The Molecular Epidemiology of Epizootic Hemorrhagic Disease Viruses Identified in Israel between 2015 and 2023
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Samples
2.2. Nucleic Acid Extraction and Pan-EHDV Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
2.3. Type-Specific RT-PCR and Sanger Sequencing
2.4. Whole Genome Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. Virus Isolation
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Signs in Affected Animals and Geographic Distribution of Israeli EHDVs
3.2. EHDV Detection by Pan-EHDV RT-qPCR from Field Samples Collected in 2020–2021 and 2023
3.3. Virus Isolation
3.4. Sequence Analyses of EHDV-1, -6, -7, and -8
3.5. Phylogenetic Analysis of Israeli EHDV Strains
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ICTV. Virus Taxonomy. Available online: https://ictv.global/report/chapter/sedoreoviridae/sedoreoviridae/orbivirus (accessed on 5 September 2023).
- Matthijnssens, J.; Attoui, H.; Bányai, K.; Brussaard, C.P.D.; Danthi, P.; Del Vas, M.; Dermody, T.S.; Duncan, R.; Fāng, Q.; Johne, R.; et al. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Sedoreoviridae 2022. J. Gen. Virol. 2022, 103, 001782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, A.M.; Adams, M.J.; Carstens, E.B.; Lefkowitz, E.J. Virus Taxonomy, 9th ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2012; p. 66. [Google Scholar]
- Anthony, S.J.; Maan, N.; Maan, S.; Sutton, G.; Attoui, H.; Mertens, P.P. Genetic and phylogenetic analysis of the core proteins VP1, VP3, VP4, VP6 and VP7 of epizootic haemorrhagic disease virus (EHDV). Virus Res. 2009, 145, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anthony, S.J.; Maan, N.; Maan, S.; Sutton, G.; Attoui, H.; Mertens, P.P. Genetic and phylogenetic analysis of the non-structural proteins NS1, NS2 and NS3 of epizootic haemorrhagic disease virus (EHDV). Virus Res. 2009, 145, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maclachlan, N.J.; Zientara, S.; Wilson, W.C.; Richt, J.A.; Savini, G. Bluetongue and Epizootic Hemorrhagic Disease Viruses: Recent Developments with These Globally Re-Emerging Arboviral Infections of Ruminants. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2019, 34, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epizootic Haemorrhagic Disease (Infection with Epizootic Hemorrhagic Disease Virus). Available online: https://www.woah.org/fileadmin/Home/fr/Health_standards/tahm/3.01.07_EHD.pdf (accessed on 5 December 2023).
- Jiménez-Cabello, L.; Utrilla-Trigo, S.; Lorenzo, G.; Ortego, J.; Calvo-Pinilla, E. Epizootic Hemorrhagic Disease Virus: Current Knowledge and Emerging Perspectives. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, I.M. 2013: Serological and Genetic Characterisation of Putative New Serotypes of Bluetongue Virus and Epizootic Haemorrhagic Disease Virus Isolated from an Alpaca; North-West University: Potchefstroom, South Africa, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yanase, T.; Murota, K.; Hayama, Y. Endemic and emerging arboviruses in domestic ruminants in east asia. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 168. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Yang, Z.; Liao, D.; Zhu, J.; Li, H. Novel serotype of epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 3081–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shope, R.E.; Lester, G.M.; Robert, M. Deer Mortality Epizootic Hemorrhagic Disease of Deer. N. J. Outdoors 1955, 6, 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- Rivera, N.A.; Varga, C.; Ruder, M.G.; Dorak, S.J.; Roca, A.L.; Novakofski, J.E.; Mateus-Pinilla, N.E. Bluetongue and Epizootic Hemorrhagic Disease in the United States of America at the Wildlife-Livestock Interface. Pathogens 2021, 10, 915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maclachlan, N.J.; Zientara, S.; Savini, G.; Daniels, P.W. Epizootic haemorrhagic disease. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2015, 34, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omori, T.; Inaba, Y.; Morimoto, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Ishitani, R. Ibaraki virus, an agent of epizootic disease of cattle resembling bluetongue. I. Epidemiologic, clinical and pathologic observations and experimental transmission to calves. Jpn. J. Microbiol. 1969, 13, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inaba, U. Ibaraki disease and its relationship to bluetongue. Aust. Vet. J. 1975, 51, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitano, Y. Ibaraki disease in cattle. In Infectious Diseases of Livestock, 2nd ed.; Coetzer, J.A.W., Tustin, R.C., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 1221–1226. [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi, S.; Yoshida, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Tsuda, T. Identification and PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of a variant of the Ibaraki virus from naturally infected cattle and aborted fetuses in Japan. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 3800–3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirafuji, H.; Kato, T.; Yamakawa, M.; Tanaka, T.; Minemori, Y.; Yanase, T. Characterization of genome segments 2, 3 and 6 of epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus strains isolated in Japan in 1985–2013: Identification of their serotypes and geographical genetic types. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 53, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamomae, Y.; Kamomae, M.; Ohta, Y.; Nabe, M.; Kagawa, Y.; Ogura, Y.; Kato, T.; Tanaka, S.; Yanase, T.; Shirafuji, H. Epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus serotype 6 infection in cattle, Japan, 2015. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 902–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temizel, E.M.; Yesilbag, K.; Batten, C.; Senturk, S.; Maan, N.S.; Mertens, P.P.C.; Batmaz, H. Epizootic hemorrhagic disease in cattle, Western Turkey. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 317–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golender, N.; Khinich, Y.; Gorohov, A.; Abramovitz, I.; Bumbarov, V. Epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus serotype 6 outbreak in Israeli cattle in 2015. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2017, 29, 885–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Dhaou, S.; Sailleau, C.; Babay, B.; Viarouge, C.; Sghaier, S.; Zientara, S.; Hammami, S.; Bréard, E. Molecular characterisation of epizootic haemorrhagic disease virus associated with a Tunisian outbreak among cattle in 2006. Acta. Vet. Hung. 2016, 64, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, S.; Yoshida, K.; Yanase, T.; Tsuda, T. Analysis of intratypic variation evident in an Ibaraki virus strain and its epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus serogroup. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 3684–3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadin, H.; Brenner, J.; Bumbrov, V.; Oved, Z.; Stram, Y.; Klement, E.; Perl, S.; Anthony, S.; Maan, S.; Batten, C.; et al. Epizootic haemorrhagic disease virus type 7 infection in cattle in israel. Vet. Rec. 2008, 162, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, Y.; Miyazato, S.; Kubo, M.; Goto, Y.; Kono, Y. Kawanabe virus, an isolate from a calf in Japan: A new virus belonging to the New Jersey serotype of the epizootic hemorrhagic disease serogroup of genus Orbivirus. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1988, 50, 942–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golender, N.; Bumbarov, V.Y. Detection of epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus serotype 1, Israel. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 825–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sghaier, S.; Sailleau, C.; Marcacci, M.; Thabet, S.; Curini, V.; Ben Hassine, T.; Teodori, L.; Portanti, O.; Hammami, S.; Jurisic, L.; et al. Epizootic Haemorrhagic Disease Virus Serotype 8 in Tunisia, 2021. Viruses 2022, 15, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorusso, A.; Cappai, S.; Loi, F.; Pinna, L.; Ruiu, A.; Puggioni, G.; Guercio, A.; Purpari, G.; Vicari, D.; Sghaier, S.; et al. Epizootic Hemorrhagic Disease Virus Serotype 8, Italy, 2022. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2023, 29, 1063–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Lin, J.; Cao, Y.Y.; Zhu, J.B.; Du, Y.C.; Yang, Z.X.; Yao, J.; Li, H.C.; Wu, J.M. Investigation of the serotypes of epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus and analysis of their distribution in Guangxi. Shanghai J. Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 2016, 61, 19–21. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kato, T.; Shirafuji, H.; Tanaka, S.; Sato, M.; Yamakawa, M.; Tsuda, T.; Yanase, T. Bovine arboviruses in culicoides biting midges and sentinel cattle in Southern Japan from 2003 to 2013. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2016, 63, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Wang, F.; Chang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Li, H.; Yu, L. Identification and complete-genome phylogenetic analysis of an epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus serotype 7 strain isolated in China. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 3121–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maan, N.S.; Maan, S.; Nomikou, K.; Johnson, D.J.; El Harrak, M.; Madani, H.; Yadin, H.; Incoglu, S.; Yesilbag, K.; Allison, A.B.; et al. RT-PCR assays for seven serotypes of epizootic haemorrhagic disease virus & their use to type strains from the Mediterranean region and North America. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12782. [Google Scholar]
- Kedmi, M.; Galon, N.; Herziger, Y.; Yadin, H.; Bombarov, V.; Batten, C.; Shpigel, N.Y.; Klement, E. Comparison of the epidemiology of epizootic haemorrhagic disease and bluetongue viruses in dairy cattle in Israel. Vet. J. 2011, 190, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albayrak, H.; Ozan, E.; Gur, S. A serologic investigation of epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus (EHDV) in cattle and gazella subgutturosa subgutturosa in Turkey. Trop. Anim. Health. Prod. 2010, 42, 1589–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, C.H.; St George, T.D. A preliminary report of a comparison of epizootic haemorrhagic disease viruses from Australia with others from North America, Japan and Nigeria. Aust. Vet. J. 1986, 63, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aradaib, I.E.; Mederos, R.A.; Osburn, B.I. Evaluation of epizootic haemorrhagic disease virus infection in sentinel calves from the San Joaquin Valley of California. Vet. Res. Commun. 2005, 29, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raabis, S.M.; Byers, S.R.; Han, S.; Callan, R.J. Epizootic hemorrhagic disease in a yak. Can. Vet. J. 2014, 55, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Allen, S.E.; Rothenburger, J.L.; Jardine, C.M.; Ambagala, A.; Hooper-McGrevy, K.; Colucci, N.; Furukawa-Stoffer, T.; Vigil, S.; Ruder, M.; Nemeth, N.M. Epizootic hemorrhagic disease in white-tailed deer, Canada. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 832–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casey, C.L.; Rathbun, S.L.; Stallknecht, D.E.; Ruder, M.G. Spatial analysis of the 2017 outbreak of hemorrhagic disease and physiographic region in the Eastern United States. Viruses 2021, 13, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cottingham, S.L.; White, Z.S.; Wisely, S.M.; Campos-Krauer, J.M. A mortality-based description of EHDV and BTV prevalence in farmed white-tailed deer (odocoileus virginianus) in Florida, USA. Viruses 2021, 13, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viarouge, C.; Lancelot, R.; Rives, G.; Bréard, E.; Miller, M.; Baudrimont, X.; Doceul, V.; Vitour, D.; Zientara, S.; Sailleau, C. Identification of bluetongue virus and epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus serotypes in French Guiana in 2011 and 2012. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 174, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdezoto, J.; Breard, E.; Viarouge, C.; Quenault, H.; Lucas, P.; Sailleau, C.; Zientara, S.; Augot, D.; Zapata, S. Novel serotype of bluetongue virus in South America and first report of epizootic haemorrhagic disease virus in Ecuador. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 244–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetre-Sossah, C.; Roger, M.; Sailleau, C.; Rieau, L.; Zientara, S.; Breard, E.; Viarouge, C.; Beral, M.; Esnault, O.; Cardinale, E. Epizootic haemorrhagic disease virus in Reunion Island: Evidence for the circulation of a new serotype and associated risk factors. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 170, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejri, S.; Dhaou, S.B.; Jemli, M.; Breard, E.; Sailleau, C.; Sghaier, S.; Zouari, M.; Lorusso, A.; Savini, G.; Zientara, S.; et al. Epizootic haemorrhagic disease virus circulation in Tunisia. Vet. Ital. 2018, 54, 87–90. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud, A.; Danzetta, M.L.; di Sabatino, D.; Spedicato, M.; Alkhatal, Z.; Dayhum, A.; Tolari, F.; Forzan, M.; Mazzei, M.; Savini, G. First seroprevalence investigation of epizootic haemorrhagic disease virus in Libya. Open Vet. J. 2021, 11, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breard, E.; Sailleau, C.; Hamblin, C.; Graham, S.D.; Gourreau, J.M.; Zientara, S. Outbreak of epizootic haemorrhagic disease on the island of Reunion. Vet. Rec. 2004, 155, 422–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sailleau, C.; Zanella, G.; Breard, E.; Viarouge, C.; Desprat, A.; Vitour, D.; Adam, M.; Lasne, L.; Martrenchar, A.; Bakkali-Kassimi, L.; et al. Co-circulation of bluetongue and epizootic haemorrhagic disease viruses in cattle in Reunion island. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 155, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toye, P.G.; Batten, C.A.; Kiara, H.; Henstock, M.R.; Edwards, L.; Thumbi, S.; Poole, E.J.; Handel, I.G.; Bronsvoort, B.M.; Hanotte, O.; et al. Bluetongue and epizootic haemorrhagic disease virus in local breeds of cattle in Kenya. Res. Vet. Sci. 2013, 94, 769–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dommergues, L.; Viarouge, C.; Metras, R.; Youssouffi, C.; Sailleau, C.; Zientara, S.; Cardinale, E.; Cetre-Sossah, C. Evidence of bluetongue and epizootic haemorrhagic disease circulation on the island of Mayotte. Acta Trop. 2019, 191, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bluetongue and Epizootic Hemorrhagic Disease: Incursion, Recent Developments and Control Strategies in the Context of North Africa. Available online: https://rr-africa.woah.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/9-tunisia-bluetongue-and-epizootic-hemorrhagic-disease-incursion-recent-developments-and-control-strategies-in-the-context-of-nort-a.pdf (accessed on 8 December 2023).
- Epizootic Haemorrhagic Disease in Europe. Available online: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/1124406/Epizootic_haemorrhagic_disease_in_europe.pdf (accessed on 8 December 2023).
- Komarov, A.; Goldsmit, L. A disease, similar to blue tongue in cattle and sheep in Israel. Ref. Vet. 1951, 8, 96–100. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, S.; Mahmoud, M.A.E.; Viarouge, C.; Sailleau, C.; Zientara, S.; Breard, E. Presence of bluetongue and epizootic hemorrhagic disease viruses in Egypt in 2016 and 2017. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 73, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernike, K.; Hoffmann, B.; Beer, M. Simultaneous detection of five notifiable viral diseases of cattle by single-tube multiplex real-time RT-PCR. J. Virol. Methods 2015, 217, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golender, N.; Varsano, J.S.; Nissimyan, T.; Tiomkin, E. Identification of novel reassortant Shuni virus strain in clinical cases of Israeli ruminants, 2020–2021. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 13, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrzastek, K.; Lee, D.H.; Smith, D.; Sharma, P.; Suarez, D.; Pantin-Jackwood, M.; Kapczynski, D.R. Use of Sequence-Independent, Single-Primer-Amplification (SISPA) for rapid detection, identification, and characterization of avian RNA viruses. Virology 2017, 509, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ries, C.; Domes, U.; Janowetz, B.; Böttcher, J.; Burkhardt, K.; Miller, T.; Beer, M.; Hoffmann, B. Isolation and Cultivation of a New Isolate of BTV-25 and Presumptive Evidence for a Potential Persistent Infection in Healthy Goats. Viruses 2020, 12, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golender, N.; Bumbarov, V.; Elda, R.A.; Lorusso, A.; Kenigswald, G.; Varsano, J.S.; David, D.; Schainin, S.; Dagoni, I.; Gur, I.; et al. Bluetongue Serotype 3 in Israel 2013–2018: Clinical Manifestations of the Disease and Molecular Characterization of Israeli Strains. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 6, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golender, N.; Klement, E.; Kovtunenko, A.; Even-Tov, B.; Zamir, L.; Tiomkin, E.; Kenigswald, G.; Hoffmann, B. Comparative Molecular and Epidemiological Analyses of Israeli Bluetongue Viruses Serotype 1 and 9 Causing Outbreaks in 2018–2020. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golender, N.; Eldar, A.; Ehrlich, M.; Khinich, Y.; Kenigswald, G.; Varsano, J.S.; Ertracht, S.; Abramovitz, I.; Assis, I.; Shlamovitz, I.; et al. Emergence of a Novel Reassortant Strain of Bluetongue Serotype 6 in Israel, 2017: Clinical Manifestations of the Disease and Molecular Characterization. Viruses 2019, 11, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
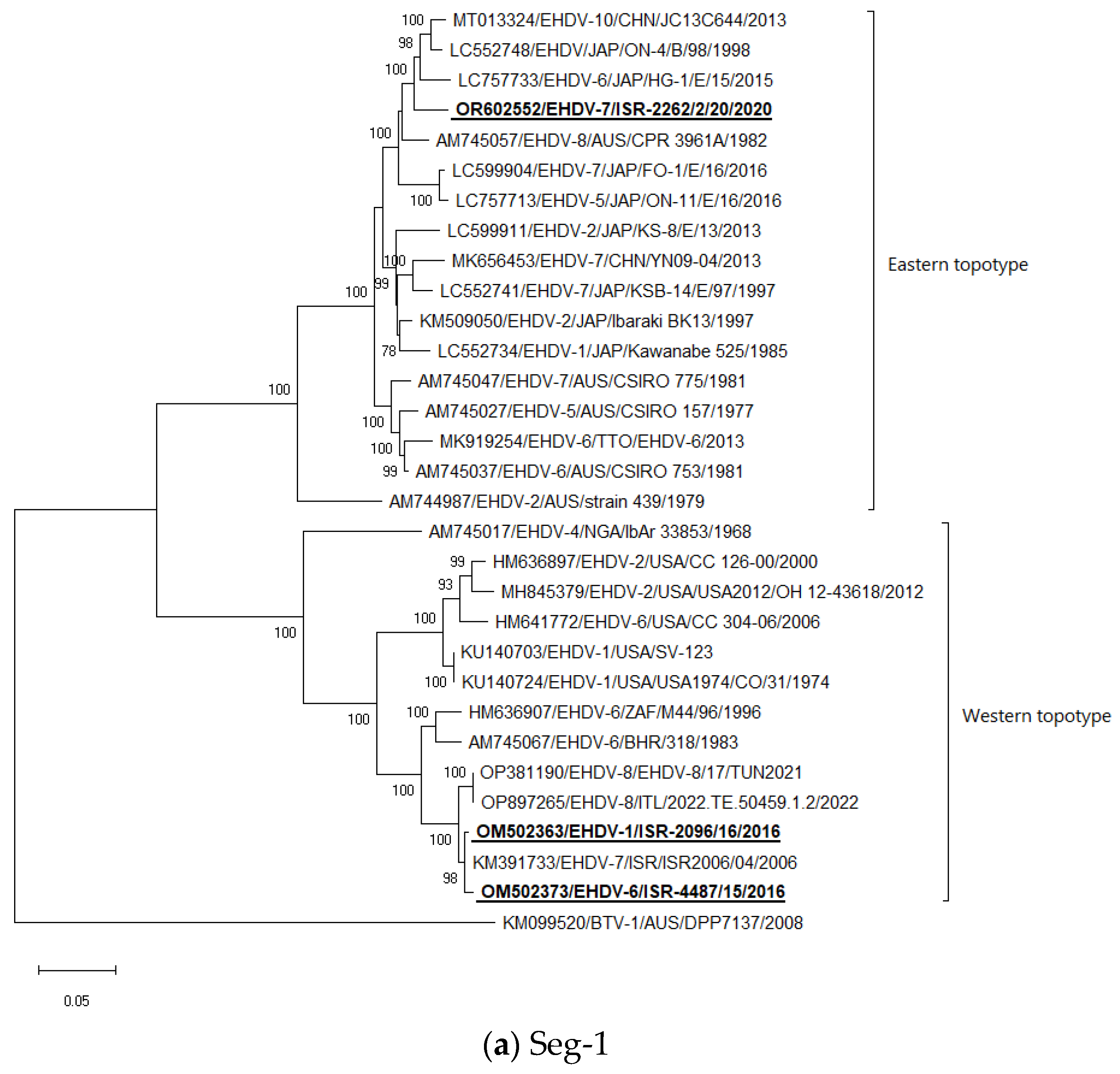
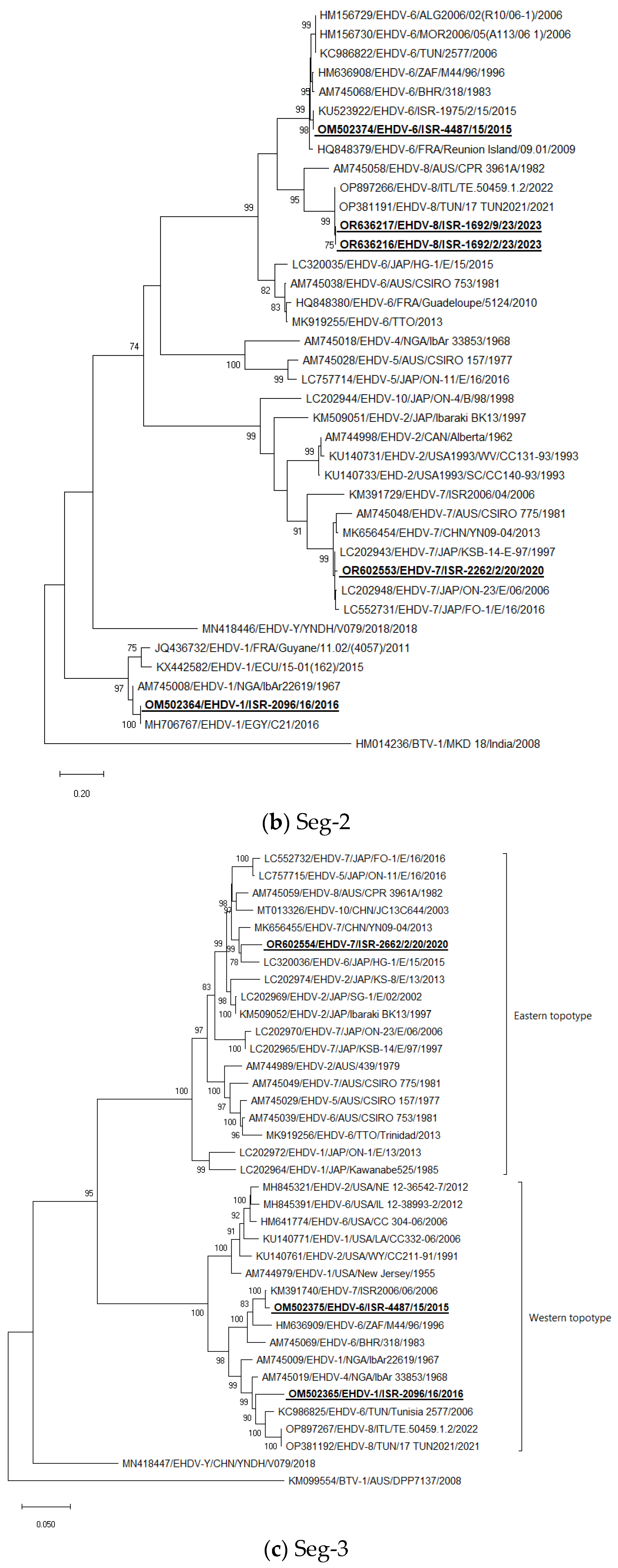
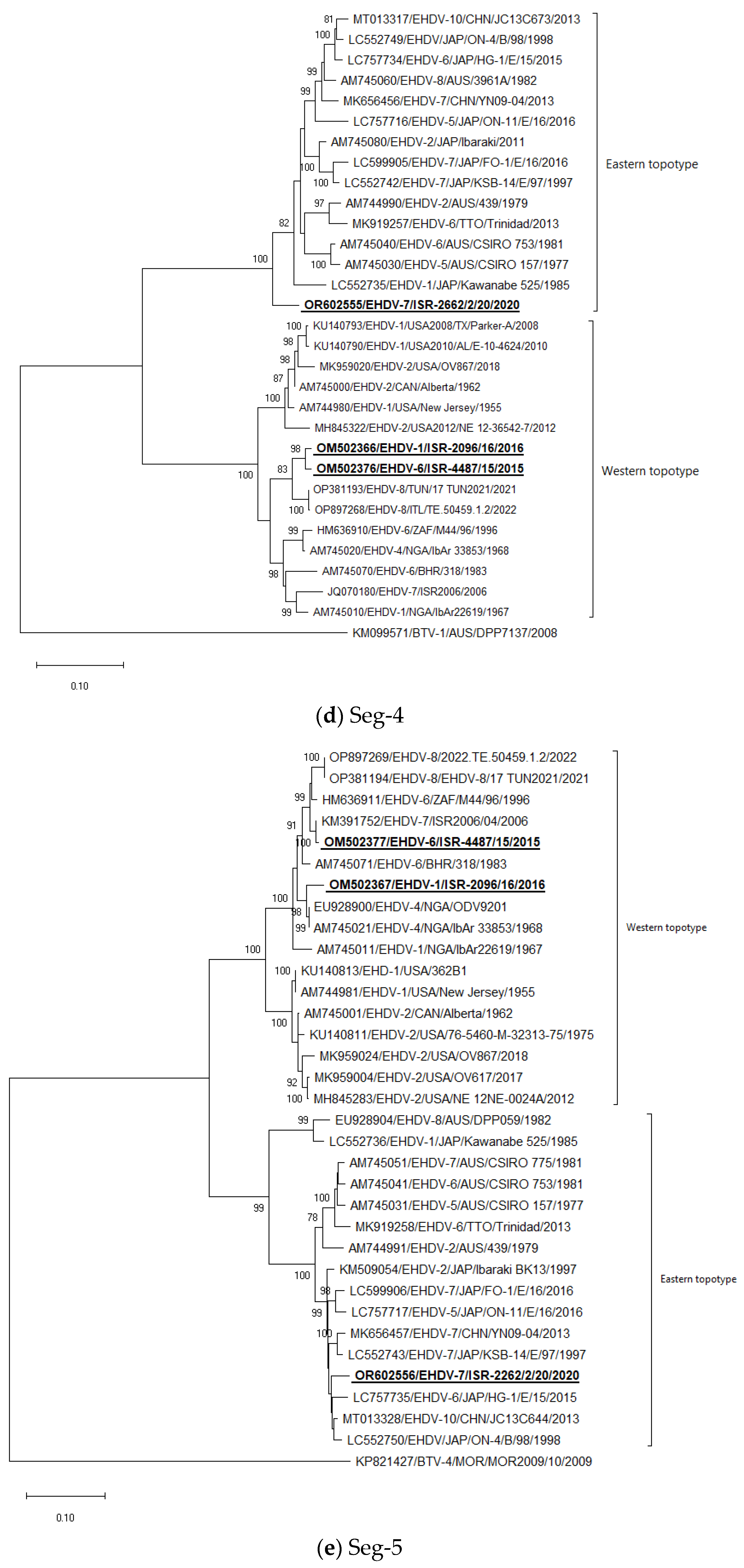

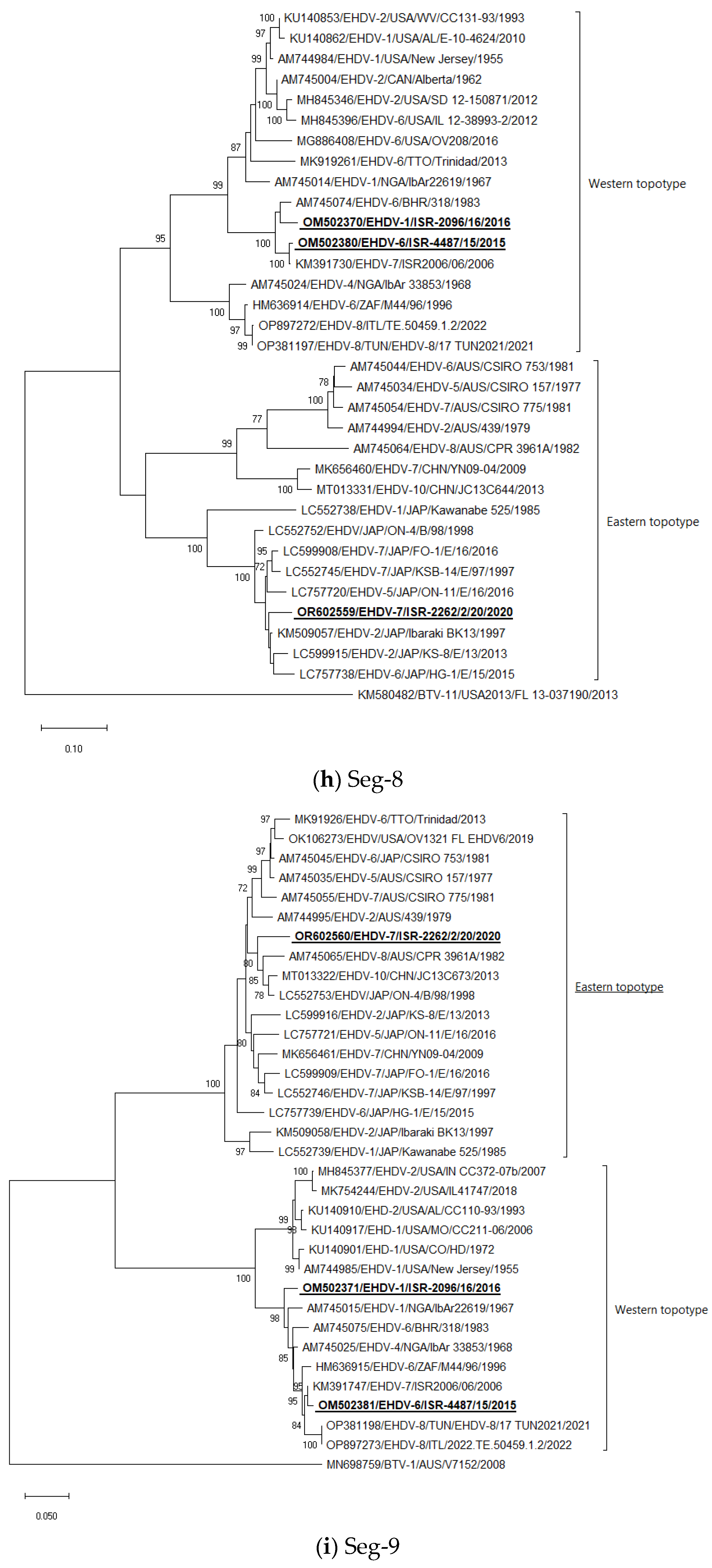

| Year/Organ | Cattle | Wild Ruminants | Total | VI | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| w.b. | s/l | a.f | w.b. | s/l | a.f | ||||
| 2020 | No. tested samples | 323 | 19 | 20 (14) | 0 | 10 | 1 | 373 (367) | |
| No. of pos. samples | 128 | 3 | 3 (2) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 134 (133) | 9 | |
| 2021 | No. tested samples | 635 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 635 | |
| No. of pos. samples | 149 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 149 | ||
| 2023 | No. tested samples | 1067 | 50 (44) | 26 (19) | 2 | 30 (26) | 3 | 1178 (1163) | |
| No. of pos. samples | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | ||
| total | No. tested samples | 2025 | 69 (63) | 46 (35) | 2 | 40 (36) | 4 | 2186 (2165) | 9 |
| No. of pos. samples | 279 | 3 | 3 (2) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 285 (284) | ||
| Name of Oligo | Oligo Sequence (5′ → 3′) | Source |
|---|---|---|
| EHD6/8-1F | GTT AAA TTR TTC CAG GAT GGA WA | [22] |
| EHD6/8-250R | CAT CAT CAT AYC TCA TTA TYC CA | |
| EHD8-S2-178F | AGA GGC GCG TAA TGT TTT C | this study |
| EHD8-S2-522R | TGC TGA ATC ATA TCG TAA TGT A | |
| EHD8-S2-447F | CCA AAT TTG TGG AAA GCT TG | this study |
| EHD8-S2-705R | CGC ACT TTT GTT TGC TTA TCT TTA T |
| Serotype/Israeli Strain | Segment | Identity (%) | Accession Number/Serotype/Strain/Year | Country of Isolation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EHDV-6/ISR-4487/15 | 1 | 99.26 | KM391733/EHDV-7/ISR2006/04/2006 | Israel |
| 2 | 96.02 | HM156729/EHDV-6/ALG2006/02/2006 | Algeria | |
| 3 | 99.37 | KM391740/ EHDV-7/ISR2006/04/2006 | Israel | |
| 4 | 92.71 | AM745020/ EHDV-4/IbAr 33853/1968 | Nigeria | |
| 5 | 99.46 | JQ070181/EHDV-7/ISR2006/04/2006 | Israel | |
| 6 | 96.28 | AM745072/EHDV-6/318/1983 | Bahrain | |
| 7 | 97.05 | AY351653/EHDV/2003? | France, Reunion | |
| 8 | 97.06 | KM391730/EHDV-7/ISR2006/06/2006 | Israel | |
| 9 | 98.89 | KM391747/EHDV-7/ISR2006/06/2006 | Israel | |
| 10 | 99.71 | KM391724/ EHDV-7/ISR2006/06/2006 | Israel | |
| EHDV-1/ISR-2096/16 | 1 | 99.57 | KM391733/EHDV-7/ISR2006/04/2006 | Israel |
| 2 | 87.45 | AM745008/EHDV-1/bAr22619/1967 | Nigeria | |
| 3 | 96.22 | AM745019/EHDV-4/IbAr 33853/1968 | Nigeria | |
| 4 | 92.51 | AM745020/EHDV-4/IbAr 33853/1968 | Nigeria | |
| 5 | 97.52 | AM745021/EHDV-4/IbAr 33853/1968 | Nigeria | |
| 6 | 96.09 | AM745012/EHDV-1/IbAr22619/1967 | Nigeria | |
| 7 | 97.43 | AM745013/ EHDV-1/IbAr22619/1967 | Nigeria | |
| 8 | 95.63 | AM745074/EHDV-6/318/1983 | Bahrain | |
| 9 | 95.59 | AM745025/EHDV-4/IbAr 33853/1968 | Nigeria | |
| 10 | 95.05 | EU928893 EHDV-3/Nigeria-ODV0001 | Nigeria | |
| 10 | 95.05 | AM745016/EHDV-1/ IbAr22619/1967 | Nigeria | |
| EHDV-7/ISR-2262/2/20 | 1 | 96.30 | LC552748/EHDV/ON-4/B/98/1998 | Japan |
| 2 | 98.13 | LC202943/EHDV-7/KSB-14/E/97/1997 | Japan | |
| 3 | 96.42 | MK656455/EHDV-7/YN09-04/2013 | China | |
| 4 | 92.48 | AM745080/EHDV-2/Ibaraki/1959 | Japan | |
| 5 | 97.09 | MT013328/EHDV-10/JC13C644/2013 | China | |
| 6 | 98.52 | LC202954/EHDV-7/KSB-14/E/97/1997 | Japan | |
| 7 | 98.60 | LC552744/EHDV-7/KSB-14/E/97/1997 | Japan | |
| 8 | 95.75 | KM509057/EHDV-2/Ibaraki BK13/1997 | Japan | |
| 9 | 95.20 | LC552753/EHDV/ON-4/B/98/1998 | Japan | |
| 10 | 97.87 | LC552747/EHDV-7/KSB-14/E/97/1997 | Japan | |
| EHDV-8/ISR-1692/2/23 | 2 | 99.70 | OP937332/EHDV-8/Culicoides sp/2 TUN2022/2022 | Tunisia |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Golender, N.; Hoffmann, B. The Molecular Epidemiology of Epizootic Hemorrhagic Disease Viruses Identified in Israel between 2015 and 2023. Epidemiologia 2024, 5, 90-105. https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia5010006
Golender N, Hoffmann B. The Molecular Epidemiology of Epizootic Hemorrhagic Disease Viruses Identified in Israel between 2015 and 2023. Epidemiologia. 2024; 5(1):90-105. https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia5010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleGolender, Natalia, and Bernd Hoffmann. 2024. "The Molecular Epidemiology of Epizootic Hemorrhagic Disease Viruses Identified in Israel between 2015 and 2023" Epidemiologia 5, no. 1: 90-105. https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia5010006
APA StyleGolender, N., & Hoffmann, B. (2024). The Molecular Epidemiology of Epizootic Hemorrhagic Disease Viruses Identified in Israel between 2015 and 2023. Epidemiologia, 5(1), 90-105. https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia5010006







