Poly-Ether-Ether-Ketone (PEEK) in orthopaedic practice-A current concept review. J. Orthop. Rep. 2022, 1, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghavi, S.A.; Lin, C.; Sun, C.; Tamaddon, M.; Basiouny, M.; Garcia-Souto, P.; Taylor, S.; Hua, J.; Li, D.; Wang, L.; et al. Stress shielding and bone resorption of press-fit polyether–ether–ketone (PEEK) hip prosthesis: A sawbone model study. Polymers 2022, 14, 4600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Liu, P.; Zhang, X.; Zou, X.; Mei, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, S. Strategies to improve bioactive and antibacterial properties of polyetheretherketone (PEEK) for use as orthopedic implants. Mater. Today Bio 2022, 16, 100402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Wu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Yang, L.; Xu, X.; Luo, F. Multifunctional modifications of polyetheretherketone implants for bone repair: A comprehensive review. Biomater. Adv. 2023, 154, 213607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghavi, S.A.; Lin, C.; Sun, C.; Tamaddon, M.; Basiouny, M.; Garcia-Souto, P.; Taylor, S.; Hua, J.; Li, D.; Wang, L.; et al. Enhancing distraction osteogenesis with carbon fiber reinforced polyether ether ketone bone pins and a three-dimensional printed transfer device to permit artifact-free three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2021, 32, 360–364. [Google Scholar]
- Fabris, D.; Moura, J.P.; Fredel, M.C.; Souza, J.C.; Silva, F.S.; Henriques, B. Biomechanical analyses of one-piece dental implants composed of titanium, zirconia, PEEK, CFR-PEEK, or GFR-PEEK: Stresses, strains, and bone remodeling prediction by the finite element method. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2022, 110, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shash, Y.H.; El-Wakad, M.T.; El-Dosoky, M.A.; Dohiem, M.M. Evaluation of stresses on mandible bone and prosthetic parts in fixed prosthesis by utilizing CFR-PEEK, PEKK and PEEK frameworks. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladapo, B.I.; Zahedi, S.A. Improving bioactivity and strength of PEEK composite polymer for bone application. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 266, 124485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, M.; Hu, J.; Li, G.; Wang, B.; Zhou, Z. A new strategy for PEEK-based biocomposites to achieve porous surface for bioactivity and adjustable mechanical properties for orthopedic stress matching. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2024, 177, 107909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhao, D.; Chen, W.M.; Chu, P.; Wang, S.; Zhang, C.; Huang, J.; Wang, X.; Ma, X. Finite element stress analysis of the bearing component and bone resected surfaces for total ankle replacement with different implant material combinations. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2022, 23, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Zhao, H.; Dong, E.; Kang, J.; Liu, C.; Sun, C.; Li, D.; Wang, L. Additively-manufactured PEEK/HA porous scaffolds with highly-controllable mechanical properties and excellent biocompatibility. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 128, 112333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carman, L.; Besier, T.; Stott, N.S.; Choisne, J. Sex differences in linear bone measurements occur following puberty but do not influence femoral or tibial torsion. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilczyński, M.; Bieniek, M.; Krakowski, P.; Karpiński, R. Cemented vs. cementless fixation in primary knee replacement: A narrative review. Materials 2024, 17, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagneaux, L.; Canovas, F.; Jourdan, F. Finite element analysis in the optimization of posterior-stabilized total knee arthroplasty. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2024, 110, 103765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, T.; Zheng, K.; Zhang, W.; Li, W.; Zhang, W.; Xu, Y.; Geng, D. Biomechanical and finite-element analysis of femoral pin-site fractures following navigation-assisted total knee arthroplasty. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2022, 104, 1738–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficarella, E.; Minooei, M.; Santoro, L.; Toma, E.; Trentadue, B.; De Spirito, M.; Papi, M.; Pruncu, C.I.; Lamberti, L. Visco-Hyperelastic Characterization of the Equine Immature Zona Pellucida. Materials 2021, 14, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ceddia, M.; Solarino, G.; Tucci, M.; Lamberti, L.; Trentadue, B. Stress analysis of tibial bone using three different materials for bone fixation plates. J. Compos. Sci. 2024, 8, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galas, A.; Banci, L.; Innocenti, B. The effects of different femoral component materials on bone and implant response in total knee arthroplasty: A finite element analysis. Materials 2023, 16, 5605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gefen, A. Computational simulations of stress shielding and bone resorption around existing and computer-designed orthopaedic screws. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2002, 40, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huiskes, R.I.K.; Weinans, H.; Van Rietbergen, B. The relationship between stress shielding and bone resorption around total hip stems and the effects of flexible materials. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1992, 274, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheuren, A.C.; Vallaster, P.; Kuhn, G.A.; Paul, G.R.; Malhotra, A.; Kameo, Y.; Müller, R. Mechano-regulation of trabecular bone adaptation is controlled by the local in vivo environment and logarithmically dependent on loading frequency. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 566346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, H.; Zhu, D.; Gao, J.; Lv, L.; Zhang, X. An adaptation model for trabecular bone at different mechanical levels. Biomed. Eng. Online 2010, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, T.; Sharma, G.K.; Ghosh, R. Design of functionally graded porous lattice structure tibial implant for TAR. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2024, 281, 109671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducheyne, P.A.U.L.; Kagan, A., 2nd; Lacey, J.A. Failure of total knee arthroplasty due to loosening and deformation of the tibial component. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 1978, 60, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Han, J.; Zhang, J.; Peng, Y.; Guo, L.; Chen, S.; Jin, Z. Tibial post loading increases the risk of aseptic loosening of posterior-stabilized tibial prosthesis. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H J. Eng. Med. 2024, 238, 886–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasudevan, B.; Megaraj, M.; Palanivel, A.; Durvasulu, R.; Manjunathan, K.; Dillibabu, S.P. Analysis of bone prosthesis for cementless tibal prosthesis fixation and the influence of loading condition. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing: Melville, NY, USA, 2023; Volume 2766. [Google Scholar]
- Linke, P.; Wilhelm, P.; Levent, A.; Gehrke, T.; Salber, J.; Akkaya, M.; Suero, E.M.; Citak, M. Anatomical risk factors for aseptic loosening of full hinge knee prosthesis in primary and revision TKAs. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2023, 143, 4299–4307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiyakit, P.; Ompornnuwat, K. Stress Shielding in the Proximal Tibia after Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Finite Element Analysis of 2-and 4-mm-thick Tibia Prosthesis Models. Vajira Med. J. J. Urban Med. 2022, 66, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceddia, M.; Solarino, G.; Dramisino, P.; De Giosa, G.; Rizzo, S.; Trentadue, B. Comparison of Stress between Three Different Functionally Graded Hip Stem Implants Made of Different Titanium Alloys and Composite Materials. J. Compos. Sci. 2024, 8, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azbari, Z.S.; Rad, M.R.; Nahvinejad, A.; Gilakjani, H.A.; Khorsandi, M. Biomechanical Analysis of Hip Replacement Stem Design: A Finite Element Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2022 29th National and 7th International Iranian Conference on Biomedical Engineering (ICBME), Tehran, Iran, 21–22 December 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 305–309. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, M.G.; Advani, S.G.; Miller, F.; Santare, M.H. Analysis of a femoral hip prosthesis designed to reduce stress shielding. J. Biomech. 2000, 33, 1655–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glassman, A.H.; Bobyn, J.D.; Tanzer, M. New femoral designs: Do they influence stress shielding? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2006, 453, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, K.T.; Chun, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Yeom, J.S.; Park, K.M.; Hwang, I.H.; Lee, K.I. Finite element analysis of instrumented posterior lumbar interbody fusion cages for reducing stress shielding effects: Comparison of the CFRP cage and titanium cage. Compos. Res. 2012, 25, 98–104. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, T.T.; Haines, C.M.; Uhl, R.L. Allergic or hypersensitivity reactions to orthopaedic implants. JAAOS-J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2017, 25, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benakatti, V.B.; Sajjanar, J.A.; Acharya, A. Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) in dentistry. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2019, 13, e46485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Chowdhary, R. PEEK materials as an alternative to titanium in dental implants: A systematic review. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2019, 21, 208–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Liu, Y.; Peng, B.; Chen, M.; Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; Kuang, H.; Gong, B.; Li, Z.; Sun, H. PEEK for oral applications: Recent advances in mechanical and adhesive properties. Polymers 2023, 15, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Martínez, J.; Farré-Lladós, M.; Cano-Batalla, J.; Cabratosa-Termes, J. Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) as a medical and dental material. A literature review. Med. Res. Arch. 2017, 5, 4. [Google Scholar]

| Material Properties | Cortical Osteoporotic Bone | Cancellous Osteoporotic Bone |
|---|---|---|
| Young’s modulus (MPa) | Ex = 7820 | Ex = 6252 |
| Ey = 7820 | Ey = 2.380 | |
| Ez = 11,560 | Ez = 2.890 | |
| Poisson’s ratio | ||
| Material Properties | Ti6Al4V | PEEK | UHMWPE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Young’s modulus (MPa) | E = 110,000 | E = 18,000 | E = 920 |
| Poisson’s ratio | ν = 0.3 | ν = 0.3 | ν = 0.3 |
| Mesh Element Size (mm) | von Mises Stress | Computation Time (min) |
|---|---|---|
| 3.0 | 15 MPa | 5 |
| 2.5 | 18 MPa | 8 |
| 2.0 | 22 MPa | 14 |
| 1.8 | 22.3 MPa | 22 |
| Sections | von Mises Stress (MPa) Model A | von Mises Stress (MPa) Model B |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.965 | 1.243 |
| 2 | 1.065 | 1.136 |
| 3 | 1.764 | 2.269 |
| 4 | 2.046 | 2.663 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ceddia, M.; Morizio, A.; Solarino, G.; Trentadue, B. Evaluation of the Stress-Shielding Effect of a PEEK Knee Prosthesis. A Finite Element Study. Osteology 2025, 5, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/osteology5030024
Ceddia M, Morizio A, Solarino G, Trentadue B. Evaluation of the Stress-Shielding Effect of a PEEK Knee Prosthesis. A Finite Element Study. Osteology. 2025; 5(3):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/osteology5030024
Chicago/Turabian StyleCeddia, Mario, Arcangelo Morizio, Giuseppe Solarino, and Bartolomeo Trentadue. 2025. "Evaluation of the Stress-Shielding Effect of a PEEK Knee Prosthesis. A Finite Element Study" Osteology 5, no. 3: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/osteology5030024
APA StyleCeddia, M., Morizio, A., Solarino, G., & Trentadue, B. (2025). Evaluation of the Stress-Shielding Effect of a PEEK Knee Prosthesis. A Finite Element Study. Osteology, 5(3), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/osteology5030024







