Single-Center 5-Year Observational Study of Thrice-Weekly Single-Strength Sulfamethoxazole–Trimethoprim as Adequate Prophylaxis for Pneumocystis jirovecii Pneumonia in Patients with Heart Transplants
Abstract
1. Introduction
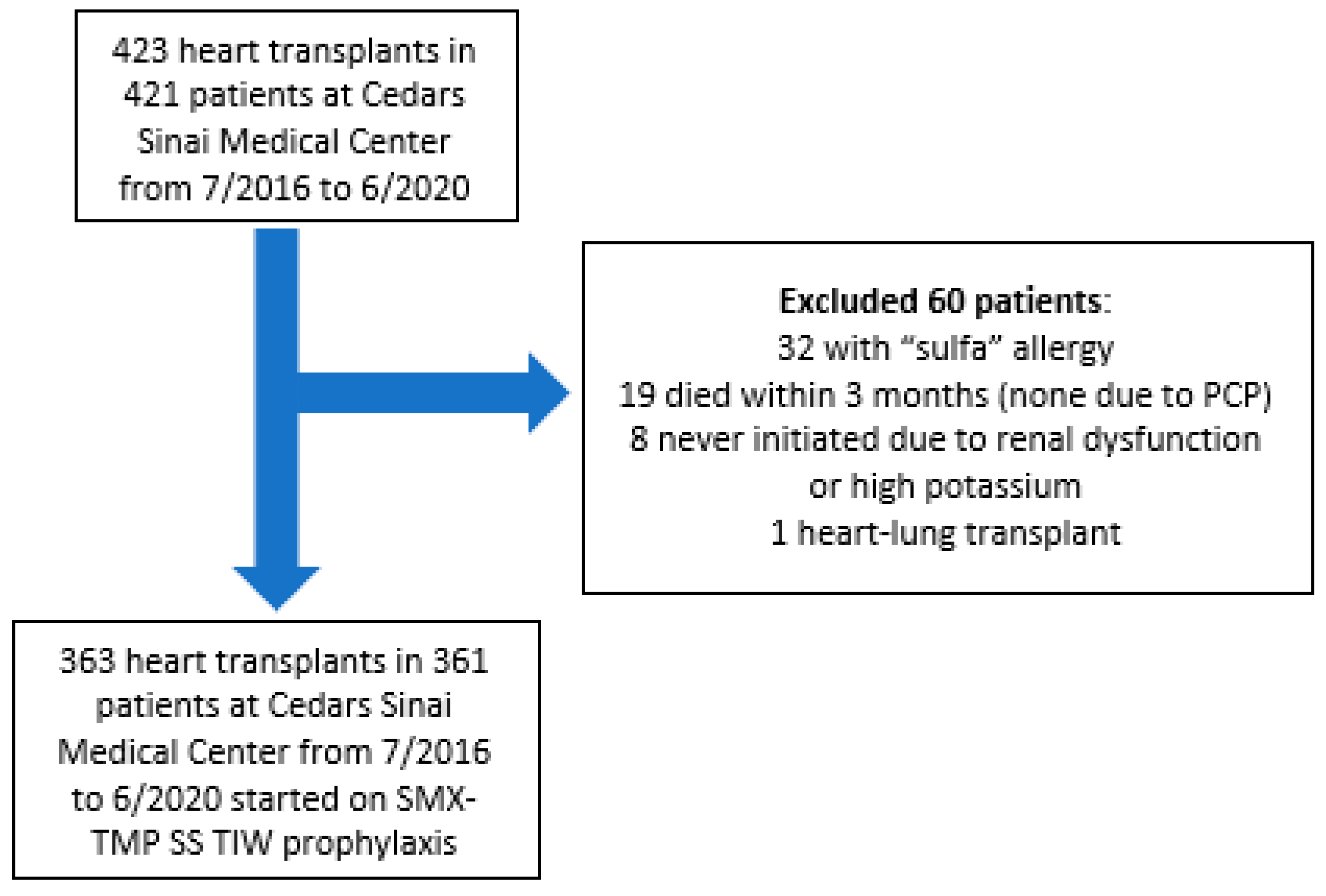
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. PCP Incidence
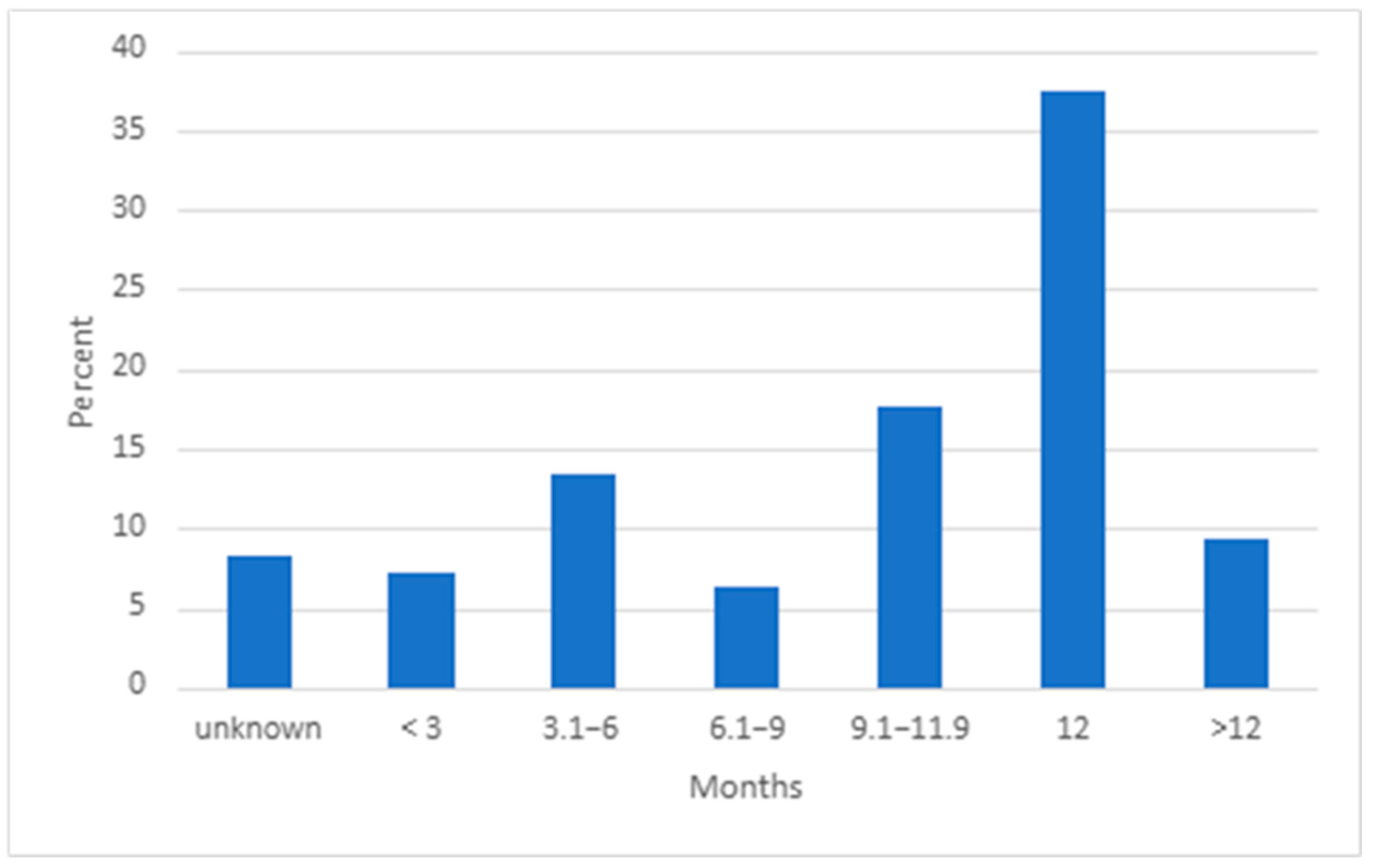
3.3. PCP Prophylaxis Timing
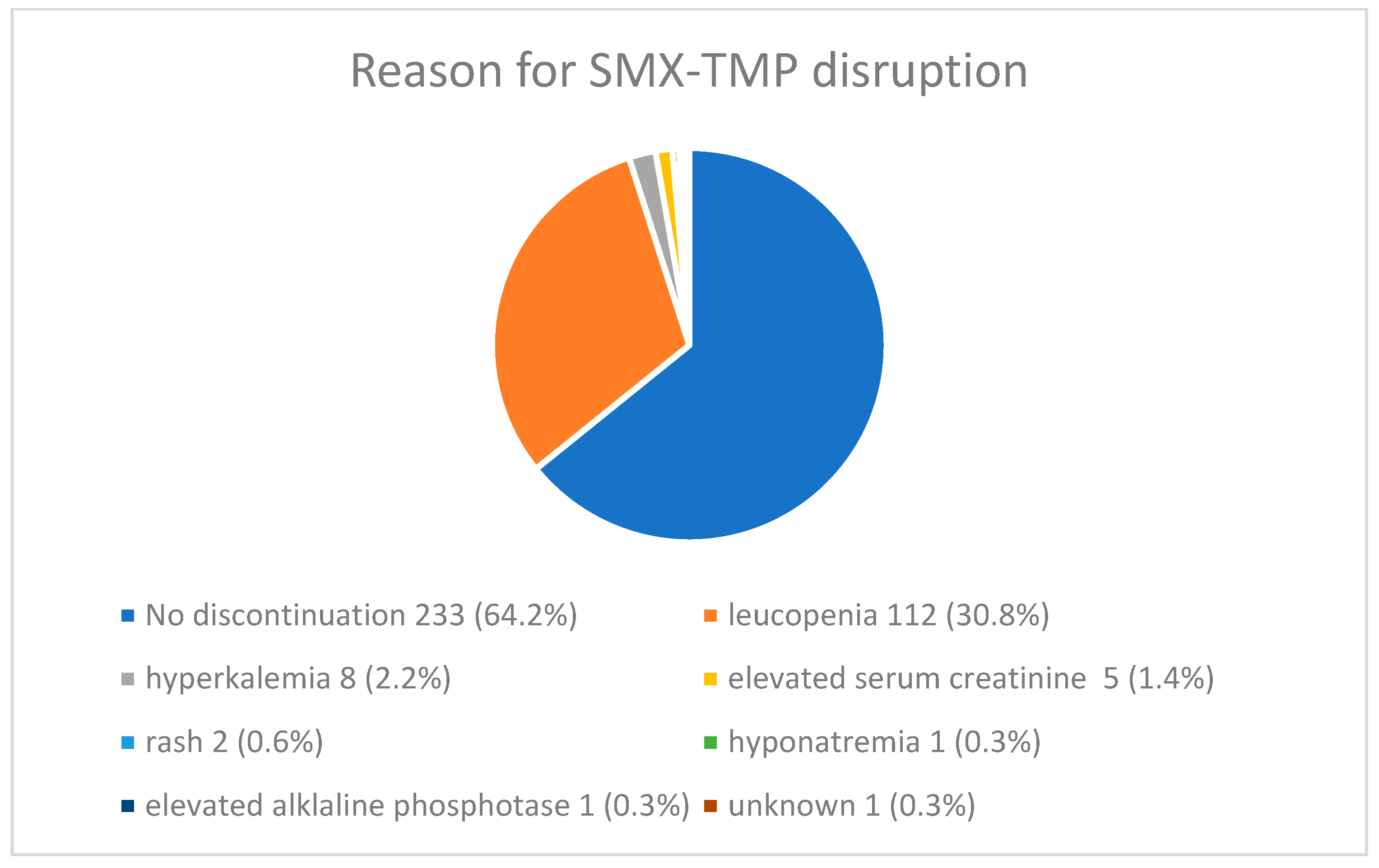
3.4. SMX-TMP Adverse Effects
3.5. Immunosuppression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kovacs, J.A.; Gill, V.J.; Meshnick, S.; Masur, H. New insights into transmission, diagnosis, and drug treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. JAMA 2001, 286, 2450–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catherinot, E.; Lanternier, F.; Bougnoux, M.E.; Lecuit, M.; Couderc, L.J.; Lortholary, O. Pneumocystis jirovecii Pneumonia. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2010, 24, 107–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fishman, J.A.; Gans, H.; AST Infectious Diseases Community of Practice. Pneumocystis jiroveci in solid organ transplantation: Guidelines from the American Society of Transplantation Infectious Diseases Community of Practice. Clin. Transplant. 2019, 33, e13587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, E.; Lionet, A.; Kipnis, E.; Noël, C.; Hazzan, M. Risk factors for Pneumocystis pneumonia after the first 6 months following renal transplantation. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2017, 19, e12735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iriart, X.; Bouar, M.L.; Kamar, N.; Berry, A. Pneumocystis Pneumonia in Solid-Organ Transplant Recipients. J. Fungi 2015, 1, 293–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, H.; Paul, M.; Vidal, L.; Leibovici, L. Prophylaxis of Pneumocystis pneumonia in immunocompromised non-HIV-infected patients: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2007, 82, 1052–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, S.M.; LaRosa, S.P.; Kalmadi, S.; Arroliga, A.C.; Avery, R.K.; Truesdell-LaRosa, L.; Longworth, D.L. Should prophylaxis for Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in solid organ transplant recipients ever be discontinued? Clin. Infect. Dis. 1999, 28, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, P.; Muñoz, R.M.; Palomo, J.; Rodríguez-Creixéms, M.; Muñoz, R.; Bouza, E. Pneumocystis carinii infection in heart transplant recipients. Efficacy of a weekend prophylaxis schedule. Medicine 1997, 76, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utsunomiya, M.; Dobashi, H.; Odani, T.; Saito, K.; Yokogawa, N.; Nagasaka, K.; Takenaka, K.; Soejima, M.; Sugihara, T.; Hagiyama, H.; et al. Optimal regimens of sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim for chemoprophylaxis of Pneumocystis pneumonia in patients with systemic rheumatic diseases: Results from a non-blinded, randomized controlled trial. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Prasad, G.V.R.; Beckley, J.; Mathur, M.; Gunasekaran, M.; Nash, M.M.; Rapi, L.; Huang, M.; Zaltzman, J.S. Safety and efficacy of prophylaxis for Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia involving trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole dose reduction in kidney transplantation. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, K.; Berrigan, L.; Popovic, K.; Wiebe, C.; Sun, S.; Ho, J. Lifelong, universal Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia prophylaxis: Patient uptake and adherence after kidney transplant. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2021, 23, e13509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghembaza, A.; Vautier, M.; Cacoub, P.; Pourcher, V.; Saadoun, D. Risk Factors and Prevention of Pneumocystis jirovecii Pneumonia in Patients with Autoimmune and Inflammatory Diseases. Chest 2020, 158, 2323–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oz, H.S.; Hughes, W.T. Novel anti-Pneumocystis carinii effects of the immunosuppressant mycophenolate mofetil in contrast to provocative effects of tacrolimus, sirolimus, and dexamethasone. J. Infect. Dis. 1997, 175, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azevedo, L.S.; Castro, M.C.; Paula, F.J.; Ianhez, L.E.; David-Neto, E. Mycophenolate mofetil may protect against Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in renal transplanted patients. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 2005, 47, 143–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perazella, M.A. Crystal-induced acute renal failure. Am. J. Med. 1999, 106, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delanaye, P.; Mariat, C.; Cavalier, E.; Maillard, N.; Krzesinksi, J.; White, C.A. Trimethoprim, Creatinine and creatinine-based equations. Nephro Clin. Pract. 2011, 119, c187–c194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Permpalung, N.; Kittipibul, V.; Mekraksakit, P.; Rattanawong, P.; Nematollahi, S.; Zhang, S.X.; Steinke, S.M. A Comprehensive Evaluation of Risk Factors for Pneumocystis jirovecii Pneumonia in Adult Solid Organ Transplant Recipients: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Transplantation 2021, 105, 2291–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Boer, M.G.; Kroon, F.P.; le Cessie, S.; de Fijter, J.W.; van Dissel, J.T. Risk factors for Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in kidney transplant recipients and appraisal of strategies for selective use of chemoprophylaxis. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2011, 13, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neff, R.T.; Jindal, R.M.; Yoo, D.Y.; Hurst, F.P.; Agodoa, L.Y.; Abbott, K.C. Analysis of USRDS: Incidence and risk factors for Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia. Transplantation 2009, 88, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limper, A.H.; Knox, K.S.; Sarosi, G.A.; Ampel, N.M.; Bennett, J.E.; Catanzaro, A.; Davies, S.F.; Dismukes, W.E.; Hage, C.A.; Marr, K.A.; et al. An official American Thoracic Society statement: Treatment of fungal infections in adult pulmonary and critical care patients. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 96–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yale, S.H.; Limper, A.H. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in patients without acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: Associated illness and prior corticosteroid therapy. Mayo Clin. Proc. 1996, 71, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepkowitz, K.A.; Brown, A.E.; Telzak, E.E.; Gottlieb, S.; Armstrong, D. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia among patients without AIDS at a cancer hospital. JAMA 1992, 267, 832–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mecoli, C.A.; Saylor, D.; Gelber, A.C.; Christopher-Stine, L. Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia in rheumatic disease: A 20-year single-centre experience. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2017, 35, 671–673. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez Santiago, T.M.; Wetter, D.A.; Kalaaji, A.N.; Limper, A.H.; Lehman, J.S. Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia in patients treated with systemic immunosuppressive agents for dermatologic conditions: A systematic review with recommendations for prophylaxis. Int. J. Dermatol. 2016, 55, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, C.F., Jr.; Limper, A.H. Pneumocystis pneumonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 2487–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Center for Disease Control. Pneumocystis Pneumonia 2024. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/pneumocystis-pneumonia/about/index.html (accessed on 8 August 2024).
- Medrano, F.J.; Montes-Cano, M.; Conde, M.; de la Horra, C.; Respaldiza, N.; Gasch, A.; Perez-Lozano, M.J.; Varela, J.M.; Calderon, E.J. Pneumocystis jirovecii in general population. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, J.M. Pneumocystis carinii and geographic clustering: Evidence for transmission of infection. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 162, 1605–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumoulin, A.; Mazars, E.; Seguy, N.; Gargallo-Viola, D.; Vargas, S.; Cailliez, J.C.; Aliouat, E.M.; Wakefield, A.E.; Dei-Cas, E. Transmission of Pneumocystis carinii disease from immunocompetent contacts of infected hosts to susceptible hosts. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2000, 19, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brakemeier, S.; Pfau, A.; Zukunft, B.; Budde, K.; Nickel, P. Prophylaxis and treatment of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia after solid organ transplantation. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 134, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, A.; Beard, C.B.; Huang, L. Update on the epidemiology and transmission of Pneumocystis carinii. Microbes Infect. 2002, 4, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pifer, L.L.; Hughes, W.T.; Stagno, S.; Woods, D. Pneumocystis carinii infection: Evidence for high prevalence in normal and immunosuppressed children. Pediatrics 1978, 61, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, C.B.; Carter, J.L.; Keely, S.P.; Huang, L.; Pieniazek, N.J.; Moura, I.N.; Roberts, J.M.; Hightower, A.W.; Bens, M.S.; Freeman, A.R.; et al. Genetic variation in Pneumocystis carinii isolates from different geographic regions: Implications for transmission. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2000, 6, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, M.S.; Vermund, S.H.; Jacobs, R.; Durant, P.J.; Shaw, M.M.; Smith, J.W.; Tang, X.; Lu, J.J.; Li, B.; Jin, S.; et al. Detection of Pneumocystis carinii DNA in air samples: Likely environmental risk to susceptible persons. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 2511–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choukri, F.; Menotti, J.; Sarfati, C.; Lucet, J.C.; Nevez, G.; Garin, Y.J.; Derouin, F.; Totet, A. Quantification and spread of Pneumocystis jirovecii in the surrounding air of patients with Pneumocystis pneumonia. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 51, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vindrios, W.; Argy, N.; Le Gal, S.; Lescure, F.-X.; Massias, L.; Le, M.P.; Wolff, M.; Yazdanpanah, Y.; Nevez, G.; Houze, S.; et al. Outbreak of Pneumocystis jirovecii Infection Among Heart Transplant Recipients: Molecular Investigation and Management of an Interhuman Transmission. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 65, 1120–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiannakis, E.P.; Boswell, T.C. Systematic review of outbreaks of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia: Evidence that P. jirovecii is a transmissible organism and the implications for healthcare infection control. J. Hosp. Infect. 2016, 93, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarcz, L.; Chen, M.J.; Vittinghoff, E.; Hsu, L.; Schwarcz, S. Declining incidence of AIDS-defining opportunistic illnesses: Results from 16 years of population-based AIDS surveillance. AIDS 2013, 27, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lor, K.; Le, C.; Kransdorf, E.; Kittleson, M. Single-Center 5-Year Observational Study of Thrice-Weekly Single-Strength Sulfamethoxazole–Trimethoprim as Adequate Prophylaxis for Pneumocystis jirovecii Pneumonia in Patients with Heart Transplants. Transplantology 2025, 6, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/transplantology6010003
Lor K, Le C, Kransdorf E, Kittleson M. Single-Center 5-Year Observational Study of Thrice-Weekly Single-Strength Sulfamethoxazole–Trimethoprim as Adequate Prophylaxis for Pneumocystis jirovecii Pneumonia in Patients with Heart Transplants. Transplantology. 2025; 6(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/transplantology6010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleLor, Kevin, Catherine Le, Evan Kransdorf, and Michelle Kittleson. 2025. "Single-Center 5-Year Observational Study of Thrice-Weekly Single-Strength Sulfamethoxazole–Trimethoprim as Adequate Prophylaxis for Pneumocystis jirovecii Pneumonia in Patients with Heart Transplants" Transplantology 6, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/transplantology6010003
APA StyleLor, K., Le, C., Kransdorf, E., & Kittleson, M. (2025). Single-Center 5-Year Observational Study of Thrice-Weekly Single-Strength Sulfamethoxazole–Trimethoprim as Adequate Prophylaxis for Pneumocystis jirovecii Pneumonia in Patients with Heart Transplants. Transplantology, 6(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/transplantology6010003





