Glomerular Hyperfiltration in Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Cross-Sectional Observational Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Participants
2.3. Study Parameters
2.4. Statistics
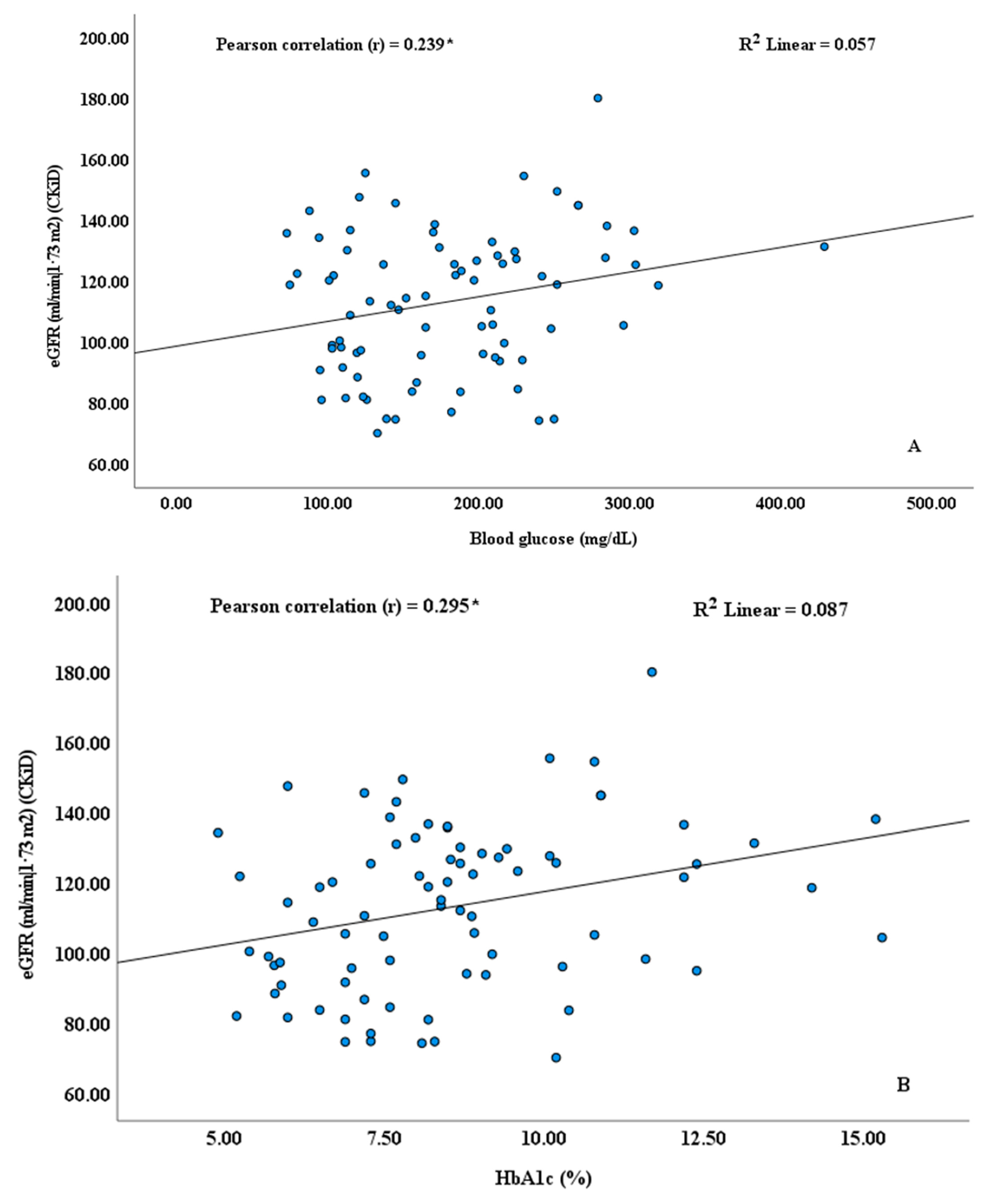
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alhazmi, A.S. Protective Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation Against Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Model. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2025, 25, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagundes Melo, R.; Laurindo, L.F.; Sloan, K.P.; Sloan, L.A.; Cressoni Araújo, A.; Bitelli, P.; Laís Menegucci Zutin, T.; Haber Mellen, R.; Junqueira Mellen, L.; Landgraf Guiguer, E.; et al. Investigating the Incidence of Dyslipidemia among Brazilian Children and Adolescents Diagnosed with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Cross-Sectional Study. Diseases 2024, 12, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, Z. Engineered Extracellular Vesicles as “Supply Vehicles” to Alleviate Type 1 Diabetes. Extracell. Vesicles Circ. Nucl. Acids 2024, 5, 718–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lin, C.; Jin, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Du, X.; Hutchinson, M.R.; Zhao, H.; Fang, L.; Wang, X. The Pharmacology and Therapeutic Role of Cannabidiol in Diabetes. Exploration 2023, 3, 20230047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Santos Haber, J.F.; Barbalho, S.M.; Sgarbi, J.A.; de Argollo Haber, R.S.; de Labio, R.W.; Laurindo, L.F.; Chagas, E.F.B.; Payão, S.L.M. The Relationship between Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus, TNF-α, and IL-10 Gene Expression. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, G.A.; Robinson, T.I.G.; Linklater, S.E.; Wang, F.; Colagiuri, S.; de Beaufort, C.; Donaghue, K.C.; International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas Type 1 Diabetes in Adults Special Interest Group; Magliano, D.J.; Maniam, J.; et al. Global Incidence, Prevalence, and Mortality of Type 1 Diabetes in 2021 with Projection to 2040: A Modelling Study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 741–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, S.; Jabakhanji, S.B.; Mehta, R.; McCaffrey, J.; Mairghani, M.; Bhatia, D.; James, O.; Kehlenbrink, S.; Boulle, P.; Mejia Mehta, K.; et al. The Status of Care for Youth with Type 1 Diabetes within and Coming from Humanitarian Crises Settings: A Narrative Review. Confl. Health 2025, 19, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menegucci, T.; Chagas, E.F.B.; de Oliveira Zanuso, B.; Quesada, K.; dos Santos Haber, J.F.; Menegucci Zutin, T.L.; Felipe Pimenta, L.; Cressoni Araújo, A.; Landgraf Guiguer, E.; Rucco, P.; et al. The Influence of Body Fat and Lean Mass on HbA1c and Lipid Profile in Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Diseases 2023, 11, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bille, N.; Christensen, D.L.; Byberg, S.; Gishoma, C.; Villadsen, S.F.; Calopietro, M. A Qualitative Exploration of the Early Adoption of an Electronic Medical Record System for Type 1 Diabetes Management in Rwanda. Digit. Health 2025, 11, 20552076241311057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.C.N.; Lim, L.-L.; Wareham, N.J.; Shaw, J.E.; Orchard, T.J.; Zhang, P.; Lau, E.S.H.; Eliasson, B.; Kong, A.P.S.; Ezzati, M.; et al. The Lancet Commission on Diabetes: Using Data to Transform Diabetes Care and Patient Lives. Lancet 2020, 396, 2019–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl-Pehe, A.; Baechle, C.; Lanzinger, S.; Urschitz, M.S.; Holl, R.W.; Rosenbauer, J. Type 1 Diabetes Incidence Curves Differ by Age for Girls and Boys between 1996 and 2022: Results from the North Rhine-Westphalia Diabetes Registry, Germany. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2025, 220, 111996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisinger, F.; Neumann, M.; Wörn, M.; Fritsche, A.; Heyne, N.; Peter, A.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; von Schwartzenberg, R.J.; Artunc, F. Comparison of GFR Estimation in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus Using the EKFC and CKD-EPI Equations. J. Nephrol. 2025, 38, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulsen, C.G.; Jesse, K.; Carstensen, B.; Frimodt-Møller, M.; Hansen, T.W.; Persson, F.; Vistisen, D.; Rossing, P. Prognosis for Type 1 Diabetes with Diabetic Nephropathy between 2000 and 2020—Changes in Kidney Function Decline Over Time and Development of Cardiovascular Disease, Kidney Failure, and Mortality. Kidney Int. Rep. 2024, 9, 3403–3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Ni, Q. Global, Regional and National Burdens of Chronic Kidney Disease Due to T1DM and T2DM among Adolescents and Young Adults Aged 10–35 Years from 1990–2021: A Trend Analysis Based on the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2025, 220, 111985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgharzadeh, A.; Patel, M.; Connock, M.; Damery, S.; Ghosh, I.; Jordan, M.; Freeman, K.; Brown, A.; Court, R.; Baldwin, S.; et al. Hybrid Closed-Loop Systems for Managing Blood Glucose Levels in Type 1 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Economic Modelling. Health Technol. Assess. 2024, 28, 1–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedulovs, A.; Janevica, J.; Kruzmane, L.; Sokolovska, J. Glucose Control and Variability Assessed by Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes and Diabetic Kidney Disease. Biomed. Rep. 2024, 22, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolignano, D.; Greco, M.; Presta, P.; Duni, A.; Zicarelli, M.; Mercuri, S.; Pappas, E.; Lakkas, L.; Musolino, M.; Naka, K.K.; et al. The Mitochondrial-Derived Peptide MOTS-c May Refine Mortality and Cardiovascular Risk Prediction in Chronic Hemodialysis Patients: A Multicenter Cohort Study. Blood Purif. 2024, 53, 824–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girisgen, İ.; Altıncık, S.A.; Avcı, E.; Öcal, M.; Becerir, T.; Malaş Öztekin, G.; Özhan, B.; Yuksel, S. Could MOTS-C Levels in Children with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Be an İndicator for Early Diabetic Kidney Disease? J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2024, 17, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunke, M.; Knöfler, H.; Dahlke, E.; Zanon Rodriguez, L.; Böttner, M.; Larionov, A.; Saudenova, M.; Ohrenschall, G.M.; Westermann, M.; Porubsky, S.; et al. Targeted Deletion of Von-Hippel-Lindau in the Proximal Tubule Conditions the Kidney against Early Diabetic Kidney Disease. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, L.N.; Wang, W.; Loomba, L.; Afkarian, M.; Butani, L. Diabetic Kidney Disease in Children and Adolescents: An Update. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2022, 37, 2583–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigers, T.; Vinovskis, C.; Li, L.-P.; Prasad, P.; Heerspink, H.; D’Alessandro, A.; Reisz, J.A.; Piani, F.; Cherney, D.Z.; van Raalte, D.H.; et al. Plasma Levels of Carboxylic Acids Are Markers of Early Kidney Dysfunction in Young People with Type 1 Diabetes. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2023, 38, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogeveen, E.K. The Epidemiology of Diabetic Kidney Disease. Kidney Dial. 2022, 2, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattman, A.; Eintracht, S.; Mock, T.; Schick, G.; Seccombe, D.W.; Hurley, R.M.; White, C.T. Estimating Pediatric Glomerular Filtration Rates in the Era of Chronic Kidney Disease Staging. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Grams, M.E.; Inker, L.A. Uses of GFR and Albuminuria Level in Acute and Chronic Kidney Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 2120–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaebe, K.; White, C.A.; Mahmud, F.H.; Scholey, J.W.; Elia, Y.T.; Sochett, E.B.; Cherney, D.Z. Evaluation of Novel Glomerular Filtration Rate Estimation Equations in Adolescents and Young Adults with Type 1 Diabetes. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2022, 36, 108081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pottel, H.; Björk, J.; Delanaye, P.; Nyman, U. Evaluation of the Creatinine-Based Chronic Kidney Disease in Children (under 25 Years) Equation in Healthy Children and Adolescents. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2022, 37, 2213–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnapp, A.; Egger, Y.; Bignall, O.N.R.; Issler, N.; Volovelsky, O. Estimated Pediatric Glomerular Filtration Rate Presentation Improves the Detection Rate of Kidney Impairment in Children. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2023, 38, 3091–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favel, K.; Irvine, M.; Ronsley, R.; Panagiotopoulos, C.; Mammen, C. Glomerular Filtration Rate Abnormalities in Children With Type 1 Diabetes. Can. J. Diabetes 2022, 46, 457–463.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Departamento Científico de Nefrologia. Doença Renal Crônica Em Pediatria: Diagnóstico e Prevenção; Sociedade Brasileira de Pediatria–SBP: Rio de Janeiro, Brasil, 2020; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Sá, J.R.; Canani, L.H.; Rangel, E.B.; Bauer, A.C.; Escott, G.M.; Zelmanovitz, T.; Silveiro, S.P.; Bertoluci, M. Doença Renal Do Diabetes. In Diretriz Oficial da Sociedade Brasileira de Diabetes; Conectando Pessoas: Brasília, Brasil, 2022; pp. 1–54. [Google Scholar]
- Moça, A.B.F.; Girotto, R.; Perozo, A.F.D.F.; Marques, T.; Queiroz, L.L.d.; Pagung, L.S. Fatores Preditores Do Bom e Mau Controle Glicêmico Dos Pacientes Com Diabetes Mellitus Tipo 2 Acompanhados Em Um Serviço Especializado No Rio de Janeiro. Rev. Eletrônica Acervo Saúde 2024, 24, e14621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, K.; Tan, L.; Li, S.; Li, Z.; Yu, F.; Liang, H.; Gao, S.; Ren, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z. Comparison of Different BMI Cut-Offs to Screen for Child and Adolescent Obesity in Urban China. Public. Health Nutr. 2020, 23, 2485–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Shen, W.; Gallagher, D.; Jones, A.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Heshka, S.; Heymsfield, S.B. Total-Body Skeletal Muscle Mass: Estimation by Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry in Children and Adolescents. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 84, 1014–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European Consensus on Definition and Diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchard, C.; Tremblay, A.; Leblanc, C.; Lortie, G.; Savard, R.; Thériault, G. A Method to Assess Energy Expenditure in Children and Adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1983, 37, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, C. Basal Metabolic Rate Studies in Humans: Measurement and Development of New Equations. Public. Health Nutr. 2005, 8, 1133–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO/WHO/UNU. Human Energy Requirements. Scientific Background Papers from the Joint FAO/WHO/UNU Expert Consultation. October 17–24, 2001. Rome, Italy. Public. Health Nutr. 2005, 8, 929–1228. [Google Scholar]
- ElSayed, N.A.; Aleppo, G.; Aroda, V.R.; Bannuru, R.R.; Brown, F.M.; Bruemmer, D.; Collins, B.S.; Hilliard, M.E.; Isaacs, D.; Johnson, E.L.; et al. 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2023. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, S19–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pititto, B.d.A.; Dias, M.L.; de Moura, F.F.; Lamounier, R.; Vencio, S.; Calliari, L.E.; Bertoluci, M. Metas No Tratamento Do Diabetes. In Diretriz Oficial da Sociedade Brasileira de Diabetes; Conectando Pessoas: Brasília, Brasil, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Pottel, H.; Adebayo, O.C.; Nkoy, A.B.; Delanaye, P. Glomerular Hyperfiltration: Part 1—Defining the Threshold—Is the Sky the Limit? Pediatr. Nephrol. 2023, 38, 2523–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, R.; Dorman, J.S.; Bosnyak, Z.; Tajima, N.; Becker, D.J.; Orchard, T.J. Incidence of ESRD and Survival after Renal Replacement Therapy in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes: A Report from the Allegheny County Registry. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2003, 42, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bebu, I.; Braffett, B.H.; Schade, D.; Sivitz, W.; Malone, J.I.; Pop-Busui, R.; Lorenzi, G.M.; Lee, P.; Trapani, V.R.; Wallia, A.; et al. An Observational Study of the Equivalence of Age and Duration of Diabetes to Glycemic Control Relative to the Risk of Complications in the Combined Cohorts of the DCCT/EDIC Study. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 2478–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElSayed, N.A.; Aleppo, G.; Bannuru, R.R.; Bruemmer, D.; Collins, B.S.; Ekhlaspour, L.; Hilliard, M.E.; Johnson, E.L.; Khunti, K.; Lingvay, I.; et al. Chronic Kidney Disease and Risk Management: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2024. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, S219–S230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sá, J.R.; Canani, L.H.; Rangel, É.B.; Bauer, A.C.; Escott, G.M.; Zelmanovitz, T.; Silveiro, S.P.; Betônico, C.d.C.R.; Lauria, M.W.; Lamounier, R.N.; et al. Avaliação e Tratamento Da Doença Renal Do Diabetes. In Diretriz da Sociedade Brasileira de Diabetes; Conectando Pessoas: Brasília, Brasil, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, R.; Turner, C.; Aken, S.V.; Bahu, T.K.; Watts, A.; Lindsell, D.R.M.; Dalton, R.N.; Dunger, D.B. The Relationship between Microalbuminuria and Glomerular Filtration Rate in Young Type 1 Diabetic Subjects: The Oxford Regional Prospective Study. Kidney Int. 2005, 68, 1740–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, H.S.; McGill, J.B.; Hirsch, I.B.; Wu, C.; Galecki, A.; de Boer, I.H.; Mauer, M.; Doria, A. Poor Glycemic Control Is Associated With More Rapid Kidney Function Decline After the Onset of Diabetic Kidney Disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 109, 2124–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovshin, J.A.; Škrtic, M.; Bjornstad, P.; Moineddin, R.; Daneman, D.; Dunger, D.; Reich, H.N.; Mahmud, F.; Scholey, J.; I Cherney, D.Z.; et al. Hyperfiltration, Urinary Albumin Excretion, and Ambulatory Blood Pressure in Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2018, 314, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westreich, K.D.; Isom, S.; Divers, J.; D’Agostino, R.; Lawrence, J.M.; Kanakatti Shankar, R.; Dolan, L.M.; Imperatore, G.; Dabelea, D.; Mayer-Davis, E.J.; et al. Trajectories in Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate in Youth-Onset Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes: The SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2021, 35, 107768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, Y.-T.; Yu, H.-Y.; Tsay, P.-K.; Chen, C.-W.; Chang, C.-W.; Hsu, C.-L.; Lo, F.-S.; Moons, P. Effectiveness of the User-Centered “Healthcare CEO” App for Patients With Type 1 Diabetes Transitioning From Adolescence to Early Adulthood: Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial. JMIR Res. Protoc. 2025, 14, e59871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mynarek, I.M.; Krogvold, L.; Mørk, F.B.; Lawaetz, T.W.H.; Roald, T.; Fagerland, M.W.; Lindblom, N.; Westman, J.; Barker, P.; Hyöty, H.; et al. Three-Year Follow-up After Antiviral Treatment in New-Onset Type 1 Diabetes: Results From the Diabetes Virus Detection and Intervention Trial. Diabetes Care 2025, 48, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alicic, R.Z.; Rooney, M.T.; Tuttle, K.R. Diabetic Kidney Disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 12, 2032–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.P.; Chang, C.H.; Tsai, M.K.; Lee, J.H.; Lu, P.J.; Tsai, S.P.; Wen, C.; Chen, C.H.; Kao, C.W.; Tsao, C.K.; et al. Diabetes with Early Kidney Involvement May Shorten Life Expectancy by 16 Years. Kidney Int. 2017, 92, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alguwaihes, A.M.; Alotaibi, N.; Alotaibi, M.; Masry, N.; Safarini, S. The Use of MiniMed780G System Is Associated With Stable Glycemic Control in People With Type 1 Diabetes Before, During, and After Ramadan: An Observational Study. J. Diabetes Res. 2025, 2025, 4144787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjahjono, H.A.; Barlianto, W.; Handayani, D.; Kalim, H. Correlation between Transforming Growth Factor-Β1 (TGF-Β1) with Premature Atherosclerosis in Type 1 Diabetes. ARYA Atheroscler. 2024, 20, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, F.; Rossing, P. Diagnosis of Diabetic Kidney Disease: State of the Art and Future Perspective. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2018, 8, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, R.; Lopez-Trevino, S.; Kankanamalage, H.R.; Jha, J.C. Diabetes and Renal Complications: An Overview on Pathophysiology, Biomarkers and Therapeutic Interventions. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Variable | Categories | eGFR Quartile (mL/min/1.73 m2) | Total | p-Value a | p-Value b | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| >130 (n = 20) | 115 to 130 (n = 21) | <115 (n = 39) | |||||||||
| N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | ||||
| Sex | Male | 11 | 55.0% | 10 | 47.6% | 26 | 66.7% | 47 | 58.8 | 0.118 | 0.284 |
| Female | 9 | 45.0% | 11 | 52.4% | 13 | 33.3% | 33 | 41.3 | |||
| Length of disease | <5 years | 15 | 75.0% | 11 | 52.4% | 20 | 51.3% | 46 | 57.5 | 0.180 | 0.107 |
| ≥5 years | 5 | 25.0% | 10 | 47.6% | 19 | 48.7% | 34 | 42.5 | |||
| Insulin administration method | CIIS | 4 | 20.0% | 5 | 23.8% | 13 | 33.3% | 22 | 27.5 | <0.001 * | 0.255 |
| MID | 16 | 80.0% | 16 | 76.2% | 26 | 66.7% | 58 | 72.5 | |||
| Insulin administration schedule (Insulin/kg) | Below expected for the weight | 5 | 25.0% | 1 | 4.8% | 8 | 20.5% | 14 | 17.5 | <0.001 * | 0.374 |
| Adequate for the weight | 14 | 70.0% | 19 | 90.5% | 25 | 64.1% | 58 | 72.5 | |||
| Above expected for the weight | 1 | 5.0% | 1 | 4.8% | 6 | 15.4% | 8 | 10.0 | |||
| Associated comorbidities | Yes | 2 | 10.0% | 1 | 4.8% | 1 | 2.6% | 4 | 5.0 | <0.001 * | 0.228 |
| No | 18 | 90.0% | 20 | 95.2% | 38 | 97.4% | 76 | 95.0 | |||
| Practice physical exercise | Yes | 16 | 80.0% | 14 | 66.7% | 27 | 69.2% | 57 | 71.3 | <0.001 * | 0.450 |
| No | 4 | 20.0% | 7 | 33.3% | 12 | 30.8% | 23 | 28.8 | |||
| Level of physical activity | Mild | 12 | 60.0% | 12 | 57.1% | 23 | 59.0% | 47 | 58.8 | 0.118 | 0.965 |
| Moderate | 8 | 40.0% | 9 | 42.9% | 16 | 41.0% | 33 | 41.3 | |||
| HbA1c | <7% | 2 | 10.0% | 4 | 19.0% | 14 | 35.9% | 20 | 25.0 | <0.001 * | 0.039 ** |
| 7 a 8% | 6 | 30.0% | 1 | 4.8% | 8 | 20.5% | 15 | 18.8 | |||
| >8% | 12 | 60.0% | 16 | 76.2% | 17 | 43.6% | 45 | 56.3 | |||
| Variable | eGFR Quartile (mL/min/1.73 m2) | p-Value | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| >130 (n = 20) | 115 to 130 (n = 21) | <115 (n = 39) | ||||||||
| Mean | CI 95% | Mean | CI 95% | Mean | CI 95% | |||||
| LB | UB | LB | UB | LB | UB | |||||
| Age (years) | 13.1 | 11.8 | 14.4 | 12.7 | 11.0 | 14.4 | 12.2 | 11.0 | 13.5 | 0.674 |
| Length of disease (years) | 3.5 | 2.5 | 4.5 | 5.1 | 3.4 | 6.9 | 4.2 | 3.3 | 5.1 | 0.207 |
| Physical activity score | 1.3 | 1.2 | 1.4 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.3 | 0.822 |
| Total insulin per kg (unit/day/kg) | 0.91 | 0.79 | 1.04 | 0.94 | 0.86 | 1.03 | 0.90 | 0.82 | 0.99 | 0.814 |
| HbA1c (%) | 9.3 | 8.1 | 10.5 | 8.9 | 8.0 | 9.9 | 8.0 | 7.3 | 8.7 | 0.086 |
| Blood glucose (mg/dL) | 195 | 152 | 238 | 193 | 161 | 224 | 163 | 146 | 180 | 0.136 |
| % fat | 23.2 a,b | 20.0 | 26.4 | 24.2 a | 20.3 | 28.1 | 19.4 b | 17.1 | 21.6 | 0.033 * |
| Lean mass (%) | 76.8 a,b | 73.6 | 80.0 | 75.8 a | 71.9 | 79.7 | 80.9 b | 78.8 | 83.0 | 0.017 * |
| Skeletal muscle mass (kg) | 7.36 | 6.57 | 8.16 | 7.16 | 6.26 | 8.07 | 7.09 | 6.26 | 7.92 | 0.905 |
| Skeletal muscle mass index (kg/m2) | 2.84 | 2.67 | 3.00 | 3.02 | 2.83 | 3.20 | 3.01 | 2.85 | 3.18 | 0.310 |
| Variable | B | p-Value | Model | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent | Independent | R | R2 | p-Value | ||
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | (Constant) | 181.480 | <0.001 * | 0.477 | 0.228 | <0.001 ** |
| HbA1c (%) | 2.293 | 0.035 * | ||||
| Lean mass (%) | −0.860 | 0.011 * | ||||
| Length of disease (group) | −14.278 | 0.004 * | ||||
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | (Constant) | 149.360 | 0.000 | 0.371 | 0.138 | 0.003 ** |
| HbA1c (%) | 2.473 | 0.030 | ||||
| Lean mass (%) | −0.730 | 0.037 | ||||
| Variable | B | p-Value a | Model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent | Independent | R2 | p-Value b | ||
| eGFR ≥ 135 (mL/min/1.73 m2) | HbA1c (%) | 0.209 | 0.131 | 0.200 | 0.014 ** |
| Lean mass (%) | −0.094 | 0.065 | |||
| Length of disease (years) | −0.333 | 0.034 * | |||
| Constant | 5.185 | 0.247 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Argollo Haber, L.S.; Laurindo, L.F.; de Melo, R.F.; Carneiro, D.P.; Biteli, P.; Chagas, H.V.; Mellem, L.J.; Haber, J.F.d.S.; Sloan, L.A.; Sloan, K.P.; et al. Glomerular Hyperfiltration in Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Cross-Sectional Observational Study. Endocrines 2025, 6, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/endocrines6030035
de Argollo Haber LS, Laurindo LF, de Melo RF, Carneiro DP, Biteli P, Chagas HV, Mellem LJ, Haber JFdS, Sloan LA, Sloan KP, et al. Glomerular Hyperfiltration in Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Cross-Sectional Observational Study. Endocrines. 2025; 6(3):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/endocrines6030035
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Argollo Haber, Luiza Santos, Lucas Fornari Laurindo, Rafael Fagundes de Melo, Dennis Penna Carneiro, Piero Biteli, Henrique Villa Chagas, Luciano Junqueira Mellem, Jesselina Francisco dos Santos Haber, Lance Alan Sloan, Kátia Portero Sloan, and et al. 2025. "Glomerular Hyperfiltration in Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Cross-Sectional Observational Study" Endocrines 6, no. 3: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/endocrines6030035
APA Stylede Argollo Haber, L. S., Laurindo, L. F., de Melo, R. F., Carneiro, D. P., Biteli, P., Chagas, H. V., Mellem, L. J., Haber, J. F. d. S., Sloan, L. A., Sloan, K. P., Maria Barbalho, S., & Chagas, E. F. B. (2025). Glomerular Hyperfiltration in Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Cross-Sectional Observational Study. Endocrines, 6(3), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/endocrines6030035









