Abstract
The autosomal dominant familial form of neurohypophyseal diabetes insipidus (adFNDI) is a rare inherited endocrine disorder characterized by hypotonic polyuria, severe thirst and polydipsia, which results from a deficient neurosecretion of the antidiuretic hormone, also known as arginine vasopressin (AVP). To date, adFNDI has been linked to more than 70 different heterozygous point mutations of the 2.5 kb AVP gene, encoding the composite precursor protein of AVP. A minority of disease-causing mutations, such as the common c.55G>A variant, are predicted to affect amino acid residues close to the signal peptide (SP) cleavage site, and result in abnormal post-translational processing and intracellular trafficking of AVP precursors exerting neurotoxic activity on vasopressinergic magnocellular neurons. Generally, SP variants cause a gradual decline in the neurohypophyseal secretion of AVP in small children, although a wide variability in clinical onset and severity of manifestations has been reported. For the first time, we describe a kindred from Calabria (Southern Italy) with adFNDI and document a partial clinical phenotype in one female young adult member of the family. Methods: A young adult woman was subjected to clinical, neuroradiological and genetic assessments for a mild, adolescent-onset, polyuric state at our Endocrinology Unit. Her family medical history revealed an early-onset (<12 years of age) occurrence of polyuria and polydipsia, which was successfully managed with high doses of oral desmopressin, and a typical adFNDI inheritance pattern that was seen over three generations. Results: In the index patient, the extensive hypertonic dehydration during fluid deprivation test elicited a prompt elevation of urine osmolality and diuresis contraction, indicative of a partial adFNDI phenotype. Diagnosis was confirmed by concordant hormonal tests and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) evidence of a reduced hyperintense signal of the neurohypophysis, which was regarded as compatible with the depletion of the vasopressinergic magnocellular neurons. Direct DNA sequencing and restriction enzyme cleavage analysis revealed that a heterozygous c.55G>A transition, predicting a p.Ala19Thr replacement in the C-terminal region of SP, was the cause of adFNDI in the investigated kindred. Conclusions: The identification of the genetic cause of aFNDI in this Calabrian kindred provides further information and confirms the wide variability of disease onset and severity of manifestations related to SP variants of the AVP gene, supporting the need for genetic testing in all patients with familial occurrence of polyuria, regardless of their clinical and radiological phenotype. Even though sexual differences in the antidiuretic responses are documented, it is unclear whether female gender would attenuate clinical disease progression in the presence of a pathogenic c.55G>A mutation.
1. Introduction
Neurohypophyseal diabetes insipidus (NDI) is a rare and heterogeneous endocrine disorder characterized by hypotonic polyuria, severe thirst and polydipsia, which results from a deficient neurosecretion of the antidiuretic hormone, also known as arginine vasopressin (AVP). In the large majority of cases, it is caused by traumatic brain injury or tumors, and only 1% of the affected patients are diagnosed with an autosomal dominant familial form of NDI (adFNDI) [1,2]. To date, adFNDI has been linked to more than 70 heterozygous point mutations in different parts of the 2.5-kb AVP gene, located in chromosome region 20p13 and encoding the composite precursor protein of AVP (preproAVP) [1,3]. The AVP gene contains three coding exons and two introns: exon 1 encodes the signal peptide (SP), the nonapeptide AVP and the N-terminal of the carrier protein neurophysin II (NP); exon 2 encodes the central portion of NP; exon 3 encodes the C-terminal of NP and the hormone associated glycoprotein copeptin (CP) [1]. Normally, after mRNA translation, the preproAVP is converted to proAVP by cleavage of the SP moiety within the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), where proper folding, formation of disulfide-bridge pairing, dimerization and glycosylation reactions occur. Then, the appropriately folded proAVP is packaged into granules via the Golgi apparatus, and cleaved to yield mature AVP, NP, and CP during axonal transport to the neurohypophysis [4]. Upon appropriate secretory stimuli, such as rising plasma osmolality and arterial underfilling caused by dehydration, the mature AVP is released from the neurohypophysis to maximize water reabsorption in distal nephron segments and counteract fluid loss [5]. The mutation pattern of the AVP gene, initiating the pathogenic cascade of events in adFNDI, determines the accumulation of misfolded (or unfolded) AVP precursor proteins in the ER, causing ER stress and progressive degeneration of vasopressinergic magnocellular neurons [6,7]. A minority of AVP gene variants causing adFNDI, such as the common G to A transition in position 55 of the coding DNA reference sequence (c.55G>A), also known as g.279G>A, according to previous nomenclature based on genomic location, are predicted to affect amino acid residues close to the SP cleavage site [8,9], resulting in abnormal post-translational processing and intracellular trafficking of preproAVP and proAVP [10]. Generally, these SP mutations cause a gradual decline in neurohypophyseal secretion of AVP during the first years of life, although wide variations in the age of onset and severity of symptoms have been reported [10], and are speculated to be consequences of environmental factors and individual abilities of scavenging the retained pathogenic aggregates of AVP precursors [6,11,12].
Herein, we describe the first kindred from Calabria (Southern Italy) with adFNDI, characterized by an inhomogeneity in clinical onset and manifestations of disease, together with a documented partial clinical and neuroradiological phenotype in one female young adult member of the family, related to a heterozygous c.55G>A variant of the AVP gene.
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Clinical and Radiological Assessments
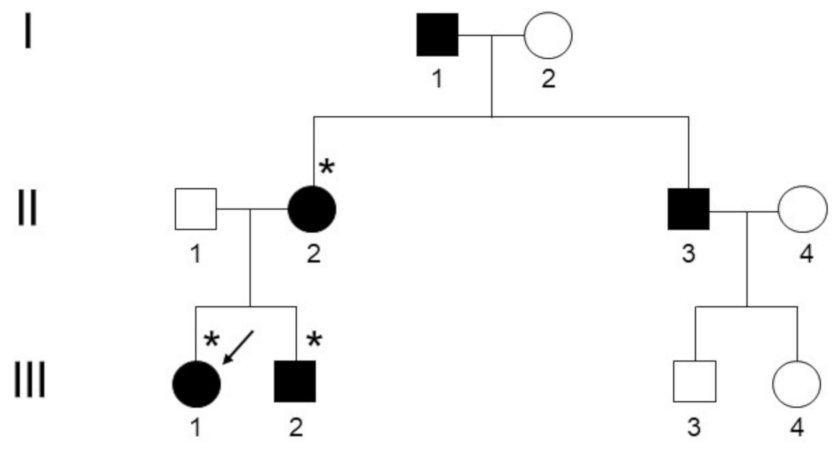
A young adult woman of 23 years of age, hereafter referred to as the index patient, sought medical attention at our endocrinology outpatient clinic (A.O.U. Mater-Domini, Catanzaro) for mild hypotonic polyuria and polydipsia (approximately 3 L/day of ad libitum fluid intake) from the age of 12. She was discharged from the pediatric practice with a diagnosis of NDI, stated ex adiuvantibus, and formerly treated with oral desmopressin (90 µg/day in 3 divided doses). A review of the past medical history revealed different early-onset autoimmune disorders, such as chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis and celiac disease, managed with thyroid hormone replacement therapy and a gluten-free diet, respectively. Due to notions of a familial occurrence of an undefined form of NDI in the kindred, additional relatives were contacted to determine disease status and onset and severity of symptoms. The pedigree, covering the indicated number of generations and consistent with a typical adFNDI inheritance pattern, was ascertained by personal interview with subjects III-1, II-2 and III-2 (Figure 1). The index patient was clinically assessed by plasma osmolality, plasma sodium, urine osmolality and diuresis during a standard fluid deprivation test, according to the Associazione Medici Endocrinologi (AME) medical guidelines [13], 24 h after the last desmopressin dose. Osmolality was automatically calculated from the actual concentrations of biochemical analytes (i.e., sodium, urea, and glucose) on the Roche Cobas 6000 system (Roche Diagnostics, Rotkreuz, Switzerland). Basal pituitary hormones (GH, prolactin, LH, FSH, TSH, and ACTH) serum levels in the morning (fasting status), as well as target hormones (IGF-1, cortisol) and AVP concentrations, were measured using sensitive immunoassay techniques. Sagittal and coronal T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans of the pituitary gland were obtained with and without gadolinium enhancement, using a 3T GE system (GE Healthcare, Rahway, NJ, USA) and compared with those of an age-matched unaffected control subject.
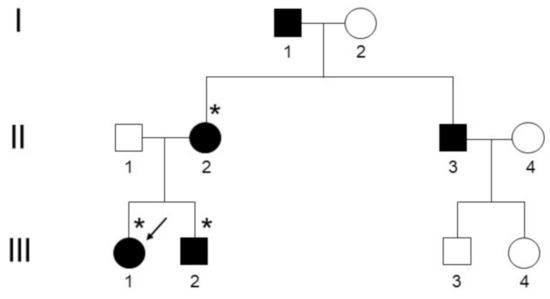
Figure 1.
Pedigree of the Calabrian kindred with adFNDI. Individuals marked with an asterisk (*) agreed to genetic testing. The arrow indicates the index patient who was clinically and radiologically assessed.
2.2. Genetic Testing
Genomic DNA was isolated from 600 µL of peripheral whole blood using the Wizard® Genomic DNA Purification Kit (Promega Corp., Madison, WI, USA), as starting material for DNA amplification procedures. For the index patient (subject III-1), the entire coding regions of all three exons of the AVP gene were amplified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) as previously described [14]. PCR products were sequenced by bidirectional direct sequencing using a BigDye Terminator v1.1 Cycle Sequencing Kit and an ABI PRISM® 3100-Avant Genetic Analyzer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). The sequence data were analyzed using the Sequencer v3.1.1 software (Gene Codes Corp., Ann Arbor, MI, USA) using the complete coding sequence of AVP (OMIM ID: 192340; ENSEMBL ID: ENSG00000101200) as a reference. Variant specific restriction enzyme cleavage analysis was performed on PCR-amplified exon 1 from the index patient, as well as for the other two affected family members (subjects III-2 and II-2), using the restriction endonuclease enzyme BstUI (New England BioLabs, Inc., Ipswich, MA, USA), according to manufacturer instructions. Resulting fragments were separated by agarose gel electrophoresis and visualized using ethidium bromide and an ultraviolet (UV) light source.
3. Results
3.1. Clinical and Radiological Assessments
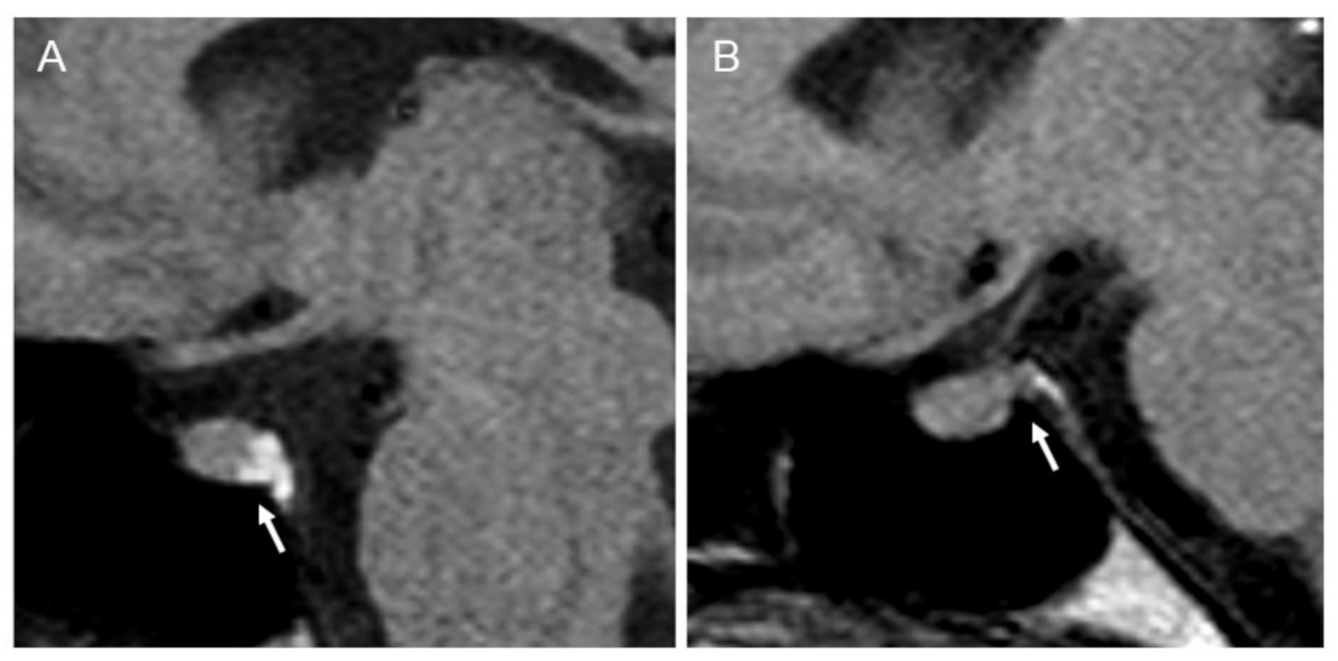
Plasma osmolality and plasma sodium increased after 3 h of fluid deprivation to 313 mOsm/L and 149 mmol/L, respectively. However, the extensive hypertonic dehydration elicited a prompt elevation of urine osmolality and diuresis contraction, without achieving a loss ≥5% of the initial body weight at the end of fluid deprivation testing, indicative of a partial clinical adFNDI phenotype [10,13]. The former diagnosis was confirmed by both normal basal pituitary function in extensive hormonal tests and evidence of normal gland morphology at neuroradiological assessment. However, in pre-enhanced T1-weighted MRI scans of the pituitary gland, the intrinsic hyperintense “bright signal” of the neurohypophysis was reduced (Figure 2) and this abnormal finding was regarded as compatible with the partial depletion and loss of function of vasopressinergic magnocellular secretory cells [15,16].
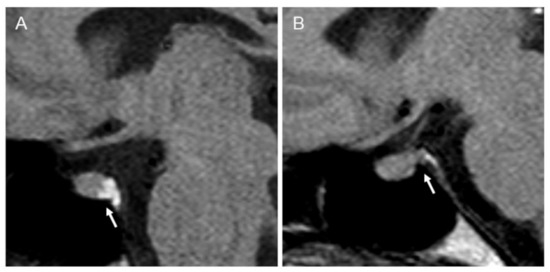
Figure 2.
Pre-enhanced T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan of the pituitary gland. Arrows indicate (A) a normal hyperintense “bright signal” of the neurohypophysis in an unaffected control subject; (B) a reduced “bright signal” in the index patient.
Data from five affected living family members were collected; two of them, who were successfully managed with high doses of oral desmopressin (240 µg/day in 2 divided doses) and agreed to genetic testing, self-reported the onset of extensive polyuria and polydipsia (>4 L/day) prior to 12 years of age (subjects III-1 and II-2, respectively), while similar early-onset manifestations of adFNDI were indirectly described for the remaining polyuric relatives (subjects II-3 and I-1; Figure 1).
3.2. Genetic Testing
Molecular genetic analysis was performed in three affected subjects of the kindred, including the index patient. When contacted, the remaining polyuric relatives refused consent for genetic testing. DNA sequencing analysis of the coding regions of the AVP gene in the index patient revealed the presence of a heterozygous c.55G>A transition, which predicts the replacement of alanine for threonine at codon 19 of the C-terminal region of SP (p.Ala19Thr) (Supplementary Figure, panels A and B). This DNA sequence change leads to a loss of a specific BstUI site (CG^CG). Accordingly, the restriction enzyme cleavage analysis of the PCR-amplified exon 1 with the restriction endonuclease BstUI confirmed that a heterozygous c.55G>A mutation was the cause of adFNDI in the investigated kindred (Supplementary Figure, panel C).
4. Discussion
It has been ascertained that the clinical symptoms of adFNDI derive from a gradual decrease in the neurohypophyseal secretion of mature AVP, and consequently, do not manifest until the affected child is several months to several years of age [14]. The variability in the age of onset and severity of manifestations for an autosomal dominant monogenic disorder as adFNDI, might reflect—at least to some extent—the specific location of the wide diversity of heterozygous point mutations in the AVP gene [12,14,17], alongside environmental factors, influencing either the transcriptional regulation of gene expression and apoptotic processes, or the individual ability of scavenging misfolded or unfolded mutant AVP precursors with cytotoxic effects on vasopressinergic magnocellular neurons [6,11,12]. Variations in the intensity of provoked AVP secretion following fluid deprivation have been reported among adult members of a large Swedish–Norwegian family, in which a rare, adolescent-onset form of adFNDI (caused by a c.251C>T substitution in the AVP gene) was segregating [14]. More recently, a high variability in both age at onset of hypotonic polyuria, which ranged from 3 to over 50 years of age, intensity of the “bright signal” in pre-enhanced T1-weighted MRI scan of the pituitary gland, and progression of developmental disabilities, has been reported in Asian patients with a definite history of adFNDI [12]. A 2delT heterozygous point mutation in the AVP gene, causing start codon shifting to the intraframe structure and depletion of the first four SP amino acids, was documented in the proband from one pedigree, whereas a c.50C>A substitution, predicting a p.Ser17Thr transition in the third amino acid residue of SP, was detected in another family [12]. Furthermore, a third c.52-54delTCC mutation, which was predicted to affect the intracellular transport of the AVP precursor hormone, was also located in the SP coding region of AVP in this study [12]. While evidence for a clear pattern of genotype–phenotype correlations in adFNDI remains limited, it has been suggested that specific AVP gene variants involving the SP coding region may be associated with low cytotoxicity and a delayed onset of symptoms, as shown in experimental murine knock-in models of the disease [7].
In our family genetic study, the index patient, presenting with an undefined and mild adolescent-onset form of NDI, still reserved some urine concentration response on fluid deprivation testing at the age of 23 years. Despite a suggestive three-generation pedigree, such spontaneous improvement of plasma osmolality and diuresis contraction following an extensive hypertonic dehydration could be misdiagnosed for other categories of polyuria and polydipsia that tend to family segregation [1], so that a definitive diagnosis of partial adFNDI, in this special circumstance, relies on concordant clinical, neuroradiological and genetic findings. The results of our mutational analysis revealed that a heterozygous c.55G>A variant of the AVP gene, resulting in p.Ala19Thr substitution of the C-terminal region of SP, was responsible for adFNDI. The c.55G>A variant of the AVP gene is one of the most common disease-causing mutation described in adFNDI, as already described in many unrelated families in Denmark, the U.S., Asia, and elsewhere in Europe [18]. The p.Ala19Thr replacement is among neutral amino acids and may potentially cause only a mild effect on the biochemical features of the mature protein, thus inducing an exceptional delayed clinical onset of the inherited condition, which does not necessarily manifest at birth or in early infancy, as it could remain silent for up to 10 years after birth in several kindreds [19]. An older child’s age at the time of clinical onset may also be due to underestimation of disease, especially in families with many affected members, where the production of large amounts of urine and persistent thirst are often regarded as “physiological” traits [19]. In rare cases, the documented adFNDI phenotype is partial, and the affected patients can concentrate their urine quite sufficiently during a standard fluid deprivation test, as occurred in our young adult index patient and two female adolescent Slovak twins of 17 years of age [17]. It is unclear whether female gender would attenuate clinical disease progression in the presence of a c.55G>A variant of the AVP gene. However, an apparent predominant female occurrence of early-onset polyuria and polydipsia has been noticed in a large Danish kindred with adFNDI inheriting the c.52-54delTCC variant that produces a deletion of a serine at position 18 (Ser18del) of SP [10]. One could hypothesize that gender may modulate (positively or negatively) the effects of an impaired SP cleavage at either the mRNA, or protein, or magnocellular neuron level, or the sensitivity to residual AVP secretion in distal nephron segments. Indeed, a partial clinical phenotype of adFNDI was documented in one male adult member of the Danish kindred, who formerly self-reported the absence of relevant disease-related symptoms [10]. Sexual differences in the antidiuretic responses constitute an emerging concept in endocrine physiology, which finds its scientific basis in the influences of sex hormones on osmoregulation and skewed inactivation of the X-linked AVP receptor 2 gene [20].
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of adFNDI specifically involving a kindred of Calabria, which is regarded as a Mediterranean region with a highly homogeneous genetic population structure [21,22]. In the last few decades, the Calabrian population has been a resource for genetic research because of its historical isolation and increased prevalence of progressive neurodegenerative disorders, inherited as Mendelian traits [23]. The limited genetic diversity typical of this geographical area has also been proven by our group to be ideal for mapping recessive variants for complex diseases (i.e., type 2 diabetes) that affect populations of European ancestry [24]. Although this kind of speculation would require further confirmation from large haplotype-based data, we believe that documenting a c.55G>A variant as the genetic cause of adFNDI in a three-generation family from this region, as well as in apparently unrelated individuals from more outbred populations, may constitute an argument against the potential role of a founder effect. The identification of the genetic cause of aFNDI in this kindred substantiates the wealth of case series describing a wide variability of disease onset and severity related to SP variants of the AVP gene, especially the c.55G>A disease-causing mutation [19], and further supports the value of genetic testing in all patients with familial occurrence of NDI regardless of their clinical and radiological phenotype [14,17,25]. This is important for both children and men and women of reproductive age, as it may ease long-term concerns over their asymptomatic (or mildly symptomatic) carrier state and the risk of disease transmission across generations.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2673-396X/2/1/4/s1. Figure S1: (A) Schematic diagram of the coding regions of the AVP gene; (B) Sequencing chromatograms; (C) Agarose gel electrophoresis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.T., M.M. and A.B.; investigation, V.T., S.G., D.L.T., A.A., and J.H.K.; writing—original draft preparation, M.M.; writing—review and editing, E.C., D.P.F. and A.B.; supervision, H.K., J.H.C. and A.B. All authors have read and agreed to the final version of the manuscript.
Funding
This publication is cofinanced with the support of the European Commission, FESR FSE 2014–2020 and Regione Calabria. The European Commission and Regione Calabria’s support for the production of this publication do not constitute an endorsement of the contents, which reflect the views only of the authors, and cannot be held responsible for any use which may be made of the information contained therein.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This family genetic study was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the ethics committee of Regione Calabria Sezione Area Centro (protocol registry n. 142 of May 23, 2019).
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was obtained from the index patient and adult relatives who agreed on genetic testing.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Babey, M.; Kopp, P.; Robertson, G.L. Familial forms of diabetes insipidus: Clinical and molecular characteristics. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2011, 7, 701–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, S.; Galiveeti, S.; Bichet, D.G.; Roth, J. Diabetes insipidus: Celebrating a century of vasopressin therapy. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 4605–4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christ-Crain, M.; Bichet, D.G.; Fenske, W.K.; Goldman, M.B.; Rittig, S.; Verbalis, J.G.; Verkman, A.S. Diabetes insipidus. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2019, 5, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burbach, J.P.; Luckman, S.M.; Murphy, D.; Gainer, H. Gene regulation in the magnocellular hypothalamo-neurohypophysial system. Physiol. Rev. 2001, 81, 1197–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knepper, M.A.; Kwon, T.H.; Nielsen, S. Molecular physiology of water balance. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1349–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, T.; Hagiwara, D.; Hodai, Y.; Miwata, T.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Kurimoto, J.; Ozaki, H.; Mitsumoto, K.; Takagi, H.; Suga, H.; et al. Degradation of Mutant Protein Aggregates within the Endoplasmic Reticulum of Vasopressin Neurons. iScience. 2020, 23, 101648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, T.A.; Ito, M.; Ito, M.; Yu, R.N.; Martinson, F.A.; Weiss, J.; Jameson, J.L. A murine model of autosomal dominant neurohypophyseal diabetes insipidus reveals progressive loss of vasopressin-producing neurons. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1697–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Castaño, A.; Madariaga, L.; de Nanclares, G.P.; Vela, A.; Rica, I.; Gaztambide, S.; Martínez, R.; De Lapiscina, I.M.; Urrutia, I.; Aguayo, A.; et al. Forty-One Individuals with Mutations in the AVP-NPII Gene Associated with Familial Neurohypophyseal Diabetes Insipidus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, dgaa069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrotta, S.; Di Iorgi, N.; Ragione, F.D.; Scianguetta, S.; Borriello, A.; Allegri, A.E.M.; Ferraro, M.; Santoro, C.; Napoli, F.; Calcagno, A.; et al. Early-onset central diabetes insipidus is associated with de novo arginine vasopressin-neurophysin II or Wolfram syndrome 1 gene mutations. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 172, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toustrup, L.B.; Kvistgaard, H.; Palmfeldt, J.; Bjerre, C.K.; Gregersen, N.; Rittig, S.; Corydon, T.J.; Christensen, J.H. The Novel Ser18del AVP Variant Causes Inherited Neurohypophyseal Diabetes Insipidus by Mechanisms Shared with Other Signal Peptide Variants. Neuroendocrinology 2018, 106, 167–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siggaard, C.; Rittig, S.; Corydon, T.J.; Andreasen, P.H.; Jensen, T.G.; Andresen, B.S.; Robertson, G.L.; Gregersen, N.; Bolund, L.; Pedersen, E.B. Clinical and molecular evidence of abnormal processing and trafficking of the vasopressin preprohormone in a large kindred with familial neurohypophyseal diabetes insipidus due to a signal peptide mutation. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1999, 84, 2933–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Cen, J.; Nie, M.; Gu, F. Identification of five novel arginine vasopressin gene mutations in patients with familial neurohypophyseal diabetes insipidus. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 38, 1243–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AME Guidelines. Available online: http://www.associazionemediciendocrinologi.it/materiali/manuali/2006-b/download_file_144.pdf (accessed on 21 December 2020).
- Jendle, J.; Christensen, J.H.; Kvistgaard, H.; Gregersen, N.; Rittig, S. Late-onset familial neurohypophyseal diabetes insipidus due to a novel mutation in the AVP gene. Clin. Endocrinol. 2012, 77, 586–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghnie, M.; Villa, A.; Arico, M.; Larizza, D.; Pezzotta, S.; Beluffi, G.; Genovese, E.; Severi, F. Correlation between magnetic resonance imaging of posterior pituitary and neurohypophyseal function in children with diabetes insipidus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1992, 74, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, N.; Berry, I.; Kucharczyk, J.; De Groot, J.; Larson, T.; Norman, D.; Newton, T.H.; Kucharczyk, W. Posterior pituitary gland: Appearance on MR images in normal and pathologic states. Radiology 1987, 165, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cizmarova, M.; Nagyova, G.; Janko, V.; Pribilincova, Z.; Virgova, D.; Ilencikova, D.; Kovacs, L. Late onset of familial neurogenic diabetes insipidus in monozygotic twins. Endocr. Regul. 2013, 47, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, J.H.; Siggaard, C.; Corydon, T.J.; DeSanctis, L.; Kovacs, L.; Robertson, G.L.; Gregersen, N. Six novel mutations in the arginine vasopressin gene in 15 kindreds with autosomal dominant familial neurohypophyseal diabetes insipidus give further insight into the pathogenesis. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2004, 12, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patti, G.; Scianguetta, S.; Roberti, D.; Di Mascio, A.; Balsamo, A.; Brugnara, M.; Cappa, M.; Casale, M.; Cavarzere, P.; Cipriani, S.; et al. Familial neurohypophyseal diabetes insipidus in 13 kindreds and 2 novel mutations in the vasopressin gene. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 181, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juul, K.V.; Klein, B.M.; Sandström, R.; Erichsen, L.; Nørgaard, J.P. Gender difference in antidiuretic response to desmopressin. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2011, 300, F1116–F1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiefari, E.; Ventura, V.; Capula, C.; Randazzo, G.; Scorcia, V.; Fedele, M.; Arcidiacono, B.; Nevolo, M.T.; Bilotta, F.L.; Vitiello, M.; et al. A polymorphism of HMGA1 protects against proliferative diabetic retinopathy by impairing HMGA1-induced VEGFA expression. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirabelli, M.; Chiefari, E.; Caroleo, P.; Arcidiacono, B.; Corigliano, D.M.; Giuliano, S.; Brunetti, F.S.; Tanyolaç, S.; Foti, D.P.; Puccio, L.; et al. Long-Term Effectiveness of Liraglutide for Weight Management and Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 17, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruni, A.C.; Momeni, P.; Bernardi, L.; Tomaino, C.; Frangipane, F.; Elder, J.; Kawarai, T.; Sato, C.; Pradella, S.; Wakutani, Y.; et al. Heterogeneity within a large kindred with frontotemporal dementia: A novel progranulin mutation. Neurology 2007, 69, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiefari, E.; Tanyolaç, S.; Paonessa, F.; Pullinger, C.R.; Capula, C.; Iiritano, S.; Mazza, T.; Forlin, M.; Fusco, A.; Durlach, V.; et al. Functional variants of the HMGA1 gene and type 2 diabetes mellitus. JAMA 2011, 305, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutishauser, J.; Kopp, P.; Gaskill, M.B.; Kotlar, T.J.; Robertson, G.L. Clinical and molecular analysis of three families with autosomal dominant neurohypophyseal diabetes insipidus associated with a novel and recurrent mutations in the vasopressin-neurophysin II gene. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2002, 146, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).