Abstract
Endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) are synthetic or natural compounds that interfere with the endocrine system, inducing harmful effects on organisms depending on the dose and period of exposure. Numerous studies have identified concerning amounts of EDCs in environmental and human samples. The thyroid gland is essential for thyroid hormone production and controls several body functions. Several EDCs have been classified as thyroid disruptors, impairing thyroid hormone production, synthesis, metabolism, transport, and/or actions. Notably, thyroid disorders are the second most prevalent endocrine disease worldwide, with incidence increasing significantly in recent years. Some studies have correlated this rise in thyroid dysfunctions and cancers with increased exposure to EDCs. Although many EDCs are linked to thyroid dysfunction, this review focuses on the deleterious effects of plasticizers, organochlorine pesticides, and per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances on thyroid function. These contaminants are commonly found in food, water, and everyday products. Although the impact of human exposure to these EDCs is controversial, numerous epidemiological, in vivo, and in vitro studies have indicated their harmful effects on thyroid function. Given the critical role of thyroid function and hormone production in growth, metabolism, and development, this review summarizes the consequences of exposure to thyroid disruptors for human health.
1. Introduction
Endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs)—also known as endocrine disruptors, endocrine toxins, or xenohormones—are natural or synthetic substances that interfere with various aspects of endocrine function, causing adverse effects on growth, development, reproduction, and metabolism [1]. Human exposure to these chemicals has been related to systemic repercussions of varying severity, depending on the duration and the developmental stage at which the individual is exposed [2,3]. Indeed, in recent years, there has been a significant increase in epidemiological data and animal studies demonstrating the harmful health effects of EDC exposure. In this context, epidemiological studies indicate an increase in the incidence and prevalence of diseases associated with EDC exposure, such as breast, thyroid, prostate, and testicular cancers, diabetes, obesity, and decreased fertility over the past 50 years [4].
The most well-known mechanism of action of these compounds involves their binding to hormone receptors, such as estrogen, androgen, progesterone, and thyroid hormone (TH) receptors. Additionally, the actions of EDCs involve their binding to other nuclear receptors, membrane receptors, neurotransmitter receptors (such as serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine), and orphan receptors. Furthermore, EDCs trigger the activation/inactivation of enzymatic pathways involved in hormone metabolism and synthesis [5].
Unlike adults, newborns and children are more susceptible to the harmful actions of EDCs, primarily because the metabolizing pathways of these substances are immature in these individuals [6]. Moreover, embryos, fetuses, and newborns are adversely impacted by maternal exposure to these contaminants, which are transferred through the placenta and maternal milk [7]. Consequently, these individuals become more vulnerable to hormonal, immunological, and neurological alterations during critical stages of their development [8]. In agreement, studies have shown that EDC exposure during intrauterine and neonatal lives is related to several diseases during adulthood [9,10,11]. In this context, it is noteworthy that a growing number of studies emphasize the importance of the intrauterine period for the programming of genes that influence an organism’s susceptibility to diseases in adulthood [12,13]. Therefore, several studies have highlighted the crucial role of epigenetic mechanisms in regulating gene expression during these critical developmental periods, when the organism is most vulnerable to environmental and nutritional stressors [14,15,16]. These regulatory mechanisms of gene expression include alterations in DNA methylation/demethylation, post-translational modifications of histones, and differential expression of noncoding RNAs [17,18,19,20]. Interestingly, studies have indicated that maternal exposure to EDCs during pregnancy triggers epigenetic modifications in the placenta and the fetus, altering gene expression and compromising fetal development [21,22,23]. These alterations can persist throughout an individual’s life and may even affect gene expression and development in subsequent generations as multigenerational and transgenerational effects [24,25].
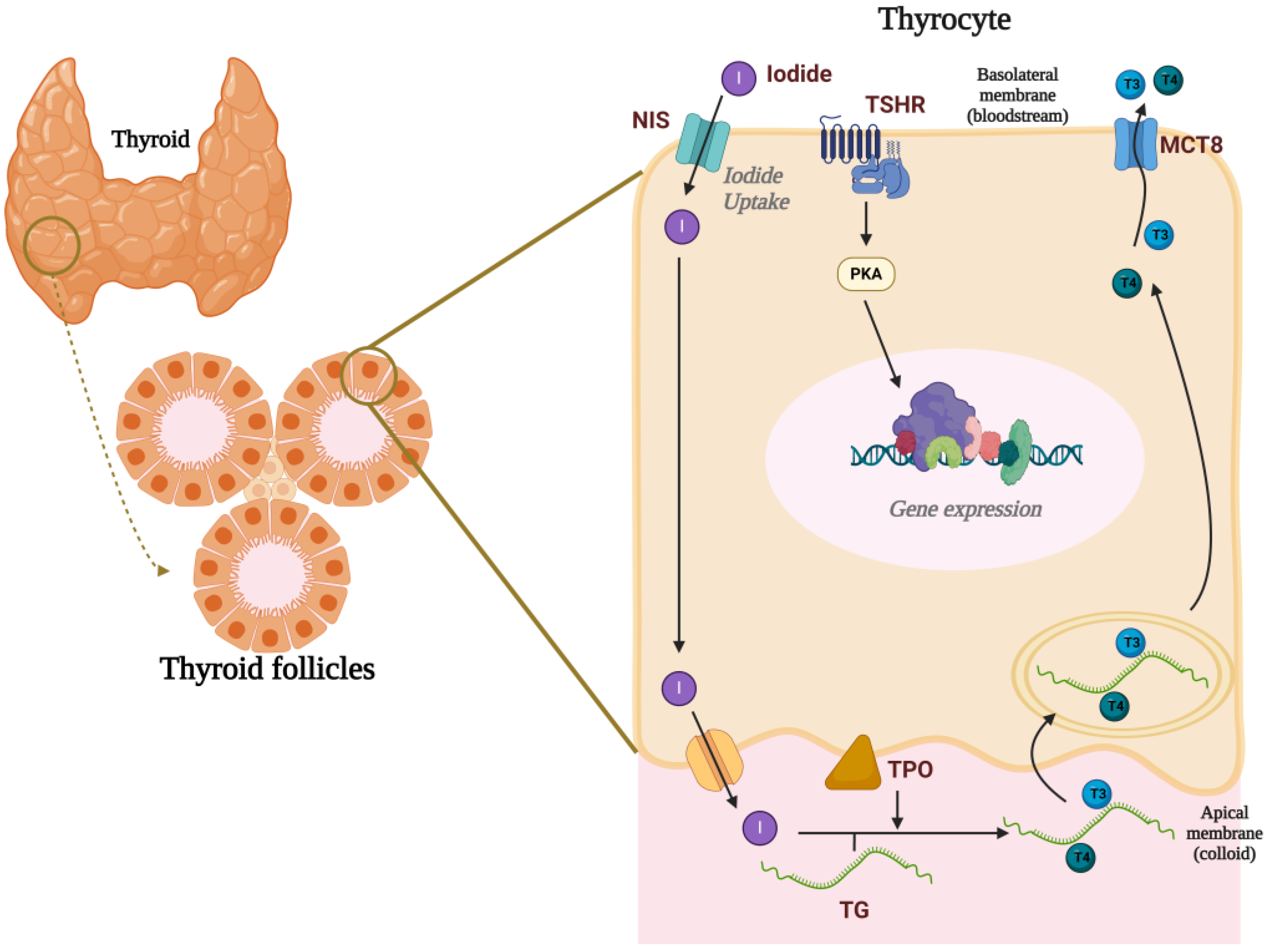
The thyroid gland is histologically organized into thyroid follicles, which are formed by a layer of cuboidal epithelial cells, the thyrocytes, that surround a luminal region filled with colloid, primarily composed of thyroglobulin (TG). TH synthesis depends on the expression and activity of several proteins [26]. The sodium–iodide symporter (NIS), located on the basolateral membrane of thyrocytes, mediates the uptake of iodide from the bloodstream, transporting it into the cell alongside two sodium ions [27]. Iodide is then transported to the luminal region via the activity of channels present in the apical membrane, such as pendrin and anoctamin-1 [28]. In the follicular lumen, iodide is oxidized to iodine by the activity of thyroid peroxidase (TPO) and incorporated into tyrosine residues of the TG molecule, forming diiodotyrosine and monoiodotyrosine. TPO is also responsible for coupling iodotyrosine to form iodothyronines, which are the actual THs: diiodothyronine (T2), triiodothyronine (T3), thyroxine (T4), and reverse T3 [29]. Upon secretion stimulation, colloid is endocytosed by the microvilli of the apical portion and processed in intracellular phagolysosomes. The T3 and T4 released from TG molecules are then secreted into circulation through the monocarboxylate transporter 8 (MCT8) [30] (Figure 1).
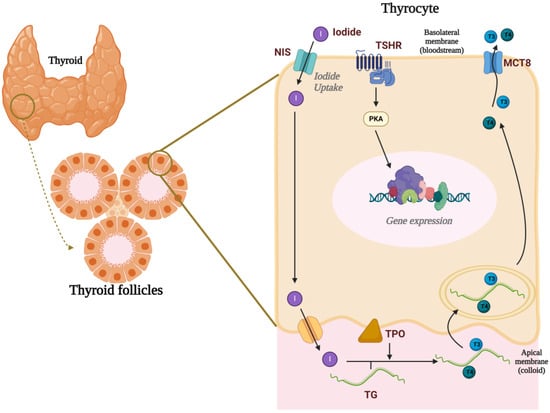
Figure 1.
Thyroid gland and thyroid hormone synthesis. The thyroid gland is organized into thyroid follicles, which consist of a single layer of cuboidal epithelial cells known as thyrocytes surrounding a lumen filled with colloid. The uptake of iodide, mediated by the sodium–iodide symporter (NIS), is the first rate-limiting step in thyroid hormone (TH) synthesis. Iodide is then transported into the lumen via pendrin and anoctamin-1, where thyroid peroxidase (TPO) oxidizes iodide to iodine. TPO also catalyzes the incorporation of iodine into tyrosine residues on thyroglobulin and couples iodotyrosines to form the thyroid hormones T3 and T4. Upon stimulation by TSH, T3 and T4 are secreted into the bloodstream via the monocarboxylate transporter 8 (MCT8). Created with Biorender.com.
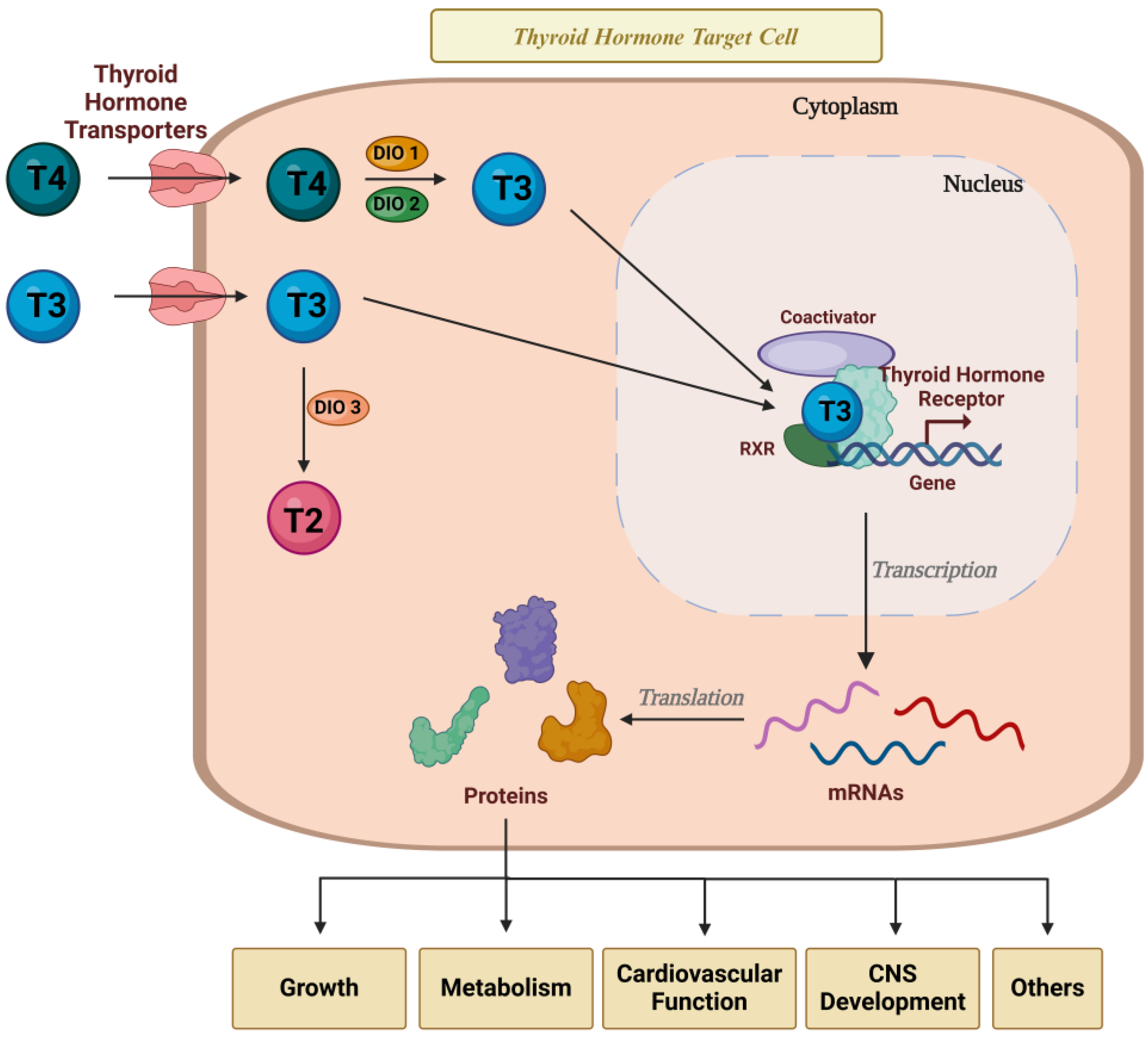
THs play a fundamental role in growth, metabolism, and fetal development and maturation, particularly in the central nervous system (CNS) [31]. TH actions are complex and rely on the expression of TH receptors, transporters, and deiodinases, which either activate or inactivate these hormones within target cells [32] (Figure 2).
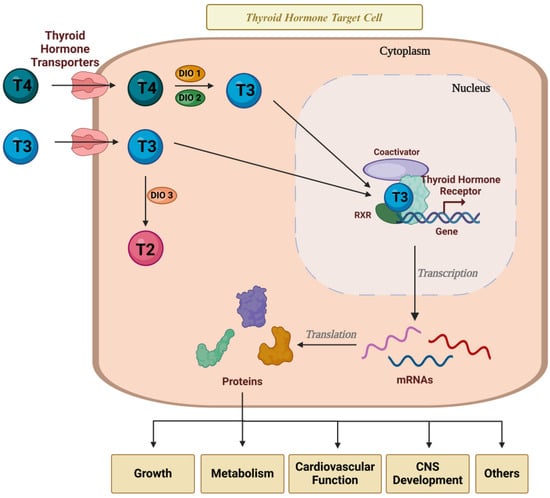
Figure 2.
Thyroid hormone action in target cells. THs are essential for controlling the metabolism, growth, and development of several tissues in the body. TH action depends on the expression and activity of TH transporters, TH receptors, and deiodinases in the target cells. Created with Biorender.com.
It is worth noting that thyroid function is finely regulated by the hypothalamic–pituitary–thyroid (HPT) axis. Parvicellular neurons of the hypothalamus secrete the thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) in the median eminence region, which reaches the anterior pituitary through the hypophyseal portal system. In thyrotropes, the TRH binds to membrane receptors and stimulates the synthesis and secretion of the thyroid-stimulating hormone or thyrotropin (TSH). Once released into circulation, the TSH reaches the thyroid, where, by binding to its receptor, TSHR, it stimulates all steps involved in the synthesis and secretion of THs. THs, in turn, feedback to the system, inhibiting the synthesis and secretion of the TRH in the hypothalamus and the TSH in the pituitary, in a mechanism known as negative feedback [33].
Interestingly, until the 12th–16th week of gestation, the fetus relies exclusively on THs produced by the mother, and even mild alterations in maternal TH levels during this period result in adverse consequences for fetal development [34]. The transfer of maternal THs to the fetus occurs through the placenta, due to the expression of specific thyroid transporters and deiodinases in the chorionic villi [35]. In addition to their direct role in fetal development, THs have important effects on the placenta’s metabolism, differentiation, and development [36,37]. Therefore, TH transport across the placenta is a critical step for the adequate development and function of fetal and placental tissues. Accordingly, previous studies have shown an increased incidence of clinical complications during pregnancy associated with poor placentation in patients with untreated thyroid disorders [38,39].
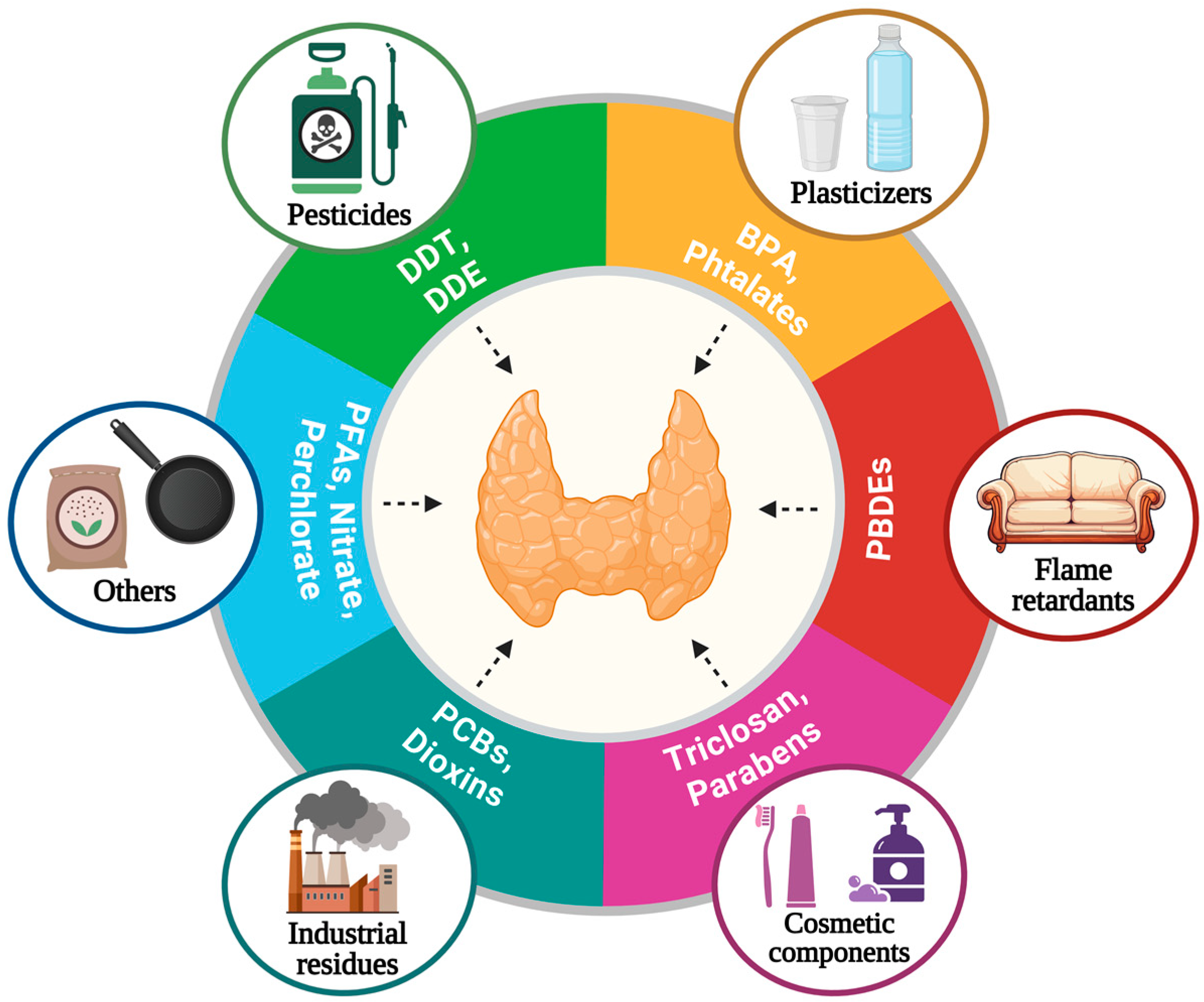
More than 100 natural and synthetic compounds have been classified as thyroid disruptors [40,41] (Figure 3).
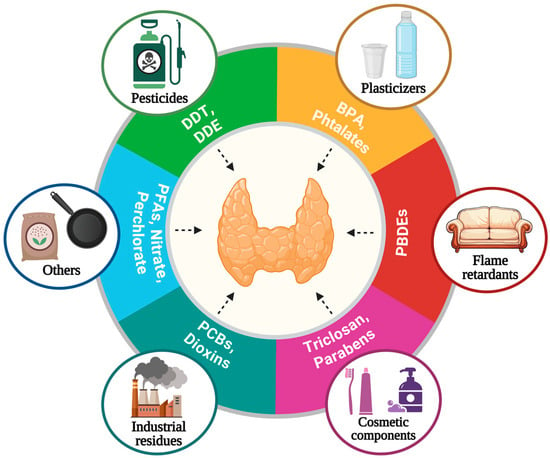
Figure 3.
Thyroid disruptors. EDCs are found in food, water, and everyday products and several studies indicated that some of them interfere with the synthesis, secretion, transport, and action of thyroid hormones. BPA: bisphenol A., PBDEs: polybrominated diphenyl ethers, PCBs: polychlorinated biphenyls, PFASs: per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances, DDT: dichloro-diphenyl-trichloroethane, DDE: dichlorodiphenyldichloroethylene. Created with Biorender.com.
Importantly, a study conducted by the European Union indicated that the costs related to impaired neural development and IQ loss attributed to two thyroid disruptors (flame retardants and organophosphate pesticides) would exceed EUR 150 billion per year [42].
In this context, several studies have described the interfering effects of several EDCs such as phthalates, bisphenol A, organochlorine pesticides, and per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances on thyroid function. This review will focus on those EDCs.
1.1. Phthalates
Plasticizers are essential compounds in the production of plastic products, enhancing flexibility, durability, and overall quality. Consequently, the demand for plasticizers continues to rise, with the plastic industry using approximately 8.23 million tons in 2020 and projected to reach up to 12.9 million tons by 2030 [43]. Due to their highly stable properties, phthalates are widely used to increase the flexibility of plastics in various commercial products such as toys, construction materials, personal care products, cosmetics, food preservation films, detergents, and medical devices [44,45].
Phthalates are a group of chemical compounds derived from phthalic acid, produced as diesters, and rapidly metabolized to monoesters upon entering the body [46]. The most used plasticizer is di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP). Human exposure to phthalates mainly occurs via ingestion, inhalation, and dermal routes. Numerous studies worldwide have detected DEHP metabolites in urine, blood, hair, amniotic fluid, and breast milk, confirming widespread human contamination of phthalates and their metabolites [47,48,49,50,51].
Phthalates Exposure and Thyroid Dysfunction
Several human studies have demonstrated associations between DEHP exposure and alterations in T3, T4, and TSH concentrations in pregnant women, newborns, and children [52,53,54]. Furthermore, in the general population, urinary concentrations of DEHP metabolites have shown a negative correlation with T4 and T3 levels [55,56,57,58].
In vivo and in vitro studies have explored the disruptive mechanisms induced by phthalates in the thyroid gland.
Indeed, chronically phthalate-exposed animals presented a significant reduction in T4 levels, and alterations in thyroid organelles morphology [59,60]. In agreement, di-n-butyl phthalate (DBP) administration caused a dose-dependent decrease in serum T3 and T4 concentrations at all studied doses. Nonetheless, DBP-treated animals have not presented alterations in TSH serum levels and thyroid weight [61]. Moreover, co-exposure to high iodine levels and DBP in an autoimmune thyroid disease model was linked to increased thyroid damage and a disruption of TH levels [62].
Furthermore, DEHP-exposed animals presented increased oxidative markers in serum, altered thyroid morphology with signs of necrosis, and the infiltration of inflammatory cells in the follicular epithelium [63,64,65]. In selenium-deficient conditions, DEHP altered the antioxidant status and induced oxidative stress in the thyroid gland of rats by increasing superoxide dismutase activity and thiobarbituric acid reactive substance levels [66,67]. In consonance, selenium and curcumin nanoparticles improved thyroid parameters and the redox status in DEHP-exposed animals [68].
Additionally, data indicated that the TH serum level reduction induced by phthalate exposure depends on the disruption of TH synthesis, transformation, transport, receptor levels, and peripheral metabolism [69,70,71,72,73]. In this regard, in vitro studies indicated that phthalate exposure significantly enhanced iodide uptake, altered TSHR expression, and interfered with TH actions in target cells [74,75,76].
Importantly, the disruption of the HPT axis caused by exposure to phthalates during critical developmental periods is particularly concerning. In this context, recent studies demonstrated that intrauterine and/or neonatal exposure to DEHP significantly increased the offspring’s susceptibility to developing thyroid dysfunctions during life [77,78,79,80,81].
Finally, a pair-matching case–control study found a positive association between urinary phthalate metabolites and the risk of developing papillary thyroid cancer [82]. In this context, it has been demonstrated that DEHP-induced thyroid hyperplasia occurs through the eicosanoid-associated pathway and suggested that this exposure could be associated with thyroid cancer [83].
In summary, phthalates, particularly DEHP, have been linked to thyroid dysfunction and an increased risk of thyroid cancer in both humans and animal models. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying these disruptions are not yet fully understood, highlighting the need for further research to clarify them.
1.2. Bisphenols
Bisphenol A (BPA) is a ubiquitous industrial plasticizer compound used in polycarbonate plastics, epoxy resin, food can linings, and dental sealants [84,85]. BPA was consistently found in urine, and serum samples from humans, in both adults and newborns [86,87,88]. Besides its estrogenic properties, it is well described that BPA acts as an antagonist of THs by binding to their nuclear receptors in target cells [89,90]. In agreement, it has been demonstrated that BPA interacts with the TH receptor beta (THRB) and induces its translocation to the nucleus [91]. Furthermore, low concentrations of BPA (10−9 M) suppressed TH receptor transcription by disrupting the physiological concentrations of the T3/T4-mediated β3 integrin/c-Src/MAPK/TR-β1 pathway, offering novel insights into the molecular mechanisms involved in BPA-mediated TH disruption [92].
1.2.1. BPA Effects in Pregnant Women and Their Progeny
Epidemiological studies have demonstrated inconclusive data about BPA exposure and thyroid function in newborns, children, adolescents, and adults.
A study found a suggestive inverse relationship between urinary BPA and total T4 and TSH in samples of U.S. adults and adolescents [93]. Another study indicated a negative correlation between serum BPA and free T4 levels in men, but not in women. Additionally, no associations were found between BPA and TSH levels in either gender [94]. A recent systematic review and meta-analysis found that the BPA concentration was negatively correlated with free T4 and TSH in males, while in females, it was positively correlated with free T4 [95].
This gender-specific response was also found in the CHAMACOS study that associated intrauterine exposure to BPA with reduced T4 in pregnant women and decreased the TSH in male neonates, but not in female ones [96]. Conversely, the HOME study indicated a negative correlation between maternal BPA exposure and the TSH in newborn girls, but not in newborn boys, especially in iodine-deficient mothers [97]. In a Korean study, BPA exposure was negatively associated with TSH levels, but no significant associations were found in TH levels [98]. In agreement, BPA cord blood levels were not associated with TH serum concentrations in newborns in two other studies [99,100]. Interestingly, maternal exposure to BPA, during the first trimester, and to bisphenol S (BPS), throughout all three trimesters, was associated with increased TSH levels in newborns [101].
BPA exposure was also associated with TPOAb positivity in both men and women. However, the mechanisms involved in the development of autoimmune thyroid disease in BPA-exposed individuals need to be further explored [102].
1.2.2. BPA Exposure and Thyroid Cancer
Regarding thyroid cancer, the exposure to environmentally significant concentrations of BPA synergizes with the BRAFV600E mutation, promoting epithelial–mesenchymal transition through the activation of the ERK signaling pathway in the human thyroid follicular epithelial cell line Nthy-ori 3-1 [103].
In a DMD-induced cancer protocol, BPA exposure alone increased the incidence of thyroid tumors in female rats, and co-exposure with DEHP enhanced the effect of BPA on cancer promotion. In vitro data of the same study indicated that the HDAC6/PTEN/AKT pathway is involved in BPA-MEHP enhanced proliferation and the migration of human thyroid cancer cells BCPAP [104].
In humans, the data about thyroid cancer and BPA are still inconsistent. In this regard, elevated urinary levels of BPA and BPS were associated with increased urinary levels of oxidative stress biomarkers and an enhanced risk of thyroid cancer. Furthermore, BPA exposure in overweight and obese individuals was significantly associated with higher TSH levels, suggesting it may be a risk factor for developing thyroid nodules [105]. Nevertheless, a recent meta-analysis study did not find a significant association between BPA exposure and thyroid cancer [106].
1.2.3. BPA Exposure Effects in Animal Models and In Vitro Studies
The results of BPA exposure during critical development periods in animal models are controversial.
Perinatal exposure to BPA (0, 4, or 40 mg/kg body weight per day) did not alter T4 serum levels or thyroid gland response to the TSH in the offspring rats [107]. Conversely, pregnant rats exposed to BPA (20 or 40 μg/kg body weight) from GD1-20 showed reduced T4 and T3 serum levels and elevated TSHs in the dams and their offspring. In addition, histopathological changes were observed in the thyroid of BPA-exposed animals, such as fibroblast proliferation, follicular hyperplasia, degeneration, and luminal obliteration [108]. In female Sprague–Dawley rats exposed to BPA injections during the neonatal period, TSH levels remained unchanged until PND13. However, these animals exhibited reduced T4 levels and increased TSH levels during adulthood [109]. Moreover, maternal exposure to low doses of BPA during intrauterine and neonatal periods did not alter TH levels in the dams. However, it reduced serum T4 levels in male and female offspring rats during adulthood, particularly at the lowest treatment dose (10 μg/kg/day) [110].
Another study indicated that BPA exposure led to a 30% decrease in total and free T4 levels in pregnant ewes and their newborns and that BPA exposure in long-gestation species can be linked to hypothyroidism in newborns, posing a potential risk for human BPA exposure [111]. Consistently, a study from the same group showed that exposing pregnant ewes to BPA at concentrations similar to those reported in epidemiological studies decreased TH levels without significantly altering TSH [112].
Additionally, BPA decelerated T4-induced changes, reduced the expression of TH receptors, and inhibited the expression of T3-regulated genes in animals that depend on THs for metamorphosis processes [113,114,115]. A recent study has shown that besides the reduction in whole-body T4 levels in zebrafish (Danio rerio), BPA exposure up to 8 days post-fertilization altered retinal layering, decreased motility across varying light conditions, and impaired responsiveness to red light, suggesting compromised neurodevelopment [116].
Even though the effects of BPA exposure on thyroid function have been extensively described in the literature, the molecular mechanisms involved in BPA-induced thyroid dysfunction are not completely comprehended. In vitro studies have shown that BPA interferes with the synthesis of THs by decreasing the expression of genes related to thyroid differentiation and function, such as NIS, TPO, TSHR, and TG, and increasing the expression of genes related to cell death and DNA damage [117,118,119]. Moreover, data from in vivo and in vitro studies demonstrated that BPA exposure increased thyroid production of reactive oxygen species, which could be related to thyroid damage [120].
1.2.4. Bisphenol Analogs and Thyroid Dysfunction
It is worth noting that BPA analogs, such as BPS, tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA), tetrabromobisphenol S (TBBPS), and bisphenol F (BPF), have also been associated with thyroid function disruption.
In this regard, both in vivo and in vitro studies have shown that BPS and BPF disrupt the TH signaling pathway by activating TH-controlled gene transcription in the absence of T3 and displaying both agonistic and antagonistic actions in the presence of this hormone [121]. In accordance, it has been shown that using a T3-induced metamorphosis assay that high concentrations of BPF (100–10,000 nM) antagonizes T3-controlled gene transcription and morphological changes. On the contrary, BPF, at low doses, stimulates T3-induced metamorphosis while inhibiting T3-induced gene transcription [122].
Interestingly, an in silico study suggested that BPA and BPS interact with thyroid transcription factors NKX2.1 and PAX8, elucidating part of the molecular mechanisms involved in BPA-elicited thyroid disruption [123].
Finally, mice exposed to TBBPS and BPS presented increased levels of TSH, altered thyroid morphology, and reduced expression of the proteins involved in TH synthesis, but showed no significant alterations in T3 and T4 levels [124].
Therefore, the data strongly indicate that BPA and its analogs are significant disruptors of thyroid function, with far-reaching implications for both human and other animals’ health. BPA’s ability to bind to TH receptors and thyroid transcription factors highlights its potent role in altering thyroid signaling pathways and gene expression. Despite the extensive data about BPA effects, particularly about thyroid dysfunction and cancer, the underlying molecular mechanisms remain incompletely understood. Moreover, inconsistent findings in epidemiological studies, particularly regarding gender-specific responses and the impact on thyroid function in various populations, underscore the complexity of BPA effects. Additionally, the emerging evidence of BPA analogs, such as BPS and BPF, disrupting thyroid function further amplifies this concern. These analogs not only mimic the actions of BPA but also exhibit unique disruptive properties, suggesting a broader environmental and public health challenge. Future research should prioritize unraveling the precise molecular pathways involved in BPA and its analogs’ thyroid-disruptive effects, particularly focusing on vulnerable populations like pregnant women and developing fetuses, to better inform regulatory policies and protective measures.
1.3. Organochloride Pesticides (OCPs)
OCPs, such as dichlorodiphenylotrichloroethane (DDT), widely used during World War II, were banned in developed countries in the 1970s, but are still used in several developing countries to combat disease vectors [125]. The main metabolite generated from DDT is DDE (dichlorodiphenyldichloroethylene). Both are highly stable, persistent in the environment and accumulate in the fatty tissue of humans and other animals [126,127]. Human exposure to these pesticides occurs mainly through consuming contaminated food and water [128,129].
DDT and DDE have a similar chemical structure to THs [130]. For this reason, they are described as potential disruptors of TH synthesis, action, and metabolism. Consistently, it has been suggested that OCPs affect serum TH levels by interacting with specific hormone-binding proteins, such as thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG) and transthyretin (TTR) [131,132].
1.3.1. OCP Exposure and Thyroid Dysfunction in Humans
DDT and its metabolites cross the placenta and have been found in breast milk samples [133,134]. Moreover, it has been reported that maternal exposure to DDT increased the methylation of the DIO3 and MCT8 genes in the placenta of humans in a sexually dimorphic manner, potentially compromising TH metabolism and action in placental and fetal tissues [135]. Interestingly, paternal exposure to DDT is also associated with disruptions in placental growth and function, affecting metabolic parameters in male offspring but not in females [136].
Previous studies have demonstrated a negative association between free T4 concentrations and serum levels of DDE in pregnant women and newborns [137,138]. Analyses of umbilical cord samples reinforced that high levels of OCPs correlate with low serum TH concentrations, especially T4, in newborns [139,140]. Conversely, it has been shown that intrauterine exposure to DDT influences fetal growth without interfering with maternal TH levels [141,142]. In addition, TSH levels were positively associated with pregnancy exposure to DDT [143,144].
Postnatal deleterious effects of OCP exposure on thyroid function have also been reported. Consistently, a negative correlation between maternal DDE/DDT exposure and birth weight, head circumference, and gestation time was observed in a Bolivian cohort [145]. In addition, newborns whose mothers had detectable levels of OCPs in serum presented decreased TH and GH levels in their umbilical cord blood samples.
Furthermore, it was suggested that the consumption of DDE-contaminated breast milk negatively affects the cognitive development of 10–12-month-old newborns [146]. Finally, detectable OCP levels in the peripheral blood of 4-year-old children reinforced the negative association between DDT exposure and total T3 serum levels [147].
The data about DDE exposure on adult human thyroid function are inconsistent. Some studies have not found any correlation between DDT/DDE contamination and thyroid disruption [148,149]. Contrarily, other studies have reported a negative correlation between DDE exposure and TH serum levels in adult individuals and a positive correlation between DDE contaminant and TSH levels [150,151,152]. In addition, in another study, DDT exposure was positively associated with T3 levels, and negatively associated with the TSH [153]. The inconsistency in data regarding DDE exposure and thyroid function in adults highlights the need for further research to clarify its true impact on thyroid health.
1.3.2. OCP Exposure and Thyroid Dysfunction in Animal Models
The exposure of zebrafish embryos/larvae to DDT and DDE increased malformations during embryonic development, altered the expression of genes involved in TH biosynthesis, and significantly reduced the total T3 content and the T3/T4 ratio in these animals [154].
Similarly, the chronic exposure of rats to DDE resulted in increased thyroid weight, reduced T3 and T4, and increased TSH serum levels [61,155]. Furthermore, rats exposed solely to DDE or DDE combined with PCB153 exhibited a significant reduction in total and free T4 levels, reduced TTR serum levels, and an increased expression of enzymes involved in the hepatic degradation of THs. Therefore, these data suggest impaired TH transport and peripheral metabolism in DDE-exposed animals [131,156].
Finally, rats exposed to DDE presented thyroid follicles with smaller lumens, various alterations in different organelles of thyrocytes, and the disrupted expression of enzymes involved in TH synthesis [157,158,159,160].
In summary, the evidence shows that OCPs, particularly DDT and its metabolite DDE, disrupt thyroid function in both humans and other animals. Although banned in many developed countries, DDT remains a concern due to its persistence and continued use in certain regions. While data in adults are inconsistent, DDE exposure has been linked to altered thyroid function, especially during pregnancy and early development, with potential long-term effects on cognitive development. Animal studies reinforce these findings, demonstrating significant changes in thyroid morphology and TH levels. These findings underscore the ongoing risks that OCP exposure poses to thyroid health.
1.4. Per- and Poly-Fluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs)
PFASs are a class of human-made chemicals characterized by the presence of at least one perfluoromethyl group (-CF3) or perfluoromethylene group (-CF2). PFASs are pollutants, highly persistent, odorless, colorless, and indestructible due to their thermal and chemical stability. They are globally used as surfactants in industrial production and are found in various consumer products, including packaging, non-stick cookware, waterproof makeup, clothing, adhesives, personal hygiene products, etc. Indeed, mixtures of PFASs are commonly found in drinking water, and serum PFASs are detected in up to 99% of the population [161,162]. The constant exposure of humans and animals to these EDCs raises serious concerns within the scientific community, given that their removal from the body can take years. Numerous studies indicate adverse health effects associated with this exposure, including thyroid dysfunctions, metabolic diseases, reproductive toxicity, and neurodevelopmental disorders [163,164].
Different generations of PFASs have been produced, and it has been demonstrated that each class triggers specific disruptive effects. Indeed, PFOA (perfluorooctanoic acid) is an older, long-chain PFAS that is listed as possibly carcinogenic to humans (Group 2B) by the International Agency for Research on Cancer [165,166].
1.4.1. PFASs Exposure and Thyroid Dysfunction in Humans
A possible link between exposure to some older-generation PFASs and thyroid disruption has been reported in several studies; however, data are still inconsistent.
Pregnant women exposed to different PFASs, especially perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS), presented slightly increased levels of TSHs [167]. In another study, only perfluorohexanesulfonic acid (PFHxS) concentrations were positively associated with maternal TSH serum levels. Moreover, higher levels of perfluorononanoic acid (PFNA), perfluoroundecanoic acid (PFUnDA), and perfluorododecanoic acid (PFDoDA) were associated with reduced T4 levels in maternal and cord blood samples [168]. Conversely, in a study with 157 paired maternal and cord serum samples, the most prevalent PFASs, PFOS and PFOA, were negatively associated with maternal TSH levels, but no significant alterations were found in TH serum concentrations [169].
Results from the SELMA study indicated that, in 2008 pregnant women in the first trimester of gestation, PFAS exposure was not associated with alterations in the TSH. However, higher PFNA, PFDA, PFHpA, and PFOA levels were associated with increased free T4 and lower total T3 levels. In addition, higher PFUnDA levels were associated with lower free T3 and total T4 levels, and an inverted U-shaped curve association was described for PFOS exposure and total T4 levels [170].
Interestingly, PFAS mixture was not associated with maternal T4 or TSH levels in the Project Viva Cohort. However, isolated analysis revealed that PFOS was positively associated with T4 levels, and PFHxS demonstrated a non-linear effect on TSH levels [171]. In addition, in a study on 300 mother–infant pairs from the Shanghai-Minhang Birth Cohort Study, higher PFAS mixture concentrations were associated with increased T3 concentrations and high levels of PFNA and PFOA were associated with a decrease or increase in TSH concentrations, respectively [172].
A sex-dimorphic effect was observed in PFAS-exposed neonates as prenatal PFOS, PFOA, and PFHxS exposure was inversely associated with T4 levels in male neonates, but this association was not observed in female neonates [173]. Consistent with this dimorphic response, results from the Hokkaido Study revealed that maternal PFAS exposure was linked to higher TSH and lower free T3 levels in male neonates, whereas in female neonates, PFAS contamination was associated with lower TSH and higher free T3 levels [174].
As previously described, THs are essential for CNS development, and PFBS and PFHxS prenatal exposures were negatively associated with TSH and FT4 levels, and early neurodevelopment [175]. In agreement, prenatal exposure to PFASs was negatively associated with the IQ of school-aged children [176]. Moreover, PFAS levels were found to be significantly higher in infants with congenital hypothyroidism compared to those in the control group [177].
In the general population, PFAS exposure was detected in almost 99% of the samples in different studies, but few statistically significant associations were found between PFASs and TH levels in U.S. adults. PFASs were only associated with thyroid disruption in adults with high TPOAb and a low iodine status, which are commonly considered a vulnerable group for thyroid dysfunctions [178]. In agreement, a study conducted in a highly contaminated area did not find an association between TSHs and PFASs in adolescents or women [179].
Conversely, in female adolescents, serum PFOA and PFAS mixtures were associated with lower free T4 and higher free T3 levels. In male adolescents, PFOA was associated with lower free T4 levels and PFAS mixture was associated with higher TSH and a lower FT4/TSH ratio [180]. In the elderly, high levels of PFAS contamination were detected and associated with decreased TSH and free T4 levels, alongside increased total T4 and T3 levels [181].
It is important to reinforce that the inconsistent data about the consequences of human exposure to PFASs on the disruption of thyroid function may be associated with sample size, region, sample type, body mass index, and exposure period [182].
1.4.2. PFAS Exposure and Thyroid Dysfunction in Animal Models
In rodent models, PFAS exposure has been shown to alter circulating TH levels [183,184].
Interestingly, although PFOS exposure reduced TH levels and altered the expression of enzymes involved in TH clearance and metabolism, it was not associated with changes in TH-responsive genes in the rat liver [185]. Similarly, rats exposed for 7 days to 3 mg PFOS/kg/day presented differentially expressed genes in the hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, and liver in comparison to the control group, but none of them aligned with TH regulating genes [186].
In addition, in an ex vivo model, the exposure of fetal thyroid explants to low concentrations of PFOS reduced the expression of Pax8 and cadherin-16, which control the apical–basal polarization of thyroid epithelial cells, suggesting that thyroid follicle organization may be disrupted by PFAS exposure during critical developmental periods [187].
Zebrafish exposed to PFASs also displayed alterations in TH levels [188,189]. In agreement, a study demonstrated that PFAS-exposed zebrafish embryos/larvae presented reduced T3 and T4 levels and altered expression of genes involved in the synthesis, regulation, and action of THs [190].
Conversely, although the exposure to some PFASs induced concentration-dependent developmental toxicity in Xenopus laevis embryos and larvae, no alterations were observed in thyroid endpoints [191]. Moreover, in rabbits, the exposure of dams to an environmentally relevant PFAS mixture did not alter T3 and T4 levels either in the dams or in the offspring [192].
1.4.3. PFAS Exposure and Thyroid Dysfunction in In Vitro Studies
In vitro studies demonstrated that PFOS acutely and reversibly inhibited NIS-mediated iodide uptake by FRTL-5 thyrocytes but did not alter iodide efflux in these cells. PFOA exposure did not change both parameters [193]. On the contrary, another study reported that PFOA, but not C6O4 or PFOS, impaired the TSH-mediated signaling pathway in thyrocytes. This impairment reduced intracellular cAMP production, decreased NIS and TPO gene expression, and diminished NIS-mediated iodide uptake. Interestingly, the same study demonstrated that PFOA, C6O4, and PFOS possibly interact with TSHR through computational analyses [194].
In a high-throughput screening assay, 38 of 149 evaluated PFAS chemicals inhibited iodide uptake in a stably transduced human NIS cell line. PFOS and PFHxS were found to be the most potent NIS inhibitors [195]. Moreover, PFOS and PFOA significantly reduced the activity of TPO in human follicular thyroid carcinoma cells stably transfected with human recombinant TPO [196]. Interestingly, despite the disruptive effect in the activity of two key proteins involved in TH synthesis, previous studies demonstrated that short-chain PFASs (PFBS, PFBA, PFPA, and PFPEA) did not significantly decrease the stimulation of cAMP induced by TSHs [197].
Regarding new-generation, short-chain PFASs, limited literature data support the hypothesis that they are less toxic, although results are still controversial [198].
For instance, a study on GenX, a new-generation PFOA substitute, demonstrated greater toxicity than PFOA and PFOS by causing cellular damage and activating the PPARα signaling pathway in mouse liver cell lines [199] In agreement, FRTL-5 cells exposed to GenX doses commonly found in human plasma presented reduced proliferation rates, DNA fragmentation, and genotoxicity, and altered the expression of thyroid transcription factors and the NIS [200]. These results agree with previously reported data that indicated reduced viability and proliferation rates due to increased cell death in PFOA and PFOS-exposed FRTL5 cells [201]. Accordingly, GenX exposure reduced cell viability and altered the expression of NKX2.1, PAX8, TSHR, and NIS in FRTL5 and primary normal human thyroid cells. Remarkably, these effects were not observed in cells exposed to another PFOS alternative, 4,8-dioxa-3H-perfluorononanoate (ADONA) [202]. C6O4, another new-generation PFAS, did not alter ROS production and cell viability, or induce apoptosis/necrosis in thyroid cells, as demonstrated for PFOS and PFOA [203]. Additionally, it has been shown that these new-generation short-chain PFASs are more efficient at crossing the placenta than their long-chain counterparts, increasing the risk of prenatal exposure [204].
1.4.4. PFAS Exposure and Thyroid Cancer
Concerning thyroid cancer, PFAS exposure has been previously associated with an increased risk of papillary thyroid tumor development in humans [166,205,206]. The carcinogenesis associated with PFAS exposure has been related to changes in epigenetic mechanisms, immunosuppression, increased oxidative stress/inflammation, alterations in hormonal/metabolic pathways, and the activation of epithelial–mesenchymal transition [207].
Indeed, studies have suggested that alterations in epigenetic events induced by PFAS exposure could synergistically amplify tumorigenicity and cancer progression, leading to a poorer prognosis [166,208,209]. In accordance, it has been shown that exposure to C6O4, PFHxA, and PFOA stimulated the secretion of the pro-tumorigenic chemokine CXCL8 and the expression of epithelial–mesenchymal transition genes in primary normal thyroid cells, in adherent and spheroid cultures. It is worth noting that the modulation of CXCL8 has clinical relevance to the tumor environment since it attracts immune system cells, which facilitate the metastatic process of tumor cells [165,210].
In conclusion, several studies suggest a potential link between older-generation PFAS exposure and thyroid disruption, but the data remain controversial in pregnant women, neonates, and adults. Additionally, prenatal PFAS exposure has been associated with adverse effects on neurodevelopment and cognitive outcomes in children. Animal models and in vitro studies further corroborate the thyroid-disrupting potential of PFASs, highlighting alterations in thyrocyte physiology and the expression of proteins involved in TH synthesis. These findings underscore the need for continued research to clarify the risks of PFAS exposure on thyroid health and its broader implications for human health.
1.5. Concluding Remarks: Gaps and Perspectives
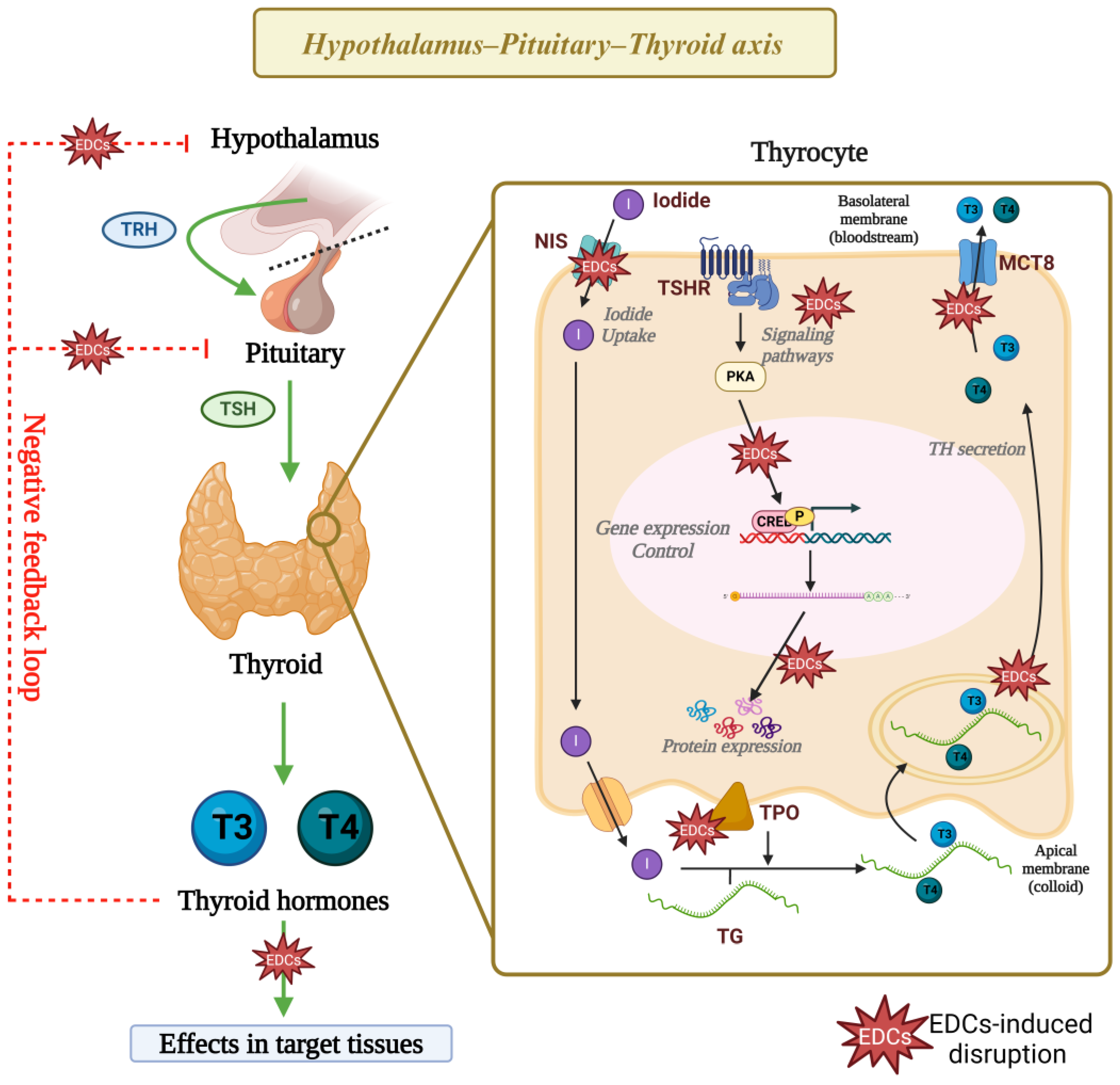
In summary, the thyroid disruptors described herein alter several pathways involved in the negative feedback loops that control the HPT axis function and impair thyrocytes’ cellular physiology and gene expression (Figure 4). Nonetheless, future studies need to further explore the molecular mechanisms involved in these disruptions, as understanding these mechanisms is crucial for developing targeted interventions and regulatory actions to mitigate adverse effects on thyroid health.
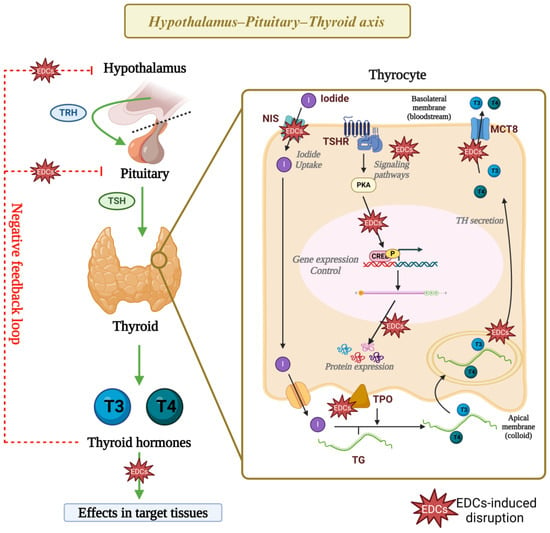
Figure 4.
Mechanism of action of thyroid disruptors. Exposure to phthalates, bisphenols, DDT, and PFASs has been linked to disruptions in the function of the hypothalamus–pituitary–thyroid axis, as well as in the cellular physiology and gene expression of thyrocytes. Research indicates that these EDCs impair the activity and expression of proteins critical for thyroid hormone synthesis. Additionally, findings suggest that these EDCs possibly alter signaling pathways and epigenetic mechanisms that regulate gene expression in thyrocytes, but these mechanisms need to be further explored. EDCs: endocrine-disrupting chemicals, TRH: thyrotropin-releasing hormone, TSH: thyrotropin, NIS: sodium–iodide symporter, TSHR: thyrotropin receptor, TPO: thyroid peroxidase, TG: thyroglobulin, T3: triiodothyronine, T4: thyroxine, CREB: cAMP-response element binding protein. Created with Biorender.com.
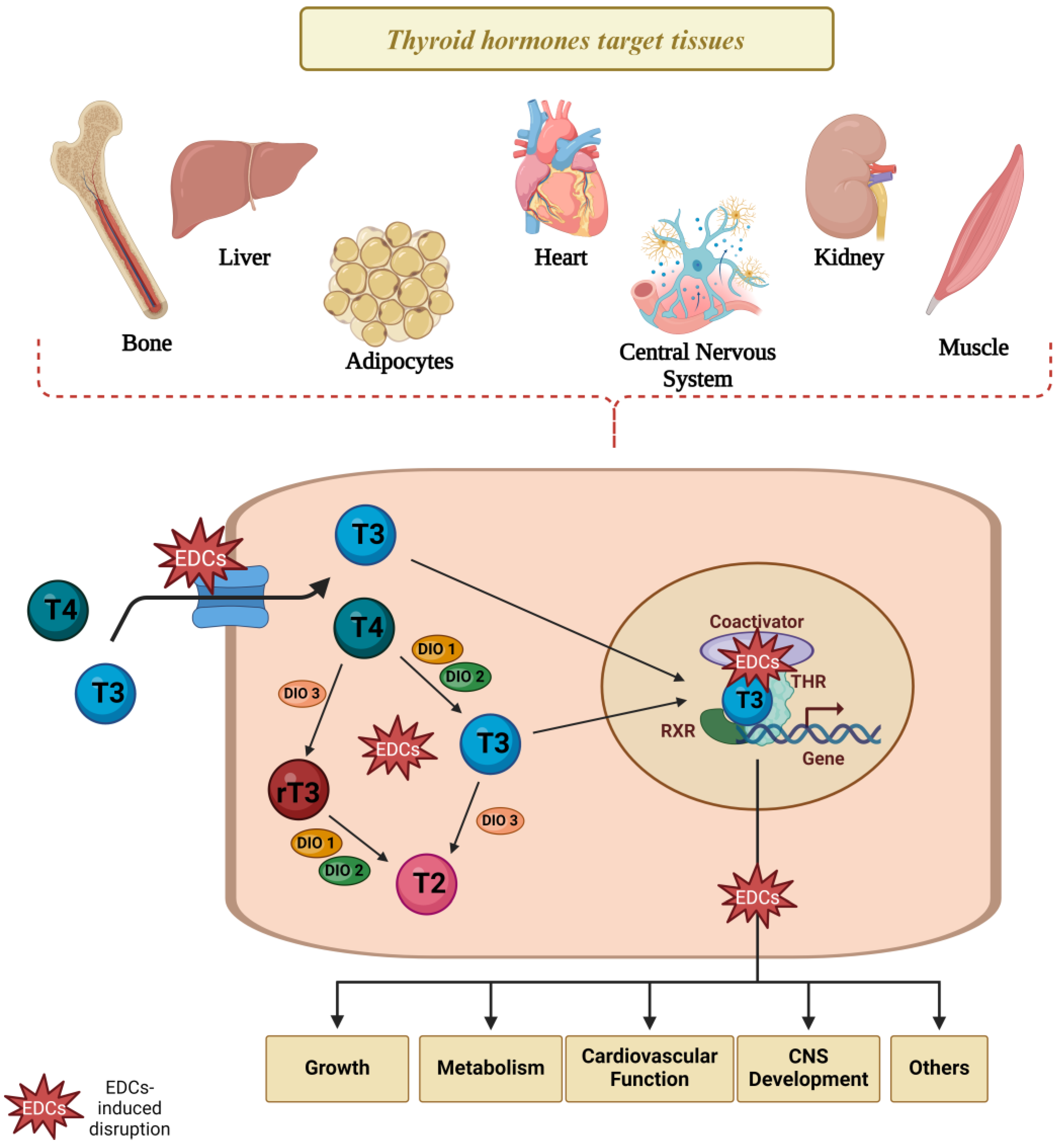
Additionally, for a long time, most studies on the disruptive effects of EDCs have focused on the reproductive system, as many of these compounds interfere with androgenic or estrogenic actions [211,212]. However, TH receptors are expressed in virtually all tissues, including in the gonads, significantly expanding the range of actions of these hormones in the body. Therefore, it is crucial to emphasize that thyroid function disruption extends beyond impairing TH synthesis, as these hormones influence virtually all organs and systems in the body (Figure 5).
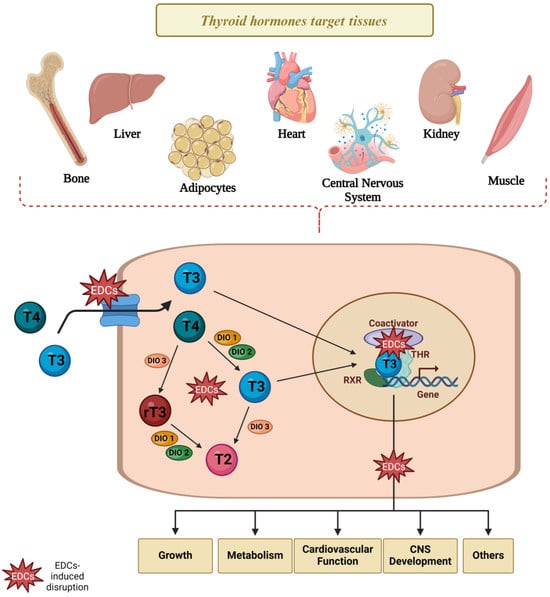
Figure 5.
Thyroid disruptors and TH signaling in target cells. Several studies suggest that the TH-induced signaling pathways and TH action in target cells are compromised in animals and cells exposed to thyroid disruptors, possibly through the impairment disruption in several steps involved in TH transport, metabolism, and action in target cells. EDCs: endocrine-disrupting chemicals, T2: diiodothyronine, T3: triiodothyronine, T4: thyroxine, rT3: reverse triiodothyronine, THR: thyroid hormone receptor; DIO1: deiodinase type 1; DIO2: deiodinase type 2; DIO3: deiodinase type 3. Created with Biorender.com.
Consistently, studies demonstrate an association between thyroid dysfunction and cardiovascular, metabolic, reproductive, neurological, behavioral, and fetal development disorders [213,214,215]. Therefore, given the importance of TH in maintaining homeostasis, chemicals that impair thyroid function are potentially deleterious, especially in vulnerable periods of development. Despite the progress in obtaining evidence about new thyroid disruptors in the last few years, the molecular mechanisms of these contaminants remain unclear. Epidemiological data are particularly controversial, and the impact of exposure to these thyroid disruptors on human health is inconclusive. These discrepancies may rely on variations in methodologies used to detect contaminants, TH and TSH levels, and differences in the exposure periods assessed. Furthermore, although data on the effects of specific and isolated classes of EDCs on thyroid function are extremely relevant, there is still a lack of studies on the impact of human and other animals’ exposure to mixtures, which would more accurately reflect the exposure to these contaminants. Moreover, studies on the programming-induced effects of thyroid disruptors in human progeny in later life are still missing. Hence, further research is needed to clarify the effects of thyroid disruptors on systems and organs beyond the hypothalamus–pituitary–thyroid axis.
Author Contributions
V.G.R., G.H., É.K.S.-V., R.M.M.d.S., E.F.C.T., N.M., T.d.O.M., B.M.A., J.A.A.P., L.N.N.I., R.E.C.d.S. and K.C.d.O.: investigation, writing—original draft preparation; V.G.R. and G.H. design of the figures; V.G.R., G.H., R.M.d.B.M., G.G. and C.S.-N.: writing—review and editing; G.G. and C.S.-N.: supervision; R.M.d.B.M. and C.S.-N.: funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by FAPESP (2022/01422-5, 2024/09279-2) to VGR, (2018/14778/7, 2021/08559-3) to GH, (2024/06102-4) to RMMS, (2022/02131-4) to EFCT, (2022/15797-0) to JAAP, (2021/02752-6) to RMBM, and (2016/18517-8) to CSN. The group is also supported by a grant from CNPq (Universal 406997/2023-3, INCT/CNPq/FNDCT/CAPES/FAPERJ 406643/2022-9).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
| AKT | protein kinase B |
| BPA | bisphenol A. |
| BPF | bisphenol F |
| BPS | bisphenol S |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| DBP | di-n-butyl phthalate |
| DDE | dichlorodiphenyldichloroethylene |
| DDT | dichloro-diphenyl-trichloroethane |
| DEHP | di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate |
| DIO1 | deiodinase type 1 |
| DIO2 | deiodinase type 2 |
| DIO3 | deiodinase type 3 |
| DMD | diethylnitrosamine(DEN)-N-methyl-N-nitrosourea (MNU)-N,N-bis(2-hydroxypropyl)nitrous amide (DHPN) |
| EDCs | endocrine-disrupting chemicals |
| ERK | extracellular signal-regulated kinases |
| GH | growth hormone |
| HDAC6 | histone deacetylase 6 |
| HPT | hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid |
| MCT8 | monocarboxylate transporter 8 |
| MEHP | phthalic acid mono-2-ethylhexy |
| NIS | sodium–iodide symporter |
| NKX2.1 | NK2 homeobox 1 or thyroid transcription factor 1 |
| OCPs | organochloride pesticides |
| Pax8 | paired box 8 |
| PBDEs | polybrominated diphenyl ethers |
| PCBs | polychlorinated biphenyls |
| PFASs | per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances |
| PFDoDA | perfluorododecanoic acid |
| PFHxS | perfluorohexanesulfonic acid |
| PFNA | perfluorononanoic acid |
| PFOA | perfluorooctanoic acid |
| PFOS | perfluorooctane sulfonate |
| PFUnDA | perfluoroundecanoic acid |
| PND | post-natal day |
| PTEN | phosphatase and tensin homolog |
| rT3 | reverse T3 |
| T2 | diiodothyronine |
| T3 | triiodothyronine |
| T4 | thyroxine |
| TBBPA | tetrabromobisphenol A |
| TBBPS | tetrabromobisphenol S (TBBPS) |
| TBG | thyroxine-binding globulin |
| TG | thyroglobulin |
| TH | thyroid hormones |
| THRB | thyroid hormone receptor beta |
| TPO | thyroid peroxidase |
| TRH | thyrotropin-releasing hormone |
| TSH | thyroid-stimulating hormone or thyrotropin |
| TSHR | thyrotropin receptor |
| TTR | transthyretin |
References
- Gore, A.C.; Chappell, V.A.; Fenton, S.E.; Flaws, J.A.; Nadal, A.; Prins, G.S.; Toppari, J.; Zoeller, R.T. EDC-2: The Endocrine Society’s Second Scientific Statement on Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals. Endocr. Rev. 2015, 36, E1–E150. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mezcua, M.; Martínez-Uroz, M.A.; Gómez-Ramos, M.M.; Gómez, M.J.; Navas, J.M.; Fernández-Alba, A.R. Analysis of Synthetic Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals in Food: A Review. Talanta 2012, 100, 90–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, W.G.; Agzarian, J. Toward Less Confusing Terminology in Endocrine Disruptor Research. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B Crit. Rev. 2008, 11, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Coster, S.; Van Larebeke, N. Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals: Associated Disorders and Mechanisms of Action. J. Environ. Public Health 2012, 2012, 713696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Merrill, M.A.; Vandenberg, L.N.; Smith, M.T.; Goodson, W.; Browne, P.; Patisaul, H.B.; Guyton, K.Z.; Kortenkamp, A.; Cogliano, V.J.; Woodruff, T.J.; et al. Consensus on the Key Characteristics of Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals as a Basis for Hazard Identification. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pietro, G.; Forcucci, F.; Chiarelli, F. Endocrine Disruptor Chemicals and Children’s Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Credico, A.; Gaggi, G.; Bucci, I.; Ghinassi, B.; Di Baldassarre, A. The Effects of Combined Exposure to Bisphenols and Perfluoroalkyls on Human Perinatal Stem Cells and the Potential Implications for Health Outcomes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ünüvar, T.; Büyükgebiz, A. Fetal and Neonatal Endocrine Disruptors. JCRPE J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2012, 4, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, M.L.Y.; Co, V.A.; El-Nezami, H. Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals and Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review of Epidemiological Studies. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 6549–6576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, R.A.; de Moura, E.G.; Lisboa, P.C. Adverse Perinatal Conditions and the Developmental Origins of Thyroid Dysfunction—Lessons from Animal Models. Endocrine 2023, 79, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledano, J.M.; Puche-Juarez, M.; Moreno-Fernandez, J.; Gonzalez-Palacios, P.; Rivas, A.; Ochoa, J.J.; Diaz-Castro, J. Implications of Prenatal Exposure to Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals in Offspring Development: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, D.J.P. The Developmental Origins of Adult Disease. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2004, 23, 588S–595S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perng, W.; Nakiwala, D.; Goodrich, J.M. What Happens In Utero Does Not Stay In Utero: A Review of Evidence for Prenatal Epigenetic Programming by Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Infants, Children, and Adolescents. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2023, 10, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Tollefsbol, T.O.; Li, S.; Chen, M. Prenatal Epigenetics Diets Play Protective Roles against Environmental Pollution. Clin. Epigenetics 2019, 11, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera, F.; Herbstman, J. Prenatal Environmental Exposures, Epigenetics, and Disease. Reprod. Toxicol. 2011, 31, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joss-Moore, L.A.; Metcalfe, D.B.; Albertine, K.H.; McKnight, R.A.; Lane, R.H. Epigenetics and Fetal Adaptation to Perinatal Events: Diversity through Fidelity. J. Anim. Sci. 2010, 88, E216–E222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cyr, A.R.; Domann, F.E. The Redox Basis of Epigenetic Modifications: From Mechanisms to Functional Consequences. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 15, 551–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagiatakis, C.; Musolino, E.; Gornati, R.; Bernardini, G.; Papait, R. Epigenetics of Aging and Disease: A Brief Overview. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2021, 33, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, G.; Heard, E. Advances in Epigenetics Link Genetics to the Environment and Disease. Nature 2019, 571, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Epstein, J.A. Epigenetics. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2024, 1441, 341–364. [Google Scholar]
- Jedynak, P.; Siroux, V.; Broséus, L.; Tost, J.; Busato, F.; Gabet, S.; Thomsen, C.; Sakhi, A.K.; Sabaredzovic, A.; Lyon-Caen, S.; et al. Epigenetic Footprints: Investigating Placental DNA Methylation in the Context of Prenatal Exposure to Phenols and Phthalates. Envrion. Int. 2024, 189, 108763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.; Kang, B.S.; Kim, O.; Won, S.; Kim, H.S.; Wie, J.H.; Shin, J.E.; Choi, S.K.; Jo, Y.S.; Kim, Y.H.; et al. The Associations between Maternal and Fetal Exposure to Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals and Asymmetric Fetal Growth Restriction: A Prospective Cohort Study. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1351786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Kinkade, J.A.; Bivens, N.J.; Rosenfeld, C.S. MiRNA Changes in the Mouse Placenta Due to Bisphenol A Exposure. Epigenomics 2021, 13, 1909–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robaire, B.; Delbes, G.; Head, J.A.; Marlatt, V.L.; Martyniuk, C.J.; Reynaud, S.; Trudeau, V.L.; Mennigen, J.A. A Cross-Species Comparative Approach to Assessing Multi- and Transgenerational Effects of Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals. Envrion. Res. 2022, 204, 112063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skipper, M. Epigenomics: Epigenetic Variation across the Generations. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, D.P.; Dupuy, C. Thyroid Hormone Biosynthesis and Release. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2017, 458, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, G.; Levy, O.; Carrasco, N. Cloning and characterization of the thyroid iodide transporter. Nature 1996, 379, 458–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silveira, J.C.; Kopp, P.A. Pendrin and anoctamin as mediators of apical iodide efflux in thyroid cells. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2015, 22, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godlewska, M.; Banga, P.J. Thyroid peroxidase as a dual active site enzyme: Focus on biosynthesis, hormonogenesis and thyroid disorders of autoimmunity and cancer. Biochimie 2019, 160, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuer, H.; Visser, T.J. Minireview: Pathophysiological importance of thyroid hormone transporters. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 1078–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, R.A.; Yen, P.M. Metabolic Messengers: Thyroid Hormones. Nat. Metab. 2024, 6, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senese, R.; Cioffi, F.; Petito, G.; Goglia, F.; Lanni, A. Thyroid hormone metabolites and analogues. Endocrine 2019, 66, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiga-Carvalho, T.M.; Chiamolera, M.I.; Pazos-Moura, C.C.; Wondisford, F.E. Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Thyroid Axis. Compr. Physiol. 2016, 6, 1387–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Q.; Zou, H.; Zhang, S.; Lin, J.; Nie, W.; Cui, Y.; Liu, S.; Han, J. Association of Maternal TSH and Neonatal Metabolism: A Large Prospective Cohort Study in China. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1052836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.Y.; Vasilopoulou, E.; Kilby, M.D. The Role of the Placenta in Thyroid Hormone Delivery to the Fetus. Nat. Clin. Pract. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 5, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salas-Lucia, F.; Stan, M.N.; James, H.; Rajwani, A.; Liao, X.H.; Dumitrescu, A.M.; Refetoff, S. Effect of the Fetal THRB Genotype on the Placenta. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 108, e944–e948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuñiga, L.F.F.; Muñoz, Y.S.; Pustovrh, M.C. Thyroid Hormones: Metabolism and Transportation in the Fetoplacental Unit. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2022, 89, 526–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Ji, L.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, N.; Sun, J.; Zhao, D. Maternal Isolated Hypothyroxinemia in the First Trimester Is Not Associated with Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes, except for Macrosomia: A Prospective Cohort Study in China. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1309787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaFranchi, S.H.; Haddow, J.E.; Hollowell, J.G. Is Thyroid Inadequacy during Gestation a Risk Factor for Adverse Pregnancy and Developmental Outcomes? Thyroid 2005, 15, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Street, M.E.; Shulhai, A.-M.; Petraroli, M.; Patianna, V.; Donini, V.; Giudice, A.; Gnocchi, M.; Masetti, M.; Montani, A.G.; Rotondo, R.; et al. The Impact of Environmental Factors and Contaminants on Thyroid Function and Disease from Fetal to Adult Life: Current Evidence and Future Directions. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1429884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Nascimento, C.; Nunes, M.T. Perchlorate, Nitrate, and Thiocyanate: Environmental Relevant NIS-Inhibitors Pollutants and Their Impact on Thyroid Function and Human Health. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 995503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellanger, M.; Demeneix, B.; Grandjean, P.; Zoeller, R.T.; Trasande, L. Neurobehavioral Deficits, Diseases, and Associated Costs of Exposure to Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals in the European Union. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 1256–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shams, M.; Alam, I.; Mahbub, M.S. Plastic Pollution during COVID-19: Plastic Waste Directives and Its Long-Term Impact on The Environment. Environ. Adv. 2021, 5, 100119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, B.; Yu, Y.; Dong, W. A Systematic Review of Global Distribution, Sources and Exposure Risk of Phthalate Esters (PAEs) in Indoor Dust. J. Hazard Mater. 2024, 471, 134423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erythropel, H.C.; Maric, M.; Nicell, J.A.; Leask, R.L.; Yargeau, V. Leaching of the Plasticizer Di(2-Ethylhexyl)Phthalate (DEHP) from Plastic Containers and the Question of Human Exposure. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 9967–9981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Guo, J.L.; Xue, J.C.; Bai, C.L.; Guo, Y. Phthalate Metabolites: Characterization, Toxicities, Global Distribution, and Exposure Assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 291, 118106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wu, D.; Guo, Y.; Mao, W.; Zhao, N.; Zhao, M.; Jin, H. Phthalate Metabolites in Paired Human Serum and Whole Blood. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 824, 153792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsikantami, I.; Tzatzarakis, M.N.; Alegakis, A.K.; Karzi, V.; Hatzidaki, E.; Stavroulaki, A.; Vakonaki, E.; Xezonaki, P.; Sifakis, S.; Rizos, A.K.; et al. Phthalate Metabolites Concentrations in Amniotic Fluid and Maternal Urine: Cumulative Exposure and Risk Assessment. Toxicol. Rep. 2020, 7, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xiao, M.; Huang, K.; Cui, J.; Liu, H.; Yu, Y.; Ma, S.; Liu, X.; Lin, M. Phthalate Metabolites in Breast Milk from Mothers in Southern China: Occurrence, Temporal Trends, Daily Intake, and Risk Assessment. J. Hazard Mater. 2024, 464, 132895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsikantami, I.; Tzatzarakis, M.N.; Karzi, V.; Stavroulaki, A.; Xezonaki, P.; Vakonaki, E.; Alegakis, A.K.; Sifakis, S.; Rizos, A.K.; Tsatsakis, A.M. Biomonitoring of Bisphenols A and S and Phthalate Metabolites in Hair from Pregnant Women in Crete. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 135651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johns, L.E.; Cooper, G.S.; Galizia, A.; Meeker, J.D. Exposure Assessment Issues in Epidemiology Studies of Phthalates. Environ. Int. 2015, 85, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryva, B.A.; Pacyga, D.C.; Anderson, K.Y.; Calafat, A.M.; Whalen, J.; Aung, M.T.; Gardiner, J.C.; Braun, J.M.; Schantz, S.L.; Strakovsky, R.S. Associations of Urinary Non-Persistent Endocrine Disrupting Chemical Biomarkers with Early-to-Mid Pregnancy Plasma Sex-Steroid and Thyroid Hormones. Envrion. Int. 2024, 183, 108433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, H.Y.; Han, Y.; Gao, H.; Huang, K.; Ge, X.; Xu, Y.Y.; Xu, Y.Q.; Jin, Z.X.; Sheng, J.; Yan, S.Q.; et al. Maternal Phthalate Exposure during the First Trimester and Serum Thyroid Hormones in Pregnant Women and Their Newborns. Chemosphere 2016, 157, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Shan, D.; Zhang, T.; Li, L.; Wang, S.; Du, R.; Li, Y.; Wu, S.; Jin, L.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Associations between Exposure to Phthalates and Subclinical Hypothyroidism in Pregnant Women during Early Pregnancy: A Pilot Case-Control Study in China. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 320, 121051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.J.; Moon, S.; Oh, B.C.; Jung, D.; Choi, K.; Park, Y.J. Association between Diethylhexyl Phthalate Exposure and Thyroid Function: A Meta-Analysis. Thyroid 2019, 29, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.C.; Kuo, P.L.; Guo, Y.L.; Liao, P.C.; Lee, C.C. Associations between Urinary Phthalate Monoesters and Thyroid Hormones in Pregnant Women. Hum. Reprod. 2007, 22, 2715–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meeker, J.D.; Calafat, A.M.; Hauser, R. Di(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate Metabolites May Alter Thyroid Hormone Levels in Men. Envrion. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 1029–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boas, M.; Frederiksen, H.; Feldt-Rasmussen, U.; Skakkebæk, N.E.; Hegedüs, L.; Hilsted, L.; Juul, A.; Main, K.M. Childhood Exposure to Phthalates: Associations with Thyroid Function, Insulin-like Growth Factor I, and Growth. Envrion. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1458–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, S.C.; Chescoe, D.; Grasso, P.; Wright, M.; Hinton, R.H. Alterations in the Thyroids of Rats Treated for Long Periods with Di-(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate or with Hypolipidaemic Agents. Toxicol. Lett. 1988, 40, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, R.H.; Mitchell, F.E.; Mann, A. Effects of Phthalic Acid Esters on the Liver and Thyroid. Envrion. Health Perspect. 1986, 70, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, J.C.; Frame, S.R.; Ladics, G.S. Evaluation of a 15-Day Screening Assay Using Intact Male Rats for Identifying Antiandrogens. Toxicol. Sci. 2002, 69, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, J.; Kang, J.; Deng, T.; Yang, X.; Chen, M. Exposure to DBP and High Iodine Aggravates Autoimmune Thyroid Disease through Increasing the Levels of IL-17 and Thyroid-Binding Globulin in Wistar Rats. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 163, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, Z.; Miao, X.; Na, X. Novel Insights into Di-(2-Ethylhexyl)Phthalate Activation: Implications for the Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Thyroid Axis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, R.; Lecavalier, P.; Mueller, R.; Valli, V.E.; Procter, B.G.; Chu, I. Subchronic Oral Toxicity of Di-n-Octyl Phthalate and Di(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate in the Rat. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1997, 35, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howarth, J.A.; Price, S.C.; Dobrota, M.; Kentish, P.A.; Hinton, R.H. Effects on Male Rats of Di-(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate and Di-n-Hexylphthalate Administered Alone or in Combination. Toxicol. Lett. 2001, 121, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkekoglu, P.; Giray, B.K.; Kizilgün, M.; Hininger-Favier, I.; Rachidi, W.; Roussel, A.M.; Favier, A.; Hincal, F. Thyroidal Effects of Di-(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate in Rats of Different Selenium Status. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 2012, 31, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Guan, X.; Yang, M.; Zeng, L.; Liu, C. Roles and Potential Mechanisms of Selenium in Countering Thyrotoxicity of DEHP. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619–620, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherif, N.A.E.H.; El-Banna, A.; Abdel-Moneim, R.A.; Sobh, Z.K.; Balah, M.I.F. The Possible Thyroid Disruptive Effect of Di-(2-Ethyl Hexyl) Phthalate and the Potential Protective Role of Selenium and Curcumin Nanoparticles: A Toxicological and Histological Study. Toxicol. Res. 2022, 11, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhao, L.; Wei, L.; Li, L. DEHP Reduces Thyroid Hormones via Interacting with Hormone Synthesis-Related Proteins, Deiodinases, Transthyretin, Receptors, and Hepatic Enzymes in Rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 12711–12719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Ha, M.; Yang, M.; Yue, P.; Xie, Z.; Liu, C. Di2-Ethylhexyl Phthalate Disrupts Thyroid Hormone Homeostasis through Activating the Ras/Akt/TRHr Pathway and Inducing Hepatic Enzymes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Dong, J.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Na, X. Effects of Long-Term in Vivo Exposure to Di-2-Ethylhexylphthalate on Thyroid Hormones and the Tsh/Tshr Signaling Pathways in Wistar Rats. Int. J. Envrion. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Zhou, L.; Wang, S.; Liu, T.; Zhu, J.; Jia, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, H.; Wang, Q.; Xu, F.; et al. Effect of Di-(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate on the Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Thyroid Axis in Adolescent Rat. Endocr. J. 2022, 69, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, K.A.; Yousaf, M.S.; Tahir, M.S.; Khan, A.R.; Khan, S.; Saeed, A.A.; Rehman, H. Effects of Subacute Exposure of Dibutyl Phthalate on the Homeostatic Model Assessment, Thyroid Function, and Redox Status in Rats. Biomed. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 5521516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, A.; Franz, C.; Breous, E.; Loos, U. Modulation of Iodide Uptake by Dialkyl Phthalate Plasticisers in FRTL-5 Rat Thyroid Follicular Cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2005, 244, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghisari, M.; Bonefeld-Jorgensen, E.C. Effects of Plasticizers and Their Mixtures on Estrogen Receptor and Thyroid Hormone Functions. Toxicol. Lett. 2009, 189, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.J.; Kim, H.H.; Song, Y.S.; Kim, O.H.; Choi, K.; Kim, S.; Oh, B.C.; Park, Y.J. DEHP Down-Regulates Tshr Gene Expression in Rat Thyroid Tissues and FRTL-5 Rat Thyrocytes: A Potential Mechanism of Thyroid Disruption. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 36, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlas, N.; Göktekin, E.; Karabulut, G. Influence of in Utero Di-n-Hexyl Phthalate and Di-Cyclohexyl Phthalate Exposure on the Endocrine Glands and T3, T4, and TSH Hormone Levels of Male and Female Rats: Postnatal Outcomes. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2020, 36, 399–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa-Vidal, É.K.; Henrique, G.; da Silva, R.E.C.; Serrano-Nascimento, C. Intrauterine Exposure to Di(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate (DEHP) Disrupts the Function of the Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Thyroid Axis of the F1 Rats during Adult Life. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 13, 995491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Hu, L.; Liao, C.; Jiang, G. Exposure to MEHP during Pregnancy and Lactation Impairs Offspring Growth and Development by Disrupting Thyroid Hormone Homeostasis. Envrion. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 3726–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Cong, Z.; You, M.; Fu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fu, H.; Wei, L.; Chen, J. Effects of Perinatal Di (2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate Exposure on Thyroid Function in Rat Offspring. Envrion. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 67, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Fu, X.; Zhou, F.; Yu, H.; Na, X. Transcriptomics and Metabonomics Analyses of Maternal DEHP Exposure on Male Offspring. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 26322–26329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, H.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, S.; Ni, S.; Wu, Y. Associations of Urinary Phthalate Metabolites with Risk of Papillary Thyroid Cancer. Chemosphere 2020, 241, 125093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.K.; Zhang, J.; Hwang, S.; Cho, S.; Yu, W.J.; Jeong, J.S.; Park, I.H.; Lee, B.C.; Jee, S.H.; Lim, K.M.; et al. Transcriptome-Metabolome-Wide Association Study (TMWAS) in Rats Revealed a Potential Carcinogenic Effect of DEHP in Thyroid Associated with Eicosanoids. Envrion. Res. 2022, 214, 113805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akash, M.S.H.; Rasheed, S.; Rehman, K.; Imran, M.; Assiri, M.A. Toxicological Evaluation of Bisphenol Analogues: Preventive Measures and Therapeutic Interventions. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 21613–21628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Gandhi, S.; Tripathi, A.D.; Gupta, A.; Iammarino, M.; Sidhu, J.K. Food Contamination from Packaging Material with Special Focus on the Bisphenol-A. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2024, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estévez-Danta, A.; Rodil, R.; Quintana, J.B.; Montes, R. Determination of the Urinary Concentrations of Six Bisphenols in Public Servants by Online Solid-Phase Extraction-Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2024, 416, 4469–4480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derakhshan, A.; Philips, E.M.; Ghassabian, A.; Santos, S.; Asimakopoulos, A.G.; Kannan, K.; Kortenkamp, A.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Trasande, L.; Peeters, R.P.; et al. Association of Urinary Bisphenols during Pregnancy with Maternal, Cord Blood and Childhood Thyroid Function. Envrion. Int. 2021, 146, 106160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhamad, M.S.; Salim, M.R.; Lau, W.J.; Yusop, Z. A Review on Bisphenol A Occurrences, Health Effects and Treatment Process via Membrane Technology for Drinking Water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 11549–11567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriyama, K.; Tagami, T.; Akamizu, T.; Usui, T.; Saijo, M.; Kanamoto, N.; Hataya, Y.; Shimatsu, A.; Kuzuya, H.; Nakao, K. Thyroid Hormone Action Is Disrupted by Bisphenol A as an Antagonist. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 5185–5190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoeller, R.T.; Bansal, R.; Parris, C. Bisphenol-A, an Environmental Contaminant That Acts as a Thyroid Hormone Receptor Antagonist in Vitro, Increases Serum Thyroxine, and Alters RC3/Neurogranin Expression in the Developing Rat Brain. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavreva, D.A.; Varticovski, L.; Levkova, L.; George, A.A.; Davis, L.; Pegoraro, G.; Blazer, V.; Iwanowicz, L.; Hager, G.L. Novel Cell-Based Assay for Detection of Thyroid Receptor Beta-Interacting Environmental Contaminants. Toxicology 2016, 368–369, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, Z.G.; Tang, Y.; Liu, Y.X.; Yuan, Y.; Zhao, B.Q.; Chao, X.J.; Zhu, B.Z. Low Concentrations of Bisphenol a Suppress Thyroid Hormone Receptor Transcription through a Nongenomic Mechanism. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 259, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meeker, J.D.; Ferguson, K.K. Relationship between Urinary Phthalate and Bisphenol a Concentrations and Serum Thyroid Measures in u.s. Adults and Adolescents from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2007–2008. Envrion. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 1396–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sriphrapradang, C.; Chailurkit, L.O.; Aekplakorn, W.; Ongphiphadhanakul, B. Association between Bisphenol A and Abnormal Free Thyroxine Level in Men. Endocrine 2013, 44, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.; Du, X.; Liu, H.; Guo, X.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, H.; Guo, H. Association between Bisphenol A Exposure and Thyroid Dysfunction in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2023, 39, 188–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevrier, J.; Gunier, R.B.; Bradman, A.; Holland, N.T.; Calafat, A.M.; Eskenazi, B.; Harley, K.G. Maternal Urinary Bisphenol a during Pregnancy and Maternal and Neonatal Thyroid Function in the CHAMACOS Study. Envrion. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, M.E.; Webster, G.M.; Vuong, A.M.; Thomas Zoeller, R.; Chen, A.; Hoofnagle, A.N.; Calafat, A.M.; Karagas, M.R.; Yolton, K.; Lanphear, B.P.; et al. Gestational Urinary Bisphenol A and Maternal and Newborn Thyroid Hormone Concentrations: The HOME Study. Envrion. Res. 2015, 138, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Choi, W.; Hwang, M.; Lee, Y.; Kim, S.; Yu, S.; Lee, I.; Paek, D.; Choi, K. Associations between Urinary Phthalate Metabolites and Bisphenol A Levels, and Serum Thyroid Hormones among the Korean Adult Population—Korean National Environmental Health Survey (KoNEHS) 2012–2014. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584–585, 950–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minatoya, M.; Sasaki, S.; Araki, A.; Miyashita, C.; Itoh, S.; Yamamoto, J.; Matsumura, T.; Mitsui, T.; Moriya, K.; Cho, K.; et al. Cord Blood Bisphenol A Levels and Reproductive and Thyroid Hormone Levels of Neonates The Hokkaido Study on Environment and Children’s Health. Epidemiology 2017, 28, S3–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanlidag, B.; Dalkan, C.; Yetkin, O.; Bahçeciler, N.N. Evaluation of Dose Dependent Maternal Exposure to Bisphenol a on Thyroid Functions in Newborns. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.; Xu, L.; Dong, X.; Cao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, K.; Guo, M.; Xu, S.; Li, Y.; Xia, W.; et al. Trimester-Specific Associations of Maternal Exposure to Bisphenols with Neonatal Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Levels: A Birth Cohort Study. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 880, 163354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chailurkit, L.O.; Aekplakorn, W.; Ongphiphadhanakul, B. The Association of Serum Bisphenol A with Thyroid Autoimmunity. Int. J. Envrion. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Gao, X.; Jin, H.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Qu, P.; et al. Bisphenol A at a Human Exposed Level Can Promote Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Harbouring BRAFV600E Mutation. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 1739–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Guo, N.; Jin, H.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, C.; Fan, Z.; Zhang, G.; Xiao, M.; Wu, S.; et al. Bisphenol A Drives Di(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate Promoting Thyroid Tumorigenesis via Regulating HDAC6/PTEN and c-MYC Signaling. J. Hazard Mater. 2022, 425, 127911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.P.; Yang, P.; Liu, C.; Deng, Y.L.; Luo, Q.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Cui, F.P.; Zeng, J.Y.; Shi, T.; et al. Urinary Concentrations of Phenols, Oxidative Stress Biomarkers and Thyroid Cancer: Exploring Associations and Mediation Effects. J. Envrion. Sci. 2022, 120, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Bai, X.; Lu, J.; Zou, R.; Ding, R.; Hua, X. Assessment of Five Typical Environmental Endocrine Disruptors and Thyroid Cancer Risk: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1283087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, K.; Miyagawa, M.; Wang, R.S.; Suda, M.; Sekiguchi, S.; Honma, T. Effects of in Utero and Lactational Exposure to Bisphenol A on Thyroid Status in F1 Rat Offspring. Ind. Health 2005, 43, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.G. Maternal Bisphenol A Alters Fetal Endocrine System: Thyroid Adipokine Dysfunction. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 95, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, M.O.; Bourguignon, N.S.; Arocena, P.; Rosa, M.; Libertun, C.; Lux-Lantos, V. Neonatal Exposure to Bisphenol A Alters the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Thyroid Axis in Female Rats. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 285, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, B.S.; Bertasso, I.M.; Pietrobon, C.B.; Lopes, B.P.; Santos, T.R.; Peixoto-Silva, N.; Carvalho, J.C.; Claudio-Neto, S.; Manhães, A.C.; Cabral, S.S.; et al. Effects of Maternal Bisphenol A on Behavior, Sex Steroid and Thyroid Hormones Levels in the Adult Rat Offspring. Life Sci. 2019, 218, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viguié, C.; Collet, S.H.; Gayrard, V.; Picard-Hagen, N.; Puel, S.; Roques, B.B.; Toutain, P.L.; Lacroix, M.Z. Maternal and Fetal Exposure to Bisphenol A Is Associated with Alterations of Thyroid Function in Pregnant Ewes and Their Newborn Lambs. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guignard, D.; Gayrard, V.; Lacroix, M.Z.; Puel, S.; Picard-Hagen, N.; Viguié, C. Evidence for Bisphenol A-Induced Disruption of Maternal Thyroid Homeostasis in the Pregnant Ewe at Low Level Representative of Human Exposure. Chemosphere 2017, 182, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwamuro, S.; Sakakibara, M.; Terao, M.; Ozawa, A.; Kurobe, C.; Shigeura, T.; Kato, M.; Kikuyama, S. Teratogenic and Anti-Metamorphic Effects of Bisphenol A on Embryonic and Larval Xenopus Laevis. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2003, 133, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwamuro, S.; Yamada, M.; Kato, M.; Kikuyama, S. Effects of Bisphenol A on Thyroid Hormone-Dependent up-Regulation of Thyroid Hormone Receptor α and β and down-Regulation of Retinoid X Receptor γ in Xenopus Tail Culture. Life Sci. 2006, 79, 2165–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Y.; Zhu, M.; Song, S.; Qin, Z. A Multiwell-Based Assay for Screening Thyroid Hormone Signaling Disruptors Using Thibz Expression as a Sensitive Endpoint in Xenopus Laevis. Molecules 2022, 27, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volz, S.N.; Poulsen, R.; Hansen, M.; Holbech, H. Bisphenol A Alters Retinal Morphology, Visually Guided Behavior, and Thyroid Hormone Levels in Zebrafish Larvae. Chemosphere 2024, 348, 140776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentilcore, D.; Porreca, I.; Rizzo, F.; Ganbaatar, E.; Carchia, E.; Mallardo, M.; De Felice, M.; Ambrosino, C. Bisphenol A Interferes with Thyroid Specific Gene Expression. Toxicology 2013, 304, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Beland, F.A.; Fang, J.L. Effect of Triclosan, Triclocarban, 2,2′,4,4′-Tetrabromodiphenyl Ether, and Bisphenol A on the Iodide Uptake, Thyroid Peroxidase Activity, and Expression of Genes Involved in Thyroid Hormone Synthesis. Toxicol. Vitr. 2016, 32, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porreca, I.; Ulloa Severino, L.; D’Angelo, F.; Cuomo, D.; Ceccarelli, M.; Altucci, L.; Amendola, E.; Nebbioso, A.; Mallardo, M.; De Felice, M.; et al. “Stockpile” of Slight Transcriptomic Changes Determines the Indirect Genotoxicity of Low-Dose BPA in Thyroid Cells. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, M.M.; Xavier, L.L.F.; Gonçalves, C.F.L.; Santos-Silva, A.P.; Paiva-Melo, F.D.; De Freitas, M.L.; Fortunato, R.S.; Miranda-Alves, L.; Ferreira, A.C.F. Bisphenol a Increases Hydrogen Peroxide Generation by Thyrocytes Both in Vivo and in Vitro. Endocr. Connect. 2018, 7, 1196–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.F.; Ren, X.M.; Li, Y.Y.; Yao, X.F.; Li, C.H.; Qin, Z.F.; Guo, L.H. Bisphenol A Alternatives Bisphenol S and Bisphenol F Interfere with Thyroid Hormone Signaling Pathway in Vitro and in Vivo. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 1072–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Chen, X.Y.; Li, Y.Y.; Yin, N.Y.; Faiola, F.; Qin, Z.F.; Wei, W.J. Bisphenol F Disrupts Thyroid Hormone Signaling and Postembryonic Development in Xenopus Laevis. Envrion. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1602–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berto-Júnior, C.; Santos-Silva, A.P.; Ferreira, A.C.F.; Graceli, J.B.; de Carvalho, D.P.; Soares, P.; Romeiro, N.C.; Miranda-Alves, L. Unraveling Molecular Targets of Bisphenol A and S in the Thyroid Gland. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 26916–26926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Xu, Y.; Wang, M.; Cui, S.; Zhang, H.; Lu, L. Bisphenol Analogues Induce Thyroid Dysfunction via the Disruption of the Thyroid Hormone Synthesis Pathway. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 900, 165711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turusov, V.; Rakitsky, V.; Tomatis, L. Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT): Ubiquity, Persistence, and Risks. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolley, D.E.; Talens, G.M. Distribution of DDT, DDD, and DDE in Tissues of Neonatal Rats and in Milk and Other Tissues of Mother Rats Chronically Exposed to DDT. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1971, 18, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-gallardo, M.I.; Guallar, E.; Martín-moreno, J.M.; Van ’T Veer, P.; Kok, F.J.; Longnecker, M.P.; Strain, J.J.; Martin, B.C.; Kardinaal, A.F.M.; Fernández-Crehuet, J.; et al. Determinants of p, p′-Dichlorodiphenyldichloroethane (DDE) Concentration in Adipose Tissue in Women from Five European Cities. Arch. Envrion. Health 1999, 54, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makgoba, L.; Abrams, A.; Röösli, M.; Cissé, G.; Dalvie, M.A. DDT Contamination in Water Resources of Some African Countries and Its Impact on Water Quality and Human Health. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio-Vargas, D.A.; de Morais, T.P.; Randi, M.A.F.; Filipak Neto, F.; Ortolani-Machado, C.F.; Martins, C.d.C.; Oliveira, A.P.; Nazário, M.G.; da, S. Ferreira, F.C.A.; Opuskevitch, I.; et al. Multispecies and Multibiomarker Assessment of Fish Health from Iguaçu River Reservoir, Southern Brazil. Envrion. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cody, V. Conformational Analysis of Environmental Agents: Use of X-ray Crystallographic Data to Determine Molecular Reactivity. Envrion. Health Perspect. 1985, 61, 163–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Shi, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, K. P, p-DDE Disturbs the Homeostasis of Thyroid Hormones via Thyroid Hormone Receptors, Transthyretin, and Hepatic Enzymes. Horm. Metab. Res. 2011, 43, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheek, A.O.; Kow, K.; Chen, J.; McLachlan, J.A. Potential Mechanisms of Thyroid Disruption in Humans: Interaction of Organochlorine Compounds with Thyroid Receptor, Transthyretin, and Thyroid-Binding Globulin. Envrion. Health Perspect. 1999, 107, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Leary, J.A.; Davies, J.E.; Edmundson, W.F.; Reich, G.A. Transplacental Passage of Pesticides. Am. J. Obs. Gynecol. 1970, 107, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueiredo, T.M.; Santana, J.d.M.; Granzotto, F.H.B.; dos Anjos, B.S.; Guerra Neto, D.; Azevedo, L.M.G.; Pereira, M. Pesticide Contamination of Lactating Mothers’ Milk in Latin America: A Systematic Review. Rev. Saude Publica 2024, 58, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Cho, Y.H.; Won, S.; Ku, J.L.; Moon, H.B.; Park, J.; Choi, G.; Kim, S.; Choi, K. Maternal Exposures to Persistent Organic Pollutants Are Associated with DNA Methylation of Thyroid Hormone-Related Genes in Placenta Differently by Infant Sex. Envrion. Int. 2019, 130, 104956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.; da Cruz, R.S.; Nascimento, A.; Joshi, M.; Pereira, D.G.; Dominguez, O.; Fernandes, G.; Smith, M.; Paiva, S.P.C.; de Assis, S. Paternal DDT Exposure Induces Sex-Specific Programming of Fetal Growth, Placenta Development and Offspring’s Health Phenotypes in a Mouse Model. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 7567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, K.; Itoh, S.; Araki, A.; Miyashita, C.; Minatoya, M.; Ikeno, T.; Kato, S.; Fujikura, K.; Mizutani, F.; Chisaki, Y.; et al. Associations between Prenatal Exposure to Organochlorine Pesticides and Thyroid Hormone Levels in Mothers and Infants: The Hokkaido Study on Environment and Children’s Health. Envrion. Res. 2020, 189, 109840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takser, L.; Mergler, D.; Baldwin, M.; de Grosbois, S.; Smargiassi, A.; Lafond, J. Thyroid Hormones in Pregnancy in Relation to Environmental Exposure to Organochlorine Compounds and Mercury. Envrion. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 1039–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Pu, Y.; Tian, H.; Wu, W.; Sun, X.; Zhou, T.; Tao, Y.; Yuan, J.; Shen, X.; Feng, Y.; et al. Association of in Utero Exposure to Organochlorine Pesticides with Thyroid Hormone Levels in Cord Blood of Newborns. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asawasinsopon, R.; Prapamontol, T.; Prakobvitayakit, O.; Vaneesorn, Y.; Mangklabruks, A.; Hock, B. The Association between Organochlorine and Thyroid Hormone Levels in Cord Serum: A Study from Northern Thailand. Envrion. Int. 2006, 32, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kezios, K.L.; Liu, X.; Cirillo, P.M.; Cohn, B.A.; Kalantzi, O.I.; Wang, Y.; Petreas, M.X.; Park, J.S.; Factor-Litvak, P. Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT), DDT Metabolites and Pregnancy Outcomes. Reprod. Toxicol. 2013, 35, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevrier, J.; Eskenazi, B.; Holland, N.; Bradman, A.; Barr, D.B. Effects of Exposure to Polychlorinated Biphenyls and Organochlorine Pesticides on Thyroid Function during Pregnancy. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2008, 168, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Mariano, J.Á.; Torres-Sánchez, L.; Bassol-Mayagoitia, S.; Escamilla-Nuñez, M.C.; Cebrian, M.E.; Villeda-Gutiérrez, É.A.; López-Rodríguez, G.; Félix-Arellano, E.E.; Blanco-Muñoz, J. Effect of Exposure to p,p′-DDE during the First Half of Pregnancy in the Maternal Thyroid Profile of Female Residents in a Mexican Floriculture Area. Envrion. Res. 2017, 156, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Espinosa, M.J.; Vizcaino, E.; Murcia, M.; Llop, S.; Espada, M.; Seco, V.; Marco, A.; Rebagliato, M.; Grimalt, J.O.; Ballester, F. Association between Thyroid Hormone Levels and 4,4′-DDE Concentrations in Pregnant Women (Valencia, Spain). Envrion. Res. 2009, 109, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrebola, J.P.; Cuellar, M.; Bonde, J.P.; González-Alzaga, B.; Mercado, L.A. Associations of Maternal o,P′-DDT and p,P′-DDE Levels with Birth Outcomes in a Bolivian Cohort. Envrion. Res. 2016, 151, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, C.C.; Que, D.E.; Bongo, S.J.; Tayo, L.L.; Lin, Y.H.; Lin, C.W.; Lin, S.L.; Gou, Y.Y.; Hsu, W.L.; Shy, C.G.; et al. Residue Levels of Organochlorine Pesticides in Breast Milk and Its Associations with Cord Blood Thyroid Hormones and the Offspring’s Neurodevelopment. Int. J. Envrion. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Pedrerol, M.; Ribas-Fitó, N.; Torrent, M.; Carrizo, D.; Grimalt, J.O.; Sunyer, J. Effects of PCBs, p,p′-DDT, p,p′-DDE, HCB and β-HCH on Thyroid Function in Preschool Children. Occup. Envrion. Med. 2008, 65, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagmar, L.; Björk, J.; Sjödin, A.; Bergman, Å.; Erfurth, E.M. Plasma Levels of Persistent Organohalogens and Hormone Levels in Adult Male Humans. Arch. Envrion. Health 2001, 56, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura-Ogasawara, M.; Ozaki, Y.; Sonta, S.I.; Makino, T.; Suzumori, K. PCBs, Hexachlorobenzene and DDE Are Not Associated with Recurrent Miscarriage. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2003, 50, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour, P.; Pirard, C.; Petrossians, P.; Beckers, A.; Charlier, C. Association between Mixture of Persistent Organic Pollutants and Thyroid Pathologies in a Belgian Population. Envrion. Res. 2020, 181, 108922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rylander, L.; Wallin, E.; Jönssson, B.A.; Stridsberg, M.; Erfurth, E.M.; Hagmar, L. Associations between CB-153 and p,p′-DDE and Hormone Levels in Serum in Middle-Aged and Elderly Men. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freire, C.; Koifman, R.J.; Sarcinelli, P.N.; Simões Rosa, A.C.; Clapauch, R.; Koifman, S. Long-Term Exposure to Organochlorine Pesticides and Thyroid Status in Adults in a Heavily Contaminated Area in Brazil. Envrion. Res. 2013, 127, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meeker, J.D.; Altshul, L.; Hauser, R. Serum PCBs, p, p′-DDE and HCB Predict Thyroid Hormone Levels in Men. Envrion. Res. 2007, 104, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Ru, H.; Ni, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xie, H.; Yao, F.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhong, L. Comparative Thyroid Disruption by o,p′-DDT and p,p′-DDE in Zebrafish Embryos/Larvae. Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 216, 105280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, J.C.; Frame, S.R.; Davis, L.G.; Cook, J.C. Detection of the Environmental Antiandrogen p,p′-DDE in CD and Long- Evans Rats Using a Tier I Screening Battery and a Hershberger Assay. Toxicol. Sci. 1999, 51, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ha, M.; Li, L.; Yang, K. PCB153 and p,p′-DDE Disorder Thyroid Hormones via Thyroglobulin, Deiodinase 2, Transthyretin, Hepatic Enzymes and Receptors. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 11361–11369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaglova, N.V.; Yaglov, V.V. Mechanisms of Disruptive Action of Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) on the Function of Thyroid Follicular Epitheliocytes. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2015, 160, 231–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaglova, N.V.; Sledneva, Y.P.; Yaglov, V.V. Morphofunctional Changes in the Thyroid Gland of Pubertal and Postpubertal Rats Exposed to Low Dose of DDT. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2016, 162, 260–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaglova, N.V.; Yaglov, V.V. Altered Thyroid Hormone Production Induced by Long-Term Exposure to Low Doses of the Endocrine Disruptor Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane. Biochem. Mosc. Suppl. B Biomed. Chem. 2015, 9, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaglova, N.V.; Yaglov, V.V. Changes in Thyroid Status of Rats after Prolonged Exposure to Low Dose Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2014, 156, 760–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coperchini, F.; Teliti, M.; Greco, A.; Croce, L.; Rotondi, M. Per-Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) as Thyroid Disruptors: Is There Evidence for Multi-Transgenerational Effects? Expert. Rev. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 19, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panieri, E.; Baralic, K.; Djukic-Cosic, D.; Djordjevic, A.B.; Saso, L. PFAS Molecules: A Major Concern for the Human Health and the Environment. Toxics 2022, 10, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenland, K.; Winquist, A. PFAS and Cancer, a Scoping Review of the Epidemiologic Evidence. Environ. Res. 2021, 194, 110690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coperchini, F.; Awwad, O.; Rotondi, M.; Santini, F.; Imbriani, M.; Chiovato, L. Thyroid Disruption by Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) and Perfluorooctanoate (PFOA). J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2017, 40, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coperchini, F.; De Marco, G.; Croce, L.; Denegri, M.; Greco, A.; Magri, F.; Tonacchera, M.; Imbriani, M.; Rotondi, M.; Chiovato, L. PFOA, PFHxA and C6O4 Differently Modulate the Expression of CXCL8 in Normal Thyroid Cells and in Thyroid Cancer Cell Lines. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 63522–63534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Gerwen, M.; Colicino, E.; Guan, H.; Dolios, G.; Nadkarni, G.N.; Vermeulen, R.C.H.; Wolff, M.S.; Arora, M.; Genden, E.M.; Petrick, L.M. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Exposure and Thyroid Cancer Risk. eBioMedicine 2023, 97, 104831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Starling, A.P.; Haug, L.S.; Eggesbo, M.; Becher, G.; Thomsen, C.; Travlos, G.; King, D.; Hoppin, J.A.; Rogan, W.J.; et al. Association between Perfluoroalkyl Substances and Thyroid Stimulating Hormone among Pregnant Women: A Cross-Sectional Study. Envrion. Health 2013, 12, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Rogan, W.J.; Chen, P.C.; Lien, G.W.; Chen, H.Y.; Tseng, Y.C.; Longnecker, M.P.; Wang, S.L. Association between Maternal Serum Perfluoroalkyl Substances during Pregnancy and Maternal and Cord Thyroid Hormones: Taiwan Maternal and Infant Cohort Study. Envrion. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, J.; Lai, J.; Luan, H.; Cai, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y. Placental Transfer of Perfluoroalkyl Substances and Associations with Thyroid Hormones: Beijing Prenatal Exposure Study. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derakhshan, A.; Kortenkamp, A.; Shu, H.; Broeren, M.A.C.; Lindh, C.H.; Peeters, R.P.; Bornehag, C.G.; Demeneix, B.; Korevaar, T.I.M. Association of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances with Thyroid Homeostasis during Pregnancy in the SELMA Study. Envrion. Int. 2022, 167, 107420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, E.V.; Webster, T.F.; Claus Henn, B.; McClean, M.D.; Gennings, C.; Oken, E.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Pearce, E.N.; Calafat, A.M.; Fleisch, A.F.; et al. Prenatal Exposure to Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances and Maternal and Neonatal Thyroid Function in the Project Viva Cohort: A Mixtures Approach. Envrion. Int. 2020, 139, 105728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.; Wang, Z.; Miao, M.; Tian, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wen, S.; Chen, Y.; Sun, X.; Yuan, W. Prenatal Exposure to Perfluoroalkyl Substances and Thyroid Hormone Concentrations in Cord Plasma in a Chinese Birth Cohort. Envrion. Health 2020, 19, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, E.V.; Webster, T.F.; Oken, E.; Henn, B.C.; McClean, M.D.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Pearce, E.N.; Braverman, L.E.; Calafat, A.M.; Ye, X.; et al. Maternal Plasma Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substance Concentrations in Early Pregnancy and Maternal and Neonatal Thyroid Function in a Prospective Birth Cohort: Project Viva (USA). Envrion. Health Perspect. 2018, 126, 027013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, S.; Araki, A.; Miyashita, C.; Yamazaki, K.; Goudarzi, H.; Minatoya, M.; Ait Bamai, Y.; Kobayashi, S.; Okada, E.; Kashino, I.; et al. Association between Perfluoroalkyl Substance Exposure and Thyroid Hormone/Thyroid Antibody Levels in Maternal and Cord Blood: The Hokkaido Study. Envrion. Int. 2019, 133, 105139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Vinturache, A.; Lei, X.; Wang, Z.; Pan, C.; Shi, R.; Yuan, T.; Gao, Y.; Tian, Y. Prenatal Exposure to Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances, Fetal Thyroid Hormones, and Infant Neurodevelopment. Envrion. Res. 2022, 206, 112561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Dai, Y.; Ding, J.; Guo, J.; Qi, X.; Wu, C.; Zhou, Z. Prenatal Exposure to Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances, Fetal Thyroid Function, and Intelligence Quotient at 7 Years of Age: Findings from the Sheyang Mini Birth Cohort Study. Envrion. Int. 2024, 187, 108720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Kim, U.J.; Kim, H.Y.; Choi, S.D.; Oh, J.E. Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Serum from South Korean Infants with Congenital Hypothyroidism and Healthy Infants—Its Relationship with Thyroid Hormones. Envrion. Res. 2016, 147, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, G.M.; Rauch, S.A.; Marie, N.S.; Mattman, A.; Lanphear, B.P.; Venners, S.A. Cross-Sectional Associations of Serum Perfluoroalkyl Acids and Thyroid Hormones in U.S. Adults: Variation According to TPOAb and Iodine Status (NHANES 2007-2008). Envrion. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, E.; Barbiellini Amidei, C.; Barbieri, G.; Fabricio, A.S.C.; Gion, M.; Pitter, G.; Daprà, F.; Russo, F.; Gregori, D.; Fletcher, T.; et al. Perfluoroalkyl Substances and Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Levels in a Highly Exposed Population in the Veneto Region. Envrion. Res. 2022, 203, 111794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Carrillo, A.; Salamanca-Fernández, E.; den Hond, E.; Verheyen, V.J.; Fábelová, L.; Murinova, L.P.; Pedraza-Díaz, S.; Castaño, A.; García-Lario, J.V.; Remy, S.; et al. Association of Exposure to Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) and Phthalates with Thyroid Hormones in Adolescents from HBM4EU Aligned Studies. Envrion. Res. 2023, 237, 116897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Hu, C.; Wang, L.; Liu, H.; Tian, Z. Associations between Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances Exposure and Thyroid Hormone Levels in the Elderly. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 920, 170761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liang, J.; Gao, A. Contact to Perfluoroalkyl Substances and Thyroid Health Effects: A Meta-Analysis Directing on Pregnancy. Chemosphere 2023, 315, 137748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curran, I.; Hierlihy, S.L.; Liston, V.; Pantazopoulos, P.; Nunnikhoven, A.; Tittlemier, S.; Barker, M.; Trick, K.; Bondy, G. Altered Fatty Acid Homeostasis and Related Toxicologic Sequelae in Rats Exposed to Dietary Potassium Perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS). J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A Curr. Issues 2008, 71, 1526–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.C.; Thibodeaux, J.R.; Eastvold, M.L.; Ehresman, D.J.; Bjork, J.A.; Froehlich, J.W.; Lau, C.; Singh, R.J.; Wallace, K.B.; Butenhoff, J.L. Thyroid Hormone Status and Pituitary Function in Adult Rats given Oral Doses of Perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS). Toxicology 2008, 243, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.; Curran, I.; Williams, A.; Bondy, G.; Yauk, C.L.; Wade, M.G. Hepatic MiRNA Profiles and Thyroid Hormone Homeostasis in Rats Exposed to Dietary Potassium Perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS). Envrion. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 41, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidsen, N.; Ramhøj, L.; Lykkebo, C.A.; Kugathas, I.; Poulsen, R.; Rosenmai, A.K.; Evrard, B.; Darde, T.A.; Axelstad, M.; Bahl, M.I.; et al. PFOS-Induced Thyroid Hormone System Disrupted Rats Display Organ-Specific Changes in Their Transcriptomes. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 305, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidsen, N.; Ramhøj, L.; Ballegaard, A.S.R.; Rosenmai, A.K.; Henriksen, C.S.; Svingen, T. Perfluorooctanesulfonic Acid (PFOS) Disrupts Cadherin-16 in the Developing Rat Thyroid Gland. Curr. Res. Toxicol. 2024, 6, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiter, S.; Baumann, L.; Färber, H.; Holbech, H.; Skutlarek, D.; Engwall, M.; Braunbeck, T. Long-Term Effects of a Binary Mixture of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) and Bisphenol A (BPA) in Zebrafish (Danio Rerio). Aquat. Toxicol. 2012, 118–119, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Liu, C.; Wu, G.; Zhou, B. Waterborne Exposure to PFOS Causes Disruption of the Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Thyroid Axis in Zebrafish Larvae. Chemosphere 2009, 77, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Guo, X.; Lu, S.; Sang, N.; Li, G.; Xie, P.; Liu, C.; Zhang, L.; Xing, Y. Exposure to PFDoA Causes Disruption of the Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Thyroid Axis in Zebrafish Larvae. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degitz, S.J.; Degoey, P.P.; Haselman, J.T.; Olker, J.H.; Stacy, E.H.; Blanksma, C.; Meyer, S.; Mattingly, K.Z.; Blackwell, B.; Opseth, A.S.; et al. Evaluating Potential Developmental Toxicity of Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Xenopus laevis Embryos and Larvae. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2024, 44, 1040–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crute, C.E.; Hall, S.M.; Landon, C.D.; Garner, A.; Everitt, J.I.; Zhang, S.; Blake, B.; Olofsson, D.; Chen, H.; Murphy, S.K.; et al. Evaluating Maternal Exposure to an Environmental per and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Mixture during Pregnancy: Adverse Maternal and Fetoplacental Effects in a New Zealand White (NZW) Rabbit Model. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conti, A.; Strazzeri, C.; Rhoden, K.J. Perfluorooctane Sulfonic Acid, a Persistent Organic Pollutant, Inhibits Iodide Accumulation by Thyroid Follicular Cells in Vitro. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2020, 515, 110922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Toni, L.; Di Nisio, A.; Rocca, M.S.; Pedrucci, F.; Garolla, A.; Dall’Acqua, S.; Guidolin, D.; Ferlin, A.; Foresta, C. Comparative Evaluation of the Effects of Legacy and New Generation Perfluoralkyl Substances (PFAS) on Thyroid Cells In Vitro. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 915096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoker, T.E.; Wang, J.; Murr, A.S.; Bailey, J.R.; Buckalew, A.R. High-Throughput Screening of ToxCast PFAS Chemical Library for Potential Inhibitors of the Human Sodium Iodide Symporter. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2023, 36, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Kim, Y.J.; Park, Y.K.; Ryu, J.C. Changes in Thyroid Peroxidase Activity in Response to Various Chemicals. J. Environ. Monit. 2012, 14, 2121–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croce, L.; Coperchini, F.; Tonacchera, M.; Imbriani, M.; Rotondi, M.; Chiovato, L. Effect of Long- and Short-Chain Perfluorinated Compounds on Cultured Thyroid Cells Viability and Response to TSH. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2019, 42, 2121–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coperchini, F.; Greco, A.; Rotondi, M. Changing the Structure of PFOA and PFOS: A Chemical Industry Strategy or a Solution to Avoid Thyroid-Disrupting Effects? J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2024, 47, 1863–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Guo, H.; Wang, J.; Dai, J. Hepatotoxicity of Perfluorooctanoic Acid and Two Emerging Alternatives Based on a 3D Spheroid Model. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coperchini, F.; Croce, L.; Denegri, M.; Pignatti, P.; Agozzino, M.; Netti, G.S.; Imbriani, M.; Rotondi, M.; Chiovato, L. Adverse Effects of in Vitro GenX Exposure on Rat Thyroid Cell Viability, DNA Integrity and Thyroid-Related Genes Expression. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coperchini, F.; Pignatti, P.; Lacerenza, S.; Negri, S.; Sideri, R.; Testoni, C.; de Martinis, L.; Cottica, D.; Magri, F.; Imbriani, M.; et al. Exposure to Perfluorinated Compounds: In Vitro Study on Thyroid Cells. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 2287–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, K.; Li, W.; Chai, Y.; Zhu, J.; Chu, B.; Li, N.; Yan, J.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Y. Varied Thyroid Disrupting Effects of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) and Its Novel Alternatives Hexafluoropropylene-Oxide-Dimer-Acid (GenX) and Ammonium 4,8-Dioxa-3H-Perfluorononanoate (ADONA) in Vitro. Envrion. Int. 2021, 156, 106745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coperchini, F.; Croce, L.; Pignatti, P.; Ricci, G.; Gangemi, D.; Magri, F.; Imbriani, M.; Rotondi, M.; Chiovato, L. The New Generation PFAS C6O4 Does Not Produce Adverse Effects on Thyroid Cells in Vitro. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2021, 44, 1625–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yan, P.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Tian, M.; Huang, Q.; Yan, J.; Tong, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; et al. Profiles and transplacental transfer of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in maternal and umbilical cord blood: A birth cohort study in Zhoushan, Zhejiang Province, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 466, 133501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, L.; Shi, Z. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Exposure Might Be a Risk Factor for Thyroid Cancer. eBioMedicine 2023, 98, 104866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirello, V.; Lugaresi, M.; Moneta, C.; Dufour, P.; Manzo, A.; Carbone, E.; Colombo, C.; Fugazzola, L.; Charlier, C.; Pirard, C. Thyroid Cancer and Endocrine Disruptive Chemicals: A Case–Control Study on per-Fluoroalkyl Substances and Other Persistent Organic Pollutants. Eur. Thyroid J. 2024, 13, e230192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durham, J.; Tessmann, J.W.; Deng, P.; Hennig, B.; Zaytseva, Y.Y. The Role of Perfluorooctane Sulfonic Acid (PFOS) Exposure in Inflammation of Intestinal Tissues and Intestinal Carcinogenesis. Front. Toxicol. 2023, 5, 1244457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsen, M.; Leung, A.M.; van Gerwen, M. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Community Water Systems (CWS) and the Risk of Thyroid Cancer: An Ecological Study. Toxics 2023, 11, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Thapar, I.; Brooks, B.W. Epigenetic Changes by Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS). Environ. Pollut. 2021, 279, 116929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coperchini, F.; Greco, A.; Croce, L.; Teliti, M.; Calì, B.; Chytiris, S.; Magri, F.; Rotondi, M. Do PFCAs Drive the Establishment of Thyroid Cancer Microenvironment? Effects of C6O4, PFOA and PFHxA Exposure in Two Models of Human Thyroid Cells in Primary Culture. Envrion. Int. 2024, 187, 108717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Liu, P.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J. The Adverse Role of Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals in the Reproductive System. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 14, 1324993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mínguez-Alarcón, L.; Gaskins, A.J.; Meeker, J.D.; Braun, J.M.; Chavarro, J.E. Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals and Male Reproductive Health. Fertil. Steril. 2023, 120, 1138–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal-Cevallos, P.; Murúa-Beltrán Gall, S.; Uribe, M.; Chávez-Tapia, N.C. Understanding the Relationship between Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Thyroid Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olanrewaju, O.A.; Asghar, R.; Makwana, S.; Yahya, M.; Kumar, N.; Khawar, M.H.; Ahmed, A.; Islam, T.; Kumari, K.; Shadmani, S.; et al. Thyroid and Its Ripple Effect: Impact on Cardiac Structure, Function, and Outcomes. Cureus 2024, 16, e51574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salari, N.; Fattahi, N.; Abdolmaleki, A.; Heidarian, P.; Shohaimi, S.; Mohammadi, M. The Global Prevalence of Sexual Dysfunction in Men with Thyroid Gland Disorders: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2024, 23, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).