Abstract
Background/Objectives: Anthropometric indices based on height (H), weight (W), waist circumference (WC) and hip circumference (HC) can identify incident and future health risks. While BMI provides a standard for relative W (adjusted for H), there is no standard for indices using WC and HC. A body shape index (ABSI) and hip index (HI) have been proposed to extend to respectively WC and HC the same allometric power-law approach used to derive BMI to be independent of H. Here, we compared the mutually independent allometric set H, BMI, ABSI, HI with other proposed indices. Methods: We examined the formulas and rationales of published indices, and used Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III) cohort data to investigate their inter-correlations and association with mortality. Results: Many of the proposed indices are based on geometric (isometric) similarity, which does not match human body variability patterns. Unlike ABSI and HI, most proposed indices showed large correlations with BMI, complicating interpretation when considered together with BMI. Indices’ association with mortality risk were generally consistent with their correlations with BMI and ABSI. Combining the separable mortality risks associated with BMI and ABSI, even in a simplified way, outperformed any single index. Conclusions: With calls for incorporating additional indices incorporating WC and HC to supplement BMI in defining obesity, only ABSI and HI are independent of BMI. Additionally, separate risk estimates from these allometric indices can be readily combined to optimize overall risk assessment.
1. Introduction
Body mass index (BMI), based on adjusting weight (more precisely, mass; W) to be independent of height (H), is now the main criterion used to operationally define overweight and obesity, which have become widespread and of great health concern [1,2,3,4]. Waist circumference (WC) is used as a secondary criterion, and hip circumference (HC) is also commonly considered [5,6,7,8,9]. In 2023, an American Heart Association Presidential Advisory called for population-wide annual measurements of BMI and WC to help prevent and treat cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic (CKM) syndrome, which is characterized by excess and dysfunction of adipose tissue leading to disorders of obesity, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, and cardiovascular disease, and for which risk factors include overweight (high BMI), abdominal adiposity (high WC), and impaired glucose tolerance [10]. Almost 90% of United States adults met criteria for CKM syndrome and 15% met criteria for its advanced stages [11].
Compared to, e.g., laboratory blood tests or imaging to estimate body composition, the basic body measurements (anthropometrics) of H, W, WC, and HC are simple and cheap to implement, and they (or indices based on them, such as BMI) perform competitively as risk indicators [12,13,14]. Indeed, the medical literature contains thousands of studies that collectively find that within many populations, BMI shows strong associations with physiological, metabolic, and biomolecular alterations related to obesity and predicts the development of many diseases [15,16,17].
Frequently stated intrinsic limitations of BMI, which drive the perceived need to supplement it, are that total mass does not differentiate between fat and muscle, nor does it differentiate between different fat depots, such as visceral versus subcutaneous and abdominal versus gluteo-femoral, which have different biological activities and relations to CKD syndrome [18,19,20]. Corresponding with these limitations, the obesity paradox is largely formulated as the observation that higher BMI may be associated with better outcomes across a range of disease states [21,22,23,24]. Moreover, given that WC and HC are highly correlated with BMI [15], in obesity paradox populations higher WC and HC may also be associated with lower mortality [25,26].
Early in 2025, the Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology Commission published recommendations for defining obesity endorsed by more than 75 international medical organizations [27,28]. For “Clinical Assessment of Obesity”, the Commission recommended (98% agreement) one “anthropometric criterion (waist circumference, waist-to-hip ratio, waist-to-height ratio) in addition to BMI” or, in the absence of BMI, two such criteria. The need is clearly felt to supplement the long-standing mainstay BMI with another anthropometric indicator of obesity. Indeed, the last two decades have seen extensive study of anthropometric indices which incorporate WC and/or HC to better capture risk for incident or future disease.
In order to derive indices that reflect health risks based on WC and HC that are independent from the information gained from BMI, it is possible to follow an analogous approach to that used to derive BMI. The core realization underlying BMI is that across adult human populations, weight is approximately proportional to the square of height. Therefore, the ratio is approximately independent of height, making it more suitable as a weight-based risk indicator than the actual weight, which is positively correlated with height. As indicated by Ansel Keys et al. [29], who advocated for BMI in 1972 and built on research going back to the previous century, “In the choice of an index of relative weight derived from measures of weight and height, apart from the requirement that the index be highly correlated with weight, the prime criterion must be the relative independence of the index from height.”
The scaling of weight as is an example of allometry [30], where different body dimensions are related in ways that are not consistent with humans of different sizes being geometrically similar. The alternative, geometric similarity or isometry, would instead imply that W should be proportional to .
This approach can be applied to, for example, derive an index based on WC. Within populations, WC shows high positive correlations with H and especially W, and hence also BMI. If isometry held, WC would be directly proportional to other length dimensions, so one might consider as indices dimensionless ratios such as or [27]. However, because allometry holds, such geometrically inspired ratios are in fact not independent of H, W, or BMI. A body shape index (ABSI) is analogous to BMI in that it divides WC by powers of H and W chosen such that the resulting index is approximately independent of H, W, and BMI across adult human populations. The empirically derived formula in this case is [31].
Hip index (HI) was similarly formulated as based on the empirical allometric relationship between HC and height and weight [32]. HI does not adjust for WC because the correlation between HI and ABSI was found to be low even without including such a factor. The overall result is that H, BMI, ABSI, and HI form an “allometric quartet” that are approximately mutually independent, unlike the underlying H, W, WC, HC measurements [33,34].
Studies have found that high ABSI is a strong predictor of many adverse health outcomes, independent of BMI [35,36,37,38]. Mortality hazard increases exponentially with ABSI, while it is a U-shaped function of BMI [39,40,41]. Although HI is a less powerful mortality predictor than ABSI [32], it also shows independent associations with disease states [42,43].
Total anthropometric risk attributable to two or more of mutually independent indices of the “allometric quartet” can be obtained by multiplication of the component risks. Equivalently, the logarithms of the individual risks can be summed to approximate the logarithm of relative risk for an individual with given values of these indices. Such a combined anthropometric risk indicator (ARI) [32,44,45,46] cannot otherwise readily be formed from highly inter-correlated measures, such as BMI and WC.
The goal of the current paper is to offer a comparison of the allometric approach that extended BMI to WC and HC based indices (resulting in ABSI and HI as derived indices to complement BMI) with other anthropometric indices found in the medical literature. A list of indices based on anthropometrics and used for risk assessment is compiled based on a recent review article. The correlations between these indices are computed based on a national population sample, highlighting the mutual independence of allometric indices, as compared to alternative indices. Associations with mortality hazard from up to 31 years of follow-up are also computed, and the potential advantage of combined risk estimates from multiple independent allometric indices illustrated. Implications for choosing anthropometric indices to complement BMI are discussed.
2. Methods
2.1. Selection of Anthropometric Indices
Anthropometric indices were selected from a literature review covering the years 1956–2020 [47]. We selected only the 10 indices that could be computed using the basic anthropometrics H, W, WC, and HC, possibly also with adjustment for age and sex. Thus, we excluded for the purpose of this comparison indices based on other body measurements (such as of the neck and limbs), body imaging, or laboratory tests. To the qualifying 10 indices extracted from that review [47], we added the more recently published Waist-Hip Index (WHI) [48] as well as Hip Index (HI) [32]. For each of 12 indices, their name was searched in PubMed on 20 March 2025 to identify a sentinel (original or at least early) publication for the index that defined its rationale and formula. The number of citations returned was also recorded as an indicator of the popularity of each index in the medical literature.
2.2. Units and Transformations of Indices
The formulas for many anthropometric indices, including allometric ones such as ABSI and BMI, include fractional powers of body dimensions, leading to them having non-intuitive units. This can be overcome by scaling the body dimensions before taking their power. For example, the basic formula for ABSI is which, if WC and H are given in m and W in kg, results in units of [31], which moreover would change if the exponents of H and W were adjusted for different populations [49]. Scaling here can involve dividing by typical values that can be the mean for some cohort before entering them in the formula [32]. If W and H are scaled but WC is left in its original units, then ABSI will have the same units as WC, and can be intuitively understood as WC adjusted to some standard weight and height (). Similarly, by scaling H and W, HI can be understood as HC adjusted to a standard weight and height [32]. This scaling (with = 73 kg, = 1.66 m [32]) was applied here for ABSI and HI. Numerically, this only multiplies all the index numerical values by a constant factor, and does not affect the relative differences in index value between people or correlations with any other quantities.
Before comparing anthropometric indices, a further step taken was to convert each to a z score by subtracting age and sex specific means and dividing by standard deviations [31]. The justification for this is that typical values for many indices differ by age and sex, and that the standardizing by the expected value and its spread is more informative about an individual’s relative risk [15]. Z scores also make different indices directly comparable regardless of original units, in that all will have a population mean close to 0 and standard deviation close to 1 [50]. This is similar to assessing growth in children by considering age- and sex-specific percentiles or z scores rather than absolute lengths or weights [51]. The age and sex specific means and standard deviations for all anthropometric indices were computed from the NHANES III cohort (described below) using smoothing splines [31].
In order to illustrate the possibility of combining independent allometric indices to improve risk prediction, ARI was also computed for the NHANES III cohort by summing the logarithms of mortality hazards separately due to BMI and ABSI, estimated from their separate nonlinear Cox proportional hazard models (described below). Hazards due to HI and H could also be added, since these are also mutually uncorrelated, but these are smaller (in the case of HI) or almost zero (for H) [32], so were left out.
Since the expression for ARI is cumbersome and potentially dependent on the outcome of interest and the cohort used to estimate it (although it has been shown to hold up across cohorts [32]), we also devised a cruder combination of mortality risk from BMI and ABSI, as . Here, are simplified z scores with population-wide rather than age and sex specific means and standard deviations; the respective means and standard deviations adopted are 27.0 and 5.8 kg m−2 for BMI and 91.9 and 6.5 cm for ABSI. This formulation relies on the finding across many studies that overall effect on mortality risk is comparable in magnitude for ABSI and BMI, and that mortality risk is elevated for both well below and well above average BMI, while it increases monotonically with increasing ABSI.
2.3. Correlations and Mortality Risk Associations
To illustrate the inter-correlation and predictive power of the various anthropometric indices, public-use data from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III) were analyzed. NHANES III sampled the civilian non-institutionalized United States population during 1988–1994, and linked mortality outcomes through 2019 were available from the National Center for Health Statistics (25–31 years of follow-up). Details about the NHANES III protocol and demographics are available elsewhere [52,53], and previous studies have reported on the correlations between anthropometric variables and between anthropometrics and mortality hazard in NHANES III [32,54]. The NHANES III protocol was approved by the NHANES Institutional Review Board, and all participants gave written informed consent [55]. We analyzed NHANES III data for all nonpregnant adults (age 18 and over) with H, W, WC, HC measurements and mortality follow-up (n = 16,066, with 6604 deaths recorded).
The full correlation matrix of all the identified anthropometric index z scores (along with those of the basic anthropometrics H, W, WC, and HC themselves, for comparison) was generated using the NHANES data. This was examined with a particular focus on the independence of each index from BMI. Additionally, the ability of each index to predict mortality hazard was quantified using Cox proportional hazard modeling, as described previously [32]. For each index, both linear and nonlinear (penalized cubic spline) hazard models were constructed. The linear model assumes that the logarithm of mortality hazard changes linearly with each increment of index z score (thus, death rate is an exponential function of index z score), while the nonlinear model allows the logarithm of mortality hazard to be an arbitrary smooth function of the index z score. The main measure of relative model performance was Akaike information coefficient (AIC) difference, AIC, given relative to a baseline model with only age and sex as predictors (no anthropometrics used). We defined AIC = AICbaseline − AICmodel so that higher values of AIC give evidence of stronger association with mortality hazard. Differences of AIC of 6 or more indicated models that perform significantly differently (at the 95% confidence level) as mortality predictors for the sampled population [39].
These analyses were carried out with R software (version 4.3.3) [56], with the survival package (version 3.5.8) for the Cox proportional hazard modeling [57].
3. Results
3.1. Index Characteristics
Table 1 lists the selected indices (and the abbreviations used for them) and provides basic data for each (sentinel paper, formula, popularity). Based on the sentinel papers cited in Table 1, the rationales for the indices could be grouped into (1) simple dimensionless ratios (WHtR, WHR); (2) approximation of the trunk or body as a simple geometric shape (AVI [cylinder and cone], BRI [ellipse]); (3) maximal correlation with non-anthropometric measures of adiposity such as percent body fat (BAI, CUN-BAE); and (4) allometry (BMI, ABSI, HI, WHI; CI and WWI can also be placed in this category, as they state as an objective minimizing correlation with height and weight or BMI). Examining the functional forms of the index formulas, it can be noted that many are products of powers of the anthropometrics (or sums of two or more terms that are such products), while BRI is just a nonlinear but monotone function of WHtR.

Table 1.
Anthropometric indices.
In terms of popularity in the medical literature, the allometric indices ABSI and HI have done relatively well compared to most others. However, BMI still overwhelmingly dominates, with the simple ratios WHR and WHtR being the next most widely used.
3.2. Correlations Between Indices
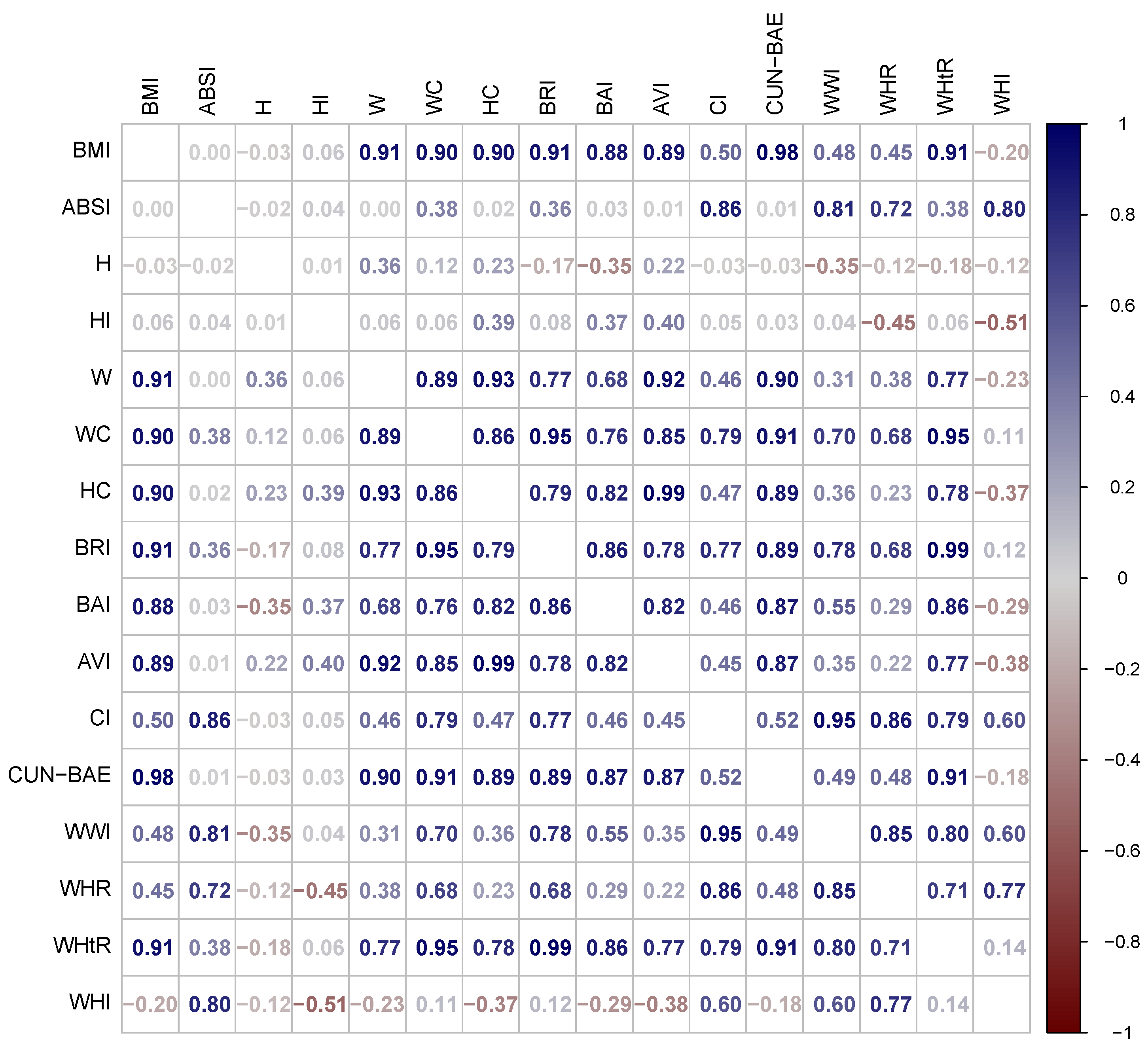
Figure 1 presents the correlation matrix for the anthropometric indices evaluated with NHANES data, after all indices were transformed to age and sex specific z scores. The “allometric quartet” of H, BMI, ABSI, HI, plotted in the upper left corner, has almost zero inter-correlation, as intended in its construction. By contrast, CUN-BAE has a correlation of 0.98 with BMI, and thus would be expected to be almost interchangeable with it, aside from their possibly different dependence on age and sex, which were removed by taking the z scores. WHtR and its close derivative BRI both have correlations of 0.91 with BMI (and 0.99 with each other), while AVI and BAI have correlations with BMI of 0.89 and 0.88 respectively. These are similar to the correlation of around 0.9 observed between WC and BMI in different populations [32], and these indices also all show large correlations with H compared to BMI or ABSI. Another grouping of indices, CI, WWI, and WHR, have moderate correlations of 0.45 to 0.50 with BMI and stronger correlations of 0.72 to 0.86 with ABSI. WHI has the weakest correlation with BMI outside the allometric quartet, in keeping with its basis of derivation, and shows a correlation of 0.80 with ABSI and the strongest correlation of any of the indices, −0.51, with HI.
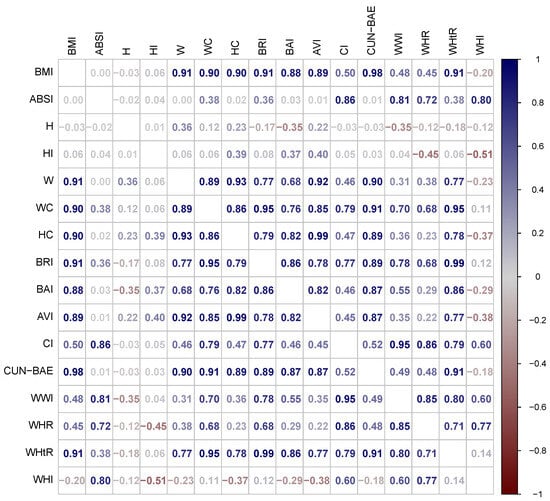
Figure 1.
Correlations between z scores of anthropometric indices in NHANES III. Larger correlations are shown in brighter colors, with blue for positive and red for negative correlations. The correlation of each index with itself is always 1 and not shown.
3.3. Associations with Mortality Hazard
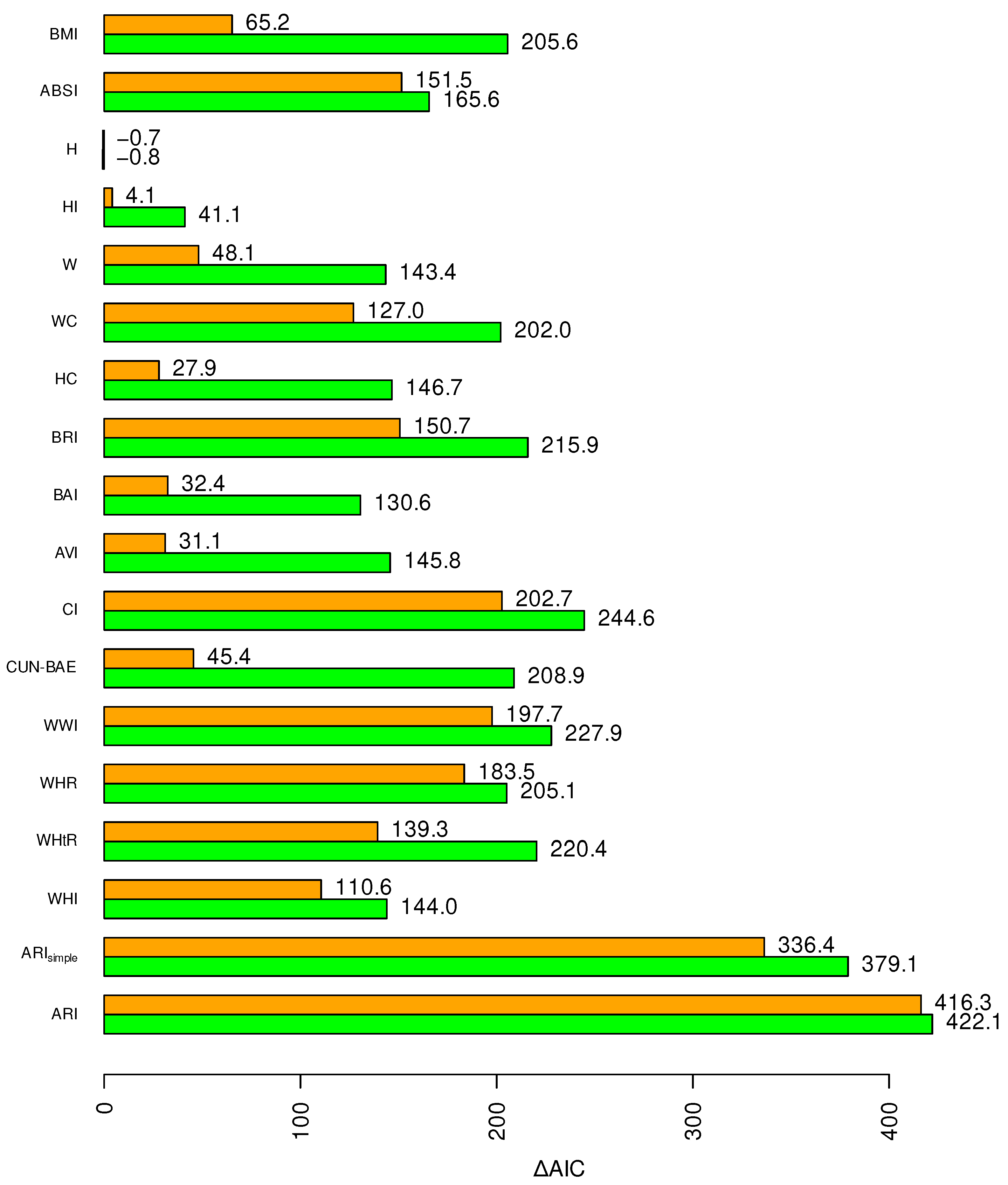
Figure 2 displays the Akaike information score relative to a baseline model without anthropometrics for mortality hazard prediction in NHANES III using each index. Beginning with the allometric quartet, BMI and ABSI are comparably strong nonlinear predictors. BMI is weaker as a linear predictor because of its U-shaped association with mortality, whereas the association of ABSI z score with the logarithm of mortality hazard is more linear. H has no significant association with mortality in this sample, and HI has a nonlinear (U-shaped) association with mortality that is weaker than that of BMI or ABSI.
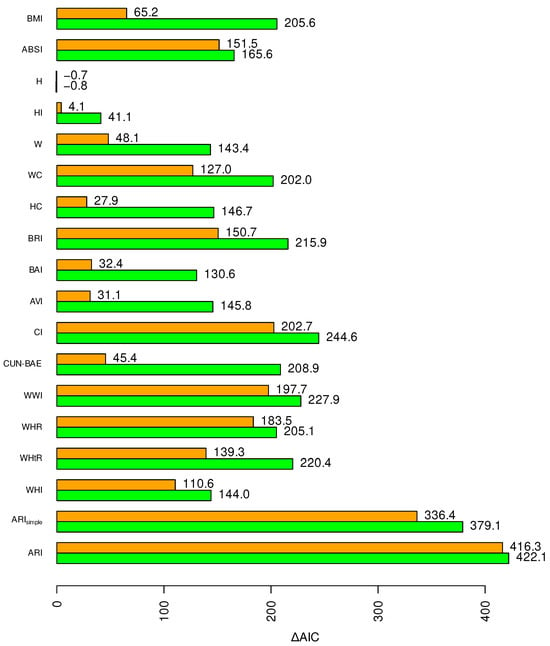
Figure 2.
AIC, a measure of predictive power, for each anthropometric index as a linear (upper, orange bar) or nonlinear predictor (lower, green bar) of mortality hazard in NHANES III.
Indices that are strongly correlated with BMI and almost not at all with ABSI (CUN-BAE, BAI, AVI) share with BMI that they are much stronger nonlinear predictors compared to linear ones. Indices that are strongly correlated with BMI but have some association with ABSI (WHtR, BRI) improve as linear predictors, but only slightly as nonlinear predictors, compared to BMI. Indices that are strongly correlated with ABSI and only moderately or weakly with BMI (CI, WWI, WHR, WHI) are comparatively strong linear predictors and in some cases (particularly CI) outperform any single member of the allometric quartet also as nonlinear predictors.
The advantage of the allometric quartet for risk prediction is not that any one of its indices is necessarily the best for mortality prediction, but that its indices are independent of each other, so that the risks attributable to each can be summed, creating risk assessments that combine multiple dimensions of size/shape variability. Thus, , created by summing ABSI and BMI risks according to crude approximations of their typical associations with mortality risk, outperforms all the tested indices either as a linear or nonlinear predictor. The full ARI approach to summing risks associated with BMI and ABSI does better yet, being a linear predictor with AIC close to the sum of the nonlinear ones for BMI and ABSI separately.
4. Discussion
What can be learned from the comparison of the different anthropometric indices, particularly in relation to the call for additional anthropometric criteria to be used for defining obesity? One clear shortcoming found for many of the indices in the literature is that they are not independent of height, and are therefore expected to be systematically biased between population groups with different average heights. Even indices of height-adjusted WC, if they are motivated by isometric reasoning (as is the case for WHtR or BRI), do not match the nonlinear (allometric) relationship empirically found between H and WC [66]. To this extent, they are inferior to BMI, which does successfully capture the nonlinear relationship seen between H and W in numerous studies of adult human populations.
Should a new anthropometric index also be independent of BMI? This criterion was used to derive the allometric indices, primarily ABSI and HI. Most of the other indices, however, either have very high correlations with BMI, matching the correlations of about 0.9 between W, BMI, and WC, or moderate correlations with BMI and higher ones with ABSI. There is currently not a definitive answer to this question.
On the one hand, to the extent that BMI is a clinically useful construct, correlation with it could be seen as validating for new indices to diagnose obesity. As well, indices that are based on maximizing prediction of measures related to body composition, such as % fat (e.g., CUN-BAE), or to disease risk might very well show high correlations with BMI while improving on BMI for their designed purpose. On the other hand, mutually independent indices are more interpretable in that ABSI and HI related risk is clearly information supplementary to that offered by BMI, while the value of other indices may be more difficult to perceive given their “entanglement” with BMI. Thus, an index with high positive correlation with BMI will almost always have elevated values when BMI is high enough and low values when BMI is low enough, so its values being above or below a given threshold would only be meaningful for some middle range of BMI [15].
One possible objection to using allometric indices such as ABSI is the relative complexity of their calculation, compared to just WC measurements or dimensionless ratios like WHR and WHtR. However, BMI also requires a calculator or lookup table to determine, but has nevertheless become standard. Even more complicated constructs, such as Framingham Risk Score, are widely advocated for health decision making [67,68,69,70]. Prototype online calculators for computing ABSI and HI and their z scores have been provided already at initial publication [32] and could likewise be integrated into increasingly computer-reliant medical practices [71].
Strengths of the current work include comparing a comprehensive suite of proposed anthropometric indices and using a large national population sample with lengthy follow-up. There are several limitations, which should be addressed in future systematic studies. Data were from only one country. Mortality was the only health outcome considered, although correlations between anthropometric parameters and other risk factors such as hypertension, hypertriglyceridemia, and hyperglycemia [37,46,72,73], as well as the development of cardiovascular disease, cancer, and other ailments [74,75,76,77] are known to exist and can also be compared between indices using similar methods. As well, only adults were considered, and in some cases indices may have different cardiovascular risk associations in children as compared to adults [78], although studies have shown value in ABSI and HI z scores (using age-appropriate means and standard deviations) as markers of health risks in children and adolescents as well [79,80,81,82].
5. Conclusions
Our main contribution is demonstrating the distinctive mutual statistical independence of allometric indices that can provide information about body shape independent of height and BMI, which leads to the possibility of a straightforward summation of risk across indices to improve predictive power and hopefully clinical relevance (the ARI approach). While the other indices studied have their own justifications and advantages, taking up ABSI and HI to improve the definition of obesity and related risks would be a logical continuation of the allometric derivation of BMI, a highly successful although imperfect construct.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, writing—original draft preparation, writing—review and editing, and visualization: N.Y.K. and J.C.K. Software, data curation, and analysis: N.Y.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data used in this article are publicly available via PubMed (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) and NHANES (https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/Default.aspx). Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Correction Statement
This article has been republished with a minor correction to Data Availability Statement. This change does not affect the scientific content of the article.
References
- Schulz, L.O. Obese, overweight, desirable, ideal: Where to draw the line in 1986? J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 1986, 86, 1702–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NHLBI. Clinical Guidelines on the Identification, Evaluation, and Treatment of Overweight and Obesity in Adults: The Evidence Report; Technical Report 98-4083; National Heart Lung and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Global Health Risks: Mortality and Burden of Disease Attributable to Selected Major Risks; Technical Report; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Flegal, K.M. Use and misuse of BMI categories. AMA J. Ethics 2023, 25, E550–E558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashwell, M.; Cole, T.J.; Dixon, A.K. Obesity: New insight into the anthropometric classification of fat distribution shown by computed tomography. BMJ 1985, 290, 1692–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snijder, M.; van Dam, R.; Visser, M.; Seidell, J. What aspects of body fat are particularly hazardous and how do we measure them? Int. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 35, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez, G.; Duval, S.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr.; Silventoinen, K. Comparison of body mass index, waist circumference, and waist/hip ratio in predicting incident diabetes: A meta-analysis. Epidemiol. Rev. 2007, 29, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huxley, R.; Mendis, S.; Zheleznyakov, E.; Reddy, S.; Chan, J. Body mass index, waist circumference and waist:hip ratio as predictors of cardiovascular risk–a review of the literature. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 64, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayedi, A.; Soltani, S.; Zargar, M.S.; Khan, T.A.; Shab-Bidar, S. Central fatness and risk of all cause mortality: Systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of 72 prospective cohort studies. BMJ 2020, m3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndumele, C.E.; Rangaswami, J.; Chow, S.L.; Neeland, I.J.; Tuttle, K.R.; Khan, S.S.; Coresh, J.; Mathew, R.O.; Baker-Smith, C.M.; Carnethon, M.R.; et al. Cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic health: A presidential advisory from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2023, 148, 1606–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, R.; Ostrominski, J.W.; Vaduganathan, M. Prevalence of cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome atages in US adults, 2011–2020. JAMA 2024, 331, 1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kengne, A.P.; Beulens, J.W.; Peelen, L.M.; Moons, K.G.; van der Schouw, Y.T.; Schulze, M.B.; Spijkerman, A.M.; Griffin, S.J.; Grobbee, D.E.; Palla, L.; et al. Non-invasive risk scores for prediction of type 2 diabetes (EPIC-InterAct): A validation of existing models. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014, 2, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhana, K.; Ikram, M.A.; Hofman, A.; Franco, O.H.; Kavousi, M. Anthropometric measures in cardiovascular disease prediction: Comparison of laboratory-based versus non-laboratory-based model. Heart 2015, 101, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakauer, N.Y.; Krakauer, J.C. Association of x-ray absorptiometry body composition measurements with basic anthropometrics and mortality hazard. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakauer, N.Y.; Krakauer, J.C. Expansion of waist circumference in medical literature: Potential clinical application of a body shape index. J. Obes. Weight Loss Ther. 2014, 4, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcidiacono, B.; Chiefari, E.; Foryst-Ludwig, A.; Currò, G.; Navarra, G.; Brunetti, F.S.; Mirabelli, M.; Corigliano, D.M.; Kintscher, U.; Britti, D.; et al. Obesity-related hypoxia via miR-128 decreases insulin-receptor expression in human and mouse adipose tissue promoting systemic insulin resistance. eBioMedicine 2020, 59, 102912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirabelli, M.; Tocci, V.; Donnici, A.; Giuliano, S.; Sarnelli, P.; Salatino, A.; Greco, M.; Puccio, L.; Chiefari, E.; Foti, D.P.; et al. Maternal preconception body mass index overtakes age as a risk factor for gestational diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevill, A.M.; Stewart, A.D.; Olds, T.; Holder, R. Relationship between adiposity and body size reveals limitations of BMI. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 2006, 129, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahima, R.S.; Lazar, M.A. The health risk of obesity—Better metrics imperative. Science 2013, 341, 856–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alser, M.; Naja, K.; Elrayess, M.A. Mechanisms of body fat distribution and gluteal-femoral fat protection against metabolic disorders. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1368966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, G.; Hedberg, P.; Öhrvik, J. Survival of the fattest: Unexpected findings about hyperglycaemia and obesity in a population based study of 75-year-olds. BMJ Open 2011, 1, e000012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cepeda-Valery, B.; Pressman, G.S.; Figueredo, V.M.; Romero-Corral, A. Impact of obesity on total and cardiovascular mortality—Fat or fiction? Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2011, 8, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavie, C.J.; De Schutter, A.; Patel, D.A.; Romero-Corral, A.; Artham, S.M.; Milani, R.V. Body composition and survival in stable coronary heart disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 60, 1374–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elagizi, A.; Kachur, S.; Lavie, C.J.; Carbone, S.; Pandey, A.; Ortega, F.B.; Milani, R.V. An overview and update on obesity and the obesity paradox in cardiovascular diseases. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2018, 61, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, A.L.; Fonarow, G.C.; Horwich, T.B. Waist circumference, body mass index, and survival in systolic heart failure: The obesity paradox revisited. J. Card. Fail. 2011, 17, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirahama, Y.; Tabata, N.; Sakamoto, K.; Sato, R.; Yamanaga, K.; Fujisue, K.; Sueta, D.; Araki, S.; Takashio, S.; Arima, Y.; et al. Validation of the obesity paradox by body mass index and waist circumference in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. Int. J. Obes. 2022, 46, 1840–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubino, F.; Cummings, D.E.; Eckel, R.H.; Cohen, R.V.; Wilding, J.P.H.; Brown, W.A.; Stanford, F.C.; Batterham, R.L.; Farooqi, I.S.; Farpour-Lambert, N.J.; et al. Definition and diagnostic criteria of clinical obesity. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2025, 13, 221–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology. Redefining obesity: Advancing care for better lives. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2025, 13, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keys, A.; Fidanza, F.; Karvonen, M.J.; Kimura, N.; Taylor, H.L. Indices of relative weight and obesity. J. Chronic Dis. 1972, 25, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayon, J. History of the concept of allometry. Am. Zool. 2000, 40, 748–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakauer, N.Y.; Krakauer, J.C. A new body shape index predicts mortality hazard independently of body mass index. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krakauer, N.Y.; Krakauer, J.C. An Anthropometric Risk Index based on combining height, weight, waist, and hip measurements. J. Obes. 2016, 2016, 8094275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakauer, N.Y.; Krakauer, J.C. Untangling waist circumference and hip circumference from body mass index with a body shape index, hip index, and anthropometric risk indicator. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2018, 16, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krakauer, N.Y.; Krakauer, J.C. The new anthropometrics and abdominal obesity: A body shape index, hip index, and anthropometric risk index. In Nutrition in the Prevention and Treatment of Abdominal Obesity, 2nd ed.; Watson, R.R., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; Chapter 2; pp. 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.; Zhang, S.; An, R. Effectiveness of A Body Shape Index (ABSI) in predicting chronic diseases and mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2018, 19, 737–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bawadi, H.; Abouwatfa, M.; Alsaeed, S.; Kerkadi, A.; Shi, Z. Body Shape Index is a stronger predictor of diabetes. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Chen, L.; Hu, W.; He, L. Association between a body shape index and subclinical carotid atherosclerosis in population free of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2021, 29, 1140–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeue, K.; Kusakabe, T.; Yamakage, H.; Ishii, K.; Satoh-Asahara, N. A Body Shape Index is useful for BMI-independently identifying Japanese patients with obesity at high risk of cardiovascular disease. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2023, 34, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakauer, N.Y.; Krakauer, J.C. Dynamic association of mortality hazard with body shape. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosugi, T.; Eriguchi, M.; Yoshida, H.; Tamaki, H.; Uemura, T.; Tasaki, H.; Furuyama, R.; Nishimoto, M.; Matsui, M.; Samejima, K.; et al. Association of body indices with mortality in older population: Japan Specific Health Checkups (J-SHC) Study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2024, 73, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafran, I.; Krakauer, N.Y.; Krakauer, J.C.; Goshen, A.; Gerber, Y. The predictive ability of ABSI compared to BMI for mortality and frailty among older adults. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 5330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christakoudi, S.; Tsilidis, K.K.; Evangelou, E.; Riboli, E. A Body Shape Index (ABSI), hip index, and risk of cancer in the UK Biobank cohort. Cancer Med. 2021, 10, 5614–5628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christakoudi, S.; Riboli, E.; Evangelou, E.; Tsilidis, K.K. Associations of body shape index (ABSI) and hip index with liver, metabolic, and inflammatory biomarkers in the UK Biobank cohort. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consalvo, V.; Krakauer, J.C.; Krakauer, N.Y.; Antonio, C.; Romano, M.; Vincenzo, S. ABSI (A Body Shape Index) and ARI (Anthropometric Risk Indicator) in bariatric surgery. First application on a bariatric cohort and possible clinical use. Obes. Surg. 2018, 27, 1966–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, M.; Sheng, G.; Hu, C.; Lu, S.; Peng, N.; Zou, Y. The value of combining the simple anthropometric obesity parameters, Body Mass Index (BMI) and a Body Shape Index (ABSI), to assess the risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Lipids Health Dis. 2022, 21, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewage, N.; Wijesekara, U.; Perera, R. Determining the best method for evaluating obesity and the risk of non-communicable diseases in females of childbearing age by using the body mass index, waist circumference, waist-to-hip ratio, waist-to-height ratio, A Body Shape Index, and hip index. Nutrition 2023, 114, 112135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piqueras, P.; Ballester, A.; Durá-Gil, J.V.; Martinez-Hervas, S.; Redón, J.; Real, J.T. Anthropometric indicators as a tool for diagnosis of obesity and other health risk factors: A literature review. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 631179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christakoudi, S.; Evangelou, E.; Riboli, E.; Tsilidis, K.K. GWAS of allometric body-shape indices in UK Biobank identifies loci suggesting associations with morphogenesis, organogenesis, adrenal cell renewal and cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, Y.B. “A Body Shape Index” in middle-age and older Indonesian population: Scaling exponents and association with incident hypertension. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimai, H.P. Use of dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) for diagnosis and fracture risk assessment; WHO-criteria, T- and Z-score, and reference databases. Bone 2017, 104, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Onis, M.; Habicht, J.P. Anthropometric reference data for international use: Recommendations from a World Health Organization Expert Committee. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1996, 64, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westat, Inc. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey III Body Measurements (Anthropometry); Westat, Inc.: Rockville, MD, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Ezzati, T.M.; Massey, J.T.; Waksberg, J.; Chu, A.; Maurer, K.R. Sample Design: Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey; Vital and Health Statistics. Series 2, Data Evaluation and Methods Research 113; National Center for Health Statistics (US): Washington, DC, USA, 1992.
- Dong, B.; Peng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Adegbija, O.; Hu, J.; Ma, J.; Ma, Y.H. Joint association between body fat and its distribution with all-cause mortality: A data linkage cohort study based on NHANES (1988–2011). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Center for Health Statistics (US). Plan and Operation of the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988–1994; Number 32 in Vital and Health Statistics, Series 1: Programs and Collection Procedures; National Center for Health Statistics (US): Washington, DC, USA, 1994.
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Therneau, T.M.; Grambsch, P.M. Modeling Survival Data: Extending the Cox Model; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Hartz, A.J.; Rupley, D.C.; Rimm, A.A. The association of girth measurements with disease in 32,856 women. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1984, 119, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdez, R. A simple model-based index of abdominal adiposity. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1991, 44, 955–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, S.D.; Yoshinaga, H. Waist/height ratio as a simple and useful predictor of coronary heart disease risk factors in women. Intern. Med. 1995, 34, 1147–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Romero, F.; Rodr’iguez-Mor’an, M. Abdominal volume index. an anthropometry-based index for estimation of obesity is strongly related to impaired glucose tolerance and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Arch. Med Res. 2003, 34, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergman, R.N.; Stefanovski, D.; Buchanan, T.A.; Sumner, A.E.; Reynolds, J.C.; Sebring, N.G.; Xiang, A.H.; Watanabe, R.M. A better index of body adiposity. Obesity 2011, 19, 1083–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Silva, C.; Galofré, J.; Escalada, J.; Santos, S.; Millán, D.; Vila, N.; Ibañez, P.; Gil, M.; Valentí, V.; et al. Body mass index classification misses subjects with increased cardiometabolic risk factors related to elevated adiposity. Int. J. Obes. 2012, 36, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, D.M.; Bredlau, C.; Bosy-Westphal, A.; Mueller, M.; Shen, W.; Gallagher, D.; Maeda, Y.; McDougall, A.; Peterson, C.M.; Ravussin, E.; et al. Relationships between body roundness with body fat and visceral adipose tissue emerging from a new geometrical model. Obesity 2013, 21, 2264–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.; Kim, N.H.; Kwon, T.Y.; Kim, S.G. A novel adiposity index as an integrated predictor of cardiometabolic disease morbidity and mortality. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevill, A.M.; Leahy, G.D.; Mayhew, J.; Sandercock, G.R.; Myers, T.; Duncan, M.J. ‘At risk’ waist-to-height ratio cut-off points recently adopted by NICE and US Department of Defense will unfairly penalize shorter adults. What is the solution? Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2023, 17, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, R.B., Sr.; Grundy, S.; Sullivan, L.M.; Wilson, P. Validation of the Framingham Coronary Heart Disease Prediction Scores. J. Am. Med Assoc. 2001, 286, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Chen, Y.; Chang, Y.; Sun, G.; Sun, Y. New anthropometric indices or old ones: Which perform better in estimating cardiovascular risks in Chinese adults. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2018, 18, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbatón Anchuelo, A.; Martínez-Larrad, M.T.; Serrano-García, I.; Fernández Pérez, C.; Serrano-Ríos, M. Body fat anthropometric indexes: Which of those identify better high cardiovascular risk subjects? A comparative study in Spanish population. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacıağaoğlu, N.; Öner, C.; Çetin, H.; Şimşek, E.E. Body shape index and cardiovascular risk in individuals with obesity. Cureus 2022, 14, e21259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, B.B.; Anderson, M.L.; Cook, A.J.; Catz, S.; Fishman, P.A.; McClure, J.B.; Reid, R. Using body mass index data in the electronic health record to calculate cardiovascular risk. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2012, 42, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Xu, L.; Li, J.; Sun, L.; Qin, W.; Ding, G.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Z.; Xie, S. Association of anthropometric indices of obesity with hypertension in Chinese elderly: An analysis of age and gender differences. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, X.; Shi, F.; Yu, W.; Gao, C.; Gou, S.; Fu, P. Associations between anthropometric indices and biological age acceleration in American adults: Insights from NHANES 2009–2018 data. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 22691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, W.; Park, J.H.; Ryu, O.H.; Yu, J.M.; Yoo, H.J.; Moon, S. Association of z-score of the log-transformed a body shape index with cardiovascular disease in people who are obese but metabolically healthy: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007–2010. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2018, 27, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parra-Soto, S.; Malcomson, F.C.; Ho, F.K.; Pell, J.P.; Sharp, L.; Mathers, J.C.; Celis-Morales, C. Associations of A Body Shape Index (ABSI) with cancer incidence, all-cause and at 23 sites- Findings from the UK Biobank prospective cohort study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2021, 31, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajikawa, M.; Maruhashi, T.; Kishimoto, S.; Yamaji, T.; Harada, T.; Saito, Y.; Mizobuchi, A.; Tanigawa, S.; Nakano, Y.; Chayama, K.; et al. A Body Shape Index as a simple anthropometric marker of abdominal obesity and risk of cardiovascular events. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 109, 3272–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rontogianni, M.O.; Bouras, E.; Aglago, E.K.; Freisling, H.; Murphy, N.; Cotterchio, M.; Hampe, J.; Lindblom, A.; Pai, R.K.; Pharoah, P.D.P.; et al. Allometric versus traditional body-shape indices and risk of colorectal cancer: A Mendelian randomization analysis. Int. J. Obes. 2024, 48, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sodero, G.; Rigante, D.; Pane, L.C.; Sessa, L.; Quarta, L.; Candelli, M.; Cipolla, C. Cardiometabolic risk assessment in a cohort of children and adolescents diagnosed with hyperinsulinemia. Diseases 2024, 12, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mameli, C.; Krakauer, J.C.; Krakauer, N.Y.; Bosetti, A.; Ferrari, C.M.; Schneider, L.; Borsani, B.; Arrigoni, S.; Pendezza, E.; Zuccotti, G.V. Effects of a multidisciplinary weight loss intervention in overweight and obese children and adolescents: 11 years of experience. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mameli, C.; Krakauer, N.Y.; Krakauer, J.C.; Bosetti, A.; Ferrari, C.M.; Moiana, N.; Schneider, L.; Borsani, B.; Genoni, T.; Zuccotti, G. The association between a body shape index and cardiovascular risk in overweight and obese children and adolescents. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todorova, S.A. Application of a body shape index as an anthropometric predictor of cardiometabolic risks in children and adolescents (systematic review). Mod. Technol. Med. 2024, 16, 1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, C.; Davison, B.; Singh, G.R. Small for gestational age and anthropometric body composition from early childhood to adulthood: The Aboriginal Birth Cohort study. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1349040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).