Abstract
Deep vein arterialization (DVA) is a therapeutic option in “no option” for revascularization chronic limb-threatening ischemia patients, creating an arteriovenous bypass between a proximal artery and a distal deep venous target at the ankle. Imaging plays a crucial role in peripheral arterial disease (PAD) patient management. We present the case of a 71-year-old PAD patient (Rutherford class 5) with focal gangrene of the first and second toes of the right foot, who was admitted to the vascular surgery department to undergo revascularization surgery by femoro-tibial artery bypass. During surgery a DVA was performed because of an unsatisfactory distal artery target. The post-operative computed tomography angiography showed the saphenous graft patency and opacification of distal foot veins. Subsequent angiography documented the presence of a large venous collateral, responsible for extensive early wash-out to leg venous vessels, which was then embolized. After two months, the patient underwent amputation of the right first and second necrotic toes at the level of the metatarsophalangeal joints. The post-operative course was excellent, with disappearance of pain at rest and good trophism of the surgical wound.
1. Introduction
Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) is a common cardiovascular pathology (affecting approximately 202 million people worldwide) in which atherosclerotic plaques are responsible for vessel stenosis, reducing blood flow to the arteries of the leg and foot [1,2]. The classic spectrum of disease ranges from walking leg pain which resolves with rest (intermittent claudication) to chronic limb-threatening ischemia (CLTI). CLTI is characterized by ischemic rest pain or tissue loss, a complication that occurs in 5–10% of patients older than 50 years within 5 years of their PAD diagnosis [3]. CLTI is associated with a 30% rate of major amputation and with a reported mortality of 20% at 6 months and >50% at 5 years [4]. Thus, revascularization, including either open bypass or endovascular therapies, plays a key role in this critical disease. Usually, endovascular treatment is the primary approach followed by open strategies; however, in up to 20% of CLTI patients conventional revascularization is not an option because of the absence of an adequate distal arterial outflow target (e.g., advanced occlusive disease in pedal arteries) [5]. In this scenario, major leg amputation was substantially the only alternative to manage pain or tissue loss. In these “no option” patients, deep venous arterialization (DVA) can be performed [6].
DVA creates an arteriovenous bypass between a proximal artery and a distal deep venous target at the ankle allowing adequate timing for arterialization of the veins to occur in order to provide adequate blood flow to the foot, improving resting pain or the healing of a chronic wound [7]. Imaging plays a critical role in adequate pre-surgical planning, in the subsequent follow-up of these subjects and helps during surgical and endovascular treatment with digital subtraction angiography (DSA); radiologists need to be aware of this therapeutic option for proper interpretation of images.
We discuss a patient with severe PAD where the femoro-tibial bypass surgery was converted into DVA due to an unsatisfactory distal artery target. This is followed by an in-depth discussion about the role of imaging in this type of patient in accordance with the latest literature data.
2. Case Description
We present the case of a 71-year-old patient heavy smoker with history of hypertension and previous coronary artery bypass graft, who had been reporting lower extremity pain of the right foot for about 9 months, worsening to the point of complaining about pain at rest and development of focal gangrene of the right first and second toes (Rutherford class 5 [8]). On medical examination, the femoral pulses were present, while the distal pulses were absent. The ankle-brachial index (ABI) was <0.4 on the right side and between 0.9 and 0.7 on the left side. The transcutaneous partial pressure of O2 (TcPO2) at the level of the right capillary bed was 15 mm Hg. Doppler Ultrasound (DUS) showed irregularly walled and calcified aorta, patent iliac arteries with numerous parietal irregularities, and non-stenosing plaque of the right common femoral artery. Furthermore, the examination documented multiple stenosis of the right superficial femoral and the right three main leg arteries with occlusion of the right popliteal artery and very low-flow reperfusion of the right posterior tibial and right anterior tibial arteries in the perimalleolar tract. Similar findings were observed on the left side, other than patency of the peroneal artery, but the patient was asymptomatic on this side. The right great saphenous vein (GSV) presented a good caliber for a bypass.
Thus, the patient was admitted to the vascular surgery department to undergo revascularization surgery by right femoro-tibial artery bypass. Medical therapy on admission included: allopurinol 300 mg, amiodarone 200 mg, atorvastatin 20 mg, carvedilol 6.25 mg, clopidogrel 75 mg, levothyroxine 75 mcg, low-dose aspirin 100 mg, pantoprazole 20 mg, pregabalin 75 mg, and ramipril 5 mg. Clopidogrel was suspended while enoxaparin sodium 4000 IU was started. During surgery, anastomosis between the proximal superficial femoral artery and the GSV was sutured. The GSV was devalvulated and left in situ. A distal terminolateral anastomosis was then packed between the arterialized vein and the retro-malleolar posterior tibial artery. DUS showed good pulsatility of the graft, but buffered flow distally on the posterior tibial artery. The previously packed anastomosis was then dissected, and a terminolateral anastomosis was performed between the arterialized vein and the anterior tibial artery. On DUS unsatisfactory distal flow was again documented and, therefore, it was decided to perform arteriovenous bypass on the posterior tibial vein with a distal valvulotomy through a Fogarty catheter. DUS showed good arterialized flows on posterior tibial vein and plantar veins. The posterior tibial vein was partially ligated proximally to anastomosis, in order to reduce proximal vein flow. No prostaglandin E1 therapy had been implemented.
The post-operative (3 days following the surgery) computed tomography angiography (CTA, Figure 1 and Figure 2) showed the saphenous graft patency and opacification of distal foot veins. In addition, on the right side, popliteal artery occlusion, segmental occlusion of the anterior tibial artery in the distal tract, occlusion of the peroneal artery, and segmental occlusion of the posterior tibial artery in the middle tract with distal patency were confirmed. Early opacification (during the angiographic phase of the study) and ectasia of the deep and superficial venous circles of the right leg were also observed, related to the presence of the arteriovenous bypass. On the left side, CTA showed occlusion of the anterior tibial artery and posterior tibial artery with patency of the peroneal artery.
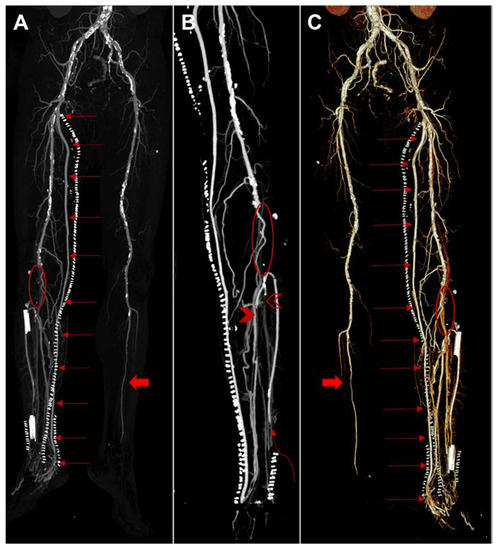
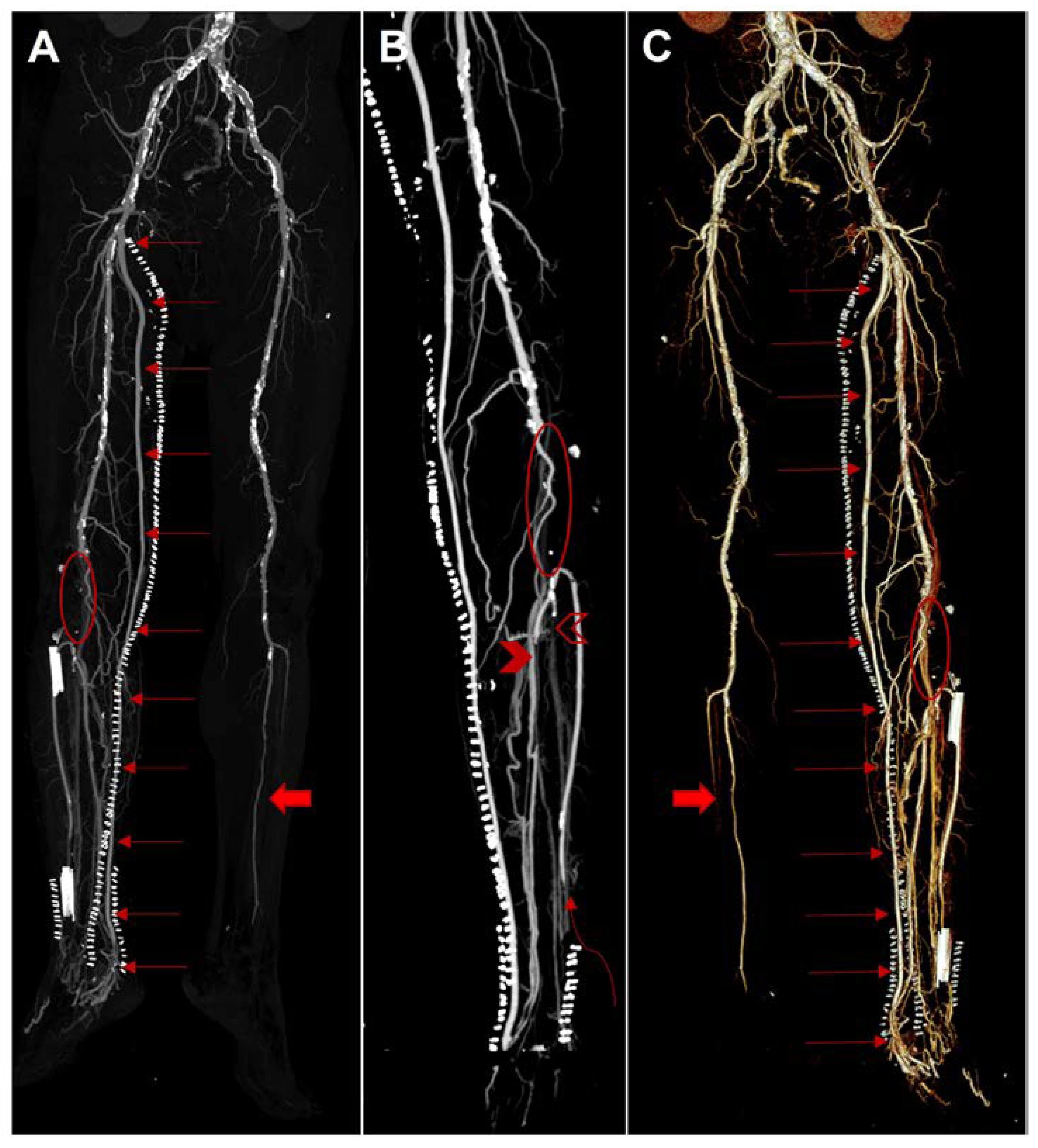
Figure 1.
Three-dimensional reconstruction computed tomography angiography (Siemens Somatom Definition AS, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany) after open deep vein arterialization; all images show diffuse calcified atherosclerosis and a greater enhancement of the vessels of the right leg compared to the left side in relation to the presence of arteriovenous bypass resulting in early opacification and ectasia of the superficial and deep venous vessels. (A), anterior view of maximum intensity projection (MIP) shows patency of the right saphenous graft from the superficial femoral artery to the posterior tibial vein (red arrows). Note occlusion of the right popliteal artery (red ellipse) and left leg arteries apart from the left peroneal artery (full red arrow). (B), posterior view of MIP on right leg shows occlusion of the popliteal artery (red ellipse), segmental occlusion of the anterior tibial artery in the distal tract (curved red arrow), occlusion of the peroneal artery (empty red arrowhead), and segmental occlusion of the posterior tibial artery in the middle tract with distal patency (full red arrowhead). (C), posterior view of Volume Rendering Technique shows patency of the saphenous graft from the superficial femoral artery to the posterior tibial vein (red arrows). Note occlusion of the right popliteal artery (red ellipse) and left leg arteries apart from the left peroneal artery (full red arrow).
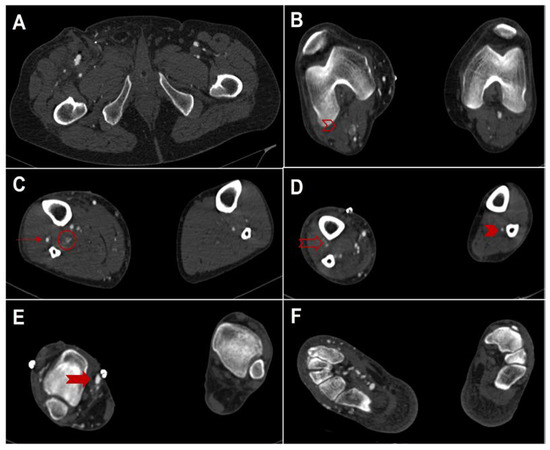
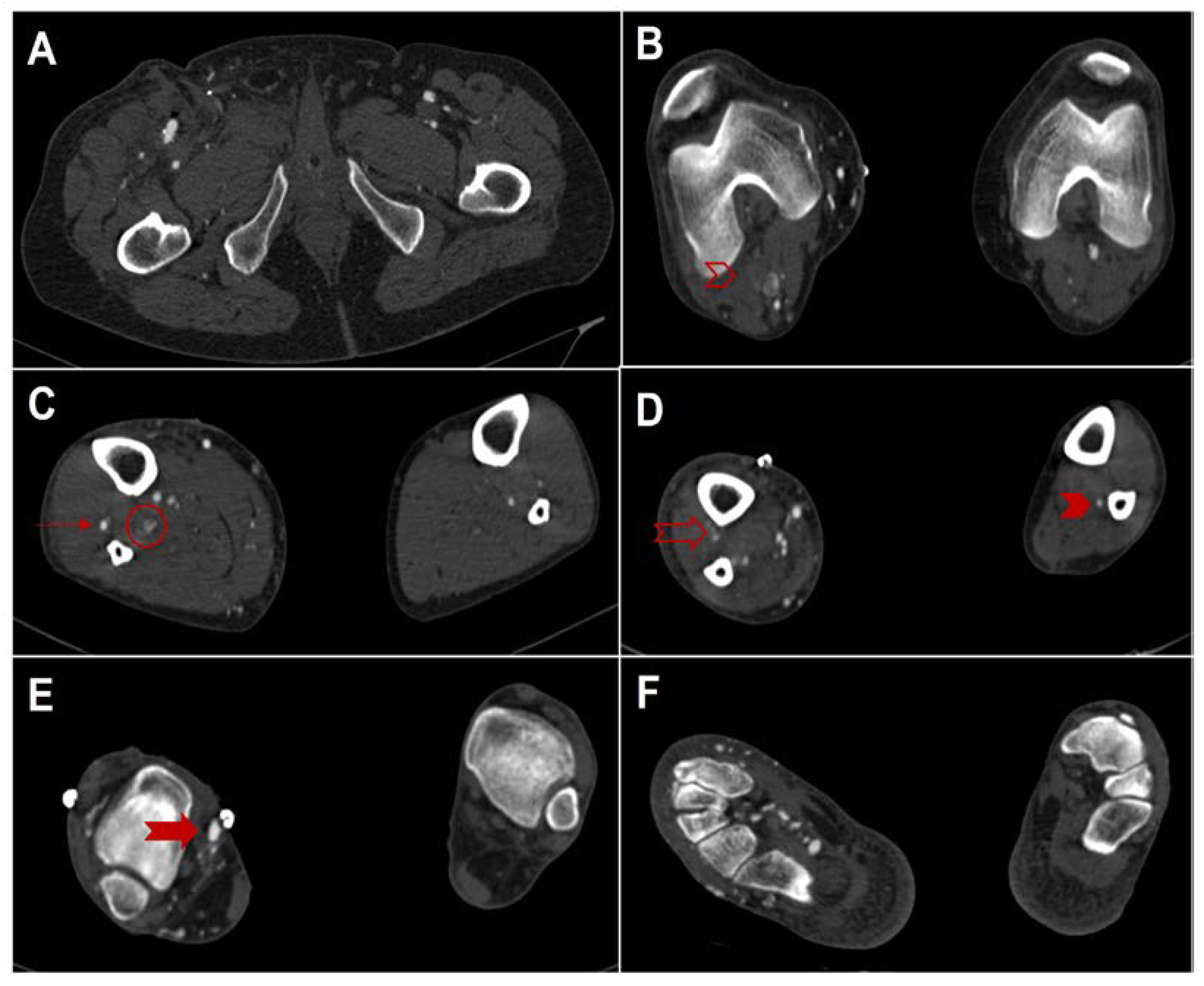
Figure 2.
Computed tomography angiography (Siemens Somatom Definition AS, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany) on axial planes (from top to bottom) after open deep vein arterialization. (A), on the right side, patent proximal anastomosis between the great saphenous vein and the superficial femoral artery. (B), occlusion of the right peroneal artery (empty red right arrowhead). (C), on the right side, patent proximal anterior tibial artery (red arrow) and occlusion of poster tibial and peroneal arteries (red circle). (D), occlusion also of the right distal anterior tibial artery; on the left side note the patency of the peroneal artery alone (full red arrowhead). (E), on the right side, patent distal anastomosis between the great saphenous vein and posterior tibial vein (full red arrow) (F), on the right side note the enhancement and ectasia of the plantar venous circles, related to the presence of arteriovenous bypass, while on the left side no vessel is enhanced.
The subsequent angiographic examination of the right lower limb (performed 5 days after surgery) confirmed good patency of the venous graft and excellent discharge of the bypass over the plantar veins. Angiography also documented the presence of a large venous collateral, responsible for extensive early wash-out to proximal leg venous vessels, which was then embolized by Ruby® Coil (Penumbra, Inc., Alameda, CA, USA), POD® (Penumbra Occlusion Device, Penumbra, Inc., Alameda, CA, USA) (Figure 3). Post-operative TcPO2 was increased to 37 mm Hg after surgery, and to 64 mm Hg after the endovascular procedure. Five days after the procedure, the patient was discharged in good clinical condition with the implementation of anticoagulant therapy (enoxaparin sodium 4000 IU followed by the provision of Rivaroxaban).
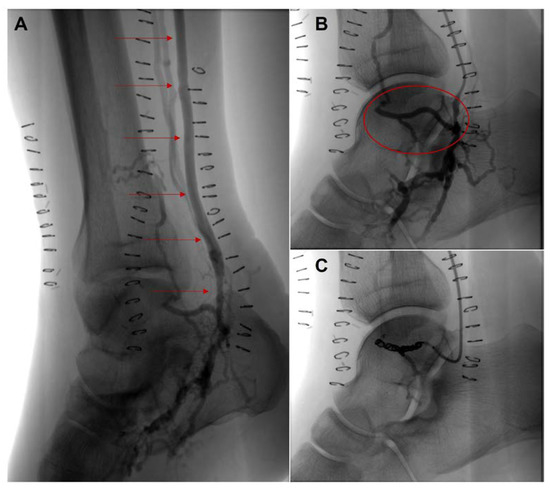
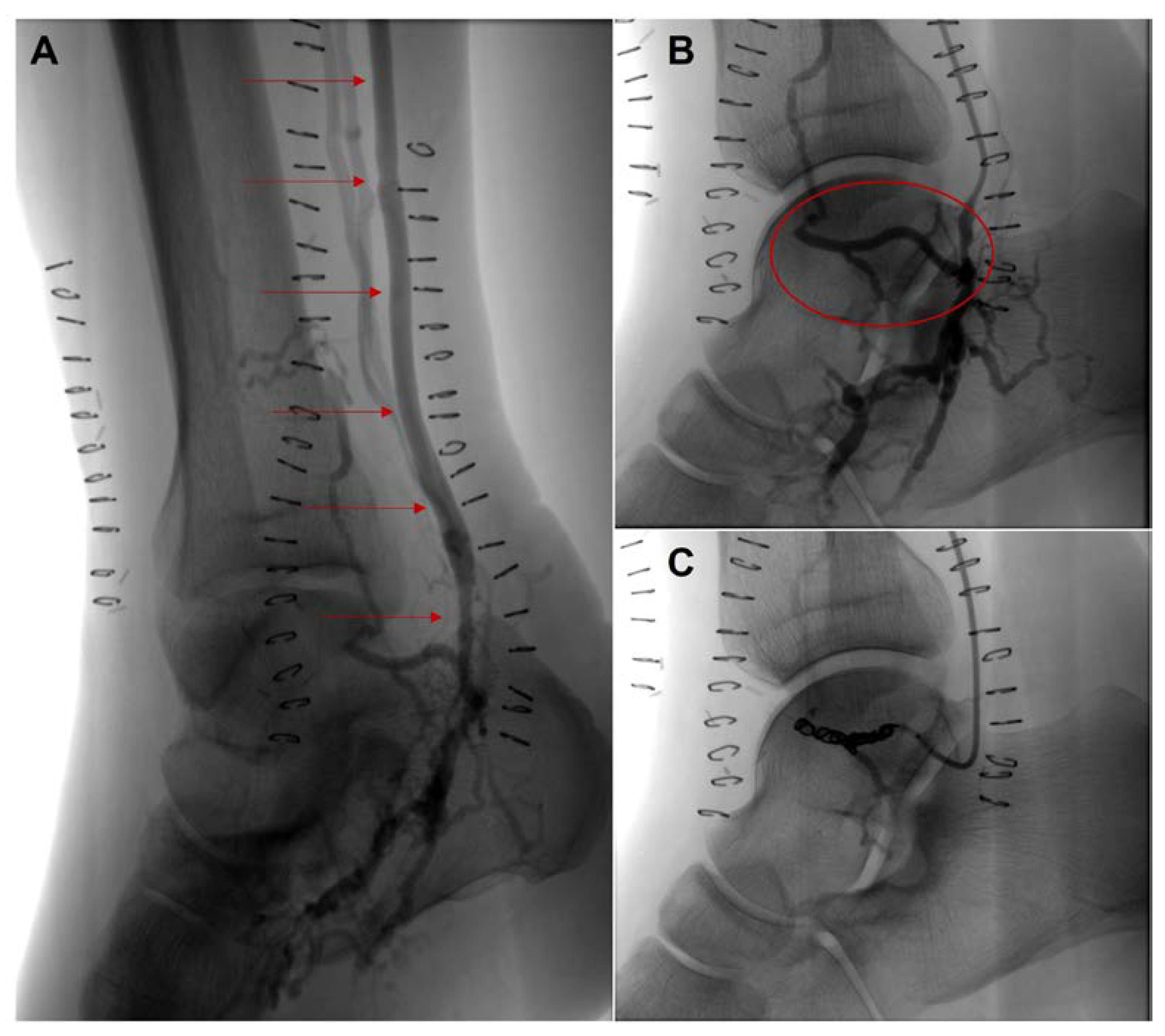
Figure 3.
Angiography study of the right lower limb after open deep vein arterialization. (A), patent venous graft (red arrows) and excellent discharge of the bypass over the plantar veins. (B), a large venous collateral (red ellipse), responsible for early wash-out to leg venous vessels (C), coiling embolization of the large venous collateral.
Arterialization of the venous circulation of the foot allowed good demarcation of the digital necrosis. So, after two months, the patient was admitted again to the vascular surgery department to undergo amputation of the right first and second necrotic toes at the level of the metatarsophalangeal joints. The post-operative course was excellent, with disappearance of pain at rest and good trophism of the surgical wound. The 6-month follow-up showed optimal healing of amputations with no further signs of CLTI.
3. Discussion
We showed the case of a successful conversion of femoral-tibial bypass surgery into DVA with a special focus on post-operative imaging findings.
Typical indication for DVA is a Rutherford category 5 or 6 disease where the open or endovascular revascularization is not feasible because of deficiency of the distal arterial outflow and the presence of an angiographically “desert” foot (defined as the absence of both plantar arteries, the plantar arch, and the dorsalis pedis and lateral tarsal arteries) [9]. Therefore, the patients most likely to undergo this procedure are those with diabetes, end-stage renal disease, and thromboangiitis obliterans, who develop disease in the small arteries of the foot and tibial arteries. Relative contraindications for DVA include occlusion of the deep venous arch and extensive tissue loss [7].
Three modes of DVA execution are currently available: open, percutaneous, and hybrid. In open DVA, conduits that can be used are the GSV, cephalic vein, or poly-tetra-flour-ethylene with vein patch in rarer cases. Proximal arterial inflow can be insured by the common femoral artery, superficial femoral artery, popliteal artery, or proximal tibial arteries. Distal venous outflow should be at least 3 mm in diameter, including the vena comitans of the posterior tibial vein and dorsal venous arch. Valvulotomy of the distal venous target vessels can be performed through a retrograde balloon catheter, dilators, direct valvulectomy, valvulotome, or cutting balloons to break the valves [7]. In percutaneous DVA a patent proximal tibial artery is required to allow antegrade arterial cannulation; the venous access site can be the posterior tibial vein or peroneal vein via the lateral plantar vein or near the medial malleolus [10]. In summary, the procedure is performed by cannulating the posterior tibial vein at the ankle retrogradely and the inflow artery in anterograde, creating a channel between them that is bridged by a covered stent. Valvulotomy of the distal venous target vessels is done percutaneously [7]. In the hybrid DVA approach (the one used in our case), an open surgical arteriovenous bypass, as in the standard open DVA, is performed with the conventional proximal arterial and distal venous anastomoses, but the subsequent valvulotomy or embolization of collateral venous branches is done with an endovascular approach immediately or in the following weeks [7,11]. The open technique appears to have better outcomes related to fewer complications (such as stent occlusion), direct ligation of collateral venous vessels, and more effective valvulotomy, but further studies with standardization of patient enrolment and approach are needed for proper outcome assessment [7,10].
In general, non-invasive and invasive imaging techniques play a key role in the management of patients with lower extremity PAD as reflected in the latest guidelines of the European Society of Cardiology [2]. Resting ABI, defined as the ratio of the systolic blood pressure measured over the ankle to the systolic blood pressure measured over the brachial artery [12], is the main screening test for PAD. The systolic blood pressure is measured using a Doppler probe and ABI values of 1.00–1.40 are considered normal [12]. DUS is commonly useful in detecting and quantifying stenosis in different territories of the vascular bed, with the application of velocity and pressure gradient criteria (sensitivity of 85–90% and specificity >95% to detect stenosis >50%) [13]. Thus, it is often the first-line test in the diagnostic algorithm both for screening and diagnosis of PAD [13]. DUS is also performed to assess veins before executing bypass grafts and in routine follow-ups after revascularization procedures. On the other hand, DUS does not have the ability to provide a complete roadmap of vasculature, therefore further, more panoramic investigations are required before revascularization surgeries [14]. CTA provides a panoramic high-resolution anatomical view of the vessels (lesion localization and severity, upstream/downstream status), which is critical before interventional strategies (sensitivity of 96% and specificity of 98% to detect aorto-iliac stenosis >50%; sensitivity of 97% and specificity of 94% to detect femoro-popliteal disease) [15]. CTA does not allow routine acquisition of functional and hemodynamic data; in addition, other major limitations of the technique are related to exposure to ionizing radiation and the need to use iodinated contrast agent (contraindicated in patients with an estimated glomerular filtration rate <30 mL/min/1.73 m2) [16]. CTA is very useful in providing visualization of concomitant aortic pathologies [17], calcifications, stents, and bypass grafts, although the presence of severe calcifications can interfere with the estimation of stenosis, mainly in distal arteries [14]. Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) can be used in the diagnosis of PAD (sensitivity and specificity of 95% for the diagnosis of segmental stenosis and occlusion) [18] using contrast and non-contrast techniques (i.e., phase contrast and time-of-flight sequences) but the latter present inferior resolution. Major limitations of MRA are the inability to identify calcifications, the overestimation of the degree of stenosis in the lower extremities, and the difficulty in studying stents [14]. DSA has been mostly replaced by the others imaging technique because of the invasiveness and the risk of complications. However, is the gold standard for below-the-knee arterial disease and is often performed in percutaneous peripheral interventional procedures or for the visualization of patent arteries for distal bypass [14].
When a DVA is planned, the pre-operative evaluation should include a venous DUS examination and a lower extremity DSA to document the patency of the venous circulation of the foot and the presence of veins of adequate size (at least 3 mm). Imaging is also essential in post-operative follow-ups to evaluate any complications (with CTA), graft or stent patency (with DUS), assess blood flow to the foot (with DSA), and possibly embolize collateral venous circles responsible for blood theft from the extremity during angiography (as in our case).
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, imaging plays a crucial role in adequate pre-surgical planning, in the intraoperative setting, and in the subsequent follow-up of PAD patients. DVA can be a viable alternative to the femoro-popliteal bypass when unsatisfactory distal arterial flow is detected during surgery, to avoid a subsequent major amputation. Radiologists should be aware of DVA and its possible approaches for proper interpretation of post-operative images.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.P., D.D.S., and C.A.M.; methodology, V.C., F.S. (Francesco Spinelli), and C.A.M.; software, M.P.; validation, C.A.M., F.S. (Francesco Spinelli), F.S. (Francesco Stilo), and C.C.Q.; formal analysis, M.P.; investigation, M.P.; resources, M.P.; data curation, M.P.; writing—original draft preparation, M.P.; writing—review and editing, M.P., D.D.S., V.C., C.A.M., F.S. (Francesco Spinelli), F.S. (Francesco Stilo), and C.C.Q.; visualization, D.D.S.; supervision, D.D.S.; project administration, M.P. and C.C.Q. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study due to the nature of the study (case report).
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent for the possible use of existing anonymized data for research purposes is obtained from the patient as an institutional policy.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sibley, R.C.; Reis, S.P.; MacFarlane, J.J.; Reddick, M.A.; Kalva, S.P.; Sutphin, P.D. Noninvasive Physiologic Vascular Studies: A Guide to Diagnosing Peripheral Arterial Disease. Radiogr. Rev. Publ. Radiol. Soc. N. Am. Inc. 2017, 37, 346–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboyans, V.; Ricco, J.-B.; Bartelink, M.-L.E.L.; Björck, M.; Brodmann, M.; Cohnert, T.; Collet, J.-P.; Czerny, M.; De Carlo, M.; Debus, S.; et al. 2017 ESC Guidelines on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Peripheral Arterial Diseases, in Collaboration with the European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS): Document Covering Atherosclerotic Disease of Extracranial Carotid and Vertebral, Mesenteric, Renal, Upper and Lower Extremity ArteriesEndorsed by: The European Stroke Organization (ESO)The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Peripheral Arterial Diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and of the European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS). Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 763–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norgren, L.; Hiatt, W.R.; Dormandy, J.A.; Nehler, M.R.; Harris, K.A.; Fowkes, F.G.R.; TASC II Working Group; Bell, K.; Caporusso, J.; Durand-Zaleski, I.; et al. Inter-Society Consensus for the Management of Peripheral Arterial Disease (TASC II). Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Vasc. Surg. 2007, 33 (Suppl. S1), S1–S75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu Dabrh, A.M.; Steffen, M.W.; Undavalli, C.; Asi, N.; Wang, Z.; Elamin, M.B.; Conte, M.S.; Murad, M.H. The Natural History of Untreated Severe or Critical Limb Ischemia. J. Vasc. Surg. 2015, 62, 1642–1651.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, D.J.; Beard, J.D.; Cleveland, T.; Bell, J.; Bradbury, A.W.; Forbes, J.F.; Fowkes, F.G.R.; Gillepsie, I.; Ruckley, C.V.; Raab, G.; et al. Bypass versus Angioplasty in Severe Ischaemia of the Leg (BASIL): Multicentre, Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2005, 366, 1925–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, M.S.; Bradbury, A.W.; Kolh, P.; White, J.V.; Dick, F.; Fitridge, R.; Mills, J.L.; Ricco, J.-B.; Suresh, K.R.; Murad, M.H.; et al. Global Vascular Guidelines on the Management of Chronic Limb-Threatening Ischemia. J. Vasc. Surg. 2019, 69, 3S–125S.e40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, V.T.; Gologorsky, R.; Kibrik, P.; Chandra, V.; Prent, A.; Lee, J.; Dua, A. Open, Percutaneous, and Hybrid Deep Venous Arterialization Technique for No-Option Foot Salvage. J. Vasc. Surg. 2020, 71, 2152–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutherford, R.B.; Baker, J.D.; Ernst, C.; Johnston, K.W.; Porter, J.M.; Ahn, S.; Jones, D.N. Recommended Standards for Reports Dealing with Lower Extremity Ischemia: Revised Version. J. Vasc. Surg. 1997, 26, 517–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, R.S.; Belli, A.M.; Jacob, S. Distal Venous Arterialisation for Salvage of Critically Ischaemic Inoperable Limbs. Lancet Lond. Engl. 1999, 354, 1962–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilyas, S.; Powell, R.J. Management of the No-Option Foot: Deep Vein Arterialization. Semin. Vasc. Surg. 2022, 35, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montelione, N.; Catanese, V.; Gabellini, T.; Codispoti, F.A.; Nenna, A.; Spinelli, F.; Stilo, F. Duplex and Angiographic-Assisted Evaluation of Outcomes of Endovascular Embolization after Surgical Deep Vein Arterialization for the Treatment No-Option Critical Limb Ischemia Patients. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.; Murray, A. Comparison of Three Arterial Pulse Waveform Classification Techniques. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 1996, 20, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, R.; Cranny, G.; Burch, J.; Aguiar-Ibáñez, R.; Craig, D.; Wright, K.; Berry, E.; Gough, M.; Kleijnen, J.; Westwood, M. A Systematic Review of Duplex Ultrasound, Magnetic Resonance Angiography and Computed Tomography Angiography for the Diagnosis and Assessment of Symptomatic, Lower Limb Peripheral Arterial Disease. Health Technol. Assess. Winch. Engl. 2007, 11, 1–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlachopoulos, C.; Georgakopoulos, C.; Koutagiar, I.; Tousoulis, D. Diagnostic Modalities in Peripheral Artery Disease. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2018, 39, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Met, R.; Bipat, S.; Legemate, D.A.; Reekers, J.A.; Koelemay, M.J.W. Diagnostic Performance of Computed Tomography Angiography in Peripheral Arterial Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA 2009, 301, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESUR Guidelines 10. Available online: https://www.esur.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/esur-guidelines-10_0-final-version.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2022).
- Parillo, M.; Vaccarino, F.; Beomonte Zobel, B.; Quattrocchi, C.C. A Rare Case of Contained Chronic Rupture of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Associated With Vertebral Erosion: Pre- and Post-Operative Findings on Computed Tomography and a Narrative Review. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2022, 56, 15385744221108040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menke, J.; Larsen, J. Meta-Analysis: Accuracy of Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Angiography for Assessing Steno-Occlusions in Peripheral Arterial Disease. Ann. Intern. Med. 2010, 153, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).