The Non-Muscle-Splitting Mini-Incision Donor Nephrectomy Remains a Feasible Technique in the Laparoscopic Era of Living Kidney Donation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
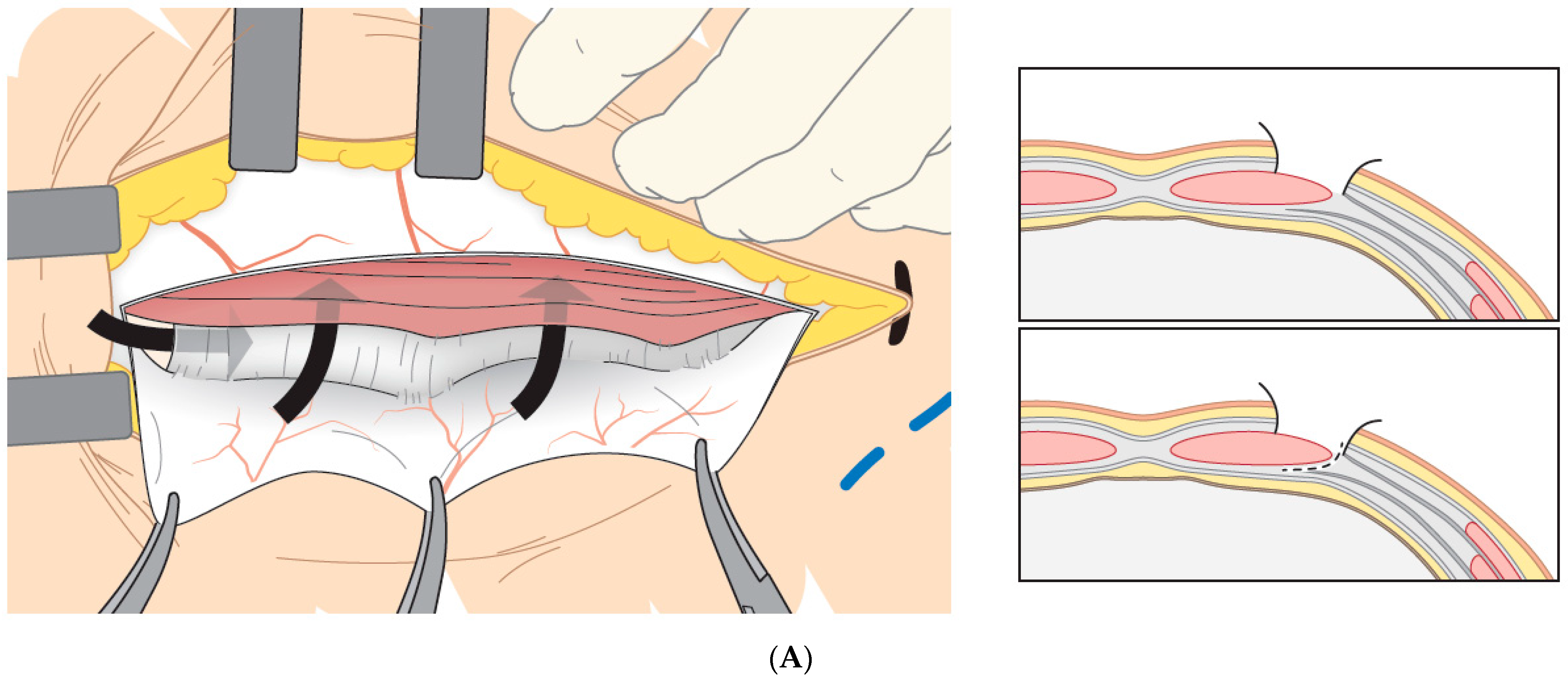
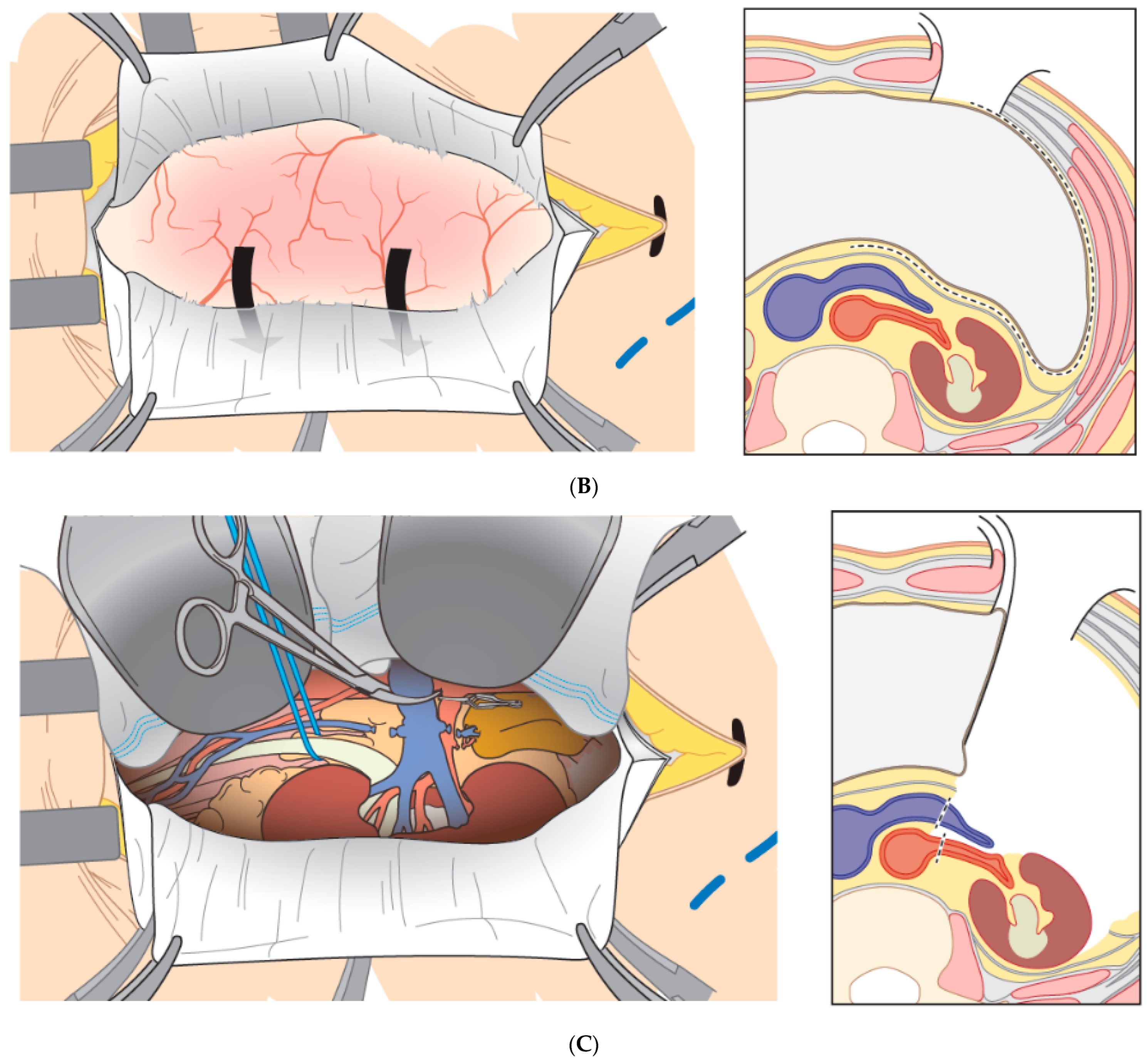
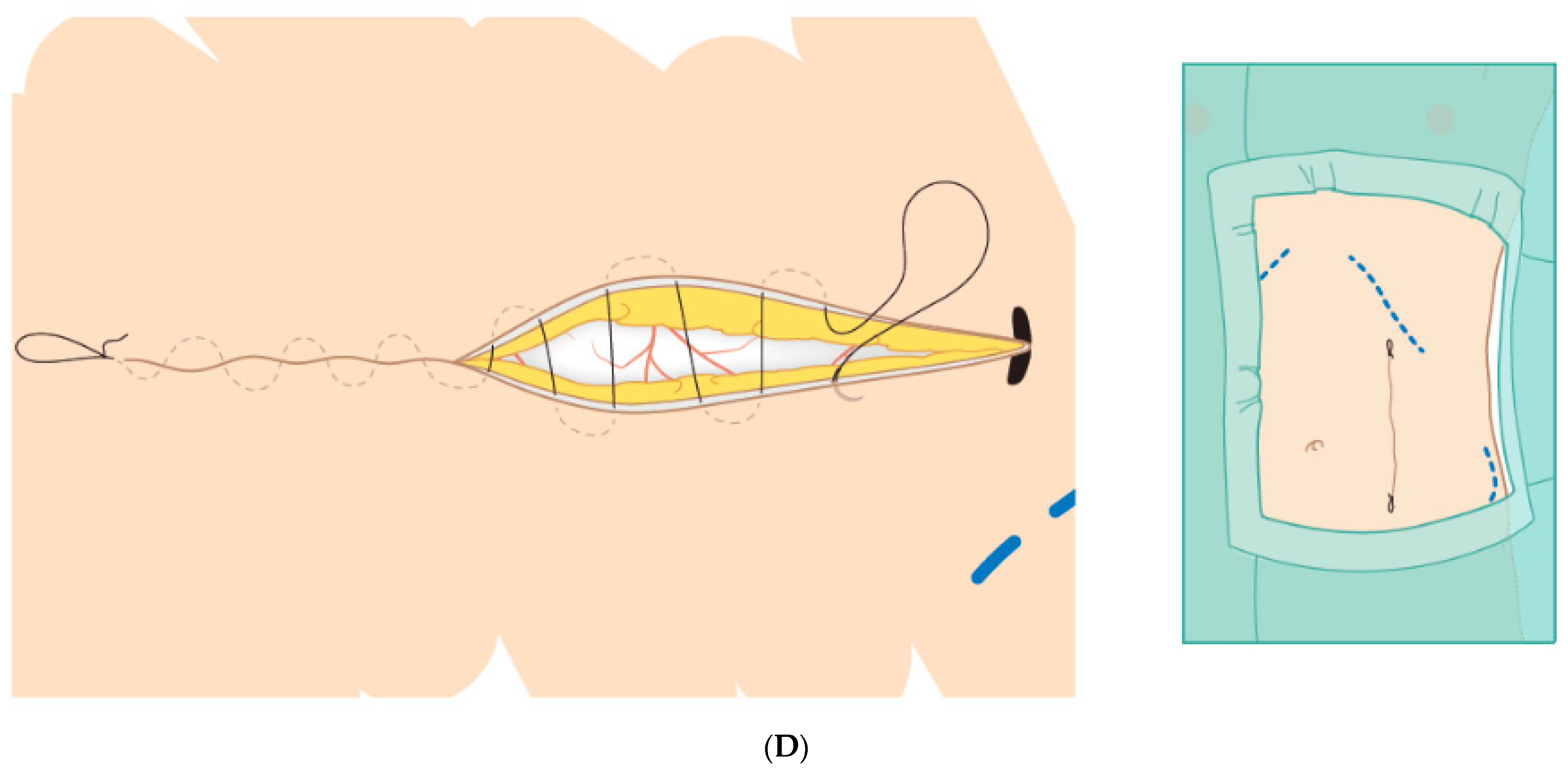
2.2. Non-Muscle-Splitting Mini Open Donor Nephrectomy (MINI)
2.3. Laparoscopic Donor Nephrectomy (LDN)
3. Outcome Measures
4. Statistical Analysis
5. Results
5.1. Patient Preference and Previously Undergone Surgical Treatments
5.2. Donor Characteristics
5.3. Primary Outcome
5.4. Secondary Outcomes
5.5. Impact of MINI on Perioperative Parameters: A Multivariable Model
6. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMI | Body mass index |
| CDS | Clavien–Dindo score |
| CIT | Cold ischemic time |
| EBL | Estimated blood loss |
| EGFR | Estimated glomerular filtration rate |
| HAP | Hospital-acquired pneumonia |
| HARP | Hand-assisted retro peritoneoscopy |
| LDN | Laparoscopic donor nephrectomy |
| MINI | Non-muscle-splitting mini donor nephrectomy |
| OT | Operation time |
| WIT | Warm ischemic time |
References
- Dutch Transplant Foundation. Annual Report 2018. 2020. Available online: https://www.transplantatiestichting.nl/files/Jaarverslag/nts-jaarverslag-2018.pdf (accessed on 13 August 2020).
- Nemati, E.; Einollahi, B.; Lesan Pezeshki, M.; Porfarziani, V.; Fattahi, M.R. Does kidney transplantation with deceased or living donor affect graft survival? Nephrourol. Mon. 2014, 6, e12182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, G.; Holden, R. Transplantation of kidneys, experimentally and in human cases. Am. J. Surg. 1954, 87, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kok, N.F.; Alwayn, I.P.; Schouten, O.; Tran, K.T.; Weimar, W.; Ijzermans, J.N. Mini-incision open donor nephrectomy as an alternative to classic lumbotomy: Evolution of the open approach. Transpl. Int. 2006, 19, 500–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratner, L.E.; Ciseck, L.J.; Moore, R.G.; Cigarroa, F.G.; Kaufman, H.S.; Kavoussi, L.R. Laparoscopic live donor nephrectomy. Transplantation 1995, 60, 1047–1049. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Giacomoni, A.; Di Sandro, S.; Lauterio, A.; Concone, G.; Buscemi, V.; Rossetti, O.; Rossetti, O.; De Carlis, L. Robotic nephrectomy for living donation: Surgical technique and literature systematic review. Am. J. Surg. 2016, 211, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Galley, R.; Hood, N.; Young, C.J.; Deierhoi, M.; Urban, D.A. Donor nephrectomy: A comparison of techniques and results of open, hand assisted and full laparoscopic nephrectomy. J. Urol. 2004, 171, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonouni, H.; Mehrabi, A.; Golriz, M.; Zeier, M.; Muller-Stich, B.P.; Schemmer, P.; Werner, J. Comparison of the laparoscopic versus open live donor nephrectomy: An overview of surgical complications and outcome. Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 2014, 399, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, H.N.; Foley, R.; Tan, L.; Rogers, T.; Bailey, R.F.; Guo, H.; Gross, C.R.; Matas, A.J. Long-term consequences of kidney donation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, C.H.; Sanni, A.; Rix, D.A.; Soomro, N.A. Laparoscopic versus open nephrectomy for live kidney donors. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2011, CD006124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dindo, D.; Demartines, N.; Clavien, P.A. Classification of surgical complications: A new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann. Surg. 2004, 240, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simforoosh, N.; Basiri, A.; Tabibi, A.; Shakhssalim, N.; Hosseini Moghaddam, S.M. Comparison of laparoscopic and open donor nephrectomy: A randomized controlled trial. BJU Int. 2005, 95, 851–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanidis, T.G.; Antcliffe, D.; Kokkinos, C.; Borysiewicz, C.A.; Darzi, A.W.; Tekkis, P.P.; Papalois, V.E. Laparoscopic versus open live donor nephrectomy in renal transplantation: A meta-analysis. Ann. Surg. 2008, 247, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antcliffe, D.; Nanidis, T.G.; Darzi, A.W.; Tekkis, P.P.; Papalois, V.E. A meta-analysis of mini-open versus standard open and laparoscopic living donor nephrectomy. Transpl. Int. 2009, 22, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greco, F.; Hoda, M.R.; Alcaraz, A.; Bachmann, A.; Hakenberg, O.W.; Fornara, P. Laparoscopic living-donor nephrectomy: Analysis of the existing literature. Eur. Urol. 2010, 58, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basiri, A.; Simforoosh, N.; Heidari, M.; Moghaddam, S.M.; Otookesh, H. Laparoscopic v open donor nephrectomy for pediatric kidney recipients: Preliminary report of a randomized controlled trial. J. Endourol. 2007, 21, 1033–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofker, H.S.; Nijboer, W.N.; Niesing, J.; Krikke, C.; Seelen, M.A.; van Son, W.J.; van Wijhe, M.; Groen, H.; vd Heide, J.J.H.; Ploeg, R.J. A randomized clinical trial of living donor nephrectomy: A plea for a differentiated appraisal of mini-open muscle splitting incision and hand-assisted laparoscopic donor nephrectomy. Transpl. Int. 2012, 25, 976–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano, O.K.; Kirchner, V.; Bangdiwala, A.; Vock, D.M.; Dunn, T.B.; Finger, E.B.; Payne, W.D.; Pruett, T.L.; Sutherland, D.E.R.; Najarian, J.S.; et al. Evolution of Living Donor Nephrectomy at a Single Center: Long-term Outcomes With 4 Different Techniques in Greater Than 4000 Donors Over 50 Years. Transplantation 2016, 100, 1299–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prionas, A.; Craddock, C.; Papalois, V. Feasibility, Safety and Efficacy of Enhanced Recovery After Living Donor Nephrectomy: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, M.L.; Sommer, M.; de Rijke, J.M.; Kessels, F.; Heineman, E.; Patijn, J.; Marcus, M.A.E.; Vlaeyen, J.W.S.; van Kleef, M. Somatic and psychologic predictors of long-term unfavorable outcome after surgical intervention. Ann. Surg. 2007, 245, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| MINI (N = 287) | LDN (N = 355) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Donor Related | |||
| Age (years) | 55 ± 11 | 52 ± 12 | 0.002 |
| Sex (male/female) | 50.2/49.8% | 33.8/66.2% | <0.001 |
| Length (cm) | 173 ± 9.5 | 172 ± 9.5 | 0.068 |
| Weight (kg) | 78.7 ± 13.2 | 76.7 ± 13.7 | 0.050 |
| BMI | 26.0 ± 3.6 | 25.7 ± 3.7 | 0.257 |
| Pre-donation Creatinine (µmol/L) | 73.8 ± 12.5 | 74.0 ± 40.3 | 0.936 |
| Operation Related | |||
| WIT (s) | 100 ± 56 | 296 ± 117 | <0.001 |
| Operation duration (min) | 175 ± 40 | 187 ± 41 | <0.001 |
| Estimated blood loss (mL) | 275 ± 382 | 136 ± 201 | <0.001 |
| Hand assisted | - | 107 (30.1%) | - |
| Converted to hand assisted | - | 6 (1.7%) | - |
| Converted to open | - | 3 (0.8%) | - |
| Donation period | <0.001 | ||
| 2011–2013 | 113 (58.3%) | 81 (41.7%) | |
| 2014–2016 | 132 (61.4%) | 83 (38.6%) | |
| 2017–2019 | 22 (10.3%) | 191 (89.7%) | |
| Hospitalization (days) * | 3.2 ± 1.6 | 3.1 ± 1.1 | 0.504 |
| Follow up length (years) | 3.6 ± 2.4 | 2.3 ± 2.4 | <0.001 |
| Graft Related | |||
| Number of Arteries (%) | 0.114 | ||
| 1 | 232 (81%) | 300 (85%) | |
| ≥2 | 55 (19%) | 54 (15%) | |
| Number of Veins (%) | 0.308 | ||
| 1 | 276 (96%) | 345 (97%) | |
| ≥2 | 11 (4%) | 10 (3%) | |
| Right kidneys (%) | 46 (16.4%) | 60 (16.9%) | 0.426 |
| Pre-donation eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 89.4 ± 17.2 | 90.3 ± 17.1 | 0.492 |
| 1 year after donation eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 57.1 ± 12.0 | 56.6 ± 14.8 | 0.648 |
| MINI (N = 287) | LDN (N = 355) | |
|---|---|---|
| No Complications | 262 (91.3%) | 314 (88.5%) |
| Grade 1/2 (Minor) | ||
| Hematoma | 0 | 3 |
| Wound infection | 5 | 5 |
| Obstipation | 0 | 1 |
| Perioperative bleeding | 0 | 2 |
| Postoperative bleeding | 1 | 0 |
| Iatrogenic bowel injury w/o consequence | 0 | 5 |
| Iatrogenic ureter injury w/o consequence | 0 | 1 |
| Iatrogenic splenic injury | 3 | 0 |
| Iatrogenic kidney injury | 0 | 1 |
| Gastritis | 0 | 1 |
| Testicular pain | 0 | 3 |
| Bleeding out of meatus | 0 | 1 |
| Kidney function disorder | 0 | 1 |
| Pancreatitis | 0 | 1 |
| Postoperative neuropraxia | 1 | 1 |
| Chylus leakage | 0 | 1 |
| Retention of urine | 1 | 0 |
| Acute kidney disorder | 2 | 0 |
| Perioperative bleeding: transfusion | 1 | 1 |
| Pneumonia | 6 | 4 |
| Urinary tract infection | 1 | 2 |
| Pulmonary embolism | 0 | 2 |
| Hypertension | 0 | 3 |
| Deep venous thrombosis | 0 | 1 |
| Epididymitis | 0 | 1 |
| Wound dehiscence | 1 | 0 |
| Subtotal | 22 (7.7%) | 41 (11.6%) |
| Grade 3a/b (Major) | ||
| Pancreatic leakage | 1 | 0 |
| Splenectomy due to injury | 1 | 0 |
| Genitofemoral reintervention | 0 | 1 |
| Severe rebleeding | 1 | 0 |
| Incisional hernia | 0 | 1 |
| Re-exploration of scar | 0 | 1 |
| Chylus leakage | 0 | 1 |
| Subtotal | 3 (1.0%) | 4 (1.1%) |
| Parameter | Univariable Analysis B (95% CI) | p-Value | Multivariable Model B (95%CI) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Complication grade | Donor age | −0.02 (−0.54, 0.02) | 0.264 | ---- | n.s. |
| Donor male gender | −0.02 (−0.93, 0.89) | 0.97 | ---- | n.s. | |
| Donor BMI | −0.06 (−0.19, 0.07) | 0.370 | ---- | n.s. | |
| Multiple renal arteries | 0.34 (−0.60, 1.28) | 0.476 | ---- | n.s. | |
| Right kidney | −0.12 (−1.38, 1.15) | 0.855 | ---- | n.s. | |
| MINI technique | 0.07 (−0.83, 0.96) | 0.886 | ---- | n.s. | |
| Operation time | Donor age | −0.31 (−0.67, 0.04) | 0.083 | 0.09 (−0.17, 0.35) | 0.480 |
| Donor male gender | 21.30 (12.99, 29.60) | <0.001 | 23.1 (16.9, 29.2) | <0.001 | |
| Donor BMI | 1.85 (0.97, 2.72) | <0.001 | 1.90 (1.07, 2.73) | <0.001 | |
| Multiple renal arteries | 14.36 (6.95, 21.77) | <0.001 | 12.90 (5.21, 19.39) | 0.001 | |
| Right kidney | −4.72 (−13.34, 3.90) | 0.283 | ---- | n.s. | |
| MINI technique | −12.25 (−18.62, −5.87) | <0.001 | −17.57 (−23.69, −11.44) | <0.001 | |
| First warm ischemia time | Donor age | −1.60 (−2.57, −0.63) | 0.001 | −0.67 (−1.37, 0.04) | 0.063 |
| Donor male gender | 6.07 (−17.49, 29.64) | 0.613 | ---- | n.s. | |
| Donor BMI | 3.32 (−3.47, 10.12) | 0.337 | ---- | n.s. | |
| Multiple renal arteries | 19.43 (−7.55, 46.41) | 0.158 | 35.84 (16.18, 55.49) | <0.001 | |
| Right kidney | 29.29 (−1.62, 60.20) | 0.063 | 24.70 (2.53, 46.87) | 0.029 | |
| MINI technique | −195.1 (−212.5, −177.8) | <0.001 | −194.5 (−211.7, −177.3) | <0.001 | |
| Estimated blood loss | Donor age | 0.18 (−1.90, 2.26) | 0.864 | ---- | n.s. |
| Donor male gender | 93.94 (44.91, 142.97) | <0.001 | 67.43 (18.78, 116.09) | 0.007 | |
| Donor BMI | 3.32 (−3.47, 10.12) | 0.337 | ---- | n.s. | |
| Multiple renal arteries | 11.58 (−45.63, 68.78) | 0.691 | ---- | n.s. | |
| Right kidney | 3.45 (−61.88, 68,77) | 0.918 | ---- | n.s. | |
| MINI technique | 140.1 (92.4, 187.8) | <0.001 | 127.9 (79.7, 176.2) | <0.001 | |
| Length of hospital stay | Donor age | 0.01 (−0.004, 0.014) | 0.245 | ---- | n.s. |
| Donor male gender | −0.08 (−0.30, 0.13) | 0.435 | ---- | n.s. | |
| Donor BMI | −3.42 (−22.95, 16.10) | 0.731 | ---- | n.s. | |
| Multiple renal arteries | −14.29 (−178.4, 149.8) | 0.864 | ---- | n.s. | |
| Right kidney | 44.40 (−144.7, 233,5) | 0.645 | ---- | n.s. | |
| MINI technique | 0.07 (−0.14, 0.28) | 0.487 | ---- | n.s. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Habets, L.J.M.; Baranski, A.G.; Ramdhani, K.; van der Helm, D.; Haasnoot, A.; de Vries, A.P.J.; van der Bogt, K.E.A.; Braat, A.E.; Dubbeld, J.; Lam, H.-D.; et al. The Non-Muscle-Splitting Mini-Incision Donor Nephrectomy Remains a Feasible Technique in the Laparoscopic Era of Living Kidney Donation. Transplantology 2023, 4, 1-11. https://doi.org/10.3390/transplantology4010001
Habets LJM, Baranski AG, Ramdhani K, van der Helm D, Haasnoot A, de Vries APJ, van der Bogt KEA, Braat AE, Dubbeld J, Lam H-D, et al. The Non-Muscle-Splitting Mini-Incision Donor Nephrectomy Remains a Feasible Technique in the Laparoscopic Era of Living Kidney Donation. Transplantology. 2023; 4(1):1-11. https://doi.org/10.3390/transplantology4010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleHabets, Lex J. M., Andrzej G. Baranski, Khalil Ramdhani, Danny van der Helm, Ada Haasnoot, Aiko P. J. de Vries, Koen E. A. van der Bogt, Andries E. Braat, Jeroen Dubbeld, Hwai-Ding Lam, and et al. 2023. "The Non-Muscle-Splitting Mini-Incision Donor Nephrectomy Remains a Feasible Technique in the Laparoscopic Era of Living Kidney Donation" Transplantology 4, no. 1: 1-11. https://doi.org/10.3390/transplantology4010001
APA StyleHabets, L. J. M., Baranski, A. G., Ramdhani, K., van der Helm, D., Haasnoot, A., de Vries, A. P. J., van der Bogt, K. E. A., Braat, A. E., Dubbeld, J., Lam, H.-D., Nieuwenhuizen, J., Nijboer, W. N., de Vries, D. K., Alwayn, I. P. J., Schaapherder, A. F. M., & Huurman, V. A. L. (2023). The Non-Muscle-Splitting Mini-Incision Donor Nephrectomy Remains a Feasible Technique in the Laparoscopic Era of Living Kidney Donation. Transplantology, 4(1), 1-11. https://doi.org/10.3390/transplantology4010001






