Combustion Characteristics of Moxa Floss Under Nitrogen Atmosphere
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Proximate and Ultimate Analysis
2.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis
- 1.
- Initial Temperature (Ti)
- 2.
- Pyrolysis Onset Temperature (Te)
- 3.
- Pyrolysis End Temperature (Tc)
- 4.
- Maximum Mass Loss Rate (Vp) and Corresponding Peak Temperature (Tp)
2.4. Kinetic Analysis
- A is the pre-exponential factor, s−1;
- R is the gas constant, 8.314 J/(mol-K);
- T is the thermodynamic temperature, K.
- W is the starting mass of the specimen at T °C;
- W∞ is the maximum mass loss.
2.5. FTIR Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Proximate and Ultimate Analysis
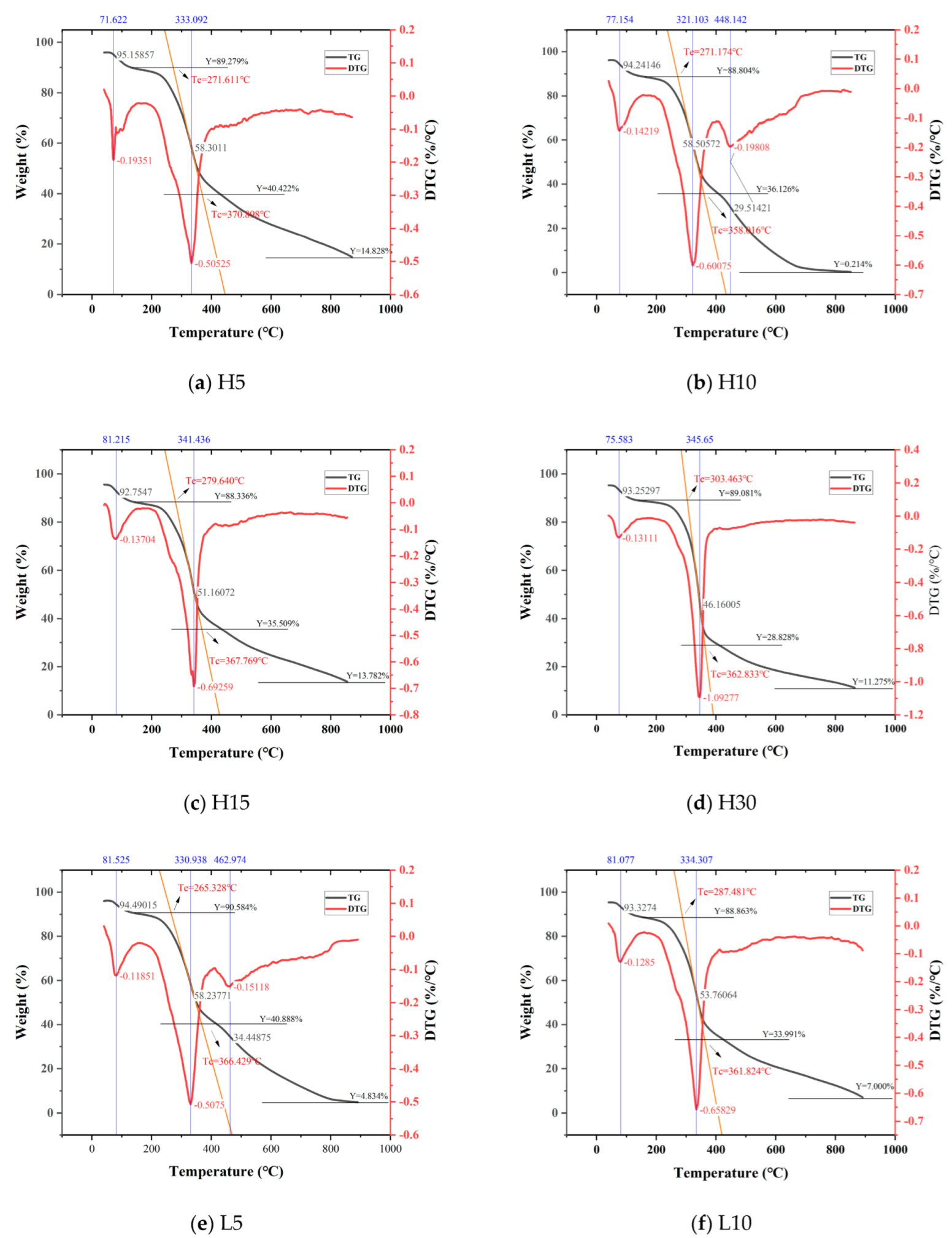
3.2. Thermogravimetric Analysis
- Pyrolysis Process
- 2.
- Thermal Stability
- 3.
- Reaction extent
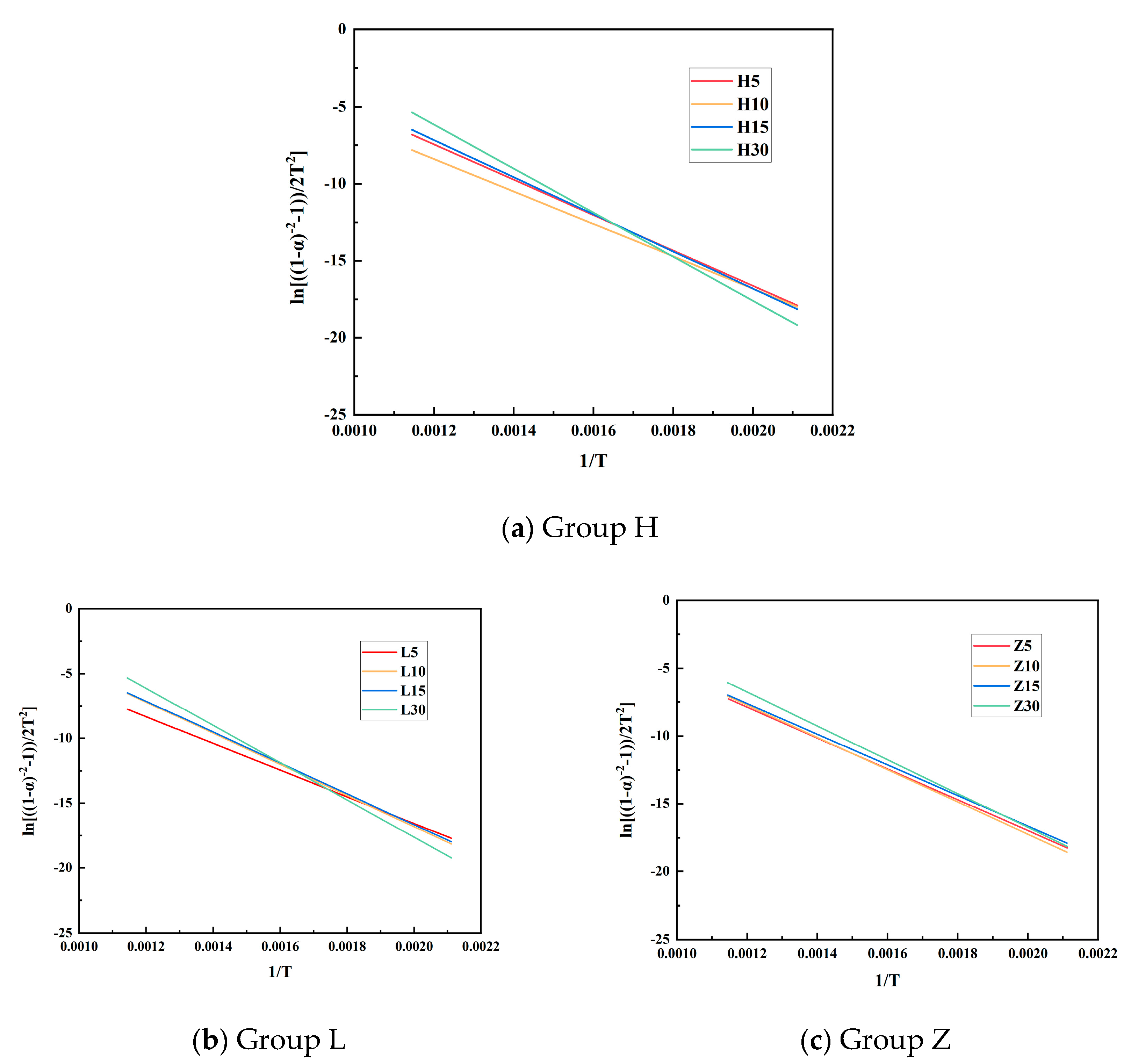
3.3. Kinetic Analysis
3.4. FTIR Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosillo-Calle, F. A review of biomass energy-shortcomings and concerns. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2016, 91, 1933–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Niu, W.; Zhang, D. Biomass Thermochemical Conversion Technology; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Du, H.; Wang, J.; Bai, X. Thermogravimetric Analysis of the Pyrolysis Process of Lignocellulosic Biomass. J. Nat. Sci. Heilongjiang Univ. 2008, 25, 85–89+94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Q.; Sun, S.; LI, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wu, S.; Qin, Y. Thermogravimetric Analysis on the Combustion Characteristics of Brown Coal Blends. J. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2001, 7, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ma, J.; Luo, L.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, X. Pyrolysis of superfine pulverized coal. Part 5. Thermogravimetric analysis. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 154, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, J.; Wang, D.; Tian, Z.; Jin, K.; Qian, B.; Pan, Y. Pyrolysis Study of Moxa Floss with Different Storage Years Using Online Photoionization Mass Spectrometry. SSRN Electron. J. 2023, 177, 106271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J. Research Progress on the Chemical Composition and Pharmacological Action of Moxa Smoke. Heilongjiang Sci. Technol. Inf. 2011, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Hu, L.; Chang, X.; Wu, H. Theoretical study on warming and dredging function of moxibustion. Chin. Acupunct. Moxibustion 2011, 31, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L. Preliminary Study on the Mechanism of Traditional Moxibustion. Chin. J. Basic Med. Tradit. Chin. Med. 1999, 5, 47–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.; Jung, W.M.; Lee, H.; Chae, Y. Psychophysical and psychophysiological effects of heat stimulation by electric moxibustion. Complement. Ther. Med. 2019, 42, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, F. Study on the Physical Characteristics of Moxibustion. Master’s Thesis, South-Central University for Nationalities, Wuhan, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, H.; Shen, X. The Mechanism of Moxibustion: Ancient Theory and Modern Research. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 379291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Jiang, D.; Yi, J.; Hong, Z. Observation on Free Radical Scavenging Effects of Artemisia argyi Combustion Products. Chin. Acupunct. Moxibustion 2009, 29, 547–549. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M. Pharmacological Study on Active Components of Artemisia argyi Combustion Products. Master’s Thesis, South-Central University for Nationalities, Wuhan, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.; Ding, G.; Wei, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, Y.; Deng, H.; Lao, L. An infrared radiation study of the biophysical characteristics of traditional moxibustion. Complement. Ther. Med. 2006, 14, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Liu, T. Preliminary Study on the Biophysical Mechanisms of Moxibustion Therapy. Chin. Acupunct. Moxibustion 1996, 16, 17–18+59. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Huang, Y.-H.; Lim, M.Y.; Zhao, B.-X.; Jin, X.-B.; Zhang, J.-L. Emission Characteristics and Concentrations of Gaseous Pollutants in Environmental Moxa Smoke. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2016, 16, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kang, L.; Li, H.; Huang, X.; Huang, L. Characterization of moxa floss combustion by TG/DSC, TG-FTIR and IR. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 288, 121516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W. Research on the Combustion Characteristics of Pure Moxa Rolls. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2000, 23, 569–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. Quality Evaluation of Moxa Wool Based on Thermal Behavior Analysis and Its Correlation with Lignin. Master’s Thesis, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y. Research on the Quality Evaluation System of Artemisia argyi Leaves Based on Moxibustion Material. Ph.D. Thesis, Shenyang Pharmaceutical University, Shenyang, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, M.Y.; Zhang, X.; Huang, J.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, B.; Hu, H.; He, F.; Xie, J.; Qiu, D. Study of Thermal Behavior of Moxa Floss Using Thermogravimetric and Pyrolysis-GC/MS Analyses. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. eCAM 2021, 2021, 6298565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, J.; Tian, Z.; Wang, D.; Jin, K.; Qian, B.; Pan, Y. Online detection of the volatile intermediates evolved from moxa floss pyrolysis with photoionization mass spectrometry. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2022, 168, 105737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.Y.; Huang, J.; He, F.R.; Zhao, B.X.; Zou, H.Q.; Yan, Y.H.; Hu, H.; Qiu, D.S.; Xie, J.J. Quality grade classification of China commercial moxa floss using electronic nose: A supervised learning approach. Medicine 2020, 99, e21556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, R.; Jiang, H.; Yang, H.; Yu, G.; Guan, G. Exploration of Quality Evaluation Standards for Moxa Wool Based on Combustion Characteristics. J. Li-Shizhen Tradit. Chin. Med. 2023, 34, 1786–1788. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Cheng, Y.; Bai, J.; Wang, W.; Meng, R.; Xin, X.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, H. Ultrasound extraction process optimization and antibacterial activity of flavonoids from Artemisiae argyi Folium ash. Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med. 2021, 43, 2286–2292. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Zhou, Y.; Yan, Z.; Li, Q. Moxa combustion waste and its bio activities on cotton—A facile and green finishing process towards a sustainable and value adding application for medical textile. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 483, 144259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Niu, Q.; Guo, Y.; Gao, X.; Gao, K. Heteroatom-doped porous carbons derived from moxa floss of different storage years for supercapacitors. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 16433–16443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClure, W. Review: 204 years of near infrared technology: 1800–2003. J. Near Infrared Spectrosc. 2003, 11, 487–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Wu, L.; Liu, M.; Leng, Q.; Gong, Z.; Xing, D.; Wu, H. Development of Near Infrared Spectroscopy Analysis Technology and Instruments. Liquor Mak. 2020, 47, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coats, A.W.; Redfern, J.P. Thermal studies on some metal complexes of hexamethylenimine carbodithioate. Nature 1964, 201, 6771. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H. Pyrolysis Characteristics of Typical Plants Around Tailings Area and the Migration Rules of Metal Elements. Master’s Thesis, Inner Mongolia University of Science & Technology, Baotou, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Liu, H.; Song, H.; Liu, J. Thermal Analysis and Thermal Decomposition Kinetics of Artemisia vulgaris L. Biomass Chem. Eng. 2024, 58, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, J.A.; Kasum, C.M. Dietary flavonoids: Bioavailability, metabolic effects, and safety. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2002, 22, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Dong, Q. Principles and Analysis of Spectroscopy; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J. FTIR Spectroscopy Study on the Effects of Different Factors on Ginkgo Leaves and Seeds. Master’s Thesis, Yunnan Normal University, Kunming, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, R.; Yu, M.; Zhao, B.; Fu, X.; Chen, Y.; Guo, H. Analysis on chemical compositions of Artemisia argyi from Qichun of different years and moxa wool refined in different proportions. Chin. Acupunct. Moxibustion 2010, 30, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample | District | Storage Years | Leaf-to-Floss Ratio | Brand |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L5 | Nanyang | 5 years | 5:1 | LvYing |
| L10 | Nanyang | 5 years | 10:1 | LvYing |
| L15 | Nanyang | 5 years | 15:1 | LvYing |
| L30 | Nanyang | 5 years | 30:1 | LvYing |
| Z5 | Qichun | 3 years | 5:1 | ZhongKang |
| Z10 | Qichun | 3 years | 10:1 | ZhongKang |
| Z15 | Qichun | 3 years | 15:1 | ZhongKang |
| Z30 | Qichun | 3 years | 30:1 | ZhongKang |
| H5 | Nanyang | 3 years | 5:1 | HuaKang |
| H10 | Nanyang | 3 years | 10:1 | HuaKang |
| H15 | Nanyang | 3 years | 15:1 | HuaKang |
| H30 | Nanyang | 3 years | 30:1 | HuaKang |
| Proximate Analysis/% | Ultimate Analysis/% | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mad | Aad | Vad | Cad | Cad | Had | Oad | Nad | Sad | |
| L5 | 7.89 | 7.27 | 67.50 | 17.34 | 43.52 | 4.12 | 50.92 | 1.29 | 0.15 |
| L10 | 7.74 | 6.36 | 69.09 | 16.81 | 43.41 | 4.20 | 51.40 | 0.86 | 0.12 |
| L15 | 7.33 | 5.71 | 70.10 | 16.86 | 43.66 | 4.25 | 51.23 | 0.75 | 0.11 |
| L30 | 7.23 | 3.83 | 73.30 | 15.64 | 42.21 | 4.13 | 53.55 | 0.05 | 0.06 |
| Z5 | 8.41 | 6.91 | 67.83 | 16.85 | 44.19 | 4.16 | 49.85 | 1.64 | 0.16 |
| Z10 | 9.20 | 6.69 | 66.17 | 17.94 | 45.13 | 4.14 | 49.18 | 1.40 | 0.15 |
| Z15 | 8.68 | 6.50 | 68.52 | 16.30 | 42.59 | 4.13 | 51.73 | 1.40 | 0.15 |
| Z30 | 7.64 | 6.47 | 69.25 | 16.64 | 43.58 | 4.16 | 50.94 | 1.19 | 0.14 |
| H5 | 8.24 | 7.65 | 67.35 | 16.76 | 43.42 | 6.13 | 48.23 | 2.05 | 0.17 |
| H10 | 8.76 | 6.84 | 67.87 | 16.53 | 42.84 | 6.49 | 48.94 | 1.58 | 0.14 |
| H15 | 9.67 | 6.38 | 68.08 | 15.87 | 41.75 | 6.70 | 50.14 | 1.29 | 0.12 |
| H30 | 7.12 | 4.41 | 73.57 | 14.90 | 41.08 | 6.57 | 51.93 | 0.37 | 0.04 |
| Sample | Mass Loss (%) | Peak Temperature (°C) | Maximum MASS Loss Rate (%/min) | Remaining Mass (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H5 | 10.72 | 71.62 | 3.87 | 89.28 |
| H10 | 11.20 | 77.15 | 2.84 | 88.80 |
| H15 | 11.66 | 81.22 | 2.74 | 88.34 |
| H30 | 10.92 | 75.58 | 2.62 | 89.08 |
| L5 | 9.42 | 81.53 | 2.37 | 90.58 |
| L10 | 11.14 | 81.08 | 2.57 | 88.86 |
| L15 | 9.86 | 78.78 | 2.41 | 90.14 |
| L30 | 9.22 | 79.80 | 2.13 | 90.78 |
| Z5 | 9.82 | 83.52 | 2.36 | 90.18 |
| Z10 | 9.06 | 81.31 | 2.39 | 90.94 |
| Z15 | 9.57 | 87.37 | 2.16 | 90.43 |
| Z30 | 10.10 | 81.57 | 2.22 | 89.90 |
| Sample | Mass Loss (%) | Initial Temperature (°C) | Peak Temperature (°C) | Pyrolysis Onset Temperature (°C) | Pyrolysis End Temperature (°C) | Maximum Mass Loss Rate (%/min) | Remaining Mass (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H5 | 48.86 | 135.28 | 333.09 | 271.61 | 370.90 | 10.11 | 40.42 |
| H10 | 52.68 | 152.50 | 321.10 | 271.17 | 358.02 | 12.02 | 36.13 |
| H15 | 52.83 | 139.33 | 341.44 | 279.64 | 367.77 | 13.85 | 35.51 |
| H30 | 60.25 | 133.50 | 345.65 | 303.46 | 362.83 | 21.86 | 28.83 |
| L5 | 49.70 | 141.56 | 330.94 | 265.33 | 366.43 | 10.15 | 40.89 |
| L10 | 54.87 | 148.21 | 334.31 | 287.48 | 361.82 | 13.17 | 33.99 |
| L15 | 53.29 | 149.71 | 336.30 | 285.30 | 367.03 | 13.00 | 36.85 |
| L30 | 60.21 | 144.84 | 344.18 | 304.59 | 363.02 | 21.27 | 30.57 |
| Z5 | 46.44 | 151.88 | 313.48 | 251.68 | 354.42 | 9.59 | 43.74 |
| Z10 | 48.24 | 152.31 | 317.06 | 266.40 | 350.72 | 11.33 | 42.70 |
| Z15 | 50.01 | 153.85 | 332.36 | 273.26 | 369.67 | 10.51 | 40.42 |
| Z30 | 48.04 | 151.05 | 334.71 | 282.83 | 362.18 | 11.71 | 41.86 |
| Sample | Mass Loss (%) | Initial Temperature (°C) | Peak Temperature (°C) | Maximum Mass Loss Rate (%/min) | Remaining Mass (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H5 | 25.59 | 422.34 | \ | \ | 14.83 |
| H10 | 35.91 | 403.86 | 448.14 | 3.96 | 0.21 |
| H15 | 21.73 | 435.06 | \ | \ | 13.78 |
| H30 | 17.55 | 410.86 | \ | \ | 11.28 |
| L5 | 36.05 | 411.82 | 462.97 | 3.02 | 4.83 |
| L10 | 26.99 | 415.78 | \ | \ | 7.00 |
| L15 | 26.53 | 414.68 | \ | \ | 10.32 |
| L30 | 17.98 | 416.57 | \ | \ | 12.58 |
| Z5 | 38.94 | 383.62 | 432.64 | 6.02 | 4.80 |
| Z10 | 37.08 | 393.89 | 430.73 | 5.96 | 5.62 |
| Z15 | 29.86 | 417.18 | \ | \ | 10.56 |
| Z30 | 19.27 | 411.07 | \ | \ | 22.59 |
| Sample | Intercept | Slope | Activation Energy E | Pre-Exponential Factor A | Correlation Coefficient r |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H5 | 6.33449 | −11,480.60284 | 95.45 | 107,856.3316 | 0.9583 |
| H10 | 4.2362 | −10,525.58922 | 87.51 | 12,129.7601 | 0.9437 |
| H15 | 7.30086 | −12,052.676 | 100.21 | 297,613.9678 | 0.9629 |
| H30 | 11.01056 | −14,304.09489 | 118.92 | 14,425,516.3137 | 0.9745 |
| L5 | 4.02953 | −10,300.41925 | 85.64 | 9653.9516 | 0.9428 |
| L10 | 7.22257 | −12,019.6974 | 99.93 | 274,449.5166 | 0.9632 |
| L15 | 7.16895 | −11,917.78927 | 99.08 | 257,915.7023 | 0.9611 |
| L30 | 11.13215 | −14,380.52373 | 119.56 | 16,377,647.4220 | 0.9772 |
| Z5 | 5.76553 | −11,372.31246 | 94.55 | 60,483.0542 | 0.8898 |
| Z10 | 6.55716 | −11,901.76537 | 98.95 | 139,700.0699 | 0.8904 |
| Z15 | 5.94554 | −11,297.28822 | 93.93 | 71,934.3685 | 0.9568 |
| Z30 | 8.20149 | −12,471.55645 | 103.69 | 757,929.5872 | 0.9659 |
| Wavenumber (cm−1) | Vibrational Modes | Assignment | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H5 | H10 | H15 | H30 | L5 | L10 | L15 | L30 | Z5 | Z10 | Z15 | Z30 | ||
| 3414 | 3402 | 3431 | 3425 | 3408 | 3431 | 3427 | 3412 | 3417 | 3431 | 3429 | 3431 | ν(O-H) | Water |
| \ | \ | \ | \ | \ | 2923 | 2921 | 2921 | 2923 | 2925 | 2925 | 2923 | νas(-CH2) | Esters |
| \ | \ | \ | \ | \ | \ | \ | \ | \ | 2854 | 2856 | 2854 | νs(-CH2) | Esters |
| 1657 | \ | 1625 | 1659 | \ | 1670 | 1663 | 1643 | 1664 | \ | \ | \ | ν(C = O) | Flavonoids |
| 1448 | 1448 | \ | 1456 | 1448 | 1458 | 1456 | \ | \ | \ | 1458 | 1456 | Aromatic ring skeletal vibration | Flavonoids |
| 1381 | 1377 | 1404 | 1377 | 1379 | \ | \ | 1381 | 1402 | 1383 | 1385 | 1385 | δ(C-H) | Cellulose |
| 1033 | 1033 | 1118 | 1031 | 1022 | 1035 | 1035 | 1026 | 1110 | 1043 | 1043 | 1045 | ν(C-O) | Flavonoids |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, Y.; Wu, Y.; Du, P.; Ma, Y.; Zhuang, Z. Combustion Characteristics of Moxa Floss Under Nitrogen Atmosphere. Fuels 2025, 6, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/fuels6020048
Feng Y, Wu Y, Du P, Ma Y, Zhuang Z. Combustion Characteristics of Moxa Floss Under Nitrogen Atmosphere. Fuels. 2025; 6(2):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/fuels6020048
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Yukun, Yifan Wu, Pengzhou Du, Yang Ma, and Zhaoyi Zhuang. 2025. "Combustion Characteristics of Moxa Floss Under Nitrogen Atmosphere" Fuels 6, no. 2: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/fuels6020048
APA StyleFeng, Y., Wu, Y., Du, P., Ma, Y., & Zhuang, Z. (2025). Combustion Characteristics of Moxa Floss Under Nitrogen Atmosphere. Fuels, 6(2), 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/fuels6020048






