Are Chronic Rhinosinusitis and Paranasal Sinus Pneumatization Related?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wine, J.J.; King, V.V.; Lewiston, N.J. Method for rapid evaluation of topically applied agents to cystic fibrosis airways. Am. J. Physiol. 1991, 261, L218–L221. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chang, E.H.; Pezzulo, A.A.; Meyerholz, D.K.; Potash, A.E.; Wallen, T.J.; Reznikov, L.R.; Sieren, J.C.; Karp, P.H.; Ernst, S.; Moninger, T.O.; et al. Sinus hypoplasia precedes sinus infection in a porcine model of cystic fibrosis. Laryngoscope 2012, 122, 1898–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodworth, B.A.; Ahn, C.; Flume, P.A.; Schlosser, R.J. The delta F508 mutation in cystic fibrosis and impact on sinus development. Am. J. Rhinol. 2007, 21, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seifert, C.M.; Harvey, R.J.; Matthews, J.W.; Meyer, T.A.; Ahn, C.; Woodworth, B.A.; Schlosser, R.J. Temporal bone pneumatization and its relationship to paranasal sinus development in cystic fibrosis. Rhinology 2010, 48, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggesbo, H.B.; Sovik, S.; Dolvik, S.; Eiklid, K.; Kolmannskog, F. Proposal of a CT scoring system of the paranasal sinuses in diagnosing cystic fibrosis. Eur. Radiol. 2003, 13, 1451–1460. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Friedman, E.M.; Sulek, M.; Duncan, N.O.; McCluggage, C. Paranasal sinus development in chronic sinusitis, cystic fibrosis, and normal comparison population: A computed tomography correlation study. Am. J. Rhinol. 1997, 11, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, V.V. Upper airway disease, sinusitis, and polyposis. Clin. Rev. Allergy 1991, 9, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jeong, J.H.; Hwang, P.H.; Do-Yeon, C.; Joo, N.S.; Wine, J.J. Secretion rates of human nasal submucosal glands from patients with chronic rhinosinusitis or cystic fibrosis. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2015, 29, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, M.J.; Weinstein, J.E.; Riley, C.A.; Levy, J.M.; Emerson, N.A.; McCoul, E.D. Assessment of pneumatization of the paranasal sinuses: A comprehensive and validated metric. Int. Forum. Allergy Rhinol. 2016, 4, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, M.J.; Riley, C.A.; Kessler, R.H.; McCoul, E.D. Clinician assessment of paranasal sinus pneumatization is correlated with total sinus volume. Int. Forum. Allergy Rhinol. 2016, 6, 1088–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, P.A.; Taylor, R.; Thielke, R.; Payne, J.; Gonzalez, N.; Conde, J.G. Research electronic data capture (REDCap): A metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. J. Biomed. Inform. 2009, 42, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, N.; Bhattacharyya, N. Determination of the “incidental” Lund score for the staing of chronic rhinosinusitis. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2001, 125, 483–486. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hill, M.; Bhattacharyya, N.; Hall, T.R.; Lufkin, R.; Shapiro, N.L. Incidental paranasal sinus imaging abnormalities and the normal Lund score in children. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2004, 130, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emirzeoglu, M.; Sahin, B.; Bilgic, S.; Celebi, M.; Uzun, A. Volumetric evaluation of the paranasal sinuses in normal subjects using computer tomography images: A stereoglogical study. Auris Nasus Larynx 2007, 34, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selcuk, O.T.; Erol, B.; Renda, L.; Osma, U.; Eyigor, H.; Gunsoy, B.; Yagci, B.; Yılmaz, D. Do climate and altitude affect paranasal sinus volume? J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 43, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, T.K.; Kocak, M.; Smith, M.M.; Smith, T.L. Coronal computed tomography analysis of frontal cells. Am. J. Rhinol. 2003, 17, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.H.; Kim, T.H.; Kim, K.R.; Lee, J.M.; Lee, D.K.; Kim, J.H.; Im, J.J.; Park, C.J.; Hwang, K.G. Factors for maxillary sinus volume and craniofacial anatomical features in adults with chronic rhinosinusitis. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2010, 136, 610–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.Y.; Kim, M.B.; Dhong, H.J.; Jung, Y.G.; Min, J.Y.; Chung, S.K.; Lee, H.J.; Chung, S.C.; Ryu, N.G. Changes of maxillary sinus volume and bony thickness of the paranasal sinuses in longstanding pediatric chronic rhinosinusitis. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2008, 72, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prokopakis, E.P.; Vlastos, I.M.; Ferguson, B.J.; Scadding, G.; Kawauchi, H.; Georgalas, C.; Papadopoulos, N.; Hellings, P.W. SCUAD and chronic rhinosinusitis. Reinforcing hypothesis driven research in difficulty cases. Rhinology 2013, 52, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
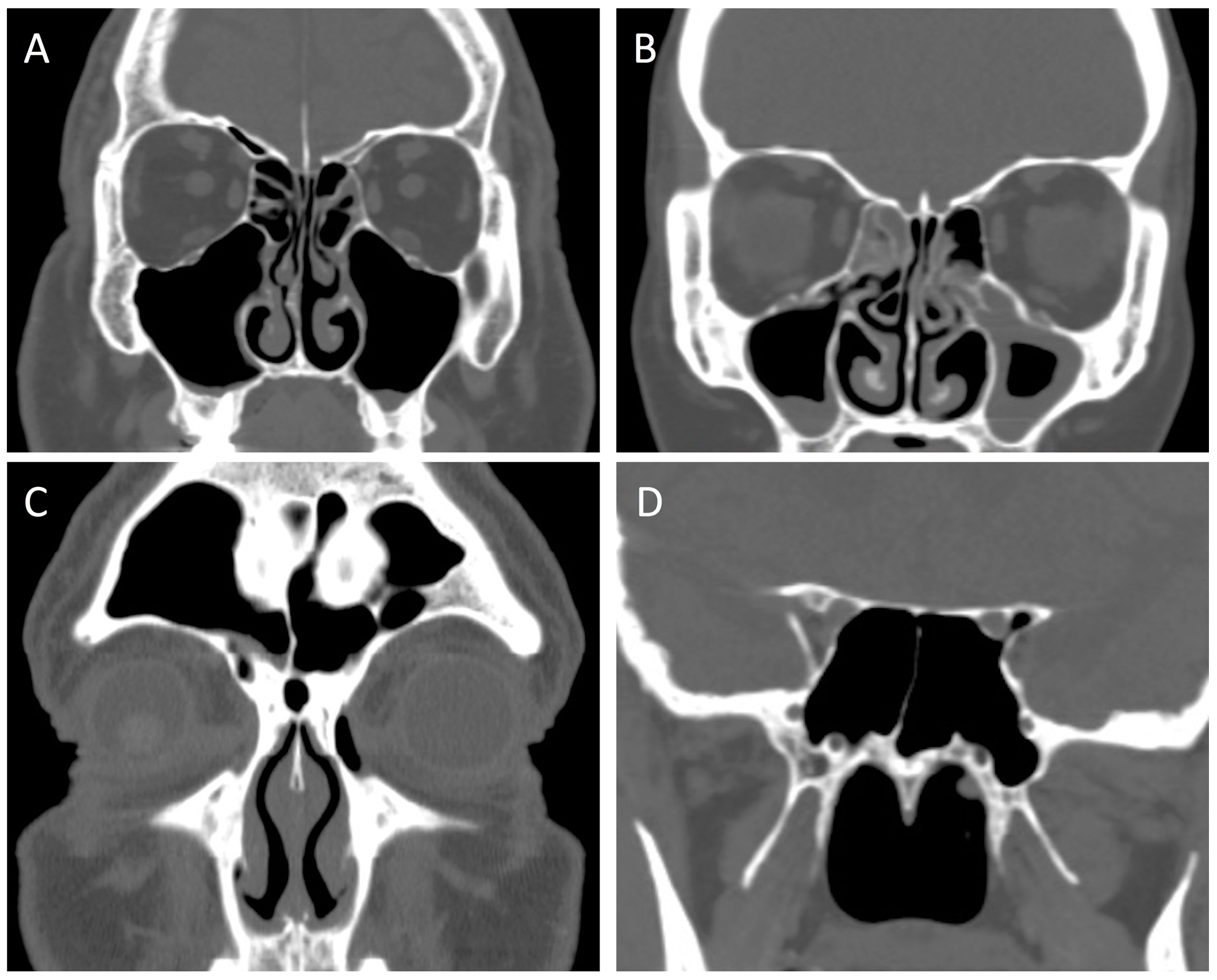
| Item | Anatomic Variant |
|---|---|
| 1 | Maxillary floor inferior to nasal floor |
| 2 | Supraorbital cell (Air cell superior to anterior ethmoid artery) |
| 3 | Middle turbinate concha bullosa presen |
| 4 | Frontal sinus present |
| 5 | Superior frontal sinus wall superior to supraorbital rim |
| 6 | Lateral frontal sinus wall lateral to medial edge of globe |
| 7 | Lateral frontal sinus wall lateral to mid-pupillary line |
| 8 | Lateral sphenoid sinus wall lateral to V2-VN line |
| 9 | Anterior clinoid process pneumatized |
| Subjects | Unaffected Controls | CRS | CF | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Study Patients | 448 | 111 | 32 | 591 |
| Mean Age ± SD | 32.42 + 22.77 | 36.96 ± 22.13 | 26.28 ± 10.33 | 32.94 ± 22.26 |
| Males | 224 (50.0%) | 64 (57.7%) | 17 (53.1%) | 305 (51.6%) |
| Females | 224 (50.0%) | 47 (42.3%) | 15 (46.9%) | 286 (48.4%) |
| Adolescent Patients | 247 | 47 | 9 | 303 |
| Mean Age ± SD | 15.82 ± 1.41 | 15.96 ± 1.43 | 15.56 ± 1.42 | 15.83 ± 1.41 |
| Males | 145 (58.7%) | 26 (55.3%) | 4 (44.4%) | 175 (57.8%) |
| Females | 102 (41.3%) | 21 (44.7%) | 5 (55.6%) | 128 (42.2%) |
| Adult Patients | 201 | 64 | 23 | 288 |
| Mean Age ± SD | 52.81 ± 19.97 | 52.39 ± 16.80 | 30.48 ± 9.17 | 50.93 ± 19.56 |
| Males | 79 (39.3%) | 38 (59.4%) | 13 (56.5%) | 130 (45.1%) |
| Females | 122 (60.7%) | 26 (40.6%) | 10 (43.5%) | 158 (54.9%) |
| Subjects | Unaffected Controls | CRS | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| APPS (All Patients) ± SD | 9.62 ± 3.19 | 10.61 ± 2.76 | 0.001 |
| LMS (All Patients) ± SD | 2.15 ± 2.51 | 6.28 ± 5.14 | <0.001 |
| APPS (Adolescents) ± SD | 9.57 ± 3.24 | 10.66 ± 3.13 | 0.035 |
| LMS (Adolescents) ± SD | 2.09 ± 2.52 | 6.09 ± 5.13 | <0.001 |
| APPS (Adults) ± SD | 9.69 ± 3.14 | 10.58 ± 2.48 | 0.021 |
| LMS (Adults) ± SD | 2.22 ± 2.51 | 6.42 ± 5.18 | <0.001 |
| Subjects | Unaffected Controls with LMS < 3 | CRS with LMS ≥ 3 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| APPS (All Patients) ± SD | 9.23 ± 3.24 (n = 304) | 10.79 ± 2.66 (n = 84) | <0.001 |
| APPS (Adolescents) ± SD | 9.21 ± 3.26 (n = 169) | 10.68 ± 3.36 (n = 34) | 0.018 |
| APPS (Adults) ± SD | 9.25 ± 3.22 (n = 135) | 10.86 ± 2.09 (n = 50) | <0.001 |
| Subjects | CRSwNP | CRSsNP | AFRS | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| APPS (All Patients) ± SD | 10.29 ± 1.96 (n = 35) | 10.77 ± 3.13 (n = 71) | 10.60 ± 2.07 (n = 5) | 0.699 |
| APPS (Adolescents) ± SD | 9.86 ± 2.30 (n = 13) | 10.97 ± 3.37 (n = 34) | n = 0 | 0.277 |
| APPS (Adults) ± SD | 10.56 ± 1.74 (n = 22) | 10.59 ± 2.92 (n = 37) | 10.60 ± 2.07 (n = 5) | 1.000 |
| Subjects | Unaffected Controls | CF | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| APPS (All Patients) ± SD | 9.62 ± 3.19 | 3.50 ± 2.92 | <0.001 |
| LMS (All Patients) ± SD | 2.15 ± 2.51 | 12.44 ± 3.87 | <0.001 |
| APPS (Adolescents) ± SD | 9.57 ± 3.24 | 4.00 ± 2.92 | <0.001 |
| LMS (Adolescents) ± SD | 2.09 ± 2.52 | 13.22 ± 3.49 | <0.001 |
| APPS (Adults) ± SD | 9.69 ± 3.14 | 3.30 ± 2.96 | <0.001 |
| LMS (Adults) ± SD | 2.22 ± 2.51 | 12.13 ± 4.04 | <0.001 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marino, M.J.; Riley, C.A.; Wu, E.L.; Weinstein, J.E.; McCoul, E.D. Are Chronic Rhinosinusitis and Paranasal Sinus Pneumatization Related? Sinusitis 2016, 1, 92-98. https://doi.org/10.3390/sinusitis1010092
Marino MJ, Riley CA, Wu EL, Weinstein JE, McCoul ED. Are Chronic Rhinosinusitis and Paranasal Sinus Pneumatization Related? Sinusitis. 2016; 1(1):92-98. https://doi.org/10.3390/sinusitis1010092
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarino, Michael J., Charles A. Riley, Eric L. Wu, Jacqueline E. Weinstein, and Edward D. McCoul. 2016. "Are Chronic Rhinosinusitis and Paranasal Sinus Pneumatization Related?" Sinusitis 1, no. 1: 92-98. https://doi.org/10.3390/sinusitis1010092
APA StyleMarino, M. J., Riley, C. A., Wu, E. L., Weinstein, J. E., & McCoul, E. D. (2016). Are Chronic Rhinosinusitis and Paranasal Sinus Pneumatization Related? Sinusitis, 1(1), 92-98. https://doi.org/10.3390/sinusitis1010092






