Happy Cow or Thinking Pig? WUR Wolf—Facial Coding Platform for Measuring Emotions in Farm Animals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Emotions
1.2. Understanding Animal Emotions
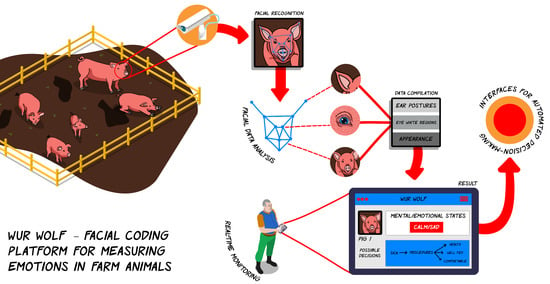
1.3. Facial Recognition Software
1.4. The Grimace Scale
1.5. Best Way to Manage Animal Emotion Recognition
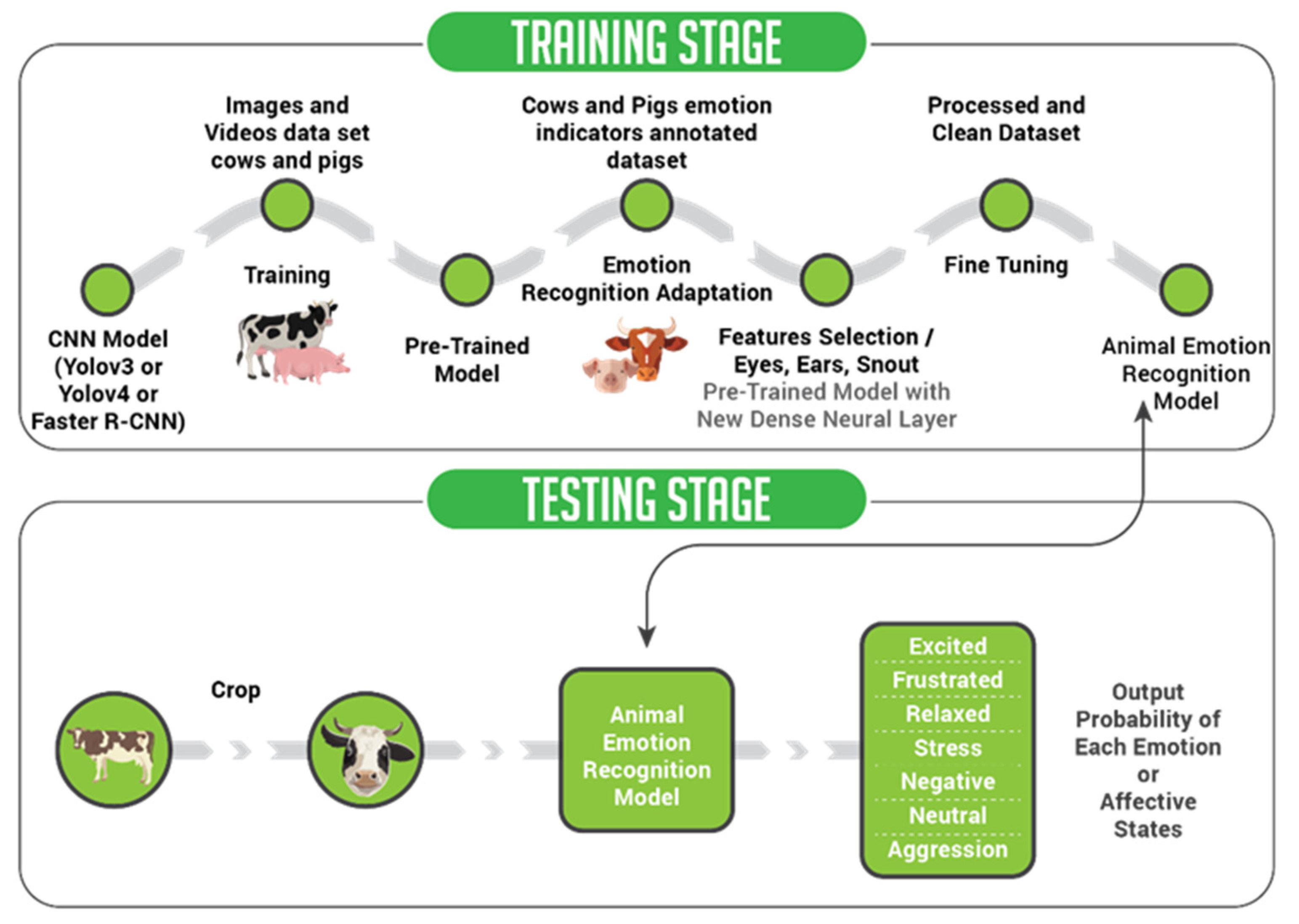
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset Characteristics
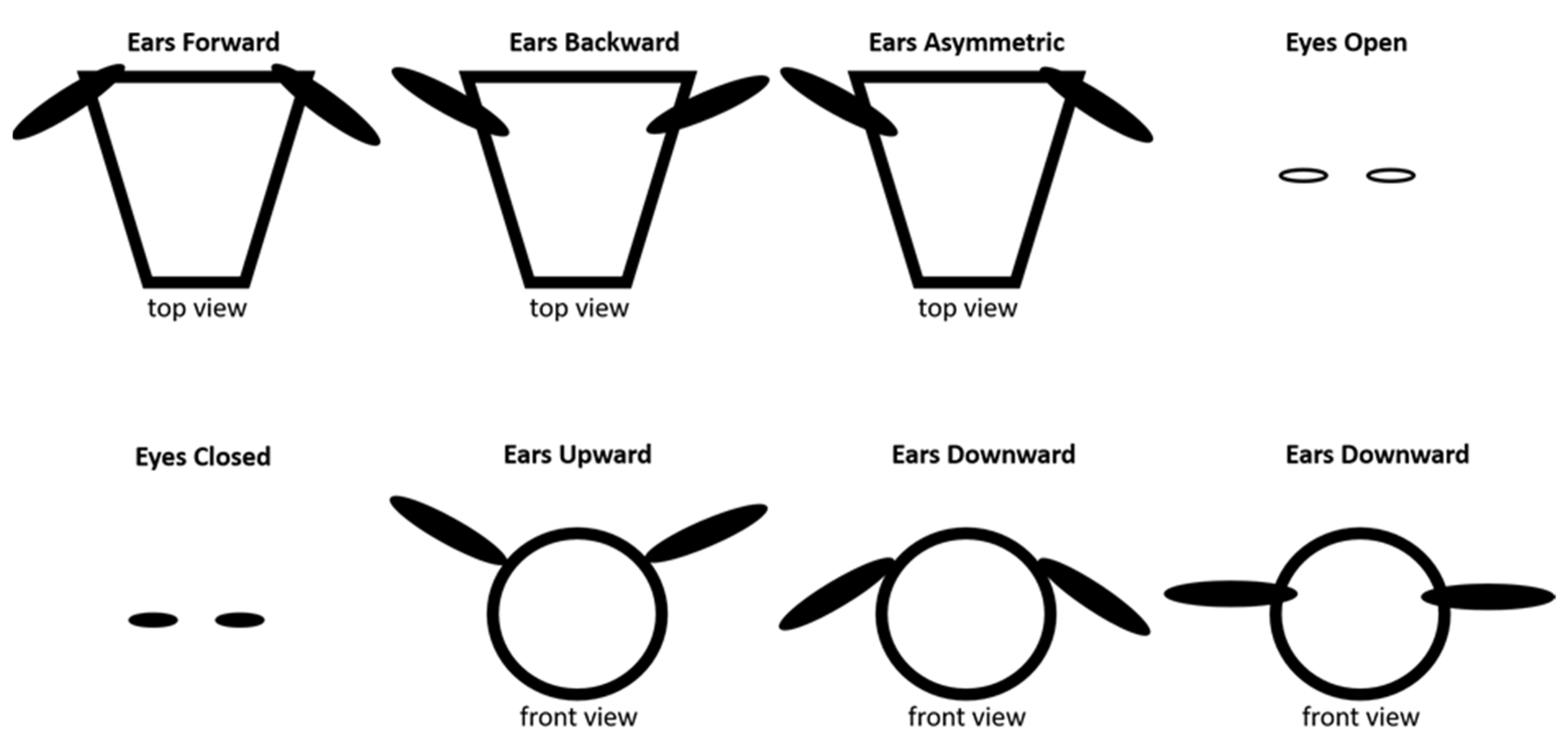
2.2. Features and Data Processing
2.3. Hardware
2.4. YOLOv3
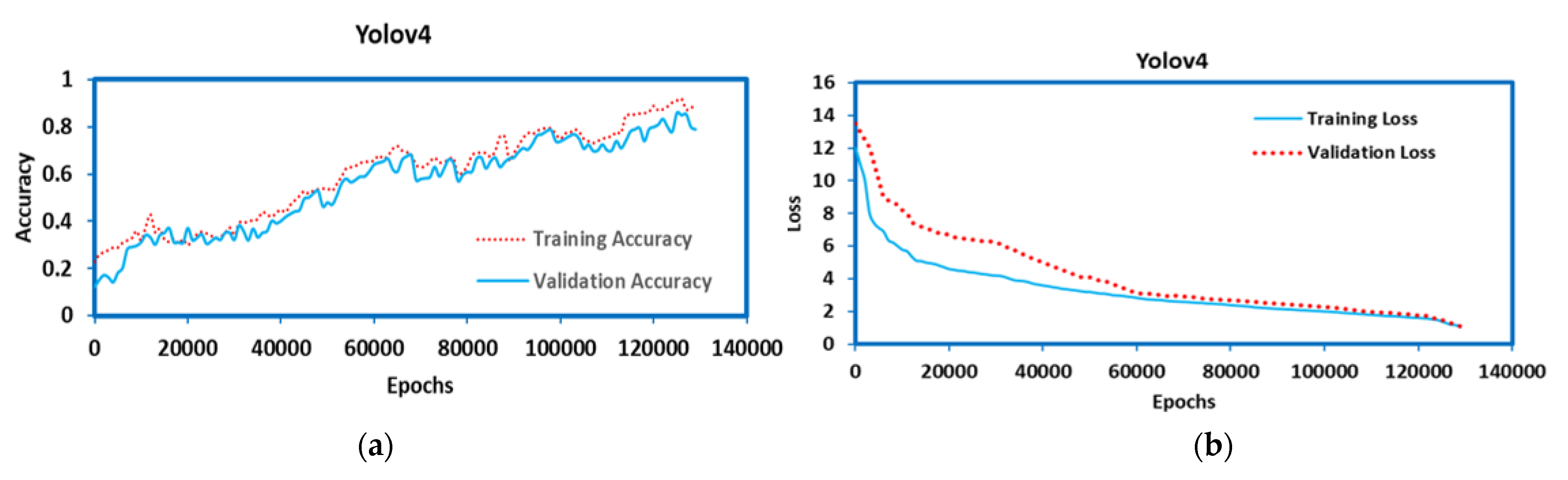
2.5. YOLOv4
2.6. Faster R-CNN
3. Results
3.1. Model Parameters
3.2. Computation Resources
3.3. Mean Average Precision (mAP)
3.4. F1 Score
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Neethirajan, S.; Kemp, B. Digital Livestock Farming. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2021, 32, 100408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neethirajan, S.; Reimert, I.; Kemp, B. Measuring Farm Animal Emotions—Sensor-Based Approaches. Sensors 2021, 21, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neethirajan, S. Transforming the adaptation physiology of farm animals through sensors. Animals 2020, 10, 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, J.P.; Defensor, E.B.; Ichim, C.V.; Lim, M.A.; Mechanic, J.A.; Rabe, M.D.; Schaevitz, L.R. Automated and Continuous Monitoring of Animal Welfare through Digital Alerting. Comp. Med. 2020, 70, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purshouse, J.; Campbell, L. Privacy, crime control and police use of automated facial recognition technology. Crim. Law Rev. 2019, 3, 188–204. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Z.; Shen, Z.; Zhu, H.; Bao, Y.; Liang, S.; Wang, S.; Xiong, G. Clinical application of an automatic facial recognition system based on deep learning for diagnosis of Turner syndrome. Endocrine 2021, 72, 865–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadj-Rabia, S.; Schneider, H.; Navarro, E.; Klein, O.; Kirby, N.; Huttner, K.; Grange, D.K. Automatic recognition of the XLHED phenotype from facial images. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2017, 173, 2408–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.; Qu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Gao, Z. Diagnosing Parkinson Disease Through Facial Expression Recognition: Video Analysis. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, e18697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Rodríguez, M.R.; Díaz-Fernández, M.C.; Gómez, C.P. Facial-expression recognition: An emergent approach to the measurement of tourist satisfaction through emotions. Telemat. Inform. 2020, 51, 101404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yolcu, G.; Oztel, I.; Kazan, S.; Oz, C.; Bunyak, F. Deep learning-based face analysis system for monitoring customer interest. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2020, 11, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siniscalchi, M.; D’Ingeo, S.; Quaranta, A. Orienting asymmetries and physiological reactivity in dogs’ response to human emotional faces. Learn. Behav. 2018, 46, 574–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kujala, M.V.; Somppi, S.; Jokela, M.; Vainio, O.; Parkkonen, L. Human empathy, personality and experience affect the emotion ratings of dog and human facial expressions. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, H.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Ruliang, P. Facial expression recognition in golden snub-nosed monkeys. Curr. Zool. 2020, 66, 695–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, E.S.; Mendl, M.T. Animal emotion: Descriptive and prescriptive definitions and their implications for a comparative perspective. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2018, 205, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawroth, C.; Langbein, J.; Coulon, M.; Gabor, V.; Oesterwind, S.; Benz-Schwarzburg, J.; von Borell, E. Farm animal cognition—linking behavior, welfare and ethics. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Howarth, E.R.I.; Kemp, C.; Thatcher, H.R.; Szott, I.D.; Farningham, D.; Witham, C.L.; Bethel, E.J. Developing and Validating Attention Bias Tools for Assessing Trait and State Affect in Animals. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2021, 234, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crump, A.; Bethel, E.; Earley, R.; Lee, V.E.; Arnott, G. Emotion in Animal Contests. Proc. R. Soc. B 2020, 287, 20201715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finka, L.R.; Stelio, P.L.; Brondani, J.; Tzimiropolos, Y.; Mills, D. Geometric morphometrics for the study of facial expressions in non-human animals, using the domestic cat as an exemplar. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mota-Rojas, D.; Olmos-Hernandez, A.; Verduzco-Mendoza, A.; Hernandez, E.; Whittaker, A. The Utility of Grimace Scales for Practical Pain Assessment in Laboratory Animals. Animals 2020, 10, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, E.; Mainau, E.; Manteca, X. Development of a Facial Expression Scale Using Farrowing as a Model of Pain in Sows. Animals 2020, 10, 2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seng, S.; Al-Ameen, M.N.; Wright, M. A first look into users’ perceptions of facial recognition in the physical world. Comput. Secur. 2021, 105, 102227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kaur, A.; Kumar, M. Face detection techniques: A review. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2019, 52, 927–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Xu, P.; Miao, Q.; Shao, G.; Li, B. Automatic Identification of Individual Primates with Deep Learning Techniques. iScience 2020, 23, 101412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crouse, D.; Jacobs, R.; Richardson, Z.; Klum, S.; Tecot, S. LemurFaceID: A face recognition system to facilitate individual identification of lemurs. BMC Zool. 2017, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Singh, S.J.; Singh, R.; Singh, A.K. Deep Learning Framework for Recognition of Cattle Using Muzzle Point Image Pattern. Measurement 2017, 116, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumrosen, G.; Hawellek, D.; Pesaran, B. Towards Automated Recognition of Facial Expressions in Animal Models. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2810–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogil, J.S.; Pang, D.S.J.; Dutra, G.G.S.; Chambers, C. The development and use of facial grimace scales for pain measurement in animals. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2020, 116, 480–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guesgen, M.; Beausoleil, N.J.; Leach, M.; Minot, E.O.; Stafford, K.J. Coding and quantification of a facial expression for pain in lambs. Behav. Process. 2016, 132, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dolensek, N.; Gehrlach, D.A.; Klein, A.S.; Gogolla, N. Facial expressions of emotion states and their neuronal correlates in mice. Science 2020, 368, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lansade, L.; Nowak, R.; Lainé, A.; Leterrier, C.; Bertin, A. Facial expression and oxytocin as possible markers of positive emotions in horses. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lambert, H.S.; Carder, G. Looking into the eyes of a cow: Can eye whites be used as a measure of emotional state? Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2017, 186, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimert, I.; Bolhuis, J.E.; Kemp, B.; Rodenburg, T.B. Indicators of positive and negative emotions and emotional contagion in pigs. Physiol. Behav. 2013, 109, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimert, I.; Bolhuis, J.E.; Kemp, B.; Rodenburg, T.B. Emotions on the loose: Emotional contagion and the role of oxytocin in pigs. Anim. Cogn. 2015, 18, 517–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krugmann, K.L.; Mieloch, F.J.; Krieter, J.; Czycholl, I. Can tail and ear postures be suitable to capture the affective state of growing pigs? J. Appl. Anim. Welf. Sci. 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czycholl, I.; Hauschild, E.; Büttner, K.; Krugmann, K.; Burfeind, O.; Krieter, J. Tail and ear postures of growing pigs in two different housing conditions. Behav. Process. 2020, 176, 104138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzutalin, D. LabelImg, Github. 2015. Available online: https://github.com/tzutalin/labelImg (accessed on 1 October 2020).
- Battini, M.; Agostini, A.; Mattiello, S. Understanding cows’ emotions on farm: Are eye white and ear posture reliable indicators? Animals 2019, 9, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gómez, Y.; Bieler, R.; Hankele, A.K.; Zähner, M.; Savary, P.; Hillmann, E. Evaluation of visible eye white and maximum eye temperature as non-invasive indicators of stress in dairy cows. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2018, 198, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camerlink, I.; Coulange, E.; Farish, M.; Baxter, E.M.; Turner, S.P. Facial expression as a potential measure of both intent and emotion. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.Y.; Liao, H.Y.M. Yolov4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10934. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R. Fast R-CNN. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Wei, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, W. Optimized faster-RCNN in real-time facial expression classification. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 790, 012148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowen, A.S.; Keltner, D.; Schroff, F.; Jou, B.; Adam, H.; Prasad, G. Sixteen facial expressions occur in similar contexts worldwide. Nature 2021, 589, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Species Type | Indicators Inferring Emotions | Emotions/Affective States | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cow | Upright ear posture longer | Excited state (positive emotion) | [31] |
| Cow | Forward facing ear posture | Frustration (negative emotion) | [31] |
| Cow | Half-closed eyes and ears backwards or hung-down | Relaxed state (positive emotion) | [37] |
| Cow | Eye white clearly visible and ears directed forward | Excited state (positive emotion) | [37] |
| Cow | Visible eye white | Stress (negative emotion) | [38] |
| Pigs | Ears forward | Alert | [32,33] |
| Pigs | Ears backward | Negative emotion | [32,33] |
| Pigs | Hanging ears flipping in the direction of eyes | Neutral emotion | [32,33] |
| Pigs | Standing upright ears | Normal (neutral state) | [32,33] |
| Pigs | Ears forward oriented | Aggression (negative emotion) | [39] |
| Pigs | Ears backward and less open eyes | Retreat from aggression or transition to neutral state | [39] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Neethirajan, S. Happy Cow or Thinking Pig? WUR Wolf—Facial Coding Platform for Measuring Emotions in Farm Animals. AI 2021, 2, 342-354. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai2030021
Neethirajan S. Happy Cow or Thinking Pig? WUR Wolf—Facial Coding Platform for Measuring Emotions in Farm Animals. AI. 2021; 2(3):342-354. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai2030021
Chicago/Turabian StyleNeethirajan, Suresh. 2021. "Happy Cow or Thinking Pig? WUR Wolf—Facial Coding Platform for Measuring Emotions in Farm Animals" AI 2, no. 3: 342-354. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai2030021
APA StyleNeethirajan, S. (2021). Happy Cow or Thinking Pig? WUR Wolf—Facial Coding Platform for Measuring Emotions in Farm Animals. AI, 2(3), 342-354. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai2030021