A Deep Learning Approach to Detect COVID-19 Patients from Chest X-ray Images †
Abstract
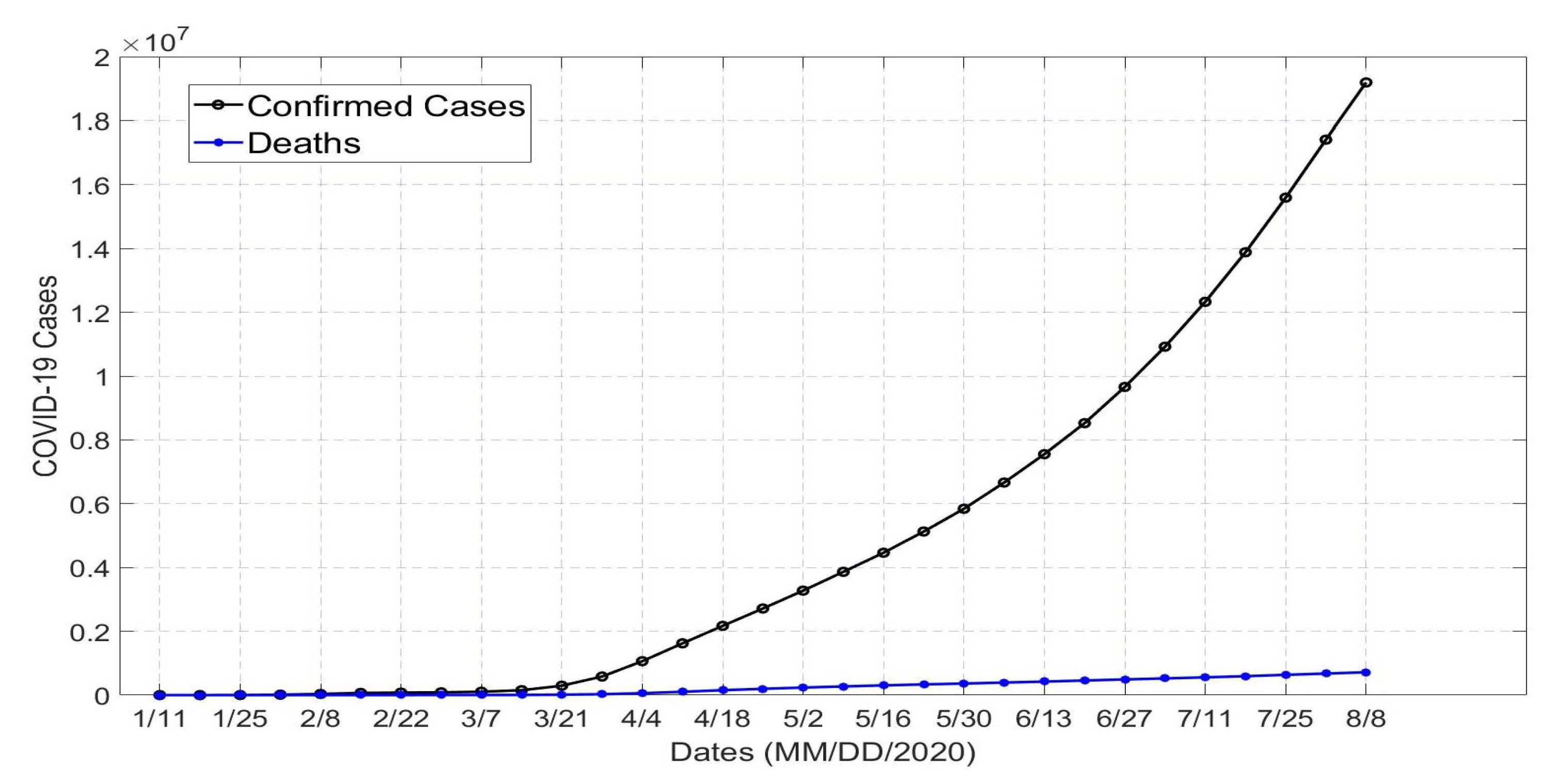
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
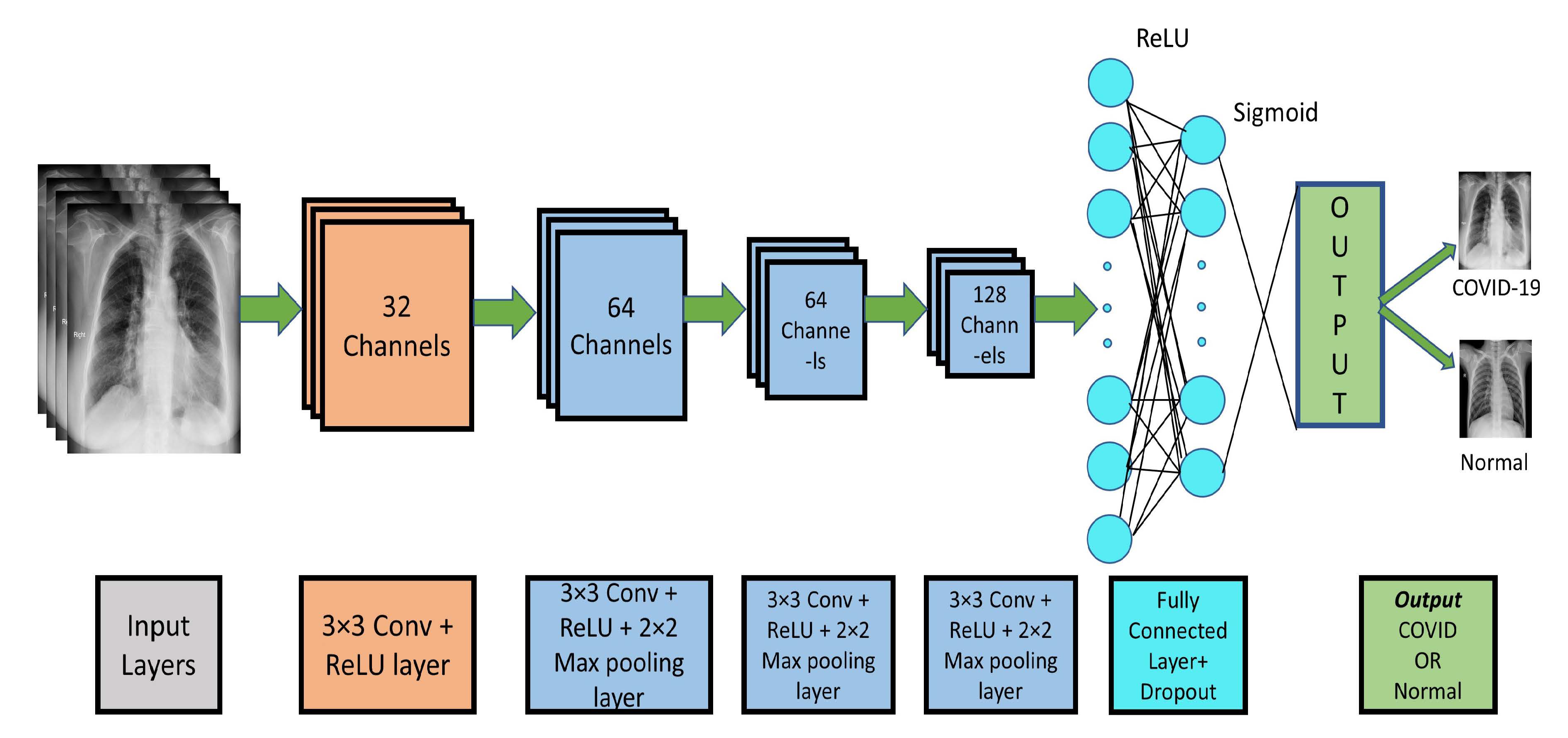
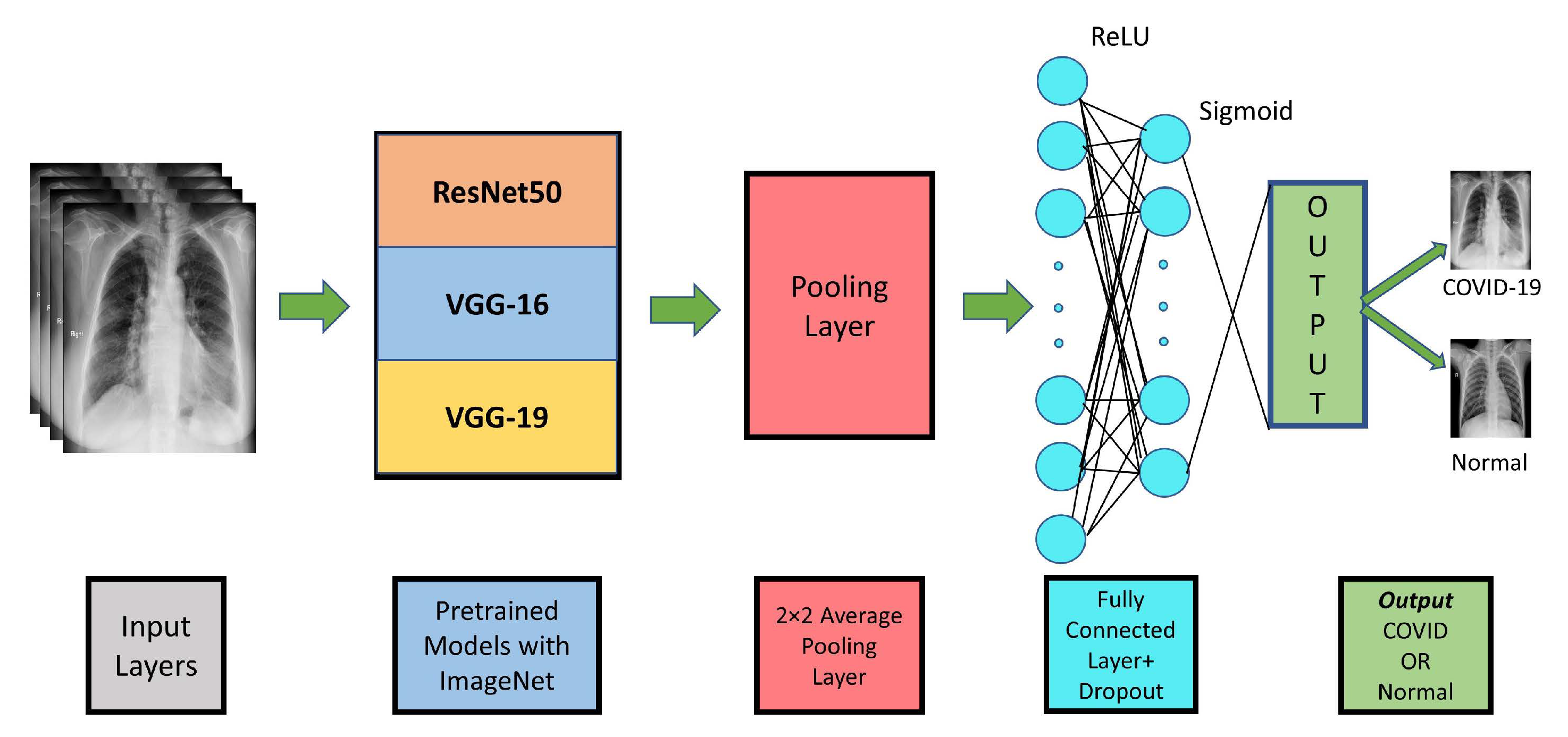
3. Proposed CNN Model for COVID-19 Detection
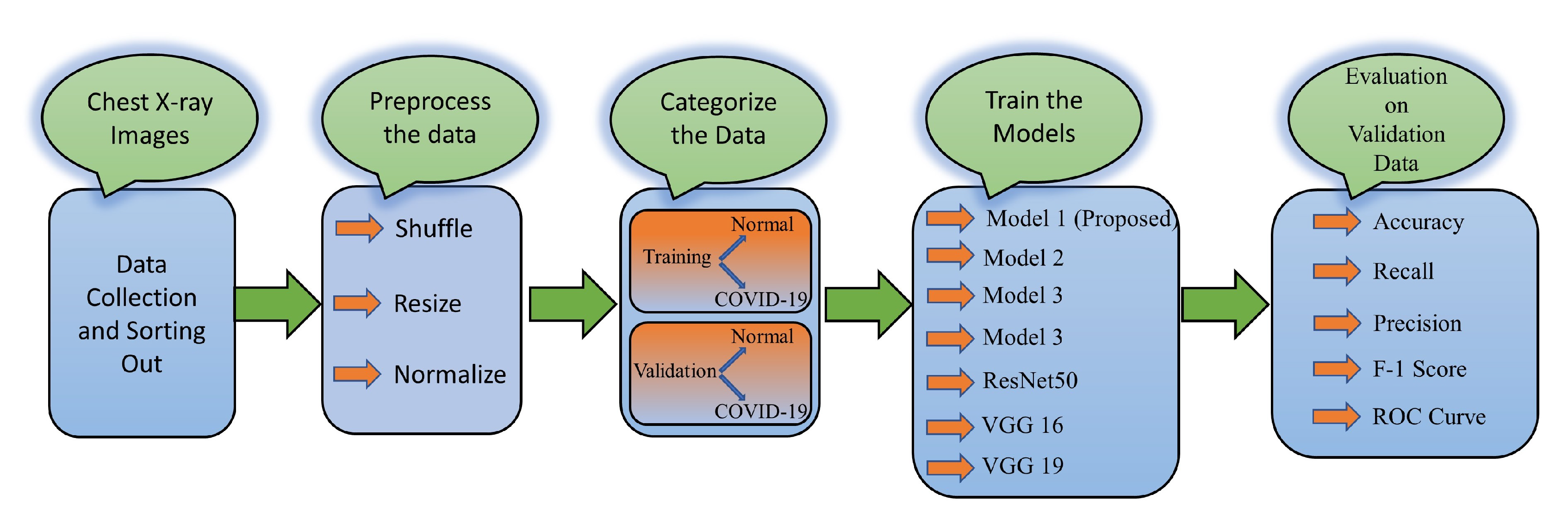
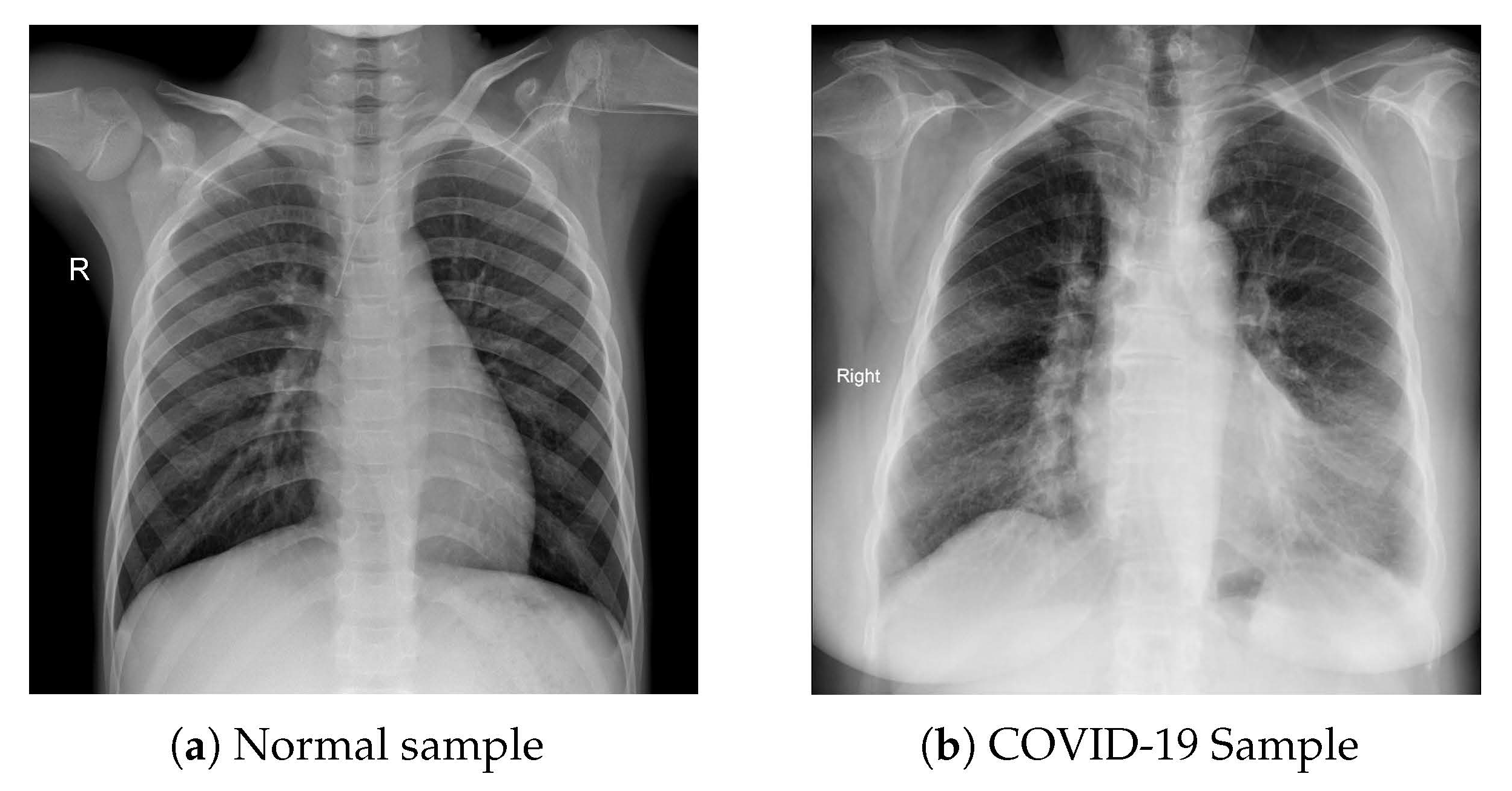
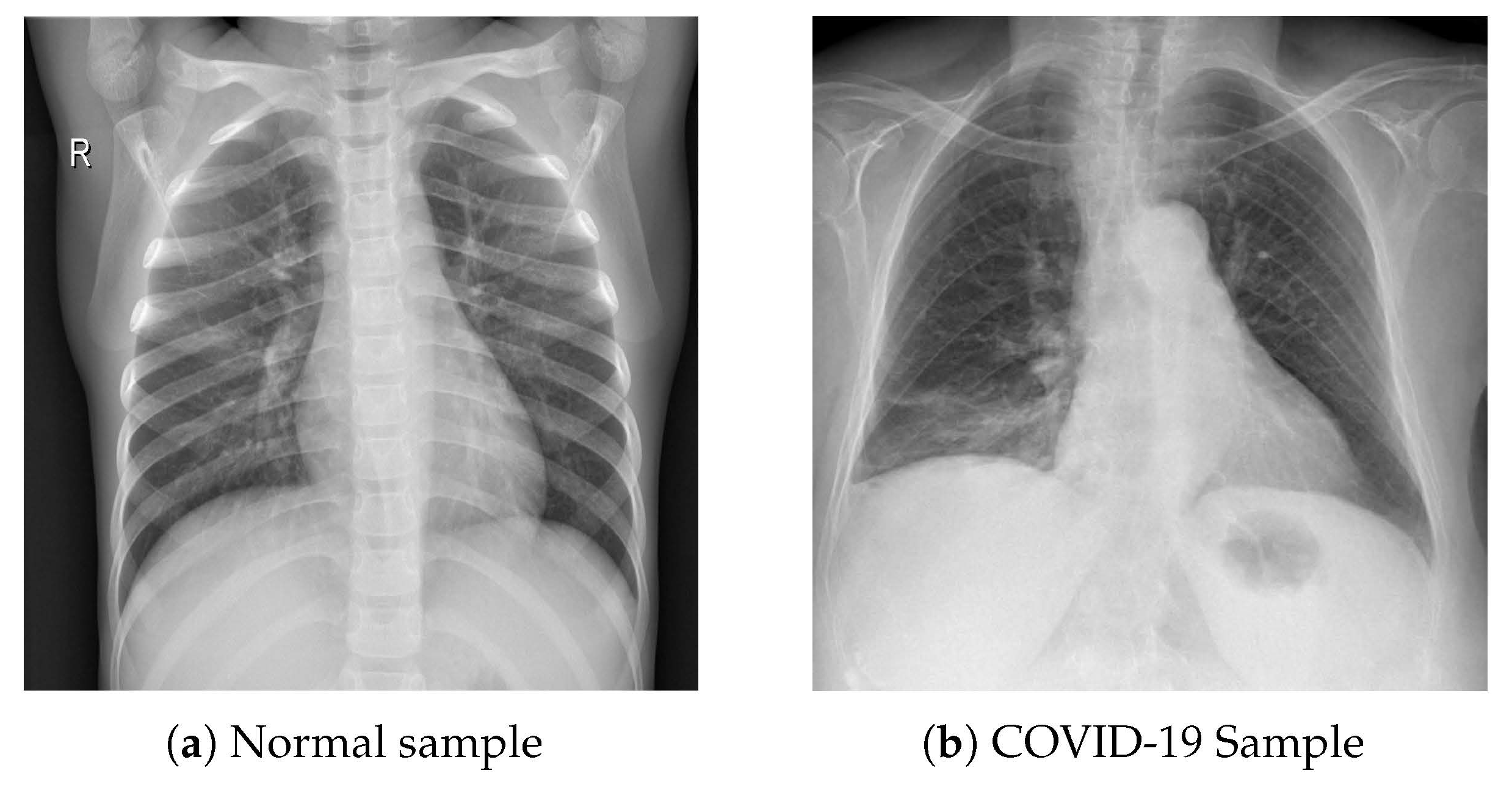
3.1. Dataset Collection and Modeling
3.2. CNN Modeling
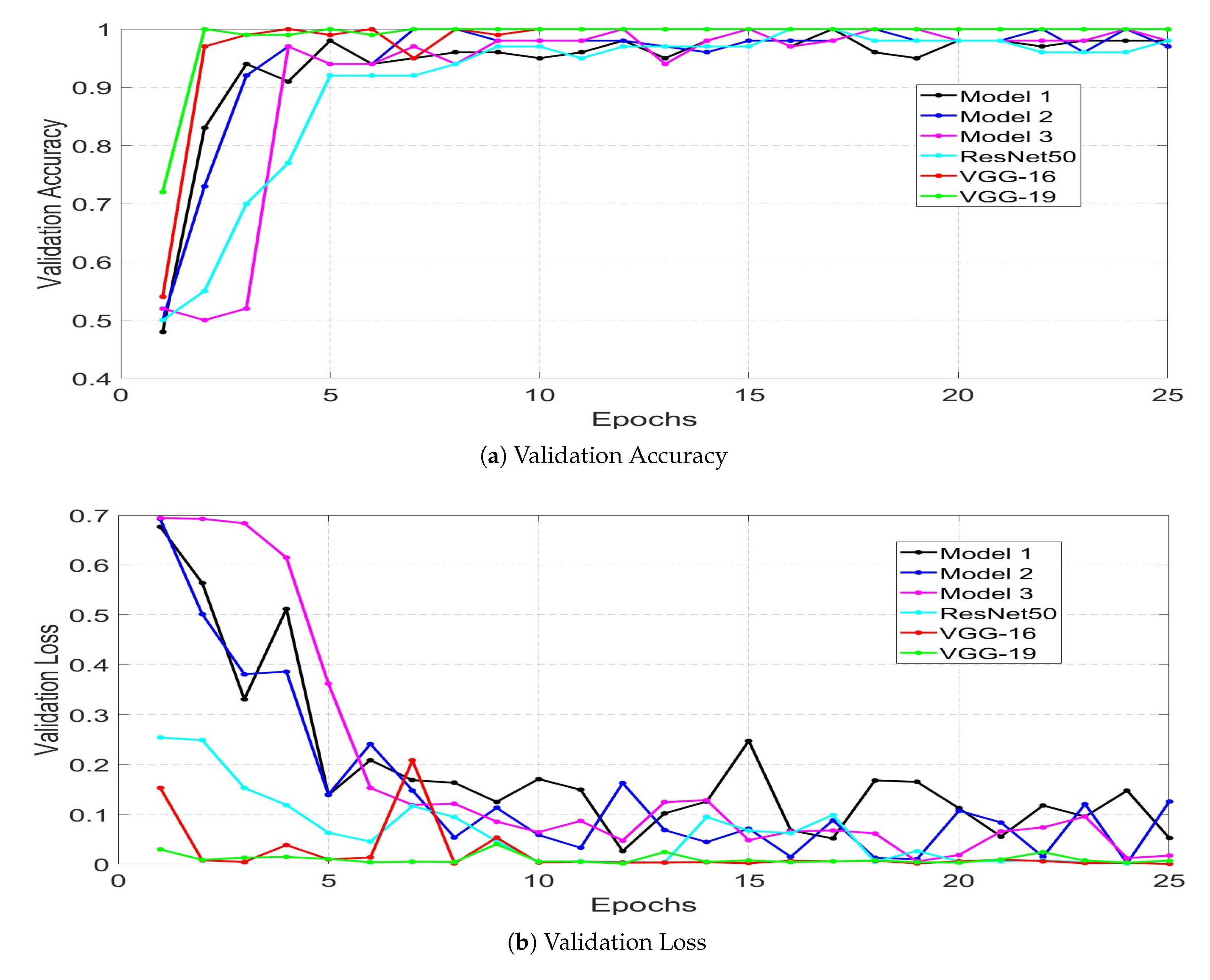
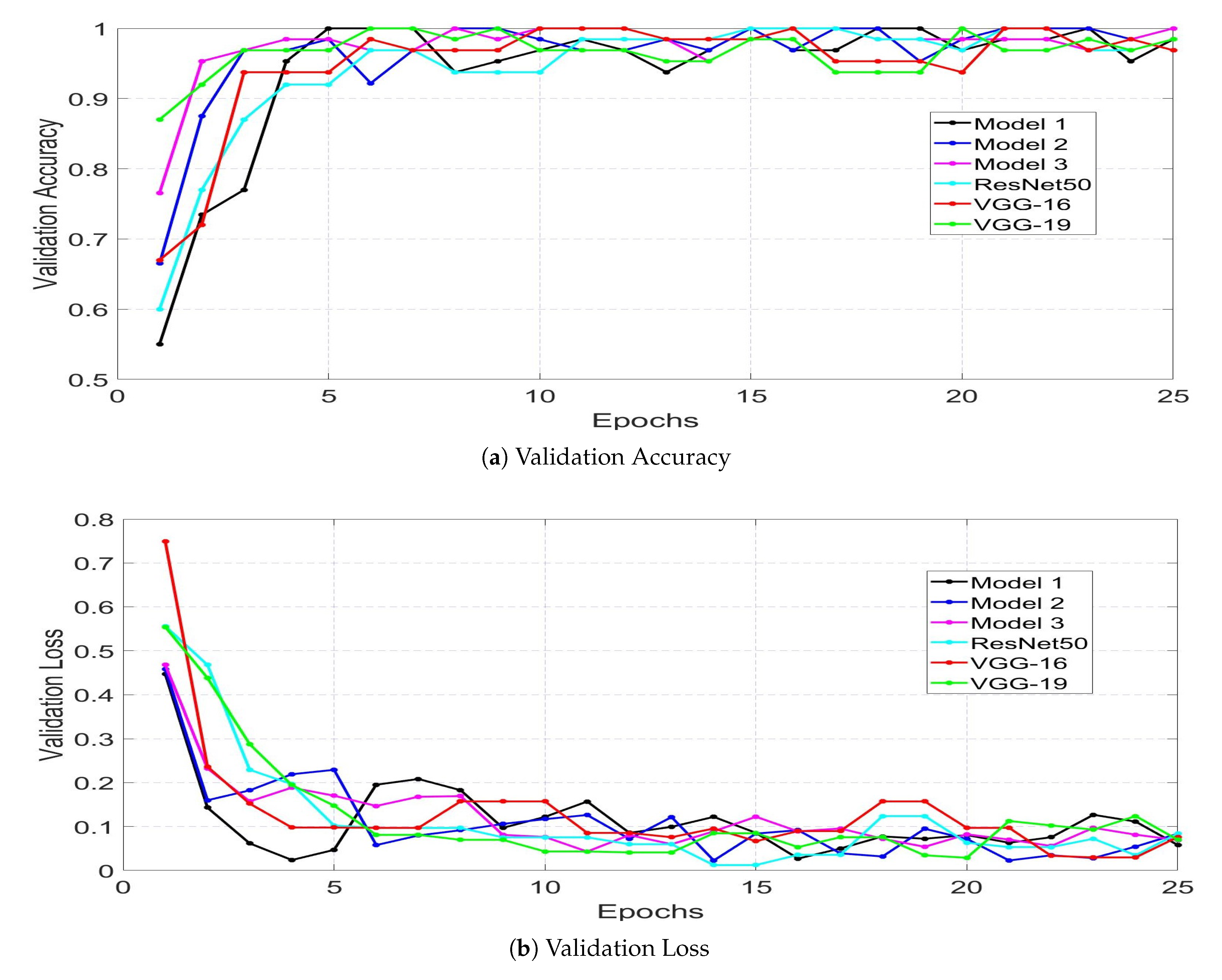
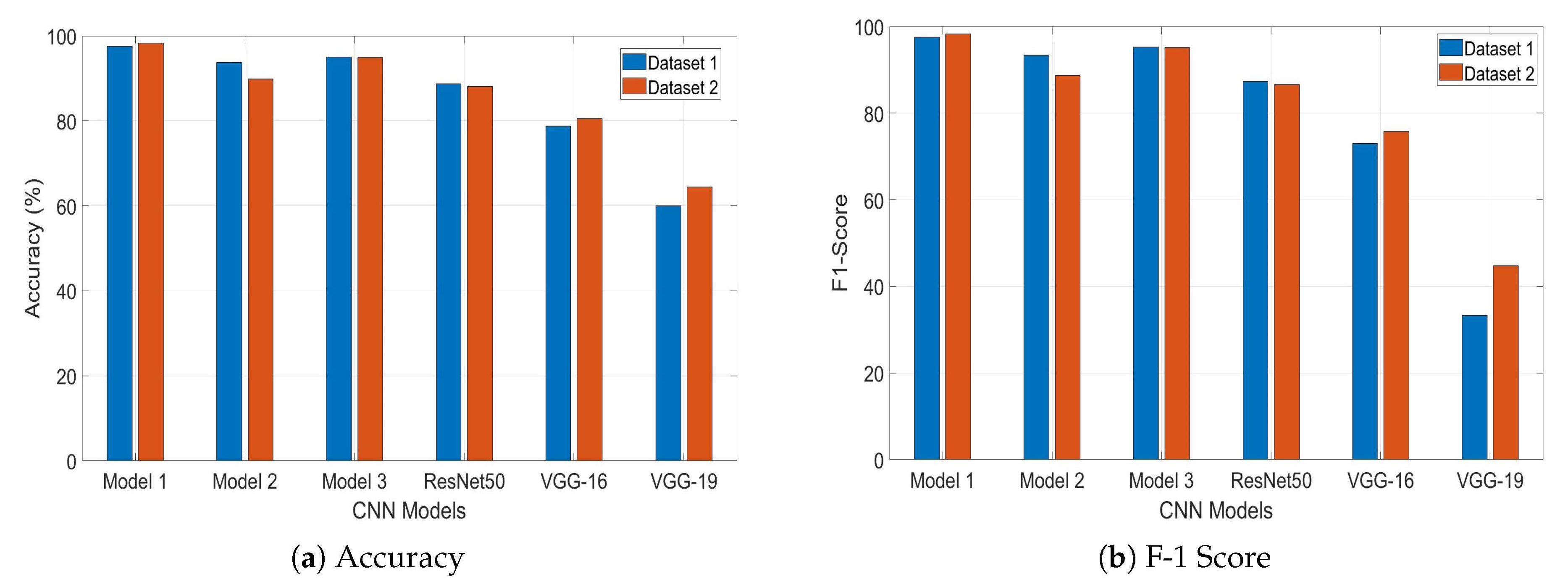
4. Results and Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simard, P.Y.; Steinkraus, D.; Platt, J.C. Best practices for convolutional neural networks applied to visual document analysis. In Proceedings of the Icdar 2003, Scotland, UK, 3–6 August 2003; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- O’Shea, K.; Nash, R. An introduction to convolutional neural networks. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.08458. [Google Scholar]
- Bhandare, A.; Bhide, M.; Gokhale, P.; Chandavarkar, R. Applications of convolutional neural networks. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Inf. Technol. 2016, 7, 2206–2215. [Google Scholar]
- Barbedo, J.G.A.; Castro, G.B. A Study on CNN-Based Detection of Psyllids in Sticky Traps Using Multiple Image Data Sources. AI 2020, 1, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K. Overview of deep learning in medical imaging. Radiol. Phys. Technol. 2017, 10, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banihabib, M.E.; Bandari, R.; Valipour, M. Improving Daily Peak Flow Forecasts Using Hybrid Fourier-Series Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average and Recurrent Artificial Neural Network Models. AI 2020, 1, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taravat, A.; Wagner, M.P.; Oppelt, N. Automatic Grassland Cutting Status Detection in the Context of Spatiotemporal Sentinel-1 Imagery Analysis and Artificial Neural Networks. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, K.T.; Wijewickrema, S.; Raj, R.G.; O’Leary, S. Street Sign Recognition Using Histogram of Oriented Gradients and Artificial Neural Networks. J. Imaging 2019, 5, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCulloch, W.S.; Pitts, W. A logical calculus of the ideas immanent in nervous activity. Bull. Math. Biophys. 1943, 5, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Hu, X. Recurrent convolutional neural network for object recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2015, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3367–3375. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, J.; Wang, Z.; Kuen, J.; Ma, L.; Shahroudy, A.; Shuai, B.; Liu, T.; Wang, X.; Wang, G.; Cai, J.; et al. Recent advances in convolutional neural networks. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 77, 354–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiler, M.D.; Fergus, R. Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 818–833. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2012, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 3–6 December 2012; pp. 1097–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Modes of Transmission of Virus Causing COVID-19: Implications for IPC Precaution Recommendations: Scientific Brief, 27 March 2020; Technical Report; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.C.; Chen, C.S.; Chan, Y.J. The outbreak of COVID-19: An overview. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2020, 83, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Newsroom, W.H.O. Available online: Https://www.who.int/news-room/detail/07-04-2020-who-lists-two-covid-19-tests-for-emergency-use/ (accessed on 7 September 2020).
- Loeffelholz, M.J.; Tang, Y.W. Laboratory diagnosis of emerging human coronavirus infections—The state of the art. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfefferle, S.; Reucher, S.; Nörz, D.; Lütgehetmann, M. Evaluation of a quantitative RT-PCR assay for the detection of the emerging coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 using a high throughput system. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2000152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litjens, G.; Kooi, T.; Bejnordi, B.E.; Setio, A.A.A.; Ciompi, F.; Ghafoorian, M.; Van Der Laak, J.A.; Van Ginneken, B.; Sánchez, C.I. A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 42, 60–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundervold, A.S.; Lundervold, A. An overview of deep learning in medical imaging focusing on MRI. Z. Med. Phys. 2019, 29, 102–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, J.; Carpenter, A. Applying faster R-CNN for object detection on malaria images. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops 2017, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 56–61. [Google Scholar]
- Acharya, U.R.; Fujita, H.; Lih, O.S.; Adam, M.; Tan, J.H.; Chua, C.K. Automated detection of coronary artery disease using different durations of ECG segments with convolutional neural network. Knowl. Based Syst. 2017, 132, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.L.; Hagiwara, Y.; Raghavendra, U.; Yuvaraj, R.; Arunkumar, N.; Murugappan, M.; Acharya, U.R. A deep learning approach for Parkinson’s disease diagnosis from EEG signals. Neural Comput. Appl. 2018, 32, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, S.A.; Nagaraj, R.; Mitra, S. Classification of dental diseases using CNN and transfer learning. In Proceedings of the 2017 5th International Symposium on Computational and Business Intelligence (ISCBI), Dubai, UAE, 11–14 August 2017; pp. 70–74. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, H. A Deep Learning Approach to Universal Skin Disease Classification; University of Rochester Department of Computer Science: Rochester, NY, USA; CSC: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Farooq, A.; Anwar, S.; Awais, M.; Rehman, S. A deep CNN based multi-class classification of Alzheimer’s disease using MRI. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Imaging Systems and Techniques (IST), Beijing, China, 18–20 October 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kruthika, K.; Maheshappa, H.; Initiative, A.D.N. Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. CBIR system using Capsule Networks and 3D CNN for Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2019, 14, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narin, A.; Kaya, C.; Pamuk, Z. Automatic detection of coronavirus disease (covid-19) using X-ray images and deep convolutional neural networks. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.10849. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Xie, Y.; Li, Y.; Shen, C.; Xia, Y. Covid-19 screening on chest X-ray images using deep learning based anomaly detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.12338. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, L.O.; Paul, R.; Goldgof, D.B.; Goldgof, G.M. Finding covid-19 from chest X-rays using deep learning on a small dataset. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.02060. [Google Scholar]
- Sethy, P.K.; Behera, S.K. Detection of coronavirus disease (covid-19) based on deep features. Preprints 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolopoulos, I.D.; Mpesiana, T.A. Covid-19: Automatic detection from X-ray images utilizing transfer learning with convolutional neural networks. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2020, 43, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Qin, L.; Xu, Z.; Yin, Y.; Wang, X.; Kong, B.; Bai, J.; Lu, Y.; Fang, Z.; Song, Q.; et al. Artificial intelligence distinguishes COVID-19 from community acquired pneumonia on chest CT. Radiology 2020, 200905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.Z.; Islam, M.M.; Asraf, A. A combined deep cnn-lstm network for the detection of novel coronavirus (covid-19) using X-ray images. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2020, 100412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemdan, E.E.D.; Shouman, M.A.; Karar, M.E. Covidx-net: A framework of deep learning classifiers to diagnose covid-19 in X-ray images. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.11055. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2017, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2016, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2818–2826. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2016, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Too, E.C.; Yujian, L.; Njuki, S.; Yingchun, L. A comparative study of fine-tuning deep learning models for plant disease identification. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 161, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Ioffe, S.; Vanhoucke, V.; Alemi, A. Inception-v4, inception-resnet and the impact of residual connections on learning. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1602.07261. [Google Scholar]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2017, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1251–1258. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.C. Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2018, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, M.E.; Rahman, T.; Khandakar, A.; Mazhar, R.; Kadir, M.A.; Mahbub, Z.B.; Islam, K.R.; Khan, M.S.; Iqbal, A.; Al-Emadi, N.; et al. Can AI help in screening viral and COVID-19 pneumonia? arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.13145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, T.; Talo, M.; Yildirim, E.A.; Baloglu, U.B.; Yildirim, O.; Acharya, U.R. Automated detection of COVID-19 cases using deep neural networks with X-ray images. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 121, 103792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghanifar, A.; Majdabadi, M.M.; Ko, S. COVID-CXNet: Detecting COVID-19 in Frontal Chest X-ray Images using Deep Learning. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.13807. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.I.; Shah, J.L.; Bhat, M.M. Coronet: A deep neural network for detection and diagnosis of COVID-19 from chest X-ray images. Comput. Methods Progr. Biomed. 2020, 196, 105581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minaee, S.; Kafieh, R.; Sonka, M.; Yazdani, S.; Soufi, G.J. Deep-covid: Predicting covid-19 from chest X-ray images using deep transfer learning. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.09363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afshar, P.; Heidarian, S.; Naderkhani, F.; Oikonomou, A.; Plataniotis, K.N.; Mohammadi, A. Covid-caps: A capsule network-based framework for identification of covid-19 cases from X-ray images. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.02696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wong, A. COVID-Net: A Tailored Deep Convolutional Neural Network Design for Detection of COVID-19 Cases from Chest X-Ray Images. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.09871. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, A.M.; AL-Jawad, M.M.; Jalab, H.A.; Shaiba, H.; Ibrahim, R.W.; AL-Shamasneh, A.R. Classification of Covid-19 Coronavirus, Pneumonia and Healthy Lungs in CT Scans Using Q-Deformed Entropy and Deep Learning Features. Entropy 2020, 22, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedik, A.; Iliyasu, A.M.; El-Rahiem, A.; Abdel Samea, M.E.; Abdel-Raheem, A.; Hammad, M.; Peng, J.; El-Samie, A.; Fathi, E.; El-Latif, A.A.A.; et al. Deploying Machine and Deep Learning Models for Efficient Data-Augmented Detection of COVID-19 Infections. Viruses 2020, 12, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, K.F.; Haque, F.F.; Gandy, L.; Abdelgawad, A. Automatic detection of COVID-19 from chest X-ray images with convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2020 3rd IEEE International Conference on Computing, Electronics & Communications Engineering (IEEE iCCECE ’20), Essex, UK, 17–18 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J.P.; Morrison, P.; Dao, L.; Roth, K.; Duong, T.Q.; Ghassemi, M. COVID-19 Image Data Collection: Prospective Predictions Are the Future. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.11988. [Google Scholar]
- Mooney, P. Chest X-ray Images (Pneumonia). Available online: Https://www.kaggle.com/paultimothymooney/chest-xray-pneumonia/ (accessed on 7 September 2020).
- COVID-19 Chest X-ray. Available online: Https://github.com/agchung/Figure1-COVID-chestxray-dataset (accessed on 7 September 2020).
- Rahimzadeh, M.; Attar, A. A New Modified Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Detecting COVID-19 from X-ray Images. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.08052. [Google Scholar]
- Loey, M.; Smarandache, F.; Khalifa, N.E.M. Within the Lack of Chest COVID-19 X-ray Dataset: A Novel Detection Model Based on GAN and Deep Transfer Learning. Symmetry 2020, 12, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Abdelsamea, M.M.; Gaber, M.M. Classification of COVID-19 in chest X-ray images using DeTraC deep convolutional neural network. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.13815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Dataset | COVID-19 | Normal | Total | Training | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dataset 1 | 201 | 201 | 402 | COVID-19: 161 Normal: 161 Total: 322 | COVID-19: 40 Normal: 40 Total: 80 |
| Dataset 2 | 295 | 659 | 954 | COVID-19: 236 Normal: 600 Total: 836 | COVID-19: 59 Normal: 59 Total: 118 |
| Model | TP | TN | FP | FN | TP Percentage (%) | TN Percentage (%) | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | ROC Area | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
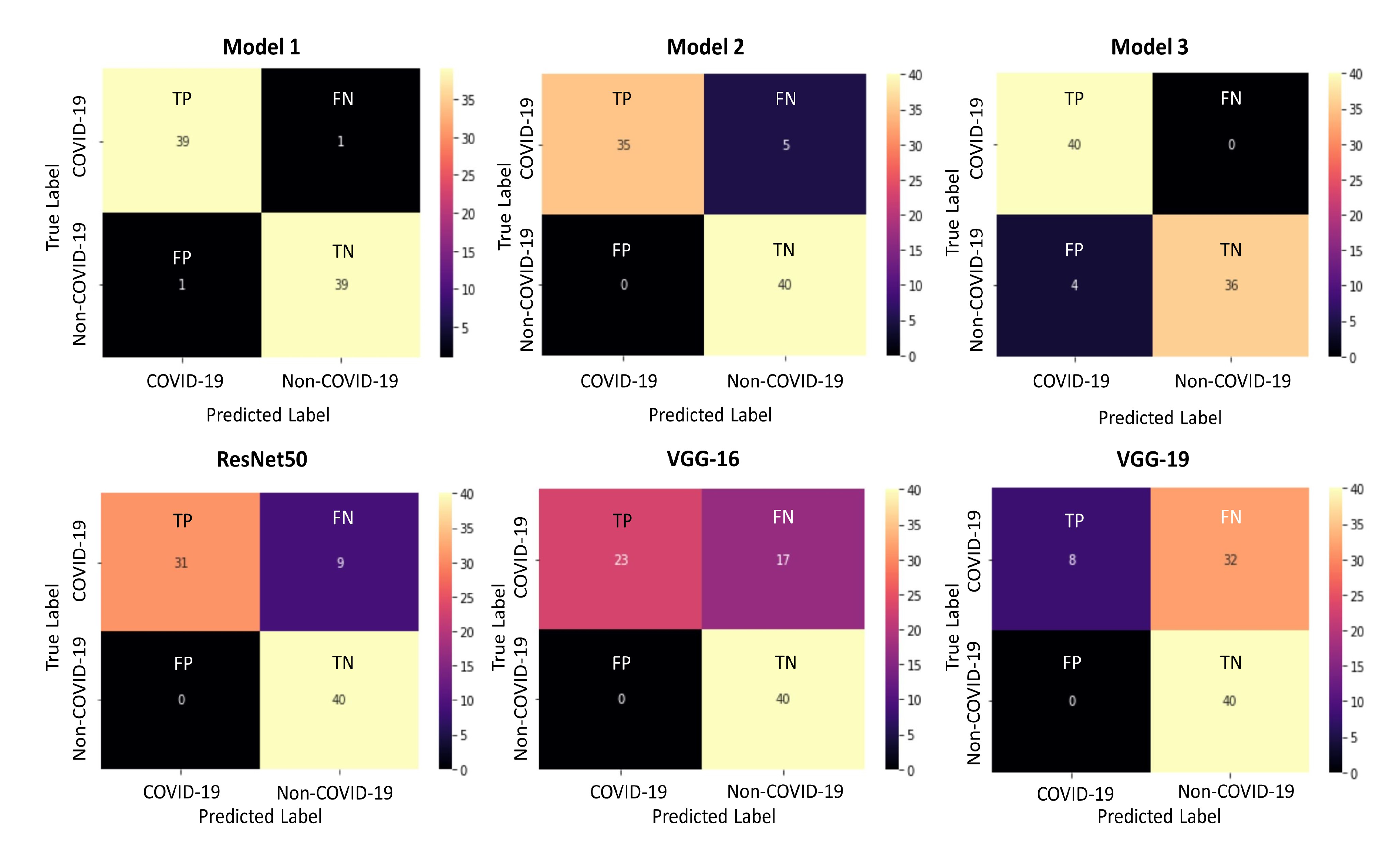
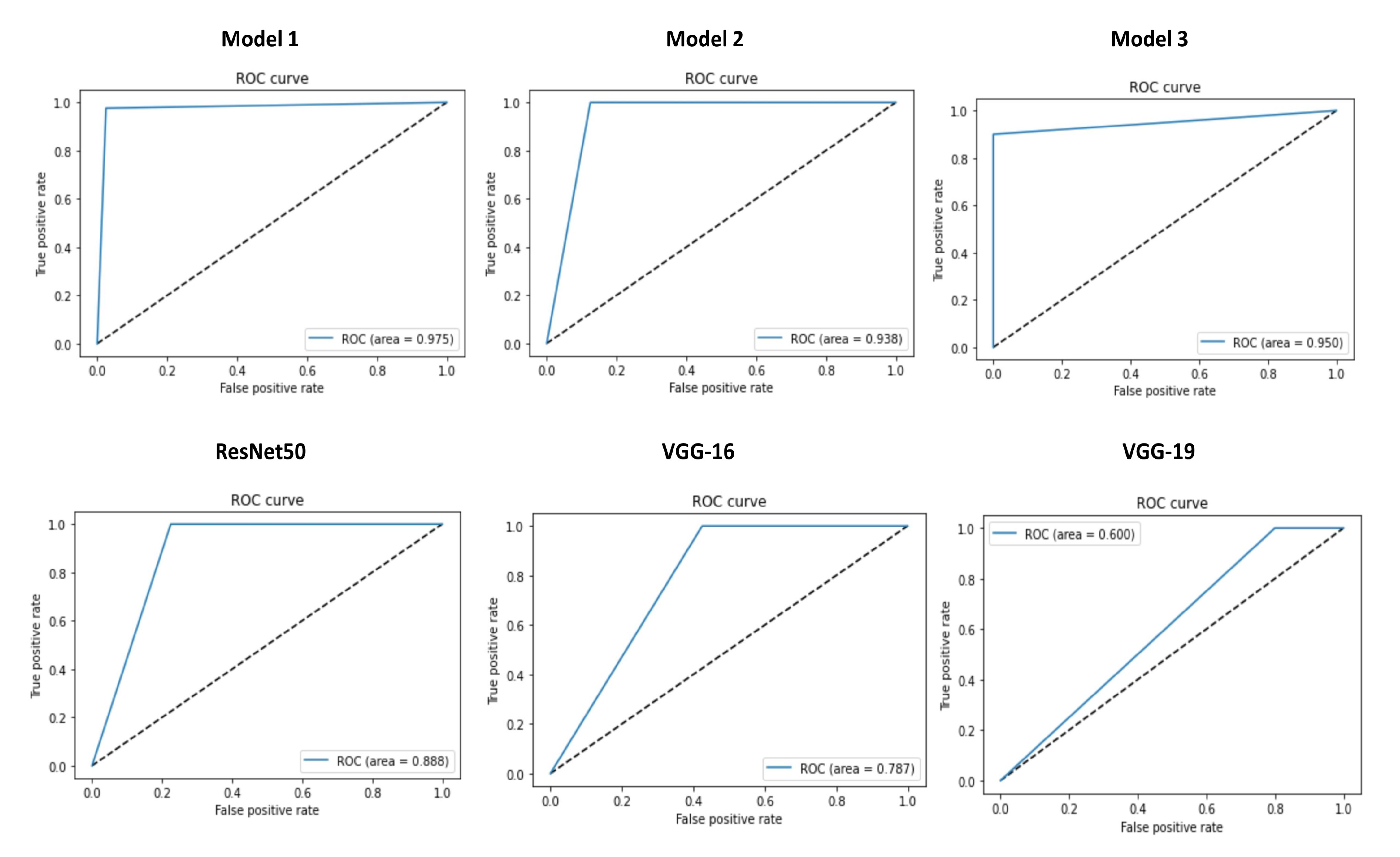
| Model 1 Trained with Dataset 1 | 39 | 39 | 1 | 1 | 97.5 | 97.5 | 97.5 | 97.5 | 97.5 | 0.975 | 97.5 |
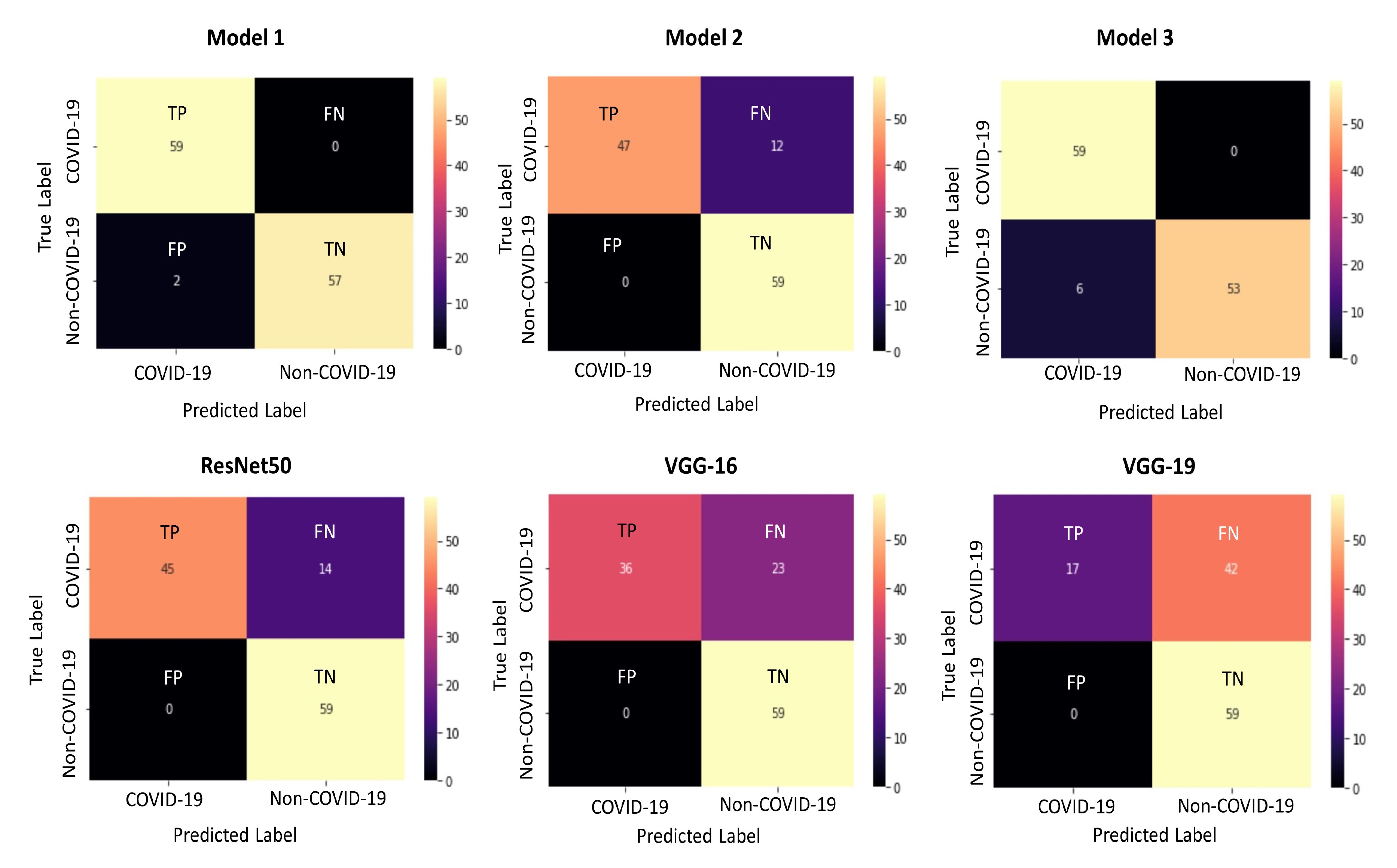
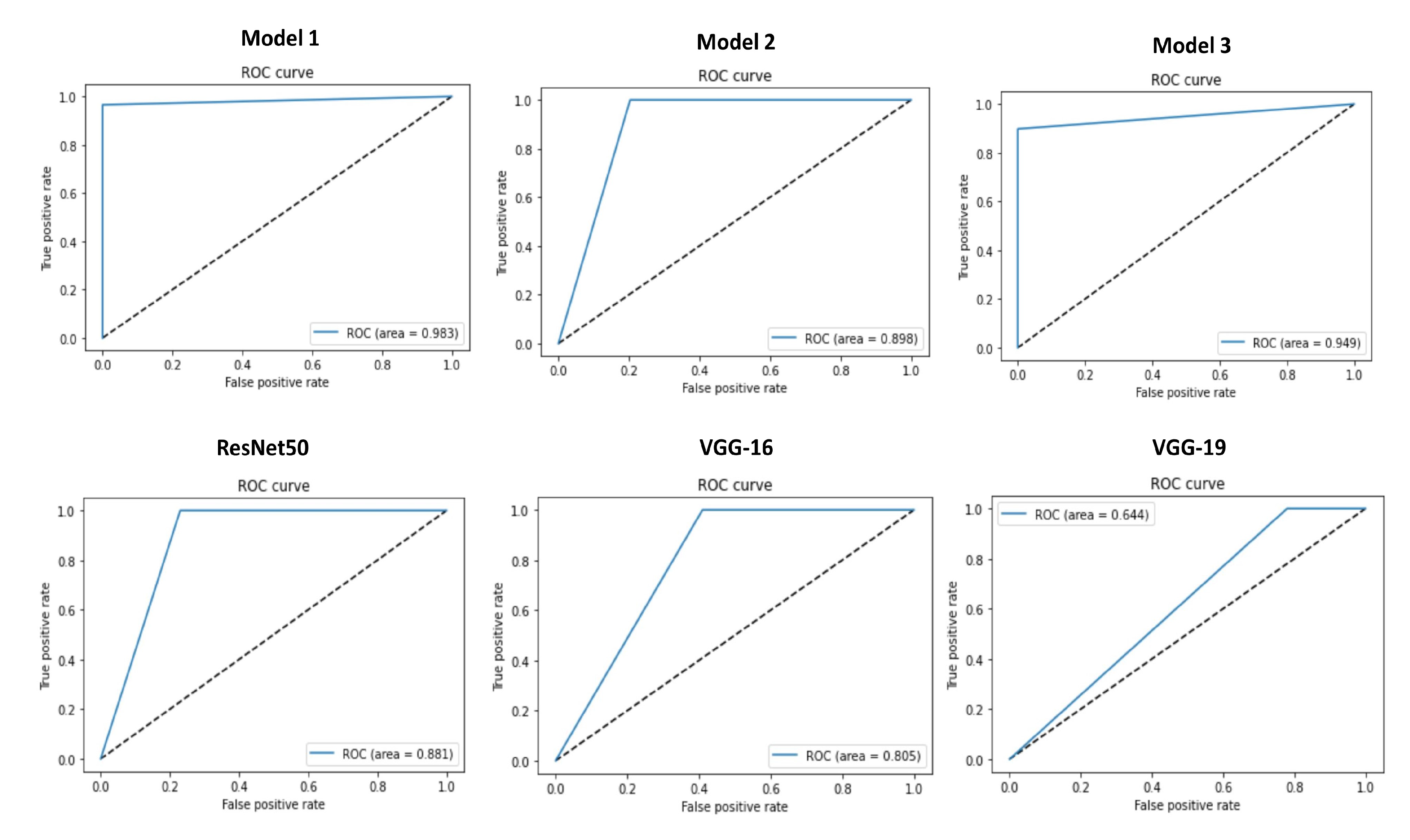
| Model 1 Trained with Dataset 2 | 59 | 57 | 2 | 0 | 100 | 96.6 | 98.3 | 96.72 | 100 | 0.983 | 98.3 |
| Model 2 Trained with Dataset 1 | 35 | 40 | 0 | 5 | 87.5 | 100 | 93.75 | 100 | 87.5 | 0.938 | 93.34 |
| Model 2 Trained with Dataset 2 | 47 | 59 | 0 | 12 | 79.7 | 100 | 89.8 | 100 | 79.7 | 0.898 | 88.7 |
| Model 3 Trained with Dataset 1 | 40 | 36 | 4 | 0 | 100 | 90 | 95 | 90.9 | 100 | 0.950 | 95.23 |
| Model 3 Trained with Dataset 2 | 59 | 53 | 6 | 0 | 100 | 89.8 | 94.9 | 90.8 | 100 | 0.949 | 95.17 |
| ResNet50 Trained with Dataset 1 | 31 | 40 | 0 | 9 | 77.5 | 100 | 88.75 | 100 | 77.5 | 0.888 | 87.32 |
| ResNet50 Trained with Dataset 2 | 45 | 59 | 0 | 14 | 76.3 | 100 | 88.1 | 100 | 76.3 | 0.881 | 86.56 |
| VGG-16 Trained with Dataset 1 | 23 | 40 | 0 | 17 | 57.5 | 100 | 78.75 | 100 | 57.5 | 0.787 | 73.01 |
| VGG-16 Trained with Dataset 2 | 36 | 59 | 0 | 23 | 61.01 | 100 | 80.5 | 100 | 61.01 | 0.805 | 75.78 |
| VGG-19 Trained with Dataset 1 | 8 | 40 | 0 | 32 | 20 | 100 | 60 | 100 | 20 | 0.60 | 33.33 |
| VGG-19 Trained with Dataset 2 | 17 | 59 | 0 | 42 | 28.8 | 100 | 64.4 | 100 | 28.8 | 0.644 | 44.72 |
| Sl. No. | Model | Architecture | Non-COVID-19 Dataset | COVID-19 Dataset | Overall Accuracy (%) | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Modified Deep CNN by Rahimzadeh and Attar [57] | Xception+ ResNet50V2 | 8851 | 180 | 91.4 | – |
| 2 | Deep Transfer Learning based Model by Loey et al. [58] | GoogleNet | 69 | 79 | 99.9 | 100 |
| 3 | Transfer Learning with CNN by Apostolopoulos and Mpesiana [33] | MobileNet V2 | 504 | 224 | 96.78 | – |
| 4 | Transfer Learning Model by Sethy and Behera [32] | ResNet50+ SVM | 25 | 25 | 95.38 | 95.52 |
| 5 | COVIDX-Net by Hemdan et al. [36] | VGG19 | 25 | 25 | 90 | 90.94 |
| 6 | Pre-trained CNN Model by Chowdhury et al. [44] | DenseNet201 | 1579 | 423 | 99.70 | 99.70 |
| 7 | Deep Neural Networks by Ozturk et al. [45] | DarkCovidNet | 500 | 127 | 98.08 | 96.51 |
| 8 | A Deep CNN-LSTM Network by Islam et al. [35] | CNN-LSTM | 1525 | 1525 | 99.4 | 98.9 |
| 9 | A CNN Model by Haque et al. [53] | Sequential CNN | 206 | 206 | 97.56 | 97.61 |
| 10 | A Deep CNN Model by Narin et al. [29] | ResNet50 | 50 | 50 | 98 | 98 |
| 11 | A Deep Learning Model by Zhang et al. [30] | Deep CNN | 1431 | 100 | 96 | – |
| 12 | Deep Learning Model by Hall et al. [31] | ResNet50 | 102 | 102 | 89.2 | – |
| 13 | COVID-CAPS by by Afshar et al. [49] | Capsule Networks | – | – | 95.7 | – |
| 14 | DeTraC Deep CNN by by Abbas et al. [59] | DeTraC | 80 | 105 | 95.12 | – |
| 15 | COVID-CXNet by by Haghanifar et al. [46] | Pre-trained CheXNet | 3200 | 428 | 99.04 | 96 |
| 16 | CoroNet by by Khan et al. [47] | Xception | 310 | 284 | 99 | 98.5 |
| 17 | Deep Transfer Learning Model by by Minaee et al. [48] | SqueezeNet | 5000 | 184 | 92.29 | – |
| 18 | Proposed Model | Sequential CNN | 659 | 295 | 98.3 | 98.3 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haque, K.F.; Abdelgawad, A. A Deep Learning Approach to Detect COVID-19 Patients from Chest X-ray Images. AI 2020, 1, 418-435. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai1030027
Haque KF, Abdelgawad A. A Deep Learning Approach to Detect COVID-19 Patients from Chest X-ray Images. AI. 2020; 1(3):418-435. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai1030027
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaque, Khandaker Foysal, and Ahmed Abdelgawad. 2020. "A Deep Learning Approach to Detect COVID-19 Patients from Chest X-ray Images" AI 1, no. 3: 418-435. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai1030027
APA StyleHaque, K. F., & Abdelgawad, A. (2020). A Deep Learning Approach to Detect COVID-19 Patients from Chest X-ray Images. AI, 1(3), 418-435. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai1030027






