Random Access Resource Configuration for LEO Satellite Communication Systems Based on TDD
Abstract
1. Introduction
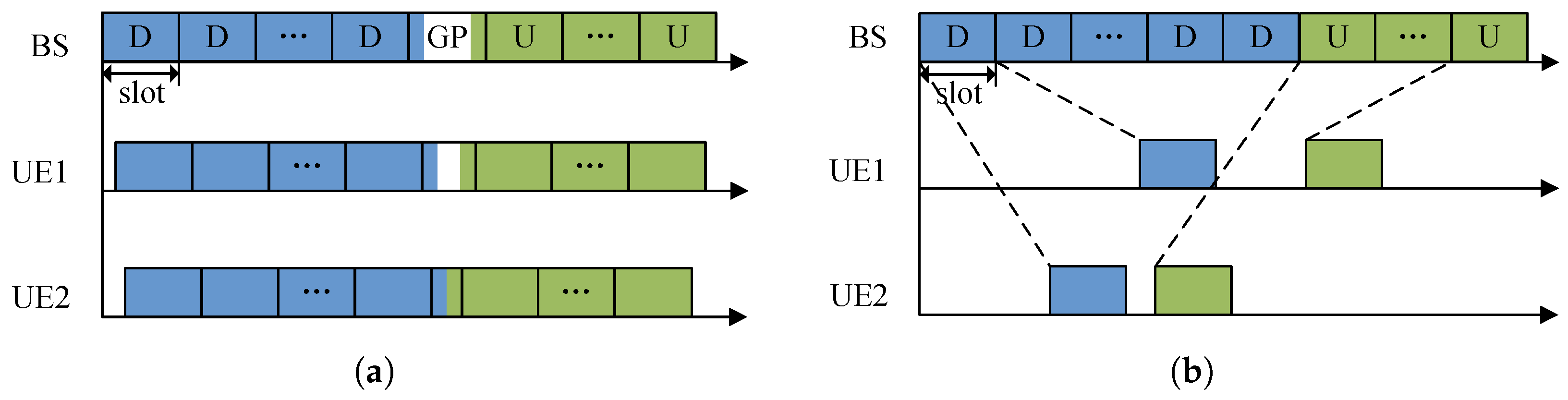
- To address the reduced resource utilization in TDD-based LEO satellite communication systems, we propose a flexible and on-demand frame structure, where the slots allocated to UE can be scheduled flexibly and on demand without being constrained by the 5G frame structure, as long as the interference-free requirement is met. Therefore, the GPs can be removed from the frame structure of the base station (BS), thereby maximizing system resource utilization.
- We formulate, for the first time, an RO allocation optimization problem that considers resource utilization in a TDD-based satellite RA scenario. Under the constraint of avoiding interference with the BS’s downlink broadcast signals, the proposed optimization algorithm selects the RO configuration with the highest utilization.
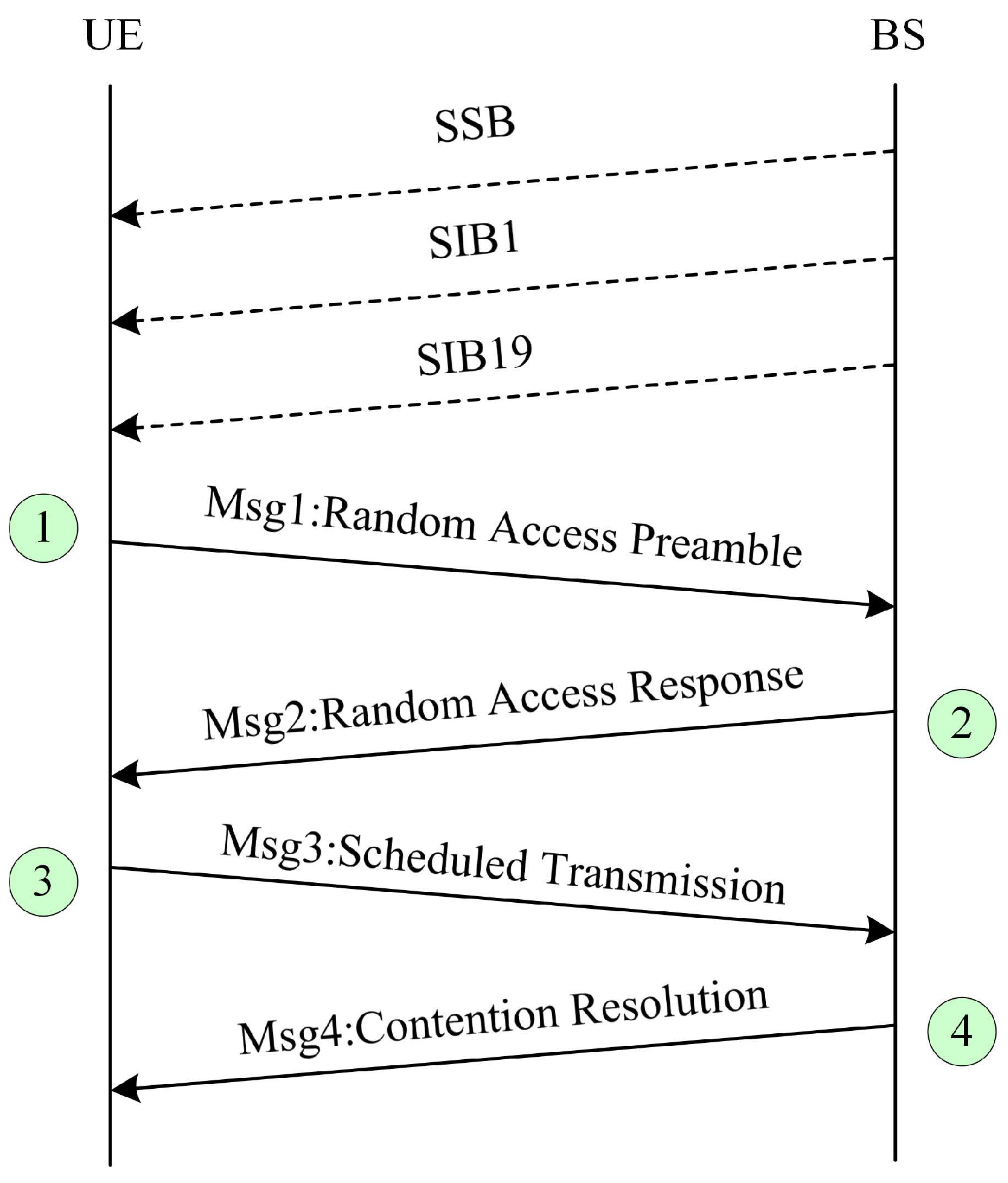
2. Synchronization and RA Procedure
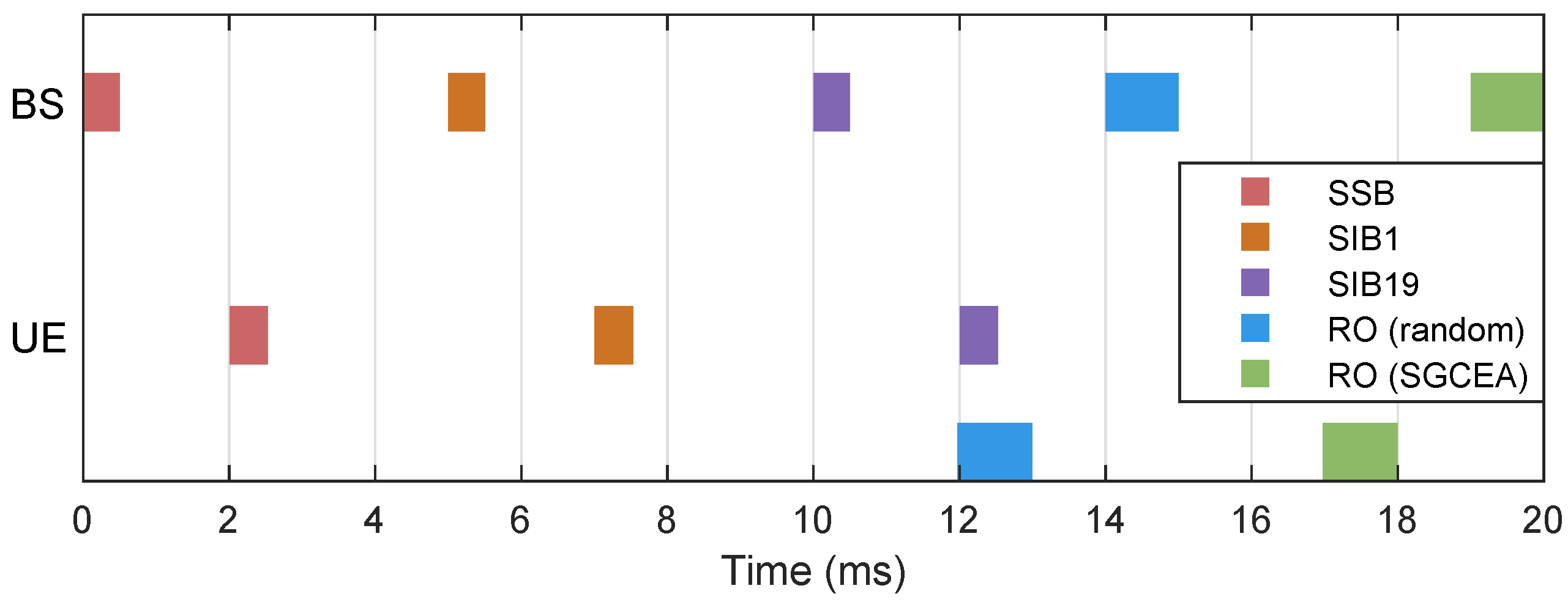
- The UE transmits a preamble on the PRACH, enabling the BS to estimate the propagation delay between them.
- After detecting the preamble, the BS returns a random access response (RAR) containing TA, power control command, and the uplink resources for transmitting Msg3. The UE attempts to detect the RAR within a configured window.
- The UE achieves uplink synchronization based on the TA and transmits Msg3 using the UL grant scheduled in the RAR. Msg3 carries the UE’s unique identifier.
- The BS transmits Msg4 on the physical downlink shared channel, which carries the contention resolution information. The UE completes the RA procedure successfully once it detects that the identification in Msg4 matches its own.
2.1. Overview of SSB and SIB
2.1.1. SSB Overview
2.1.2. SIB1 Overview
2.1.3. SIB19 Overview
2.2. RO Configuration in RA
3. System Model and Problem Formulation
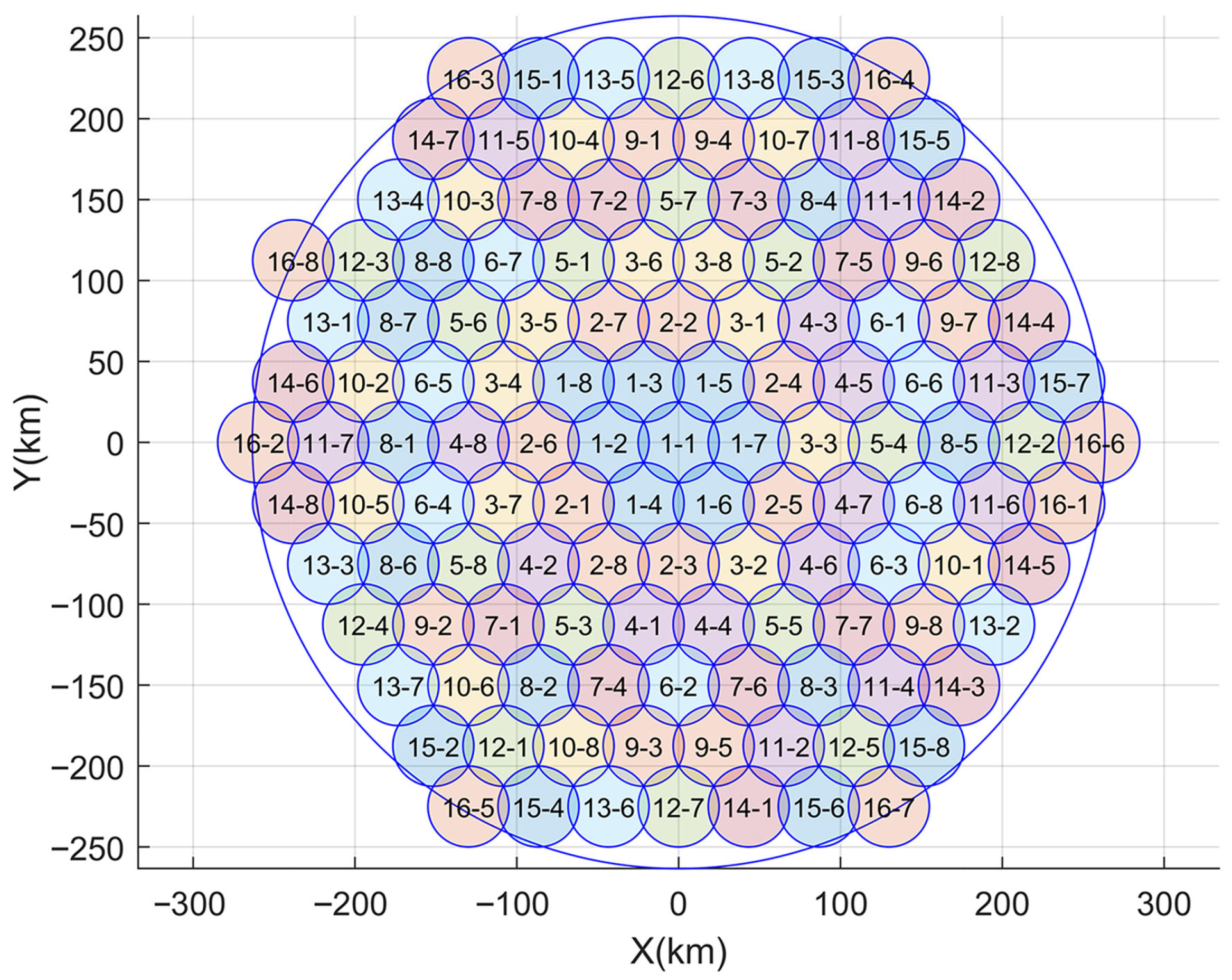
3.1. System Model
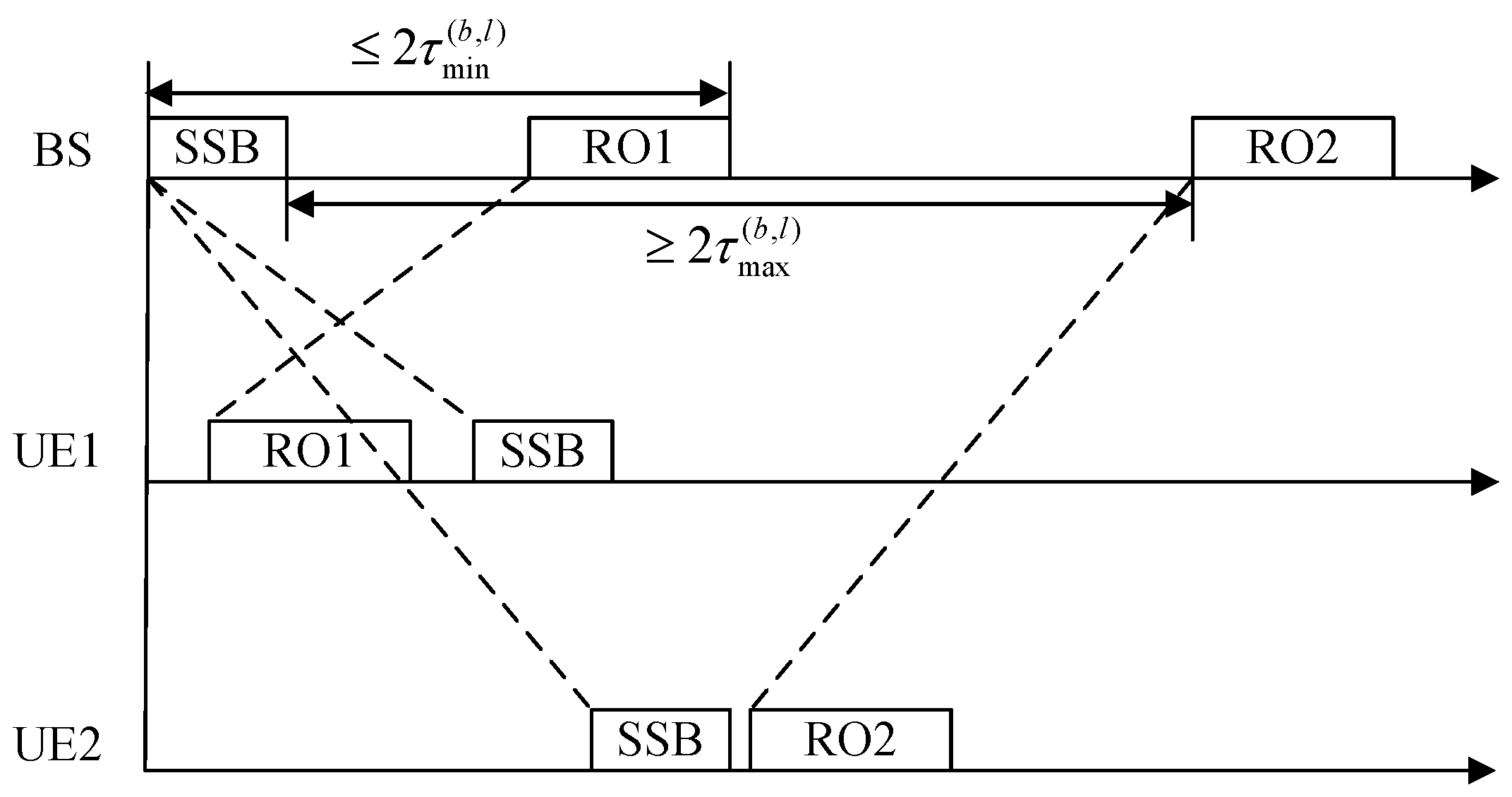
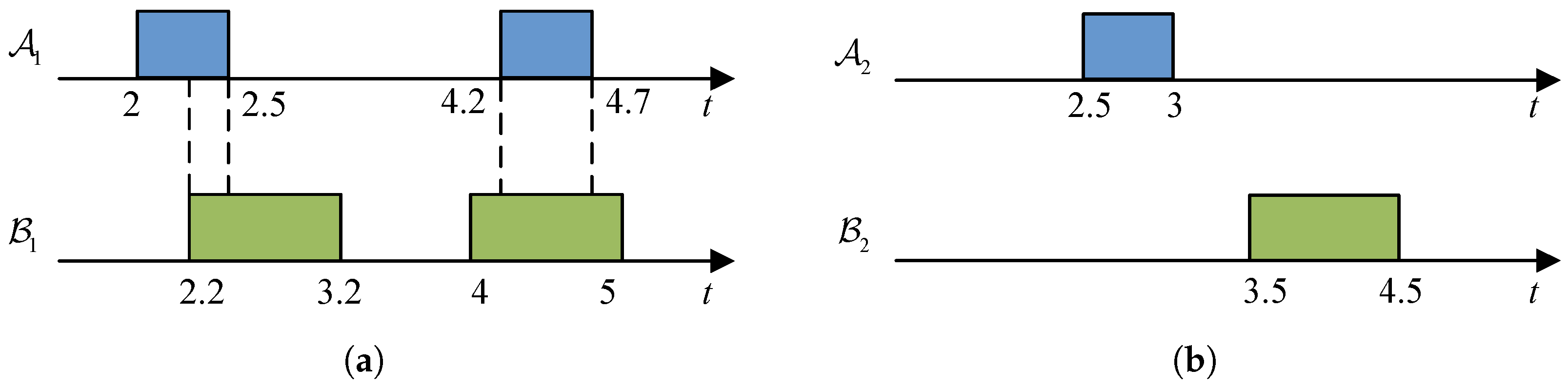
3.2. Interference Analysis
3.2.1. Analysis of SSB Transmission Duration
3.2.2. Analysis of SIB1 Transmission Duration
3.2.3. Analysis of SIB19 Transmission Duration
3.2.4. Analysis of Interference-Free Conditions of RO Configuration
3.3. RO Configuration Problem Formulation
4. Solution for RO Configuration
- Parameter initializationFirst, all relevant parameters and system configurations are prepared, including the set of candidate RO configurations , the set of beams , the set of beam positions , and the propagation delay range for each beam position . In addition, the configuration parameters of SSB, SIB1, and SIB19, as well as the TDD frame structure of the BS, are specified. The optimal RO configuration set is initially set to be empty.
- Interference assessmentAs shown in Figure 6, for each candidate RO configuration, the algorithm first determines the least common multiple of the periods of all relevant signals. Within this judgement period, the RO reception intervals are calculated and filtered to include only those located in uplink slots. Then, for each beam and each of its beam positions, the algorithm computes the transmission intervals of SSB, SIB1, and SIB19 based on their respective configuration indices. Based on the propagation delays, RO reception intervals that would interfere with any downlink signals are excluded, yielding the set of valid RO intervals for each beam position. The valid RO intervals for a beam are then obtained by intersecting those across all its beam positions. If no valid RO intervals exist for a beam under the given configuration, it will be discarded, with its RO utilization set to zero. Otherwise, the average RO utilization for this configuration is calculated.
- RO configuration determinationAfter evaluating all candidate configurations, those achieving the highest average RO utilization form the optimal configuration set , and the corresponding valid RO indicator vectors for each beam are also obtained.
| Algorithm 1 Structured global candidate exploration algorithm |
|
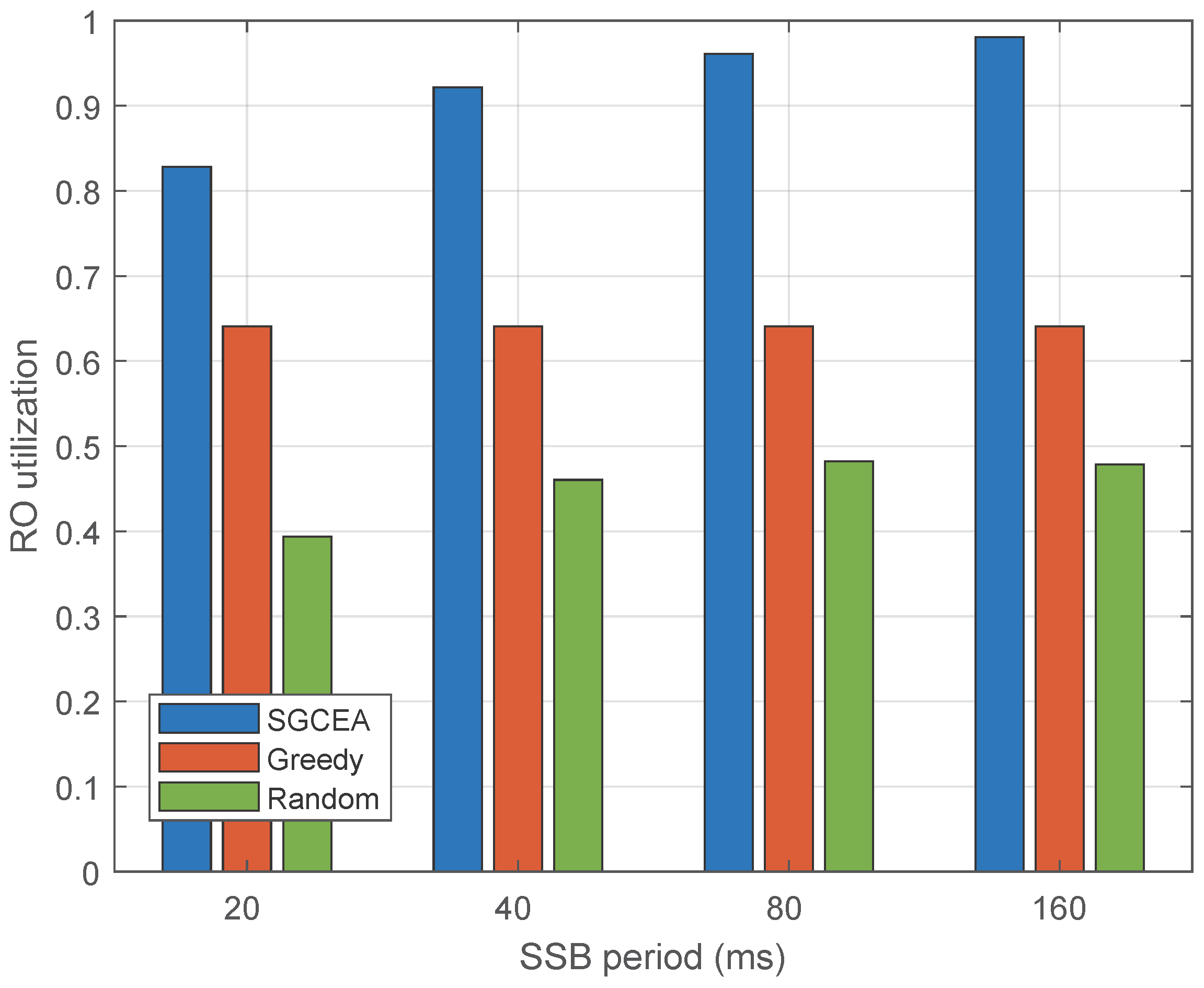
5. Simulation Results
5.1. Simulation Settings
- Random: Randomly select a feasible RO configuration.
- Greedy: Sequentially select a RO configuration with maximum utilization for each beam.
- SGCEA: Use the proposed SGCEA algorithm to obtain the RO configuration.
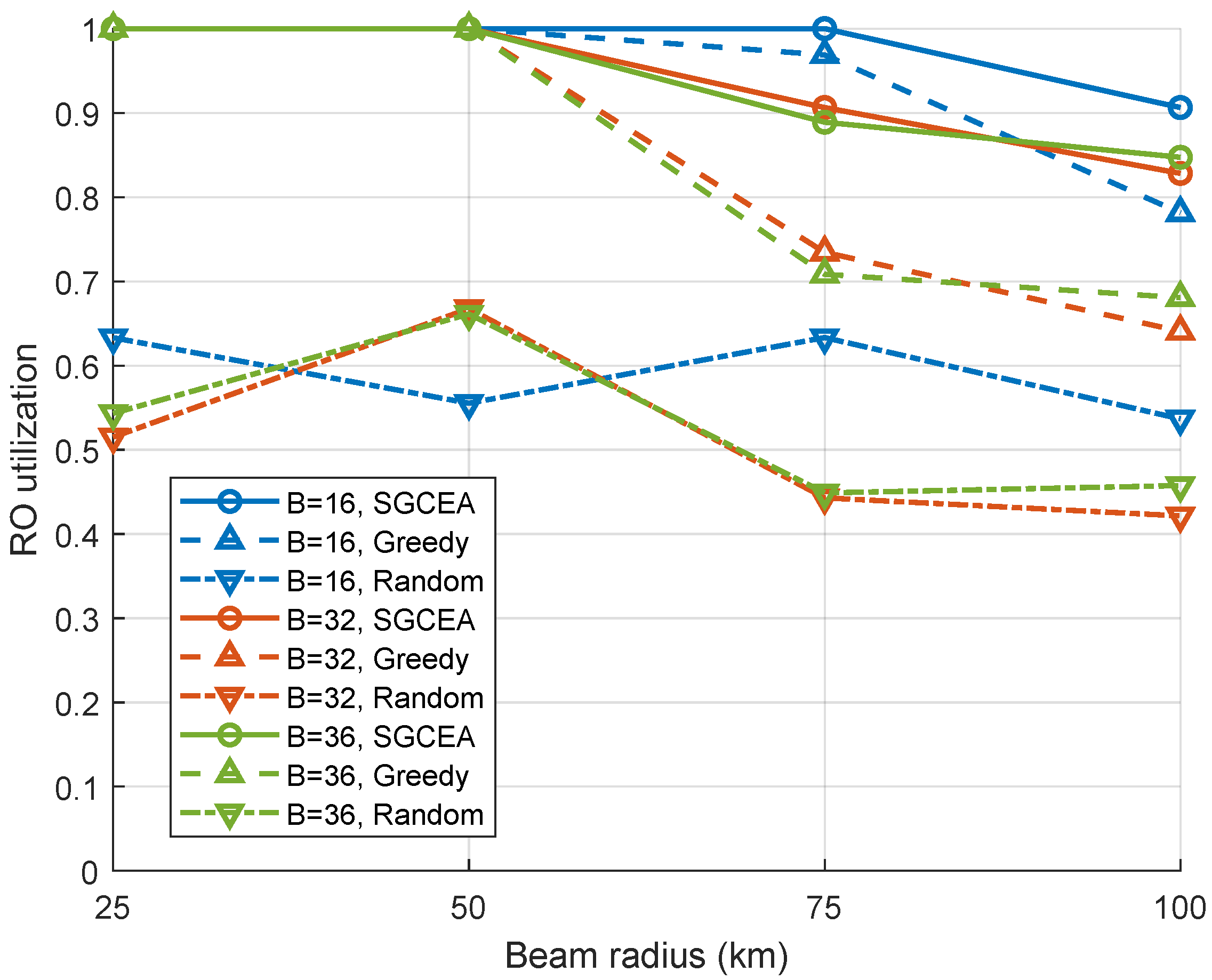
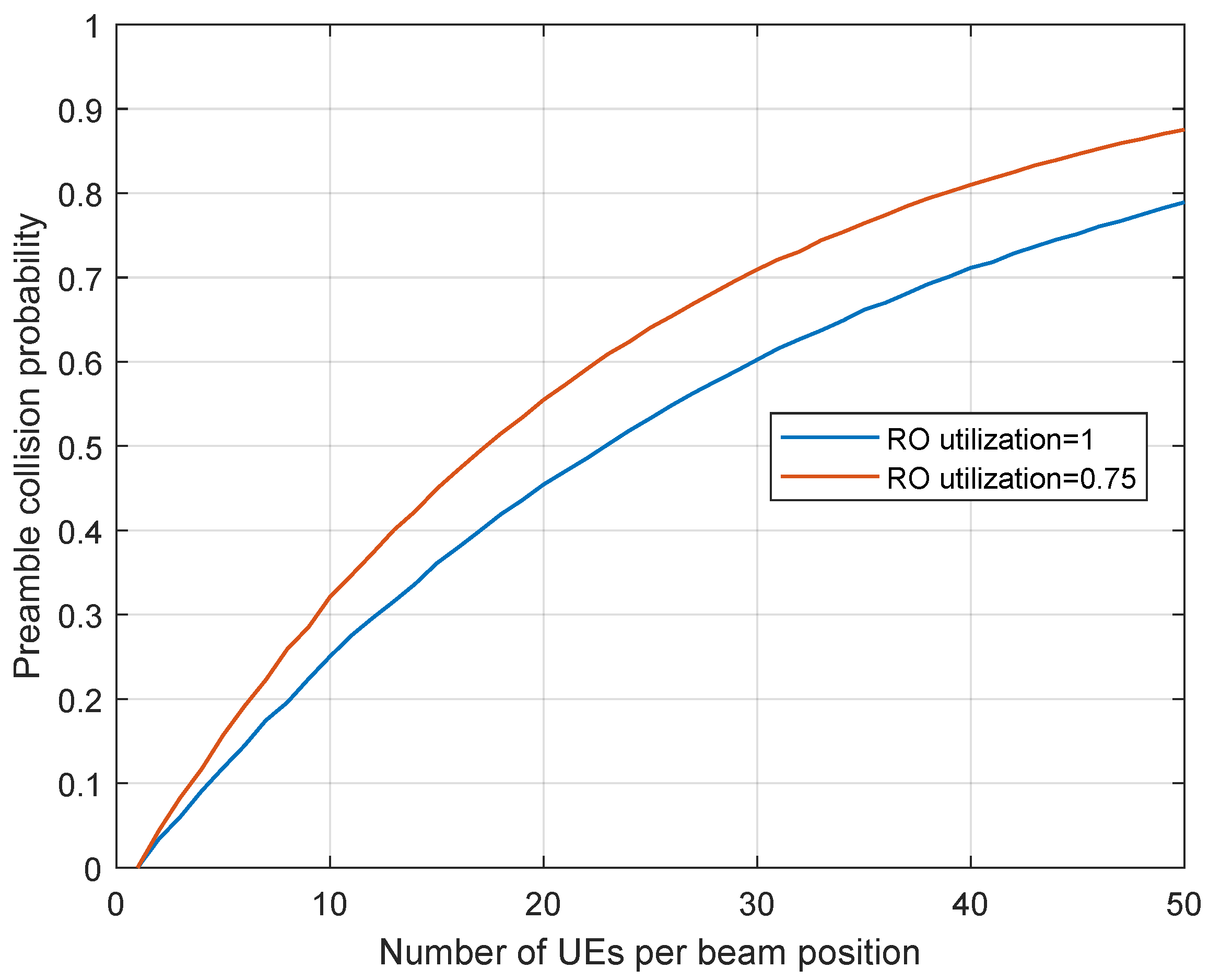
5.2. Performance Evaluation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 3GPP | Third generation partnership project |
| NTN | Non-terrestrial network |
| TDD | Time division duplex |
| RA | Random access |
| UE | User equipment |
| RACH | Random access channel |
| PRACH | Physical random access channel |
| TA | Timing advance |
| LEO | Low earth orbit |
| RO | RACH occasion |
| CLI | Cross-link interference |
| GP | Guard period |
| GNSS | Global navigation satellite system |
| BS | Base station |
| SSB | Synchronization signal block |
| SIB | System information block |
| SS burst set | Synchronization signal burst set |
| OSI | Other system information |
| SI | System information |
| RAR | Random access response |
| SGCEA | Structured global candidate exploration algorithm |
References
- 3GPP. Study on New Radio (NR) to Support Non-Terrestrial Networks. TR 38.811 v15.0.0. Available online: https://portal.3gpp.org/desktopmodules/Specifications/SpecificationDetails.aspx?specificationId=3234 (accessed on 4 September 2025).
- 3GPP. Solutions for NR to support Non-Terrestrial Networks (NTN). TR 38.821 v16.0.0. Available online: https://portal.3gpp.org/desktopmodules/Specifications/SpecificationDetails.aspx?specificationId=3525 (accessed on 4 September 2025).
- Chen, S.; Sun, S.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, G.; Tamrakar, R. A comprehensive survey of TDD-based mobile communication systems from TD-SCDMA 3G to TD-LTE(A) 4G and 5G directions. China Commun. 2015, 12, 40–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Roberts, I.P.; Heo, J.; Son, J.; Kim, H.; Lee, Y.; Hong, D. Can TDD Be Employed in LEO SatCom Systems? Challenges and Potential Approaches. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.08179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Deng, Y.; Nallanathan, A.; Yuan, J. A Decoupled Learning Strategy for Massive Access Optimization in Cellular IoT Networks. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2021, 39, 668–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miuccio, L.; Panno, D.; Riolo, S. An Energy-Efficient DL-Aided Massive Multiple Access Scheme for IoT Scenarios in Beyond 5G Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 7936–7959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saarnisaari, H.; de Lima, C.M. 5G NR over Satellite Links: Evaluation of Synchronization and Random Access Processes. In Proceedings of the 2019 21st International Conference on Transparent Optical Networks (ICTON), Angers, France, 9–13 July 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Kodheli, O.; Maturo, N.; Chatzinotas, S.; Andrenacci, S.; Zimmer, F. On the Random Access Procedure of NB-IoT Non-Terrestrial Networks. In Proceedings of the 2020 10th Advanced Satellite Multimedia Systems Conference and the 16th Signal Processing for Space Communications Workshop (ASMS/SPSC), Graz, Austria, 20–21 October 2020; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Saarnisaari, H.; Laiyemo, A.O.; de Lima, C.H.M. Random Access Process Analysis of 5G New Radio Based Satellite Links. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 2nd 5G World Forum (5GWF), Dresden, Germany, 30 September–2 October 2019; pp. 654–658. [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti, A.; Vanelli-Coralli, A.; Conti, M.; Andrenacci, S.; Chatzinotas, S.; Maturo, N.; Evans, B.; Awoseyila, A.; Ugolini, A.; Foggi, T.; et al. Architectures and Key Technical Challenges for 5G Systems Incorporating Satellites. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 1939–9359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattarzadeh, A.; Liu, Y.; Mohamed, A.; Song, R.; Xiao, P.; Song, Z.; Zhang, H.; Tafazolli, R.; Niu, C. Satellite-Based Non-Terrestrial Networks in 5G: Insights and Challenges. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 11274–11283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Park, Y.; Na, M.; Wang, H.; Hong, D. Aligned Reverse Frame Structure for Interference Mitigation in Dynamic TDD Systems. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2017, 16, 6967–6978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Hou, X.; Wang, H. Dynamic TDD and interference management towards 5G. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Barcelona, Spain, 15–18 April 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- de Olivindo Cavalcante, E.; Fodor, G.; Silva, Y.C.B.; Freitas, W.C. Distributed Beamforming in Dynamic TDD MIMO Networks With BS to BS Interference Constraints. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2018, 7, 788–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Lee, K.; Wang, H.; Hong, D. Cross Link Interference Mitigation Schemes in Dynamic TDD Systems. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 90th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2019-Fall), Honolulu, HI, USA, 22–25 September 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, S.; Miao, D.; Sun, S.; Chen, S. TDD Mode on NTN Direct to Satellite Service. IEEE Future Networks. Available online: https://futurenetworks.ieee.org/images/files/Tech_Focus_Articles/PDFs/issue16/TDD_mode.pdf (accessed on 4 September 2025).
- Traspadini, A.; Giordani, M.; Zorzi, M. Enhanced Time Division Duplexing Slot Allocation and Scheduling in Non-Terrestrial Networks. In Proceedings of the 2024 58th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems, and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 27–30 October 2024; pp. 835–841. [Google Scholar]
- Matloob, A.Z.K.; Aksoy, M.; Al-Qurabat, A.K.M.; AL lawndi, N.A. A comprehensive analysis of non-terrestrial networks impact on 5G NR random access. Telecommun. Syst. 2025, 88, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.; Srivastava, N.; Borman, L. Optimized RACH Procedure for Low Earth Orbit (LEO) Satellites in Non-Terrestrial Networks (NTN). In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE Space, Aerospace and Defence Conference (SPACE), Bangalore, India, 21–23 July 2025; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Sun, C.; Liu, L.; Li, J.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, S.; Wang, X. Beam Hopping Random Access Scheme for the Next Generation LEO Satellite Internet. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 24th International Conference on Communication Technology (ICCT), Chengdu, China, 18–20 October 2024; pp. 1112–1116. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Sun, C.; Liu, L.; Zheng, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, B.; Wang, D. Random Access Beam Hopping Management Scheme for the Next Generation LEO Satellite Internet. In Proceedings of the 2024 16th International Conference on Communication Software and Networks (ICCSN), Ningbo, China, 18–20 October 2024; pp. 189–193. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, B.; Wang, M.; Xing, Z.; Ren, G.; Su, J. Integrated Sensing and Communication Aided Dynamic Resource Allocation for Random Access in Satellite Terrestrial Relay Networks. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2023, 27, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Jiang, C.; Kuang, L.; Lu, J. Adaptive Access Control and Resource Allocation for Random Access in NGSO Satellite Networks. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2022, 9, 2721–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhou, S.; Kang, S.; Miao, D. Air Interface Design for a TDD-Based 5G NTN System. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Future Communications and Networks (FCN), Valletta, Malta, 18–22 November 2024; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Kodheli, O.; Astro, A.; Querol, J.; Gholamian, M.; Kumar, S.; Maturo, N.; Chatzinotas, S. Random Access Procedure Over Non-Terrestrial Networks: From Theory to Practice. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 109130–109143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, Y.-H.; Lee, P.-F.; Wang, S.-S.; Sheu, S.-T. Enhanced RACH Occasion in LEO-Based Non-Terrestrial Networks. In Proceedings of the ICC 2023-IEEE International Conference on Communications, Rome, Italy, 28 May–1 June 2023; pp. 283–289. [Google Scholar]
- 3GPP. Radio Resource Control (RRC) Protocol Specification. TS 38.331 V17.0.0. Available online: https://portal.3gpp.org/desktopmodules/Specifications/SpecificationDetails.aspx?specificationId=3197 (accessed on 4 September 2025).
- 3GPP. Physical Channels and Modulation. TS 38.211 v17.0.0. Available online: https://portal.3gpp.org/desktopmodules/Specifications/SpecificationDetails.aspx?specificationId=3213 (accessed on 4 September 2025).
- Huang, Y.-F.; Chiang, W.-K. Gurobi Optimization for 5GC Refactoring. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Consumer Electronics–Taiwan (ICCE–Taiwan), PingTung, Taiwan, 17–19 July 2023; pp. 115–116. [Google Scholar]
- 3GPP. Physical Layer Procedures for Control. TS 38.213 v17.0.0. Available online: https://portal.3gpp.org/desktopmodules/Specifications/SpecificationDetails.aspx?specificationId=3215 (accessed on 4 September 2025).


| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| , | The set of beams, and of beam positions |
| B, | The number of beams, and of beam positions |
| The set of candidate RO configurations | |
| The number of candidate RO configurations | |
| , | The frame index and slot index of SSB |
| , | The frame index and slot index of SIB1 |
| , | The frame index and slot index of SIB19 |
| , | The frame index and subframe index of RO |
| , , | The set of SSB, SIB1, and SIB19 intervals on the BS side |
| , , | The set of SSB, SIB1, and SIB19 intervals on the UE side |
| The set of RO intervals on the BS side | |
| The set of RO intervals on the BS side within uplink slots | |
| The set of RO intervals on the UE side | |
| The set of valid RO intervals on the BS side | |
| The set of valid RO intervals on the UE side |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Satellite orbit altitude | 600 km |
| Number of beams | 16, 32, 36 |
| Number of beam positions per beam | 8 |
| Beam radius | 25–100 km |
| Subcarrier spacing | 30 kHz |
| Frame duration | 10 ms |
| Downlink slots per half-frame | 7 |
| Uplink slots per half-frame | 3 |
| Period of SSB, SIB1, and SIB19 | 20, 20, 80 ms |
| Frame and half-frame index of SS Burst set | 0, 0 |
| Frame and slot index of the first SIB1 | 0, 10 |
| Number of consecutive SIB1 slots per beam | 4 |
| SIB1 transmission occasions per slot | 2 |
| Frame and slot index of the SI window | 1, 0 |
| Slot duration of the SI window | 10 |
| Slot offset of the first SIB19 | 0 |
| Number of consecutive SIB19 slots per beam | 4 |
| SIB19 transmission occasions per slot | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yi, J.; Fang, T.; Chai, L.; Wang, W.; Zheng, Y. Random Access Resource Configuration for LEO Satellite Communication Systems Based on TDD. Telecom 2025, 6, 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom6040094
Yi J, Fang T, Chai L, Wang W, Zheng Y. Random Access Resource Configuration for LEO Satellite Communication Systems Based on TDD. Telecom. 2025; 6(4):94. https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom6040094
Chicago/Turabian StyleYi, Jiawen, Tianhao Fang, Li Chai, Wenjin Wang, and Yi Zheng. 2025. "Random Access Resource Configuration for LEO Satellite Communication Systems Based on TDD" Telecom 6, no. 4: 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom6040094
APA StyleYi, J., Fang, T., Chai, L., Wang, W., & Zheng, Y. (2025). Random Access Resource Configuration for LEO Satellite Communication Systems Based on TDD. Telecom, 6(4), 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom6040094






