Effects of Sidewall Gas Blowing and Slag Layer on Flow and Tracer Transport in a Single-Strand Tundish
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Models and Methods
2.1. Physical Model
2.2. Mathematical Model
2.3. Experimental Method
3. Results
3.1. Bubble Behavior
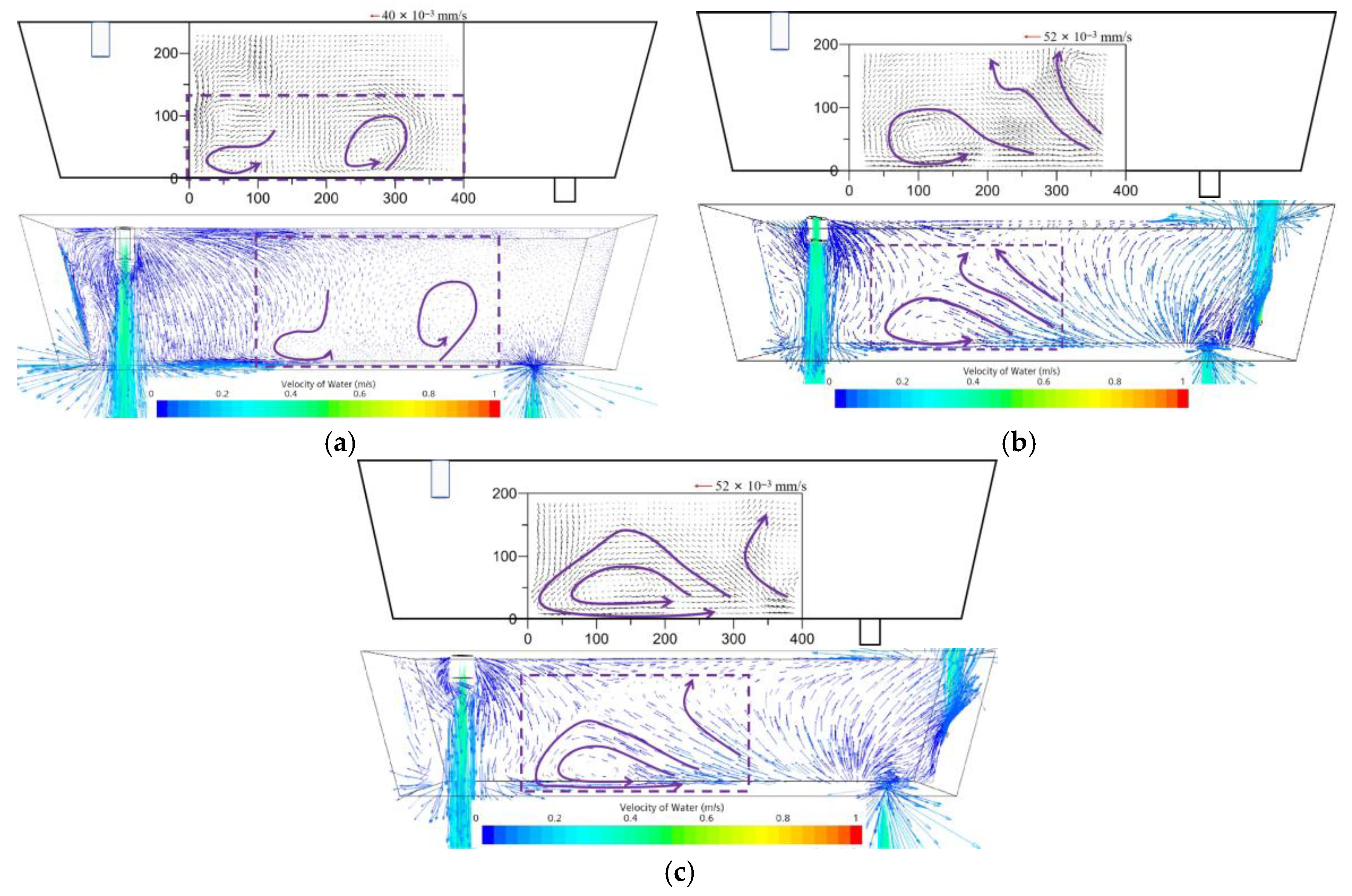
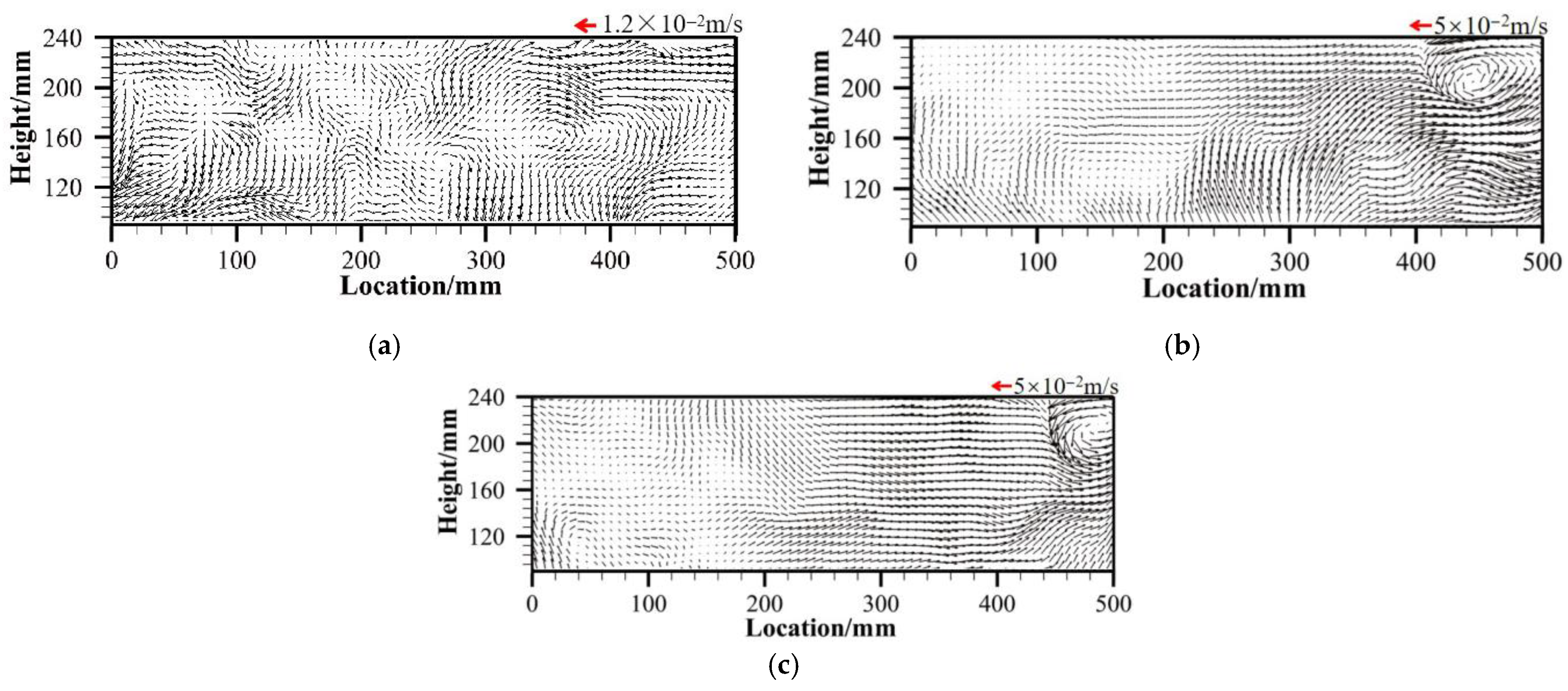
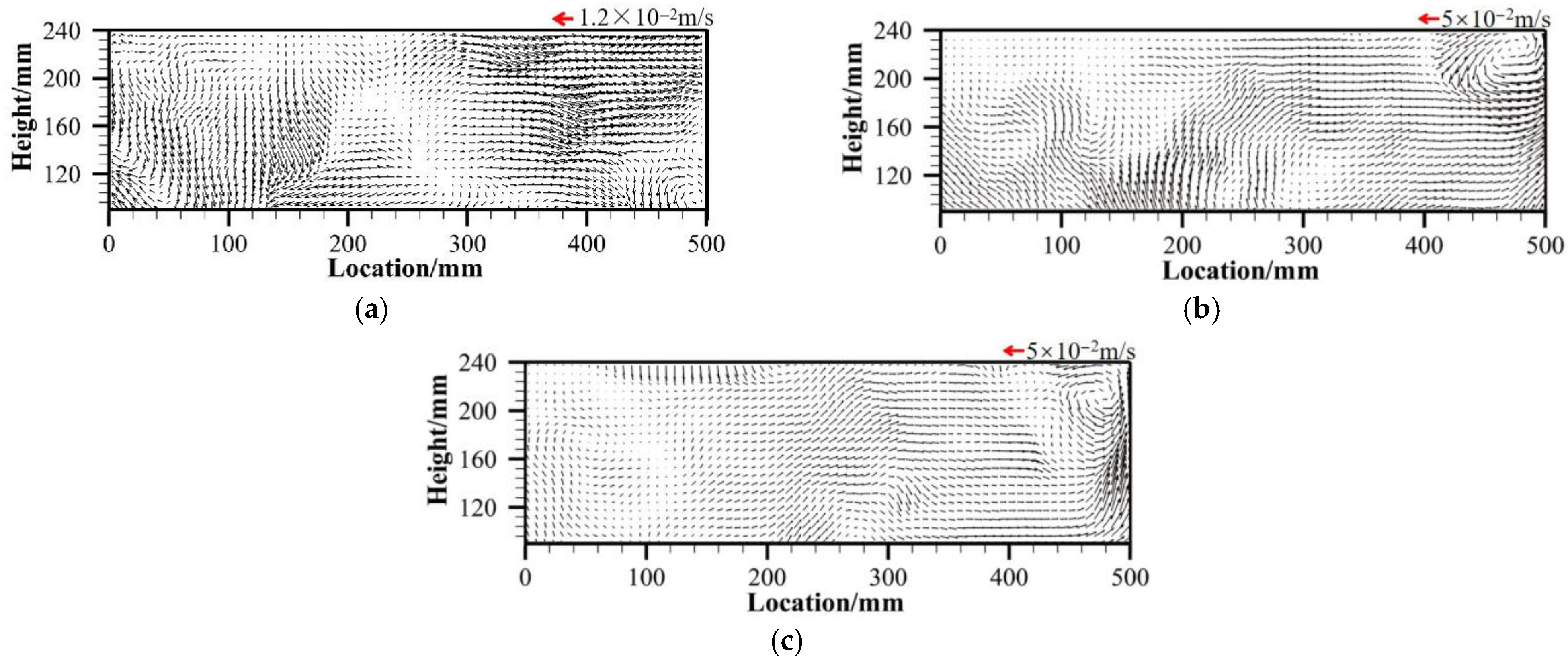
3.2. Comparison Between PIV Results and CFD Velocity Vectors
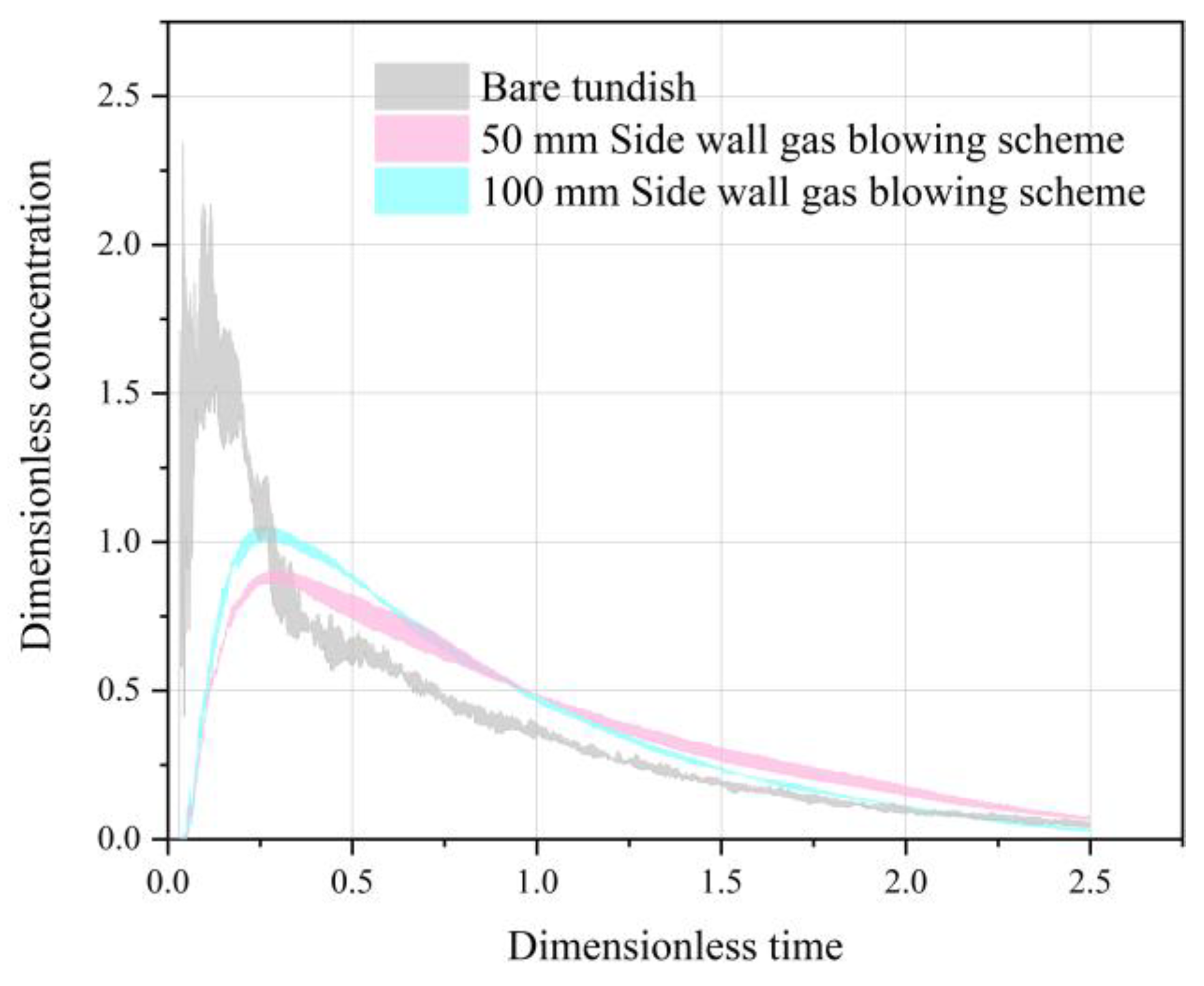
3.3. Passive Scalar Transport Process
3.4. The Streamline and Passive Scalar Transport Process of Each Scheme
3.5. Influence of Slag Layer on the Flow Field in the Tundish
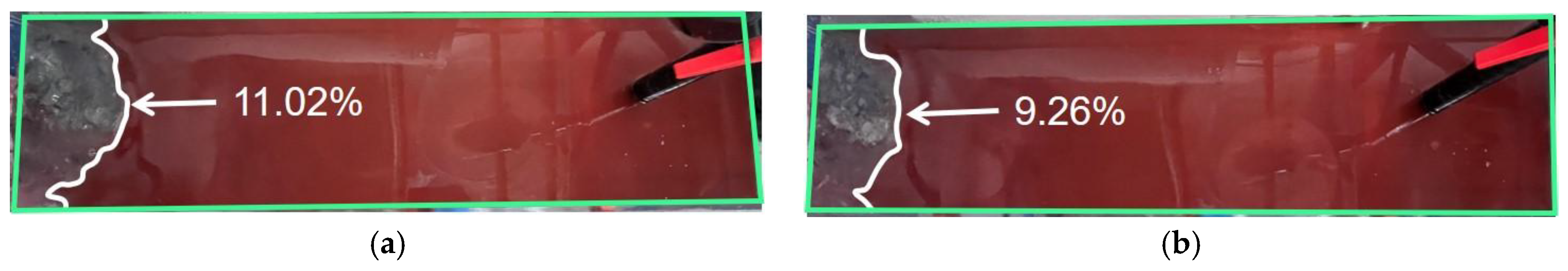
3.5.1. Statistical Results of Slag Eye Area
3.5.2. Analysis of Flow Field in the Tundish Without Slag Layer
3.5.3. Analysis of Flow Field in the Tundish with Slag Layer
3.6. Short Discussion on Future Work
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The right-sidewall gas blowing technology significantly improves the overall flow structure of the tundish. In the bare tundish, a typical low-speed stagnation zone exists in the region above the outlet. After the application of sidewall gas blowing, this region forms a stable large-scale counterclockwise rotating vortex, effectively promoting fluid movement in this region and significantly reducing the size of the stagnation zone. Additionally, the PIV experimental results from the water model and CFD simulations are highly consistent, validating the accuracy and applicability of the constructed numerical model. Sidewall blowing enhances the fluid flow rising from the wall to the liquid surface, extending the fluid migration path within the tundish and increasing the possibility of inclusion flotation and removal.
- (2)
- Sidewall gas blowing significantly improves the mixing performance of the tundish. Compared to the bare tundish, the average residence time increases to 525.48 s (+37%) and 464.00 s (+20.8%), while the dead zone volume fraction decreases to 24.70% (−18.83%) and 29.63% (−13.90%), respectively. At the same time, the RTD peak concentration decreases by 60.71%. These results indicate that the sidewall gas blowing scheme effectively suppresses the formation of short-circuit flows, expands the effective flow area, and significantly improves the mixing uniformity within the system.
- (3)
- The blowing height and slag layer conditions jointly influence the internal flow field structure of the tundish. The 50 mm gas injection height more easily induces strong vortices and upward flow, facilitating rapid fluid mixing and reducing the tracer mixing time by 89.2% compared to the bare tundish. However, the 100 mm injection height, although slightly reducing the mixing rate (mixing time reduced by 88.8%), improves the uniformity of the velocity distribution in the flow field. Furthermore, the presence of the slag layer has a significant suppressive effect on the gas blowing disturbances, weakening the upward flow induced by bubbles, resulting in a weakened vortex structure, reduced flow velocity, and a shift in the flow pattern from vertical disturbances to predominantly horizontal flow.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Szekely, J.; Ilegbusi, O.J. The Physical and Mathematical Modeling of Tundish Operations; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 34–52. [Google Scholar]
- Sahai, Y. Tundish Technology for Clean Steel Production; World Scientific Publisher: Singapore, 2007; pp. 8–12. [Google Scholar]
- Mazumdar, D.; Guthrie, R.I.L. The Physical and Mathematical Modelling of Continuous Casting Tundish Systems. ISIJ Int. 1999, 39, 524–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, K.; Isac, M.; Guthrie, R.I.L. Physical and mathematical modelling of steelmaking tundish operations: A review of the last decade (1999–2009). ISIJ Int. 2010, 50, 331–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Cheng, G.G.; Yang, H.K.; Hou, Z.B. Physical modeling of fluid flow characteristics in a delta shaped, four-strand continuous casting tundish with different flow control devices. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 284, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holappa, L.; Kekkonen, M.; Louhenkilpi, S.; Hagemann, R.; Schroder, C.; Scheller, P. Active tundish slag. Steel Res. Int. 2013, 84, 638–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.Q.; Li, Y.; Lin, W.M.; Che, J.L.; Zhou, F.; Tan, Y.F.; Li, D.L.; Dang, J.; Chen, C. Assessment of Inclusion Removal Ability in Refining Slags Containing Ce2O3. Crystals 2023, 13, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.L.; Liu, Z.T.; Li, F.C.; Lyu, B.; Chen, W.; Zhang, L.F. Numerical simulation on multiphase flow and slag entrainment during casting start of a slab continuous casting tundish. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2023, 54, 2048–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.C.; Liu, Z.T.; Chen, W.; Chen, H.L.; Zhang, L.F. Numerical simulation on the multiphase flow and reoxidation of the molten steel in a two-strand tundish during ladle change. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2024, 31, 1540–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, R.D.; Garcia-Hernandez, S.; Barreto, J.J.; Ceballos-Huertal, A.; Calderon-Ramos, I.; Gutierrez, E. Multiphase Flow Modeling of Slag Entrainment During Ladle Change-Over Operation. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2016, 47, 2595–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solhed, H.; Jonsson, L.; Jönsson, P. A theoretical and experimental study of continuous-casting tundishes focusing on slag-steel interaction. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2002, 33, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solhed, H.; Jonsson, L.; Jönsson, P. Modelling of the steel/slag interface in a continuous casting tundish. Steel Res. Int. 2008, 79, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.S.; Qin, B.M.; Liu, Y.H.; Li, Q.H.; Zuo, X.T.; Wang, C.; Yang, S.F.; Liu, Q. Multiphase flow inside a four-strand continuous casting tundish using three types of ladle shrouds. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2023, 30, 1171–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satish Kumar, D.; Rajendra, T.; Rrasad, R.; Sarkar, A.; Ranjan, M. Forced flotation of inclusions in tundish. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2009, 36, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Mazumdar, D. Physical and Mathematical Modeling of Argon Flow and Distribution Around a Ladle Shroud-Collector Nozzle (LS-CN) Assembly. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2022, 53, 2600–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Z.; Cui, H.; Li, T.; Tang, G.; Zhu, Y.; Yan, J.; Li, J. Numerical Simulation of Inclusion Removal by Bubble Injection in the Submerged Nozzle with Swirling Flow. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2022, 53, 2570–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.F.; Cheng, C.G.; Li, Y.; Wu, W.L.; Jin, Y. Effect of coarse aggregate content on bubble formation behavior in corundum permeable brick for tundish. Steel Res. Int. 2023, 94, 2200915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.F.; Cheng, C.G.; Li, Y.; Wu, W.L.; Chen, H.; Zhao, C.F.; Jin, Y. Numerical simulation on gas–liquid multiphase flow behavior under coupling effects of annular gas curtain and swirling flow at tundish upper nozzle. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2024, 31, 2693–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Cheng, C.G.; Liu, J.G.; Wu, W.L.; Chen, D.L. Theory of movement behavior of argon bubbles in upper nozzle of tundish during argon blowing process. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2023, 54, 3568–3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Zou, Z.S.; Liu, J.H.; Isac, M.; Cao, X.K.E.; Su, X.F.; Guthrie, R.I.L. Study on the slag-metal interfacial behavior under the impact of bubbles in different sizes. Powder Technol. 2021, 387, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Zou, Z.; Li, B.; Isac, M.; Guthrie, R.I.L. Modeling Inclusion Removal when Using Micro-bubble Swarm in a Full-Scale Tundish with an Impact Pad. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2022, 53, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Song, H.; Liu, Z.; Zou, Z.; Shao, L.; Li, B. Experimental Study on Bubble Entrainment by a Free Fall Jet in an Argon-Filled Continuous Casting Tundish. Steel Res. Int. 2023, 94, 2200287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Banderas, A.; Morales, R.D.; García-Demedices, L.; Díaz-Cruz, M. Mathematical Simulation and Modeling of Steel Flow with Gas Bubbling in Trough Type Tundishes. ISIJ Int. 2003, 43, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Zamora, A.; Palafox-Ramos, J.; Morales, R.D.; Díaz-Cruz, M.; Barreto-Sandoval, J.J. Inertial and buoyancy driven water flows under gas bubbling and thermal stratification conditions in a tundish model. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2004, 35, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Banderas, A.; Morales, R.D.; Barreto, J.J.; Solorio-Diza, G. Modelling study of inclusions removal by bubble flotation in the tundish. Steel Res. Int. 2006, 77, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Li, L.; Wang, B.; Jiang, M.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, L.; Chen, R. Water Modeling Experiments of Argon Bubbling Curtain in a Slab Continuous Casting Tundish. Steel Res. Int. 2006, 77, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, M.Y.; Zhou, H.B.; Wang, Y. Fluid flow and interfacial phenomenon of slag and metal in continuous casting tundish with argon blowing. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2008, 15, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, K.; Isac, M.; Guthrie, R.I.L. Physical and Mathematical Modelling of Inert Gas Shrouding in a Tundish. ISIJ Int. 2011, 51, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Chattopadhyay, K. Formation of Slag ‘eye’ in an Inert Gas Shrouded Tundish. ISIJ Int. 2015, 55, 1416–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Chattopadhyay, K. Physical Modeling of Slag ‘Eye’ in an Inert Gas-Shrouded Tundish Using Dimensional Analysis. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2016, 47, 508–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cwudziński, A. Hydrodynamic effects created by argon stirring liquid steel in a one-strand tundish. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2017, 45, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cwudziński, A. Numerical and Physical Modeling of Liquid Steel Flow Structure for One Strand Tundish with Modern System of Argon Injection. Steel Res. Int. 2017, 88, 1600484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Li, D.; Chattopadhyay, K. Modeling of Liquid Steel/Slag/Argon Gas Multiphase Flow During Tundish Open Eye Formation in a Two-Strand Tundish. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2018, 49, 756–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.T.; Chen, C.; Guo, Z.J.; Geng, M.J.; Rong, Z.R.; Wang, T.Y.; Wang, J.; E, D.; Fan, J.P.; Sun, Y.H. Analysis of Flow Field, Temperature, and Inclusion Evolution in a 12-Strand Tundish During Ladle Changeover Process. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2025, 56, 2700–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Q.; Zhang, Z.X.; Qu, T.P.; Li, X.L.; Tian, J.; Wang, D.Y. Physical and numerical investigation on fluid flow and inclusion removal behavior in a single-strand tundish. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2023, 30, 1182–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, W.; Yang, S.; Zuo, X.T.; Zhao, L.; Li, J.S. Effect of tundish impact zone optimization on inclusion removal in steel: Industrial and simulation studies. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2024, 55, 808–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.M.; Zhang, J.S.; Yang, C.H.; Yang, S.F.; Liu, Q. Study on influencing factors and their combined effects on multiphase behavior in tundish pouring zone. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2025, 56, 1176–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.Y.; Yang, S.L.; Wang, H. VOF study of mesoscale bubble flow dynamics in the side-blown gas–liquid two-phase reactor. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 480, 147983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.H.; Yang, S.L.; Kong, D.S.; Li, D.B.; Hu, J.H.; Wang, H. Numerical investigation of sinusoidal pulsating gas intake to intensify the gas-slag momentum transfer in the top-blown smelting furnace. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2024, 31, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.F.; Wan, Z.H.; Hu, Z.H.; Wang, Y.F.; Shi, P.H.; Huang, J.D.; Zhong, L.H.; Li, M.Z. Gas–slag–matte multiphase flow and bubble dynamics in an industrial side-blown smelting furnace. Phys. Fluids 2025, 37, 083356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, L.; Tavares, R.P. Analysis of the mathematical model of the gas bubbling curtain injection on the bottom and the walls of a continuous casting tundish. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2017, 44, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, C.; Chen, L.; Geng, M.J.; Song, J.T.; Fan, J.P.; Lin, W.M. Physical and numerical study on right side and front side gas blowing at walls in a single-strand tundish. Steel Res. Int. 2024, 95, 2400037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, P.; Zuo, X.; Wu, D.; Wu, D. Optimization of the Liquid Steel Flow Behavior in the Tundish through Water Model Experiment, Numerical Simulation and Industrial Trial. Metals 2022, 12, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cwudziński, A.; Pieprzyca, J.; Merder, T. Numerical and Physical Modeling of Liquid Steel Asymmetric Behavior during Non-Isothermal Conditions in a Two-Strand Slab Tundish—“Butterfly Effect”. Materials 2023, 16, 6920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walek, J.; Tkadlečková, M.; Velička, M.; Machů, M.; Cupek, J.; Huczala, T.; Cibulka, J.; Růžička, J.; Michalek, K. Physical Experiments and Numerical Simulations of the Influence of Turbulence Inhibitors and the Position of Ladle Shroud on the Steel Flow in an Asymmetric Five-Strand Tundish. Metals 2023, 13, 1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, M.J.; Wang, T.Y.; Chen, C. Assessment of the Volume Effect and Application of an Improved Tracer in Physical Model of a Single-Strand Bare Tundish. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2024, 55, 4121–4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.M.; Sun, B.C.; Wang, X.Z. Analysis model of internal residence time distribution for fluid flow in a multi-strand continuous casting tundish. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2024, 31, 2186–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.Y.; Lei, H.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, Y.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zou, Z.S. New understanding on relationship between rtd curve and inclusion behavior in the tundish. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2024, 55, 2224–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odenthal, H.J.; Bölling, R.; Pfeifer, H.; Holzhauser, J.F.; Wahlers, F.J. Mechanism of fluid flow in a continuous casting tundish with different turbo-stoppers. Steel Res. 2001, 72, 466–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odenthal, H.J.; Javurek, M.; Kirschen, M. CFD benchmark for a single strand tundish (part I). Steel Res. Int. 2009, 80, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkishriwi, N.; Meinke, M.; Schröder, W.; Braun, A.; Pfeifer, H. Large-eddy simulations and particle-image velocimetry measurements of tundish flow. Steel Res. Int. 2006, 77, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cwudziński, A. Numerical and Physical Modeling of Liquid Steel Active Flow in Tundish with Subflux Turbulence Controller and Dam. Steel Res. Int. 2013, 85, 902–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Yuan, Z.; Shi, S.; Wang, B.; Liu, C. Flow Characteristics for Two-Strand Tundish in Continuous Slab Casting Using PIV. Metals 2019, 9, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, A.; Nili-Ahmadabadi, M.; Mohammadi, S.; Joulaei, A.; Ha, M.Y. Optimizing flow patterns and residence time in a two-strand steelmaking tundish via PIV and tracer-based flow detection. Metall. Res. Technol. 2025, 122, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Fang, Q.; Deng, S.Y.; Liu, C.; Ni, H.W. Multiphase flow in a five-strand tundish using trumpet ladle shroud during steady-state casting and ladle change-over. Steel Res. Int. 2019, 90, 1800497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Q.; Yao, Y.C.; Wang, N.; Yang, J.; Xu, G.D.; Li, B.K. Physical and Numerical Simulations on the Unsteady Three-Phase Flow in a Continuous Casting Tundish During Ladle Changeover Process. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2025, 56, 1982–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, H.T.; Xu, R.; Wang, H.J.; Chang, L.Z.; Qiu, S.T. Multiphase flow behavior in a single-strand continuous casting tundish during ladle change. ISIJ Int. 2020, 60, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.X.; Wang, H.; Qu, T.P.; Wang, D.Y.; Li, X.L.; Hu, S.Y.; Tian, J.; Zhou, X.Z.; Yang, Z.H. Numerical investigation on transient flow and inclusion removal behavior in tundish during ladle change process. Steel Res. Int. 2024, 95, 2400471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.Y.; Chen, C.; Tao, X.; Wang, J.; Geng, M.J.; Song, J.T.; Li, L.B.; Fan, J.P.; Lin, W.M. Impact of slag layer on macroscopic flow inside tundish and velocity near slag-steel interface. Chin. J. Process Eng. 2024, 24, 1058–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemens PLM. STAR-CCM + User Guide, version 16.06; Siemens PLM Software Inc.: Munich, Germany, 2021.
- Fan, J.P.; Li, Y.Q.; Chen, C.; Ouyang, X.; Wang, T.Y.; Lin, W.M. Effect of Uniform and Non-Uniform Increasing Casting Flow Rate on Dispersion and Outflow Percentage of Tracers in Four Strand Tundishes under Strand Blockage Conditions. Metals 2022, 12, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.T.; Luo, Y.Z.; Li, Y.Q.; Guo, Z.J.; Wang, T.Y.; Geng, M.J.; Lin, W.M.; Fan, J.P.; Chen, C. Comparison of Fluid Flow and Tracer Dispersion in Four-Strand Tundish under Fewer Strand Casting and Sudden Blockage of Strand Conditions. Metals 2024, 14, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patankar, S.V. Numerical Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow; Hemispere Publ. Corp.: New York, NY, USA, 1980; p. 16. [Google Scholar]
- Shih, T.H.; Liou, W.W.; Shabbir, A.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, J. A new k-ϵ eddy viscosity model for high reynolds number turbulent flows. Comput. Fluids 1995, 24, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodi, W. Experience with two-layer models combining the k-epsilon model with a one-equation model near the wall. In Proceedings of the 29th Aerospace Sciences Meeting, Reno, NV, USA, 1–10 January 1991; ARC: Columbus, OH, USA, 1991; p. 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomiyama, A.; Tamai, H.; Zun, I.; Hosokawa, I. Transverse migration of single bubbles in simple shear flows. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2002, 57, 1849–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, X.; Lin, W.M.; Luo, Y.Z.; Zhang, Y.X.; Fan, J.P.; Chen, C.; Cheng, G.G. Effect of Salt Tracer Dosages on the Mixing Process in the Water Model of a Single Snorkel Refining Furnace. Metals 2022, 12, 1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Ouyang, X.; Chen, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, T.; Ren, R.; Yang, M.; Zhao, Y.; Xue, L.; Wang, J. Numerical Simulation of the Density Effect on the Macroscopic Transport Process of Tracer in the Ruhrstahl-Heraeus (RH) Vacuum Degasser. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Ling, H.T.; Wang, H.J.; Chang, L.Z.; Qiu, S.T. Investigation on the effects of ladle change operation and tundish cover powder on steel cleanliness in a continuous casting tundish. Steel Res. Int. 2021, 92, 2100072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

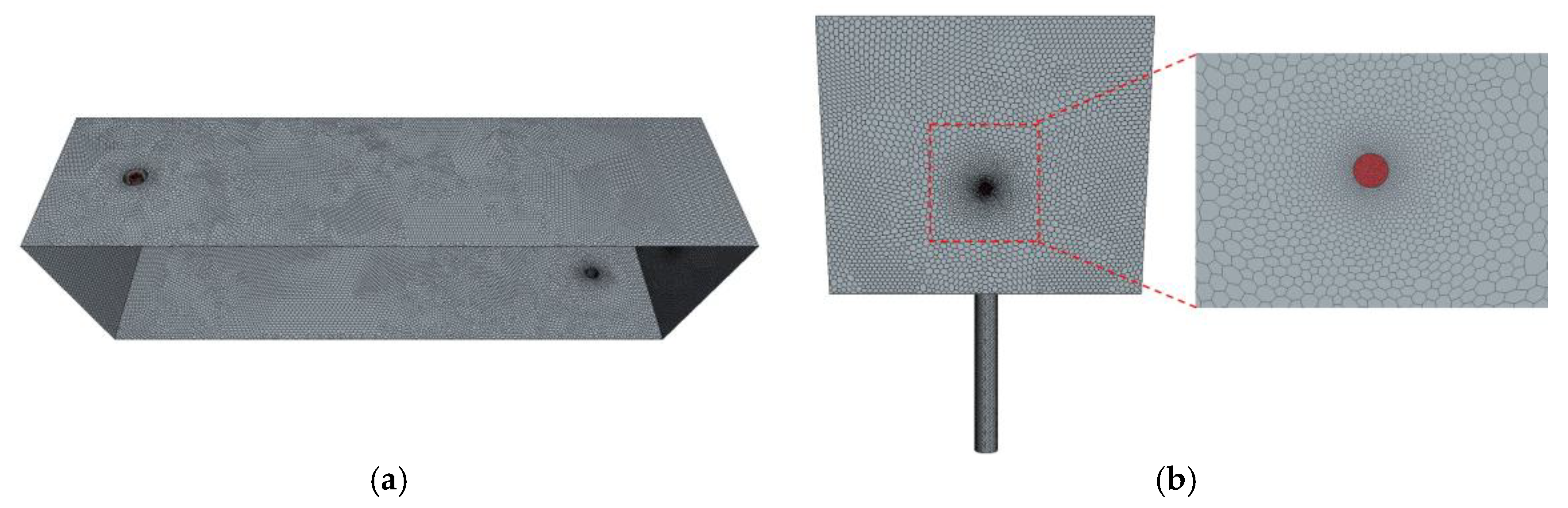


| Parameters | Water Model | Industrial Tundish |
|---|---|---|
| Volumetric flowrate nozzle [L/min] | 9.3 | 224 |
| Diameter of the outlet nozzle [mm] | 25 | 89.25 |
| Depth of liquid [mm] | 280 | 1000 |
| Diameter of the shroud [mm] | 22 | 78.54 |
| Immerse of shroud depth [mm] | 44 | 157.08 |
| Schemes | Orifice Height/mm | Gas Blowing Flow Rate/(L·min−1) |
|---|---|---|
| Scheme 1 (Bare tundish) | - | - |
| Scheme 2 | 50 | 2.5 |
| Scheme 3 | 100 | 2.5 |
| Schemes | Response Time/s | The Time of Maximum Peak Concentration/s | Maximum Peak Con-Centration | Mean Residence Time/s | Dead Zone Volume Fraction/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scheme 1 | 19.00 | 41.00 | 2.24 | 384.00 | 43.53 |
| Scheme 2 | 29.00 | 178.50 | 0.88 | 525.48 | 24.70 |
| Scheme 3 | 31.00 | 150.00 | 1.05 | 464.00 | 29.63 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Wang, T.; Geng, M.; Huang, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Yang, K.; Wang, J.; Chen, C. Effects of Sidewall Gas Blowing and Slag Layer on Flow and Tracer Transport in a Single-Strand Tundish. Modelling 2025, 6, 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/modelling6030087
Zhao Y, Wang T, Geng M, Huang Y, Liu J, Wang H, Zhang X, Yang K, Wang J, Chen C. Effects of Sidewall Gas Blowing and Slag Layer on Flow and Tracer Transport in a Single-Strand Tundish. Modelling. 2025; 6(3):87. https://doi.org/10.3390/modelling6030087
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yansong, Tianyang Wang, Mengjiao Geng, Yonglin Huang, Jiale Liu, Haozheng Wang, Xing Zhang, Kun Yang, Jia Wang, and Chao Chen. 2025. "Effects of Sidewall Gas Blowing and Slag Layer on Flow and Tracer Transport in a Single-Strand Tundish" Modelling 6, no. 3: 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/modelling6030087
APA StyleZhao, Y., Wang, T., Geng, M., Huang, Y., Liu, J., Wang, H., Zhang, X., Yang, K., Wang, J., & Chen, C. (2025). Effects of Sidewall Gas Blowing and Slag Layer on Flow and Tracer Transport in a Single-Strand Tundish. Modelling, 6(3), 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/modelling6030087







