Business Process Management Analysis with Cost Information in Public Organizations: A Case Study at an Academic Library
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Business Process Management
2.2. BPM and BPMS
2.3. BPM in the Public Sector
2.4. Activity-Based Costing and Time-Driven Activity-Based Costing
2.5. The Use of TDABC in Academic Libraries
3. Methodology
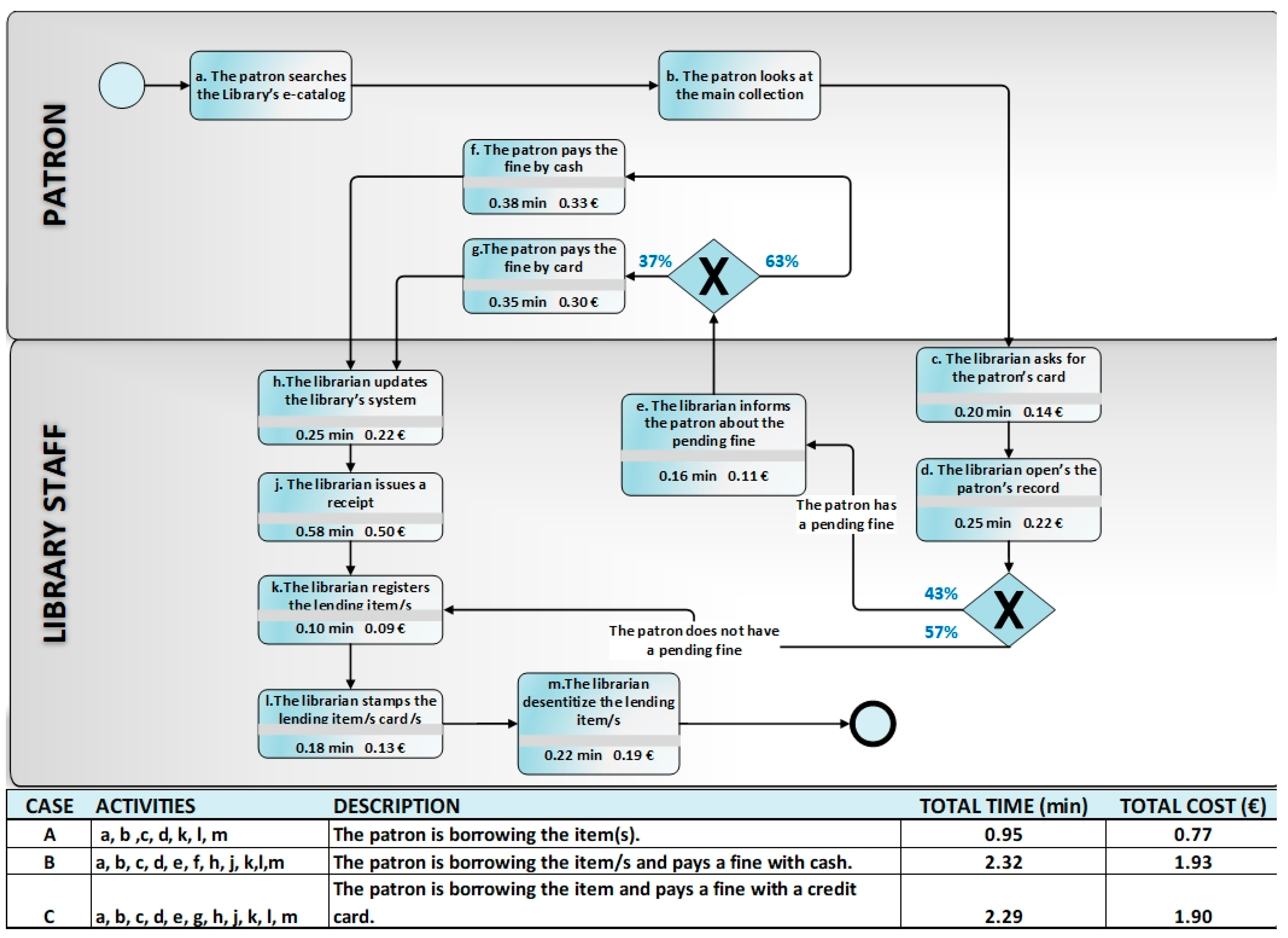
4. Results
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sigüenza Guzmán, L.; Van den Abbeele, A.; Cattrysse, D. Time-driven activity-based costing systems for cataloguing processes:A case study. LIBER Q. 2014, 23, 160–186. [Google Scholar]
- Kostagiolas, P.; Banou, C.; Vazaiou, S.; Kapellas, N. A qualitative survey for the academic libraries in the throes of a great recession. In Proceedings of the MATEC Web of Conferences (CSCC 2016), Corfu Island, Greece, 14–17 July 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Saunders, L. Academic libraries’ strategic plans: Top trends and under-recognized areas. J. Acad. Librariansh. 2015, 41, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissa, B.; Stavropoulos, A.; Karagiorgou, D.; Tsanaktsidou, E. Using time-driven activity-based costing to improve the managerial activities of academic libraries. J. Acad. Librariansh. 2019, 45, 102055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, M.B.; Rodrigues Filho, B.A.; Gonçalves, R.F. Business Process Management Notation for a Costing Model Conception. Braz. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2016, 13, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitsios, F.; Kamariotou, M. Business Strategy Modelling based on Enterprise Architecture: A State of the Art Review. Bus. Process Manag. J. 2019, 25, 606–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ougaabal, K.; Zacharewicz, G.; Ducq, Y.; Tazi, S. Visual Workflow Process Modeling and Simulation Approach Based on Non-Functional Properties of Resources. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leva, D.; Sulis, E. A business process methodology to investigate organization management: A hospital case study. WSEAS Trans. Bus. Econ. 2017, 14, 100–109. [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos, G.A.; Kechagias, E.; Legga, P.; Tatsiopoulos, I. Integrating Business Process Management with Public Sector. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management, Paris, France, 26–27 July 2018; pp. 405–414. [Google Scholar]
- Santana, A.F.L.; Alves, C.F.; Santos, H.R.M.; Lima Cavalcanti Felix, A.D. BPM governance: An exploratory study in public organizations. In Enterprise, Business-Process and Information Systems Modeling; Halpin, T., Nurcan, S., Krogstie, J., Soffer, P., Proper, E., Schmidt, R., Bider, I., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 46–60. [Google Scholar]
- Antonucci, Y.L.; Fortune, A.; Kirchmer, M. An examination of associations between business process management capabilities and the benefits of digitalization: All capabilities are not equal. Bus. Process Manag. J. 2020, 27, 124–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubaid, A.M.; Dweiri, F.T. Business process management (BPM): Terminologies and methodologies unified. Int. J. Syst. Assur. Eng. Manag. 2020, 11, 1046–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niehaves, B.; Plattfaut, R. From Bureaucratic to Quasi-market Environments: On the Co-evolution of Public Sector Business Process Management. In Electronic Government. EGOV 2010. Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Wimmer, M.A., Chappelet, J.L., Janssen, M., Scholl, H.J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 387–399. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller-Wickop, N.; Schultz, M.; Gehrke, N.; Nüttgens, M. Towards automated financial process auditing: Aggregation and visualization of process models. In Proceedings of the 4th International Workshop on Enterprise Modelling and Information Systems Architectures (EMISA 2011), Hamburg, Germany, 22–23 September 2011; pp. 121–134. [Google Scholar]
- Magnani, M.; Montesi, D. BPMN: How Much Does It Cost? An Incremental Approach. In Business Process Management; Alonso, G., Dadam, P., Rosemann, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; Brisbane, CA, USA, 2007; pp. 80–87. [Google Scholar]
- Van Looy, A. A quantitative and qualitative study of the link between business process management and digital innovation. Inf. Manag. 2021, 58, 103413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binci, D.; Belisari, S.; Appolloni, A. BPM and change management: An ambidextrous perspective. Bus. Process Manag. J. 2020, 26, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacosa, E.; Mazzoleni, A.; Usai, A. Business Process Management (BPM): How complementary BPM capabilities can build an ambidextrous state in business process activities of family firms. Bus. Process Manag. J. 2018, 24, 1145–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.L.; Varajão, J.; Uahi, R. A new approach for improving work distribution in business processes supported by BPMS. Bus. Process Manag. J. 2020, 26, 1643–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynn, M.; Low, W.; Ter Hofstede, A.; Nauta, W. A Framework for Cost-Aware Process Management: Cost Reporting and Cost Prediction. J. Univers. Comput. Sci. 2014, 20, 406–430. [Google Scholar]
- Benedict, T.; Bilodeau, N.; Vitkus, P.; Powell, E.; Morris, D.; Scarsig, M.; Lee, D.; Field, G.; Lohr, T.; Saxena, R. BPM CBOK V3.0. 2013: Guide to Business Process Management Body of Knowledge—Commom Body of Knowledge, 1st ed.; Association of Business Process Management Professionals (ABPMP): Saint Paul, MN, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ilahi, L.; Ghannouchi, S.A.; Martinho, R. BPFlexTemplate: A Business Process template generation tool based on similarity and flexibility. Int. J. Inf. Syst. Proj. Manag. 2017, 5, 67–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingos, D.; Martins, F. Using BPMN to model Internet of Things behavior within business process. Int. J. Inf. Syst. Proj. Manag. 2017, 5, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.L.; Sá, J.O. Process-based information systems development: Taking advantage of a component-based infrastructure. Bus. Syst. Res. Int. J. Soc. Adv. Innov. Res. Econ. 2017, 8, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, R.; Bandara, W.; French, E.; Stewart, G. Getting it right! Critical success factors of BPM in the public sector: A systematic literature review. Australas. J. Inf. Syst. 2018, 22, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- vom Brocke, J.; Zelt, S.; Schmiedel, T. On the role of context in business process management. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2016, 36, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Looy, A.; Van den Bergh, J. The effect of organization size and sector on adopting business process management. Bus. Inf. Syst. Eng. 2017, 60, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ongena, G.; Ravesteyn, P. Business process management maturity and performance: A multi group analysis of sectors and organization sizes. Bus. Process Manag. J. 2020, 26, 132–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helbin, T.; Van Looy, A. Is business process management (BPM) ready for ambidexterity? Conceptualization, implementation guidelines and research agenda. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharmawan, Y.S.; Divinagracia, G.G.; Woods, E.; Kwong, B. Inter-dependencies on BPM maturity model capability factors in deriving BPM roadmap. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 161, 1089–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulledge, T.R.; Sommer, R.A. Business process management: Public sector implications. Bus. Process Manag. J. 2002, 8, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, L.; Barbosa, M.B.A.; Baldam, R.D.L.; Coelho Jr, T.D.P. Challenges of Process Modeling in Architecture and Engineering to Execute Projects and Public Works. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2019, 145, 05018015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haisjackl, C.; Soffer, P.; Lim, S.Y.; Weber, B. How do humans inspect BPMN models: An exploratory study. Softw. Syst. Model. 2018, 17, 655–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häußler, M.; Borrmann, A. Knowledge-based engineering in the context of railway design by integrating BIM, BPMN, DMN and the methodology for knowledge-based engineering applications (MOKA). J. Inf. Technol. Constr. 2021, 26, 193–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recker, J. Opportunities and constraints: The current struggle with BPMN. Bus. Process Re-Eng. Manag. J. 2010, 16, 181–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genon, N.; Heymans, P.; Amyot, D. Analysing the Cognitive Effectiveness of the BPMN 2.0 Visual Notation. In Software Language Engineering. SLE 2010. Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Malloy, B., Staab, S., van den Brand, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 377–396. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, R.; Kaplan, R.S. The promise-and peril-of integrated cost systems. Harv. Bus. Rev. 1998, 76, 109–120. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis-Newman, J.; Robinson, P. The cost of library services: Activity-based costing in an Australian academic library. J. Acad. Librariansh. 1998, 24, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szychta, A. Time-Driven Activity-Based Costing in Service Industries. Soc. Sci. 2010, 67, 49–60. [Google Scholar]
- Tse, M.; Gong, M. Recognition of Idle Resources in Time-Driven Activity-Based Costing and Resource Consumption Accounting Models. J. Appl. Manag. Account. Res. 2009, 7, 41–54. [Google Scholar]
- Sigüenza Guzmán, L.; Auquilla, A.; Van den Abbeele, A.; Cattrysse, D. Using time driven activity-based costing to identify best practices in academic libraries. J. Acad. Librariansh. 2016, 42, 232–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do Nascimento, A.R.; de Lima Baldam, R.; Costa, L.; Junior, T.D.P.C. Applications of business governance and the Unified BPM Cycle in public credit recovery activities. Bus. Process Manag. J. 2019, 26, 312–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, N.J.; Miller, I.R. The library as service-learning partner: A win–win collaboration with students and faculty. Coll. Undergrad. Libr. 2008, 15, 399–413. [Google Scholar]
- Sampath, P.; Wirsing, M. Computing the cost of business processes. In Information Systems: Modeling, Development, and Integration; UNISCON 2009. Lecture Notes in Business Information Processing; Yang, J., Ginige, A., Mayr, H.C., Kutsche, R.D., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 178–183. [Google Scholar]
- Pernot, E.; Roodhooft, F.; Van den Abbeele, A. Time-driven activity-based costing for inter-library services: A case study in a university. J. Acad. Librariansh. 2007, 33, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stouthuysen, K.; Swiggers, M.; Reheul, A.M.; Roodhooft, F. Time-driven activity based costing for a library acquisition process: A case study in a Belgian University. Libr. Collect. Acquis. Tech. Serv. 2010, 34, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kont, K.R.; Jantson, S. Activity-based costing (ABC) and time-driven activity-based costing (TDABC): Applicable methods for university libraries? Evid. Based Libr. Inf. Pract. 2011, 6, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kont, K.R. What do acquisition activities really cost? A case study in Estonian university libraries. Libr. Manag. 2015, 36, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everaert, P.; Bruggeman, W.; Sarens, G.; Anderson, S.R.; Levant, Y. Cost modeling in logistics using time-driven ABC: Experiences from a wholesaler. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2008, 38, 172–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.K. Case Study Research: Design and Methods, 5th ed.; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gounopoulos, E.; Kontogiannis, S.; Valsamidis, S.; Kazanidis, I. Blended Learning Evaluation in Higher Education Courses. KnE Soc. Sci. 2017, 1, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigcha, E.; Morocho, V.; Siguenza-Guzman, L. Towards the implementation of a software platform based on BPMN and TDABC for strategic management. In Proceedings of the Technology Trends: 4th International Conference, CITT 2018, Revised Selected Papers 4, Babahoyo, Ecuador, 29–31 August 2018; Springer: New York City, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 259–273. [Google Scholar]

| Feature | ABC Method | TDABC Method |
|---|---|---|
| Cost allocation | In two stages | In one stage |
| Estimation of drivers | Subjective | Objective |
| Action for an additional activity | Survey | Estimation of the unit time of the new activity |
| Method cost | Expensive | Easy to create and maintain |
| System building | Per season or per year | Per event |
| System update | Expensive | Flexible |
| Information | Less precise | Precise |
| Transparency | Good | Very good |
| Overestimation of costs | Yes, possible overestimation of unit cost and sale price | No |
| Differentiation of service level | No | Yes |
| Oversimplification of activities | Yes | No |
| Capacity planning | Neglects unused capacity | May perform further capacity analysis |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kissa, B.; Gounopoulos, E.; Kamariotou, M.; Kitsios, F. Business Process Management Analysis with Cost Information in Public Organizations: A Case Study at an Academic Library. Modelling 2023, 4, 251-263. https://doi.org/10.3390/modelling4020014
Kissa B, Gounopoulos E, Kamariotou M, Kitsios F. Business Process Management Analysis with Cost Information in Public Organizations: A Case Study at an Academic Library. Modelling. 2023; 4(2):251-263. https://doi.org/10.3390/modelling4020014
Chicago/Turabian StyleKissa, Barbara, Elias Gounopoulos, Maria Kamariotou, and Fotis Kitsios. 2023. "Business Process Management Analysis with Cost Information in Public Organizations: A Case Study at an Academic Library" Modelling 4, no. 2: 251-263. https://doi.org/10.3390/modelling4020014
APA StyleKissa, B., Gounopoulos, E., Kamariotou, M., & Kitsios, F. (2023). Business Process Management Analysis with Cost Information in Public Organizations: A Case Study at an Academic Library. Modelling, 4(2), 251-263. https://doi.org/10.3390/modelling4020014











