Abstract
The combination of high-temperature fermentation and membrane separation has the potential to realize a simple on-site process to produce concentrated bioethanol. The performance of dehydration membranes in separating bioethanol was investigated in this study. Three types of zeolite membranes, LTA, MFI, and MOR, were synthesized. Their dehydration ability was compared using a bioethanol solution produced by high-temperature fermentation followed by vacuum distillation. The LTA zeolite membranes deformed and became amorphous while treating the distillate. On the contrary, no significant changes were observed in the MFI and MOR zeolite membranes analyzed by X-ray diffraction after treating the distillate. However, the flux declined when the membranes were in contact with the distillate (pH = 3.8). Neutralizing the distillate to pH 6.6 with sodium hydroxide did not prevent the flux decline. Even though flux decreased by about 20–30%, the MOR membrane showed quite high water-selectivity, with a water concentration of over 99.9% in the permeate, suggesting the feasibility of its application to concentrate bioethanol.
1. Introduction
The overreliance on fossil fuels is causing environmental challenges today. A shift to more sustainable energy sources is urgently required. Biofuels are alternative choices that can be renewable, if managed properly. Biorefinery is often proposed to be centralized at a large scale to obtain benefits from the scaled-up process [1]. One of the drawbacks of such a model is the high cost of collecting and transporting the feedstock to the biorefinery plant. An alternative idea is the conversion of the biomass closer to its production area [2]. For example, transporting a concentrated ethanol solution instead of raw biomass, which contains a large amount of water, will drastically reduce the energy required for transport. Such an on-site conversion process may also facilitate recycling residues, for example as animal feed. One of the keys to realizing an on-site biomass conversion process is the development of environmentally friendly technology that is simple to operate and maintain, and has a low capital cost. A small-scale refinery process can be made portable. This allows the process to be moved according to the seasonal changes in biomass production. In addition, the capital cost can be shared between a larger number of users, which facilitates the implementation of the process.
We propose the combination of high-temperature fermentation and membrane separation for an on-site biorefinery process. A high-temperature fermentation uses thermotolerant yeasts that are capable of growth at 40–50 °C, whereas conventional fermentation is performed typically at 30–35 °C [3,4]. The advantages of high-temperature fermentation are the higher fermentation rate, lower risk of contamination, reduced cooling cost, and the reduced enzyme cost in biomass hydrolysis for the simultaneous saccharification and fermentation [5,6]. If designed well, the radiation heat from the fermenter may be enough to remove the heat generated by the fermentation; then, the cooling water system can be eliminated and a simpler fermenter can be achieved. On the other hand, the ethanol concentration after the fermentation is low as a few percent. Therefore, a downstream concentration process is required.
Distillation is often employed to concentrate ethanol after fermentation. Membrane separation is an alternative choice that consists of a simple modular system and offers easy operation [7]. Recently, a hybrid process combining distillation and membrane dehydration was reported to significantly reduce the energy consumption compared to a conventional distillation and azeotropic distillation process [8]. Since the successful industrial application of such hybrid process with LTA zeolite membranes [9], a type of microporous hydrophilic inorganic membrane, the application of membrane dehydration is expanding.
Employing ethanol-selective membranes instead of distillation is an option to concentrate bioethanol after fermentation that can reduce the energy required for the concentration [10]. For example, the permeate through hydrophobic inorganic membranes, such as silicalite membranes, can be over 85% when 10% ethanol solution is applied [11]. After an ethanol-selective membrane, a dehydration membrane can be applied to concentrate the ethanol further [10]. The separation properties of membranes are often evaluated by a pervaporation (PV) process, where a mixture liquid is supplied to the membrane and some fraction permeates through the membrane as a vapor. Typically, a vacuum is applied to the permeate side [12]. Alternatively, a sweep gas, such as compressed air, can be used [13]. In both cases, the permeated ethanol-enriched vapor needs to be collected. In laboratory tests, liquid nitrogen traps are commonly used for this purpose [12]. A chiller may be used in larger-scale applications. The possibility of concentrating a few percent of ethanol to over 80% in a single step using an ethanol-selective membrane is attractive; however, the energy demand at the chiller can be similar to the energy demand of distillation [10]. In addition, the capital cost of the chiller and related facilities may be a challenge to realize in a small-scale process.
The application of a water-selective membrane is another option to concentrate ethanol after fermentation. One of the major drawbacks of this approach is the requirement of large membrane area, as a huge amount of water needs to be removed through the membrane to concentrate a few percent of ethanol to over 80%. Recycling the feed or applying the membrane in a batch feed tank will reduce the membrane area, but it will require a long separation time to increase the ethanol concentration. The advantage of this method is the possibility of emitting the permeate vapor to the air if no toxic components permeate through the membrane with water. A condensation facility is not required if sweep gas, such as compressed air, is applied to the permeate side of the membrane at ambient pressure. In this way, the configuration of a membrane process becomes simpler compared to employing an ethanol-selective membrane.
Even though dehydration zeolite membranes, such as LTA membranes, are commercially available [9], the application of these membranes is limited to fluids with a low water concentration. The prediction of their performance and stability in separating water-rich bioethanol is difficult to predict. Therefore, in this study, we examined the performance of dehydration membranes using bioethanol obtained by a high-temperature fermentation. This study focused on the influence of volatile components in the fermented solution. Vacuum distillation was applied to remove solid materials in the fermented broth, such as biomass, yeasts, salts, sugars, and other non-volatile fractions. Three types of membranes, LTA zeolite membranes and newly developed MFI [14] and MOR [15] zeolite membranes, with higher acid stability than a LTA membrane, were compared. A flux decline after treating the distillate was observed in all types of membranes. MOR membranes showed the least flux decline with a decline ratio about 20%. Ethanol and other contaminants were not detected in the permeate of MOR membranes when the distillate was applied, suggesting that MOR membranes are one of the promising candidates for the process mentioned above.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Yeast Strain and Media Used in this Study
For pre-cultivation, Kluyveromyces marxianus DMKU 3-1042 [16] cells were grown in YPD medium containing 1% (w/v) yeast extract, 2% (w/v) peptone, and 3% (w/v) glucose. For the process of semi-simultaneous fermentation and distillation, YP-20% rice medium containing 1% (w/v) yeast extract, 2% (w/v) peptone, and 20% (w/v) rice hydrolysate (equivalent to 13% glucose) was used. The rice hydrolysate was prepared from steamed rice and Yuniase S containing α-amylase and glucoamylase (2000 U/g rice; Yakult Pharmaceutical Industry Co., Tokyo, Japan) by incubation at 55 °C for 24 h.
2.2. Semi-Simultaneous Fermentation and Distillation
Semi-simultaneous fermentation and distillation was performed with a system consisting of a 10 L fermentation and distillation tank, a distillation apparatus, an ethanol recovery unit, a vacuum pump, and a drain unit, as described previously [5]. K. marxianus was pre-cultivated in 50 mL of KMYP-5% rice medium at 30 °C for 18 h with shaking at 160 rpm. The pre-culture was inoculated at 1% (v/v) into 5 L of KMYP-20% rice medium. Fermentation was conducted in a fermentation and distillation tank at 160 rpm for 36 h at 41 °C. During fermentation, samples from the culture were collected for the determination of cell growth, ethanol concentration, and glucose concentration. The fermentation was almost complete after 36 h.
Vacuum distillation was applied when the fermentation was almost complete. Figure 1a shows a schematic of the experimental rig. The vapor pressure of the fermentation and distillation tank was decreased to 70 mbar (the theoretical value of the saturation vapor pressure of ethanol is 177.8 mbar at 40 °C). The line between the tank and the ethanol collection bottle was chilled for 12 h. Solid materials in the fermented broth were completely separated from the ethanol solution after the distillation. The ethanol yield from rice was about 66% of the average theoretical yield.
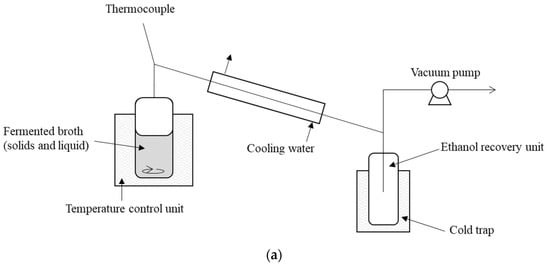
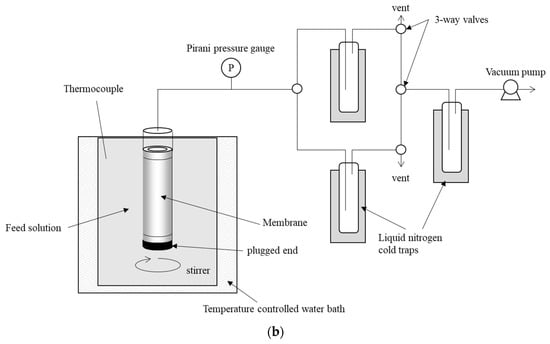
Figure 1.
Schematic views of the apparatus: (a) vacuum evaporation rig, (b) pervaporation test rig.
Glucose and ethanol concentrations in culture medium were determined by an HPLC system, consisting of an L-2130 Pump, L-2490 Refractive Index Detector, L-2200 Autosampler, L-2350 Column oven, and Hitachi Model D-2000 Elite HPLC System Manager, equipped with a GL-C610-S Gelpack® column (Hitachi Chemical, Tokyo, Japan) using distilled water (ADVANTEC, Tokyo, Japan) as the mobile phase at a flow rate of 0.3 mL/min. Analysis of pyruvate, malate, fumarate, succinate, formate, acetate, and propionate in the sample was performed using Waters 2695 Alliance HPLC (Waters) equipped with RSpak KC-811 column (Shodex) under a running condition; 1 mM perchloric acid as mobile phase at a flow rate of 0.6 mL/min, and the column was maintained at 50 °C. The HPLC profile was monitored using a refractive index and a photodiode array detector at 210 nm. Data were collected and processed by Empower 3 software (Waters).
2.3. Membrane Preparation and Characterization
Zeolite membranes were synthesized on the outer surface of porous mullite tubes purchased from Nikkato Co., Tokyo, Japan (o.d. 12 mm, i.d. 10 mm, length 100 mm, pore size 1.3 μm). First, zeolite seed crystals were mechanically scrubbed on the outer surface of the support. Then, the seeded supports were treated hydrothermally to grow the seeds and to form dense zeolite membranes. Three types of zeolite membranes were prepared in this study: LTA (A-type zeolite), with the smallest zeolitic pore size of ca. 0.4 nm, while that of MFI (ZSM-5) and MOR (mordenite) was ca. 0.5 and 0.65 nm, respectively [17]. The composition and the hydrothermal conditions used to synthesize these membranes are listed in Table 1. Detailed preparation conditions can be found elsewhere [14,15]. After the hydrothermal synthesis, membranes were washed with water until the pH of the rinse water became neutral, then dried at 358 K in the air. Membranes were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD, XRD-6100, SHIMADZU, Kyoto, Japan) with Cu-Kα radiation and by scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM, JEOL JSM 6335 F, JSM-7600 F).

Table 1.
Membrane preparation conditions.
2.4. Membrane Separation
Permeation and separation properties of the membranes were tested with the pervaporation (PV) rig at 75 °C. Figure 1b shows a schematic view of the apparatus. A membrane with a plugged end was immersed into a feed solution at a controlled temperature. The feed solution was stirred vigorously to prevent concentration and temperature polarization close to the membrane surface. The other end of the membrane was connected to a vacuum line. Liquid feed permeated through the membrane as vapor using the chemical potential difference across the membrane as a driving force. Permeated vapor was collected using a liquid nitrogen cold trap. After condensation for 30 to 60 min, the line was changed using a three-way valve to introduce the permeate to a new cold trap. The test was continued for more than three hours until the membrane properties were stable. After measuring the mass of the permeate, its concentration was measured by a gas chromatograph (GC-TCD, Shimadzu GC-8A). PV test was continued for at least a few hours to confirm a steady flux and permeate concentration.
A synthetic mixture solution of 90 wt% ethanol and 10 wt% water was used as a standard. The same conditions were used to evaluate dehydration membranes in previous studies [14,15]. The standard tests were performed from time to time to evaluate the membrane property changes. Flux (J) [kg∙m−2∙h−1] and separation factor (α) [-] were used to represent the membrane permeation and separation properties, which were calculated as:
where m is the mass collected in time t, S is the effective membrane area (ca. 0.002 m2 in this study), xH2O (EtOH) is the water (ethanol) concentration in the feed, and yH2O (EtOH) is that in the permeate. Before changing the feed solution, membranes were washed with water.
J = m/(S∙t)
α = (y(H2O)/y(EtOH))/(x(H2O)/x(EtOH)),
The distillate obtained by vacuum evaporation of a fermented solution was applied to the membranes as it is. In some cases, the distillates were pre-treated before being applied to membranes. In the first pre-treatment, the distillate was neutralized by adding 0.1 mol/L sodium hydroxide solution dropwise. The pH of the distillate became 6.6 after adding about 20 mL of 0.1 mol/L NaOH solution to 1000 mL of distillate. In the second pre-treatment, the distillate was treated with activated carbon by dispersing 10 g of the activated carbon granules (Fujifilm Wako Pure Chemical Co., Tokyo, Japan) to 1000 g of the distillate. After keeping the solution in contact with the activated carbon for 100 h at room temperature, the activated carbon was removed by filtration from the solution.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Comparison of Dehydration Performance between Different Types of Zeolite Membranes
A synthetic mixture of 90% ethanol and 10% water was applied at 75 °C to three different types of zeolite membranes. The results are shown in Table 2, indicated as “Before”. All the membranes showed water-selective permeation with a water concentration in the permeate of over 98%. The LTA membrane showed the highest water selectivity and flux. The higher dehydration performance of LTA membranes was due to its lower Si/Al ratio (Si/Al = 1) compared to the MOR (Si/Al = 4.5) [15] and MFI (Si/Al = 13.1) [14] membranes, which gives a strong hydrophilic property to the membrane. In addition, the small zeolitic pore size of LTA (4.0 nm [17]) inhibited ethanol molecules with a 4.5 nm kinetic diameter [18,19], penetrating through the zeolitic pores.

Table 2.
Dehydration performance measured by pervaporation tests with a 90 wt% ethanol solution as feed at 75 °C.
After checking the membrane properties of a synthetic mixture, the distillate obtained after fermentation followed by vacuum distillation was applied to the membranes. The distillate contained about 0.92 mM of fumarate and 1.77 mM of acetate, as measured by HPLC. Due to the existence of organic acids, the distillate was acidic, with a pH of ca. 3.8.
Figure 2 shows an example of the dehydration performance in distillate as a function of separation time. The results for the MFI zeolite membrane are shown. The deviation of feed ethanol concentration over time was due to the continuous removal of water through the membrane and the occasional back-mixing of the permeate to the feed solution after GC analyses. The permeate ethanol concentration was less than 0.2% throughout the separation test, which showed the good dehydration performance of the membrane. On the contrary, the flux through the membrane gradually decreased and reached a stable value after about 8 h. The time required to reach stable separation properties was much longer with distillate than with a synthetic mixture, in which case the membrane properties were generally stabilized in less than two hours.
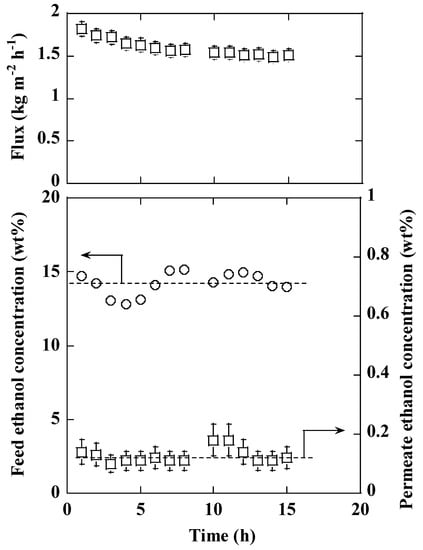
Figure 2.
Membrane dehydration performance as a function of PV test time measured at 75 °C with a MFI zeolite membrane.
Table 3 shows the separation and permeation properties when distillate was applied to different types of zeolite membranes. Values in the table are the average after the membrane performance reached steady-state. The permeate had a water concentration of over 99% for all types of membranes, showing water-selective permeation. While the LTA membrane showed the highest dehydration performance for separating a synthetic mixture among the three types of zeolite membranes studied, as shown in Table 2, the MOR membrane showed the best dehydration performance for separating the distillate: the ethanol concentration in the permeate was below the detection limit, and the flux was more than twice that of the flux of LTA and MFI membranes.

Table 3.
Dehydration performance measured by pervaporation tests with a distillate solution as feed supplied at 75 °C.
3.2. Distillate Separation with LTA Membrane
The separation and permeation properties were reproducible when a standard test with a synthetic binary mixture was repeated. On the contrary, membrane properties in standard tests changed after treating distillate, as shown in Table 2. For example, ethanol concentration in the permeate through fresh membrane (“Before” in the table) was less than 0.1%, which increased to ca. 23% after treating the distillate with a LTA membrane (“After” in the table). The total flux was 2.1 kg m−2 h−1 with a fresh membrane, which was reduced to less than half after treating the distillate. On the other hand, the ethanol partial flux increased by about 100 times. Apparently, the LTA membrane lost its water-selective properties after treating the distillate. The performance was not recovered by washing the membrane with water.
A drastic change in the membrane morphology was observed by SEM and XRD analyses. Figure 3a,b show the surface morphology of LTA membrane as synthesized and after treating the distillate, respectively. The surface of the fresh membrane was totally covered with cubic crystals, which is a typical shape for LTA zeolite crystals. On the contrary, no cubes were found on the membrane after separating the distillate, but the membrane surface was completely covered with a gel-like material. Figure 3c shows the XRD patterns analyzed before and after separating the distillate. The fresh membrane showed peaks corresponding to the LTA zeolite and the mullite used as a support. On the contrary, only mullite peaks were found in the membrane after the distillate separation. These results suggest that the LTA zeolite became amorphous during distillate separation. The aluminum in the zeolitic framework dissolves into an acidic medium [20], which resulted in the deformation of a LTA zeolite membrane in the acidic distillate. The change in hydrophilic LTA film to an amorphous layer caused the reduction in water selectivity and flux.
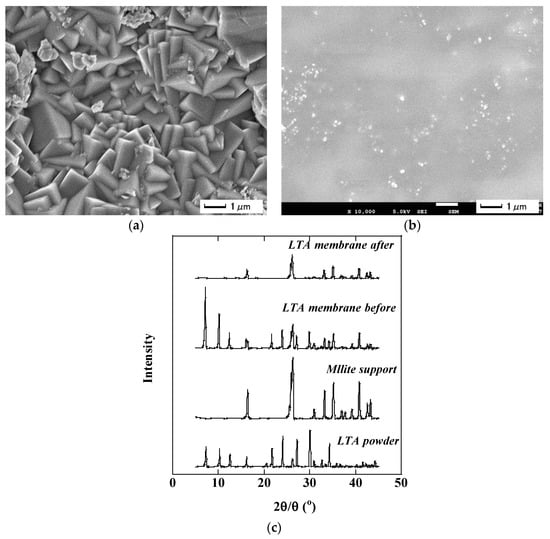
Figure 3.
LTA membrane morphology: (a) fresh membrane surface; (b) membrane surface after treating the distillate; (c) XRD patterns.
3.3. Distillate Separation with MFI and MOR Membranes
The influence of distillate treatment was smaller for the MFI and MOR membranes compared to the LTA membrane, as shown in Table 2. The water content in the permeate was over 98% for both membranes, even after treating the distillate. The total flux, however, declined about 35% with MFI membrane and 20% with MOR membrane. The flux was not recovered by washing the membranes with water nor by permeating water through the membranes at 75 °C for a few hours.
Figure 4a,b shows the surface morphology of an MFI membrane as observed by SEM. The surface of the membrane was completely covered with needle-like crystals and no major changes were observed after the distillate separation. Figure 4c,d shows the XRD patterns of the MFI and MOR zeolite membranes. No drastic changes were observed by XRD. For example, the intensity ratios of the MFI zeolite peak (7.9°) and the mullite peak (26.3°) were 0.18 and 0.18 for before and after treating the distillate, respectively. These results suggest no major deformation of zeolite crystals by treating distillate. These MFI and MOR membranes were reported to show stable dehydration performance with acetic acid solutions over 50% [14,15]. The higher acid stability of these membranes is considered to be due to the higher Si/Al ratio than that of the LTA membrane [21,22].
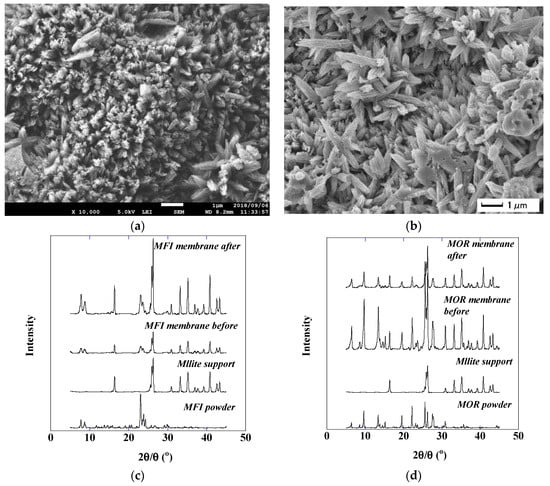
Figure 4.
Membrane morphologies: (a) fresh MFI membrane surface; (b) MFI membrane surface after treatment; (c) XRD patterns of MFI membrane; (d) XRD patterns of MOR membrane.
3.4. Changes in the Membrane Properties by Contacting a Distillate Solution
The change in membrane flux and separation ability with time of the separation test includes influences of transition to a steady state permeation and some changes in membranes by e.g., adsorption. To understand the influence of contacting the membranes with distillate, membranes were soaked in the distillate and the property changes were measured using a synthetic mixture separation. The MFI and MOR membranes were soaked in a distillate solution for a fixed time and then washed with water before the separation test. Each test was run for more than three hours to confirm stable flux and separation properties. The stable values are shown in Figure 5 as a function of total immersed time.
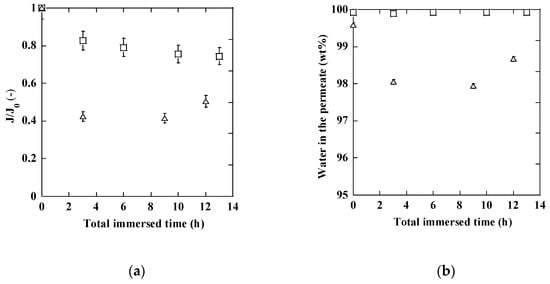
Figure 5.
Standard membrane performance measured after immersing the membranes into a distillate solution at 75 °C (□: MOR zeolite membrane, △: MFI membrane) (a): normalized flux as a function of total immersed time, (b): water content in the permeate as a function of total immersed time).
The membranes showed reproducible flux and water-selectivity when the separation tests with a synthetic mixture was repeated. On the contrary, flux decreased after immersing the membranes in a distillate solution (Figure 5a). Apparently, the flux change was caused by the contaminants in the distillate. A major flux reduction occurred after the first immersion of three hours. After soaking for more than ten hours in total, the flux was about 75% and half compared to the fresh membrane for MOR membrane and MFI membrane, respectively. Different from flux changes, water-selective properties were more or less maintained (Figure 5b). A small decrease in water selectivity was observed with the MFI membrane after the first immersion for three hours (Figure 5a). On the contrary, the water concentration in the permeate was constantly over 99.9% with the MOR membrane and no changes were observed by the immersion for 13 h in total.
3.5. Influence of Pre-Treatments
The adsorption of contaminants in the distillate was suspected as the main cause of flux decline. In attempting to to reduce the flux decline ratio in bioethanol dehydration, the distillate was treated with activated carbon. The acetic acid amount in the treated distillate became about half of the untreated distillate. However, the flux in synthetic mixture separation measured after testing the distillate became about 80% to the original flux as shown in Table 4 (MOR-3 membrane, conditions F and A). This decline ratio is almost the same with a membrane used to treat distillate without any pre-treatment (MOR-2 membrane). Even a small amount of acid may reduce the membrane flux. The permeate was almost water with ethanol under the detection limit.

Table 4.
Influence of distillate pretreatments on the dehydration performance of MOR membranes.
As another pre-treatment, the distillate was neutralized by the addition of NaOH solution and then applied to a fresh MOR membrane. The pH of the distillate was 3.3, which became 6.6 after the neutralization. The membrane properties are shown in Table 4 (indicated as MOR-4, D + NaOH). The flux in the dehydration of neutralized distillate was similar to the flux when a distillate without any treatment was applied. On the contrary, the flux decreased by about 40% in the standard test with a synthetic mixture after treating distillate, a ratio decrease that was about twice that observed with distillate without any pretreatment. Flux can be improved by neutralizing the bioethanol solution, which increases the electrostatic repulsion between negatively charged acid ions and membrane surface [23]. However, no strong influence of pH on the flux was observed in this study. Neutralization may form some adsorbent and reduce the membrane properties.
3.6. Other Possible Causes of the Flux Decline
Cation exchange from sodium to proton is another possible cause of the change in membrane properties. As the neutralized distillate did not prevent the flux decline, such influence is expected to be minor. To confirm, the membranes after distillate treatment were soaked in a 1 M of NaCl solution for more than one day and the standard test was performed. The post treatment did not recover the membrane performance, suggesting that the influence of cation exchange was negligible.
When comparing different types of zeolite membranes, the silicalite membrane resulted in about a 50% decrease after treating the distillate [10], a reduction rate that was larger than the decrease observed with the MFI membrane (34%, shown in Table 2) and the MOR membranes (ca. 20%, shown in Table 2 and Table 3) in this study. The dilicalite membrane has the same pore size as the MFI membrane (ca. 0.5 nm [17]), but is more hydrophobic (Si/Al = ∞). The least influenced MOR membranes among these membranes had the largest pore size (0.7 nm [17]) and the most hydrophilic property, as the Si/Al ratio of the membrane was 4.5 [15] and smaller than the MFI membranes used in this study (Si/Al = 13.1 [14]). Acids or some other molecules in the distillate solution may adsorb favorably to the hydrophobic sites of zeolite [24]. If an organic acid molecule, for example acetic acid with molecule size of ca. 0.44 nm [25], enters the zeolitic pores and strongly adsorbs in the pore, water and ethanol molecules, with a kinetic diameter of ca. 0.27 nm [18] and ca. 0.45 nm [18,19], respectively, can hardly pass over the acid. In this way, water and ethanol fluxes through zeolite membranes will be suppressed. Zeolites with a higher Si/Al ratio are more strongly influenced by pore blockage by the contaminant molecules and resulted in the larger flux reduction. If this is the major cause of the flux decline, the surface modification of the membrane to narrow the zeolitic pore opening size and inhibit the entry of contaminants may reduce the flux decrease in a distillate separation. Increasing the separation temperature is an alternative to improve the flux [26], but it will require more energy for the separation. In addition, the permeation of ethanol and other chemicals may increase with temperature as the hindrance of adsorption by water decreased. For a realization of the membrane process downstream of fermentation, further study to improve the flux in distillate dehydration and a process simulation to optimize the separation conditions are required.
4. Conclusions
The dehydration performance of three types of zeolite membranes was compared using bioethanol solution obtained from high-temperature fermentation followed by vacuum distillation. The distillate was acidic, with a pH of 3.8, and contained various contaminants in small concentrations, such as acetate and fumarate. While the LTA zeolite became amorphous in the distillate, the MOR and MFI membranes maintained their crystal structures. Treating the distillate did not have a significant influence on the water-selectivity of the MOR and MFI membranes, but decreased the flux measured in a synthetic mixture separation before and after treating the distillate. The flux decrease seemed to be larger when the Si/Al ratio of the membrane was higher.
The major flux decrease was observed in the first few hours when the membranes were in contact with the distillate. Then, the flux reached a steady state and an almost stable value for about 10 h of separation. The MOR membranes maintained their high water-selectivity in the dehydration of the distillate with the concentration of contaminants in the permeate under the detection limit. The results showed that the MOR membranes were promising candidates for the dehydration of a bioethanol solution. The application of these membranes is not limited to the dehydration of a distillate solution of high-temperature fermentation, but can be applied to other types of fermentation solutions. A further understanding of the causes for the flux decline and the developments of the distillate pre-treatment or membrane surface modification will improve the flux, which will reduce the required membrane area.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.K. and M.Y.; methodology, I.K. and M.Y.; validation, Y.M., R.K. and M.M.; formal analysis, Y.M., R.K. and T.K.; writing—original draft preparation, I.K., M.Y.; writing—review and editing, I.K.; funding acquisition, M.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by e-ASIA Joint Research Program, which was granted by Japan Science (JPMJSC16E5).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Marino Hara and Yusuke Shiota for their assistance in the research on ethanol fermentation and analysis of organic acids, respectively.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sokhansanj, S.; Mani, S.; Turhollow, A.; Kumar, A.; Bransby, D.; Lynd, L.; Laser, M. Large-Scale production, harvest and logistics of switchgrass (Panicum virgatum L.)—Current technology and envisioning a mature technology. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefin. 2009, 3, 124–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruins, M.E.; Sanders, J.P. Small-Scale processing of biomass for biorefinery. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefining 2012, 6, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Banat, B.M.; Hoshida, H.; Ano, A.; Nonklang, S.; Akada, R. High-temperature fermentation: How can processes for ethanol production at high temperatures become superior to the traditional process using mesophilic yeast? Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azhar, S.H.M.; Abdulla, R.; Jambo, S.A.; Marbawi, H.; Gansau, J.A.; Faik, A.A.M.; Rodrigues, K.F. Yeasts in sustainable bioethanol production: A review. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2017, 10, 52–61. [Google Scholar]
- Murata, M.; Nitiupn, S.; Lertwattanasakul, N.; Sootsuwan, K.; Kosaka, T.; Thanonkeo, P.; Limtong, S.; Yamada, M. High-temperature fermentation technology for low-cost bioethanol. J. Jpn. Inst. Energy 2015, 94, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kosaka, T.; Lertwattanasakul, N.; Rodrussamee, N.; Nurcholis, M.; Dung, N.T.P.; Keo-Oudone, C.; Murata, M.; Götz, P.; Theodoropoulos, C.; Maligan, J.M. Potential of thermotolerant ethanologenic yeasts isolated from ASEAN countries and their application in high-temperature fermentation. In Fuel Ethanol Production from Sugarcane; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; pp. 121–154. [Google Scholar]
- Rathore, A.; Shirke, A. Recent developments in membrane-based separations in biotechnology processes. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2011, 41, 398–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, A.; Aslam, M.; Qyyum, M.A.; Faisal, A.; Khan, A.L.; Ahmed, F.; Lee, M.; Kim, J.; Jang, N.; Chang, I.S. Membrane separation processes for dehydration of bioethanol from fermentation broths: Recent developments, challenges, and prospects. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 105, 427–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morigami, Y.; Kondo, M.; Abe, J.; Kita, H.; Okamoto, K. The first large-scale pervaporation plant using tubular-type module with zeolite NaA membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2001, 25, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumakiri, I.; Yokota, M.; Tanaka, R.; Shimada, Y.; Kiatkittipong, W.; Lim, J.W.; Murata, M.; Yamada, M. Process Intensification in Bio-Ethanol Production–Recent Developments in Membrane Separation. Processes 2021, 9, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, K.; Negishi, H.; Okuno, T.; Saito, T.; Tawarayama, H.; Ishikawa, S.; Miyamoto, M.; Uemiya, S.; Sawada, Y.; Oumi, Y. A simple secondary growth method for the preparation of silicalite-1 membrane on a tubular silica support via gel-free steam-assisted conversion. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 542, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumakiri, I.; Yamaguchi, T.; Nakao, S.-i. Preparation of zeolite A and faujasite membranes from a clear solution. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1999, 38, 4682–4688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza, A.; Merlet, G.; Hasanoglu, A.; Isaacs, M.; Sanchez, J.; Romero, J. Separation of butanol from ABE mixtures by sweep gas pervaporation using a supported gelled ionic liquid membrane: Analysis of transport phenomena and selectivity. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 444, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, M.-H.; Kumakiri, I.; Tanaka, K.; Kita, H. Dehydration of acetic acid and esterification product by acid-stable ZSM-5 membrane. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 181, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.-H.; Xia, S.-L.; Hua, X.-M.; Feng, Z.-J.; Hu, N.; Zhang, F.; Kumakiri, I.; Lu, Z.-H.; Chen, X.-S.; Kita, H. Rapid preparation of acid-stable and high dehydration performance mordenite membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 19168–19174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limtong, S.; Sringiew, C.; Yongmanitchai, W. Production of fuel ethanol at high temperature from sugar cane juice by a newly isolated Kluyveromyces marxianus. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 3367–3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: http://www.iza-structure.org/databases/ (accessed on 10 October 2021).
- Borjigin, T.; Sun, F.; Zhang, J.; Cai, K.; Ren, H.; Zhu, G. A microporous metal–organic framework with high stability for GC separation of alcohols from water. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 7613–7615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Kumakiri, I.; Tanaka, K.; Chen, X.; Kita, H. NaY zeolite membranes with high performance prepared by a variable-temperature synthesis. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 182, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, R.; Millot, Y.; Onfroy, T.; Krafft, J.-M.; Dzwigaj, S. Influence of the nitric acid treatment on Al removal, framework composition and acidity of BEA zeolite investigated by XRD, FTIR and NMR. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2012, 163, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravenelle, R.M.; Schüβler, F.; D’Amico, A.; Danilina, N.; Van Bokhoven, J.A.; Lercher, J.A.; Jones, C.W.; Sievers, C. Stability of zeolites in hot liquid water. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 19582–19595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, K.; Chen, B.; White, J.L.; Resasco, D.E. Factors that determine zeolite stability in hot liquid water. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 11810–11819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikegami, T.; Negishi, H.; Kitamoto, D.; Sakaki, K.; Imura, T.; Okamoto, M.; Idemoto, Y.; Koura, N.; Sano, T.; Haraya, K. Stabilization of bioethanol recovery with silicone rubber-Coated ethanol-Permselective silicalite membranes by controlling the pH of acidic feed solution. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. Int. Res. Process., Environ. Clean Technol. 2005, 80, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljundi, I.H.; Belovich, J.M.; Talu, O. Adsorption of lactic acid from fermentation broth and aqueous solutions on Zeolite molecular sieves. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2005, 60, 5004–5009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Shi, R.; Du, P.; Qiu, X.; Gu, X. Pervaporation dehydration of acetic acid through hollow fiber supported DD3R zeolite membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 204, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, M.; Hu, N.; Zhang, F.; Wu, T.; Chen, X.; Kita, H. Scale-up of high performance mordenite membranes for dehydration of water-acetic acid mixtures. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 564, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).