Design Simulation of Czerny–Turner Configuration-Based Raman Spectrometer Using Physical Optics Propagation Algorithm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
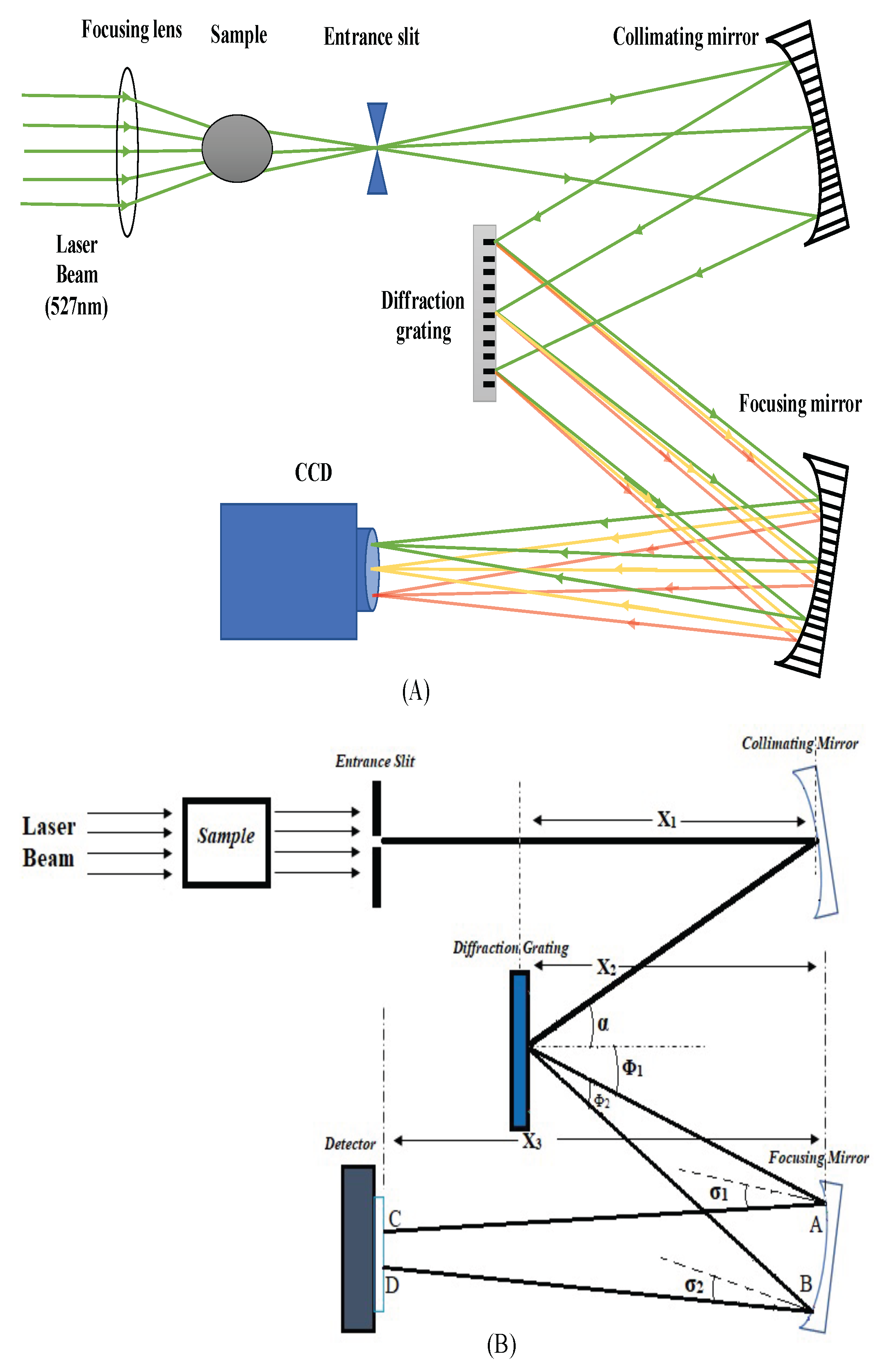
2. Design Parameters for the Simulation of the Raman Spectrometer
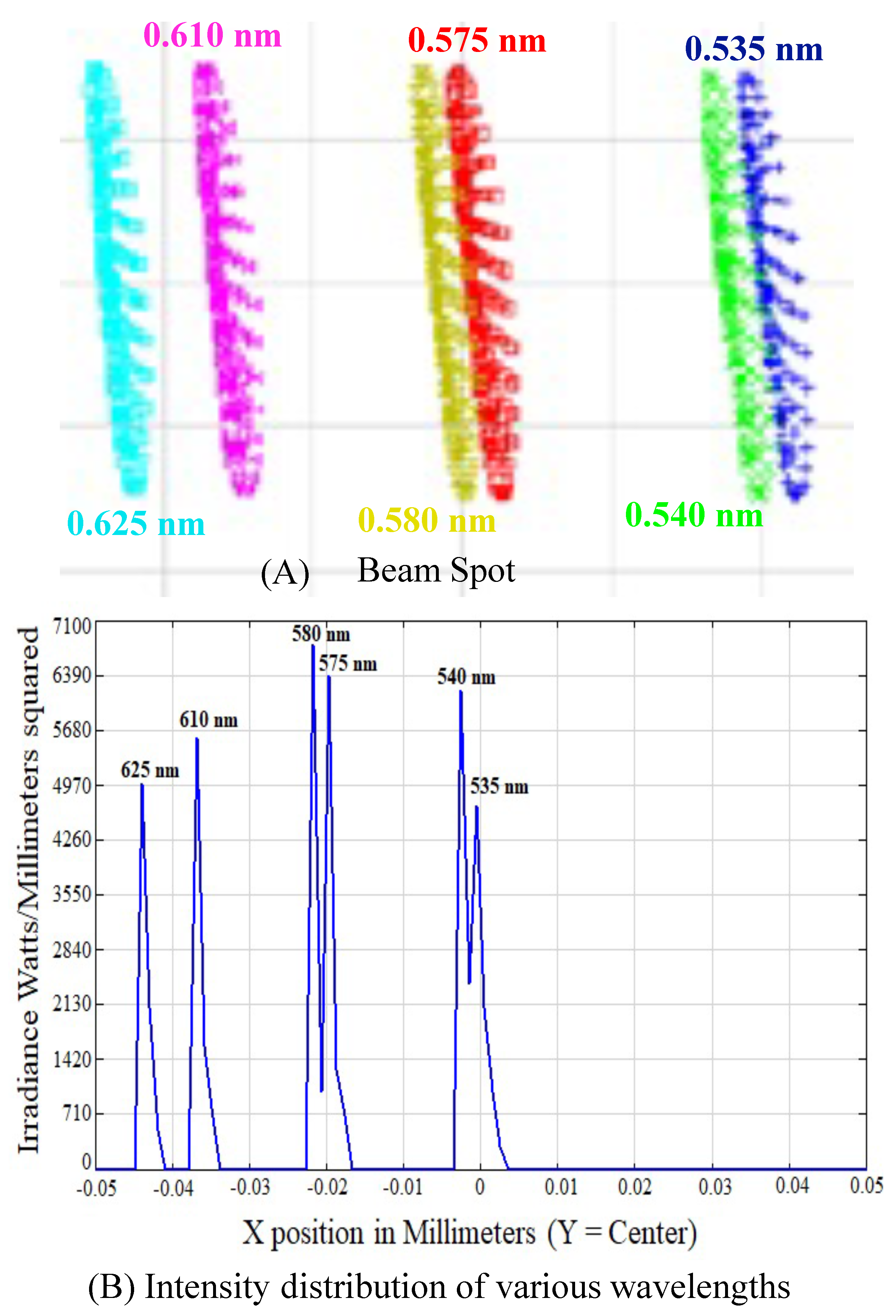
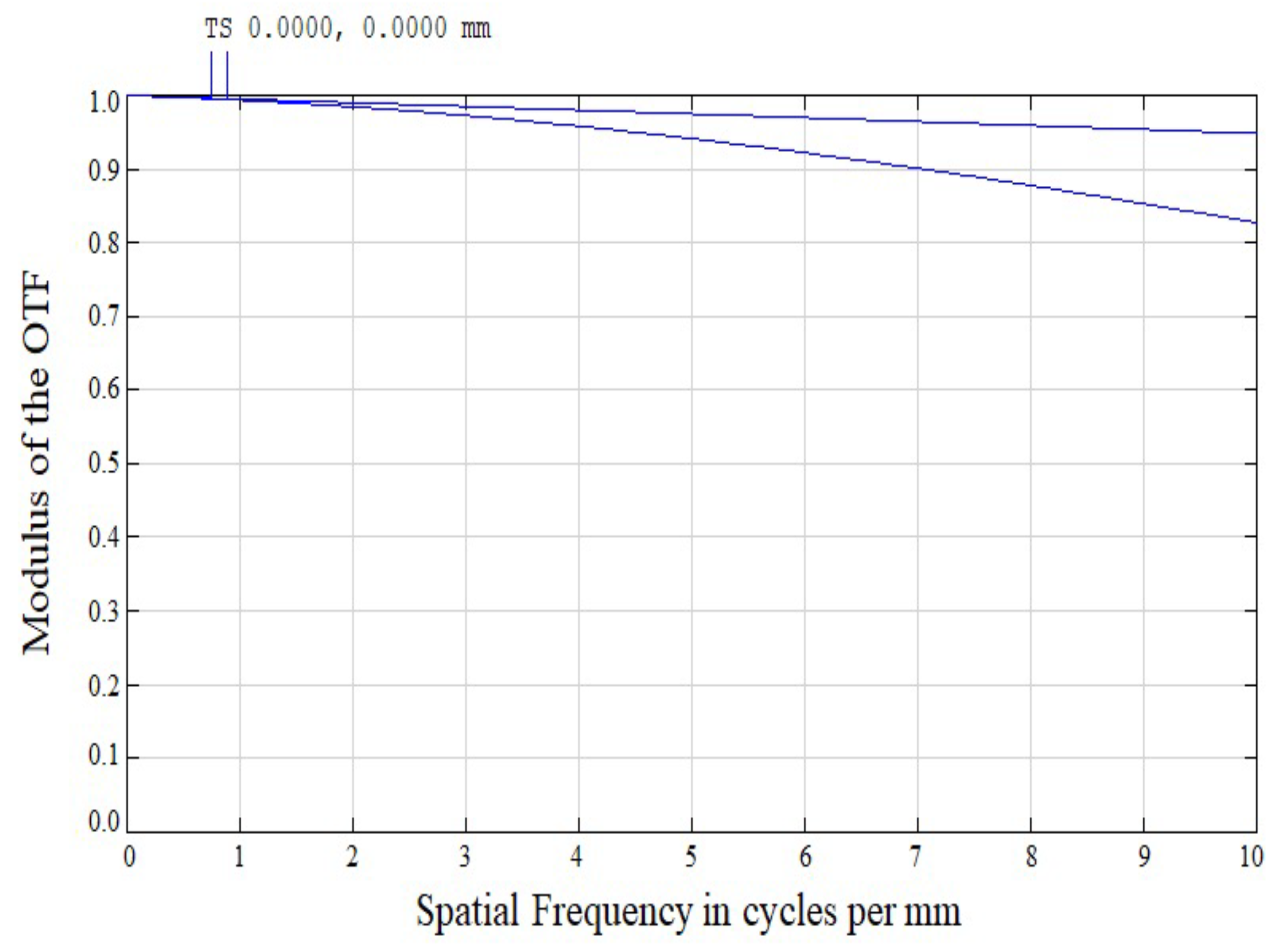
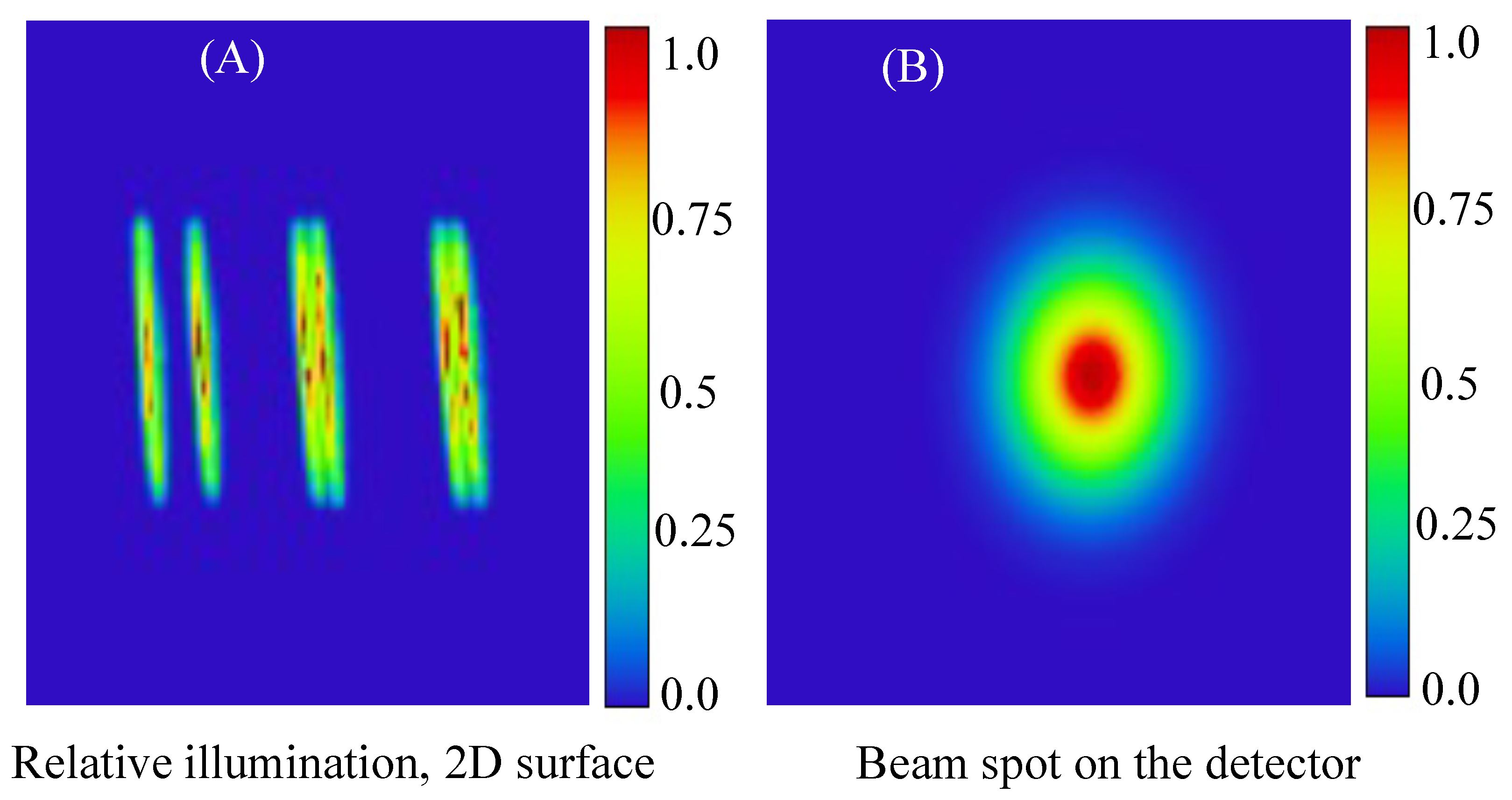
3. Simulation Results and Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baranska, H.; Anna, L.; Jacek, T. Laser Raman Spectrometry: Analytical Applications; Ellis Horwood: Chichester, UK; Wiley: New York, NY, USA; PWN-Polish Scientific Publishers: Warsaw, Poland, 1987; Volume 38, pp. 138–139. Available online: https://www.osti.gov/biblio/6748775 (accessed on 10 September 2021).
- Stöckle, R.M.; Suh, Y.D.; Deckert, V.; Zenobi, R. Nanoscale chemical analysis by tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2000, 318, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Chen, H.; Dong, J.; Chen, S.; Guo, P.; Zhang, Y. Optical design of concave grating Raman spectrometer. Chin. J. Opt. 2015, 35, 0930004–1. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Guo, P.; Wang, L. Optical design of a crossed Czerny–Turner spectrometer with a linear array photomultiplier tube. Appl. Opt. 2019, 58, 7789–7794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Chen, H.; Chen, S.; Guo, P.; He, J.; Wang, L. Optical design of a crossed double-grating spectrometer for extracting pure rotational Raman lines of N2. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2020, 134, 106291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto-Blanco, X.; Montero-Orille, C.; González-Nuñez, H.; Mouriz, M.D.; Lago, E.L.; de la Fuente, R. The Offner imaging spectrometer in quadrature. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 12756–12769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.S.; Thompson, K.P.; Rolland, J.P. Broadband astigmatism-corrected Czerny–Turner spectrometer. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 23378–23384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafer, A.B.; Megill, L.R.; Droppleman, L. Optimization of the Czerny–Turner spectrometer. JOSA 1964, 54, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.zemax.com/products/opticstudio (accessed on 10 September 2021).
- Tang, M.; Fan, X.; Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Que, J.; He, J. General study of asymmetrical crossed Czerny—Turner spectrometer. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, 9966–9975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerner, J.M.; Chambers, R.J.; Passereau, G. Flat field imaging spectroscopy using aberration corrected holographic gratings. Int. Soc. Opt. Photonics 1981, 268, 122–128. [Google Scholar]
- An, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Q. Design and development of optical system for portable Raman spectrometer. Acta Opt. Sin. 2013, 33, 0330001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.K.; Schowengerdt, R.; Kaczynski, M.A. Modulation-transfer-function analysis for sampled image systems. Appl. Opt. 1984, 23, 2572–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Oldendick, J.; Ordonez, C.E.; Chang, W. The geometric response function for convergent slit-slat collimators. Phys. Med. Biol. 2009, 54, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Everson, M.; Duma, V.F.; Dobre, G. Geometric and Radiometric Vignetting Associated with a 72-Facet, Off-Axis, Polygon Mirror for Swept Source Optical Coherence Tomography (SS-OCT); AIP Publishing LLC: Melville, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 1796, p. 04004. [Google Scholar]
| Object Type | Radius of Curvature (mm) | Thickness (mm) | Semi-Diameter (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Infinity | 0.90 | 0.00 |
| Sample | Infinity | 0.90 | 0.30 |
| Slit | Infinity | 4.50 | 0.08 |
| Collimating mirror | −10.00 | −3.00 | 0.61 |
| Diffraction Grating | Infinity | 3.00 | 0.52 |
| Focusing mirror | −10.00 | −4.50 | 0.61 |
| CCD | Infinity | - | 0.30 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Laser wavelength | 527 nm |
| Observed Raman spectra | 530–630 nm |
| Entrance pupil diameter | 0.16 |
| Grating constant | 0.100 lines/m |
| CCD pixel | 1024 × 1024 |
| Slit width | 30 m |
| Size of pixel | 5 m |
| R | −10 mm |
| R | −10 mm |
| x | 3 mm |
| x | 3 mm |
| x | 4.5 mm |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Naeem, M.; Fatima, N.-u.-a.; Hussain, M.; Imran, T.; Bhatti, A.S. Design Simulation of Czerny–Turner Configuration-Based Raman Spectrometer Using Physical Optics Propagation Algorithm. Optics 2022, 3, 1-7. https://doi.org/10.3390/opt3010001
Naeem M, Fatima N-u-a, Hussain M, Imran T, Bhatti AS. Design Simulation of Czerny–Turner Configuration-Based Raman Spectrometer Using Physical Optics Propagation Algorithm. Optics. 2022; 3(1):1-7. https://doi.org/10.3390/opt3010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleNaeem, Muddasir, Noor-ul-ain Fatima, Mukhtar Hussain, Tayyab Imran, and Arshad Saleem Bhatti. 2022. "Design Simulation of Czerny–Turner Configuration-Based Raman Spectrometer Using Physical Optics Propagation Algorithm" Optics 3, no. 1: 1-7. https://doi.org/10.3390/opt3010001
APA StyleNaeem, M., Fatima, N.-u.-a., Hussain, M., Imran, T., & Bhatti, A. S. (2022). Design Simulation of Czerny–Turner Configuration-Based Raman Spectrometer Using Physical Optics Propagation Algorithm. Optics, 3(1), 1-7. https://doi.org/10.3390/opt3010001







