Prescription Patterns of Sacubitril/Valsartan in an Outpatient Population Diagnosed with Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction After a Recent Hospitalization
Abstract
1. Background
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACE inhibitor | Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor |
| ARNI | Angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor |
| ACC | American College of Cardiology |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| ED | Emergency Department |
| ESC | European Society of Cardiology |
| GDMT | Guideline-directed medical therapy |
| HFmrEF | Heart Failure with Mildly Reduced Ejection Fraction |
| HFpEF | Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction |
| HFrEF | Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction |
| ICER | Incremental Cost-Effectiveness Ratio |
| LVEF | Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction |
| MRA | Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist |
| QALY | Quality-adjusted life year |
| SGLT-2 inhibitors | Sodium-Glucose Transporter-2 inhibitors |
| S/V | Sacubitril/Valsartan |
References
- Groenewegen, A.; Rutten, F.H.; Mosterd, A.; Hoes, A.W. Epidemiology of heart failure. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2020, 22, 1342–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Böhm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Čelutkienė, J.; Chioncel, O.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3599–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCullough, P.A.; Mehta, H.S.; Barker, C.M.; Van Houten, J.; Mollenkopf, S.; Gunnarsson, C.; Ryan, M.; Cork, D.P. Mortality and guideline-directed medical therapy in real-world heart failure patients with reduced ejection fraction. Clin. Cardiol. 2021, 44, 1192–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurray, J.J.V.; Packer, M.; Desai, A.S.; Gong, J.; Lefkowitz, M.P.; Rizkala, A.R.; Pharm, D.; Rouleau, J.L.; Victor, C.; Shi, M.D.; et al. Angiotensin–Neprilysin Inhibition versus Enalapril in Heart Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 993–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senni, M.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Wachter, R.; McIntyre, H.F.; Reyes, A.; Majercak, I.; Andreka, P.; Shehova-Yankova, N.; Anand, I.; Yilmaz, M.B.; et al. Initiating sacubitril/valsartan (LCZ696) in heart failure: Results of TITRATION, a double-blind, randomized comparison of two uptitration regimens. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2016, 18, 1193–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeffer, M.A.; Claggett, B.; Lewis, E.F.; Granger, C.B.; Køber, L.; Maggioni, A.P.; Mann, D.L.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Rouleau, J.-L.; Solomon, S.D.; et al. Angiotensin Receptor–Neprilysin Inhibition in Acute Myocardial Infarction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1845–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardeny, O.; Claggett, B.; Packer, M.; Zile, M.R.; Rouleau, J.; Swedberg, K.; Teerlink, J.R.; Desai, A.S.; Lefkowitz, M.; Shi, V.; et al. Efficacy of sacubitril/valsartan vs. enalapril at lower than target doses in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: The PARADIGM-HF trial. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2016, 18, 1228–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentz, R.J.; Ward, J.H.; Hernandez, A.F.; Lepage, S.; Morrow, D.A.; Sarwat, S.; Sharma, K.; Starling, R.C.; Velazquez, E.J.; Williamson, K.M.; et al. Angiotensin-Neprilysin Inhibition in Patients with Mildly Reduced or Preserved Ejection Fraction and Worsening Heart Failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2023, 82, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, P.; Beliën, H.; Dupont, M.; Mullens, W. Insights into implementation of sacubitril/valsartan into clinical practice. ESC Heart Fail. 2018, 5, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, A.R.; Lee, C. Pharmacist- or Nurse Practitioner-Led Assessment and Titration of Sacubitril/Valsartan in a Heart Failure Clinic: A Cohort Study. Can. J. Hosp. Pharm. 2020, 73, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lin, Z.; Miao, D.; Zhang, H.; Fu, K.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, J.; Hu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, F.; et al. Dose titration of sacubitril/valsartan for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: A real-world study. ESC Heart Fail. 2023, 10, 1961–1971. [Google Scholar]
- Dewan, P.; Jackson, A.; Jhund, P.S.; Shen, L.; Ferreira, J.P.; Petrie, M.C.; Abraham, W.T.; Desai, A.S.; Dickstein, K.; Køber, L.; et al. The prevalence and importance of frailty in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction—An analysis of PARADIGM-HF and ATMOSPHERE. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2020, 22, 2123–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, J.H.; Dewan, P.; Jhund, P.S.; Anand, I.S.; Atar, D.; Ge, J.; Desai, A.S.; Echeverria, L.E.; Køber, L.; Lam, C.S.P.; et al. Sacubitril/Valsartan and Frailty in Patients with Heart Failure and Preserved Ejection Fraction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 80, 1130–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, P.; Verluyten, L.; Van De Broek, H.; Somers, F.; Dauw, J.; Dupont, M.; Mullens, W. Determinants of maximal dose titration of sacubitril/valsartan in clinical practice. Acta Cardiol. 2021, 76, 20–29. [Google Scholar]
- Heidenreich, P.A.; Bozkurt, B.; Aguilar, D.; Allen, L.A.; Byun, J.J.; Colvin, M.M.; Deswal, A.; Drazner, M.H.; Dunlay, S.M.; Evers, L.R.; et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2022, 145, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rindone, J.P.; Mellen, C.K. Sacubitril/valsartan compared to equivalent/sub-equivalent dose angiotensin receptor blocker or angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: A meta-analysis of randomized trials. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2024, 80, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Jiang, J.; Gao, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.L.; Dang, H.Q. Efficacy and safety of low-dose sacubitril/valsartan in heart failure patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Cardiol. 2023, 46, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Januzzi, J.L.; Prescott, M.F.; Butler, J.; Felker, G.M.; Maisel, A.S.; McCague, K.; Camacho, A.; Piña, I.L.; Felker, G.M.; Maisel, A.S.; et al. Association of Change in N-Terminal Pro–B-Type Natriuretic Peptide Following Initiation of Sacubitril-Valsartan Treatment with Cardiac Structure and Function in Patients with Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction. JAMA 2019, 322, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohebi, R.; Liu, Y.; Piña, I.L.; Prescott, M.F.; Butler, J.; Felker, G.M.; Ward, J.H.; Solomon, S.D.; Januzzi, J.L., Jr. Dose-Response to Sacubitril/Valsartan in Patients with Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 80, 1529–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kido, K.; Bianco, C.; Caccamo, M.; Fang, W.; Sokos, G. Evaluating Sacubitril/Valsartan Dose Dependence on Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction. Ann. Pharmacother. 2021, 55, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar]
- Doi, S.; Kida, K.; Nasu, T.; Ishii, S.; Kagiyama, N.; Fujimoto, W.; Ijichi, T.; Shibata, T.; Kanaoka, K.; Matsumoto, S.; et al. Uptitration of Sacubitril/Valsartan and Outcomes in Patients with Heart Failure—Insight From the REVIEW-HF Registry—. Circ. J. 2024, 89, 93–100. [Google Scholar]
- Rung, J.M.; Barrett, T.S.; LeJeune, K.; Richards, S.B.; Raina, A.; Sinoway, L. Dosing patterns and dose effects of sacubitril/valsartan: A claims-based retrospective cohort study. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0320216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Park, C.S.; Rhee, T.M.; Choi, H.J.; Choi, H.M.; Lee, H.J.; Park, J.B.; Yoon, Y.E.; Lee, S.P.; Kim, Y.J.; et al. On-treatment blood pressure and dose-dependent effects of ARNI in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: Insights from a multicenter registry. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0328971. [Google Scholar]
- Gaziano, T.A.; Fonarow, G.C.; Claggett, B.; Chan, W.W.; Deschaseaux-Voinet, C.; Turner, S.J.; Rouleau, J.L.; Zile, M.R.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Solomon, D.S.; et al. Cost-effectiveness Analysis of Sacubitril/Valsartan vs Enalapril in Patients with Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction. JAMA Cardiol. 2016, 1, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, J.B.; Shah, R.U.; Bress, A.P.; Nelson, R.E.; Bellows, B.K. Cost-Effectiveness of Sacubitril-Valsartan Combination Therapy Compared with Enalapril for the Treatment of Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction. JACC Heart Fail. 2016, 4, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezapour, A.; Azari, S.; Arabloo, J.; Kolivand, P.; Behzadifar, M.; Omidi, N.; Asiabar, A.S.; Saberian, P.; Pourasghari, H.; Bragazzi, N.L.; et al. Cost-Effectiveness of Sacubitril/Valsartan Compared with Enalapril in Patients with Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction: A Systematic Review. JTHC 2023, 17, 168. [Google Scholar]
- Maddox, T.M.; Januzzi, J.L.; Allen, L.A.; Breathett, K.; Brouse, S.; Butler, J.; Davis, L.L.; Fonarow, G.C.; Ibrahim, N.E.; Lindenfeld, J.; et al. 2024 ACC Expert Consensus Decision Pathway for Treatment of Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction: A Report of the American College of Cardiology Solution Set Oversight Committee. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2024, 83, 1444–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics of Patients with Suboptimal S/V at Discharge (n = 40) | |
|---|---|
| Characteristics | |
| Age—Median [IQR] | 77 [66.8–82] |
| Male sex—no. (%) | 31 (77%) |
| LVEF category | |
| 0–9% | 0 |
| 10–19% | 3 |
| 20–29% | 10 |
| 30–39% | 17 |
| 40–49% | 7 |
| Unknown | 3 |
| LVEF—Mean ± SD | 30% ± 7.9 |
| LVEF—Median [IQR] | 30% [10] |
| BMI (kg/m2)—Median [IQR] | 28.9 [25.3–31.9] |
| Comorbidities | |
| Arterial Hypertension | 52.5% (21/40) |
| Diabetes | 30% (12/40) |
| Chronic Kidney Disease | 35% (14/40) |
| Atrial Fibrillation | 52.5% (21/40) |
| Proven cardiac ischemia | 65% (26/40) |
| Valvular anomalies | |
| Aortic Stenosis | 10% (4/40) |
| Aortic Regurgitation | 30% (12/40) |
| Mitral Stenosis | 2.5% (1/40) |
| Mitral Regurgitation | 53% (21/40) |
| Tricuspid Stenosis | 0% (0/40) |
| Tricuspid Regurgitation | 38% (15/40) |
| Pulmonary Stenosis | 0% (0/40) |
| Pulmonary Regurgitation | 5% (2/40) |
| Average Blood values at discharge—Mean ± SD or Median [IQR] | |
| Hemoglobin (g/L) | 123 [114–135] |
| Sodium (mmol/L) | 138 ± 4 |
| Potassium (mmol/L) | 4.3 [3.98–4.9] |
| Creatinine (µmol/L) | 104 [80–120] |
| Other heart failure medications received by patients | |
| Beta Blockers | 88% (35/40) |
| MRA | 30% (12/40) |
| Diuretic | 75% (30/40) |
| Diuretic dose—mg of Torasemide | |
| 1–10 | 18 |
| 11–20 | 8 |
| 21–30 | 2 |
| ≥30 | 2 |
| SGLT-2 inhibitors | 27.5% (11/40) |
| Patients with prior Heart Failure hospitalization during the year | 25% (10/40) |
| Index hospitalization for heart failure | 65% (22/40) |
| Frontline physicians for follow-up (absolute number—patients followed) | |
| General Practitioner | 80% (28/35)—29 patients |
| Cardiologist | 20% (7/35)—11 patients |
| Questionnaire Results | |
|---|---|
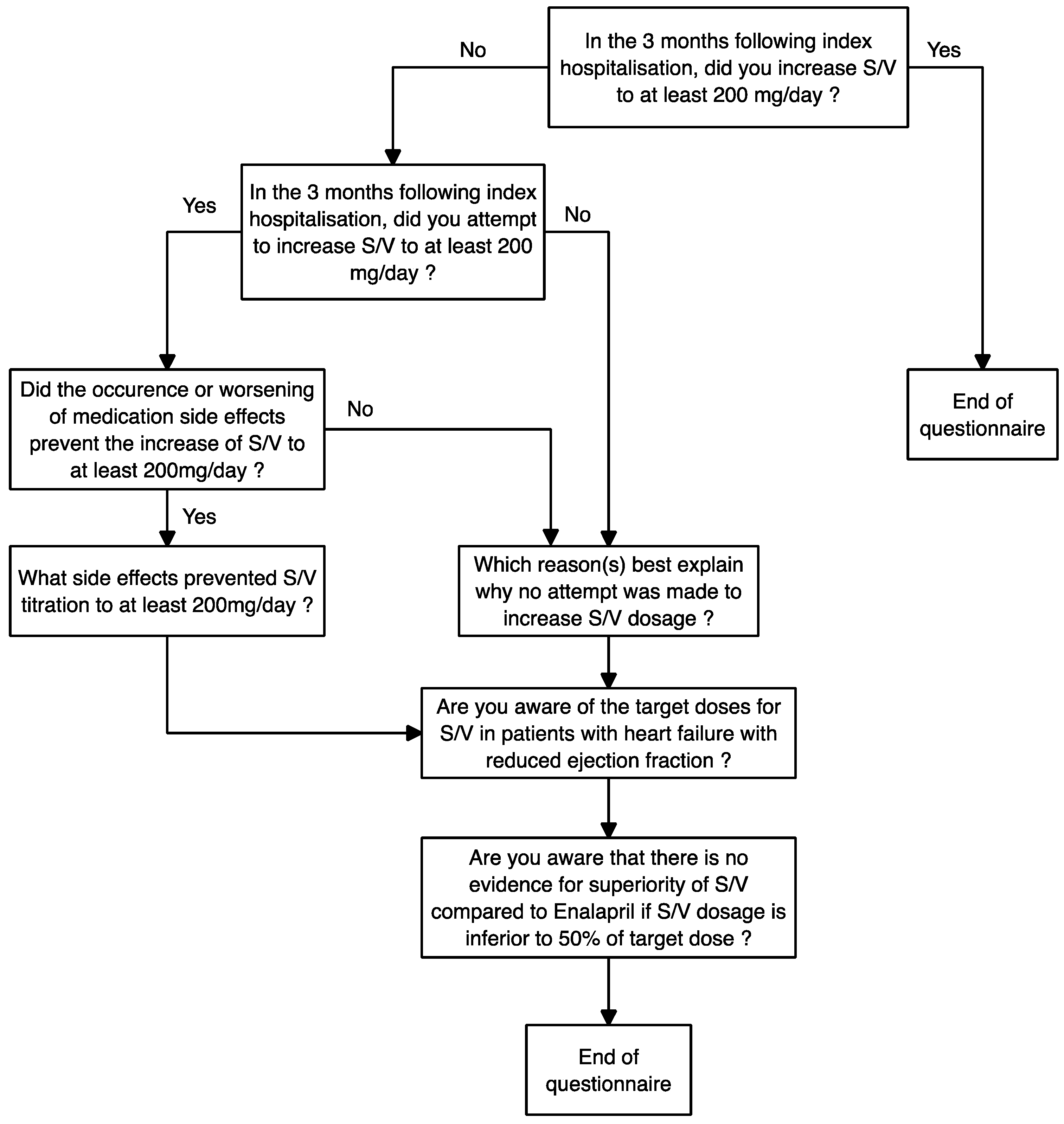
| Patients increased to ≥200 mg/day—% | 25% (10/40) |
| Patients in whom an unsuccessful attempt to increase to ≥200 mg/day was made | 10% (3/30) |
| Patients in whom physician attempted to increase to ≥200 mg/day but presented side effects that prevented the increase | 100% (3/3) |
| Side effects presented by the patients in whom there was an attempt to increase to ≥200 mg/day | Symptomatic hypotension (3) |
| Fatigue (1) | |
| AKI (1) | |
| Reasons for which no attempt was made to increase the patient to ≥200 mg/day * | Titration was assumed to be cardiologist’s role: 56% (15/27) |
| Pre-existing hypotension: 19% (5/27) | |
| Clinical stability: 15% (4/27) | |
| Lost to follow-up: 7% (2/27) | |
| Difficult follow-up: 4% (1/27) | |
| Other medication titration priorities: 4% (1/27) | |
| Potassium upper limit of normal: 4% (1/27) | |
| No specific reason provided: 4% (1/27) | |
| Previous failure to titrate: 4% (1/27) | |
| Double GP follow-up: 4% (1/27) | |
| Physicians knowing target doses of S/V † | 65.7% (23/35) |
| Awareness concerning undemonstrated effect of S/V compared to Enalapril if S/V < 200 mg/day, in post hoc analysis of PARADIGM-HF | 17.1% (6/35) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roustan, D.; Bothorel, H.; Kherad, O. Prescription Patterns of Sacubitril/Valsartan in an Outpatient Population Diagnosed with Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction After a Recent Hospitalization. Epidemiologia 2025, 6, 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia6030055
Roustan D, Bothorel H, Kherad O. Prescription Patterns of Sacubitril/Valsartan in an Outpatient Population Diagnosed with Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction After a Recent Hospitalization. Epidemiologia. 2025; 6(3):55. https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia6030055
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoustan, Dimitri, Hugo Bothorel, and Omar Kherad. 2025. "Prescription Patterns of Sacubitril/Valsartan in an Outpatient Population Diagnosed with Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction After a Recent Hospitalization" Epidemiologia 6, no. 3: 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia6030055
APA StyleRoustan, D., Bothorel, H., & Kherad, O. (2025). Prescription Patterns of Sacubitril/Valsartan in an Outpatient Population Diagnosed with Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction After a Recent Hospitalization. Epidemiologia, 6(3), 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia6030055






