Evaluation of Pain in the Pediatric Patient Admitted to Sub-Intensive Care: What Is the Evidence? A Scoping Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design
2.2. Review Methods
2.2.1. Review Question
2.2.2. Inclusion Criteria
2.2.3. Search Strategy
2.2.4. Study/Source of Evidence Selection
2.2.5. Data Extraction
2.2.6. Data Analysis and Presentation
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Included Studies
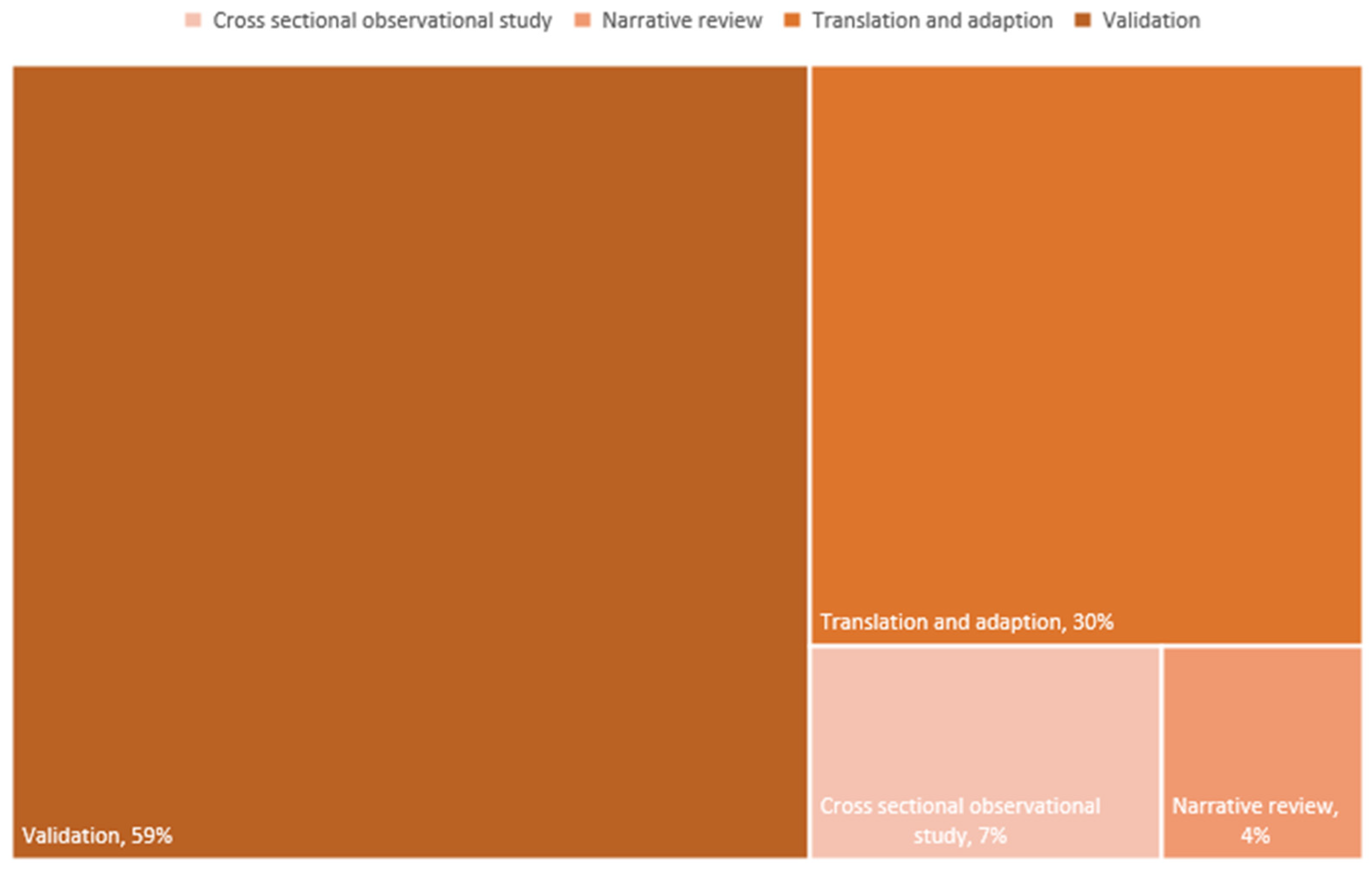
3.1.1. Study Design
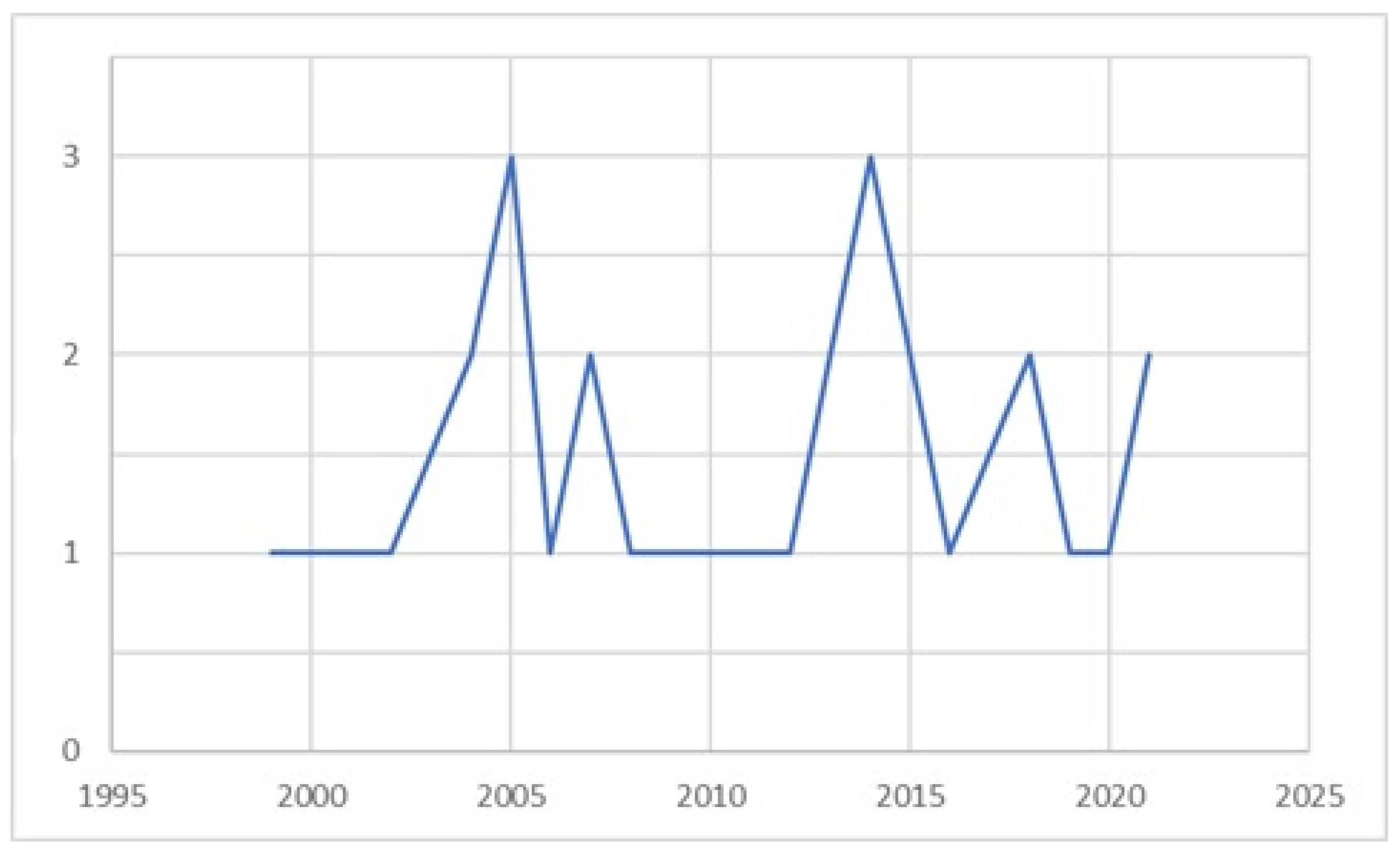
3.1.2. Time Distribution of Studies
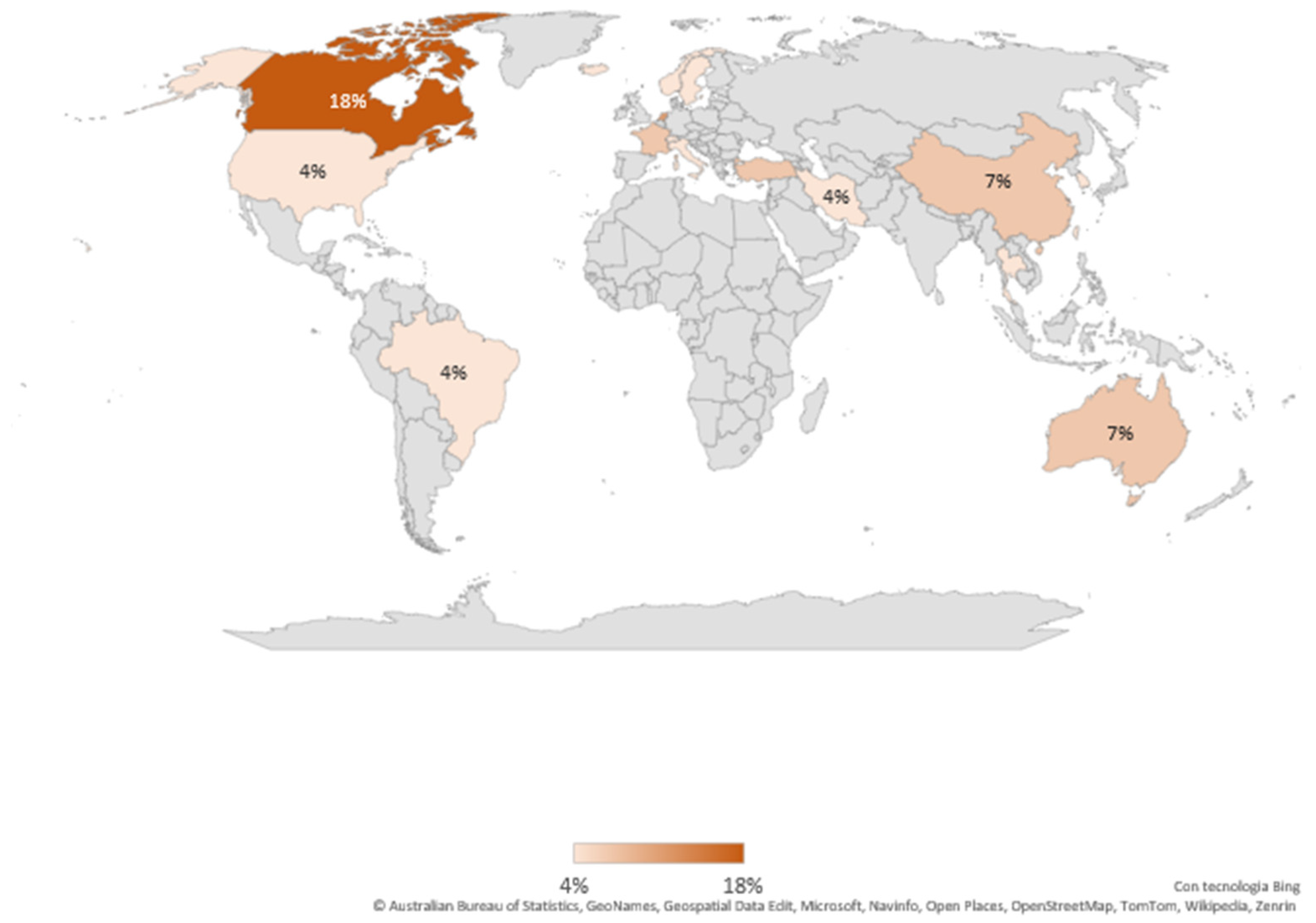
3.1.3. Provenance of Included Studies
3.1.4. Population
3.1.5. Context of the Studies
3.1.6. Scales
3.2. Premature Infant Pain Profile (PIPP)
3.3. Premature Infant Pain Profile-R (PIPP-R)
3.4. COMFORT Scale and COMFORT-Neo
3.5. Other Scales Who Consider Both Behavioral and Physiological Aspects
3.6. Scales That Consider Only the Behavioral Aspects
3.7. Scales Descripted by Ramelet et al. in Their Narrative Review [64]
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary of Evidence
4.2. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| PubMed | (“Infant, Newborn”[Mesh] OR “infant”[Mesh] OR “Child”[Mesh] OR “child” OR “children” OR “newborn” OR “newborns” OR “baby” OR “babies” OR “pediatric” OR “paediatric” OR “pediatrics” OR “paediatric” OR “infant” OR “infants” OR “neonate” OR “neonates”) AND (“Pain”[Mesh] OR “Pain Measurement”[Mesh] OR “pain” OR “pains” OR “physical suffering” OR “physical sufferings” OR “ache” OR “aches” OR “pain measurement” OR “pain measurements” OR “nociception tests” OR “nociception test” OR “analgesia test” OR “analgesia tests” OR “pain assessment” OR “pain assessments” OR “pain scale” OR “pain scales” OR “pain rating scale” OR “pain intensities” OR “pain severities” OR “pain severity” OR “pain tool” OR “pain tools” OR “pain evaluation” OR “pain assessment score” OR “pain rating score”) AND (“Intensive Care Units”[Mesh] OR “Intensive Care Units, Neonatal”[Mesh] OR “Intensive Care Units, Pediatric”[Mesh] OR “Intensive Care Units” OR “Intensive Care Unit” OR “Neonatal intensive care unit” OR “ Neonatal intensive care” OR “Pediatric intensive care unit” OR “Pediatric intensive care” OR “Paediatric intensive care unit” OR “Paediatric intensive care” OR “PICU” OR “NICU” OR “high dependency unit”) |
Appendix B
| Title | Authors | Journal | Year | Country | Design | Number of Participants | Scales | Population | Concept | Context |
| Validation of the premature infant pain profile in the clinical setting [38] | Ballantyne, M., Stevens, B., McAllister, M., Dionne, K. and Jack, A. | The Clinical journal of pain | 1999 | Canada | Validation | 43 | PIPP | Preterm and term infants | Construct validity and reliability of PIPP | NICU |
| The reliability and validity of the COMFORT scale as a postoperative pain instrument in 0 to 3-year-old infants [50] | Van Dijk, M., De Boer, J. B., Koot, H. M., Tibboel, D., Passchier, J., and Duivenvoorden, H. J. | Pain | 2000 | Netherlands | Validation | 158 | COMFORT | Preterm and term infants, bambini | Validity and reliability of the COMFORT scale | Pediatric surgical intensive care unit (PSICU) |
| Development and initial validation of the EDIN scale, a new tool for assessing prolonged pain in preterm infants [41] | Debillon, T., Zupan, V., Ravault, N., Magny, J.-F., and Dehan, M. | Archives of disease in childhood. Fetal and neonatal edition | 2001 | France | Validation | 76 | EDIN | Preterm infants | To evaluate whether the EDIN scale can assess prolonged pain in preterm infants | NICU - Neonatal Care |
| Validation of the Pain Assessment in Neonates (PAIN) scale with the Neonatal Infant Pain Scale (NIPS) [45] | Hudson-Barr, D., Capper-Michel, B., Lambert, S., Mizell Palermo, T., Morbeto, K., and Lombardo, S. | Neonatal network | 2002 | USA | Validation | 196 | PAIN (Test) NIPS and CRIES (Control) | Preterm and term infants | Validity of PAIN scale | NICU and sub-intensive |
| Pain assessment in the neonate using the Bernese Pain Scale for Neonates [40] | Cignacco E and Mueller R and Hamers JP and Gessler P | Early human development | 2004 | Switzerland | Validation | 12 | BPSN | Preterm and term infants | Validity of BPSN scale in both ventilated and not ventilated infants | NICU |
| The challenges of pain measurement in critically ill young children: a comprehensive review [64] | Ramelet, A.-S., Abu-Saad, H. H., Rees, N., and McDonald, S | Australian critical care: | 2004 | Australia | Narrative review | PIPP, PAIN, SUN, PAT, DSVNI, N—PASS, CRIES, NIPS, EDIN, DAN, LIDS, IBCS, MIPS, POCIS, PEPPS, TPPPS, CFCS, CHEOPS, NFCS, COMFORTRIPS, POPS, NAPI, CHIPPS, BPS, MBPS, FLACC, OPS | Infants, children between 0 and 3 years old, children > 12 years old | Problems in measuring pain in critically ill children, with list of specific measures for children 0 to 3 years old | PICU | |
| Pain assessment using CRIES, FLACC and PIPP in high-risk infants [62] | Ahn, Y., Kang, H., and Shin, E. | Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing | 2005 | Korea | Cross-sectional | 68 | CRIES, FLACC, PIPP | Preterm and term infants | Comparison among CRIES—FLACC— PIPP scales | NICU |
| A reliable pain assessment tool for clinical assessment in the neonatal intensive care unit [48] | Spence, K., Gillies, D., Harrison, D., Johnston, L., and Nagy, S. | Journal of obstetric, gynecologic, and neonatal nursing | 2005 | Australia | Validation | 144 | PAT (Test), CRIES (Control) | Preterm and term infants | Assessing the reliability of the PAT scale | NICU |
| The sensitivity of the premature infant pain profile—PIPP to measure pain in hospitalized neonates [57] | Jonsdottir, R. B. and Kristjansdottir, G. | Journal of evaluation in clinical practice | 2005 | Iceland | Translation and adaptation | 24 | PIPP | Preterm and term infants | Validation of PIPP scale in Iceland | NICU |
| Psychometric testing of a Norwegian version of the Premature Infant Pain Profile: an acute pain assessment tool. A clinical validation study [61] | Vederhus, B. J., Eide, G. E., and Natvig, G. K. | International Journal of Nursing Practice | 2006 | Norway | Translation and adaptation | 123 | PIPP | Preterm and term infants | Validation of PIPP scale in Norway | NICU and Neonatal care |
| Measurement of pain in premature infants with a gestational age between 28 to 37 weeks: validation of the adapted COMFORT scale [39] | Caljouw, M. A. A., Kloos, M. A. C., Olivier, M. Y., Heemskerk, I. W., Pison, W. C. R., Stigter, G. D., and Verhoef, A.-M. J. H. | Journal of Neonatal Nursing | 2007 | Netherlands | Validation | 57 | Adapted COMFORT scale (Test), VAS (Control) | Preterm infants | Reliability of COMFORT scale | NICU |
| Initial validation of the Behavioral Indicators of Infant Pain (BIIP) [44] | Holsti, L. and Grunau, R. E. | Pain | 2007 | Canada | Validation | 92 | BIIP | Preterm infants | Improve NIPS and PIPP by combining them into a single scale | NICU |
| Is it painful or not? Discriminant validity of the Behavioral Indicators of Infant Pain (BIIP) scale [43] | Holsti, L., Grunau, R. E., Oberlander, T. F., and Osiovich, H. | The Clinical journal of pain | 2008 | Canada | Validation | 69 | BIIP | Preterm infants | To determine whether BIIP is useful for the assessment of acute procedural pain | NICU |
| Taking up the challenge of measuring prolonged pain in (premature) neonates: the COMFORTneo scale seems promising [51] | Van Dijk, M., Roofthooft, D. W. E., Anand, K. J. S., Guldemond, F., De Graaf, J., Simons, S., De Jager, Y., Van Goudoever, J. B., and Tibboel, D. | The Clinical journal of pain | 2009 | Netherlands | Validation | 286 | COMFORT neo (Test), NRS (Control) | Preterm infants | Validity of COMFORT —Neo scale for prolonged pain | NICU |
| Validation of a neonatal pain scale adapted to the new practices in caring for preterm newborns [47] | Milesi, C., Cambonie, G., Jacquot, A., Barbotte, E., Mesnage, R., Masson, F., Pidoux, O., Ferragu, F., Thevenot, P., Mariette, J.-B., and Picaud, J.-C. | Archives of disease in childhood. Fetal and neonatal edition | 2010 | France | Validation | 53 | FANS (Test), DAN (Control) | Preterm infants | Validity of FANS scale | NICU |
| Validity and reliability of neonatal infant pain scale in neonatal intensive care units in Iran [59] | Sarhangi, F., Mollahadi, M., Ebadi, A., Matinzadeh, Z. K., and Tadrisi, S. D. | Pakistan Journal of Medical Sciences | 2011 | Iran | Translation and adaptation | 68 | NIPS (Test), VAS (Control) | Preterm infants | Validity and reliability of NIPS | NICU |
| Psychometric analysis of a Taiwan-version pain assessment scale for preterm infants [46] | Liaw, J., Yang, L., Chou, H., Yin, T., Chao, S., and Lee, T. | Journal of Clinical Nursing | 2012 | Taiwan | Validation | 60 | PASPI (Test), PIPP e VAS (Control) | Preterm and term infants | Validity of PASPI | NICU |
| Avaliação da dor prolongada no recém-nascido: adaptação da escala EDIN para a cultura brasileira [55] | de Souza Barbosa Dias, F., and Martins Marba, S. T. | Texto and Contexto Enfermagem | 2014 | Brazil | Translation and adaptation | 76 | EDIN | Preterm infants | Validation of EDIN in Brazil | NICU and sub-intensive |
| The premature infant pain profile-revised (PIPP-R): initial validation and feasibility [49] | Stevens, B. J., Gibbins, S., Yamada, J., Dionne, K., Lee, G., Johnston, C., and Taddio, A. | The Clinical journal of pain | 2014 | Canada | Validation | 52 | PIPP-R (Test), PIPP (Control) | Preterm and term infants | Validity of PIPP—R scale | NICU |
| Validation of the Premature Infant Pain Profile-Revised (PIPP-R) [42] | Gibbins, S., Stevens, B. J., Yamada, J., Dionne, K., Campbell-Yeo, M., Lee, G., Caddell, K., Johnston, C., and Taddio, A. | Early human development | 2014 | Canada | Validation | 202 | PIPP-R | Preterm and term infants | Validity of PIPP-R scale | NICU |
| La scala algometrica PIPP: valutazione dell’accuratezza per la rilevazione del dolore procedurale nel neonate [63] | Tasca, T., Spata, M., Badon, P., Pellegatta, F., Buchini, S., Monterosso, A., and Canesi, M. | Pain Nursing Magazine | 2016 | Italy | Cross-sectional | 60 | PIPP | Preterm and term infants | To evaluate the reliability of PIPP in comparison with the findings from the “pain monitor”. | NICU |
| Development of a Clinical Pain Scale for Preterm Neonates [52] | Woragidpoonpol, P., Tiansawad, S., Mesukko, J., and Klunklin, P. | Pacific Rim International Journal of Nursing Research | 2018 | Thailand | Validation | 8 (phase 1), 19 (phase 2) | CPSPN (Test), PIPP-R (Control) | Preterm infants | Development and validation of CPSPN | NICU |
| Cultural adaptation and harmonization of four Nordic translations of the revised Premature Infant Pain Profile (PIPP-R) [58] | Olsson, E., Anderzén-Carlsson, A., Atladóttir, S. M., Axelin, A., Campbell-Yeo, M., Eriksson, M., Kristjánsdóttir, G., Peltonen, E., Stevens, B., Vederhus, B., and Andersen, R. D. | BMC pediatrics | 2018 | Sweden | Translation and adaptation | (video) | PIPP—R | Preterm and term infants | Validating PIPP—R in Finnish, Norwegian, Icelandic, Swedish | NICU |
| Psychometric Testing of the Turkish Version of the Premature Infant Pain Profile Revised-PIPP-R [60] | Taplak, A. Ş. and Bayat, M. | Journal of Pediatric Nursing | 2019 | Turkey | Translation and adaptation | 200 | PIPP-R | Preterm and term infants | Validation of PIPP-R in Turkey | NICU |
| Evaluation of the Reliability and Validity of the Behavioral Indicators of Infant Pain Scale in Chinese Neonates [54] | Chen, Y., Tong, Y., Xue, Z., Cheng, Y., and Li, X. | Pain management nursing: | 2020 | China | Translation and adaptation | 369 | C-BIIP (Test), FLACC (Control) | Preterm and term infants | Validation of C-BIIP in China | NICU |
| Assessment of four pain scales for evaluating procedural pain in premature infants undergoing heel blood collection [53] | Xie, W., Wang, X., Huang, R., Chen, Y., and Guo, X. | Pediatric research | 2021 | Cina | Validation | 111 | NFCS, DAN, NIPS, PIPP | Preterm infants | Validation of NFCS, DAN, NIPS, PIPP scales for procedural pain | NICU |
| Turkish validity and reliability of the COVERS pain scale [56] | İncekar, M. Ç., Öğüt, N. U., Mutlu, B., Çeçen, E., and Can, E. | Revista da Associacao Medica Brasileira | 2021 | Turkey | Translation and adaptation | 41 | COVERS (Test), PIPP and NIPS (Control) | Preterm and term infants | Validation of COVERS, in Turkey | NICU |
References
- Scher, C.; Meador, L.; Van Cleave, J.H.; Reid, M.C. Moving Beyond Pain as the Fifth Vital Sign and Patient Satisfaction Scores to Improve Pain Care in the 21st Century. Pain Manag. Nurs. 2018, 19, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raja, S.N.; Carr, D.B.; Cohen, M.; Finnerup, N.B.; Flor, H.; Gibson, S.; Keefe, F.J.; Mogil, J.S.; Ringkamp, M.; Sluka, K.A.; et al. The Revised International Association for the Study of Pain Definition of Pain: Concepts, Challenges, and Compromises. Pain 2020, 161, 1976–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drendel, A.L.; Kelly, B.T.; Ali, S. Pain Assessment for Children: Overcoming Challenges and Optimizing Care. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 2011, 27, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.Z.D.; Kusahara, D.M.; Pedreira, M.D.L.G. Vivências de Enfermeiros Intensivistas na Avaliação e Intervenção para Alívio da Dor na Criança. Rev. Esc. Enferm. USP 2012, 46, 1074–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granata, C.; Guasconi, M.; Ruggeri, F.; Bolzoni, M.; Grossi, C.F.; Biasucci, G.; Cella, A. Assessment and Pain Management during the Triage Phase of Children with Extremity Trauma. A Retrospective Analysis in a Pediatric Emergency Room after the Introduction of the PIPER Recommendations. Acta Biomed. 2020, 91, e2020006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, T.; Kudchadkar, S.R. Pain and Sedation Management: 2018 Update for the Rogers’ Textbook of Pediatric Intensive Care. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 20, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaglani, A.; Gross, T. Pediatric Pain Management. Emerg. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 36, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freund, D.; Bolick, B.N. CE: Assessing a Child’s Pain. AJN Am. J. Nurs. 2019, 119, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Available online: https://www.who.int (accessed on 3 February 2025).
- Grupo de Trabajo de Doloren Neonatología, Comité de Estudios Feto-Neonatales (CEFEN). Manejo del Dolor en Neonatología. Arch. Argent. Pediatr. 2019, 117, S59–S70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence|NICE. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/population-groups/children-and-teenagers (accessed on 4 February 2025).
- The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP). Available online: https://www.aap.org/en/ (accessed on 4 February 2025).
- Ferrante, P.; Cuttini, M.; Zangardi, T.; Tomasello, C.; Messi, G.; Pirozzi, N.; Losacco, V.; Piga, S.; Benini, F.; Group, P.S.; et al. Pain Management Policies and Practices in Pediatric Emergency Care: A Nationwide Survey of Italian Hospitals. BMC Pediatr. 2013, 13, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benini, F.; Congedi, S.; Scalfaro, C.; Barbi, E.; Podestà, A.F. Up-Date of Paediatric Pain Management in Emergency Units. Med. Bambino 2019, 38, 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- Treede, R.-D. The International Association for the Study of Pain Definition of Pain: As Valid in 2018 as in 1979, but in Need of Regularly Updated Footnotes. Pain Rep. 2018, 3, e643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crellin, D.J.; Harrison, D.; Santamaria, N.; Huque, H.; Babl, F.E. The Psychometric Properties of the FLACC Scale Used to Assess Procedural Pain. J. Pain 2018, 19, 862–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kochman, A.; Howell, J.; Sheridan, M.; Kou, M.; Shelton Ryan, E.E.; Lee, S.; Zettersten, W.; Yoder, L. Reliability of the Faces, Legs, Activity, Cry, and Consolability Scale in Assessing Acute Pain in the Pediatric Emergency Department. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 2017, 33, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manworren, R.C.B.; Hynan, L.S. Clinical Validation of FLACC: Preverbal Patient Pain Scale. Pediatr. Nurs. 2003, 29, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Garra, G.; Singer, A.J.; Taira, B.R.; Chohan, J.; Cardoz, H.; Chisena, E.; Thode, H.C. Validation of the Wong-Baker FACES Pain Rating Scale in Pediatric Emergency Department Patients. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2010, 17, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong-Baker FACES Foundation Wong-Baker FACES® Pain Rating Scale. Available online: https://wongbakerfaces.org/ (accessed on 4 February 2025).
- Bailey, B.; Daoust, R.; Doyon-Trottier, E.; Dauphin-Pierre, S.; Gravel, J. Validation and Properties of the Verbal Numeric Scale in Children with Acute Pain. Pain 2010, 149, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miró, J.; Castarlenas, E.; Huguet, A. Evidence for the Use of a Numerical Rating Scale to Assess the Intensity of Pediatric Pain. Eur. J. Pain 2009, 13, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malviya, S.; Voepel-Lewis, T.; Burke, C.; Merkel, S.; Tait, A.R. The Revised FLACC Observational Pain Tool: Improved Reliability and Validity for Pain Assessment in Children with Cognitive Impairment. Pediatr. Anesth. 2006, 16, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breau, L.M.; McGrath, P.J.; Camfield, C.S.; Finley, A.G. Psychometric Properties of the Non-Communicating Children’s Pain Checklist-Revised. Pain 2002, 99, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dijk, M.; Peters, J.W.B.; Van Deventer, P.; Tibboel, D. The COMFORT Behavior Scale: A Tool for Assessing Pain and Sedation in Infants. AJN Am. J. Nurs. 2005, 105, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boerlage, A.A.; Ista, E.; De Jong, M.; Tibboel, D.; Van Dijk, M. The COMFORT Behavior Scale: Is a Shorter Observation Period Feasible? Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 13, e124–e125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guasconi, M.; Granata, C.; Sulla, F.; Rubbi, I.; Artioli, G.; Sarli, L.; Scelsi, S. Validation of the Italian Version of Behavioral Pain Scale in Sedated, Intubated, and Mechanically Ventilated Pediatric Patients. Acta Biomed. Atenei Parm. 2021, 92, e2021370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arksey, H.; O’Malley, L. Scoping Studies: Towards a Methodological Framework. Int. J. Soc. Res. Methodol. 2005, 8, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.D.; Godfrey, C.; McInerney, P.; Munn, Z.; Tricco, A.C.; Khalil, H. Scoping Reviews. In JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis; Aromataris, E., Lockwood, C., Porritt, K., Pilla, B., Jordan, Z., Eds.; JBI: Adelaide, Australia, 2024; ISBN 978-0-648-84882-0. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, M.D.J.; Marnie, C.; Tricco, A.C.; Pollock, D.; Munn, Z.; Alexander, L.; McInerney, P.; Godfrey, C.M.; Khalil, H. Updated Methodological Guidance for the Conduct of Scoping Reviews. JBI Evid. Synth. 2020, 18, 2119–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollock, D.; Davies, E.L.; Peters, M.D.J.; Tricco, A.C.; Alexander, L.; McInerney, P.; Godfrey, C.M.; Khalil, H.; Munn, Z. Undertaking a Scoping Review: A Practical Guide for Nursing and Midwifery Students, Clinicians, Researchers, and Academics. J. Adv. Nurs. 2021, 77, 2102–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granata, C.; Guasconi, M.; Ambrosi, F.; Anderle, L.; Marone, B.; Dimonte, D.; Tumbiolo, F.; Bassi, M.C.; Anderson, G.; Sarli, L.; et al. Evaluation of Pain in the Paediatric Patient Admitted to Sub-Intensive Care: A Scoping Review Protocol. Acta Bio-Medica Atenei Parm. 2023, 94, e2023039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. Int. J. Surg. 2021, 88, 105906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.J.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senato della Repubblica Italiana. Disposizioni in Materia di Definizione di Età Pediatrica e Ampliamento della Competenza Assistenziale dei Medici Pediatri di Libera Scelta Fino al Compimento del Diciottesimo Anno d’Età. 2015. Available online: https://www.senato.it/leg/19/BGT/Schede/Ddliter/57328.htm (accessed on 4 February 2025).
- Ouzzani, M.; Hammady, H.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Elmagarmid, A. Rayyan—A Web and Mobile App for Systematic Reviews. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollock, D.; Peters, M.D.J.; Khalil, H.; McInerney, P.; Alexander, L.; Tricco, A.C.; Evans, C.; De Moraes, É.B.; Godfrey, C.M.; Pieper, D.; et al. Recommendations for the Extraction, Analysis, and Presentation of Results in Scoping Reviews. JBI Evid. Synth. 2023, 21, 520–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballantyne, M.; Stevens, B.; McAllister, M.; Dionne, K.; Jack, A. Validation of the Premature Infant Pain Profile in the Clinical Setting. Clin. J. Pain 1999, 15, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caljouw, M.A.A.; Kloos, M.A.C.; Olivier, M.Y.; Heemskerk, I.W.; Pison, W.C.R.; Stigter, G.D.; Verhoef, A.-M.J.H. Measurement of Pain in Premature Infants with a Gestational Age between 28 to 37 Weeks: Validation of the Adapted COMFORT Scale. J. Neonatal Nurs. 2007, 13, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cignacco, E.; Mueller, R.; Hamers, J.P.H.; Gessler, P. Pain Assessment in the Neonate Using the Bernese Pain Scale for Neonates. Early Hum. Dev. 2004, 78, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debillon, T.; Zupan, V.; Ravault, N.; Magny, J.-F.; Dehan, M. Development and Initial Validation of the EDIN Scale, a New Tool for Assessing Prolonged Pain in Preterm Infants. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2001, 85, 36F–41F. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbins, S.; Stevens, B.J.; Yamada, J.; Dionne, K.; Campbell-Yeo, M.; Lee, G.; Caddell, K.; Johnston, C.; Taddio, A. Validation of the Premature Infant Pain Profile-Revised (PIPP-R). Early Hum. Dev. 2014, 90, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holsti, L.; Grunau, R.E.; Oberlander, T.F.; Osiovich, H. Is It Painful or Not?: Discriminant Validity of the Behavioral Indicators of Infant Pain (BIIP) Scale. Clin. J. Pain 2008, 24, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holsti, L.; Grunau, R.E. Initial Validation of the Behavioral Indicators of Infant Pain (BIIP). Pain 2007, 132, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson-Barr, D.; Capper-Michel, B.; Lambert, S.; Mizell Palermo, T.; Morbeto, K.; Lombardo, S. Validation of the Pain Assessment in Neonates (PAIN) Scale with the Neonatal Infant Pain Scale (NIPS). Neonatal Netw. 2002, 21, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaw, J.; Yang, L.; Chou, H.; Yin, T.; Chao, S.; Lee, T. Psychometric Analysis of a Taiwan-version Pain Assessment Scale for Preterm Infants. J. Clin. Nurs. 2012, 21, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milesi, C.; Cambonie, G.; Jacquot, A.; Barbotte, E.; Mesnage, R.; Masson, F.; Pidoux, O.; Ferragu, F.; Thevenot, P.; Mariette, J.-B.; et al. Validation of a Neonatal Pain Scale Adapted to the New Practices in Caring for Preterm Newborns. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2010, 95, F263–F266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, K.; Gillies, D.; Harrison, D.; Johnston, L.; Nagy, S. A Reliable Pain Assessment Tool for Clinical Assessment in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Neonatal Nurs. 2005, 34, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, B.J.; Gibbins, S.; Yamada, J.; Dionne, K.; Lee, G.; Johnston, C.; Taddio, A. The Premature Infant Pain Profile-Revised (PIPP-R): Initial Validation and Feasibility. Clin. J. Pain 2014, 30, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dijk, M.; De Boer, J.B.; Koot, H.M.; Tibboel, D.; Passchier, J.; Duivenvoorden, H.J. The Reliability and Validity of the COMFORT Scale as a Postoperative Pain Instrument in 0 to 3-Year-Old Infants. Pain 2000, 84, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dijk, M.; Roofthooft, D.W.E.; Anand, K.J.S.; Guldemond, F.; De Graaf, J.; Simons, S.; De Jager, Y.; Van Goudoever, J.B.; Tibboel, D. Taking Up the Challenge of Measuring Prolonged Pain in (Premature) Neonates: The COMFORTneo Scale Seems Promising. Clin. J. Pain 2009, 25, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woragidpoonpol, P.; Tiansawad, S.; Mesukko, J.; Klunklin, P. Development of a Clinical Pain Scale for Preterm Neonates. Pac. Rim Int. J. Nurs. Res. 2018, 22, 347–359. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, W.; Wang, X.; Huang, R.; Chen, Y.; Guo, X. Assessment of Four Pain Scales for Evaluating Procedural Pain in Premature Infants Undergoing Heel Blood Collection. Pediatr. Res. 2021, 89, 1724–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Tong, Y.; Xue, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Li, X. Evaluation of the Reliability and Validity of the Behavioral Indicators of Infant Pain Scale in Chinese Neonates. Pain Manag. Nurs. 2020, 21, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza Barbosa Dias, F.; Martins Marba, S.T. Avaliação da dor Prolongada no Recém-Nascido: Adaptação da Escala EDIN para a Cultura Brasileira. Texto Contexto-Enferm. 2014, 23, 964–970. [Google Scholar]
- İncekar, M.Ç.; Öğüt, N.U.; Mutlu, B.; Çeçen, E.; Can, E. Turkish Validity and Reliability of the COVERS Pain Scale. Rev. Assoc. Médica Bras. 2021, 67, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsdottir, R.B.; Kristjansdottir, G. The Sensitivity of the Premature Infant Pain Profile—PIPP to Measure Pain in Hospitalized Neonates. J. Eval. Clin. Pract. 2005, 11, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, E.; Anderzén-Carlsson, A.; Atladóttir, S.M.; Axelin, A.; Campbell-Yeo, M.; Eriksson, M.; Kristjánsdóttir, G.; Peltonen, E.; Stevens, B.; Vederhus, B.; et al. Cultural Adaptation and Harmonization of Four Nordic Translations of the Revised Premature Infant Pain Profile (PIPP-R). BMC Pediatr. 2018, 18, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarhangi, F.; Mollahadi, M.; Ebadi, A.; Matinzadeh, Z.K.; Tadrisi, S.D. Validity and Reliability of Neonatal Infant Pain Scale in Neonatal Intensive Care Units in Iran. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2011, 27, 1087–1091. [Google Scholar]
- Taplak, A.Ş.; Bayat, M. Psychometric Testing of the Turkish Version of the Premature Infant Pain Profile Revised-PIPP-R. J. Pediatr. Nurs. 2019, 48, e49–e55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vederhus, B.J.; Eide, G.E.; Natvig, G.K. Psychometric Testing of a Norwegian Version of the Premature Infant Pain Profile: An Acute Pain Assessment Tool. A Clinical Validation Study. Int. J. Nurs. Pract. 2006, 12, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, Y.; Kang, H.; Shin, E. Pain Assessment Using CRIES, FLACC and PIPP in High-Risk Infants. J. Korean Acad. Nurs. 2005, 35, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasca, T.; Spata, M.; Badon, P.; Pellegatta, F.; Buchini, S.; Monterosso, A.; Canesi, M. La Scala Algometrica PIPP: Valutazione dell’Accuratezza per la Rilevazione del Dolore Procedurale nel Neonato. Pain Nurs. Mag. 2016, 5, 121. [Google Scholar]
- Ramelet, A.-S.; Abu-Saad, H.H.; Rees, N.; McDonald, S. The Challenges of Pain Measurement in Critically Ill Young Children: A Comprehensive Review. Aust. Crit. Care 2004, 17, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, S. Assessing Infant Pain: A Review of the Pain Assessment Tools Available. J. Neonatal Nurs. Lond. 2003, 9, 122–127. [Google Scholar]
- Melo, G.M.D.; Lélis, A.L.P.D.A.; Moura, A.F.D.; Cardoso, M.V.L.M.L.; Silva, V.M.D. Escalas de Avaliação de Dor em Recém-nascidos: Revisão Integrativa1. Rev. Paul. Pediatr. 2014, 32, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagoni, N.; Bellini, L.; Bonora, R.; Botteri, M.; Migliari, M.; Pagliosa, A.; Sechi, G.M.; Signorelli, C.; Zoli, A.; Stirparo, G. Changing the Stroke Network during Pandemic Scenarios Does Not Affect the Management of Patients with a Positive Cincinnati Prehospital Stroke Scale. Neurol. Sci. 2024, 45, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stirparo, G.; Pireddu, R.; Andreassi, A.; Sechi, G.M.; Signorelli, C. Social Illness Before and After the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Regional Study. Prehospital Disaster Med. 2023, 38, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Multidimensional Scales | Physiological Indicators | Behavioral Indicators | Purpose | Populations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PIPP: Premature Infant Pain Profile | HR, SaO2 | Facial expressions | Procedural and postoperative pain | Preterm and term infant |
| NIPS: Neonatal Infant Pain Scale | Breathing pattern State of arousal | Facial expressions Cry/verbal expressions Body movements | Procedural pain | Neonates |
| CRIES: Crying, Requires Oxygen, Increased vital signs, Expression, Sleepless | HR, BP, SaO2 | Facial expressions Cry/verbal expressions | Postoperative pain | Preterm infant (32–36 weeks) |
| PIPP-R: Premature Infant Pain Profile-R | A revision of the PIPP scale in which modifications have been made with the aim of simplifying the calculation of the final score. | |||
| COMFORT | BP, HR | Facial expressions Cry/verbal expressions Body movements | Discomfort caused by pain | Children aged 0–18 years |
| COMFORT-neo | Evolution of the COMFORT scale used specifically in the neonatal intensive care unit setting | |||
| BPSN: Bernese Pain Scale for Neonates | RR, HR, SaO2 | Facial expressions Cry/verbal expressions Body movements | Acute pain | Preterm and term infants |
| PAT: Pain Assessment Tool | HR, SaO2, BP | Facial expressions Cry/verbal expressions Posture | Postoperative pain | Term and preterm infants |
| FANS: Faceless Acute Neonatal Pain Scale | HR, SaO2 | Cry Body movements | Acute pain | Preterm infants |
| PAIN: Pain Assessment in Neonates | HR, SaO2 | Facial expressions Cry/verbal expressions Body movements | Procedural pain | Neonates |
| PASPI | HR | Facial expressions Body movements Sleep–wake state transition | Pain | Preterm infants |
| COVERS | HR, BP, O2 requirement | Expression, resting, and signaling distress | Procedural pain | Term and preterm infants |
| CPSPN: Clinical Pain Scale for Preterm Neonates | BP, HR, SaO2, Breathing pattern | Facial expressions Cry/verbal expressions Body movements | Procedural pain | Preterm infants |
| SUN: Scale for Use in Neonates | HR, SaO2, Breathing pattern | Facial expressions Body movements | Acute pain | Preterm infants |
| DISVNI: Distress Scale for Ventilated Infants | HR, BP, SaO2 | Facial expressions Body movements | Acute and procedural pain | Neonates |
| N-PASS: Neonatal-Pain, Agitation and Sedation Scale | HR, RR, BP, SaO2 | Facial expressions Cry/verbal expressions Body movements | Acute pain | Neonates |
| MIPS: Modified Infant Pain Scale | HR, BP, SaO2 | Facial expressions Cry/verbal expressions Body movements | Postoperative pain | Term and preterm infants |
| PEPPS: Early Verbal Pediatric Pain Scale | HR | Facial expressions Cry/verbal expressions Body movements | Pain | Children between the ages of one and two |
| CHEOPS: Children’s Hospital of Eastern Ontario Pain Scale | HR, BP, Breathing pattern | Facial expressions Cry/verbal expressions Body movements | Pain | Children ranging in age from 1 to 5 years old |
| NAPI: Nursing Assessment of Pain Intensity | HR, SaO2, Breathing pattern | Facial expressions Cry/verbal expressions Body movements | Postoperative pain | Children up to three years of age |
| OPS: Objective Pain Scale | BP | Cry/verbal expressions Body movements | Postoperative pain | Children over the age of three |
| Single-Dimensional Scale | Behavioral Factors | Purpose | Populations |
|---|---|---|---|
| NFCS: Neonatal Facial Coding System | Facial expressions | Procedural pain | Child between the ages of 0 and 18 months |
| DAN: Doleur Aigue du Nouveau-né scales | Facial expressions Cry/verbal expressions Body movements | Acute pain | Term and preterm infants |
| FLACC | Facial expressions Cry/verbal expressions Body movements | Acute and prolonged pain | Children younger than 3 years of age |
| EDIN: Echelle Doleur Inconfort Noveau-né | Facial expressions Cry/verbal expressions | Prolonged pain | Preterm infants between 25 and 36 weeks gestational age |
| BIIP: Behavioral Indicators of Infant Pain scale | Sleep–wake rhythm Body movements | Acute and procedural pain | Preterm infants |
| C-BIIP | BIIP version of the scale in its Chinese version | ||
| LIDS: Liverpool Infant Distress Scale | Facial expressions Cry/verbal expressions Body movements | Postoperative pain | Neonates |
| IBCS: Infant Body Coding System | Body movements | Pain | Neonates |
| POCIS: the Pain Observation Scale for Young Children | Body movements Facial expressions | Postoperative pain | Children from one to four years old |
| TPPS: Toddler-Preschooler Postoperative Pain Scale | Facial expressions Cry/verbal expressions Rub or touch painful area | Postoperative pain | Children who are between the ages of 1 and 5 years old |
| CFCS: Child Facial Coding System | Facial expressions | Postoperative pain | Children aged 1 year up to 6 years old |
| POPS: Postoperative Pain Score | Facial expressions Cry/verbal expressions Body movements | Postoperative pain | Children aged 1 year up to 6 years old |
| CHIPPS | Facial expressions Cry/verbal expressions Body movements | Postoperative pain | From the newborn to the child with 5 years of age |
| BPS: Behavioral Pain Score | Facial expressions Cry/verbal expressions Body movements | Patients undergoing invasive and noninvasive mechanical ventilation | All ages |
| MBPS: Modified Behavioral Pain Score | Facial expressions Cry/verbal expressions Body movements | Procedural pain | Infants 4 to 6 months old |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bonacaro, A.; Granata, C.; Canini, C.; Anderle, L.; Ambrosi, F.; Bassi, M.C.; Biasucci, G.; Contini, A.; Artioli, G.; La Malfa, E.; et al. Evaluation of Pain in the Pediatric Patient Admitted to Sub-Intensive Care: What Is the Evidence? A Scoping Review. Epidemiologia 2025, 6, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia6010009
Bonacaro A, Granata C, Canini C, Anderle L, Ambrosi F, Bassi MC, Biasucci G, Contini A, Artioli G, La Malfa E, et al. Evaluation of Pain in the Pediatric Patient Admitted to Sub-Intensive Care: What Is the Evidence? A Scoping Review. Epidemiologia. 2025; 6(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia6010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleBonacaro, Antonio, Carlotta Granata, Chiara Canini, Lucrezia Anderle, Federica Ambrosi, Maria Chiara Bassi, Giacomo Biasucci, Andrea Contini, Giovanna Artioli, Elisa La Malfa, and et al. 2025. "Evaluation of Pain in the Pediatric Patient Admitted to Sub-Intensive Care: What Is the Evidence? A Scoping Review" Epidemiologia 6, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia6010009
APA StyleBonacaro, A., Granata, C., Canini, C., Anderle, L., Ambrosi, F., Bassi, M. C., Biasucci, G., Contini, A., Artioli, G., La Malfa, E., & Guasconi, M. (2025). Evaluation of Pain in the Pediatric Patient Admitted to Sub-Intensive Care: What Is the Evidence? A Scoping Review. Epidemiologia, 6(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia6010009









