Modeling and Optimization of Maintenance Strategies in Leasing Systems Considering Equipment Residual Value
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Model Descriptions
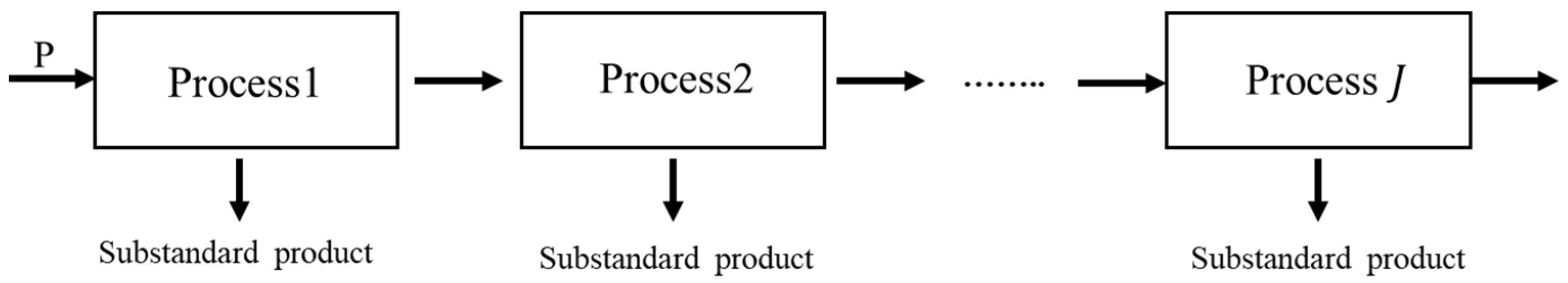
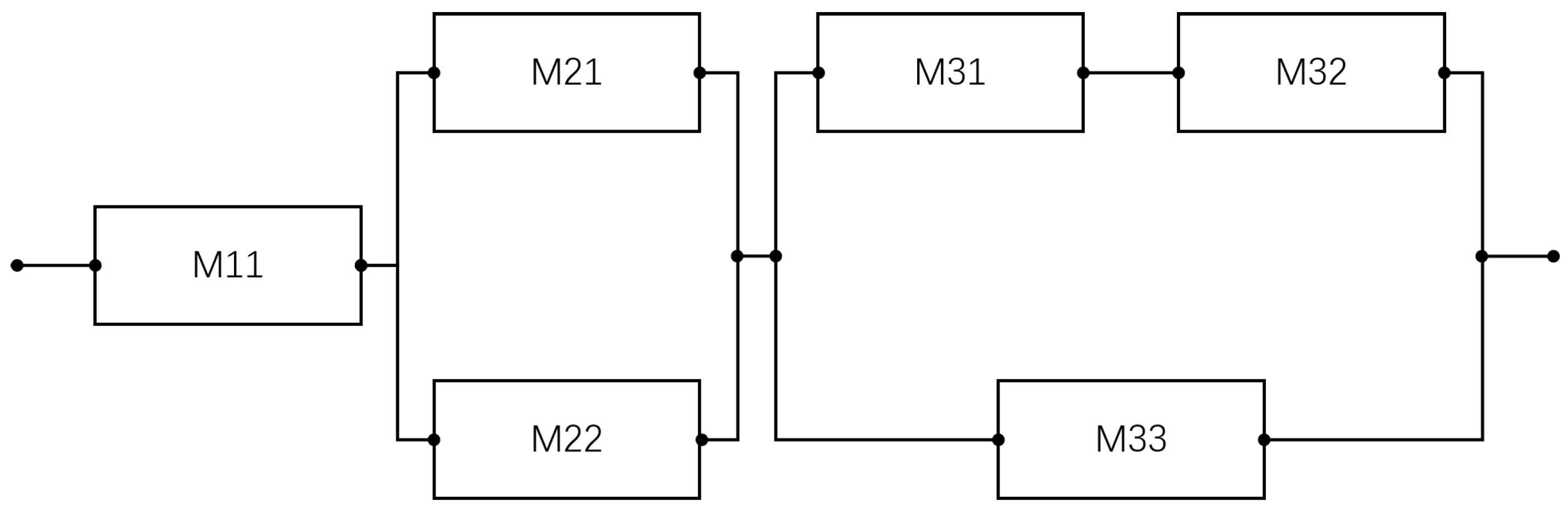
2.1. Leased Production System
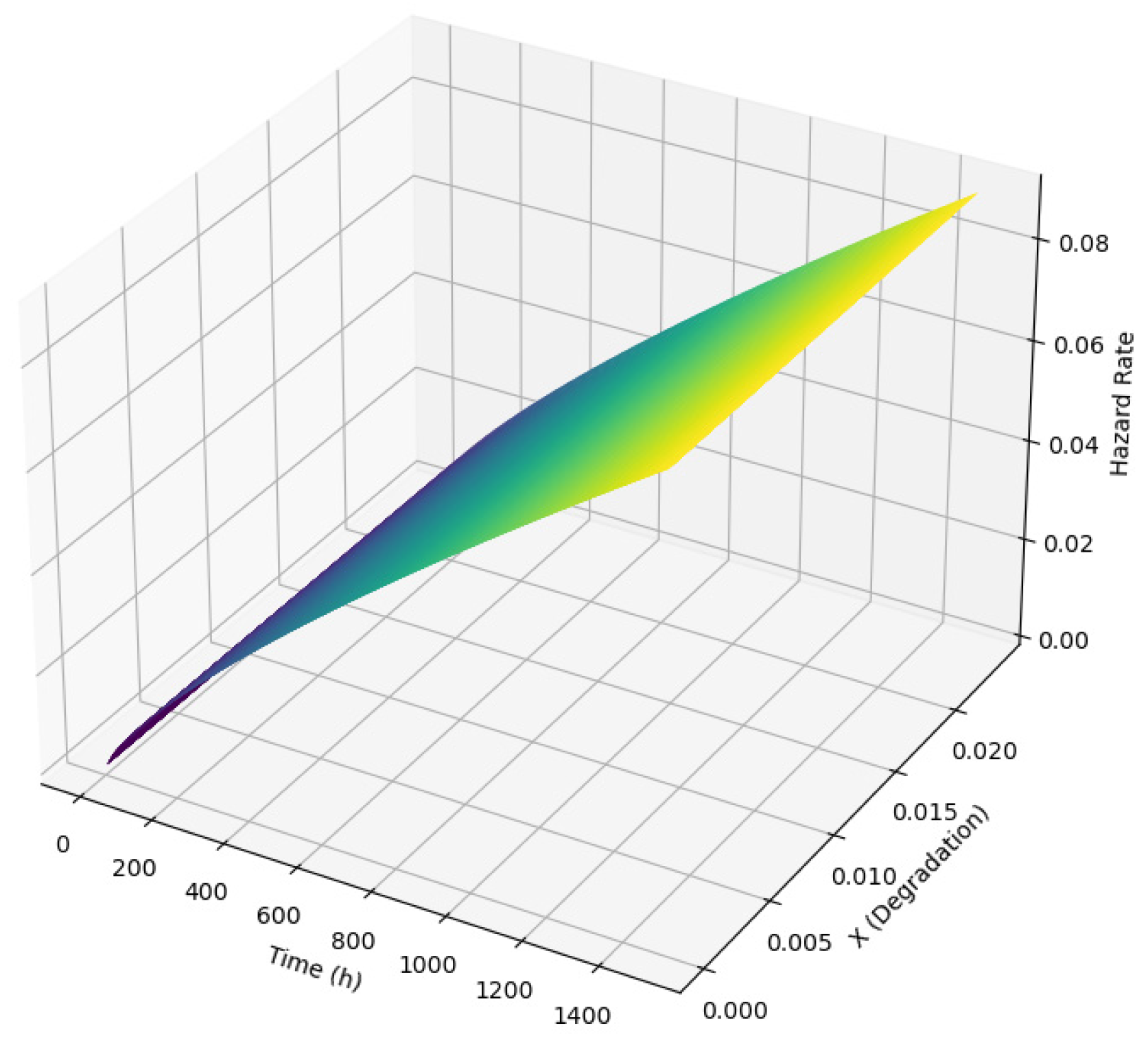
2.1.1. Degradation Process of Critical Components
2.1.2. Proportional Hazards Model
2.1.3. Overview of Maintenance Strategy
2.1.4. Model Assumptions
- (1)
- The generation of defective products is solely determined by the condition of the equipment.
- (2)
- Maintenance activities do not introduce new failures; that is, after each maintenance action, the equipment is restored to a reasonable operational state through appropriate repair measures.
- (3)
- Compared to the duration of the lease period, maintenance time is negligible.
- (4)
- Corrective maintenance (CM) restores the equipment to operational status without altering its degradation level.
3. Optimization Modeling of Leasing Maintenance Strategy
3.1. Imperfect Maintenance Cost of the Lessor
3.1.1. Maintenance Cost
3.1.2. Failure and Penalty Costs
3.1.3. Leased Equipment Residual Value Model
3.2. Customer Cost Model
3.3. Cost Models for Both Parties in the Leasing System
4. Experimentation and Analysis of the Results
4.1. Case Study
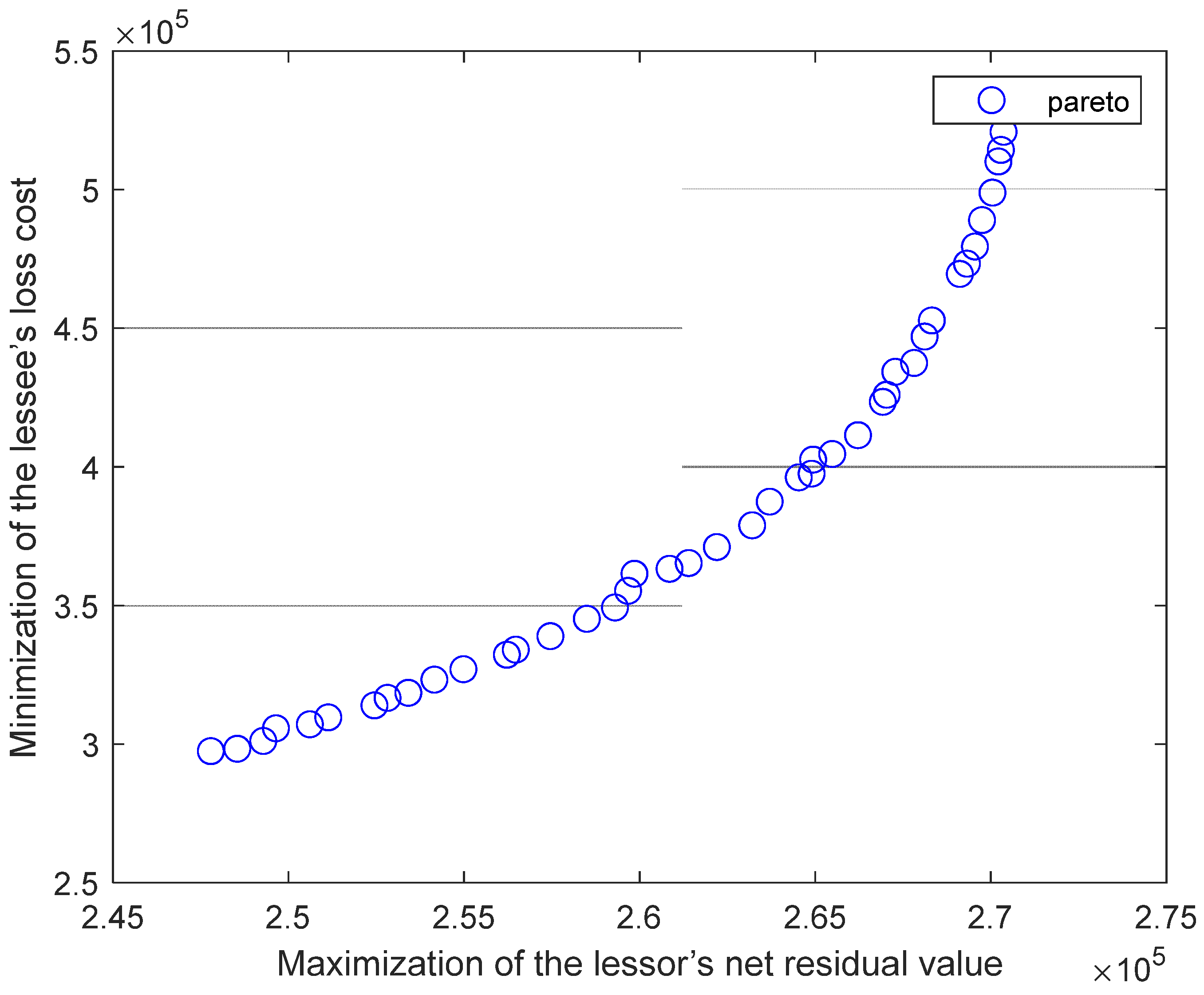
4.2. Sensitivity Analysis
4.3. Comparison of the Proposed Model with Two Other Conventional Models
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wireman, T. Benchmarking Best Practices for Maintenance, Reliability and Asset Management; Industrial Press: Norwalk, CT, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Shi, Y.; Yang, H. Optimal production and carbon reduction investment decision for manufacturers with leasing–selling strategies considering financing. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. 2025, 32, 3168–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, M.-L.; Tan, R.R.; Chiu, A.S.; Chien, C.-F.; Kuo, T.C. Circular economy meets industry 4.0: Can big data drive industrial symbiosis? Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 131, 146–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H.; Segerstedt, A.; Zhang, L. Maintenance service strategy for leased equipment: Integrating lessor-preventive maintenance and lessee-careful protection efforts. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2021, 156, 107257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Yu, J. Leasing as a mitigation of financial accelerator effects. Rev. Financ. 2023, 27, 2015–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tukker, A. Product services for a resource-efficient and circular economy–a review. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 97, 76–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, M. Fluid transitions to more sustainable product service systems. Environ. Innov. Soc. Transit. 2014, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tlili, L.; Anis, C.; Bouazizi, M. Optimal preventive maintenance policy for leased equipment for free with minimum quantity of consumables purchasing commitment by the lessee. J. Qual. Maint. Eng. 2023, 29, 708–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Jing, H.; Wang, D.-D.; Jiang, F. Joint quality and maintenance decisions under servitization business model. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2024, 62, 1567–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Mabrouk, A.; Chelbi, A. Optimal maintenance policy for equipment leased with base and extended warranty. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2023, 61, 898–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Pang, J.; Yang, H.; Zhao, Y. Optimal condition-based maintenance policy for leased equipment considering hybrid preventive maintenance and periodic inspection. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2024, 242, 109724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, J.; Wang, J.; Xue, S. Lessees’ satisfaction and optimal condition-based maintenance policy for leased system. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2019, 191, 106532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Lu, C.; Dong, W. Importance measures for multi-state systems with multiple components under hierarchical dependences. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2024, 248, 110142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Wang, S.; Zhang, C.; Dui, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y. Component uncertainty importance measure in complex multi-state system considering epistemic uncertainties. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2024, 37, 31–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Shen, J.; Wang, F.; Li, L.; Yang, N. Optimal mission abort policy for a multi-component system with failure interaction. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2024, 242, 109791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Xu, F.; Liang, B.; Zhang, J.; Song, P. A condition-based opportunistic maintenance strategy for multi-component system. Struct. Health Monit. 2019, 18, 270–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Yang, H.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Z. A two-stage integrating optimization of production scheduling, maintenance and quality. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2020, 234, 1448–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Mabrouk, A.; Chelbi, A. Joint preventive maintenance and extended warranty strategy for leased unreliable equipment submitted to imperfect repair at failure. IFAC-Pap. 2022, 55, 1201–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Sun, B.; Chen, Z.; Pan, E.; Wang, H.; Xi, L. Opportunistic maintenance policy integrating leasing profit and capacity balancing for serial-parallel leased systems. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2021, 205, 107233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, B.; Yang, H. Optimal pricing and financing strategies for leased equipment considering maintenance and lessees’ options. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2024, 269, 109157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milošević, I.; Petronijević, P.; Arizanović, D. Determination of residual value of construction machinery based on machine age. Građevinar 2020, 72, 45–55. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, W.L.; Lo, H.-C. Joint determination of lease period and preventive maintenance policy for leased equipment with residual value. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2011, 61, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, P.; Xv, W.; Dong, W. Joint optimization of quality-based multi-level maintenance and buffer stock within multi-specification and small-batch production. Front. Eng. Manag. 2025, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, W.; Fan, Y.; Xu, X.; Jiang, A. Grouping-maintenance of multi-components production system under ecological background. J. Ind. Eng. Manag. 2024, 17, 664–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Xiang, Y.; Zeng, B. Multicomponent maintenance optimization: A stochastic programming approach. Inf. J. Comput. 2021, 33, 898–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Hernández, D.; Pinar-Pérez, J.M.; Delgado-Gómez, D. Multi-machine preventive maintenance scheduling with imperfect interventions: A restless bandit approach. Comput. Oper. Res. 2020, 119, 104927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, H.C.; Do, P.; Fouladirad, M.; Grall, A. Dynamic opportunistic maintenance planning for multi-component redundant systems with various types of opportunities. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2020, 198, 106854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Hameed, M. A gamma wear process. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 1975, 24, 152–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Mabrouk, A.; Chelbi, A.; Radhoui, M. Optimal imperfect maintenance strategy for leased equipment. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2016, 178, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, D.R. Regression models and life-tables. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodol.) 1972, 34, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.Q.; Zhou, B.H.; Li, L. Integrated production, quality control and condition-based maintenance for imperfect production systems. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2018, 175, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-S.; Ho, J.-W.; Hung, J.-W.; Tseng, T.-L. A customized warranty model by considering multi-usage levels for the leasing industry. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2021, 215, 107769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Li, L. Joint optimization of production, quality control and maintenance for serial-parallel multistage production systems. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2020, 204, 107146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramasinghe, A.; Vilathgamuwa, M.; Nourbakhsh, G.; Corry, P. A Review of Dynamic Operating Envelopes: Computation, Applications and Challenges. Modelling 2025, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Zhou, X. Opportunistic preventive maintenance scheduling for serial-parallel multistage manufacturing systems with multiple streams of deterioration. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2017, 168, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, W.; Goupee, A.; Hallowell, S.; Viselli, A. Development of a Multi-Objective Optimization Tool for Screening Designs of Taut Synthetic Mooring Systems to Minimize Mooring Component Cost and Footprint. Modelling 2021, 2, 728–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| 1.81 | 138.2 | 0.013 | 2.96 | 0.0336 | |
| 2.28 | 234.6 | 0.257 | 2.35 | 0.0216 | |
| 2.16 | 204.6 | 0.173 | 3.43 | 0.0241 | |
| 1.17 | 142.1 | 0.417 | 1.86 | 0.0152 | |
| 1.56 | 154.3 | 0.325 | 3.23 | 0.0217 | |
| 2.18 | 254.6 | 0.207 | 2.15 | 0.0306 |
| 100,000 | 7224 | 200 | 310 | 500 | 1000 | 120 | |
| 120,000 | 6000 | 220 | 350 | 400 | 1200 | 70 | |
| 130,000 | 5544 | 280 | 340 | 410 | 1210 | 70 | |
| 160,000 | 3024 | 160 | 310 | 420 | 1220 | 60 | |
| 110,000 | 10,800 | 140 | 320 | 310 | 1110 | 60 | |
| 100,000 | 6600 | 180 | 210 | 410 | 1010 | 80 |
| RM Cost | OM Cost | PM Cost | CM Cost | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3000 | 1550 | 5500 | 5000 | |
| 4400 | 4200 | 0 | 0 | |
| 4760 | 2170 | 1200 | 0 | |
| 800 | 5100 | 0 | 0 | |
| 1400 | 2880 | 6820 | 0 | |
| 1980 | 3360 | 0 | 1010 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | … | 10 | … | 19 | 20 | … | 30 | … | 38 | … | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | … | 2 | … | 2 | 3 | … | 4 | … | 2 | … | |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | … | 1 | … | 2 | 2 | … | 2 | … | 2 | … | |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | … | 2 | … | 2 | 2 | … | 2 | … | 2 | … | |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | … | 2 | … | 2 | 3 | … | 2 | … | 2 | … | |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | … | 3 | … | 3 | 2 | … | 2 | … | 2 | … | |
| 1 | 1 | 2 | … | 2 | … | 2 | 2 | … | 2 | … | 4 | … |
| Parameters | Variation Range | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | Basic case | 26 | (0.324, 0.29, 0.259, 0.294, 0.3, 0.3) | (0.534, 0.61, 0.6, 0.498, 0.503, 0.555) | 270,362.00 | 297,499.59 | (0.36, 0.64) |
| −50% | 25 | (0.324, 0.312, 0.244, 0.309, 0.272, 0.283) | (0.558, 0.515, 0.43, 0.497, 0.475, 0.448) | 284,726.26 | 297,418.7 | (0.21, 0.79) | |
| −25% | 23 | (0.332, 0.304, 0.269, 0.292, 0.3, 0.32) | (0.547, 0.523, 0.481, 0.485, 0.482, 0.487) | 277,222.67 | 293,226.43 | (0.28, 0.72) | |
| +25% | 27 | (0.314, 0.292, 0.254, 0.299, 0.291, 0.305) | (0.529, 0.515, 0.45, 0.532, 0.509, 0.52) | 263,831.90 | 300,082.93 | (0.47, 0.53) | |
| +50% | 29 | (0.333, 0.282, 0.275, 0.297, 0.298, 0.297) | (0.553, 0.47, 0.446, 0.464, 0.468, 0.468) | 251,487.78 | 295,633.28 | (0.22, 0.78) | |
| −50% | 23 | (0.324, 0.286, 0.267, 0.285, 0.308, 0.291) | (0.566, 0.496, 0.484, 0.521, 0.485, 0.478) | 284,037.09 | 285,734.19 | (0.22, 0.78) | |
| −25% | 26 | (0.331, 0.299, 0.244, 0.304, 0.312, 0.308) | (0.518, 0.514, 0.452, 0.514, 0.579, 0.536) | 272,973.42 | 295,680.75 | (0.37, 0.63) | |
| +25% | 28 | (0.33, 0.302, 0.255, 0.298, 0.298, 0.301) | (0.543, 0.488, 0.462, 0.541, 0.489, 0.498) | 266,501.74 | 290,989.52 | (0.49, 0.51) | |
| +50% | 23 | (0.339, 0.294, 0.253, 0.277, 0.312, 0.318) | (0.509, 0.469, 0.446, 0.471, 0.521, 0.472) | 261,948.23 | 306,060.34 | (0.16, 0.84) | |
| −50% | 27 | (0.326, 0.291, 0.246, 0.284, 0.293, 0.288) | (0.511, 0.527, 0.439, 0.484, 0.505, 0.509) | 279,190.44 | 292,488.05 | (0.55, 0.45) | |
| −25% | 23 | (0.331, 0.307, 0.256, 0.295, 0.297, 0.304) | (0.534, 0.499, 0.454, 0.487, 0.524, 0.534) | 271,576.38 | 310,204.82 | (0.54, 0.46) | |
| +25% | 26 | (0.328, 0.287, 0.247, 0.299, 0.284, 0.3) | (0.528, 0.495, 0.471, 0.485, 0.465, 0.481) | 266,885.17 | 291,254.45 | (0.38, 0.62) | |
| +50% | 27 | (0.333, 0.293, 0.27, 0.296, 0.299, 0.28) | (0.589, 0.522, 0.466, 0.495, 0.492, 0.492) | 264,099.12 | 287,070.96 | (0.57, 0.43) | |
| −50% | 26 | (0.321, 0.287, 0.257, 0.29, 0.295, 0.29) | (0.523, 0.504, 0.465, 0.486, 0.528, 0.512) | 282,432.84 | 288,921.15 | (0.34, 0.66) | |
| −25% | 29 | (0.321, 0.291, 0.272, 0.295, 0.295, 0.302) | (0.544, 0.481, 0.455, 0.495, 0.503, 0.488) | 275,080.84 | 312,090.74 | (0.63, 0.37) | |
| +25% | 23 | (0.311, 0.294, 0.256, 0.281, 0.29, 0.319) | (0.481, 0.505, 0.456, 0.477, 0.491, 0.514) | 269,673.04 | 302,211.79 | (0.38, 0.62) | |
| +50% | 26 | (0.318, 0.293, 0.267, 0.294, 0.301, 0.283) | (0.517, 0.473, 0.493, 0.473, 0.526, 0.517) | 261,344.01 | 305,649.21 | (0.2, 0.8) | |
| −50% | 28 | (0.342, 0.3, 0.269, 0.298, 0.293, 0.301) | (0.521, 0.508, 0.46, 0.52, 0.476, 0.506) | 282,656.92 | 289,264.27 | (0.49, 0.51) | |
| −25% | 25 | (0.316, 0.296, 0.261, 0.299, 0.307, 0.297) | (0.492, 0.488, 0.45, 0.483, 0.512, 0.516) | 272,439.97 | 294,761.94 | (0.71, 0.29) | |
| +25% | 27 | (0.323, 0.277, 0.257, 0.295, 0.291, 0.316) | (0.506, 0.443, 0.487, 0.503, 0.515, 0.511) | 265,870.04 | 283,623.92 | (0.23, 0.77) | |
| +50% | 24 | (0.325, 0.282, 0.259, 0.301, 0.288, 0.286) | (0.534, 0.487, 0.455, 0.522, 0.502, 0.502) | 260,254.04 | 308,731.47 | (0.48, 0.52) | |
| −50% | 23 | (0.347, 0.273, 0.263, 0.273, 0.31, 0.308) | (0.516, 0.455, 0.498, 0.464, 0.485, 0.501) | 276,322.51 | 270,063.93 | (0.2, 0.8) | |
| −25% | 25 | (0.326, 0.292, 0.248, 0.275, 0.3, 0.302) | (0.534, 0.472, 0.474, 0.481, 0.463, 0.501) | 274,621.1 | 285,059.54 | (0.13, 0.87) | |
| +25% | 24 | (0.316, 0.288, 0.245, 0.29, 0.316, 0.291) | (0.529, 0.495, 0.446, 0.431, 0.53, 0.505) | 279,944.42 | 299,299.74 | (0.32, 0.68) | |
| +50% | 23 | (0.317, 0.307, 0.247, 0.308, 0.282, 0.292) | (0.519, 0.497, 0.448, 0.501, 0.491, 0.508) | 275,580.67 | 302,928.61 | (0.12, 0.88) | |
| −50% | 24 | (0.307, 0.287, 0.263, 0.293, 0.289, 0.289) | (0.506, 0.513, 0.461, 0.503, 0.465, 0.527) | 261,154.58 | 266,494.19 | (0.24, 0.76) | |
| −25% | 28 | (0.329, 0.294, 0.256, 0.303, 0.307, 0.29) | (0.533, 0.493, 0.463, 0.538, 0.522, 0.484) | 259,996.8 | 276,709.62 | (0.61, 0.39) | |
| +25% | 27 | (0.331, 0.31, 0.264, 0.282, 0.309, 0.318) | (0.513, 0.498, 0.496, 0.499, 0.497, 0.489) | 282,357.61 | 312,884.12 | (0.2, 0.8) | |
| +50% | 24 | (0.317, 0.294, 0.281, 0.305, 0.303, 0.297) | (0.49, 0.446, 0.481, 0.513, 0.501, 0.473) | 269,540.08 | 328,939.72 | (0.35, 0.65) |
| Dimension/Strategy | I-OBAM | S-RLPM | F-PRPM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trigger mechanism | , with RM | , considers RM or PM | only, RM not considered |
| System-level opportunity maintenance | Yes | No | No |
| Maintenance resource allocation | Dynamically scheduled using system downtime windows | Independently scheduled per device | Reactive to individual device condition |
| Application suitability | Multi-unit systems with high reliability and low loss | Small/medium-scale rentals focusing on operability | Rapid deployment with simplified logic |
| Strategy | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| I-OBAM | 270,362.00 | 297,499.59 | (0.36, 0.64) |
| S-RLPM | 285,800.71 | 397,802.77 | (0.34, 0.66) |
| F-PRPM | 271,798.65 | 448,551.21 | (0.35, 0.65) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, B.; Shao, S.; Cheng, G.; Wang, Y. Modeling and Optimization of Maintenance Strategies in Leasing Systems Considering Equipment Residual Value. Modelling 2025, 6, 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/modelling6030052
Deng B, Shao S, Cheng G, Wang Y. Modeling and Optimization of Maintenance Strategies in Leasing Systems Considering Equipment Residual Value. Modelling. 2025; 6(3):52. https://doi.org/10.3390/modelling6030052
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Boxing, Siyuan Shao, Guoqing Cheng, and Yujia Wang. 2025. "Modeling and Optimization of Maintenance Strategies in Leasing Systems Considering Equipment Residual Value" Modelling 6, no. 3: 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/modelling6030052
APA StyleDeng, B., Shao, S., Cheng, G., & Wang, Y. (2025). Modeling and Optimization of Maintenance Strategies in Leasing Systems Considering Equipment Residual Value. Modelling, 6(3), 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/modelling6030052






