Gastric Autonomic Neuropathy in Diabetes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Neuroanatomy of the Gastrointestinal Tract
2.1. The Enteric Nervous System
2.2. The Autonomic Nervous System and the Gastrointestinal Tract
3. Physiology of Gastric Emptying
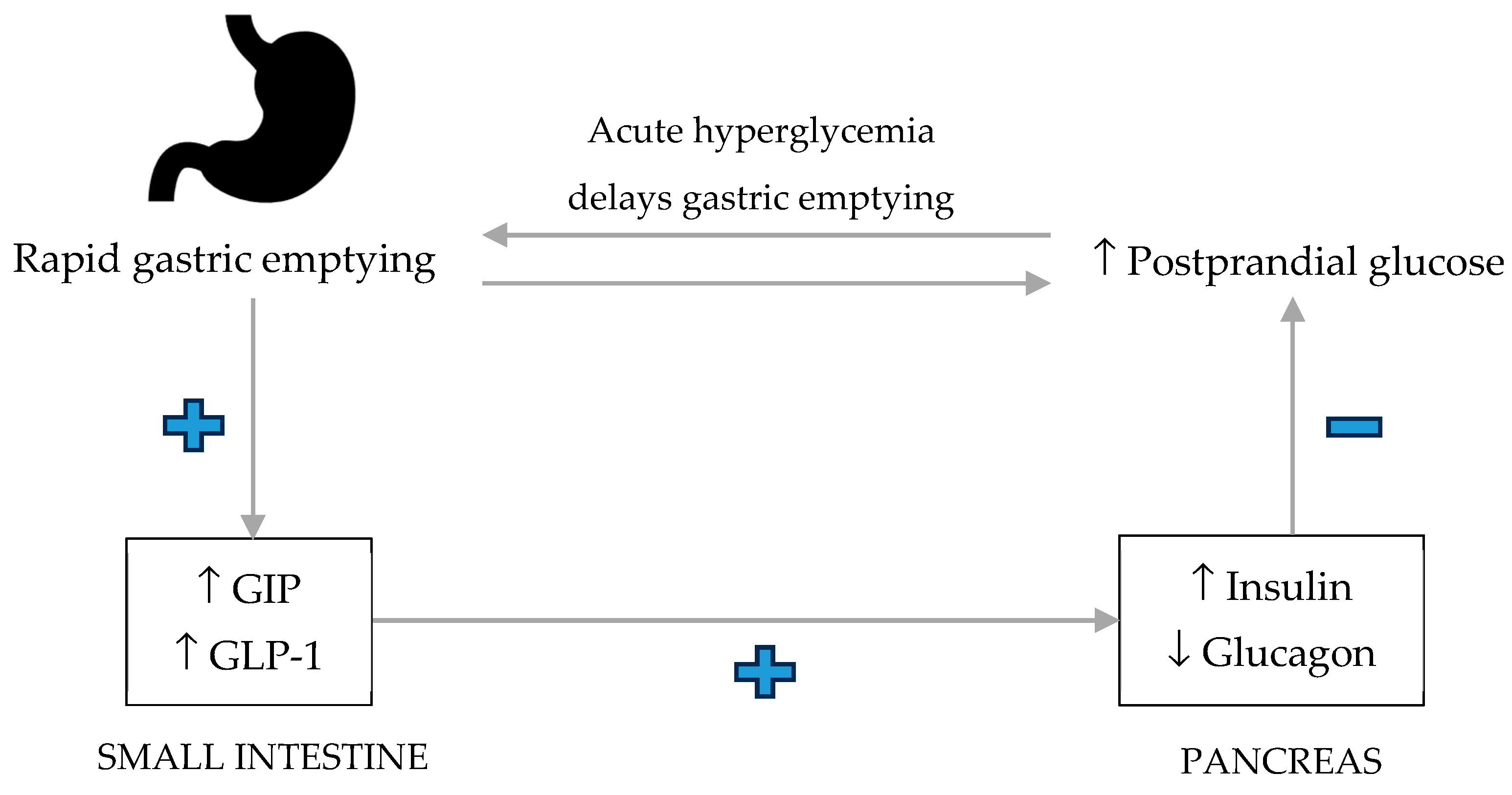
3.1. Gastric Emptying and Postprandial Glycemia
3.2. Gastric Emptying in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
3.3. Pathogenesis of Gastroparesis
3.4. Diagnosis of Gastroparesis
3.4.1. Diagnostic Methods for Gastroparesis
3.4.2. Surrogate Measures of Gastrointestinal Autonomic Neuropathy
3.4.3. Questionnaires for Assessing Gastrointestinal Symptoms and Autonomic Neuropathy
4. Treatment of Gastroparesis
4.1. Altering Food/Fiber Composition, Particle Size, and Frequency of Meals
4.2. Interventions to Accelerate Gastric Emptying in People with Gastroparesis
4.2.1. Non-Pharmacological Interventions
4.2.2. Pharmacological Treatments
4.3. Severe and Refractory Gastroparesis
4.4. Gastric Electrical Stimulation
5. The Impact of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists on Gastric Emptying
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tesfaye, S.; Boulton, A.J.; Dyck, P.J.; Freeman, R.; Horowitz, M.; Kempler, P.; Lauria, G.; Malik, R.A.; Spallone, V.; Vinik, A. Diabetic neuropathies: Update on definitions, diagnostic criteria, estimation of severity, and treatments. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 2285–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinik, A.I.; Maser, R.E.; Mitchell, B.D.; Freeman, R. Diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 1553–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trotta, D.; Verrotti, A.; Salladini, C.; Chiarelli, F. Diabetic neuropathy in children and adolescents. Pediatr. Diabetes 2004, 5, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinik, A.; Maser, R.; Ziegler, D. Autonomic imbalance: Prophet of doom or scope for hope? Diabet. Med. 2011, 28, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitropoulos, G.; Tahrani, A.A.; Stevens, M.J. Cardiac autonomic neuropathy in patients with diabetes mellitus. World J. Diabetes 2014, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. 3. Comprehensive medical evaluation and assessment of comorbidities. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, S25–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marathe, C.S.; Jones, K.L.; Wu, T.; Rayner, C.K.; Horowitz, M. Gastrointestinal autonomic neuropathy in diabetes. Auton. Neurosci. 2020, 229, 102718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bytzer, P.; Talley, N.J.; Leemon, M.; Young, L.J.; Jones, M.P.; Horowitz, M. Prevalence of gastrointestinal symptoms associated with diabetes mellitus: A population-based survey of 15,000 adults. Arch. Intern. Med. 2001, 161, 1989–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.R.; Fisher, R.S.; Parkman, H.P. Gastroparesis-related hospitalizations in the United States: Trends, characteristics, and outcomes, 1995–2004. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furness, J.B.; Callaghan, B.P.; Rivera, L.R.; Cho, H.-J. The enteric nervous system and gastrointestinal innervation: Integrated local and central control. In Microbial Endocrinology: The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Health and Disease; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 39–71. [Google Scholar]
- Stevens, J.E.; Jones, K.L.; Rayner, C.K.; Horowitz, M. Pathophysiology and pharmacotherapy of gastroparesis: Current and future perspectives. Expert. Opin. Pharmacother. 2013, 14, 1171–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, M.; Dent, J. Disordered gastric emptying: Mechanical basis, assessment and treatment. Bailliere’s Clin. Gastroenterol. 1991, 5, 371–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vittal, H.; Farrugia, G.; Gomez, G.; Pasricha, P.J. Mechanisms of disease: The pathological basis of gastroparesis—A review of experimental and clinical studies. Nat. Clin. Pract. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 4, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Rayner, C.K.; Jones, K.L.; Horowitz, M. Diabetic gastroparesis: Diagnosis and management. Drugs 2009, 69, 971–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuiken, S.D.; Samsom, M.; Camilleri, M.; Mullan, B.P.; Burton, D.D.; Kost, L.J.; Hardyman, T.J.; Brinkmann, B.H.; O’connor, M.K. Development of a test to measure gastric accommodation in humans. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 1999, 277, G1217–G1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacGregor, I.; Martin, P.; Meyer, J. Gastric emptying of solid food in normal man and after subtotal gastrectomy and truncal vagotomy with pyloroplasty. Gastroenterology 1977, 72, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirra, J.; Nicolaus, M.; Roggel, R.; Katschinski, M.; Storr, M.; Woerle, H.J.; Göke, B. Endogenous glucagon-like peptide 1 controls endocrine pancreatic secretion and antro-pyloro-duodenal motility in humans. Gut 2006, 55, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri, M. Gastrointestinal hormones and regulation of gastric emptying. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2019, 26, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, T.; Mochiki, E.; Kuwano, H. The roles of motilin and ghrelin in gastrointestinal motility. Int. J. Pept. 2010, 2010, 820794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tack, J.; Depoortere, I.; Coulie, B.; Peeters, T.; Bisschops, R.; Meulemans, Q.; Janssens, J. Influence of ghrelin on interdigestive motility in man. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2003, 15, 43. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.; Rayner, C.K.; Young, R.L.; Horowitz, M. Gut motility and enteroendocrine secretion. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2013, 13, 928–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, N.A. Impact of Different Calorific Meals and Pharmacological Blocker Agent on the Emptying Behaviour of the Whole Stomach and Its Three Regions Using Simultaneous Scintigraphy and Electrical Impedance Epigastrography; University of Surrey: Guildford, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ziessman, H.A.; Chander, A.; Clarke, J.O.; Ramos, A.; Wahl, R.L. The added diagnostic value of liquid gastric emptying compared with solid emptying alone. J. Nucl. Med. 2009, 50, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moxon, T. Mathematical Modelling of Gastric Emptying and Nutrient Absorption in the Human Digestive System. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Birmingham, Birmingham, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Camilleri, M. Integrated upper gastrointestinal response to food intake. Gastroenterology 2006, 131, 640–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brener, W.; Hendrix, T.R.; Mchugh, P.R. Regulation of the gastric emptying of glucose. Gastroenterology 1983, 85, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horowitz, M.; Maddox, A.F.; Wishart, J.M.; Harding, P.E.; Chatterton, B.E.; Shearman, D.J. Relationships between oesophageal transit and solid and liquid gastric emptying in diabetes mellitus. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 1991, 18, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, M.; Wishart, J.M.; Jones, K.L.; Hebbard, G.S. Gastric emptying in diabetes: An overview. Diabet. Med. 1996, 13, S16–S22. [Google Scholar]
- Cardoso-Júnior, A.; Coelho, L.G.; Savassi-Rocha, P.R.; Vignolo, M.C.; Abrantes, M.M.; de Almeida, A.M.; Dias, E.E.; Vieira, G., Jr.; de Castro, M.M.; Lemos, Y.V. Gastric emptying of solids and semi-solids in morbidly obese and non-obese subjects: An assessment using the 13C-octanoic acid and 13C-acetic acid breath tests. Obes. Surg. 2007, 17, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.F.; Horowitz, M.; Jones, K.L.; Wishart, J.M.; Harding, P.E. Natural history of diabetic gastroparesis. Diabetes Care 1999, 22, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, L.E.; Xie, C.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Phillips, L.K.; Sun, Z.; Jones, K.L.; Horowitz, M.; Rayner, C.K.; Wu, T. Gastric Emptying in Patients with Well-Controlled Type 2 Diabetes Compared with Young and Older Control Subjects Without Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 3311–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Huang, W.; Wang, X.; Trahair, L.G.; Pham, H.T.; Marathe, C.S.; Young, R.L.; Jones, K.L.; Horowitz, M.; Rayner, C.K. Gastric emptying in health and type 2 diabetes: An evaluation using a 75 g oral glucose drink. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 171, 108610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, W.T. Gastric emptying in ethnic populations: Possible relationship to development of diabetes and metabolic syndrome. Ethn. Dis. 2006, 16, 682–692. [Google Scholar]
- Marathe, C.S.; Horowitz, M.; Trahair, L.G.; Wishart, J.M.; Bound, M.; Lange, K.; Rayner, C.K.; Jones, K.L. Relationships of early and late glycemic responses with gastric emptying during an oral glucose tolerance test. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 3565–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalleh, R.J.; Wu, T.; Jones, K.L.; Rayner, C.K.; Horowitz, M.; Marathe, C.S. Relationships of glucose, GLP-1, and insulin secretion with gastric emptying after a 75-g glucose load in type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, e3850–e3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marathe, C.S.; Rayner, C.K.; Jones, K.L.; Horowitz, M. Relationships between gastric emptying, postprandial glycemia, and incretin hormones. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 1396–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharucha, A.E.; Batey-Schaefer, B.; Cleary, P.A.; Murray, J.A.; Cowie, C.; Lorenzi, G.; Driscoll, M.; Harth, J.; Larkin, M.; Christofi, M.; et al. Delayed Gastric Emptying Is Associated with Early and Long-term Hyperglycemia in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, M.; Edelbroek, M.; Wishart, J.; Straathof, J. Relationship between oral glucose tolerance and gastric emptying in normal healthy subjects. Diabetologia 1993, 36, 857–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, R.J.; Horowitz, M.; Maddox, A.F.; Harding, P.E.; Chatterton, B.E.; Dent, J. Hyperglycaemia slows gastric emptying in Type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 1990, 33, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentilcore, D.; Chaikomin, R.; Jones, K.L.; Russo, A.; Feinle-Bisset, C.; Wishart, J.M.; Rayner, C.K.; Horowitz, M. Effects of fat on gastric emptying of and the glycemic, insulin, and incretin responses to a carbohydrate meal in type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 2062–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Stevens, J.E.; Cukier, K.; Maddox, A.F.; Wishart, J.M.; Jones, K.L.; Clifton, P.M.; Horowitz, M.; Rayner, C.K. Effects of a protein preload on gastric emptying, glycemia, and gut hormones after a carbohydrate meal in diet-controlled type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 1600–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonlachanvit, S.; Hsu, C.W.; Boden, G.H.; Knight, L.C.; Maurer, A.H.; Fisher, R.S.; Parkman, H.P. Effect of altering gastric emptying on postprandial plasma glucose concentrations following a physiologic meal in type-II diabetic patients. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2003, 48, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, M.; Nakamura, T.; Kasai, F.; Onuma, T.; Baba, T.; Takebe, K. Altered postprandial insulin requirement in IDDM patients with gastroparesis. Diabetes Care 1994, 17, 901–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lysy, J.; Israeli, E.; Strauss-Liviatan, N.; Goldin, E. Relationships between hypoglycaemia and gastric emptying abnormalities in insulin-treated diabetic patients 1. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2006, 18, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, L.K.; Deane, A.M.; Jones, K.L.; Rayner, C.K.; Horowitz, M. Gastric emptying and glycaemia in health and diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2015, 11, 112–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaikomin, R.; Rayner, C.K.; Jones, K.L.; Horowitz, M. Upper gastrointestinal function and glycemic control in diabetes mellitus. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 5611–5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groop, L.C.; Defronzo, R.A.; Luzi, L.; Melander, A. Hyperglycaemia and absorption of sulphonylurea drugs. Lancet 1989, 334, 129–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camilleri, M.; Chedid, V.; Ford, A.C.; Haruma, K.; Horowitz, M.; Jones, K.L.; Low, P.A.; Park, S.-Y.; Parkman, H.P.; Stanghellini, V. Gastroparesis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locke III, R.G.; Schleck, C.D.; Zinsmeister, A.R.; Melton III, J.L.; Talley, N.J. Risk of gastroparesis in subjects with type 1 and 2 diabetes in the general population. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 107, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.T.; Rayner, C.K.; Jones, K.L.; Talley, N.J.; Horowitz, M. Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Diabetes: Prevalence, Assessment, Pathogenesis, and Management. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayvargiya, P.; Jameie-Oskooei, S.; Camilleri, M.; Chedid, V.; Erwin, P.J.; Murad, M.H. Association between delayed gastric emptying and upper gastrointestinal symptoms: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gut 2019, 68, 804–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punkkinen, J.; Färkkilä, M.; Mätzke, S.; Korppi-Tommola, T.; Sane, T.; Piirilä, P.; Koskenpato, J. Upper abdominal symptoms in patients with Type 1 diabetes: Unrelated to impairment in gastric emptying caused by autonomic neuropathy. Diabet. Med. 2008, 25, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogliandro, R.F.; Rizzoli, G.; Bellacosa, L.; De Giorgio, R.; Cremon, C.; Barbara, G.; Stanghellini, V. Is gastroparesis a gastric disease? Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2019, 31, e13562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aswath, G.S.; Foris, L.A.; Ashwath, A.K.; Patel, K. Diabetic gastroparesis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Petri, M.; Singh, I.; Baker, C.; Underkofler, C.; Rasouli, N. Diabetic gastroparesis: An overview of pathogenesis, clinical presentation and novel therapies, with a focus on ghrelin receptor agonists. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2021, 35, 107733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, P.; Farrugia, G. Diabetic gastroparesis: What we have learned and had to unlearn in the past 5 years. Gut 2010, 59, 1716–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tougas, G.; Hunt, R.H.; Fitzpatrick, D.; Upton, A. Evidence of impaired afferent vagal function in patients with diabetes gastroparesis. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 1992, 15, 1597–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafi, M.A.; Pasricha, P.J. Post-surgical and obstructive gastroparesis. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2007, 9, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harberson, J.; Thomas, R.M.; Harbison, S.P.; Parkman, H.P. Gastric neuromuscular pathology in gastroparesis: Analysis of full-thickness antral biopsies. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2010, 55, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordög, T.; Takayama, I.; Cheung, W.; Ward, S.M.; Sanders, K.M. Remodeling of networks of interstitial cells of Cajal in a murine model of diabetic gastroparesis. Diabetes 2000, 49, 1731–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashashati, M.; McCallum, R.W. Is interstitial cells of Cajal–opathy present in gastroparesis? J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2015, 21, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompili, S.; Latella, G.; Gaudio, E.; Sferra, R.; Vetuschi, A. The Charming World of the Extracellular Matrix: A Dynamic and Protective Network of the Intestinal Wall. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 610189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekharan, B.; Srinivasan, S. Diabetes and the enteric nervous system. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2007, 19, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goshi, E.; Zhou, G.; He, Q. Nitric oxide detection methods in vitro and in vivo. Med. Gas Res. 2019, 9, 192. [Google Scholar]
- Vlassara, H.; Palace, M. Diabetes and advanced glycation endproducts. J. Intern. Med. 2002, 251, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korenaga, K.; Micci, M.a.; Taglialatela, G.; Pasricha, P. Suppression of nNOS expression in rat enteric neurones by the receptor for advanced glycation end-products. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2006, 18, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonkowski, S.; Rytel, L. Somatostatin as an active substance in the mammalian enteric nervous system. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillemin, R. Somatostatin inhibits the release of acetylcholine induced electrically in the myenteric plexus. Endocrinology 1976, 99, 1653–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, J.D. Enteric nervous system: Neuropathic gastrointestinal motility. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2016, 61, 1803–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proks, P.; Lippiat, J. Membrane ion channels and diabetes. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2006, 12, 485–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, M. Intestinal ion transport and the pathophysiology of diarrhea. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 931–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavely, R.; Ott, L.C.; Rashidi, N.; Sakkal, S.; Nurgali, K. The oxidative stress and nervous distress connection in gastrointestinal disorders. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sifuentes-Franco, S.; Pacheco-Moisés, F.P.; Rodríguez-Carrizalez, A.D.; Miranda-Díaz, A.G. The role of oxidative stress, mitochondrial function, and autophagy in diabetic polyneuropathy. J. Diabetes Res. 2017, 2017, 1673081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakane, S.; Mukaino, A.; Okumura, Y.; Hirosawa, H.; Higuchi, O.; Matsuo, H.; Kainuma, M.; Nakatsuji, Y. The Presence of Ganglionic Acetylcholine Receptor Antibodies in Sera from Patients with Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders: A Preliminary Study. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Giorgio, R.; Guerrini, S.; Barbara, G.; Stanghellini, V.; De Ponti, F.; Corinaldesi, R.; Moses, P.L.; Sharkey, K.A.; Mawe, G.M. Inflammatory neuropathies of the enteric nervous system. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 1872–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Yang, Y.; Geng, Z.; Zhu, L.; Yuan, S.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Fu, H. The change of insulin-like growth factor-1 in diabetic patients with neuropathy. Chin. Med. J. 1999, 112, 76–79. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Wu, B.; Sun, H.; Sun, T.; Han, K.; Li, D.; Ji, F.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, D. Impaired insulin/IGF-1 is responsible for diabetic gastroparesis by damaging myenteric cholinergic neurones and interstitial cells of Cajal. Biosci. Rep. 2017, 37, BSR20170776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri, M.; Bharucha, A.E.; Farrugia, G. Epidemiology, mechanisms, and management of diabetic gastroparesis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 9, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uppaluri, S.; Jain, M.A.; Ali, H.; Shingala, J.; Amin, D.; Ajwani, T.; Fatima, I.; Patel, N.; Kaka, N.; Sethi, Y. Pathogenesis and management of diabetic gastroparesis: An updated clinically oriented review. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2024, 18, 102994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri, M.; Parkman, H.P.; Shafi, M.A.; Abell, T.L.; Gerson, L. Clinical guideline: Management of gastroparesis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 18–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, M.; Harding, P.E.; Maddox, A.F.; Wishart, J.M.; Akkermans, L.M.; Chatterton, B.E.; Shearman, D.J. Gastric and oesophageal emptying in patients with type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 1989, 32, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Prather, C.; Fisher, R.; Meyer, J.; Summers, R.; Pimentel, M.; McCallum, R. 646 Akkermans LM, Loening-Baucke V.; AMS Task Force Committee on Gastrointestinal 647 Transit. Measurement of gastrointestinal transit. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2005, 50, 648. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, S.K.; Prom-On, P.; Sangkue, S.; Thiangsook, W. Assessment of Radiation Exposure in a Nuclear Medicine Department during (99m)Tc-MDP Bone Scintigraphy. Toxics 2023, 11, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Febo-Rodriguez, L.; Chumpitazi, B.P.; Sher, A.C.; Shulman, R.J. Gastric accommodation: Physiology, diagnostic modalities, clinical relevance, and therapies. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2021, 33, e14213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilja, O.H.; Hausken, T.; Ødegaard, S.; Berstad, A. Gastric emptying measured by ultrasonography. World J. Gastroenterol. 1999, 5, 93–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abell, T.L.; Camilleri, M.; Donohoe, K.; Hasler, W.L.; Lin, H.C.; Maurer, A.H.; McCallum, R.W.; Nowak, T.; Nusynowitz, M.L.; Parkman, H.P. Consensus recommendations for gastric emptying scintigraphy: A joint report of the American Neurogastroenterology and Motility Society and the Society of Nuclear Medicine. J. Nucl. Med. Technol. 2008, 36, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, C.; Søfteland, E.; Gunterberg, V.; Frøkjær, J.B.; Lelic, D.; Brock, B.; Dimcevski, G.; Gregersen, H.; Simrén, M.; Drewes, A.M. Diabetic autonomic neuropathy affects symptom generation and brain-gut axis. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 3698–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegeberg, A.M.L.; Brock, C.; Ejskjaer, N.; Karmisholt, J.S.; Jakobsen, P.E.; Drewes, A.M.; Brock, B.; Farmer, A.D. Gastrointestinal symptoms and cardiac vagal tone in type 1 diabetes correlates with gut transit times and motility index. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2021, 33, e13885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, K.M.; Horowitz, M.; Riddell, P.S.; Maddern, G.J.; Myers, J.C.; Holloway, R.H.; Wishart, J.M.; Jamieson, G.G. Relations among autonomic nerve dysfunction, oesophageal motility, and gastric emptying in gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Gut 1991, 32, 1436–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, T.W. Pancreatic polypeptide: A unique model for vagal control of endocrine systems. J. Auton. Nerv. Syst. 1983, 9, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, K.; Hartmann, B.; Fedorova, T.D.; Østergaard, K.; Krogh, K.; Møller, N.; Holst, J.J.; Borghammer, P. Pancreatic polypeptide in Parkinson’s disease: A potential marker of parasympathetic denervation. J. Park. Dis. 2017, 7, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, A.; Low, P.A.; Camilleri, M.; Singer, W.; Burton, D.; Chakraborty, S.; Bharucha, A.E. Utility of the plasma pancreatic polypeptide response to modified sham feeding in diabetic gastroenteropathy and non-ulcer dyspepsia. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2020, 32, e13744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terkelsen, A.J.; Karlsson, P.; Lauria, G.; Freeman, R.; Finnerup, N.B.; Jensen, T.S. The diagnostic challenge of small fibre neuropathy: Clinical presentations, evaluations, and causes. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 934–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rentz, A.; Kahrilas, P.; Stanghellini, V.; Tack, J.; Talley, N.; De La Loge, C.; Trudeau, E.; Dubois, D.; Revicki, D. Development and psychometric evaluation of the patient assessment of upper gastrointestinal symptom severity index (PAGI-SYM) in patients with upper gastrointestinal disorders. Qual. Life Res. 2004, 13, 1737–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revicki, D.A.; Rentz, A.M.; Dubois, D.; Kahrilas, P.; Stanghellini, V.; Talley, N.J.; Tack, J. Gastroparesis Cardinal Symptom Index (GCSI): Development and validation of a patient reported assessment of severity of gastroparesis symptoms. Qual. Life Res. 2004, 13, 833–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, Y.J.; Hong, S.M.; Chon, S.; Oh, S.; Woo, J.T.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, Y.S.; Rhee, S.Y. Effects of Rebamipide on Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Metab. J. 2016, 40, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sletten, D.M.; Suarez, G.A.; Low, P.A.; Mandrekar, J.; Singer, W. COMPASS 31: A refined and abbreviated Composite Autonomic Symptom Score. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2012, 87, 1196–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egboh, S.-m.C.; Abere, S. Gastroparesis: A Multidisciplinary Approach to Management. Cureus 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahamsson, H. Treatment options for patients with severe gastroparesis. Gut 2007, 56, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suresh, H.; Zhou, J.; Ho, V. The Short-Term Effects and Tolerability of Low-Viscosity Soluble Fibre on Gastroparesis Patients: A Pilot Clinical Intervention Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homko, C.; Duffy, F.; Friedenberg, F.; Boden, G.; Parkman, H. Effect of dietary fat and food consistency on gastroparesis symptoms in patients with gastroparesis. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2015, 27, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olausson, E.A.; Alpsten, M.; Larsson, A.; Mattsson, H.; Andersson, H.; Attvall, S. Small particle size of a solid meal increases gastric emptying and late postprandial glycaemic response in diabetic subjects with gastroparesis. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2008, 80, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Törnblom, H. Treatment of gastrointestinal autonomic neuropathy. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limketkai, B.N.; LeBrett, W.; Lin, L.; Shah, N.D. Nutritional approaches for gastroparesis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quianzon, C.C.; Cheikh, I. History of insulin. J. Community Hosp. Intern. Med. Perspect. 2012, 2, 18701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Bi, X.; Yu, B.; Chen, D. Isoflavones: Anti-inflammatory benefit and possible caveats. Nutrients 2016, 8, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setchell, K.D.; Nardi, E.; Battezzati, P.-M.; Asciutti, S.; Castellani, D.; Perriello, G.; Clerici, C. Novel soy germ pasta enriched in isoflavones ameliorates gastroparesis in type 2 diabetes: A pilot study. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 3495–3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahjoub, F.; Salari, R.; Yousefi, M.; Mohebbi, M.; Saki, A.; Rezayat, K.A. Effect of Pistacia atlantica kurdica gum on diabetic gastroparesis symptoms: A randomized, triple-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. Electron. Physician 2018, 10, 6997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J. D-Limonene: Safety and clinical applications. Altern. Med. Rev. 2007, 12, 259. [Google Scholar]
- Camilleri, M. Novel diet, drugs, and gastric interventions for gastroparesis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 14, 1072–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCallum, R.W.; Ricci, D.A.; Rakatansky, H.; Behar, J.; Rhodes, J.B.; Salen, G.; Deren, J.; Ippoliti, A.; Olsen, H.W.; Falchuk, K.; et al. A Multicenter Placebo-controlled Clinical Trial of Oral Metoclopramide in Diabetic Gastroparesis. Diabetes Care 1983, 6, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heckert, J.; Parkman, H. Therapeutic response to domperidone in gastroparesis: A prospective study using the GCSI-daily diary. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 30, e13246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, R.D.; Davenport, K.; McCallum, R.W. The treatment of idiopathic and diabetic gastroparesis with acute intravenous and chronic oral erythromycin. Am. J. Gastroenterol. (Springer Nat.) 1993, 88, 203–207. [Google Scholar]
- Erbas, T.; Varoglu, E.; Erbas, B.; Tastekin, G.; Akalin, S. Comparison of metoclopramide and erythromycin in the treatment of diabetic gastroparesis. Diabetes Care 1993, 16, 1511–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.D.; Martin, N.M.; Patterson, M.; Taylor, S.; Ghatei, M.A.; Kamm, M.A.; Johnston, C.; Bloom, S.R.; Emmanuel, A.V. Ghrelin enhances gastric emptying in diabetic gastroparesis: A double blind, placebo controlled, crossover study. Gut 2005, 54, 1693–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, A.; Camilleri, M.; Busciglio, I.; Burton, D.; Smith, S.A.; Vella, A.; Ryks, M.; Rhoten, D.; Zinsmeister, A.R. The ghrelin agonist RM-131 accelerates gastric emptying of solids and reduces symptoms in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 11, 1453–1459.e1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, A.; Camilleri, M.; Busciglio, I.; Burton, D.; Stoner, E.; Noonan, P.; Gottesdiener, K.; Smith, S.A.; Vella, A.; Zinsmeister, A.R. Randomized controlled phase Ib study of ghrelin agonist, RM-131, in type 2 diabetic women with delayed gastric emptying: Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, B.; Camilleri, M.; Burton, D.; Viramontes, B.; McKinzie, S.; Thomforde, G.; O’Connor, M.K.; Brinkmann, B.H. Effects of 5-HT(3) antagonism on postprandial gastric volume and symptoms in humans. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2002, 16, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri, M.; McCallum, R.W.; Tack, J.; Spence, S.C.; Gottesdiener, K.; Fiedorek, F.T. Efficacy and Safety of Relamorelin in Diabetics with Symptoms of Gastroparesis: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 1240–1250.e1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, M.E.; Otiker, T.; Johnson, L.V.; Robertson, D.C.; Dobbins, R.L.; Parkman, H.P.; Hellström, P.M.; Tack, J.F.; Kuo, B.; Hobson, A. 70 A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase II Study (MOT114479) to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy and Dose Response of 28 Days of Orally Administered Camicinal, a Motilin Receptor Agonist, in Diabetics with Gastroparesis. Gastroenterology 2014, 5, S-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellström, P.M.; Tack, J.; Johnson, L.V.; Hacquoil, K.; Barton, M.E.; Richards, D.B.; Alpers, D.H.; Sanger, G.J.; Dukes, G.E. The pharmacodynamics, safety and pharmacokinetics of single doses of the motilin agonist, camicinal, in type 1 diabetes mellitus with slow gastric emptying. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 1768–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCallum, R.; Cynshi, O.; Team, I. Clinical trial: Effect of mitemcinal (a motilin agonist) on gastric emptying in patients with gastroparesis–A randomized, multicentre, placebo-controlled study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 26, 1121–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feinle, C.; Read, N.W. Ondansetron reduces nausea induced by gastroduodenal stimulation without changing gastric motility. Am. J. Physiol. 1996, 271, G591–G597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamanolis, G.; Tack, J. Nutrition and motility disorders. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2006, 20, 485–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharadwaj, S.; Meka, K.; Tandon, P.; Rathur, A.; Rivas, J.M.; Vallabh, H.; Jevenn, A.; Guirguis, J.; Sunesara, I.; Nischnick, A. Management of gastroparesis-associated malnutrition. J. Dig. Dis. 2016, 17, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, R.A. Role of dietitians in reducing malnutrition in hospital. CMAJ 2019, 191, E139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, M.; Rayner, C.K.; Marathe, C.S.; Wu, T.; Jones, K.L. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and the appropriate measurement of gastric emptying. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020, 22, 2504–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.A.; Meier, J.J. Management of endocrine disease: Are all GLP-1 agonists equal in the treatment of type 2 diabetes? Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 181, R211–R234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deane, A.M.; Nguyen, N.Q.; Stevens, J.E.; Fraser, R.J.; Holloway, R.H.; Besanko, L.K.; Burgstad, C.; Jones, K.L.; Chapman, M.J.; Rayner, C.K.; et al. Endogenous glucagon-like peptide-1 slows gastric emptying in healthy subjects, attenuating postprandial glycemia. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trujillo, J.M.; Goldman, J. Lixisenatide, a once-daily prandial glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist for the treatment of adults with type 2 diabetes. Pharmacother. J. Human Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2017, 37, 927–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnebjerg, H.; Park, S.; Kothare, P.A.; Trautmann, M.E.; Mace, K.; Fineman, M.; Wilding, I.; Nauck, M.; Horowitz, M. Effect of exenatide on gastric emptying and relationship to postprandial glycemia in type 2 diabetes. Regul. Pept. 2008, 151, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, M.; Pfeiffer, C.; Steinsträßer, A.; Becker, R.H.; Rütten, H.; Ruus, P.; Horowitz, M. Effects of lixisenatide once daily on gastric emptying in type 2 diabetes—Relationship to postprandial glycemia. Regul. Pept. 2013, 185, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.L.; Huynh, L.Q.; Hatzinikolas, S.; Rigda, R.S.; Phillips, L.K.; Pham, H.T.; Marathe, C.S.; Wu, T.; Malbert, C.H.; Stevens, J.E. Exenatide once weekly slows gastric emptying of solids and liquids in healthy, overweight people at steady-state concentrations. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020, 22, 788–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umapathysivam, M.M.; Lee, M.Y.; Jones, K.L.; Annink, C.E.; Cousins, C.E.; Trahair, L.G.; Rayner, C.K.; Chapman, M.J.; Nauck, M.A.; Horowitz, M.; et al. Comparative effects of prolonged and intermittent stimulation of the glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor on gastric emptying and glycemia. Diabetes 2014, 63, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelsing, J.; Vrang, N.; Hansen, G.; Raun, K.; Tang-Christensen, M.; Bjerre Knudsen, L. Liraglutide: Short-lived effect on gastric emptying—Long lasting effects on body weight. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2012, 14, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halawi, H.; Khemani, D.; Eckert, D.; O’Neill, J.; Kadouh, H.; Grothe, K.; Clark, M.M.; Burton, D.D.; Vella, A.; Acosta, A.; et al. Effects of liraglutide on weight, satiation, and gastric functions in obesity: A randomised, placebo-controlled pilot trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2, 890–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri, M.; Carlson, P.; Dilmaghani, S. Prevalence and variations in gastric emptying delay in response to GLP-1 receptor agonist liraglutide. Obes. (Silver Spring) 2024, 32, 232–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nauck, M.A.; Niedereichholz, U.; Ettler, R.; Holst, J.J.; Orskov, C.; Ritzel, R.; Schmiegel, W.H. Glucagon-like peptide 1 inhibition of gastric emptying outweighs its insulinotropic effects in healthy humans. Am. J. Physiol. 1997, 273, E981–E988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deane, A.M.; Chapman, M.J.; Fraser, R.J.; Summers, M.J.; Zaknic, A.V.; Storey, J.P.; Jones, K.L.; Rayner, C.K.; Horowitz, M. Effects of exogenous glucagon-like peptide-1 on gastric emptying and glucose absorption in the critically ill: Relationship to glycemia. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 38, 1261–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawatani, M.; Yamada, Y.; Kawatani, M. Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) action in the mouse area postrema neurons. Peptides 2018, 107, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellström, P.M.; Näslund, E.; Edholm, T.; Schmidt, P.T.; Kristensen, J.; Theodorsson, E.; Holst, J.J.; Efendic, S. GLP-1 suppresses gastrointestinal motility and inhibits the migrating motor complex in healthy subjects and patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2008, 20, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamori, H.; Iida, K.; Hashitani, H. Mechanisms underlying the prokinetic effects of endogenous glucagon-like peptide-1 in the rat proximal colon. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2021, 321, G617–G627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hosseini-Marnani, E.; Marathe, J.A.; Triplett, J.D.; Kamruzzaman, M.; Yin, K.; Jones, K.L.; Horowitz, M.; Marathe, C.S. Gastric Autonomic Neuropathy in Diabetes. Endocrines 2025, 6, 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/endocrines6030040
Hosseini-Marnani E, Marathe JA, Triplett JD, Kamruzzaman M, Yin K, Jones KL, Horowitz M, Marathe CS. Gastric Autonomic Neuropathy in Diabetes. Endocrines. 2025; 6(3):40. https://doi.org/10.3390/endocrines6030040
Chicago/Turabian StyleHosseini-Marnani, Elham, Jessica A. Marathe, James D. Triplett, Md Kamruzzaman, Kevin Yin, Karen L. Jones, Michael Horowitz, and Chinmay S. Marathe. 2025. "Gastric Autonomic Neuropathy in Diabetes" Endocrines 6, no. 3: 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/endocrines6030040
APA StyleHosseini-Marnani, E., Marathe, J. A., Triplett, J. D., Kamruzzaman, M., Yin, K., Jones, K. L., Horowitz, M., & Marathe, C. S. (2025). Gastric Autonomic Neuropathy in Diabetes. Endocrines, 6(3), 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/endocrines6030040





